Form 497K VALIC Co I
September 28, 2021 3:09 PM EDTSummary Prospectus
October 1, 2021
VALIC Company I
Dynamic Allocation Fund
(Ticker: VDAFX)
The
Fund’s Statutory Prospectus and Statement of Additional Information, each dated October 1, 2021, as amended and
supplemented from time to time, and the most recent shareholder reports are incorporated into and made part of this Summary Prospectus
by reference. The Fund is offered only to registered and unregistered separate accounts of The Variable Annuity Life Insurance Company and its affiliates and to qualifying retirement plans and IRAs and is not intended for use by other
investors.
Before you invest, you may want to review
the Fund’s Statutory Prospectus, which contains more information about the Fund and its risks. You can find the Statutory Prospectus and the above-incorporated information online at
http://valic.onlineprospectus.net/VALIC/FundDocuments/index.html. You can also get this information at no cost by calling 800-448-2542 or by sending an e-mail request to [email protected].
The Securities and Exchange Commission has not approved or
disapproved these securities, nor has it determined that this Summary Prospectus is accurate or complete. It is a criminal offense to state otherwise.
Investment Objective
The Fund’s investment objectives are capital
appreciation and current income while managing net equity exposure.
Fees and Expenses of the Fund
This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay
if you buy, hold and sell shares of the Fund. The table and the example below do not reflect the separate account fees charged in the variable annuity or variable life insurance policy (“Variable
Contracts”) in which the Fund is offered. If separate account fees were shown, the Fund’s annual operating expenses would be higher. Please see your Variable Contract prospectus for more details on the separate account fees. As an
investor in the Fund, you pay the expenses of the Fund and indirectly pay a proportionate share of the expenses of the investment companies in which the Fund invests (the “Underlying Funds”).
Annual Fund
Operating Expenses (expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the value of your investment)
|
Management
Fees |
0.25% |
|
Other
Expenses |
0.07% |
|
Acquired Fund Fees and
Expenses1,2 |
0.49% |
|
Total Annual Fund Operating
Expenses1 |
0.81% |
| 1 | The Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses for the Fund do not correlate to the ratio of net expenses to average net assets provided in the Financial Highlights table of the Fund’s annual report, which reflects the gross operating expenses of the Fund and does not include Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses. “Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses” include fees and expenses incurred indirectly by the Fund as a result of investments in shares of one or more mutual funds, hedge funds, private equity funds or other pooled investment vehicles. |
| 2 | “Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses” have been estimated for the current fiscal year. |
Expense
Example
This Example is intended to help you
compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem or hold all of your shares at the end of those
periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and that the Fund’s operating expenses include fee waivers for one year. The Example does not reflect charges imposed by the Variable Contract. If the Variable
Contract fees were reflected, the expenses would be higher. See the Variable Contract prospectus for information on such charges. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions and the net expenses shown in the fee
table, your costs would be:
| 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years | |||
| $83 | $259 | $450 | $1,002 |
Portfolio Turnover
The portion of the Fund that operates as a fund-of-funds
does not pay transaction costs when it buys and sells shares of Underlying Funds (or “turns over” its portfolio). An Underlying Fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it turns over its portfolio, and a higher portfolio
turnover rate may indicate higher transaction costs. These costs, which are not reflected in annual Fund operating expenses or in the Example, affect the performance of both the Underlying Funds and the Fund. The Fund does, however, pay transaction
costs when it
- 1 -
VALIC Company I
Dynamic Allocation Fund
buys and sells the financial instruments held in the Overlay
Component of the Fund (defined below).
During the most
recent fiscal year, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate was 24% of the average value of its portfolio.
Principal Investment Strategies of the Fund
The Fund seeks to achieve its objectives by investing under
normal conditions approximately 70% to 90% of its assets in shares of the Underlying Funds, which are portfolios of VALIC Company I, (the “Fund-of-Funds Component”) and 10% to 30% of its assets in a portfolio of derivative instruments,
fixed income securities and short-term investments (the “Overlay Component”).
The Fund-of-Funds Component will allocate approximately 50%
to 80% of its assets to Underlying Funds investing primarily in equity securities and 20% to 50% of its assets to Underlying Funds investing primarily in fixed income securities and short-term investments, which may include mortgage- and
asset-backed securities, to seek capital appreciation and generate income.
The Variable Annuity Life Insurance Company is the
Fund’s investment adviser (“VALIC” or the “Adviser”). The Fund is sub-advised by SunAmerica Asset Management, LLC (“SunAmerica”) and AllianceBernstein L.P. (“AllianceBernstein”). The Adviser will
determine the allocation between the Fund-of-Funds Component and the Overlay Component. SunAmerica is responsible for managing the Fund-of-Funds Component’s investment in Underlying Funds, so it will determine the target allocation between
Underlying Funds that invest primarily in equity securities and Underlying Funds that invest primarily in fixed income securities. SunAmerica performs an investment analysis of possible investments for the Fund and selects the universe of permitted
Underlying Funds as well as the allocation to each Underlying Fund. The Adviser may change the Fund’s asset allocation between the Fund-of-Funds Component and the Overlay Component from time to time without prior notice. SunAmerica may change
the Fund-of-Funds Component’s allocation among the Underlying Funds, and may invest in other funds not currently among the Underlying Funds, from time to time without prior notice to investors.
The Fund-of-Funds Component seeks to achieve capital
appreciation primarily through its investments in Underlying Funds that invest in equity securities of both U.S. and non-U.S. companies of all market capitalizations, but expects to invest to a lesser extent in Underlying Funds that invest primarily
in small- and mid-cap U.S. companies and foreign companies. The Fund normally
does not expect to have more than 25% of its total assets allocated to
Underlying Funds investing primarily in foreign securities, and no more than 5% of its total assets to Underlying Funds investing primarily in emerging markets (an emerging market is any country that is included in the MSCI Emerging Markets Index).
The Fund-of-Funds Component seeks to achieve current income through its investments in Underlying Funds that primarily invest in fixed income securities, including both U.S. and foreign investment grade securities, but the Fund normally does not
expect to have more than 5% of total assets allocated to Underlying Funds investing primarily in high-yield, high-risk bonds (commonly known as “junk bonds”), which are considered speculative. Fund cash flows are expected to be used to
maintain or move Underlying Fund exposure close to target allocations, but sales and purchases of Underlying Funds may also be used to change or remain near target allocations.
The Overlay Component comprises the remaining 10%-30% of
the Fund’s total assets. AllianceBernstein is responsible for managing the Overlay Component, which includes management of the derivative instruments, fixed income securities and short-term investments.
AllianceBernstein may invest the Overlay Component in
derivative instruments to increase or decrease the Fund’s overall net equity exposure and, therefore, its volatility and return potential. Volatility is a statistical measurement of the magnitude of up and down fluctuations in the value of a
financial instrument or index over time. High levels of volatility may result from rapid and dramatic price swings. Through its use of derivative instruments, AllianceBernstein may adjust the Fund’s net equity exposure down to a minimum of 25%
or up to a maximum of 100%, although the Fund’s average net equity exposure over long term periods is expected to be approximately 60%-65%. The Fund’s net equity exposure is primarily adjusted through the use of derivative instruments,
such as stock index futures and stock index options, and to a lesser extent options on stock index futures and stock index swaps, as the allocation among Underlying Funds in the Fund-of-Funds Component is expected to remain fairly stable. For
example, when the market is in a state of higher volatility, AllianceBernstein may decrease the Fund’s net equity exposure by taking a short position in derivative instruments. A short sale involves the sale by the Fund of a security or
instrument it does not own with the expectation of purchasing the same security or instrument at a later date at a lower price. The operation of the Overlay Component may therefore expose the Fund to leverage. Because derivative instruments may be
purchased with a fraction of the assets that would be needed to purchase the equity securities directly, the remainder of the assets in the
VALIC Company I
- 2 -
Dynamic
Allocation Fund
Overlay Component will be invested in a variety of fixed
income securities.
The Fund’s performance may
be lower than similar Funds that do not seek to manage their equity exposure. If AllianceBernstein increases the Fund’s net equity exposure and equity markets decline, the Fund may underperform traditional or static allocation funds. Likewise,
if AllianceBernstein reduces the Fund’s net equity exposure and equity markets rise, the Fund may also underperform traditional or static allocation funds. Efforts to manage the Fund’s volatility may also expose the Fund to additional
costs. In addition, AllianceBernstein will seek to reduce exposure to certain downside risks by purchasing equity index put options that aim to reduce the Fund exposure to certain severe and unanticipated market events that could significantly
detract from returns.
In addition to managing the
Fund’s overall net equity exposure as described above, AllianceBernstein will, within established guidelines, manage the Overlay Component in an attempt to generate income, manage Fund cash flows and liquidity needs, and manage collateral for
the derivative instruments. AllianceBernstein will manage the fixed income investments of the Overlay Component by investing in securities rated investment grade or higher by a nationally recognized statistical ratings organization, or, if unrated,
determined by AllianceBernstein to be of comparable quality. At least 50% of the Overlay Component’s fixed income investments will be invested in U.S. Government securities, cash, repurchase agreements, and money market securities. A portion
of the Overlay Component may be held in short-term investments as needed, in order to manage daily cash flows to or from the Fund or to serve as collateral. AllianceBernstein may also invest the Overlay Component in derivative instruments to
generate income and manage Fund’s cash flows and liquidity needs.
The following chart sets forth the target allocations of
the Fund on or about May 31, 2021, to equity and fixed income Underlying Funds and securities. These target allocations represent the Fund’s current goal for the allocation of its assets and does not take into account any change in net equity
exposure from use of derivatives in the Overlay Component. The Fund’s actual allocations could vary substantially from the target allocations due to market valuation changes, changes in the target allocations and AllianceBernstein’s
management of the Overlay Component in response to volatility changes.
| Asset Class | % of Fund-of-Fund | % of Total Fund | |
|
Equity |
75% | 60% |
| Asset Class | % of Fund-of-Fund | % of Total Fund | |
|
U.S. Large
Cap |
55.8% | 44.8% | |
|
U.S. Small and Mid
Cap |
6.8% | 5.4% | |
|
Foreign
Equity |
11.6% | 9.2% | |
|
Alternatives
(REITs) |
0.8% | 0.6% | |
|
Fixed
Income |
25% | 40% | |
|
U.S. Investment
Grade |
23.5% | 38.8% | |
|
U.S. High Yield and MultiSector |
1.0% | 0.8% | |
|
Foreign Fixed
Income |
0.5% | 0.4% | |
| 100.0% | 100.0% |
Principal Risks of Investing in the
Fund
As with any mutual fund, there can be no assurance that the
Fund’s investment objectives will be met or that the net return on an investment in the Fund will exceed what could have been obtained through other investment or savings vehicles. Shares of the Fund are not bank deposits and are not
guaranteed or insured by any bank, government entity or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. If the value of the assets of the Fund goes down, you could lose money.
The risks of investing in the Fund include indirect risks
associated with the Fund’s investments in Underlying Funds. The risks of investing in the Fund include indirect risks associated with the Fund’s investments in Underlying Funds. The value of your investment in the Fund may be affected by
one or more of the following risks, which are described in more detail in the sections “Additional Information About the Funds’ Investment Objectives, Strategies and Investment Risks” and the “Investment Glossary” in
the Prospectus, any of which could cause the Fund’s return, the price of the Fund’s shares or the Fund’s yield to fluctuate. Please note that there are many other circumstances that could adversely affect your investment and
prevent the Fund from reaching its objective, which are not described here.
Market Risk. Market risk is
both a direct and indirect risk of investing in the Fund. The Fund’s or an Underlying Fund’s share price can fall because of weakness in the broad market, a particular industry, or specific holdings.
VALIC Company I
- 3 -
Dynamic
Allocation Fund
The market as a whole can decline for many reasons,
including adverse political or economic developments here or abroad, changes in investor psychology, or heavy institutional selling. The prospects for an industry or company may deteriorate because of a variety of factors, including disappointing
earnings or changes in the competitive environment. In addition, the investment adviser’s assessment of companies held in an Underlying Fund may prove incorrect, resulting in losses or poor performance even in a rising market. Finally, the
Fund’s or an Underlying Fund’s investment approach could fall out of favor with the investing public, resulting in lagging performance versus other comparable portfolios.
The coronavirus pandemic and the related governmental and public responses
have had and may continue to have an impact on the Fund’s or an Underlying Fund’s investments and net asset value and have led and may continue to lead to increased market volatility and the potential for illiquidity in certain classes
of securities and sectors of the market. Preventative or protective actions that governments may take in respect of pandemic or epidemic diseases may result in periods of business disruption, business closures, inability to obtain raw materials,
supplies and component parts, and reduced or disrupted operations for the issuers in which the Underlying Funds invest. Government intervention in markets may impact interest rates, market volatility and security pricing. The occurrence,
reoccurrence and pendency of such diseases could adversely affect the economies (including through changes in business activity and increased unemployment) and financial markets either in specific countries or worldwide.
Derivatives Risk.
Derivatives risk is both a direct and indirect risk of investing in the Fund. A derivative is any financial instrument whose value is based on, and determined by, another security, index or benchmark (i.e., stock option, futures, caps, floors,
etc.). To the extent a derivative contract is used to hedge another position in the Fund or an Underlying Fund, the Fund or Underlying Fund will be exposed to the risks associated with hedging described below. To the extent an option, futures
contract, swap, or other derivative is used to enhance return, rather than as a hedge, the Fund or Underlying Fund will be directly exposed to the risks of the contract. Gains or losses from non-hedging positions may be substantially greater than
the cost of the position. By purchasing over-the-counter derivatives, the Fund or Underlying Fund is exposed to credit quality risk of the counterparty.
Counterparty Risk.
Counterparty risk is both a direct and indirect risk of investing in the Fund. Counterparty risk is the risk that a counterparty to a security, loan or derivative held by the Fund or an Underlying Fund becomes
bankrupt or otherwise fails to perform its obligations due to financial
difficulties. The Fund or an Underlying Fund may experience significant delays in obtaining any recovery in a bankruptcy or other reorganization proceeding, and there may be no recovery or limited recovery in such circumstances.
Leverage Risk. Leverage
risk is a direct risk of investing in the Fund. Certain managed futures instruments, and some other derivatives the Fund buys involve a degree of leverage. Leverage occurs when an investor has the right to a return on an investment that exceeds the
return that the investor would be expected to receive based on the amount contributed to the investment. The Fund’s use of certain economically leveraged futures and other derivatives can result in a loss substantially greater than the amount
invested in the futures or other derivative itself. Certain futures and other derivatives have the potential for unlimited loss, regardless of the size of the initial investment. When the Fund uses futures and other derivatives for leverage, a
shareholder’s investment in the Fund will tend to be more volatile, resulting in larger gains or losses in response to the fluctuating prices of the Fund’s investments.
Risk of Investing in Bonds.
This is both a direct and indirect risk of investing in the Fund. As with any fund that invests significantly in bonds, the value of an investment in the Fund or an Underlying Fund may go up or down in response to changes in interest rates or
defaults (or even the potential for future defaults) by bond issuers.
Interest Rate Fluctuations Risk. Fixed income securities may be subject to volatility due to changes in interest rates. Duration is a measure of interest rate risk that indicates how price-sensitive a bond is to changes in interest rates. Longer-term
and lower coupon bonds tend to be more sensitive to changes in interest rates. Interest rates have been historically low, so the Fund faces a heightened risk that interest rates may rise. For example, a bond with a duration of three years will
decrease in value by approximately 3% if interest rates increase by 1%. Recent and potential future changes in monetary policy made by central banks and/or their governments are likely to affect the level of interest rates.
Credit Risk. Credit risk is
both a direct and indirect risk of investing in the Fund. Credit risk applies to most debt securities, but is generally not a factor for obligations backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. Government. The Fund or an Underlying
Fund could lose money if the issuer of a debt security is unable or perceived to be unable to pay interest or repay principal when it becomes due. Various factors could affect the issuer’s actual or perceived willingness or ability to
make
VALIC Company I
- 4 -
Dynamic
Allocation Fund
timely interest or principal payments, including changes
in the issuer’s financial condition or in general economic conditions.
Hedging Risk. Hedging risk
is both a direct and indirect risk of investing in this Fund. A hedge is an investment made in order to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in a currency or other investment, by taking an offsetting position (often through a derivative, such
as an option or forward). While hedging strategies can be very useful and inexpensive ways of reducing risk, they are sometimes ineffective due to the unexpected changes in the market. Hedging also involves the risk that changes in the value of the
related security will not match those of the instruments being hedged as expected, in which case any losses on the instruments being hedged may not be reduced. For gross currency hedges by Underlying Funds, there is an additional risk, to the extent
that these transactions create exposure to currencies in which an Underlying Fund’s securities are not denominated.
Short Sales Risk. Short
sale risk is both a direct and indirect risk of investing in the Fund. Short sales by the Fund or an Underlying Fund involve certain risks and special considerations. Possible losses from short sales differ from losses that could be incurred from a
purchase of a security, because losses from short sales are potentially unlimited, whereas losses from purchases can be no greater than the total amount invested.
U.S. Government Obligations Risk. This is both a direct and indirect risk of investing in the Fund. U.S. Treasury obligations are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. Government and are generally considered to have minimal
credit risk. Securities issued or guaranteed by federal agencies or authorities and U.S. Government-sponsored instrumentalities or enterprises may or may not be backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government. For example,
securities issued by the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation, the Federal National Mortgage Association and the Federal Home Loan Banks are neither insured nor guaranteed by the U.S. Government; the securities may be supported only by the
ability to borrow from the U.S. Treasury or by the credit of the issuing agency, authority, instrumentality or enterprise and, as a result, are subject to greater credit risk than securities issued or guaranteed by the
U.S. Treasury.
Risk of Investing in Money
Market Securities. This is both a direct and indirect risk of investing in the Fund. An investment in the Fund is subject to the risk that the value of its investments in high-quality short-term obligations
(“money market securities”) may be subject to changes in interest rates, changes in the rating of any money market
security and in the ability of an issuer to make payments of interest and
principal.
Issuer Risk. The value of a security may decline for a number of reasons directly related to the issuer, such as management performance, financial leverage and reduced demand for the issuer’s goods and services.
Dynamic Allocation Risk.
The Fund’s risks will directly correspond to the risks of the Underlying Funds and other direct investments in which it invests. The Fund is subject to the risk that the investment process that will determine the selection of the Underlying
Funds and the allocation and reallocation of the Fund’s assets among the various asset classes may not produce the desired result. The Fund is also subject to the risk that AllianceBernstein may be prevented from trading certain derivatives
effectively or in a timely manner.
Risk of
Conflict with Insurance Company Interests. Managing the Fund’s net equity exposure may serve to reduce the risk from equity market volatility to the affiliated insurance companies and facilitate their ability
to provide guaranteed benefits associated with certain Variable Contracts. While the interests of Fund shareholders and the affiliated insurance companies providing guaranteed benefits associated with the Variable Contracts are generally aligned,
the affiliated insurance companies (and the Adviser by virtue of its affiliation with the insurance companies) may face potential conflicts of interest. In particular, certain aspects of the Fund’s management have the effect of mitigating the
financial risks to which the affiliated insurance companies are subjected by providing those guaranteed benefits. In addition, the Fund’s performance may be lower than similar Funds that do not seek to manage their equity
exposure.
Investment Company Risk. The risks of the Fund owning other investment companies, including the Underlying Funds, generally reflect the risks of owning the underlying securities they are designed to track, although lack of liquidity in these
investments could result in it being more volatile than the underlying Fund of securities. Disruptions in the markets for the securities held by other investment company companies, including the Underlying Funds purchased or sold by the Fund could
result in losses on the Fund’s investment in such securities. The other investment company companies, including Underlying Funds also have fees that increase their costs versus owning the underlying securities directly.
Affiliated Fund Risk. In
managing the portion of the Fund that invests in Underlying Funds, SunAmerica will have the authority to select and substitute the Underlying Funds. SunAmerica may be subject to potential conflicts
VALIC Company I
- 5 -
Dynamic
Allocation Fund
of interest in allocating the Fund’s assets among
the various Underlying Funds because the fees payable to it by the Adviser for some of the Underlying Funds are higher than the fees payable by other Underlying Funds and because SunAmerica also is responsible for managing and administering certain
of the Underlying Funds.
Other indirect principal
risks of investing in the Fund (direct risks of investing in the Underlying Funds) include:
Large-Cap Companies Risk.
Large-cap companies tend to be less volatile than companies with smaller market capitalizations. In exchange for this potentially lower risk, an Underlying Fund’s value may not rise as much as the value of Funds that emphasize smaller
companies.
“Passively Managed”
Strategy Risk. An Underlying Fund following a passively managed strategy will not deviate from its investment strategy. In most cases, it will involve a passively managed strategy utilized to achieve investment
results that correspond to a particular market index. Such a Fund will not sell securities in its portfolio and buy different securities for other reasons, even if there are adverse developments concerning a particular security, company or industry.
There can be no assurance that the strategy will be successful.
Small- and Medium-Sized Companies Risk. Securities of small- and medium-sized companies are usually more volatile and entail greater risks than securities of large companies.
Growth Stock Risk. Growth
stocks are historically volatile, which will affect certain Underlying Funds.
Value Investing Risk. The
investment adviser’s judgments that a particular security is undervalued in relation to the company’s fundamental economic value may prove incorrect, which will affect certain Underlying Funds.
Foreign Investment Risk.
Investments in foreign countries are subject to a number of risks. A principal risk is that fluctuations in the exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and foreign currencies may negatively affect the value of an investment. In addition, there may be
less publicly available information about a foreign company and it may not be subject to the same uniform accounting, auditing and financial reporting standards as U.S. companies. Foreign governments may not regulate securities markets and companies
to the same degree as the U.S. government. Foreign investments will also be affected by local political or economic developments and governmental actions by the United States or other
governments. Consequently, foreign securities may be less liquid, more
volatile and more difficult to price than U.S. securities. These risks are heightened for emerging markets issuers. Historically, the markets of emerging market countries have been more volatile than more developed markets; however, such markets can
provide higher rates of return to investors.
Credit
Quality Risk. The creditworthiness of an issuer is always a factor in analyzing fixed income securities. An issuer with a lower credit rating will be more likely than a higher rated issuer to default or otherwise
become unable to honor its financial obligations. Issuers with low credit ratings typically issue junk bonds, which are considered speculative. In addition to the risk of default, junk bonds may be more volatile, less liquid, more difficult to value
and more susceptible to adverse economic conditions or investor perceptions than investment grade bonds.
Mortgage- and Asset-Backed Securities Risk. Mortgage- and asset-backed securities represent interests in “pools” of mortgages or other assets, including consumer loans or receivables held in trust. The characteristics of these mortgage-backed and
asset-backed securities differ from traditional fixed-income securities. Mortgage-backed securities are subject to “prepayment risk” and “extension risk.” Prepayment risk is the risk that, when interest rates fall, certain
types of obligations will be paid off by the obligor more quickly than originally anticipated and the Fund may have to invest the proceeds in securities with lower yields. Extension risk is the risk that, when interest rates rise, certain
obligations will be paid off by the obligor more slowly than anticipated, causing the value of these securities to fall. Small movements in interest rates (both increases and decreases) may quickly and significantly reduce the value of certain
mortgage-backed securities. These securities also are subject to risk of default on the underlying mortgage, particularly during periods of economic downturn.
Performance Information
The following Risk/Return Bar Chart and Table illustrate
the risks of investing in the Fund by showing changes in the Fund’s performance from calendar year to calendar year and comparing the Fund’s average annual returns to those of the S&P 500® Index, the Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index, and a Blended Index. The blended index is comprised of the S&P 500® Index (60%) and the Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index (40%). Fees and expenses incurred at the contract level are not reflected in the bar
chart or table. If these amounts were reflected, returns would be less than those shown. Of course, past
VALIC Company I
- 6 -
Dynamic
Allocation Fund
performance of the Fund is not necessarily an indication of
how the Fund will perform in the future.
The
percentage of the Fund’s assets that each sub-adviser manages may, at the adviser’s discretion, change from time to time.
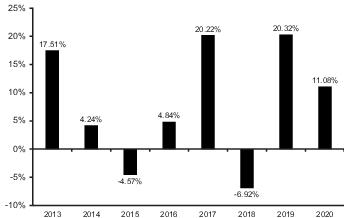
During the period shown
in the bar chart:
| Highest
Quarterly Return: |
March 31, 2019 | 9.62% |
| Lowest
Quarterly Return: |
December 31, 2018 | -10.10% |
| Year
to Date Most Recent Quarter: |
June 30, 2021 | 6.68% |
Average Annual Total Returns (For the periods ended December 31, 2020)
| 1
Year |
5
Years |
Since
Inception |
Inception
Date | ||||
|
Fund |
11.08% | 9.41% | 7.80% | 12/19/2012 | |||
|
Blended
Index |
14.73% | 11.11% | 10.41% | ||||
|
Bloomberg U.S. Aggregate Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or
taxes) |
7.51% | 4.44% | 3.34% | ||||
|
S&P 500® Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or
taxes) |
18.40% | 15.22% | 14.92% |
Investment Adviser
The Fund’s investment adviser is VALIC.
The Fund-of-Funds Component is sub-advised by SunAmerica.
The Overlay Component of the Fund is sub-advised by AllianceBernstein.
Portfolio Managers
| Name and Title | Portfolio
Manager of the Fund Since | |
| SunAmerica | ||
|
Andrew Sheridan Senior Vice President and Lead Portfolio
Manager |
2021 | |
|
Manisha Singh, CFA Senior Vice President and Co-Portfolio
Manager |
2017 | |
|
Robert Wu, CFA Vice President and Co-Portfolio
Manager |
2021 | |
| AllianceBernstein | ||
|
Joshua Lisser Chief Investment Officer and Lead Portfolio Manager - Index
Strategies |
2012 | |
|
Benjamin Sklar Portfolio Manager - Index Strategies, Lead Portfolio
Manager |
2012 |
Purchases and Sales of Fund
Shares
Shares of the Funds may only be purchased or redeemed
through Variable Contracts offered by the separate accounts of VALIC or other participating life insurance companies and through qualifying retirement plans (“Plans”) and IRAs. Shares of each Fund may be purchased and redeemed each day
the New York Stock Exchange is open, at the Fund’s net asset value determined after receipt of a request in good order.
The Funds do not have any initial or subsequent investment
minimums. However, your insurance company may impose investment or account value minimums. The prospectus (or other offering document) for your Variable Contract contains additional information about purchases and redemptions of the Funds’
shares.
Tax Information
A Fund will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax so
long as it qualifies as a regulated investment company and distributes its income and gains each year to its shareholders. However, contractholders may be subject to federal income tax (and a federal Medicare tax of 3.8% that applies to net income,
including taxable annuity payments, if applicable) upon withdrawal from a Variable
VALIC Company I
- 7 -
Dynamic
Allocation Fund
Contract. Contractholders should consult the prospectus
(or other offering document) for the Variable Contract for additional information regarding taxation.
Payments to Broker-Dealers and
Other Financial Intermediaries
Other Financial Intermediaries
The Funds are not sold directly to the general public but
instead are offered to registered and unregistered separate accounts of VALIC and its affiliates and to Plans
and IRAs. The Funds and their related companies may make payments to the
sponsoring insurance company or its affiliates for recordkeeping and distribution. These payments may create a conflict of interest as they may be a factor that the insurance company considers in including the Funds as underlying investment options
in a variable contract. Visit your sponsoring insurance company’s website for more information.
VALIC Company I
- 8 -
FREE Breaking News Alerts from StreetInsider.com!
StreetInsider.com Top Tickers, 4/26/2024
- Stocks face worst month since September, yen swings after BoJ
- Microsoft fiscal Q3 results top estimates as AI revolution spurs cloud growth
- Alphabet stock surges 11% to record high on Q1 earnings beat, first-ever dividend
- Intel slides in afterhours trading as Q1 revenue misses, Q2 outlook falls short
- Oil prices on track to snap two-week losing streak
- Rubrik (RBRK) Prices Upsized 23.5M Share IPO at $32/sh
- Union Pacific beats profit estimates on stronger pricing, resumes share buyback
- IBM tumbles on soft Q1 revenue; announces HashiCorp $6.4bn acquisition
- Hertz Global (HTZ) misses earnings expectations as fleet costs weigh
- Teladoc (TDOC) Misses Q1 EPS by 3c, offers outlook
- After-hours movers: Alphabet, Microsoft, Snap, Intel, and more
- Midday movers: Meta, IBM, Caterpillar fall; Chipotle rises
- After-hours movers: Meta, Ford, IBM, ServiceNow and more
- Midday movers: Tesla, Boeing rise; Uber, Old Dominion Freight fall
- After-hours movers: Tesla, Texas Instruments, Seagate, Visa and more
Serious News for Serious Traders! Try StreetInsider.com Premium Free!
You May Also Be Interested In
- American International Group (AIG) PT Raised to $87 at Deutsche Bank, New Buy Catalyst Call Idea
- Dimensional Fund Advisors Ltd. : Form 8.3 - QUANEX BUILDING PRODUCTS - Ordinary Shares
- AIG (AIG) Announces Retirement of David McElroy
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share