Form 8-K INFINITY PHARMACEUTICALS For: Jul 27
Exhibit 99.1

Infinity Pharmaceuticals Reports Second Quarter 2021 Financial Results and Provides
Company Update
–New clinical data from MARIO-275 and MARIO-3 suggest that the addition of eganelisib
to standard of care regimens provides patient benefit –
–Increases seen in overall survival in 2L urothelial cancer (UC) and in progression free
survival in 1L triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), in both cases regardless of PD-L1 status –
–Stéphane Peluso, Ph.D., returns to Infinity as Chief Scientific Officer –
–Cash balance of $97.3M to fund eganelisib development –
–MARIO-275 and MARIO-3 data update on KOL webcast event today, 8:00AM ET –
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., July 27, 2021 /Business Wire/ -- Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (NASDAQ: INFI) (“Infinity” or the “Company”), a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing eganelisib (IPI-549), a potentially first-in-class, oral, immuno-oncology macrophage reprogramming therapeutic, today announced its second quarter 2021 financial results and provided a corporate update.
Adelene Perkins, Chief Executive Officer and Chair, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, said, “Today we report data indicating that eganelisib re-programs macrophages in the tumor microenvironment, turning pro-tumor, M2, macrophages into anti-tumor, M1, macrophages and improves outcomes for patients in two distinct types of cancer. Specifically, when combined with current standard of care therapies, the data showed that eganelisib increased overall survival in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer and prolonged progression free survival in patients with TNBC. These data provide preliminary, but compelling evidence of eganelisib’s potential to improve outcomes for patients with these two types of cancer. Validation of the fundamental biologic hypothesis of eganelisib, and the resulting prospect of patient benefit, gives us great confidence in the future of eganelisib, Infinity and our ability to realize our vision of bringing better therapies to patients. In the months ahead, Infinity plans to work with investigators, key opinion leaders and regulatory authorities to carefully choose the most appropriate clinical paths forward and expects to provide an update by year end, together with an update on our maturing TNBC data.”
Ms. Perkins continued, “We’re thrilled to have Dr. Peluso return to Infinity in the role of Chief Scientific Officer during this exciting time for Infinity. Stéphane served as a valued member of Infinity’s R&D Leadership Team during the discovery and preclinical development of eganelisib. His deep expertise will be incredibly valuable as we work to apply our clinical and translational learnings to maximize eganelisib’s unique role in re-programming macrophages and design the next set of clinical programs.”
Dr. Peluso said, “I’m excited to return to Infinity to continue building on the extraordinary work of the Infinity team in the discovery and development of eganelisib. The translational and clinical data presented to date continue to support that eganelisib is working on-mechanism, as intended and described in Infinity’s earlier preclinical work, and I look forward to leveraging these data in helping select the best future development paths.”
Corporate Update
•Appointed Stéphane Peluso, Ph.D, as Chief Scientific Officer. Effective August 2, 2021, Dr. Peluso returns to Infinity from Ipsen Bioscience where he was most recently Vice President, Global Head of Oncology External Innovation. Prior to Ipsen, Dr. Peluso worked at Infinity where he held positions of increasing responsibility in medicinal chemistry and drug discovery ultimately leading Infinity’s early discovery and pipeline expansion efforts through both internal R&D and business development. Dr. Peluso started his career as a medicinal chemist at Millennium Pharmaceuticals. He graduated from the Ecole Supérieure de Chimie Industrielle de Lyon (ESCIL), France, obtained his Ph.D. from the University of Lausanne, Switzerland and completed postdoctoral studies at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Recent Eganelisib Updates and Program Guidance – data updates from MARIO-275 and MARIO-3 during KOL event today at 8:00AM ET are summarized in a separate press release to be issued this morning.
Second Quarter 2021 Financial Results:
•At June 30, 2021, Infinity had total cash, cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities of $97.3 million, compared to $106.8 million at March 31, 2021.
•Research and development expense for the second quarter of 2021 was $8.0 million, compared to $6.1 million in the same period in 2020. The increase is primarily related to clinical, development and consulting expenses to support continued development of eganelisib.
•General and administrative expense was $3.5 million for the second quarter of 2021, compared to $2.9 million for the same period in 2020. The increase in general and administrative expense is primarily due to an increase in consulting expenses and stock compensation.
•Net loss for the second quarter of 2021 was $11.3 million, or a basic and diluted loss per common share of $0.13, compared to a net loss of $9.5 million, or a basic and diluted loss per common share of $0.16, in the same period in 2020.
Financial Outlook: Infinity’s 2021 financial guidance, following the closing in February 2021 of a $92 million public offering of Infinity’s common stock remains unchanged:
•Net Loss: Infinity expects net loss for 2021 to range from $40 million to $50 million.
•Cash and Investments: Infinity expects to end 2021 with a year-end-cash, cash equivalents and available for sale securities balance ranging from $70 million to $80 million. Infinity’s financial guidance does not include any potential additional funding or business development activities.
KOL Event Information
In lieu of an earnings conference call, Infinity will host a KOL event today, July 27, 2021, at 8:00AM ET to provide updates on the MARIO-3 TNBC and MARIO-275 UC clinical studies. Erika P. Hamilton, M.D. of Sarah Cannon Research Institute at Tennessee Oncology, and MARIO-3 lead investigator, and Brian Schwartz, M.D., Consulting Chief Physician of Infinity, will review the data for MARIO-3 and MARIO-275, respectively.
To register for the webinar, please click here.
About Infinity and Eganelisib
Infinity is a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing eganelisib (IPI-549), a potentially first-in-class, oral, immuno-oncology macrophage reprogramming therapeutic which addresses a fundamental biologic mechanism of immune suppression in cancer in multiple clinical studies. MARIO-275 is a randomized, controlled combination study of eganelisib combined with Opdivo® in I/O naïve urothelial cancer. MARIO-3 is the first eganelisib combination study in front-line advanced cancer patients and is evaluating eganelisib in combination with Tecentriq® and Abraxane® in front-line TNBC and in combination with Tecentriq and Avastin® in front-line renal cell carinoma. In collaboration with Arcus Biosciences, Infinity is evaluating a checkpoint inhibitor-free, novel combination regimen of eganelisib plus etrumadenant (AB928, a dual adenosine receptor antagonist) plus Doxil® in advanced TNBC patients. In 2019, Infinity completed enrollment in MARIO-1, a Phase 1/1b study evaluating eganelisib as a monotherapy and in combination with Opdivo (nivolumab) in patients with advanced solid tumors including patients refractory to checkpoint inhibitor therapy. With these studies Infinity is evaluating eganelisib in the anti-PD-1 refractory, I/O-naïve, and front-line settings. For more information on Infinity, please refer to Infinity's website at www.infi.com.
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such forward-looking statements include those regarding: the therapeutic potential of eganelisib; registrational trial planning; plans to present data; the timing of further clinical trial updates from the Company; the Company’s guidance with respect to net loss and cash and cash equivalents; and the Company's ability to execute on its strategic plans. Such statements are subject to numerous important factors, risks and uncertainties that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from the Company's current expectations. For example, there can be no guarantee that eganelisib will successfully complete necessary preclinical and clinical development phases. Further, there can be no guarantee that any positive developments in Infinity's product portfolio will result in stock price appreciation. Management's expectations and, therefore, any forward-looking statements in this press release could also be affected by risks and uncertainties relating to a number of other factors, including the following: the cost, timing and results of clinical trials and other development activities that may be delayed or disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic or otherwise; the content and timing of decisions made by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and other regulatory authorities; Infinity's ability to obtain and maintain requisite regulatory approvals; unplanned cash requirements and expenditures; development of agents by Infinity's competitors for diseases in which Infinity is currently developing or intends to develop eganelisib; and Infinity's ability to obtain, maintain and enforce patent and other intellectual property protection for eganelisib. These and other risks which may impact management's expectations are described in greater detail under the caption "Risk Factors" included in Infinity's annual report and quarterly reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and in other filings that Infinity makes with the SEC, available through the Company’s website at www.infi.com. Any forward-looking statements contained in this press release speak only as of the date hereof, and Infinity does not undertake and expressly disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Opdivo® is a registered trademark of Bristol Myers Squibb.
Tecentriq® is a registered trademark of Genentech, Inc.
Abraxane® is a registered trademark of Abraxis BioScience, LLC., a wholly owned subsidiary of Bristol Myers Squibb Company.
Avastin® is a registered trademark of Genentech, Inc.
Doxil® is a registered trademark of Baxter Healthcare Corporation.
INFINITY PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands)
(unaudited)
| June 30, 2021 | December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities | $ | 97,258 | $ | 34,108 | |||||||
| Other current assets | 2,419 | 1,912 | |||||||||
| Property and equipment, net | 1,471 | 1,710 | |||||||||
| Other long-term assets | 1,450 | 1,589 | |||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 102,598 | $ | 39,319 | |||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | $ | 10,554 | $ | 11,047 | |||||||
Liabilities related to sale of future royalties, net1 | 49,083 | 28,021 | |||||||||
Liability related to sale of future royalties to a related party, net1 | — | 21,559 | |||||||||
| Operating lease liability, less current portion | 1,188 | 1,436 | |||||||||
| Long-term liabilities | 233 | 245 | |||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | 41,540 | (22,989) | |||||||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 102,598 | $ | 39,319 | |||||||
1 The company is not obligated to repay the liabilities related to sale of future royalties but these are recorded as a liability on the balance sheet in accordance with accounting guidance for royalty monetization. During the first quarter of 2021, the liability related to sale of future royalties to a related party was reclassified to liability related to sale of future royalties since the Biotechnology Value Fund, L.P. (BVF) is no longer considered a related party.
INFINITY PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
(unaudited)
| Three Months Ended June 30, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Royalty revenue | $ | 512 | $ | 360 | $ | 979 | $ | 788 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development | 7,957 | 6,125 | 16,158 | 13,470 | |||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | 3,498 | 2,937 | 7,064 | 6,261 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Royalty expense | 308 | 217 | 590 | 475 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses | 11,763 | 9,279 | 23,812 | 20,206 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Loss from operations | (11,251) | (8,919) | (22,833) | (19,418) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense): | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment and other income (expense) | 27 | 50 | 25 | 235 | |||||||||||||||||||
Non-cash interest expense1 | (45) | (39) | (90) | (77) | |||||||||||||||||||
Non-cash related party interest expense1 | — | (565) | — | (1,099) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total other expense | (18) | (554) | (65) | (941) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (11,269) | $ | (9,473) | $ | (22,898) | $ | (20,359) | |||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted loss per common share: | $ | (0.13) | $ | (0.16) | $ | (0.28) | $ | (0.35) | |||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of common shares outstanding: | 88,661,934 | 57,442,332 | 82,230,784 | 57,392,965 | |||||||||||||||||||
1 The liabilities related to sale of future royalties will be amortized using the effective interest method over the life of the arrangements. During the first quarter of 2021, the non-cash related party interest expense was reclassified to non-cash interest expense since BVF is no longer considered a related party.
Investor Relations:
Irina Koffler
LifeSci Advisors, LLC
646-970-4681
ikoffler@lifesciadvisors.com

Eganelisib Re-Programming Macrophages To Develop Best-In-Class Next-Generation Immunotherapies July 27, 2021

2 Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements and information of Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“we,” “us,” “our,” “Infinity” or the “Company”) within the meaning of The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this presentation, are forward-looking statements. We often use words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “predict,” “project,” “target,” “milestone,” “goal,” “potential,” “will,” “would,” “could,” “should,” “continue,” and other words and terms of similar meaning to help identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. You also can identify these forward- looking statements by the fact that they do not relate strictly to historical or current facts. Such forward-looking statements include those regarding the company’s expectations about: the therapeutic potential of PI3K-gamma selective inhibition and eganelisib, alone and in combination with other therapies; clinical trial plans, progress and enrollment projections; plans to present data; planning for a registration-enabling study in urothelial cancer and triple negative breast cancer; and the company’s ability to execute on its strategic plans. Such statements are subject to numerous important factors, risks and uncertainties that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from the company’s current expectations. For example, there can be no guarantee that eganelisib will successfully complete necessary preclinical and clinical development phases or that any positive developments with eganelisib will result in stock price appreciation. Management’s expectations and, therefore, any forward-looking statements in this presentation, could also be affected by risks and uncertainties relating to a number of other factors, including the following: Infinity’s results of clinical trials and preclinical studies, including subsequent analysis of existing data and new data received from ongoing and future studies; Infinity’s ability to obtain, maintain and enforce patent and other intellectual property protection for eganelisib; the content and timing of decisions made by the U.S. FDA and other regulatory authorities; Infinity’s ability to obtain and maintain requisite regulatory approvals and to enroll patients in its clinical trials; unplanned cash requirements and expenditures; and development of agents by Infinity's competitors for diseases in which Infinity is currently developing or intends to develop eganelisib. These and other risks which may impact management’s expectations are described in greater detail under the caption “Risk Factors” included in Infinity’s annual report and quarterly reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and other filings filed by Infinity with the SEC, available on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. Any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation speak only as of the date hereof, and Infinity expressly disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. Infinity regularly uses its website to post information regarding its business, product development programs and governance.

3 Today’s Agenda MARIO-275 Overall Survival Results and Next Steps Brian Schwartz, MD, Consulting Chief Physician, Infinity Pharmaceuticals Q&A Discussion Erika Hamilton, MD; Brian Schwartz, MD; Adelene Perkins Eganelisib: Macrophage Reprogramming Therapeutic Candidate to Address High Unmet Medical Needs Adelene Perkins, Chair & CEO, Infinity Pharmaceuticals MARIO-3 Initial Durability & Early Look at PFS Erika Hamilton, MD, Medical Oncologist & MARIO-3 Lead Investigator, Tennessee Oncology

4 The Next Generation of Immunotherapy: Focus on the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) The future of cancer immunotherapy: microenvironment-targeting combinations1 Future of immune checkpoint inhibitors: focus on tumor immune microenvironment2 Next-generation immuno-oncology agents: current momentum shifts in cancer immunotherapy3 Advantages of targeting the tumor immune microenvironment over blocking immune checkpoint in cancer immunotherapy4 TIME: Tumor Immune Microenvironment; 1: Yonina R. Murciano-Goroff, Allison Betof Warner, Jedd D. Wolchok Cell Research Published: 28 May 2020 volume 30, pages 507–519; 2. Yunlong Jia, Lihua Liu, & Baoen Shan. Ann Transl Med. 2020 Sep; 8(17): 1095; 3. Chongxian Pan, Hongtao Liu, Elizabeth Robins, Wenru Song, Delong Liu, Zihai Li, Lei Zheng. Journal of Hematology & Oncology 2020 April 3, 13 (1): 29; 4. Tianyu Tang, Xing Huang, Gang Zhang, Zhengtao Hong, Xueli Bai & Tingbo Liang. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy Published: 20 February 2021. volume 6, Article number: 72 (2021) . 5. Martina Molgora and Marco Colonna. CellPress Med. 666–681, June 11, 2021. 6. Xiaonan Xiang et al. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. Published 2021. 6:75

5 Macrophages in the TME Are Compelling Targets for the Next Generation of Immunotherapy TIME: Tumor Immune Microenvironment; 1: Yonina R. Murciano-Goroff, Allison Betof Warner, Jedd D. Wolchok Cell Research Published: 28 May 2020 volume 30, pages 507–519; 2. Yunlong Jia, Lihua Liu, & Baoen Shan. Ann Transl Med. 2020 Sep; 8(17): 1095; 3. Chongxian Pan, Hongtao Liu, Elizabeth Robins, Wenru Song, Delong Liu, Zihai Li, Lei Zheng. Journal of Hematology & Oncology 2020 April 3, 13 (1): 29; 4. Tianyu Tang, Xing Huang, Gang Zhang, Zhengtao Hong, Xueli Bai & Tingbo Liang. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy Published: 20 February 2021. volume 6, Article number: 72 (2021) . 5. Martina Molgora and Marco Colonna. CellPress Med. 666–681, June 11, 2021. 6. Xiaonan Xiang et al. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. Published 2021. 6:75

6 Eganelisib Reprograms Macrophages to Turn Tumor Microenvironment From Immune Suppressed to Immune Activated Suppressed T cells M2 Tumor cells PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
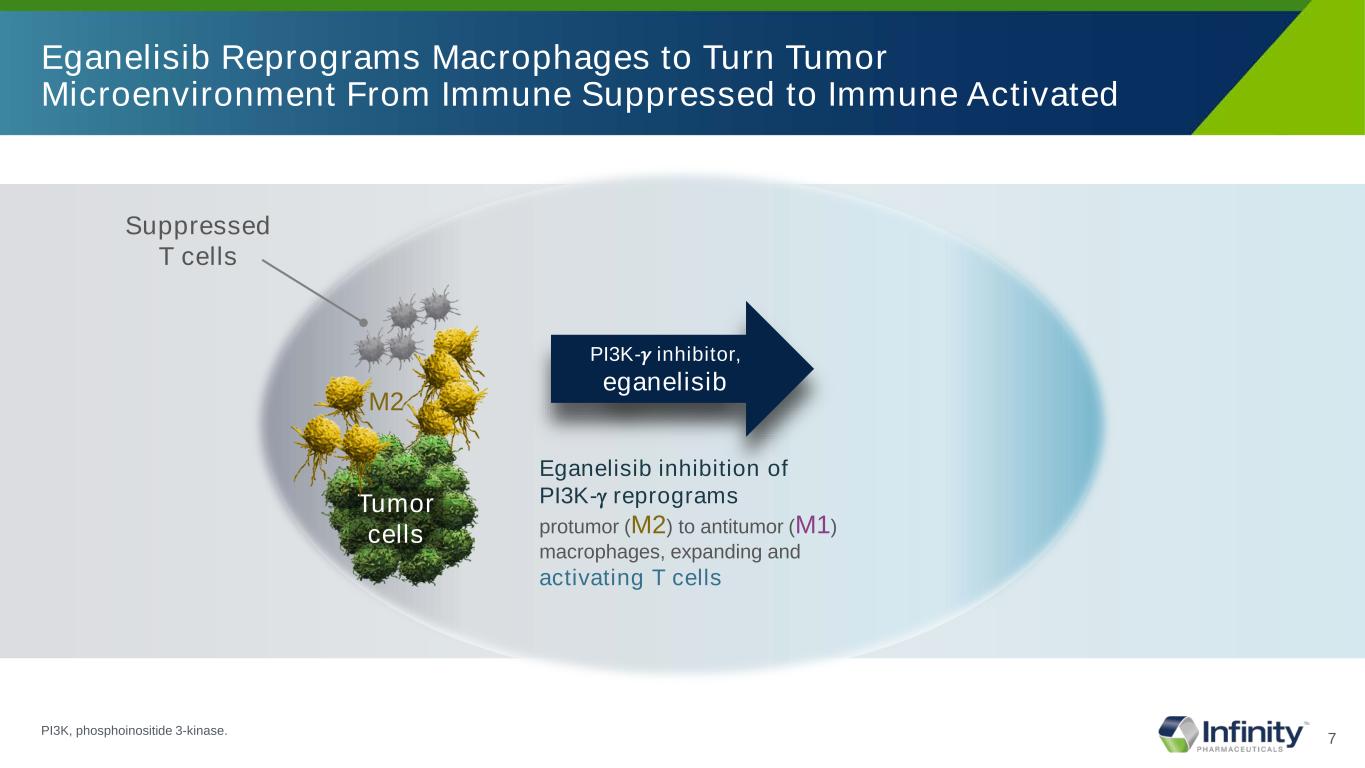
7 Eganelisib Reprograms Macrophages to Turn Tumor Microenvironment From Immune Suppressed to Immune Activated Suppressed T cells M2 Tumor cells Eganelisib inhibition of PI3K-γ reprograms protumor (M2) to antitumor (M1) macrophages, expanding and activating T cells PI3K-𝛾𝛾 inhibitor, eganelisib PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
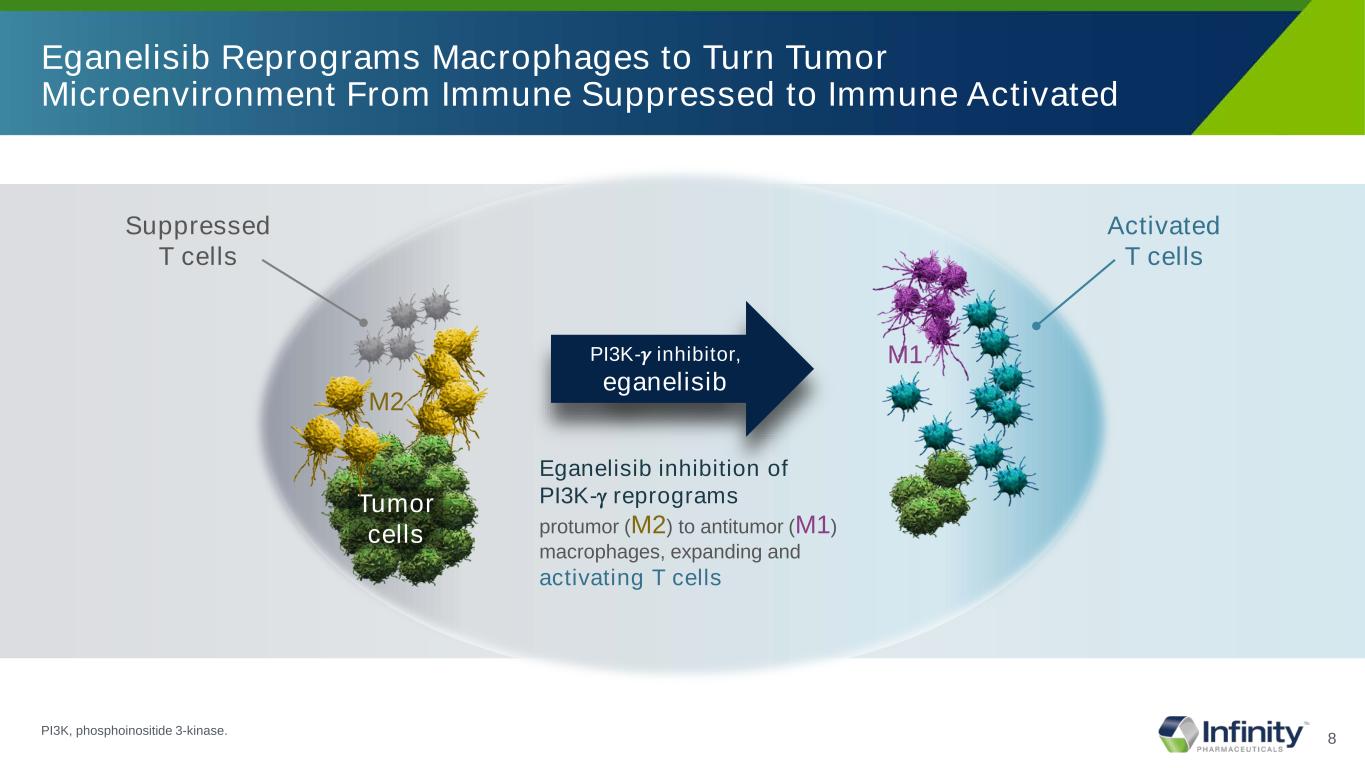
8 Eganelisib Reprograms Macrophages to Turn Tumor Microenvironment From Immune Suppressed to Immune Activated Suppressed T cells M2 Tumor cells Eganelisib inhibition of PI3K-γ reprograms protumor (M2) to antitumor (M1) macrophages, expanding and activating T cells PI3K-𝛾𝛾 inhibitor, eganelisib M1 Activated T cells PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase.

9 2L UC MARIO-2751 1L TNBC MARIO-32 Advanced TNBC ARC-23 Advanced Ovarian ARC-23 Melanoma MARIO-14 SCCHN MARIO-15 Combination Eganelisib + Nivolumab n=49 Eganelisib + Tecentriq + Abraxane N=13 efficacy N= 20 for safety Eganelisib + Etrumadenant + Doxil N=8 Eganelisib + Etrumadenant + Doxil N=4 Eganelisib + Nivolumab N=40 Eganelisib + Nivolumab N=20 Data Presented GU ASCO Feb 2021 SABCS Dec 2020 SABCS Dec 2020 SABCS Dec 2020 SITC Nov 2020 SITC Nov 2020 Benchmarks MARIO-275 Nivo control arm Checkmate-275 Nivo monoTx6 IMpassion130 Approval study: Tecentriq + Abraxane Etrumadenant + Doxil Etrumadenant + Doxil Immediately prior CPI progression Immediately prior CPI progression Eganelisib Benefit vs Benchmarks PFS DCR ORR Immune activation- blood DCR ORR Immune activation- blood ORR ORR ORR Immune activation-blood ORR Biomarker: HPV+ Validation of Biologic Hypothesis and Potential Patient Benefit Robust Data Set Presented Through February 2021 in 5 Tumor Types, 3 Combination Regimens and Multiple Lines of Therapy in >130 Patients 1. Tomczak et al. ASCO GU 2021 2. Hamilton E et al. SABCS 2020 3. Gardner O et al. SABCS 2020 4. Postow et al. SITC 2020 5. Cohen et al. SITC 2020 6. Sharma et al. AACR Annual Meeting 2018 ORR, overall response rate; DCR, disease control rate; ITT, intention-to-treat; PFS, progression free survival; SCCHN, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; CPI, checkpoint inhibitor
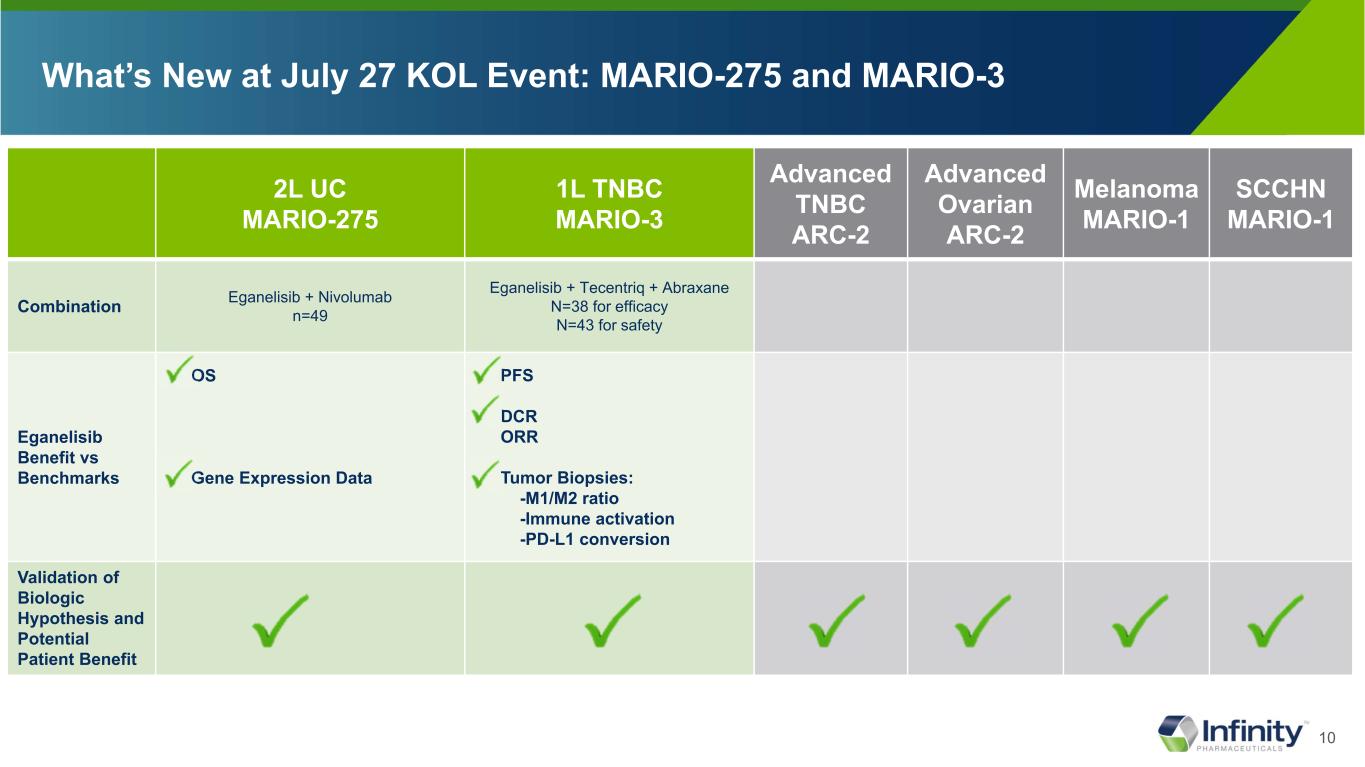
10 What’s New at July 27 KOL Event: MARIO-275 and MARIO-3 2L UC MARIO-275 1L TNBC MARIO-3 Advanced TNBC ARC-2 Advanced Ovarian ARC-2 Melanoma MARIO-1 SCCHN MARIO-1 Combination Eganelisib + Nivolumab n=49 Eganelisib + Tecentriq + Abraxane N=38 for efficacy N=43 for safety Eganelisib Benefit vs Benchmarks OS Gene Expression Data PFS DCR ORR Tumor Biopsies: -M1/M2 ratio -Immune activation -PD-L1 conversion Validation of Biologic Hypothesis and Potential Patient Benefit

11 Infinity Value Proposition: Data Suggest Eganelisib Could Be An Important Treatment Option for Patients in Need of Better Therapies • Validation of Biologic Hypothesis For Re-Programming Macrophages in TME • Data Demonstrate Prolonged PFS and OS • Several Attractive Options For Potential Registrational Trials and Follow-on Studies in UC and TNBC • Findings Suggest Opportunity For Expansion Beyond Existing Trials and Settings

12 MARIO-275 2L Metastatic Urothelial Cancer

13 Significant Unmet Need in Metastatic Urothelial Cancer: 5-Year Survival Rate of ~5% aEstimated cases based on 2013-2017 cases. *5-Year relative survival percent, UC by SEER Summary Stage 2000. mUC, metastatic urothelial cancer; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; SEER, Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results; UC, urothelial cancer. 1. National Cancer Institute. Accessed December 16, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html 2. National Cancer Institute. Accessed December 16, 2020. https://www.cancer.gov/types/bladder/patient/bladder-treatment-pdq#Keypoint2 3. Bellmunt J et al. National Cancer Institute. Accessed July 20, 2021. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(4):812-817. 4. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html Majority of mUCs are PD-L1 negative3 In 2020, it is estimated that there were 81,400 of urothelial cancer1,a new cases UC Is the Most Common Type of Bladder Cancer1 95% of bladder cancers are urothelial cancer 5-Year Survival Rate by Stage at Diagnosis of UC2,* Pe rc en t 5% 0 20 40 60 80 100 Localized Regional MetastaticMet tatic 36% 70% Bladder cancer is estimated to be the 6th highest in new cases and 7th highest for death in 20214

14 FDA Fast-Track Designation Eganelisib 40/30mg QD** + Nivolumab 480 mg Q4W Placebo + Nivolumab 480 mg Q4W Advanced Platinum Refractory 2nd Line Urothelial Cancer Patients • MDSC all comers (pre-specified and stratified) • PD-L1* status all comers (pre-specified) Primary objective: ORR in MDSC High Secondary objectives: DOR, PFS, OS, ORR in Total population + MDSC subset MARIO-275: Addition of Eganelisib to Standard of Care Nivolumab in I/O Naïve Urothelial Cancer Patients, Including PD-L1(-) Patients C ro ss -o ve r R • Preliminary data from the Phase II trial, which enrolled 49 patients demonstrated activity, particularly in patients with low levels of PD-L1 expression • Based on this encouraging data, Infinity is exploring the optimal study design for a potential registration study PD DOR, duration of response; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; ORR, overall response rate; OS, overall survival; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PFS, progression-free survival; Q4W, once every four weeks; QD, once a day; *PD-L1 expression measured in baseline/archival tumor biopsies with Dako PD-L1 immunohistochemical 28-8 pharmDx kit approved for nivolumab in UC, except 2 biopsies tested with 22C3 PD-L1 antibody prior to study (Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)); **Infinity voluntarily paused enrollment in May 2020 and implemented a dose reduction of eganelisib from 40mg QD to 30mg QD to address reversible liver enzyme elevations. In September 2020, the Independent Data Monitoring Committee determined that there was a favorable benefit/risk ratio at 30mg; Findings presented include data up to June 26, 2021 2:1 randomization

15 Combination Arm mOS of 15.4 mos vs 7.9 mos on Control Arm HR of 0.62 Indicating 38% Reduction in Risk of Death Eganelisib + Nivolumab Median Percentile (95% confidence interval) Nivolumab + Eganelisib: 15.4 (6.2, NE) months Nivolumab + Placebo: 7.9 (2.3, NE) months HR: 0.62 (0.28, 1.36) Placebo + Nivolumab Eganelisib + Nivo (N=33) 33 31 27 23 20 18 17 14 5 0 Placebo + Nivo (N=16) 16 13 10 9 7 6 4 4 2 1 1 0 16 (48.5) 10 (62.5) Death, n (%) Overall Survival Results – All Patients OS (mITT): Censoring based on last available clinical visit Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021

16 Eganelisib + Nivo (N=33) 33 31 27 23 20 18 17 14 5 0 Placebo + Nivo (N=16) 16 13 10 9 7 6 4 4 2 1 1 0 Combination Arm mOS of 15.4 mos vs 7.9 mos on Control Arm HR of 0.62 Indicating 38% Reduction in Risk of Death OS (mITT): Censoring based on last available clinical visit Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 Eganelisib + Nivolumab Median Percentile (95% confidence interval) Nivolumab + Eganelisib: 15.4 (6.2, NE) months Nivolumab + Placebo: 7.9 (2.3, NE) months HR: 0.62 (0.28, 1.36) One Year Landmark: 59% in Combo versus 32% in Nivolumab Placebo + Nivolumab 16 (48.5) 10 (62.5) Death, n (%) Overall Survival Results – All Patients

17 Median Percentile (95% confidence interval) Nivolumab + Eganelisib: 15.4 (4.7, NE) months Nivolumab + Placebo: 7.9 (1.9, NE) months HR: 0.60 (0.21, 1.71) PD-L1(-) Pts on Combo Arm mOS of 15.4 mos vs 7.9 mos on Control HR of 0.60 Indicating 40% Reduction of Risk of Death Overall Survival Results – PD-L1 Negative Patients Eganelisib + Nivolumab Placebo + Nivolumab 12 (52.2) 5 (71.4) Death, n (%) Censoring based on last available clinical visit; Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-) Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 Eganelisib + Nivo (N=23) 23 21 18 15 13 11 10 9 3 0 Placebo + Nivo (N=7) 7 5 5 4 2 2 1 1 1 0

18 Eganelisib + Nivo (N=23) 23 21 18 15 13 11 10 9 3 0 Placebo + Nivo (N=7) 7 5 5 4 2 2 1 1 1 0 Median Percentile (95% confidence interval) Nivolumab + Eganelisib: 15.4 (4.7, NE) months Nivolumab + Placebo: 7.9 (1.9, NE) months HR: 0.60 (0.21, 1.71) PD-L1(-) Pts on Combo Arm mOS of 15.4 mos vs 7.9 mos on Control HR of 0.60 Indicating 40% Reduction of Risk of Death Overall Survival Results – PD-L1 Negative Patients Censoring based on last available clinical visit; Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-) Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 One Year Landmark: 54% in Combo versus 17% in Nivolumab Eganelisib + Nivolumab Placebo + Nivolumab 12 (52.2) 5 (71.4) Death, n (%)

19 Stable Disease Contribution to Disease Control Rate Best Overall Response per RECIST All Patients PD-L1 (-) Patients PD-L1 (+) Patients Eganelisib + Nivo N = 33 Nivo + Placebo N = 16 Eganelisib + Nivo N = 23 Nivo + Placebo N = 7 Eganelisib + Nivo N = 5 Nivo + Placebo N = 5 n % n % n % n % n % n % CR 4* 12% 1* 6% 2 9% 0 0% 2 40% 0 0% PR 5** 15% 3 19% 3 13% 1 14% 2 40% 2 40% ORR^ 9 27% 4 25% 5 22% 1 14% 4 80% 2 40% SD 8 24% 1 6% 7 30% 0 0% 0 0% 1 20% DCR^^ 17 51% 5 31% 12 52% 1 14% 4 80% 3 60% PD 12 36% 8 50% 7 30% 5 71% 1 20% 1 20% NE 4 12% 3 19% 4 17% 1 14% 0 0% 1 20% *Confirmed CR **3 patients had PD at C3, then PR at later cycles ^Unconfirmed overall response rate (ORR) (CR+PR) ^^Unconfirmed disease control rate (DCR) (CR,PR+SD) Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021; Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)

20 Overall Survival Benefit Seen in Patients with SD, PR and CR Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 Note: All 33 patients on the treatment arm are included in the OS analysis. These graphs exclude 4 patients for whom target lesions were not measured post baseline. ■ CR ■ PR ■ SD ■ PD 24% SD

21 OS Benefit in Patients with SD, PR and CR on Combination vs Control Arm 24% SD 6% SD Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 Note: All 33 patients on the treatment arm and 16 on the control arm are included in the OS analysis. These graphs exclude 4 patients on the treatment arm and 5 on the control arm for whom target lesions were not measured post baseline. Eganelisib + Nivolumab Placebo + Nivolumab ■ CR ■ PR ■ SD ■ PD

22 Durability of OS Benefit Continue to Mature For 45% of Patients on Combination Arm vs 25% on the Control Arm Eganelisib + Nivolumab Placebo + Nivolumab ■ CR ■ PR ■ SD ■ PD Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 Note: All 33 patients on the treatment arm and 16 on the control arm are included in the OS analysis. These graphs exclude 4 patients on the treatment arm and 5 on the control arm for whom target lesions were not measured post baseline.
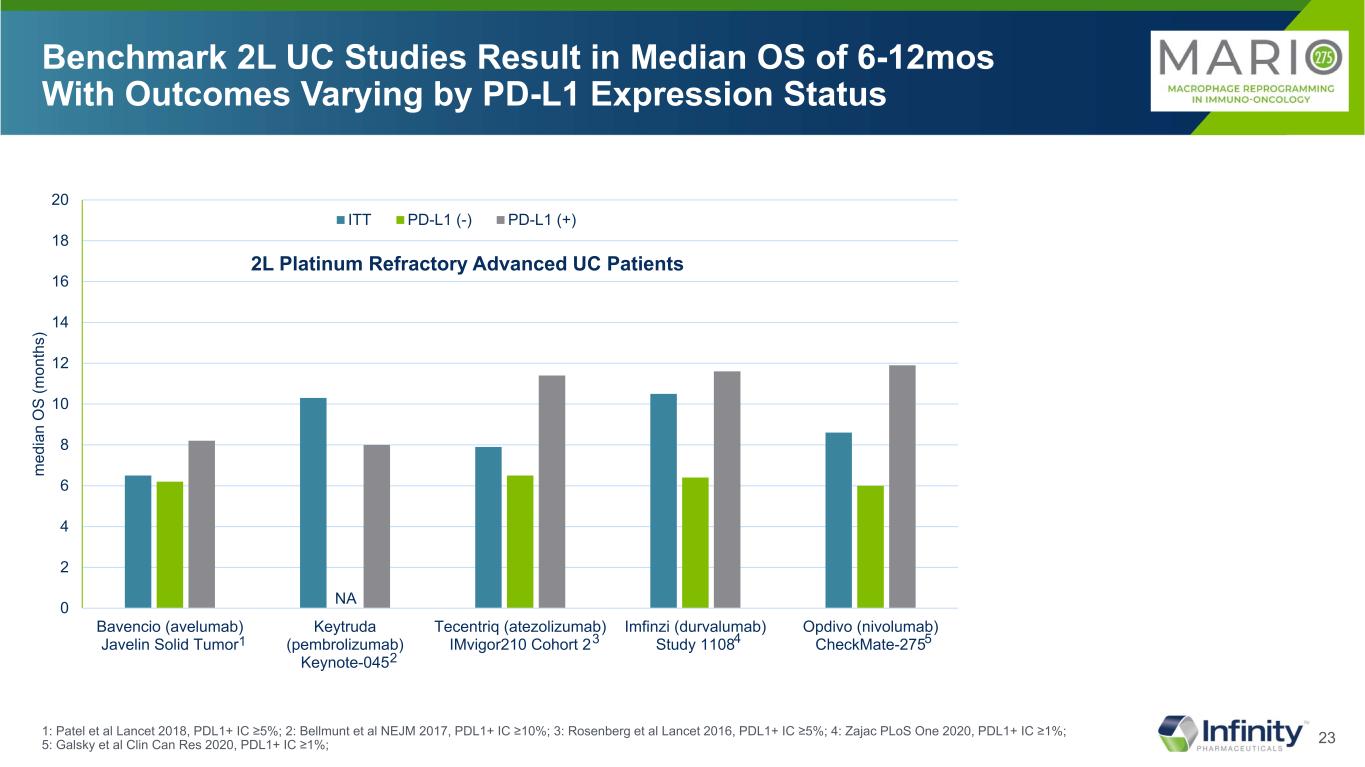
23 Benchmark 2L UC Studies Result in Median OS of 6-12mos With Outcomes Varying by PD-L1 Expression Status 1: Patel et al Lancet 2018, PDL1+ IC ≥5%; 2: Bellmunt et al NEJM 2017, PDL1+ IC ≥10%; 3: Rosenberg et al Lancet 2016, PDL1+ IC ≥5%; 4: Zajac PLoS One 2020, PDL1+ IC ≥1%; 5: Galsky et al Clin Can Res 2020, PDL1+ IC ≥1%; 2L Platinum Refractory Advanced UC Patients NA 1 2 3 4 5 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Bavencio (avelumab) Javelin Solid Tumor Keytruda (pembrolizumab) Keynote-045 Tecentriq (atezolizumab) IMvigor210 Cohort 2 Imfinzi (durvalumab) Study 1108 Opdivo (nivolumab) CheckMate-275 m ed ia n O S (m on th s) ITT PD-L1 (-) PD-L1 (+)

24 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Bavencio (avelumab) Javelin Solid Tumor Keytruda (pembrolizumab) Keynote-045 Tecentriq (atezolizumab) IMvigor210 Cohort 2 Imfinzi (durvalumab) Study 1108 Opdivo (nivolumab) CheckMate-275 Placebo + Nivolumab MARIO-275 Eganelisib + Nivolumab MARIO-275 m ed ia n O S (m on th s) ITT PD-L1 (-) PD-L1 (+) NE mOS 50-100% Greater Than Benchmark 2L Studies 2L UC Patients Treated with Eganelisib Plus Nivolumab 2L Platinum Refractory Advanced UC Patients NA NE 1: Patel et al Lancet 2018, PDL1+ IC ≥5%; 2: Bellmunt et al NEJM 2017, PDL1+ IC ≥10%; 3: Rosenberg et al Lancet 2016, PDL1+ IC ≥5%; 4: Zajac PLoS One 2020, PDL1+ IC ≥1%; 5: Galsky et al Clin Can Res 2020, PDL1+ IC ≥1%; 6: Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 1 2 3 4 5 In MARIO-275 randomized controlled study, eganelisib roughly doubles overall survival levels over SOC nivolumab monotherapy, in all patients, including PD-L1(-) 6 6

25 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Bavencio (avelumab) Javelin Solid Tumor Keytruda (pembrolizumab) Keynote-045 Tecentriq (atezolizumab) IMvigor210 Cohort 2 Imfinzi (durvalumab) Study 1108 Opdivo (nivolumab) CheckMate-275 Placebo + Nivolumab MARIO-275 Eganelisib + Nivolumab MARIO-275 m ed ia n O S (m on th s) ITT PD-L1 (-) PD-L1 (+) NE mOS 50-100% Greater Than Benchmark 2L Studies 2L UC Patients Treated with Eganelisib Plus Nivolumab 1: Patel et al Lancet 2018, PDL1+ IC ≥5%; 2: Bellmunt et al NEJM 2017, PDL1+ IC ≥10%; 3: Rosenberg et al Lancet 2016, PDL1+ IC ≥5%; 4: Zajac PLoS One 2020, PDL1+ IC ≥1%; 5: Galsky et al Clin Can Res 2020, PDL1+ IC ≥1%; 6: Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 MARIO-275 control arm consistent with CheckMate-275 2L Platinum Refractory Advanced UC Patients NA NE 1 2 3 4 5 6 6
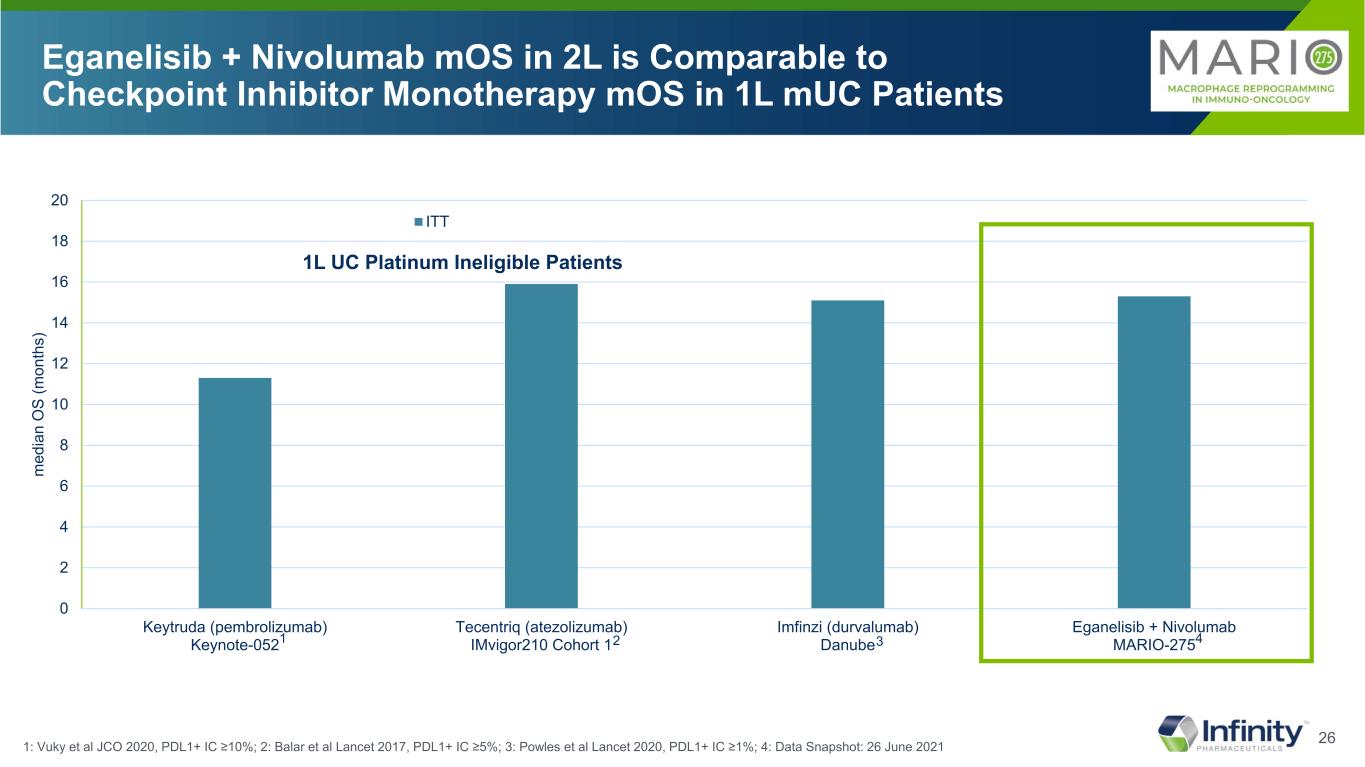
26 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Keytruda (pembrolizumab) Keynote-052 Tecentriq (atezolizumab) IMvigor210 Cohort 1 Imfinzi (durvalumab) Danube Eganelisib + Nivolumab MARIO-275 m ed ia n O S (m on th s) ITT Eganelisib + Nivolumab mOS in 2L is Comparable to Checkpoint Inhibitor Monotherapy mOS in 1L mUC Patients 1: Vuky et al JCO 2020, PDL1+ IC ≥10%; 2: Balar et al Lancet 2017, PDL1+ IC ≥5%; 3: Powles et al Lancet 2020, PDL1+ IC ≥1%; 4: Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 1L UC Platinum Ineligible Patients 1 2 3 4

27 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0.90.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Greater Immune Activation -- Higher Gene Set Enrichment Scores and Lower P Values For Pro-inflammatory Pathways -- With Eganelisib + Nivolumab Compared to Nivolumab Alone Regardless of PD-L1 Status in Peripheral Blood Interferon Gamma Pathway En ric hm en t S co re (E S) En ric hm en t S co re (E S) En ric hm en t S co re (E S) En ric hm en t S co re (E S) Interferon Alpha Pathway ES=0.81 p<0.01 ES=0.87 p<0.01 ES=0.53 p=0.39 ES=0.51 p=0.28 All Patients Day 15 vs Day 0 PD-L1 Negative Day 15 vs Day 0 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0.9 Rank in Gene List Rank in Gene List Day 15 Correlated Day 15 Correlated ES=0.82 p<0.01 ES=0.55 p=0.15 ES=0.89 p<0.01 ES=0.53 p=0.35 Rank in Gene ListDay 15 Correlated Rank in Gene ListDay 15 Correlated Combination Nivolumab Combination Nivolumab Combination Nivolumab Combination Nivolumab Interferon Gamma Pathway Interferon Alpha Pathway (n=31) (n=14) (n=31) (n=14) (n=21) (n=5) (n=21) (n=5) PD-L1 Positive Subset had insufficient n to achieve confidence in GSEA (Gene Set Enrichment Analysis); Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)
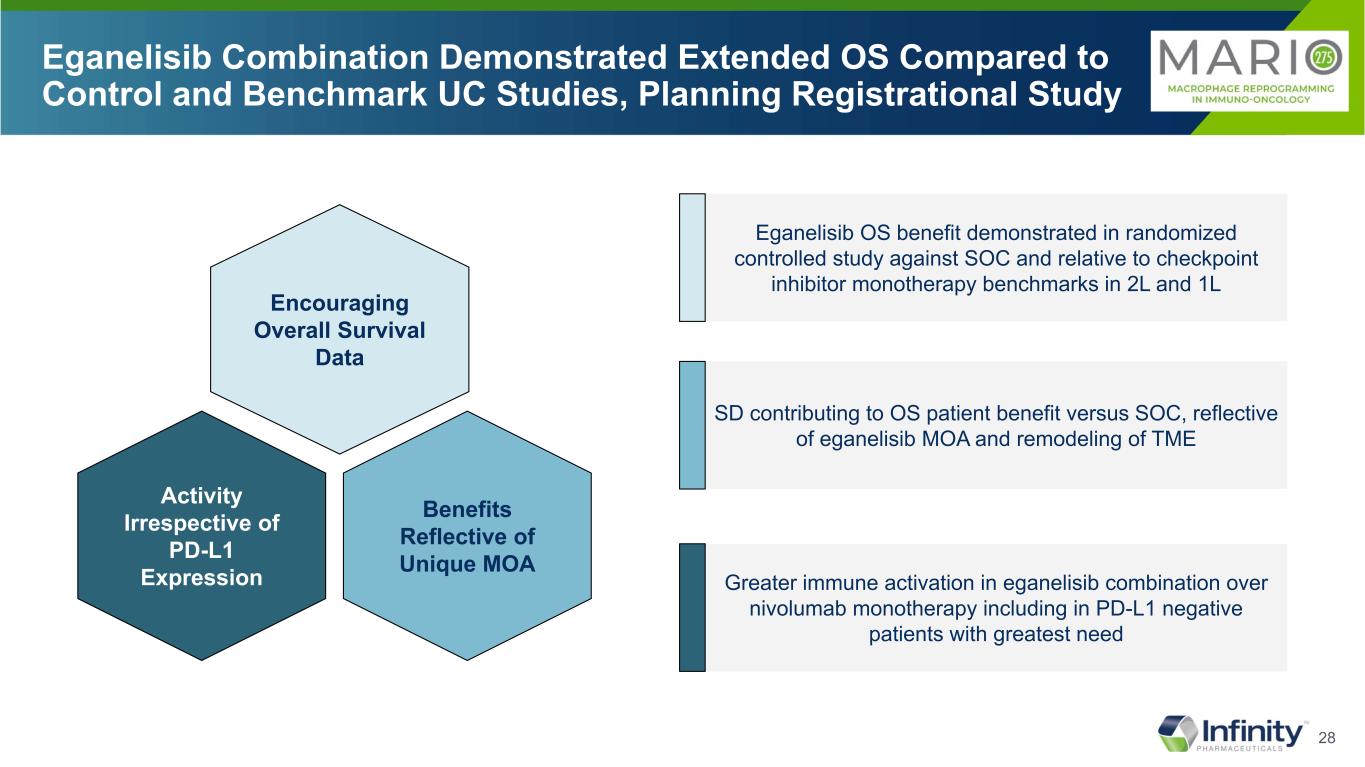
28 Eganelisib Combination Demonstrated Extended OS Compared to Control and Benchmark UC Studies, Planning Registrational Study Benefits Reflective of Unique MOA Activity Irrespective of PD-L1 Expression Encouraging Overall Survival Data Eganelisib OS benefit demonstrated in randomized controlled study against SOC and relative to checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy benchmarks in 2L and 1L SD contributing to OS patient benefit versus SOC, reflective of eganelisib MOA and remodeling of TME Greater immune activation in eganelisib combination over nivolumab monotherapy including in PD-L1 negative patients with greatest need

29 MARIO-3 1L Metastatic TNBC

30 Metastatic TNBC and PD-L1 Negative TNBC are Associated with Poor Prognosis and 5-year Survival Rate of 12% aEstimated cases based on 2013-2017 cases. †5-Year relative survival percent, TNBC by SEER Summary Stage 2000. ‡PD-L1–stained tumor-infiltrating immune cells; positive PD-L1 threshold of 0.01 (≥1% of tumor area). 1. National Cancer Institute. Accessed November 24, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html 2. American Cancer Society. Accessed November 24, 2020. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/understanding-a-breast-cancer-diagnosis/types-of-breast-cancer/triple-negative.html 3. National Cancer Institute. Accessed November 23, 2020. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html 4. Davis AA, Patel VG. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):278. 5. Matikas A et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(18):5717-5726. (ie, negative for ER, PR, and HER2) 15% of breast cancer is triple negative2 PD-L1 negative cancers are associated with poor prognosis4 ≈ 60% of TNBCs are PD-L1 negative5,‡ 5-year survival rate by stage at diagnosis of TNBC3,† 91 % 65 % 0 20 40 60 80 100 Localized Regional Distant Pe rc en t Metastatic 12% In 2020, it is estimated that there will be 276,480 new cases of breast cancer in women1,a Advanced TNBC and PD-L1 Negative TNBC Are Both Associated With Poor Prognosis

31 Trial Designed to Demonstrate Eganelisib’s Ability to Improve the Clinical Benefit of Atezolizumab + Nab-Paclitaxel in 1L mTNBC CR, complete response; DCR, disease control rate; ITT, intent-to-treat; ORR, overall response rate; PD, pharmacodynamics; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PFS, progression-free survival; PK, pharmacokinetics; QD, once daily; SOC, standard of care; mTNBC, metastatic triple-negative breast cancer; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer. Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-) 1. Schmid P et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(22):2108-2121. Eganelisib FDA Fast Track Designation for TNBC MARIO-3 TNBC exploring the potential of eganelisib to improve on IMpassion130 results1 Addition of eganelisib to SOC, atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel, in front-line TNBC • Inclusion/exclusion criteria per IMpassion130 study • Two prespecified cohorts: PD-L1(-) and PD-L1(+) • Primary objective: CR rate CR benchmark ≈7% ITT; 10% PD-L1(+) • Secondary objectives: PK, PD, ORR, DCR, and PFS; ORR for PD-L1(-) cohort • PDL1 status determined via central lab (histogeneX) with Ventana SP142 antibody to align with IMpassion130 Total enrollment (n≈60) TNBC PD-L1(-) (n=up to 30) TNBC PD-L1(+) (n=up to 30) eganelisib 30mg QD + atezolizumab + nab-paclitaxel

32 38 of 43 Enrolled Patients Have Had Their Scan for Tumor Response and Were Treated for an Average of ~18 weeks Screened (n = 59) Enrolled (n = 43) Screen failures (n = 16) Treated (n = 43) Discontinued treatment (n = 18) • Disease Progression (n = 12) • Adverse Event (n = 2) • Investigator Decision (n = 2) • Death* (n = 1) • Other (n = 1) Tumor Response Assessment Available (n = 38) TNBC Duration of IPI-549 Exposure, weeks TNBC, N = 43 Mean ± SD 18.3 ± 11.6 Min, Max 2.4, 48.0 Demographics TNBC, N = 43 Age, mean ± SD 58 ± 14 Gender, n (%) Male Female 0 43 (100) ECOG performance status, n (%) 0 1 26 (60.5) 17 (39.5) Race/ethnicity, n (%) White Hispanic or Latino Black or African American Asian 35 (81.4) 5 (11.6) 4 (9.3) 1 (2.3) *Cause of death – unrelated AE Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021

33 Baseline Characteristics As Expected for A Front Line TNBC Patient Population *Neo-adjuvant or adjuvant therapies Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 Prior Therapies n (%) Total N = 38 PD-L1 (-) N = 23 PD-L1 (+) N = 12 Radiotherapy 16 (42.1) 7 (30.4) 7 (58.3) Surgery 32 (84.2) 20 (87.0) 9 (75.0) Systemic therapy* Alkylating agent Anthracycline Antimetabolite Hormone associated Mitotic inhibitor (taxane) Other 22 (57.9) 20 (52.6) 13 (34.2) 6 (15.8) 6 (15.8) 18 (47.4) 3 (7.9) 14 (60.9) 13 (56.5) 9 (39.1) 5 (21.7) 3 (13.0) 13 (56.5) 2 (8.7) 6 (50.0) 5 (41.7) 4 (33.3) 1 (8.3) 3 (25.0) 3 (25.0) 1 (8.3) Cancer History n (%) Total N = 38 PD-L1 (-) N = 23 PD-L1 (+) N = 12 Initial diagnosis Local, resectable Locally advanced Metastatic 18 (47.4) 2 (5.3) 18 (47.4) 13 (56.5) 2 (8.7) 8 (34.8) 3 (25.0) 0 9 (75.0) Metastatic sites at enrollment Bone Liver Lung Lymph Node Skin Other 14 (36.8) 10 (26.3) 12 (31.6) 14 (36.8) 2 (5.3) 10 (26.3) 12 (52.2) 7 (30.4) 7 (30.4) 7 (30.4) 2 (8.7) 6 (26.1) 1 (8.3) 3 (25.0) 3 (25.0) 5 (41.7) 0 4 (33.3)

34 No New or Additive Safety Signals Were Observed, Safety Profile Consistent with Expectations for Three From Component Drugs Most Common TEAEs in ≥25% of All Treated Patients (N=43) Preferred Term TEAE (All) Eganelisib-related TEAE (All) TEAE (≥ Gr. 3) Eganelisib-related TEAE (≥ Gr. 3) Nausea 22 (51.2) 14 (32.6) 0 0 Fatigue 21 (48.8) 17 (39.5) 3 (7.0) 1 (2.3) Alopecia 14 (32.6) 3 (7.0) 0 0 Diarrhea 14 (32.6) 11 (25.6) 3 (7.0) 1 (2.3) Rash maculo-papular 13 (30.2) 11 (25.6) 4 (9.3) 4 (9.3) Alanine aminotransferase increased* 12 (27.9) 9 (20.9) 8 (18.6) 8 (18.6) Aspartate aminotransferase increased 11 (25.6) 10 (23.3) 6 (14.0) 6 (14.0) Presented in descending order of All Causality in TEAE *1 Grade 4 For Hepatic AE No Hy’s Law and No Grade 5 Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021

35 86.8% of Evaluable Patients Achieved Tumor Reduction B es t P er ce nt C ha ng e in T ar ge t L es io n fr om B as el in e PR SD PD CR PD-L1 positive PD-L1 negative + - + - + + + + - - -- - - - - - - - - + + + - - + - - - - + +- - - + - Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-) Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 * * * PD-L1 unknown*

36 MARIO-3 Early mPFS is Promising in Both PD-L1(+) and PD-L1(-) Patients NOTE: MARIO-3 data are early with many patients early in treatment and approximately 20 more patients to enroll; Of total patients without events (N = 21), 19 patients still ongoing for response assessments 1: Schmid P et al. Lancet. 2020; PDL1(+) IC ≥1%; 2: Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 - Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-) 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Atezo + Nab-Pac IMpassion130 Eganelisib + Atezo + Nab-Pac MARIO-3 m ed ia n PF S (m on th s) PD-L1 (-) PD-L1 (+) 1 2

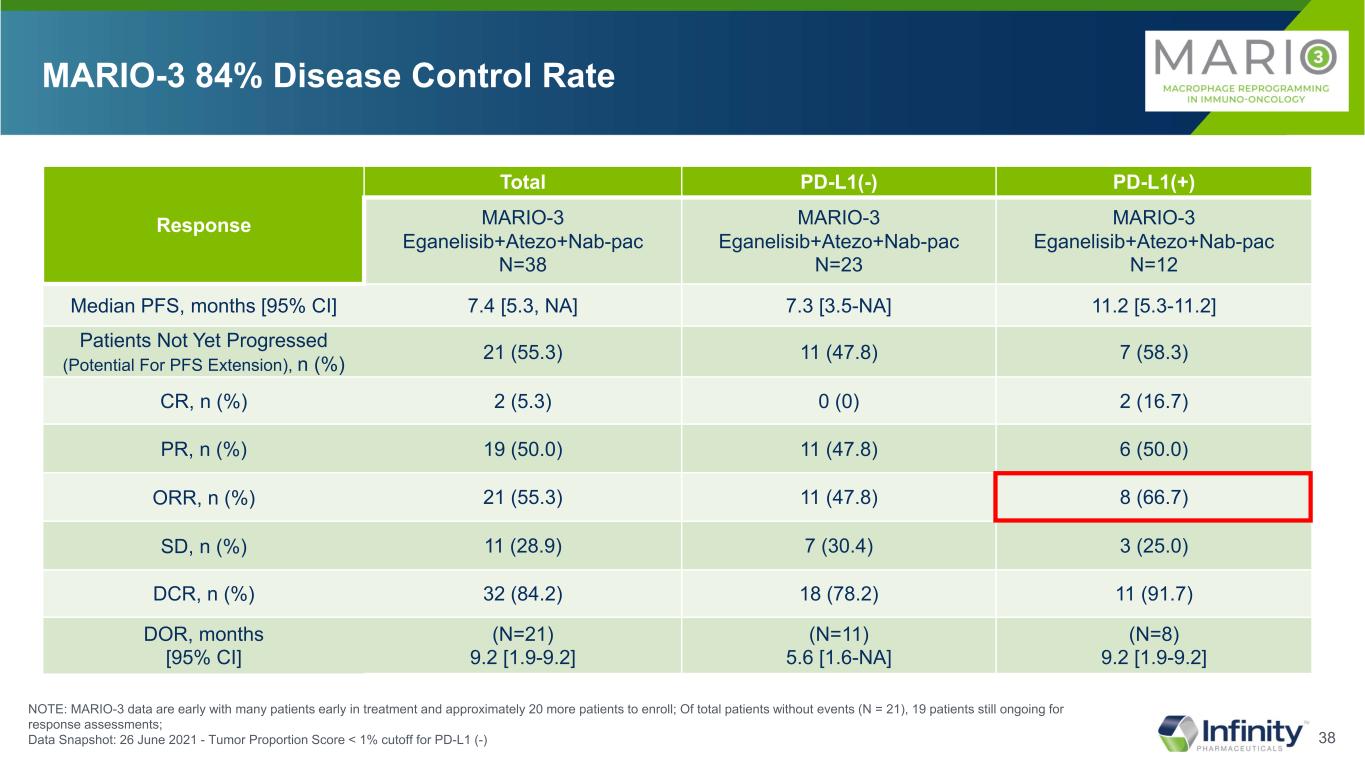
37 Response Total PD-L1(-) PD-L1(+) MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=38 MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=23 MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=12 Median PFS, months [95% CI] 7.4 [5.3, NA] 7.3 [3.5-NA] 11.2 [5.3-11.2] Patients Not Yet Progressed (Potential For PFS Extension), n (%) 21 (55.3) 11 (47.8) 7 (58.3) CR, n (%) 2 (5.3) 0 (0) 2 (16.7) PR, n (%) 19 (50.0) 11 (47.8) 6 (50.0) ORR, n (%) 21 (55.3) 11 (47.8) 8 (66.7) SD, n (%) 11 (28.9) 7 (30.4) 3 (25.0) DCR, n (%) 32 (84.2) 18 (78.2) 11 (91.7) DOR, months [95% CI] (N=21) 9.2 [1.9-9.2] (N=11) 5.6 [1.6-NA] (N=8) 9.2 [1.9-9.2] MARIO-3 84% Disease Control Rate NOTE: MARIO-3 data are early with many patients early in treatment and approximately 20 more patients to enroll; Of total patients without events (N = 21), 19 patients still ongoing for response assessments; Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 - Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)
38 Response Total PD-L1(-) PD-L1(+) MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=38 MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=23 MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=12 Median PFS, months [95% CI] 7.4 [5.3, NA] 7.3 [3.5-NA] 11.2 [5.3-11.2] Patients Not Yet Progressed (Potential For PFS Extension), n (%) 21 (55.3) 11 (47.8) 7 (58.3) CR, n (%) 2 (5.3) 0 (0) 2 (16.7) PR, n (%) 19 (50.0) 11 (47.8) 6 (50.0) ORR, n (%) 21 (55.3) 11 (47.8) 8 (66.7) SD, n (%) 11 (28.9) 7 (30.4) 3 (25.0) DCR, n (%) 32 (84.2) 18 (78.2) 11 (91.7) DOR, months [95% CI] (N=21) 9.2 [1.9-9.2] (N=11) 5.6 [1.6-NA] (N=8) 9.2 [1.9-9.2] MARIO-3 84% Disease Control Rate NOTE: MARIO-3 data are early with many patients early in treatment and approximately 20 more patients to enroll; Of total patients without events (N = 21), 19 patients still ongoing for response assessments; Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 - Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)

39 Response Total PD-L1(-) PD-L1(+) MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=38 MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=23 MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=12 Median PFS, months [95% CI] 7.4 [5.3, NA] 7.3 [3.5-NA] 11.2 [5.3-11.2] Patients Not Yet Progressed (Potential For PFS Extension), n (%) 21 (55.3) 11 (47.8) 7 (58.3) CR, n (%) 2 (5.3) 0 (0) 2 (16.7) PR, n (%) 19 (50.0) 11 (47.8) 6 (50.0) ORR, n (%) 21 (55.3) 11 (47.8) 8 (66.7) SD, n (%) 11 (28.9) 7 (30.4) 3 (25.0) DCR, n (%) 32 (84.2) 18 (78.2) 11 (91.7) DOR, months [95% CI] (N=21) 9.2 [1.9-9.2] (N=11) 5.6 [1.6-NA] (N=8) 9.2 [1.9-9.2] MARIO-3 84% Disease Control Rate NOTE: MARIO-3 data are early with many patients early in treatment and approximately 20 more patients to enroll; Of total patients without events (N = 21), 19 patients still ongoing for response assessments; Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 - Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)

40 Response Total PD-L1(-) PD-L1(+) MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=38 MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=23 MARIO-3 Eganelisib+Atezo+Nab-pac N=12 Median PFS, months [95% CI] 7.4 [5.3, NA] 7.3 [3.5-NA] 11.2 [5.3-11.2] Patients Not Yet Progressed (Potential For PFS Extension), n (%) 21 (55.3) 11 (47.8) 7 (58.3) CR, n (%) 2 (5.3) 0 (0) 2 (16.7) PR, n (%) 19 (50.0) 11 (47.8) 6 (50.0) ORR, n (%) 21 (55.3) 11 (47.8) 8 (66.7) SD, n (%) 11 (28.9) 7 (30.4) 3 (25.0) DCR, n (%) 32 (84.2) 18 (78.2) 11 (91.7) DOR, months [95% CI] (N=21) 9.2 [1.9-9.2] (N=11) 5.6 [1.6-NA] (N=8) 9.2 [1.9-9.2] MARIO-3 84% Disease Control Rate NOTE: MARIO-3 data are early with many patients early in treatment and approximately 20 more patients to enroll; Of total patients without events (N = 21), 19 patients still ongoing for response assessments; Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 - Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)

41 ■ CR ■ PR ■ SD ■ PD Durable Clinical Benefit in Patients with SD, PR and CR Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 * * * PD-L1 positive PD-L1 negative + - PD-L1 unknown*

42 Durability of Clinical Benefit Continues to Mature For 55% of Treated Patients Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 * * * ■ CR ■ PR ■ SD ■ PD PD-L1 positive PD-L1 negative + - PD-L1 unknown*

43 CD8 T Cells Activated T Cell Tumor M2 HLADR+ M1Tumor Reduced Immune Suppression and Increased Immune Activation Day 0 2 mo PD-L1(-) Patient with PR Patient Ongoing Over 10 Months Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)

44 CD8 T Cells Activated T Cell TumorCD8 T Cells Activated T Cell Tumor M2 HLADR+ M1TumorM2 HLADR+ M1Tumor Reduced Immune Suppression and Increased Immune Activation Regardless of PD-L1 Status Day 0 2 mo Day 0 2 mo PD-L1(-) Patient with PR PD-L1(+) Patient with PR Patient Ongoing Over 10 Months Patient Ongoing Over 10 Months Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)

45 CD8 T Cells Activated T Cell TumorCD8 T Cells Activated T Cell Tumor M2 HLADR+ M1TumorM2 HLADR+ M1Tumor Reduced Immune Suppression and Increased Immune Activation Regardless of PD-L1 Status, Quantified in 11 Paired Tumor Biopsies *n=8 pairs; + mean (Multiomyx Analysis) Day 0 2 mo Day 0 2 mo PD-L1(-) Patient with PR PD-L1(+) Patient with PR Patient Ongoing Over 10 Months Patient Ongoing Over 10 Months Tumor Proportion Score < 1% cutoff for PD-L1 (-)

46*conversion from PD-L1(-) to PD-L1(+) (> 1% cutoff , SP142 IHC) Conversion of Patients from PD-L1(-) to PD-L1(+) and Increase in PD-L1 Expression in PD-L1(+) Patients in 11 Paired Tumor Biopsies 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 PD-L1(-) at Baseline PD-L1(+) at Baseline Baseline 2 months 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 9 10 11 1% PD-L1 cutoff 1% PD-L1 cutoff * * * * % tu m or a re a co ve re d by P D -L 1+ im m un e ce lls % tu m or a re a co ve re d by P D -L 1+ im m un e ce lls Patient Patient *

47 MARIO-3 TNBC Early Data Demonstrated That Eganelisib Combination Was Well Tolerated With Promising PFS and On-Target Mechanism PFS Data Still Maturing On Mechanism Macrophage Reprogramming Encouraging Early PFS Data Early mPFS is encouraging 11.2 months in PD-L1 (+) vs IMpassion130 at 7.5 months 7.3 months in PD-L1 (-) vs IMpassion130 at 5.6 months PFS data is still maturing, over 50% of evaluable patients remain progression free, continuing to be followed for PFS and enrollment is ongoing Changes in tumor are consistent with on mechanism macrophage reprogramming resulting in immune activation with PD-L1 conversion from negative to positive
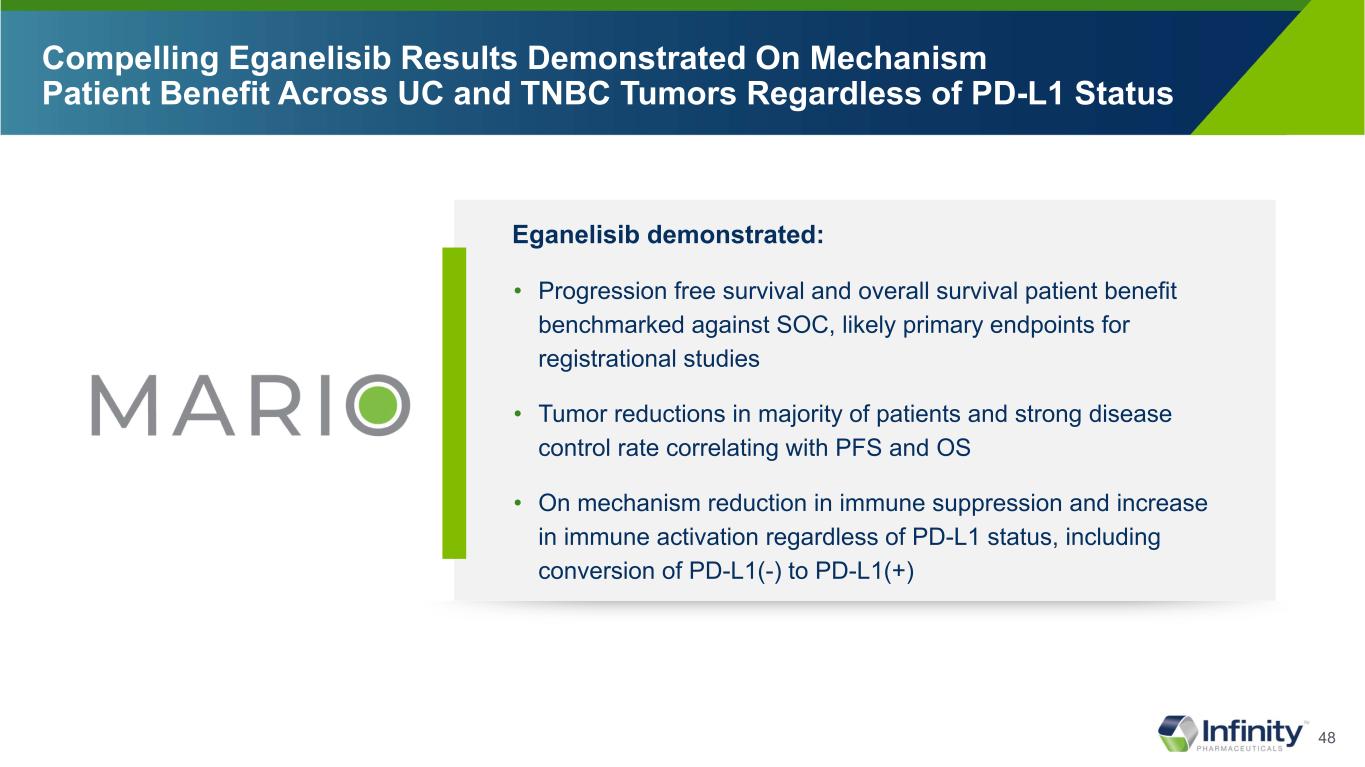
48 Eganelisib demonstrated: • Progression free survival and overall survival patient benefit benchmarked against SOC, likely primary endpoints for registrational studies • Tumor reductions in majority of patients and strong disease control rate correlating with PFS and OS • On mechanism reduction in immune suppression and increase in immune activation regardless of PD-L1 status, including conversion of PD-L1(-) to PD-L1(+) Compelling Eganelisib Results Demonstrated On Mechanism Patient Benefit Across UC and TNBC Tumors Regardless of PD-L1 Status

49 Next Steps: Many Attractive Paths Forward With Eganelisib in Advancing The Next Generation of Immunotherapy Broad potential in areas of high unmet need for immuno-oncology therapies going forward • PD-L1 negative patients • Patients with “cold” tumors • Checkpoint inhibitor refractory patients Triple-Negative Breast Cancer • 43 patients enrolled as of June 26, 2021 – enrollment completion of ~60 patients expected by year end • Data update planned by year end Urothelial Cancer • Encouraging OS data: optimal setting for registrational study now being evaluated – Follow up with investigators, KOLs and FDA • Status update planned by year end

Q&A Discussion

Thank You

53 A Majority of Treated Patients Had Low PD-L1 Tumor Expression and Were Treated Over a Median of ~16 Weeks Parameter Eganelisib + Nivolumab (N = 33) Nivolumab + Placebo (N = 16) Age, mean ± SD 64.5 ± 8.9 68.1 ± 7.4 Male, n (%) 24 (72.7) 12 (75.0) ECOG performance status, n (%) 0 1 20 (60.6) 13 (39.4) 5 (31.3) 11 (68.8) Primary tumor location, n (%) Urinary bladder Renal pelvis Ureter Urethra 24 (72.7) 5 (15.2) 2 (6.1) 2 (6.1) 13 (81.3) 2 (12.5) 1 (6.3) 0 Liver metastases, n (%) 8 (24.2) 5 (31.3) MDSC level, n (%) Low (< 22.3) High (≥ 22.3) 26 (78.8) 7 (21.2) 13 (81.3) 3 (18.8) PD-L1 status, n (%) ≥1% <1% Unknown 5 (15.2) 23 (69.7) 5 (15.2) 5 (31.3) 7 (43.8) 4 (25.0) Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 Parameter Eganelisib + Nivolumab (N = 33) Nivolumab + Placebo (N = 16) Duration of exposure, median weeks (min, max) 16.1 (2, 75) 11.1 (2, 84) Eganelisib/placebo median average daily dose mg, (min, max) 29.9 (12.2, 39.9) 34.6 (14.2, 40.0) Ongoing treatment, n (%) 6 (18.2) 3 (18.8) Discontinued treatment, n (%) Progression of disease Adverse event, related to treatment Adverse event, unrelated to treatment Investigator decision Death Voluntary withdrawal 27 (81.8) 11 (40.7) 8 (29.6) 3 (11.1) 3 (11.1) 1 (3.7) 1 (3.7) 13 (81.3) 5 (38.5) 3 (23.1) 0 2 (15.4) 2 (15.4) 1 (7.7) Disposition and ExposureDemographics and Baseline

54 Safety Overview Preferred Term Nivolumab + Eganelisib (N = 33) Nivolumab + Placebo (N = 16) All Causality Related to Eganelisib Related to Nivolumab All Causality Related to Placebo Related to Nivolumab Pyrexia 11 (33.3) 4 (12.1) 2 (6.1) 0 0 0 Decreased appetite 10 (30.3) 7 (21.2) 5 (15.2) 5 (31.3) 1 (6.3) 0 Disease progression 9 (27.3) 0 0 4 (25.0) 0 0 Asthenia 9 (27.3) 6 (18.2) 5 (15.2) 5 (31.3) 2 (12.5) 1 (6.3) Pruritus 9 (27.3) 6 (18.2) 9 (27.3) 1 (6.3) 0 0 Rash 9 (27.3) 8 (24.2) 5 (15.2) 1 (6.3) 0 0 Treatment-Emergent AEs in ≥25% Patients in the Nivolumab + Eganelisib Arm Presented in descending order of All Causality in Nivolumab + Eganelisib arm; * 1 Grade 4, ** 2 Grade 4 Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021 Preferred Term Nivolumab + Eganelisib (N = 33) Nivolumab + Placebo (N = 16) All Causality Related to Eganelisib Related to Nivolumab All Causality Related to Placebo Related to Nivolumab Disease progression 9 (27.3) 0 0 4 (25.0) 0 0 Hepatotoxicity* 5 (15.2) 5 (15.2) 5 (15.2) 0 0 0 Alanine aminotransferase increased** 4 (12.1) 4 (12.1) 4 (12.1) 1 (6.3) 1 (6.3) 1 (6.3) Aspartate aminotransferase increased* 4 (12.1) 4 (12.1) 4 (12.1) 1 (6.3) 1 (6.3) 1 (6.3) Anemia 4 (12.1) 1 (3.0) 1 (3.0) 1 (6.3) 0 0 Grade ≥3 TEAEs in ≥10% Patients in the Nivolumab + Eganelisib Arm
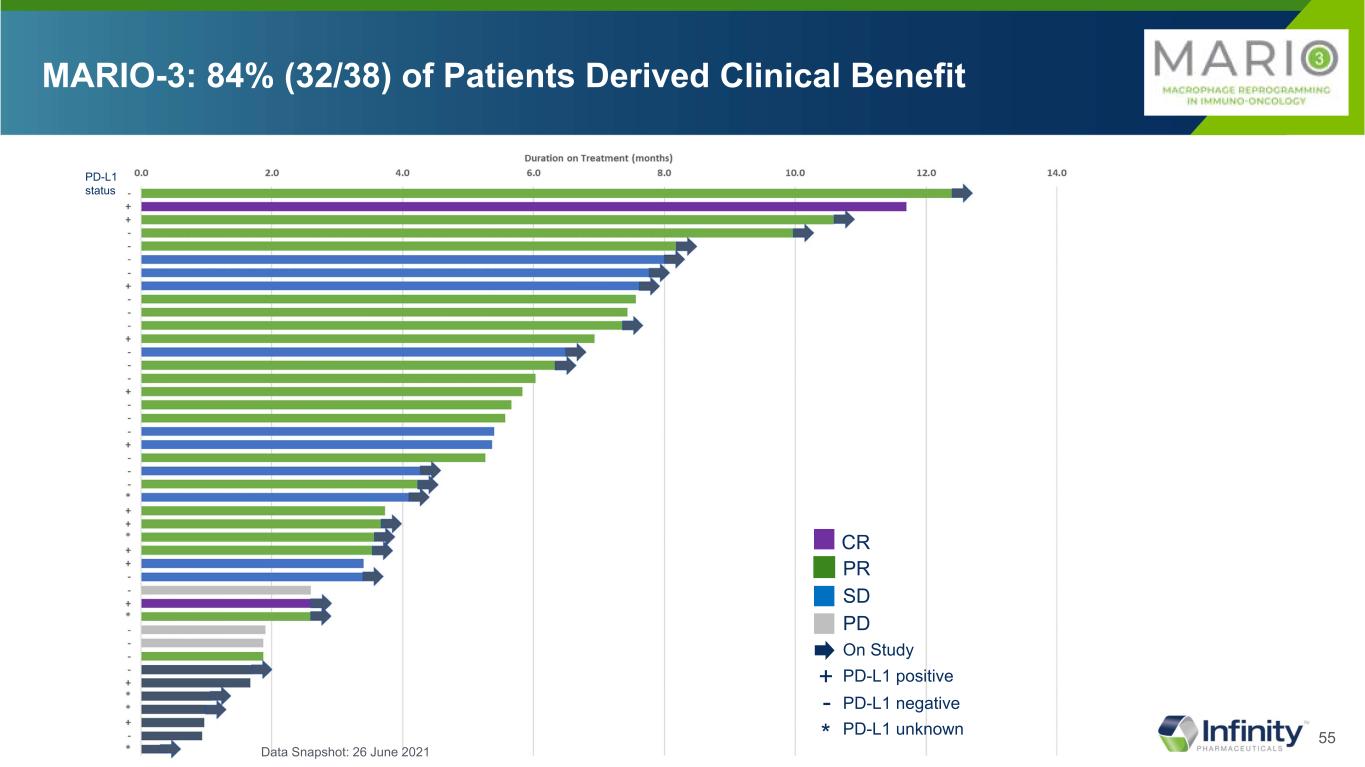
55 MARIO-3: 84% (32/38) of Patients Derived Clinical Benefit PR SD PD CR On Study PD-L1 positive+ PD-L1 negative- PD-L1 unknown* PD-L1 status Data Snapshot: 26 June 2021
Exhibit 99.3

Infinity Pharmaceuticals Presents Updated Data from Phase 2 MARIO-275 Trial in
Urothelial Cancer (UC) and Phase 2 MARIO-3 Trial in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)
– MARIO-275 median overall survival data show combination of eganelisib with nivolumab achieves
15.4 months compared to 7.9 months on nivolumab control arm in 2L UC –
– MARIO-3 TNBC early data suggest the addition of eganelisib to standard of care regimens extends
progression free survival regardless of PD-L1 status with majority of patients still on treatment –
– 86.8% of evaluable 1L patients with TNBC in MARIO-3 achieved tumor reduction with a total
disease control rate of 84.2% –
– MARIO-275 and MARIO-3 translational data demonstrated on-mechanism increased immune
activation and decreased immune suppression –
– KOL event scheduled for today, July 27, 8:00 am ET –
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., July 27, 2021 /Business Wire/ -- Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Nasdaq: INFI) (“Infinity” or the “Company”), a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing eganelisib, a potentially first-in-class, oral, immuno-oncology macrophage reprogramming therapeutic which has been shown to reverse a fundamental biologic mechanism of immune suppression in cancer and activate an anti-tumor immune response, today presents data updates from MARIO-275, the Company’s randomized, placebo-controlled Phase 2 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of eganelisib in combination with nivolumab (Opdivo®) in platinum-refractory, I/O naïve patients with advanced UC as well as data from MARIO-3, the Company’s ongoing Phase 2 study evaluating eganelisib in a novel triple combination in the front-line setting with atezolizumab (Tecentriq®) and nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane®) in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic TNBC.
Adelene Perkins, Chief Executive Officer and Chair, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, said, “Today we report data indicating that eganelisib re-programs macrophages in the tumor microenvironment, turning pro-tumor, M2, macrophages into anti-tumor, M1, macrophages and improves outcomes for patients in two distinct types of cancer. Specifically, when combined with current standard of care therapies, the data showed that eganelisib increased overall survival in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer and prolonged progression free survival in patients with TNBC. These data provide preliminary, but compelling evidence of eganelisib’s potential to improve outcomes for patients with these two types of cancer. Validation of the fundamental biologic hypothesis of eganelisib, and the resulting prospect of patient benefit, gives us great confidence in the future of eganelisib, Infinity and our ability to realize our vision of bringing better therapies to patients. In the months ahead, Infinity plans to work with investigators, key opinion leaders and regulatory authorities to carefully choose the most appropriate clinical paths forward and expects to provide an update by year end, together with an update on our maturing TNBC data.”
Brian Schwartz, M.D., consulting Chief Physician, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, said, “The promising survival benefit was noted after over a year of following MARIO-275 patients versus the control arm as well as compared to historical trials including CheckMate-275, particularly given the magnitude of the unmet need in 2L UC, including in the PD-L1 negative patient population. These results are reinforced by the progression free survival data which we presented at ASCO GU in February 2021 as well as the translational data that support our thesis that eganelisib reprograms macrophages in the tumor microenvironment and that validate eganelisib’s mechanism of action. We believe overall survival represents a key registrational endpoint, and given these exciting new OS data, we are exploring the optimal study design for a potential registration study and expect to provide a program update by the end of 2021.”
Erika Hamilton, M.D., Director, Breast Cancer and Gynecologic Cancer Research Program, Tennessee Oncology, and Lead Study Investigator for MARIO-3, said, “The emerging progression free survival data from MARIO-3 are very encouraging and suggest that the impressive disease control rate observed, regardless of PD-L1 status, is translating to a benefit in progression free survival. These results are consistent with the results from MARIO-275, which show the similar translation of disease control into a meaningful survival benefit for patients. For patients with TNBC, the potential to extend progression free survival, regardless of PD-L1 status, would be a transformational breakthrough. We are on track to complete enrollment by year end, and with the majority of patients still on treatment, look forward to presenting additional, more mature data at that time.”
MARIO-275 Key Data Updates:
•49 patients were enrolled in the trial with the last patient enrolled in June 2020.
•Median overall survival (mOS) in the intent to treat (ITT) population was 15.4 months (6.2, NE) on the eganelisib plus nivolumab combination arm as compared to 7.9 months (2.3, NE) on the control arm of nivolumab alone with a hazard ratio of 0.62 (0.28, 1.36), which reflects a 38% lower probability of death on the combination arm.
◦At the one-year landmark, 59% of patients in the ITT population receiving the eganelisib plus nivolumab combination remained alive, compared to 32% in the nivolumab control arm.
•The mOS benefit observed in patients with PD-L1(-) tumors was the same as in the ITT population, with a mOS of 15.4 months (4.7, NE) on the eganelisib plus nivolumab combination arm as compared to 7.9 months (1.9, NE) on the control arm of nivolumab alone with a hazard ratio of 0.60 (0.21, 1.71), which reflects a 40% lower probability of death on the combination arm.
◦At the one-year landmark, 54% of the patients with PD-L1(-) tumors receiving the eganelisib plus nivolumab combination remained alive, compared to 17% in the nivolumab control arm.
•The most common treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) across all doses, all causality, were pyrexia (33.3%), decreased appetite (30.3%), pruritus (27.3%), asthenia (27.3%), rash (27.3%), disease progression (27.3%) and increased alanine aminotransferase (24.2%); and the most common ≥Grade 3 TEAEs across all doses, all causality, were disease progression (27.3%), anemia (12.1%), and hepatic AEs including hepatotoxicity (15.2%), increased ALT (12.1%) and increased AST (12.1%) with no Hy’s Law. No Grade 5 hepatic AEs were reported.
•Translational data: Gene expression studies from peripheral blood, followed by gene set enrichment analysis using Hallmark gene signature sets show the pro-inflammatory interferon gamma and interferon alpha pathways were the most significantly enriched pathways in the combination arm when comparing Day 15 to baseline, regardless of PD-L1 status, with higher enrichment scores and lower p values than on the control arm. These data are consistent with eganelisib’s mechanism of action which decreases immune suppression and increases immune activation.
MARIO-3 Key Data Updates:
•This data update includes 43 patients enrolled with 38 evaluable, which compares to 20 patients enrolled with 13 evaluable at our update at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium in December 2020.
•86.8% (33/38) of evaluable patients demonstrated tumor reduction.
•Disease control rate (DCR)
◦78.2% (18/23) DCR in patients with PD-L1 negative tumors: complete response (CR) 0% (0/23), partial response (PR) 47.8% (11/23), stable disease (SD) 30.4% (7/23)
◦91.7% (11/12) DCR in patients with PD-L1 positive tumors: CR 16.7% (2/12), PR 50% (6/12), SD 25% (3/12)
◦84.2% (32/38) DCR in all patients: CR 5.3% (2/38), PR 50% (19/38), SD 28.9% (11/38)
•Early progression free survival (PFS)
◦In patients with PD-L1(-) tumors, PFS was extended as compared to benchmark data for atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel alone, increasing from 5.6 months to 7.3 months (3.5, NA).
◦In patients with PD-L1(+) tumors, PFS was extended as compared to benchmark data for atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel alone, increasing from 7.5 to 11.2 months (5.3, 11.2).
◦In the ITT population, PFS was extended as compared to benchmark data for atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel alone, increasing from 7.2 months to 7.4 months (5.3, NA).
•MARIO-3 did not demonstrate any new or additive safety signals compared to benchmark trials. The most common TEAEs, all causality, were nausea (51.2%), fatigue (48.8%), alopecia (32.6%), diarrhea (32.6%), rash maculo-papular (30.2%) increased ALT (27.9%) with only one Grade 4 and increased AST (25.6%) with one grade 4. No Hy’s Law or Grade 5 hepatic AEs were reported, and only one patient permanently discontinued study treatment due to an elevated liver function test.
•Quantification across 11 paired tumor biopsies shows increased immune activation and decreased immune suppression including an increase in CD8+ T cells, activated T cells, and anti-tumor M1 macrophages and a decrease in tumor cells and pro-tumor M2 macrophages resulting in an increase in the M1:M2 ratio.
•Paired tumor biopsy data show 5 of 8 patients with PD-L1(-) tumors converting to PD-L1(+) two months after treatment utilizing the 1% PD-L1 cutoff standard. PD-L1 expression also increased in the three patients with PD-L1(+) tumors who started the study above the 1% cutoff. None of the patients converting to PD-L1(+) or patients with PD-L1(+) tumors who experienced increased PD-L1 expression had disease progression.
KOL Event Information
In lieu of an earnings conference call, Infinity will host a KOL event today, July 27, 2021, at 8:00AM ET to provide updates on the MARIO-3 TNBC and MARIO-275 UC clinical studies. Erika P. Hamilton, M.D. of Sarah Cannon Research Institute at Tennessee Oncology, and MARIO-3 lead investigator, and Brian Schwartz, M.D., Consulting Chief Physician of Infinity, will review the data for MARIO-3 and MARIO-275, respectively.
To register for the webinar, please click here.
About Infinity and Eganelisib
Infinity is an innovative biopharmaceutical company dedicated to advancing novel medicines for people with cancer. Infinity is advancing eganelisib, a first-in-class, oral immuno-oncology development candidate that selectively inhibits PI3K-gamma, in multiple clinical studies. MARIO-275 is a global, randomized, controlled combination study of eganelisib combined with Opdivo® in I/O naïve urothelial cancer. MARIO-3 is the first eganelisib combination study in front-line advanced cancer patients and is evaluating eganelisib in combination with Tecentriq® and Abraxane® in front-line TNBC and in combination with Tecentriq and Avastin® in front-line RCC. In collaboration with Arcus Biosciences, Infinity is evaluating a checkpoint inhibitor-free, novel combination regimen of eganelisib plus etrumadenant (AB928, a dual adenosine receptor antagonist) plus Doxil® in advanced TNBC patients. In 2019, Infinity completed enrollment in MARIO-1, a Phase 1/1b study evaluating eganelisib as a monotherapy and in combination with Opdivo (nivolumab) in patients with advanced solid tumors including patients refractory to checkpoint inhibitor therapy. With these studies Infinity is evaluating eganelisib in the anti-PD-1 refractory, I/O-naïve, and front-line settings. For more information on Infinity, please refer to Infinity's website at www.infi.com.
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such forward-looking statements include those regarding: the therapeutic potential of eganelisib; registration trial planning; plans to present data; clinical trial enrollment projections; the timing of further clinical trial updates from the Company; and the Company's ability to execute on its strategic plans. Such statements are subject to numerous important factors, risks and uncertainties that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from the Company's current expectations. For example, there can be no guarantee that eganelisib will successfully complete necessary preclinical and clinical development phases. Further, there can be no guarantee that any positive developments in Infinity's product portfolio will result in stock price appreciation. Management's expectations and, therefore, any forward-looking statements in this press release could also be affected by risks and uncertainties relating to a number of other factors, including the following: the cost, timing and results of clinical trials and other development activities that may be delayed or disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic or otherwise; the content and timing of decisions made by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and other regulatory authorities; Infinity's ability to obtain and maintain requisite regulatory approvals; unplanned cash requirements and expenditures; development of agents by Infinity's competitors for diseases in which Infinity is currently developing or intends to develop eganelisib; and Infinity's ability to obtain, maintain and enforce patent and other intellectual property protection for eganelisib. These and other risks which may impact management's expectations are described in greater detail under the caption "Risk Factors" included in Infinity's annual report and quarterly reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and in other filings that Infinity makes with the SEC, available through the Company’s website at www.infi.com. Any forward-looking statements contained in this press release speak only as of the date hereof, and Infinity does not undertake and expressly disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Opdivo® is a registered trademark of Bristol Myers Squibb.
Tecentriq® is a registered trademark of Genentech, Inc.
Abraxane® is a registered trademark of Abraxis BioScience, LLC., a wholly owned subsidiary of Bristol Myers Squibb Company.
Avastin® is a registered trademark of Genentech, Inc.
Doxil® is a registered trademark of Baxter Healthcare Corporation.
Investor Relations:
Irina Koffler
LifeSci Advisors, LLC
646-970-4681
ikoffler@lifesciadvisors.com
Serious News for Serious Traders! Try StreetInsider.com Premium Free!
You May Also Be Interested In
- CIDARA Therapeutics ALERT: Bragar Eagel & Squire, P.C. is Investigating Cidara Therapeutics, Inc. on Behalf of Cidara Therapeutics Stockholders and Encourages Investors to Contact the Firm
- HRT Class Action Notice: Robbins LLP Reminds Stockholders of the Lead Plaintiff Deadline in the HireRight Holdings Corp. Class Action
- ROSEN, A LEADING LAW FIRM, Encourages VinFast Auto Ltd. f/k/a Black Spade Acquisition Co. Investors to Secure Counsel Before Important Deadline in Securities Class Action – VFS
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share