Form 8-K PROGENICS PHARMACEUTICAL For: Jul 30
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 8-K
CURRENT REPORT
Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the
Securities Exchange Act of 1934
Date of Report (Date of earliest event reported): July 30, 2018
Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Charter)
|
Delaware |
|
000-23143 |
|
13-3379479 |
|
(State or other jurisdiction |
(Commission File Number) |
(IRS Employer |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
One World Trade Center, 47th Floor, New York, New York 10007 |
||||
|
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) (Zip Code) |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (646) 975-2500 |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Not Applicable |
||||
|
(Former name or former address, if changed since last report) |
||||
Check the appropriate box below if the Form 8-K filing is intended to simultaneously satisfy the filing obligation of the registrant under any of the following provisions:
| ☐ | Written communications pursuant to Rule 425 under the Securities Act (17 CFR 230.425) |
| ☐ | Soliciting material pursuant to Rule 14a-12 under the Exchange Act (17 CFR 240.14a-12) |
| ☐ | Pre-commencement communications pursuant to Rule 14d-2(b) under the Exchange Act (17 CFR 240.14d-2(b)) |
| ☐ | Pre-commencement communications pursuant to Rule 13e-4(c) under the Exchange Act (17 CFR 240.13e-4(c)) |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is an emerging growth company as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act of 1933 (17 CFR §230.405) or Rule 12b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (17 CFR §240.12b-2).
Emerging growth company ☐
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Item 7.01. Regulation FD Disclosure.
On July 30, 2018, Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc. issued a press release announcing it had received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) approval of its New Drug Application for AZEDRA®, which is the first and only approved therapy in the U.S. for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older with iobenguane scan positive, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma who require systemic anticancer therapy. A copy of the foregoing press release and full Prescribing Information for AZEDRA are furnished as Exhibits 99.1 and 99.2, respectively, to this Current Report on Form 8-K and are incorporated in this Item 7.01 by reference.
The information in this Item 7.01, including Exhibits 99.1 and 99.2 attached hereto, are being furnished and shall not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”) or otherwise subject to the liabilities of that section, nor shall it be deemed incorporated by reference in any filing under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Exchange Act, except as expressly set forth by specific reference in such a filing.
Item 9.01 Financial Statements and Exhibits
(d) Exhibits.
|
Exhibit No. |
|
Description |
|
99.1 |
|
|
| 99.2 | Prescribing Information for AZEDRA | |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned hereunto duly authorized.
|
|
PROGENICS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ Patrick Fabbio |
|
|
|
Patrick Fabbio |
|
|
|
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
| (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | ||
Date: July 31, 2018
Exhibit 99.1

Progenics Pharmaceuticals Announces FDA Approval for AZEDRA® (iobenguane I 131) to Treat Unresectable, Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pheochromocytoma or Paraganglioma
The First FDA-Approved Treatment for These Rare, Life-Threatening Neuroendocrine Cancers in Patients Aged 12 and Older
Company to Host Conference Call Tomorrow at 8:00 AM ET
NEW YORK, July 30, 2018 – Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Nasdaq: PGNX) today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the New Drug Application (NDA) for AZEDRA (iobenguane I 131) 555 MBq/mL injection for intravenous use. AZEDRA, a radiotherapeutic, is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older with iobenguane scan positive, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma who require systemic anticancer therapy. AZEDRA is the first and only approved therapy for this indication.
AZEDRA can cause serious side effects including risk from radiation exposure, bone marrow problems and other cancers (myelosuppression and secondary malignancies), thyroid problems (hypothyroidism), elevations in blood pressure, kidney problems (renal toxicity), respiratory problems (pneumonitis), pregnancy warning (embryo-fetal toxicity), and fertility problems. Please see Important Safety Information below and Full Prescribing Information.
Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma are neuroendocrine cancers that arise from cells in and around the adrenal glands. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma tumors frequently secrete high levels of hormones that can lead to life-threatening high blood pressure, heart failure, and stroke in these patients. Metastatic pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma may result in unresectable disease with a poor prognosis, including a five-year survival rate as low as 12%1. Before AZEDRA’s approval, there were no FDA-approved anti-tumor therapeutics for these cancers.
"AZEDRA is a true breakthrough in treating pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma delivering an effective anticancer therapy to these tumors,” said Dr. Daniel Pryma, Associate Professor of Radiology & Radiation Oncology and Chief, Division of Nuclear Medicine & Clinical Molecular Imaging at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, the trial's lead investigator. “With this innovative, rationally designed treatment, we finally have a therapeutic option that helps address patients’ needs.”
“As the first FDA approved therapy for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma who require systemic anticancer therapy, AZEDRA provides a new treatment option for physicians and their patients,” said Mark Baker, Chief Executive Officer of Progenics. “AZEDRA has been shown to decrease the need for blood pressure medication and reduce tumor size in some patients. We are extremely grateful to the patients, their families and the investigators who participated in AZEDRA’s clinical development program. We also thank those who have contributed to the development of AZEDRA over many years.”
Emily Collins, President of the Pheo Para Alliance stated, “The FDA's approval of AZEDRA is welcome news to patients with pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma, who have an extremely limited number of treatment options available to them. The drug's Fast-Track status and Breakthrough Therapy designation by the FDA underscores the dire need for the development and expeditious review of diagnostic and therapeutic agents for pheo/para that, generally, don’t get adequate prioritization despite the growing prevalence of these and other NET cancers globally.”
Page 2
The FDA approval of AZEDRA was based on data from a pivotal phase 2 open-label, multi-center trial that was conducted under a Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) with the FDA. The final results showed that 17 of the 68 evaluable patients (25%) experienced a 50% or greater reduction of all antihypertensive medication for at least 6 months, achieving the primary endpoint specified in the SPA. The study also showed favorable results from a key secondary endpoint evaluating the proportion of patients with overall tumor response as measured by Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST). Overall tumor response was achieved in 15 of the patients studied (22%). Of these 15 patients, 53% experienced durable tumor responses lasting 6 months or longer. The most common severe (Grade 3-4) adverse reactions were decrease in a specific type of white blood cell (lymphopenia, 78%), decrease in another type of white blood cell (neutropenia, 59%), decrease in platelets which are involved in blood clotting (thrombocytopenia, 50%), fatigue (26%), decrease in red blood cells (anemia, 24%), decrease in blood clotting time (increased international normalized ratio, 18%), nausea (16%), dizziness (13%), high blood pressure (hypertension, 11%), and vomiting (10%). Twelve percent of patients discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions.
Investor Conference Call
Progenics will host a conference call tomorrow, July 31, 2018 at 8:00 AM Eastern Time to discuss the approval. The live and replayed webcast of the call will be available through the Company's website at www.progenics.com. To participate in the live call by phone, dial (877) 250-8889 (USA) or (720) 545-0001 (international) and enter the passcode 2787849. The replay of the call will be available for 90 days. This conference call will replace the quarterly call the Company usually hosts following its earnings announcement.
Approved Use:
AZEDRA® (iobenguane I 131) is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older with iobenguane scan positive, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma who require systemic anticancer therapy.
Important Safety Information
AZEDRA can cause serious side effects. If you experience these side effects, your health care provider may need to adjust or stop your treatment. You should always follow your health care provider’s instructions. Serious side effects may include:
Radiation exposure: Treatment with AZEDRA will expose you to radiation which can contribute to your overall long-term radiation exposure. Overall radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk for cancer. Radiation risk is greater in children than in adults. You should stay well hydrated before, during, and after your treatment and urinate frequently. Your doctor will advise you on how to lessen exposure to people who may come into contact with you after AZEDRA treatment.
Bone marrow problems and other cancers: Treatment with AZEDRA may cause your blood cell counts to drop (myelosuppression). You may experience blood-related side effects such as low numbers of cells that are responsible for blood clotting (thrombocytopenia), low numbers of a type of white blood cells (neutropenia), and low red blood cells (anemia). Among the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA, 33% experienced Grade 4 thrombocytopenia, 16% experienced Grade 4 neutropenia, and 7% experienced Grade 4 anemia. Five percent of patients experienced febrile neutropenia (neutropenia with fever). People with low blood counts can develop serious infections. Your health care provider will routinely check your blood counts and tell you if they are too low. Tell your doctor if you experience any symptoms of low blood counts or infection, such as fever, chills, dizziness, shortness of breath, or increased bleeding or bruising. Your health care provider may need to adjust or stop your treatment accordingly. Other conditions that you may develop as a direct result of treatment with AZEDRA are blood and bone marrow cancers known as secondary myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and leukemia. MDS or acute leukemias were reported in 6.8% of the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA. The time to development of MDS or acute leukemia ranged from 12 months to 7 years. Two of the 88 patients developed other types of cancer.
Page 3
Thyroid problems: Treatment with AZEDRA may increase your long-term risk of developing an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) or thyroid cancer. Hypothyroidism was reported in 3.4% of the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA. Take all thyroid-blocking agents as prescribed by your doctor to reduce the risk of these problems. You may need life-long monitoring for signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Elevations in blood pressure: During or 24 hours following AZEDRA treatment, you may experience increases of blood pressure (hypertension) as a result of hormones released from your cancer. Eleven percent of the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA experienced a worsening of pre-existing hypertension. All changes in blood pressure occurred within the first 24 hours after treatment. No life-threatening hypertensive crises have been observed. Monitor blood pressure frequently during the first 24 hours after each therapeutic dose of AZEDRA. Tell your doctor if you experience any cardiac-related symptoms.
Kidney problems: Treatment with AZEDRA will expose your kidneys to radiation and may impair their ability to work as normal. In some cases, patients have experienced kidney failure after treatment with AZEDRA. Of the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA, 9% developed kidney failure or acute kidney injury, and 22% experienced a decrease in kidney function measured at 6 or 12 months. Your health care provider will monitor your kidneys after treatment using blood tests, particularly if you already have kidney impairment before treatment.
Respiratory problems: Treatment with AZEDRA may cause noninfectious lung inflammation (pneumonitis). Tell your doctor if you experience shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, or cough.
Pregnancy warning: Before treatment with AZEDRA, tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Exposure to radiation from treatment with AZEDRA can harm your unborn baby. Use an effective method of birth control during treatment with AZEDRA and for 7 months (for females) and 4 months (for males) after your final dose. Do not breastfeed during treatment with AZEDRA and for 80 days after your final dose.
Fertility problems: Treatment with AZEDRA may cause infertility due to radiation absorbed by your testes or ovaries over the treatment period that is within the range of exposure where temporary or permanent infertility may be expected.
The most common and most serious side effects of AZEDRA include decreased blood cell counts, nausea, vomiting and fatigue. These are not all the possible side effects of AZEDRA. For more information, ask your health care provider.
Drugs that reduce catecholamine uptake or that deplete catecholamine stores may interact with AZEDRA and may affect how well it works. These drugs were not permitted in the clinical trials. Tell your doctor before starting any medication, including over the counter medications, herbal or dietary supplements.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see full Prescribing Information for AZEDRA.
Distributed by: Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc., NY 10007
Page 4
Reference:
AZEDRA® prescribing information. New York, NY: Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 07 2018.
About PROGENICS
Progenics develops innovative medicines and other technologies to target and treat cancer, including: 1) therapeutic agents designed to treat cancer (AZEDRA, PSMA TTC and 1095), 2) PSMA-targeted imaging agents for prostate cancer (1404 and PyL™), and 3) imaging analysis technology. Progenics has two commercial products, RELISTOR® (methylnaltrexone bromide) for opioid-induced constipation, which is partnered with Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc.; and AZEDRA, for the treatment of unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma (rare neuroendocrine tumors of neural crest origin) who require systemic anticancer therapy.
This press release contains "forward-looking statements" regarding future events. Statements contained in this communication that refer to Progenics' estimated or anticipated future results or other non-historical facts are forward-looking statements that reflect Progenics' current perspective of existing trends and information as of the date of this communication. Forward looking statements are generally accompanied by words such as "anticipate," "believe," "plan," "could," "should," "estimate," "expect," "forecast," "outlook," "guidance," "intend," "may," "might," "will," "possible," "potential," "predict," "project," or other similar words, phrases or expressions. Such statements are predictions only, and are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual events or results to differ materially. These risks and uncertainties include, among others, market acceptance for approved products; the risk that the planned commercial launch of AZEDRA may not meet revenue and income expectations; the cost, timing and unpredictability of results of clinical trials and other development activities and collaborations, such as the Phase 3 clinical program for 1404; our ability to successfully develop and commercialize the products of EXINI Diagnostics AB; the effectiveness of the efforts of our partners to market and sell products on which we collaborate and the royalty revenue generated thereby; generic and other competition; the possible impairment of, inability to obtain and costs of obtaining intellectual property rights; possible product safety or efficacy concerns, general business, financial, regulatory and accounting matters, litigation and other risks. More information concerning Progenics and such risks and uncertainties is available on its website, and in its press releases and reports it files with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, including those risk factors included in its Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017, as updated in its subsequent Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q. Progenics is providing the information in this press release as of its date and, except as expressly required by law, Progenics disclaims any intent or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or circumstances or otherwise.
Additional information concerning Progenics and its business may be available in press releases or other public announcements and public filings made after this release. For more information, please visit www.progenics.com. Information on or accessed through our website or social media sites is not included in the company's SEC filings.
PGNX-F
Contact:
Melissa Downs
Investor Relations
(646) 975-2533
1Park, J., Korean J Urology 2011;52:241-246.
2AZEDRA Prescribing Information. New York, NY: Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; July 30, 2018
Exhibit 99.2
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AZEDRA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AZEDRA.
AZEDRA® (iobenguane I 131) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
—————————INDICATIONS AND USAGE————————
AZEDRA is a radioactive therapeutic agent indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older with iobenguane scan positive, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma who require systemic anticancer therapy. (1)
————————DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION——————
|
● |
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to administering AZEDRA. (2.1) |
|
● |
Block thyroid prior to administering AZEDRA. (2.2) |
|
● |
Do not administer if platelet count is less than 80,000/mcL or absolute neutrophil count is less than 1,200/mcL. (2.4) |
|
● |
Administer AZEDRA intravenously as a dosimetric dose followed by two therapeutic doses administered 90 days apart.(2.2) |
|
● |
The recommended dosimetric dose is: |
|
o |
Patients greater than 50 kg: 185 to 222 MBq (5 to 6 mCi) |
|
o |
Patients 50 kg or less: 3.7 MBq/kg (0.1 mCi/kg) |
|
● |
The recommended therapeutic dose for each of the 2 doses is: |
|
o |
Patients greater than 62.5 kg: 18,500 MBq (500 mCi) |
|
o |
Patients 62.5 kg or less: 296 MBq/kg (8 mCi/kg) |
|
● |
Adjust AZEDRA therapeutic doses based on radiation dose estimates results from dosimetry, if needed. (2.2) |
————————DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS——————
Injection: 555 MBq/mL (15 mCi/ml) at TOC as a clear solution in a single-dose vial. (3)
——————————CONTRAINDICATIONS—————————
None.
—————————–WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS——————
|
● |
Risk from Radiation Exposure: Minimize radiation exposure consistent with institutional radiation safety practices and patient management procedures. (2.1, 5.1) |
|
● |
Myelosuppression: Monitor blood cell counts. Withhold and dose reduce AZEDRA as recommended based on severity of cytopenia. (5.2) |
|
● |
Secondary Myelodysplastic Syndrome, Leukemia and Other Malignancies: The time to development of MDS or acute leukemia ranged from 12 months to 7 years. (5.3) |
|
● |
Hypothyroidism: Initiate thyroid-blocking medication prior to administration and continue after each dose. Monitor for hypothyroidism and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels before starting AZEDRA and annually thereafter. (2.3, 5.4) |
|
● |
Elevations in blood pressure: Monitor blood pressure frequently during the first 24 hours after each therapeutic dose. (5.5) |
|
● |
Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function during and after treatment. (5.6) |
|
● |
Pneumonitis: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of pneumonitis and treat appropriately. (5.7) |
|
● |
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females and males of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.8) |
|
● |
Risk of Infertility: May cause infertility (5.9) |
——————————ADVERSE REACTIONS—————————
The most common Grade 3-4 adverse reactions (≥ 10%) were lymphopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, fatigue, anemia, increased international normalized ratio, nausea, dizziness, hypertension, and vomiting. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 844-668-3950 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
——————————DRUG INTERACTIONS——————————
|
● |
Drugs that Reduce Catecholamine Uptake or Deplete Stores: Discontinue these drugs prior to and following AZEDRA administration. (2.3, 7.1) |
————————USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS——————
|
● |
Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed. (8.2) |
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Revised: 7/2018
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Safety Information
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Thyroid Blockade and Other Pre-and Concomitant Medications
2.4 Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.5 Preparation and Administration
2.6 Radiation Dosimetry
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk from Radiation Exposure
5.2 Myelosuppression
5.3 Secondary Myelodysplastic Syndrome, Leukemia and Other Malignancies
5.4 Hypothyroidism
5.5 Elevations in Blood Pressure
5.6 Renal Toxicity
5.7 Pneumonitis
5.8 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
5.9 Risk of Infertility
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs that Reduce Catecholamine Uptake or Deplete Stores
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Physical Characteristics
11.2 External Radiation
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AZEDRA is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older with iobenguane scan positive, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma who require systemic anticancer therapy.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Safety Information
AZEDRA is a radiopharmaceutical. Handle with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Use waterproof gloves and effective radiation shielding when handling AZEDRA. Radiopharmaceuticals, including AZEDRA, should be used by or under the control of physicians who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radiopharmaceuticals, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate governmental agency authorized to license the use of radiopharmaceuticals.
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating AZEDRA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Administer thyroid blockade and other pre- and concomitant medications as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Dosimetric Dose
The recommended AZEDRA dosimetric dose administered as an intravenous injection is:
|
● |
Patients weighing greater than 50 kg: 185 to 222 MBq (5 or 6 mCi) |
|
● |
Patients weighing 50 kg or less: 3.7 MBq/kg (0.1 mCi/kg) |
Dosimetry and Biodistribution Assessment
Following the AZEDRA dosimetric dose:
|
● |
Acquire anterior/posterior whole body gamma camera images within 1 hour of the AZEDRA dosimetric dose and prior to patient voiding (Day 0; Scan 1). |
|
● |
Acquire additional images on Day 1 or 2 following patient voiding (Scan 2). |
|
● |
Acquire additional images between Days 2-5 following patient voiding (Scan 3). |
For each individual patient, calculate the radiation dose estimates to normal organs and tissues per unit activity [D (organ)] of administered dose using data extracted from these 3 images. Calculate in accordance with the Medical Internal Radiation Dose (MIRD) schema or related methodology. Whenever possible, use patient-specific organ masses (e.g. estimated from imaging).
Therapeutic Dosage
The recommended AZEDRA therapeutic dose is based on body weight and reduced, if necessary, based on the dosimetry data. Administer a total of 2 therapeutic doses intravenously a minimum of 90 days apart.
Weight Based Dose per Therapeutic Cycle
|
● |
Patients weighing greater than 62.5 kg: 18,500 MBq (500 mCi) |
|
● |
Patients weighing 62.5 kg or less: 296 MBq/kg (8 mCi/kg) |
Determine if Dose Reduction Needed Based on Critical Organ Limits
|
● |
Calculate the estimated critical organ absorbed-dose by multiplying the dosimetry-derived radiation absorbed-dose per unit activity [D (organ)] by weight based therapeutic total activity (Aw). |
|
● |
If resulting estimated critical organ absorbed-dose is less than threshold absorbed-dose (T) shown in Table 1, no dose adjustment is necessary |
|
● |
If resulting estimated critical organ absorbed-dose exceeds threshold absorbed-dose (T) shown in Table 1, calculate the reduced therapeutic total activity (i.e., the cumulative activity that would be administered in 2 therapeutic cycles) using the following equation: |
Reduced Therapeutic Total Activity= Aw ×[T ÷ {Aw × D (organ)}]
|
● |
Example: A 75 kg patient qualifies for a therapeutic total activity of 1000 mCi (Aw). For the kidneys, the dosimetry yields an estimated critical organ absorbed dose per unit activity of 0.027 Gy/mCi [D (kidney)]. Thus, the estimated critical organ absorbed-dose to the kidney is 27 Gy [Aw x D (organ)], which exceeds the threshold absorbed-dose for the kidneys (T) of 18 Gy (Table 1). Using the equation above the reduced therapeutic total activity to be adminsitered to this patient is 666.7 mCi. |
1000 mCi × [18 Gy ÷ {1000 mCi × 0.027 mCi/Gy}]
|
Table 1: |
Absorbed-dose Threshold Values for Radiation Toxicity in Critical Organs |
|
Organ |
~ 1%-rate: mortality or organ failure associated with disease |
Time to death or organ failure |
Threshold* absorbed-dose for ~1%-rate mortality or organ failure (Gy) |
|
Red marrow |
H-ARS mortality |
1-2 months |
12 |
|
Lungs |
Pneumonitis mortality |
1-7 months |
16.5 |
|
Kidneys |
Renal failure |
>1 year |
18 |
|
Liver |
Hepatomegaly, ascites: possible organ failure |
0.5-3 months |
31 |
|
Small intestine |
GI-ARS mortality |
6-9 days |
40 |
*Threshold of ~0.5 Gy for both heart and carotid artery, derived from experience with external-beam radiotherapy and associated with fractionated exposure, has also been proposed to support an ~1% mortality rate of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular deaths in >10-15 years; however, uncertainty is associated with the value ~ 0.5 Gy cited for vascular disease (ICRP publication 118, p.300, Table 4.5). Consider benefits/risks to patients.
2.3 Thyroid Blockade and Other Pre-and Concomitant Medications
Thyroid Blockade
Administer inorganic iodine starting at least 24 hours before and continuing for 10 days after each AZEDRA dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hydration
Instruct patients to increase fluid intake to at least two liters a day starting at least 1 day before and continuing for 1 week after each AZEDRA dose to minimize irradiation to the bladder [see Warnings and Precaution (5.1)].
Drugs that Reduce Catecholamine Uptake or Deplete Stores
Discontinue drugs that reduce catecholamine uptake or deplete catecholamine stores for at least 5 half-lives before administration of either the dosimetry dose or a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA. Do not administer these drugs until at least 7 days after each AZEDRA dose [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Antiemetic
Administer antiemetics 30 minutes prior to administering each AZEDRA dose.
2.4 Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended dose modifications of AZEDRA for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2 and the recommended dose or dose reduction for the second therapeutic dose of AZEDRA for myelosuppression are provided in Table 3.
|
Table 2: |
Recommended Dose Modifications of AZEDRA for Adverse Reactions |
|
Adverse Reaction |
Dose Modification |
|
Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] |
Do not administer the first therapeutic dose for platelet counts less than 80,000/mcL or absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) less than 1,200/mcL.
Do not administer the second therapeutic dose until platelets and neutrophils return to baseline or to the normal range. Reduce the second therapeutic dose for the following:
● platelet count less than 25,000/mcL, ANC less than 500/mcL, or life-threatening anemia for more than 7 days ● febrile neutropenia ● platelet count less than 50,000/mcL with active bleeding |
|
Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. |
Do not administer the second therapeutic dose if pneumonitis is diagnosed after the first therapeutic dose. |
|
Table 3: |
Recommended Dose or Dose Reduction for Second Therapeutic Dose of AZEDRA for Myelosuppression |
|
Patient Population |
If first therapeutic dose was weight based, |
If first therapeutic dose was reduced based on criticial organ limits, |
|
Patients weighing greater than 62.5 kg |
Reduce the second therapeutic dose to 425 mCi |
Reduce second therapeutic dose to 85% of the first dose |
|
Patients weighing 62.5 kg or less |
Reduce the second therapeutic dose to 7 mCi/kg |
Reduce second therapeutic dose to 85% of the first dose |
|
2.5 |
Preparation and Administration |
|
● |
Refer to the Package Handling Instructions supplied with the frozen vial. Discard if the temperature recording device displays an alarm icon indicating that the temperature exceeded -70ºC during shipment. |
|
● |
Use aseptic technique and radiation shielding when administering the AZEDRA solution. Use tongs when handling vial to minimize radiation exposure. |
|
● |
Confirm the amount of radioactivity of AZEDRA in the radiopharmaceutical vial with an appropriate dose calibrator prior to and after AZEDRA administration. |
|
● |
Inspect visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. The AZEDRA solution should be a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution without any particulate matter. Discard if particulate matter or discoloration is observed. |
Dosimetric Dose Preparation
|
● |
Thaw the vial to room temperature in lead pot. Do not heat or refreeze. Confirm complete thawing and gently swirl to ensure homogeneity. |
|
● |
Insert a venting unit (consisting of a needle, 0.2-micron sterile filter, and a charcoal filter) to avoid pressurizing the contents of the vial during dilution. Swirl gently to ensure homogeneity. |
|
● |
Add sufficient volume of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution, USP to the vial to yield a concentration of 1 mCi/mL (37 MBq/mL). Swirl gently to ensure homogeneity. |
|
● |
Draw the dosimetric dose into a 10 mL shielded syringe and place in the dose calibrator to ensure that the activity is within ± 10% of dose. Discard unused medicinal product or waste material in accordance with local and federal laws. |
|
● |
Maintain at room temperature and administer within 8 hours of retrieval from frozen storage. |
Dosimetric Dose Administration
|
● |
Administer the dosimetric dose over 60 seconds. |
Therapeutic Dose Preparation
|
● |
Thaw the appropriate number of vials (2 or 3) to room temperature in lead pots. Do not heat or refreeze. |
|
● |
Swirl AZEDRA vial(s) to ensure homogeneity. |
|
● |
Insert a venting unit into each AZEDRA vial to avoid pressurizing the contents of the vial during dilution. |
|
● |
Insert a venting unit into a sterile 50-mL glass vial. Transfer the entire contents of the two therapeutic vial(s) into a 50-mL glass vial. Measure the radioactivity. |
|
o |
If radioactivity in the 50-mL glass vial exceeds the therapeutic dose, withdraw and discard the appropriate volume using a shielded syringe. Add 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution, USP to a total volume of 50 mL. |
|
o |
If radioactivity in the 50-mL glass vial is less than the therapeutic dose, use a shielded syringe to withdraw the appropriate volume from a third AZEDRA vial and add to the 50-mL glass vial. Add 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution, USP to a total volume of 50 mL. |
|
● |
Swirl gently to ensure homogeneity. |
|
● |
Remove the venting unit and place the 50-mL glass vial into a dose calibrator to ensure that the activity is within ± 10% of therapeutic dose. |
|
● |
Maintain at room temperature and administer within 8 hours of retrieval from frozen storage. |
|
● |
Discard unused medicinal product or waste material in accordance with local and federal laws. |
Therapeutic Dose Administration
|
● |
Verify line patency by infusing 250 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution for Injection, USP (primary intravenous line) at recommended rate of 200 mL/hour. |
|
● |
Insert a venting unit into the 50-mL glass vial containing the AZEDRA therapeutic dose. |
|
● |
Assemble a second intravenous line using a 19 Gauge x 5-inch aspirating needle, 24-inch M-M arterial pressure tubing and a primary set specific connector. |
|
● |
Clamp the second intravenous line and connect it to the primary intravenous line using the primary set specific connector. Flush the second intravenous line by releasing the clamp and then re-clamp the second intravenous line. |
|
● |
Insert the needle of the second intravenous line into the 50-mL glass vial containing the AZEDRA therapeutic dose. Ensure the needle reaches the bottom of the glass vial without touching the sides of the vial. |
|
● |
Clamp the primary intravenous line just above the second intravenous line and remove the clamp from the secondary intravenous line. |
|
● |
Administer the AZEDRA therapeutic dose over 30 minutes at a recommended rate of 100 mL/hour for adults; for pediatric patients 12 years and older administer over 60 minutes at a recommended rate of 50 mL/hr . Clamp the secondary intravenous line when the first air bubbles form. |
|
● |
Remove the clamp from the primary intravenous line to flush any residual AZEDRA therapeutic dose within this intravenous line with at least 50 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution for Injection, USP. |
|
● |
Remove the clamp from the secondary intravenous line to flush any residual drug in the secondary intravenous line into the 50-mL glass vial. |
2.6 Radiation Dosimetry
The mean of the estimated radiation absorbed doses for AZEDRA are shown in Table 4.
|
Table 4: |
Radiation Absorbed Dose Estimates* by Target Organ Following Intravenous Administration of ~5 mCi AZEDRA |
|
Target Organ |
Mean |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Standard Deviation (mGy/MBq) |
|
Salivary Glands |
1.499 |
0.486 |
7.957 |
1.134 |
|
LLI Wall1 |
1.184 |
0.093 |
2.770 |
0.356 |
|
Thyroid |
0.779 |
0.071 |
11.000 |
1.409 |
|
Urinary Bladder Wall |
0.614 |
0.141 |
0.930 |
0.142 |
|
ULI Wall2 |
0.514 |
0.091 |
1.120 |
0.138 |
|
Liver |
0.509 |
0.180 |
7.830 |
0.862 |
|
Kidneys |
0.360 |
0.085 |
0.772 |
0.163 |
|
Spleen |
0.343 |
0.091 |
4.470 |
0.495 |
|
Lungs |
0.323 |
0.123 |
3.170 |
0.344 |
|
Heart Wall |
0.272 |
0.073 |
1.550 |
0.215 |
|
Small Intestine |
0.194 |
0.085 |
0.347 |
0.042 |
|
Osteogenic Cells |
0.151 |
0.085 |
0.369 |
0.044 |
|
Gallbladder Wall |
0.146 |
0.083 |
0.852 |
0.094 |
|
Ovaries |
0.126 |
0.000 |
0.271 |
0.046 |
|
Pancreas |
0.117 |
0.068 |
0.484 |
0.054 |
|
Adrenals |
0.116 |
0.067 |
0.535 |
0.059 |
|
Uterus |
0.112 |
0.000 |
0.247 |
0.041 |
|
Stomach Wall |
0.100 |
0.059 |
0.279 |
0.033 |
|
Thymus |
0.083 |
0.049 |
0.212 |
0.027 |
|
Muscle |
0.082 |
0.049 |
0.188 |
0.024 |
|
Red Marrow |
0.079 |
0.048 |
0.175 |
0.022 |
|
Breasts |
0.070 |
0.040 |
0.189 |
0.024 |
|
Skin |
0.063 |
0.036 |
0.153 |
0.018 |
|
Testes |
0.061 |
0.000 |
0.183 |
0.036 |
|
Brain |
0.057 |
0.022 |
0.213 |
0.028 |
|
Total Body |
0.107 |
0.064 |
0.414 |
0.045 |
|
* Table 1 tends to yield underestimates of absorbed dose for patients weighing less than 65 kg, and tends to yield overestimates for patients weighing more than 65 kg. 1-LLI Wall- Lower Large Intestine Wall 2 ULI Wall- Upper Large Intestine Wall |
||||
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 555 MBq/mL (15 mCi/mL) as a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution in a single-dose vial.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk from Radiation Exposure
AZEDRA contributes to a patient’s overall long-term radiation exposure. Long-term cumulative radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk for cancer. These risks of radiation associated with the use of AZEDRA are greater in pediatric patients than in adults [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Minimize radiation exposure to patients, medical personnel, and household contacts during and after treatment with AZEDRA consistent with institutional good radiation safety practices and patient management procedures [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.2 Myelosuppression
Severe and prolonged myelosuppression occurred during treatment with AZEDRA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Among the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA, 33% experienced Grade 4 thrombocytopenia, 16% experienced Grade 4 neutropenia, and 7% experienced Grade 4 anemia. Five percent of patients experienced febrile neutropenia. In Study IB12B following the first therapeutic dose, patients who experienced Grade 4 neutropenia reached neutrophil nadir at a median of 36 days (27 – 55 days) and remained at nadir for a median of 12 days (8 – 22 days) until recovery to less than or equal to Grade 3. Following the second dose, patients who experienced Grade 4 neutropenia reached nadir at a median of 43 days (38 – 47 days) and remained at nadir for a median of 18.5 days (8 – 31 days) until recovery to less than or equal to Grade 3.
Monitor blood cell counts weekly for up to 12 weeks or until levels return to baseline or the normal range. Withhold and dose reduce AZEDRA as recommended based on severity of the cytopenia [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Secondary Myelodysplastic Syndrome, Leukemia and Other Malignancies
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or acute leukemias were reported in 6.8% of the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The time to development of MDS or acute leukemia ranged from 12 months to 7 years.
Two of the 88 patients developed a non-hematological malignancy. One patient developed colon cancer at 18 months and one patient developed lung adenocarcinoma at 27 months following the first therapeutic dose.
5.4 Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism was reported in 3.4% of the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The time to worsening of hypothyroidism was 4 months in one patient, and the time to development of hypothyroidism was less than one month in one patient and 18 months in one patient. Initiate thyroid-blocking medications starting at least 1 day before and continuing for 10 days after each AZEDRA dose to reduce the risk of hypothyroidism or thyroid neoplasia [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Evaluate for clinical evidence of hypothyroidism and measure thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels prior to initiating AZEDRA and annually thereafter.
5.5 Elevations in Blood Pressure
Eleven percent of the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] experienced a worsening of pre-existing hypertension defined as an increase in systolic blood pressure to ≥160 mmHg with an increase of 20 mmHg or an increase in diastolic blood pressure to ≥ 100 mmHg with an increase of 10 mmHg. All changes in blood pressure occurred within the first 24 hours post infusion. Monitor blood pressure frequently during the first 24 hours after each therapeutic dose of AZEDRA.
5.6 Renal Toxicity
Of the 88 patients who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], 7% developed renal failure or acute kidney injury and 22% demonstrated a clinically significant decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measured at 6 or 12 months. Monitor renal function during and after treatment with AZEDRA. Patients with baseline renal impairment may be at greater risk of toxicity; perform more frequent assessments of renal function in patients with mild or moderate impairment. AZEDRA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min).
5.7 Pneumonitis
Fatal pneumonitis occurred 9 weeks after a single dose in one patient in the expanded access program for Study IB12B (n=11). Pneumonitis was not diagnosed among the 88 patients enrolled in Study IB12 or IB12B [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of pneumonitis and treat appropriately.
5.8 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, AZEDRA can cause fetal harm. There are no available data on the use of AZEDRA in pregnant women. No animal studies using iobenguane I 131 have been conducted to evaluate its effect on female reproduction and embryo-fetal development; however, all radiopharmaceuticals, including AZEDRA, have the potential to cause fetal harm.
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating AZEDRA [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Advise females and males of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with AZEDRA and for 7 months after the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
5.9 Risk of Infertility
Radiation exposure associated with AZEDRA may cause infertility in males and females. The recommended cumulative dose of 37 GBq of AZEDRA results in a radiation absorbed dose to the testes and ovaries within the range where temporary or permanent infertility can be expected following external beam radiotherapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6.), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
|
● |
Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] |
|
● |
Secondary Myelodysplastic Syndrome, Leukemia and Other Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] |
|
● |
Hypothyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] |
|
● |
Elevations in Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] |
|
● |
Renal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] |
|
● |
Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] |
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in Warnings and Precautions reflect exposure to AZEDRA in 88 patients with iobenguane-scan positive recurrent or unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma (PPGL) who received a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA in one of two clinical studies (IB12 or IB12B). The Warnings and Precautions also include data from 11 patients enrolled in an expanded access program for Study IB12B [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
The safety data below was evaluated in two studies in patients with recurrent or unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic PPGL. Study IB12 was an open-label, multi-center, single-arm dose-finding study in adult patients with malignant or recurrent PPGL. The study consisted of a 12-month efficacy phase with a 1 year follow-up. Twenty-one patients received a dosimetric dose (~5 mCi), followed by one therapeutic dose (~500 mCi) of AZEDRA. Study IB12B was an open-label, multi-center, single-arm study in 68 adult and pediatric patients age 12 years and older with recurrent or unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic PPGL [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Patients with evidence of liver dysfunction (aspartate aminotransferase or alanine aminotransferase ≥ 2.5 times the upper limit of normal or total bilirubin > 1.5 times the upper limit of normal), a history of liver disease (including hepatitis and chronic alcohol abuse), or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min) were excluded. Patients who had received external beam radiation to > 25% of bone marrow, received whole body radiotherapy, or who had received any systemic radiotherapy resulting in myelosuppression within 3 months of study entry, were also excluded. The safety data described below are based on pooled safety data from studies IB12 and IB12B. A total of 88 patients received at least one therapeutic dose of AZEDRA and 50 patients received two therapeutic doses (one patient received treatment in both studies).
Adverse reactions from studies IB12 and IB12B are presented in Table 5. The most common severe (Grade 3-4) adverse reactions were lymphopenia (78%), neutropenia (59%), thrombocytopenia (50%), fatigue (26%), anemia (24%), increased international normalized ratio (18%), nausea (16%), dizziness (13%), hypertension (11%), and vomiting (10%). Twelve percent of patients discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions (thrombocytopenia, anemia, lymphopenia, nausea and vomiting, multiple hematologic adverse reactions).
|
Table 5: |
Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥10% of Patients with PPGL Receiving Therapeutic Dose of AZEDRA in Studies IB12B and IB12 |
|
Adverse Reaction |
All Gradesa, (%) |
Gradesa 3 - 4, (%) |
|
Hematologicb |
||
|
Lymphopenia |
96 |
78 |
|
Anemia |
93 |
24 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
91 |
50 |
|
Neutropenia |
84 |
59 |
|
Gastrointestinal |
||
|
Nausea |
78 |
16 |
|
Vomitingc |
58 |
10 |
|
Dry mouth |
48 |
2 |
|
Sialadenitisd |
39 |
1 |
|
Diarrhea |
25 |
3 |
|
Abdominal paine |
23 |
6 |
|
Constipation |
19 |
7 |
|
Oropharyngeal pain |
14 |
0 |
|
Dyspepsia |
10 |
0 |
|
General |
||
|
Fatiguef |
71 |
26 |
|
Pyrexia |
14 |
2 |
|
Injection site pain |
10 |
0 |
|
Hyperhidrosis |
10 |
0 |
|
Alopecia |
10 |
0 |
|
Infections |
||
|
Upper respiratory tract infectiong |
16 |
2 |
|
Urinary tract infection |
11 |
1 |
|
Investigationsb |
||
|
Increased international normalized ratioh |
85 |
18 |
|
Increased blood alkaline phosphatase |
53 |
5 |
| Adverse Reaction | All Gradesa, (%) | Gradesa 3 - 4, (%) |
|
Increased aspartate aminotransferase |
50 |
2 |
|
Increased alanine aminotransferase |
43 |
2 |
|
Metabolism and nutrition |
||
|
Decreased appetite |
30 |
5 |
|
Dehydration |
16 |
4 |
|
Decreased weight |
16 |
1 |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
||
|
Back pain |
17 |
2 |
|
Pain in extremity |
15 |
0 |
|
Nervous system |
||
|
Dizzinessi |
34 |
13 |
|
Headache |
32 |
6 |
|
Dysgeusiaj |
24 |
1 |
|
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders |
||
|
Cough |
18 |
0 |
|
Dyspnea |
18 |
7 |
|
Vascular |
||
|
Hypotension |
24 |
4 |
|
Hypertensionk |
20 |
11 |
|
Tachycardia |
10 |
3 |
a NCI CTCAE version 3.0
b Based on laboratory data
c Includes vomiting and retching
d Includes sialoadenitis, salivary gland pain, and salivary gland enlargement
e Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal pain lower.
f Incudes fatigue, asthenia.
g Includes upper respiratory tract infection, sinusitis, rhinorrhea, upper-airway cough syndrome, nasopharyngitis
h Only assessed in Study IB12B (N=68)
iIncludes dizziness and dizziness postural
jIncludes dysgeusia, hypogeusia and ageusia
k Includes blood pressure increased and hypertension.
The following clinically significant adverse reactions were observed in < 10% of patients treated with AZEDRA:
Cardiac: palpitations (9%), syncope and presyncope (8%)
Endocrine: decreased TSH (5%), hypothyroidism (3%)
Gastrointestinal: dysphagia (7%), abdominal distension (6%), gastroesophageal reflux disease (6%), stomatitis (3%)
General: insomnia (9%), chills (8%), chest pain (6%)
Infections: candida infection (6%)
Investigations: prolonged prothrombin time (9%)
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue: arthralgia (8%), neck pain (8%), pain in jaw (7%), muscle spasms (6%)
Renal and urinary disorders: proteinuria (9%), renal failure (7%),
Respiratory: epistaxis (9%), nasal congestion (7%), pulmonary embolism (3%)
Skin and subcutaneous tissue: dry skin (8%), rash (8%), petechiae (7%)
Vascular: orthostatic hypotension (9%)
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs that Reduce Catecholamine Uptake or Deplete Stores
Based on the mechanism of action of iobenguane, drugs that reduce catecholamine uptake or that deplete catecholamine stores may interfere with iobenguane uptake into cells and therefore interfere with dosimetry calculations or the efficacy of AZEDRA. These drugs were not permitted in clinical trials that assessed the safety and efficacy of AZEDRA. Discontinue drugs that reduce catecholamine uptake or deplete catecholamine stores, such as those listed below, for at least 5 half-lives before administration of either the dosimetry or a therapeutic dose of AZEDRA. Do not administer these drugs until at least 7 days after each AZEDRA dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
|
● |
CNS stimulants or amphetamines (e.g. cocaine, methylphenidate, dextroamphetamine) |
|
● |
Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors (e.g. phenteramine) |
|
● |
Norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibitors (e.g. tramadol) |
|
● |
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (e.g. phenelzine and linezolid) |
|
● |
Central monoamine depleting drugs (e.g. reserpine) |
|
● |
Non-select beta adrenergic blocking drugs (e.g. labetalol) |
|
● |
Alpha agonists or alpha/beta agonists (e.g. pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine, ephedrine, phenylpropanolamine, naphazoline) |
|
● |
Tricyclic antidepressants or norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g. amitriptyline, buproprion, duloxetine, mirtazapine, venlafaxine) |
|
● |
Botanicals that may inhibit reuptake of norephinephrine, serotonin or dopamine (e.g. ephedra, ma huang, St John’s Wort, yohimbine) |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action, AZEDRA can cause fetal harm [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on AZEDRA use in pregnant women. No animal studies using iobenguane I 131 have been conducted to evaluate its effect on female reproduction and embryo-fetal development; however, all radiopharmaceuticals, including AZEDRA, have the potential to cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women of the risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of iobenguane I 131 in human milk or its effects on the breastfed infant or milk production. No lactation studies in animals were conducted. Because of the potential risk for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with AZEDRA and for 80 days after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating AZEDRA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
AZEDRA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females
Advise women of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with AZEDRA and for 7 months following the final dose of AZEDRA.
Males
Based on its mechanism of action, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with AZEDRA and for 4 months following the final dose of AZEDRA [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Infertility
The recommended cumulative dose of 37 GBq of AZEDRA results in a radiation absorbed dose to the testes and ovaries within the range where temporary or permanent infertility can be expected following external beam radiotherapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of AZEDRA have been established in patients 12 years and older with unresectable and iobenguane scan positive, locally advanced or metastatic, pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL) which require systemic anticancer therapy. Use of AZEDRA for this indication is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled study in adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14)].
The risks of radiation associated with AZEDRA is greater in pediatric patients than that in adult patients due to greater absorbed radiation doses and longer life expectancy. Ensure the therapeutic benefit of AZEDRA outweighs these greater risks prior to administration in pediatric patients.
The safety and effectiveness of AZEDRA have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years old with unresectable and iobenguane scan positive, locally advanced or metastatic PPGL which require systemic anticancer therapy.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the patients enrolled in all clinical studies of AZEDRA, 17% were 65 years or older and 1% were 75 years or older. Clinical studies of AZEDRA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The radiation dose to patients with renal impairment may be increased due to the delayed elimination of the drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. Adjust the therapeutic dose based on radiation exposure estimates from the dosimetry assessment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. The safety of AZEDRA in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min) or end-stage renal disease has not been studied.
11 DESCRIPTION
AZEDRA (iobenguane I 131) injection, for intravenous use, is a radioactive therapeutic agent. The drug substance iobenguane I 131 is a substituted benzylguanidine with I 131 in the meta position of the benzene ring.
Iobenguane I 131 is described as I 131 meta-iodobenzlyguanidine. The molecular weight is 279.1 Daltons and the structural formula is as follows:
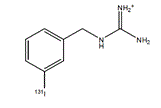
AZEDRA (iobenguane I 131) 555 MBq/mL (15 mCi/mL) injection is a sterile, clear, colorless to pale yellow solution. Each single-dose vial contains iobenguane (0.006 mg/mL), sodium ascorbate (58 mg/mL) and sodium gentisate (23 mg/mL) in Water for Injection, USP. The pH range of the solution is 4.5 to 5.5, with specific activity of ~2,500 mCi/mg (92,500 MBq/mg).
11.1 Physical Characteristics
I 131 decays with beta and gamma emissions with a physical half-life of 8.021 days. The principal beta emission has a mean energy of 191.6 keV, and the principal gamma emission has energy of 364.5 keV.
11.2 External Radiation
The specific gamma ray constant for I 131 is 2.2 R/mCi hour at 1 cm. A 2.55 cm thickness of Pb will attenuate the radiation emitted by a factor of about 1,000.
Table 6 summarizes radioactive decay properties of I 131.
|
Table 6: |
Physical Decay Chart: Iodine I 131: Half-Life = 8.021 Days. |
|
Days |
Fraction Remaining |
|
0a 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
1 0.917 0.841 0.772 0.708 0.649 0.595 0.546 0.501 0.459 0.421 0.387 0.355 0.325 0.298 |
a Calibration day.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
AZEDRA is an I 131 labeled iobenguane. Iobenguane is similar in structure to the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (NE) and is subject to the same uptake and accumulation pathways as NE. Iobenguane is taken up by the NE transporter in adrenergic nerve terminals and accumulates in adrenergically innervated tissues, such as the heart, lungs, adrenal medulla, salivary glands, liver, and spleen as well as tumors of neural crest origin. Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PPGL) are tumors of neural crest origin that express high levels of the NE transporter on their cell surfaces. Following intravenous administration, AZEDRA is taken up and accumulates within pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma cells, and radiation resulting from radioactive decay of I 131 causes cell death and tumor necrosis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The effect of AZEDRA on the QTc interval was evaluated in 74 patients with unresectable pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma. At the recommended therapeutic dosage, no large mean increases from baseline in the QTc interval (i.e., >20 ms) were detected.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of iobenguane I 131 following a dosimetric dose were characterized in patients with malignant PPGL and other malignancies. The mean blood area under curve (AUC) of iobenguane I 131 at the recommended dosimetric dose is 1 μCi*h/mL (CV 33%). The mean maximum concentration (Cmax) for iobenguane I 131 is 0.06 μCi/mL (CV 36%), which generally occurred at the end of the AZEDRA infusion.
Distribution
The volume of distribution (mean ± SD) of iobenguane I 131 is 2893 ± 592 mL/kg. The blood levels of radioactivity declined with a distribution half-life (mean ± SD) of 0.37 ± 0.22 hours. The non-radioactive form of iobenguane I 131 is 61% to 63% bound to human plasma proteins.
Elimination
The mean clearance is 62 ± 24 mL/hr/kg for iobenguane I 131 and the mean terminal blood half-life is 35 ± 14 hours.
Metabolism
Iobenguane I 131 does not undergo hepatic metabolism.
Excretion
Iobenguane I 131 is primarily eliminated renally with cumulative excretion of 50 ± 10% within 24 hours and 80 ± 10% within 120 hours following AZEDRA administration. Unchanged I 131 accounted for an average of 94% and 93% radioactivity excreted in urine collected at 0-6 and 6-24 hours post-dose, respectively. Minor metabolites detected in some patients included free I 131, quantifiable in 55% of 11 patients in Study IB11, as well as meta-iodohippuric acid (MIHA) and meta-iodobenzyl bisguanidine (MMIBG) quantifiable in one patient each.
Specific Populations
Eight of 42 patients (19%) with mild or moderate renal impairment (CLcr ≥ 30-89 mL/min by Cockcroft-Gault) required therapeutic dose reductions based on radiation dose estimates to critical organs exceeding Emami limits (absorbed renal dose exceeding 23 Gy). The pharmacokinetics of iobenguane I 131 has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min) or end-stage renal disease [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies
The non-radioactive form of iobenguane does not inhibit CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A. It does not induce CYP1A, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, or 3A. It is not a substrate or inhibitor of P-glycoprotein.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with iobenguane I 131 have not been conducted; however, radiation is a carcinogen and a mutagen. No animal studies were conducted to determine the effects of iobenguane I 131 on fertility.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of AZEDRA in patients with iobenguane scan-positive, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma (PPGL) which require systemic anticancer therapy was established in Study IB12B, an open-label, single-arm, multicenter clinical trial (NCT00874614). Patients were at least 12 years of age and were ineligible for curative therapy. Patients also progressed on prior therapy for PPGL or were not candidates for chemotherapy. Other eligibility criteria required patients’ tumors to have definitive iobenguane avidity; at least one tumor site identified by computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or iobenguane I 131 scan; Karnofsky performance status ≥60; absence of active central nervous system lesions, and no changes to their antihypertensive regimen in the 30 days prior to the first therapeutic dose.
The major efficacy outcome measure was the proportion of patients who experienced a 50% or greater reduction of all antihypertensive medication(s) lasting for at least six months (28 days per month). Overall tumor response measured by RECIST (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.0) was also evaluated. After the final 12-month assessment, patients entered into long-term follow-up for up to 4 additional years.
A total of 74 patients received the dosimetric dose of AZEDRA. Following dosimetry, 68 patients received at least one therapeutic dose and 50 patients received two therapeutic doses administered at least 90 days apart. The dosimetric dose was 185 mBq to 222 MBq (5 mCi to 6 mCi) for patients weighing > 50 kg and 3.7 MBq/kg (0.1 mCi/kg) for patients weighing ≤ 50 kg. The therapeutic dose was 18,500 MBq (500 mCi) for patients weighing > 62.5 kg and 296 MBq/kg (8 mCi/kg) for patients weighing ≤ 62.5 kg. Among the 68 patients, the median age was 55 years (16 to 72 years), 57% were male, 75% were White, 21% were Black, 4% were Asian and the remainder were not reported. For the primary tumor diagnosis, 78% had pheochromocytoma, 21% had paraganglioma, and 1% had both. Fifty percent (50%) of patients with evaluable imaging studies had lung or liver metastases and 61% had bone metastases at baseline. Eighty-eight percent (88%) underwent prior surgery, 50% received prior external radiation, 31% received prior I 131 MIBG, 31% received prior chemotherapy, 15% received prior kinase inhibitors and 4% received other prior systemic therapies. The median (range) of prior therapies per patient is 2 (0, 7).
The efficacy results are summarized in Table 7. All confirmed responses per RECIST were partial responses.
|
Table 7: |
Efficacy Results in Patients with Pheochromocytoma or Paraganglioma in Study IB12B |
|
At least the first therapeutic dose |
|
|
Reduction of all antihypertensive medications by at least 50% maintained for at least 6 months, n (%) |
|
|
Number of patients |
17 |
|
Proportion of patients (95% CIa) |
25% (16%, 37%) |
|
Best confirmed overall tumor response per RECIST |
|
|
Number of patients |
15 |
|
Overall response rate (95%CIb) |
22% (14%, 33%) |
|
% Responders with Duration of Response ≥ 6 months |
53% |
|
a Calculated using the Agresti-Coull method. b Exact Confidence Interval |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
AZEDRA injection, containing 555 MBq/mL (15 mCi/mL) of I-131 (as iobenguane I 131) and 0.006 mg/mL of iobenguane, is a sterile, clear, colorless to pale yellow solution for intravenous use supplied in a colorless Type 1 borosilicate glass 30 mL single-dose vial. AZEDRA is supplied in dosimetric (2 mL) and therapeutic (22.5 mL) presentations:
|
● |
Dosimetric: 1,110 MBq (30 mCi) of iobenguane I 131 at calibration time (NDC 71258-015-02). |
|
● |
Therapeutic: 12,488 MBq (337.5 mCi) of iobenguane I 131 at calibration time (NDC 71258-015-22). |
The product vial is in a lead shielded container placed in a re-sealable plastic bag. The product is shipped on dry ice in a USA DOT Type A Radioactive package.
Store at -70°C (-94°F).
The shelf life is 6 days post calibration time. Discard appropriately at 144 hours.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Hydration
Advise patients to drink at least 2 liters of liquid a day before and for one week following each dose of AZEDRA to minimize irradiation of the bladder [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Radiation Risks
Advise patients to minimize radiation exposure to household contacts consistent with institutional good radiation safety practices and patient management procedures [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Myelosuppression
Advise patients to contact their health care provider for any signs or symptoms of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, or anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Secondary Myelodysplastic Syndrome, Leukemia and Other Malignancies
Advise patients of the potential for secondary cancers, including myelodysplastic syndrome, acute leukemia, and other malignancies. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypothyroidism
Advise patients to take thyroid-blocking agents as prescribed. Advise patients of the need for life-long monitoring for hypothyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Elevations in Blood Pressure
Advise patients to contact their health care provider for signs or symptoms that may occur following tumor-hormone catecholamines release and possible risk of increased blood pressure during or 24 hours following each therapeutic AZEDRA dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Pneumonitis
Advise patients to contact their health care provider for signs or symptoms of pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients that some medicines interact with AZEDRA and to contact their health care provider before starting any over the counter medicines or herbal or dietary supplements.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and males and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their health care provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with AZEDRA and for 7 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), 8.3)].
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with AZEDRA and for 4 months after the final dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise females not to breastfeed during treatment with AZEDRA and for 80 days after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females and males patients that AZEDRA may impair fertility [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Manufactured for:
Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
One World Trade Center, 47th floor, Suite J
New York, NY 10007
AZEDRA® is a registered trademark of Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
17
