Form 10-K KORN FERRY INTERNATIONAL For: Apr 30
Table of Contents

UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
| ☑ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the fiscal year ended April 30, 2018 |
OR
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number 001-14505
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
| Delaware | 95-2623879 | |
| (State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) | |
| 1900 Avenue of the Stars, Suite 2600, Los Angeles, California | 90067 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip code) | |
(310) 552-1834
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered | |
| Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ☑ | Accelerated filer ☐ | Non-accelerated filer ☐ | Smaller reporting company ☐ | |||
| (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | ||||||
| Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☑
The number of shares outstanding of our common stock as of June 21, 2018 was 56,521,614 shares. The aggregate market value of the registrant’s voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant on October 31, 2017, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, (assuming that the registrant’s only affiliates are its officers, directors and 10% or greater stockholders) was approximately $2,140,950,087 based upon the closing market price of $41.83 on that date of a share of common stock as reported on the New York Stock Exchange.
Documents incorporated by reference
Portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders scheduled to be held on September 26, 2018 are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
Table of Contents

Index to Annual Report on Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended April 30, 2018
Table of Contents

About Korn Ferry
Korn/Ferry International (referred to herein as the “Company,” “Korn Ferry,” or in the first person notations “we,” “our,” and “us”) is a global organizational consulting firm. We opened our first office in Los Angeles in 1969 and currently operate in 106 offices in 52 countries. We deliver our solutions on a global basis, wherever our clients do business. As of April 30, 2018, we had 7,643 full-time employees, including 1,392 consultants (541 Executive Search, 577 Hay Group (formerly known as Leadership & Talent Consulting (“Legacy LTC”) which was combined with HG (Luxembourg) S.à.r.l (“Legacy Hay”) in December 2015), and 274 Futurestep) who are primarily responsible for client services. Our clients include many of the world’s largest and most prestigious public and private companies, middle market and emerging growth companies, as well as government and nonprofit organizations. We have built strong client loyalty with 88% of our assignments performed during fiscal 2018 on behalf of clients for whom we had conducted assignments in the previous three fiscal years. We have made significant investments in our business that have strengthened our intellectual property, enhanced our geographical presence, added complementary offerings to deepen client relationships and broadened our capabilities around talent strategy, assessment, development and rewards. We were originally formed as a California corporation in November 1969 and reincorporated as a Delaware corporation in fiscal 2000.
On June 12, 2018, the Company’s Board of Directors approved a plan (the “Plan”) to go to market under a single, master brand architecture and to simplify the Company’s organizational structure by eliminating and/or consolidating certain legal entities and implementing a rebranding of the Company to offer the Company’s current products and services using the “Korn Ferry” name, branding and trademarks. In connection with the Plan, the Company intends to sunset all sub-brands, including Futurestep, Hay Group and Lominger, among others. The Company is harmonizing under one brand to help accelerate the firm’s positioning as the preeminent organizational consultancy and bring more client awareness to its broad range of talent management solutions. While the rebranding will not impact the Company’s segment financial reporting, starting in the first quarter of fiscal 2019, the Company will rename its Hay Group segment as “Korn Ferry Advisory” and its Futurestep segment as “Korn Ferry RPO and Professional Search.” The Company’s Executive Search segment will remain unchanged. In connection with the Plan, the Company also intends to pursue a holding company reorganization as discussed in further detail below under “KF Merger.” Unless otherwise noted, the following discussion of the Company’s business in this Item 1 describes the Company’s business as currently operated and does not give effect to any changes that may be implemented as a result of the rebranding plan. The Company intends to update this discussion in its 2019 Annual Report on Form 10-K to reflect any changes implemented as of such time as a result of the Plan.
The Korn Ferry Opportunity
Rallied around our vision to be the preeminent organizational consulting firm, at Korn Ferry, we are pursuing an ambitious strategy that will help us to focus relentlessly on clients and collaborate intensively across the organization. This approach builds on the best of our past and gives us a clear path to the future with focused initiatives to increase our client and commercial impact.
Korn Ferry is transforming how clients address their spectrum of talent management needs. We have evolved from a mono-line business to a global organizational consulting firm and in the process are giving our consultants more opportunities to engage with clients—beyond our iconic talent acquisition offering.
The essence of our belief is that both Korn Ferry and our clients can be more than. We view it as a state of mind, an attitude, for how we live and interact with each other and our clients every day. Being more than makes a difference—to us, and more importantly, to our clients. More than reflects the vast expertise we bring to our clients. This is the opportunity to bring our services, solutions and products backed by rich intellectual property to our clients, inspiring and motivating individuals, teams, even entire organizations. This is how we bring companies’ strategies to life, unite boardrooms and workforces, unlock potential, realize ambitions and change lives.
1
Table of Contents

While most organizations can develop a sound strategy, they often struggle with how to make it stick. That is where we come in: synchronizing an organization’s strategy with its talent to drive superior performance. We help companies design their organization—the structure, roles and responsibilities—to seize these opportunities. As important, we help organizations select and hire the talent they need to execute their strategy—and show them the best way to compensate, develop and motivate their people.
We do this through our five solution sets:
|
Organizational Strategy |
We map talent strategy to business strategy by designing operating models and organizational structures that align to them, helping organizations put their plans into action. We make sure they have the right people, in the right roles, engaged and enabled to do the right things. |
|||
| Assessment and Succession |
We provide actionable, research-backed insights that allow organizations to understand the true capabilities of their people so they can make decisions that ensure the right leaders are ready—when and where they are needed—in the future. | |||
| Talent Acquisition |
From executive search to recruitment process outsourcing, we integrate scientific research with our practical experience and industry-specific expertise to recruit professionals of all levels and functions for client organizations. | |||
| Leadership Development |
We activate purpose, vision and strategy through leaders at all levels and organizations. We combine expertise, science and proven techniques with forward thinking and creativity to build leadership experiences that help entry to senior level leaders grow and deliver superior results. | |||
| Rewards and Benefits |
We help organizations align reward with strategy. We help them pay their people fairly for doing the right things—with rewards they value—at a cost the organization can afford.
|
|||
About Our Intellectual Property and Technology
At the core of our service, solution and product delivery is deep intellectual property (“IP”) and research that allows us to deliver meaningful business outcomes for our clients.
The Korn Ferry Institute, our research and analytics arm, unites three areas: agile client execution; applied research and analytics; and breakthrough innovation. These teams work together to help business and public-sector leaders understand the key trends and drivers of human and organizational performance, so that they make better, science-based decisions on critical leadership, people, management and policy issues.
The Korn Ferry Institute’s core IP data and assets include proprietary leadership assessment, recruitment and development models, emotional and social competencies, human motives and values, job grading, engagement and rewards systems. We integrate and build upon our unique data sets using advanced modeling and artificial intelligence (“AI”) to produce unique, predictive insights and deliver demonstrable client impact.
Our analytics are based on industry leading data sets which include six million assessments, profiles of eight million candidates, compensation data on twenty million professionals and engagement data on more than six million professionals.
At the highest level, the Korn Ferry Institute explores three themes:
| 1. | People, organization and technology innovation; |
| 2. | Data analytics for human and business performance; and |
| 3. | New demographic trends. |
In the fiscal year ahead, we will continue to integrate, harmonize and simplify our IP for greater leverage and business impact, with the goal of having one science-based engine underlying and empowering all our products and solutions.
2
Table of Contents

About Our Business Segments
Korn Ferry services, solutions, and products are delivered through the following business segments:
Executive Search: Korn Ferry Executive Search helps clients attract and hire leaders who fit in with their organization and make it stand out. The business is managed by geographical region leaders with a focus on recruiting board-level, chief executive and other senior executive positions for clients predominantly in the consumer, financial services, industrial, life sciences/healthcare provider, technology and educational/not-for-profit market sectors. We also have centers of functional expertise; our Board & CEO Services group, for example, focuses exclusively on placing CEOs and board of directors in organizations around the world. The relationships established by Executive Search allow us to add incremental value to our clients through the delivery of our other organizational consulting services and solutions.
Our Executive Search services concentrate on searches for positions with annual cash compensation of $300,000 or more, or comparable compensation in foreign locations. The industry is comprised of retained and contingency recruitment firms. Retained firms, such as Korn Ferry, typically charge a fee for their services equal to approximately one-third of the first-year annual cash compensation for the position being filled regardless of whether the position is filled. Contingency firms generally work on a non-exclusive basis and are compensated only upon successfully placing a recommended candidate.
Hay Group: Korn Ferry Hay Group is comprised of 3,454 of the world’s top leadership and organizational advisory consultants and thought leaders. Through our talented colleagues, robust solutions and world-class intellectual property that people use every day, our consultants are able to solve the most disruptive and challenging organizational and talent problems facing clients.
As a recognized advisory leader, we partner with many of the world’s most admired organizations because of our track record delivering successful outcomes, our ability to listen, and our insistence on putting our clients first. They depend on our products and platforms every day to connect our solutions to their business challenges. In essence, we help clients design their organization—the structure, roles and responsibilities—and show them the best way to compensate, develop and motivate their people. We deliver this through a combination of solutions consulting and product services that addresses how people work and shows how to nurture them so that strategies succeed. We capitalize on the breadth of our IP, service offerings and expertise to do what is right for the client. Services are delivered by an experienced team of consultants and include one of the richest and most comprehensive people data sets.
Futurestep: Korn Ferry Futurestep uses data-backed insight and IP, matched with strategic collaboration and innovative technology, to meet people challenges head-on—and succeed. Our solutions span all aspects of Recruitment Process Outsourcing (“RPO”), Professional Search and Project Recruitment.
Our scalable, best-in-class approach to RPO allows our clients to attract top people while reducing expenses and time to hire. To us, RPO is more than just handing off the responsibilities of recruitment. It’s about building a partnership, often through a co-sourced recruitment model, to discover and deliver the talent that will have the greatest impact on our clients’ business.
Korn Ferry Futurestep offers proven RPO services that are backed by years of experience and award-winning IP. Using a variety of tools, we look closely at each candidate, combining data from multiple recruitment systems to determine which candidates have the potential to match both a particular organization and a specific role. Our customizable end-to-end solutions combine recruiting expertise with state-of-the-art technology platforms and sophisticated methodologies to help clients streamline recruitment processes, enhance candidate experience, and improve quality of hire, ultimately impacting the long-term success of an organization. We see talent acquisition as a critical function of the business, one that impacts not just the bottom line but one that can also drive top line growth. Korn Ferry Futurestep also undertakes Project Recruitment. This solution focuses not on a single hire, nor on filling high-volume roles, but instead the area in between. Project recruitment addresses a specific talent acquisition need at a certain point in time.
Through our Professional Search capabilities, Korn Ferry Futurestep is uniquely positioned to help organizations identify and attract professionals at the middle to upper levels of management, in single-search engagements.
3
Table of Contents

We file annual, quarterly and current reports, proxy statements and other documents with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). You may read and copy any materials that we file with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-732-0330. Our reports, proxy statements and other documents filed electronically with the SEC are available at the website maintained by the SEC at www.sec.gov.
We also make available, free of charge on the Investor Relations portion of our website at http://ir.kornferry.com, our annual, quarterly, and current reports, and, if applicable, amendments to those reports, filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such reports with, or furnish them to, the SEC at www.sec.gov.
We also make available on the Investor Relations portion of our website at http://ir.kornferry.com earnings presentations and other important information, which we encourage you to review.
Our Corporate Governance Guidelines, Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, and the charters of the Audit Committee, Compensation and Personnel Committee, and Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee of our Board of Directors are also posted on the Investor Relations portion of our website at http://ir.kornferry.com. Stockholders may request copies of these documents by writing to our Corporate Secretary at 1900 Avenue of the Stars, Suite 2600, Los Angeles, California 90067.
Industry Trends
In this competitive global economic environment, our clients are seeking new pathways to drive sustainable profitable growth. CEOs are increasingly demanding an agile workforce that can innovate and drive growth across borders. We believe Korn Ferry is uniquely positioned to help organizations synchronize their strategy with their talent to drive superior performance.
Consolidation of Solution Providers—In choosing recruitment and human resource service providers, we believe and see evidence to support that:
| ◾ | Companies are actively in search of preferred providers in order to create efficiencies and consolidate vendor relationships; |
| ◾ | Providers that can offer a full suite of organizational consulting products and solutions are becoming increasingly attractive; and |
| ◾ | Clients seek trusted advisors who understand their business and unique organizational culture in order to manage the multiple needs of their business on a global scale. |
Skills Gaps—There are not enough highly “skilled” people coming into the labor market to fill open jobs. Particularly at the senior management levels, the available talent pool is inadequate. New leaders must step into bigger, more complex, and more global roles faster—and with less experience—than their predecessors. Given this, learning agility—one’s ability to adapt the lessons learned from previous experiences, solve complex problems, manage amid ambiguity in a constantly changing world and drive change—is more important than ever. We believe employers will increasingly seek service providers who can help them find, develop and retain highly qualified, learning-agile talent to secure a competitive advantage.
Human Capital is One of the Top CEO Challenges—Human capital challenges are found in all industries and sectors, among large and small companies, including those that are taking on the planet’s most pressing problems: sustainability, security, the environment, energy, transportation, food supply, clean water, and more. Tackling world-changing challenges requires far more than just best-in-class research and development and efficient production processes. More than ever, organizations need world-class talent motivated by a bigger vision. The people, the minds, the alliances and the culture that can create and then nurture innovative ideas are seen as central to the modern CEO agenda. In fact, according to The Conference Board, attracting and retaining talent is the single biggest challenge facing CEOs in 2018.
Talent Analytics—Companies are increasingly leveraging big data and predictive analytics to measure the influence of activities across all aspects of their business, including Human Resources (“HR”). They expect their
4
Table of Contents

service providers to deliver superior metrics and better ways of communicating results. The Korn Ferry Institute’s core IP, data and assets allow us to determine the true drivers of leadership, performance and monitor how any individual or organization measures up. We possess several of the most robust HR databases in the world. These databases enable our clients to benchmark salaries, leadership potential, employee engagement, organizational culture and review other HR data by industry and by position at a global and country level.
Increased Outsourcing of Talent Acquisition Functions—More companies are focusing on their core competencies and choosing to outsource non-core functions to providers who can offer efficient, high-quality services. Third-party providers can apply immediate and long-term approaches for improving all aspects of talent acquisition. Advantages to outsourcing part or all of the recruitment function include:
| ◾ | Access to a diverse and highly qualified pool of candidates, which is refreshed on a regular basis; |
| ◾ | Reduction or elimination of the costs required to maintain and train an in-house recruiting department in a rapidly changing industry; |
| ◾ | Ability to use the workflow methodologies we have developed over tens of thousands of assignments, which allow clients to fulfill positions on a streamlined basis; |
| ◾ | Ability to quickly review millions of resumes and provide the right fit for the client; |
| ◾ | Access to the most updated industry and geographic market information; |
| ◾ | Access to cutting-edge search technology software and proprietary IP; and |
| ◾ | Ability to maintain management focus on core strategic business issues. |
Other Industry Trends—In addition to the industry trends mentioned above, we believe the following factors will have a long-term positive impact on our industry:
| ◾ | Increasing demand for professionals with not just the right technical skills, but also the right leadership style, values and motivation to meet the specific requirements of the position and organizational culture; |
| ◾ | Decreasing executive management tenure and more frequent job changes; |
| ◾ | Retiring baby boomers, creating a skills gap in the workforce; |
| ◾ | Shifting balance of power towards the employee as more people take charge of their own careers, and the new norm of employee-driven development; |
| ◾ | Increasing importance of talent mobility in engaging and developing people within an organization; |
| ◾ | Increased attention to succession planning due to heightened scrutiny on CEOs, pressure to generate growth, shorter CEO tenures and the emphasis being placed on making succession planning a systemic governance process within global organizations; |
| ◾ | Executive pay and governance practices under more scrutiny than ever; |
| ◾ | The high turnover rate and varying high volume hiring needs commonly associated with the new shared economy; and |
| ◾ | Increasing focus on gender pay gap and the lack of women in senior roles. |
Growth Strategy
Our objective is to expand our position as the preeminent organizational consulting firm. In order to meet this objective, we will continue to pursue our strategy:
Drive an Integrated, Solutions-Based Go-to-Market Strategy
Our synergistic go-to-market strategy, bringing together all three of our business segments, is driving more integrated, scalable client relationships. This is evidenced by the fact that approximately 62% of our revenues come from clients that utilize multiple lines of business. To better compete in the market, we will evolve over time from our traditional line of business segmentation to integrated solutions and industries.
In an effort to gain operational efficiencies and drive superior performance, we expect that multinational clients will increasingly turn to strategic partners such as Korn Ferry that can manage their needs on a centralized basis. This will require vendors with a global network of offices and technological support systems to manage engagements across geographical regions. We established our Marquee Accounts program to act as a catalyst for change as we transform our Company from individual operators to an integrated solutions provider, in an effort to drive major global and regional strategic account development, as well as to provide a framework for all our client development activities.
5
Table of Contents

Our Marquee Accounts program now comprises 20% of our global fee revenues. A number of our Marquee accounts are managed by our newly hired account managers—18 at April 30, 2018. In the year ahead, we will continue to grow and expand our account management activities. This includes driving consistent account selection, assignment, planning and execution; implementing account-based marketing efforts; optimizing the pipeline and opportunity process; and hiring additional dedicated account leaders.
Deliver Unparalleled Client Excellence
Korn Ferry continues to scale and more deeply embed our industry-leading IP within the talent management processes of our global clients. In addition to technology-enabled insights for our clients, we also continue to invest in productivity enhancers for our own colleagues, recognizing that as the way they work changes and becomes more global, we need to make them productive wherever they are and however they work. We are focused on the following key areas to drive our technology plan:
Innovation—Human capital management is quickly evolving, thanks to people with new profiles, new technologies and new organizational and working contracts. Korn Ferry is actively investing in some of these developments and closely monitors others to align our business models, capture significant growth opportunities and ultimately help shape the future of work.
Market innovations contribute to more accurate, faster, cost-effective and impactful business and human decisions. Our firm is well-positioned in that context. We have a unique set of assets that are critical to such decisions: deep science on organization and human motivation, data on talent, work and rewards, and proven products and solutions.
We are integrating these assets and combining them with enhanced computing and analytical power to remain a cutting-edge organizational consulting firm. Some key innovation initiatives include:
| ◾ | Core IP: Integration of talent and work IP into a single, science-based framework organized along “identity” (the deepest drivers of human behaviors), “capabilities” (what people know), and “accountabilities” (what characteristics of roles, responsibilities and outcomes). We expect to position this model to be a market “gold-standard” associated with individual and collective performance in traditional organizations as well as in open talent networks. This model will also fuel our advisory solutions such as mergers and acquisitions (M&A), diversity and inclusion (D&I) and digital transformation. |
| ◾ | Client analytics: Historically, Korn Ferry has developed solid—yet traditional—talent analytics for Marquee clients. We are now developing better correlations between human and business performance for more systematic monetization of client analytics and introduction to new clients. |
| ◾ | Advanced analytics: We are organizing our data and reports into “always-on” blended dashboards that will help clients make better decisions. We are also strengthening our AI-machine learning (AI-ML) capacity, initially to optimize recruitment (e.g., sourcing and matching of jobs and talents) and to scale pay-related demographics and data points. We will then use AI-ML to complement our science on individuals, teams and work, and identify the variables that best help transformation and predict talent and organizational results. |
IP Driven Tools and Services—We are leveraging all IP and technology and combining into a unified single platform to deliver assessments that allow clients to make faster, better talent decisions.
Our IP-driven tools and services are being utilized by our clients for everything from organizational development and job profiling to selection, training, individual and team development, succession planning and more. Our subscription services delivered online help us generate long-term relationships with our clients through large scale and technology-based HR programs on an annuity basis. We continue to seek ways to further scale our product offering to our global clients.
Within Executive Search our databases contain profiles of approximately five million executives to assist in identifying individuals with the right background, cultural fit and abilities. Through the search process, we leverage proprietary tools such as our Four Dimensional Executive Assessment and Executive Snapshot (incorporating Hay Group’s industry standard job grading, job description and salary benchmark methodologies).
6
Table of Contents

Within Korn Ferry Hay Group, enhancements to our PayNet database and the launch of the new Korn Ferry Assessment Platform will allow us to embed analytics directly into our clients’ user experience, providing actionable insights.
New Offerings—More than 150,000 consumers have visited Korn Ferry Advance, our new business-to-consumer offering, since it launched in the United States (the “U.S.”) in July 2017. We are expanding and enhancing the offering to provide more focused assistance to people looking to make their next career move, as well as to provide tailored career services to an organization’s people. Korn Ferry Advance will continue to leverage cutting-edge technology as well as the greatest asset we have—our consultants.
In addition, we launched Korn Ferry Direct, our Client Platform Services product tailored for small and mid-sized businesses, and Consent Manager, a new enterprise tool to help clients manage their increasing responsibility for employee and candidate data privacy.
Productivity Enhancements—We will make further investments into our global SAP platform, which was put in service in the early 2000s and configured to support an executive search business. As we grow and evolve the Company to a solution and industry orientation, we will ensure that we have the proper infrastructure and technology to deliver the appropriate data and information to efficiently and effectively manage the enterprise.
Extend the Korn Ferry Brand
Next to our people, the Korn Ferry brand is the strongest asset of the Company.
Positioning Korn Ferry as the preeminent global organizational consultancy and demonstrating our unique ability to drive business performance through people remains a key tenet of our global marketing program. Our objective is to improve awareness and perceptions of the evolved Korn Ferry across our key buyer segments (Board Directors, CEOs, Chief Human Resource Officers (“CHRO”) and the C-suite) and investor base. We are also extending our presence to a professional-level audience focused on advancing their careers. We have significantly enhanced our thought leadership and digital presence in support of these goals.
As we increasingly extend our brand, broaden our solutions and attract top talent to the firm, Korn Ferry is well positioned for the future.
Advance Korn Ferry as a Premier Career Destination
We continue to invest in building a world-class organization that is aligned to our strategy and is staffed by a capable, motivated and agile workforce. A few key initiatives in this area include:
| ◾ | Career Paths and Mobility—We have architected and will implement the new Korn Ferry career model across the entire business to define career paths, as well as to encourage talent mobility and self-directed development. |
| ◾ | Onboarding—Our workforce has nearly doubled since fiscal 2015 and must continue to grow to deliver on our growth. To support this, we are providing a standardized, global onboarding experience for all Korn Ferry new hires using a common platform, materials and resources to ensure all new hires are effectively integrated into the Company with reduced ramp-up time to full productivity. |
| ◾ | Korn Ferry Academy—Our growth plans require a learning, agile organization. In fiscal 2018, we launched a new learning management system (The Korn Ferry Academy) to serve as a Center of Excellence focused on the growth and development of our colleagues through rich, personalized content. |
| ◾ | Succession and Development—We are working on aligning and building capabilities for our future needs. The process was initiated with the senior leadership team and we are now cascading it to additional levels of the Company, including emerging talent. |
Pursue Transformational Opportunities at the Intersection of Talent and Strategy
We have developed a core competency in identifying, acquiring and integrating M&A targets that have the potential to further our strategic objectives and enhance shareholder value. Our disciplined approach to M&A will continue to play a critical role in the ongoing evolution of Korn Ferry into an industry specialized, business outcomes oriented solutions provider at the intersection of talent and strategy. While we will continue to execute
7
Table of Contents

on our targeted organic growth pathways, M&A will be a vital component of our future growth and capital deployment strategies.
Our Services and Organization
Organization
The Company operates through its three global business segments: Executive Search, Hay Group, and Futurestep. Our Executive Search business is managed on a geographic basis throughout four regions: North America, Europe, the Middle East and Africa (“EMEA”), Asia Pacific and Latin America. Hay Group and Futurestep are managed on a global basis with operations in North America, EMEA, Asia Pacific and Latin America.
We address our clients’ needs through our three business segments:
Executive Search
Overview—Korn Ferry Executive Search helps clients attract and hire leaders who fit with their organization and make it stand out. Our services are typically used to fill executive-level positions, such as board directors, chief executive officers, chief financial officers, chief operating officers, chief information officers, chief human resource officers and other senior executive officers.
As part of being retained by a client to conduct a search, we assemble a team of consultants with appropriate geographic, industry and functional expertise. We utilize a standardized and differentiated approach to placing talent that integrates our research-based IP with our practical experience. Our search consultants serve as management advisors who work closely with the client in identifying, assessing and placing qualified candidates. In fiscal 2018, we executed 6,325 new executive search assignments.
Industry Specialization—Consultants in our five global markets and regional specialty practice groups bring an in-depth understanding of the market conditions and strategic management issues faced by clients within their specific industries and geographies. We are continually looking to expand our specialized expertise through internal development and strategic hiring in targeted growth areas.
Percentage of Fiscal 2018 Assignments Opened by Industry Specialization
|
Global Markets: |
||||
| Industrial |
31 | % | ||
| Financial Services |
19 | % | ||
| Life Sciences/Healthcare Provider |
17 | % | ||
| Consumer |
16 | % | ||
| Technology |
12 | % | ||
| Regional Specialties (United States): |
||||
| Education/Not-for-Profit
|
|
5
|
%
|
Functional Expertise—We have organized executive search centers of functional expertise, composed of consultants who have extensive backgrounds in placing executives in certain functions, such as board directors, CEOs and other senior executive officers. Our Board & CEO Services group, for example, focuses exclusively on placing CEOs and board directors in organizations around the world. This is a dedicated team from the most senior ranks of the Company. Their work is with CEOs and in the boardroom, and their expertise is organizational leadership and governance. They conduct hundreds of engagements every year, tapping talent from every corner of the globe. This work spans all ranges of organizational scale and purpose. Members of functional groups are located throughout our regions and across our industry groups.
8
Table of Contents

Percentage of Fiscal 2018 Assignments Opened by Functional Expertise
|
Board Level/CEO/CFO/Senior Executive and General Management |
|
69 |
% | |
| Marketing and Sales |
9 | % | ||
| Finance and Control |
9 | % | ||
| Information Systems |
6 | % | ||
| Manufacturing/Engineering/Research and Development/Technology |
4 | % | ||
| Human Resources and Administration
|
|
3
|
%
|
Regions
North America—As of April 30, 2018, we had operations in 20 cities throughout the United States and Canada. In fiscal 2018, the region generated fee revenue of $408.1 million and opened 2,665 new engagements with an average of 248 consultants.
EMEA—As of April 30, 2018, we had operations in 24 cities in 19 countries throughout the region. In fiscal 2018, the region generated fee revenue of $173.7 million and opened 1,849 new engagements with an average of 154 consultants.
Asia Pacific—As of April 30, 2018, we had operations in 18 cities in 10 countries throughout the region. In fiscal 2018, the region generated fee revenue of $96.6 million and opened 1,132 new engagements with an average of 95 consultants.
Latin America—As of April 30, 2018, we had operations in 9 cities in 7 countries covering the entire Latin America region. In fiscal 2018, the region generated fee revenue of $30.6 million in fiscal 2018 and opened 679 new engagements with an average of 33 consultants.
Client Base—Our 3,773 Search engagement clients in fiscal 2018 include many of the world’s largest and most prestigious public and private companies.
Competition—Other multinational executive search firms include Egon Zehnder, Heidrick & Struggles International, Inc., Russell Reynolds Associates and Spencer Stuart. Although these firms are our largest competitors in executive search, we also compete with smaller boutique firms that specialize in specific regional, industry or functional searches. We believe our brand name, differentiated business model, systematic approach to client service, cutting-edge technology, unique IP, global network, prestigious clientele, strong specialty practices and high-caliber colleagues are recognized worldwide. We also believe our long-term incentive compensation arrangements, as well as other executive benefits, distinguish us from most of our competitors and are important in attracting and retaining our key consultants.
Hay Group
Overview—Korn Ferry Hay Group helps clients design their organization—the structure, roles and responsibilities—and shows them the best way to compensate, develop and motivate their people. Our focus is on making change happen and helping people and organizations realize their potential.
Korn Ferry Hay Group is known for creating and owning the most widely used job evaluation methodology in the world. We have helped clients assess, select and develop hundreds of thousands of managers and executives. In addition, we have built the richest and most comprehensive database of organizational management information in the world, enabling our clients to benchmark themselves against the best performers in their industries.
We deliver a combination of solutions consulting and product services that address how people work, and how to nurture them so that business strategies succeed. We capitalize on the breadth of our IP, service offerings and expertise to do what is right for the client—transforming ideas into actionable insights. Services are delivered by an experienced team of consultants and include one of the richest and most comprehensive people data sets. We have over 3,450 employees working in 88 cities in 50 countries. Our consultants are predominately recruited from local markets, so they are sensitive to local issues and have a deep understanding of them, but are also trained and work together in international teams to offer a truly global perspective.
9
Table of Contents

Hay Group has multiple offerings across assessment and succession, leadership development, organizational strategy, and rewards and benefits, which are enhanced, enabled and optimized through various products.
Assessment and Succession: We provide actionable, research-backed insight and products that allow organizations to understand the talent they have, benchmarked against the talent they need to deliver on the business strategy.
| ◾ | By tapping into our vast talent database, we isolate the vital leadership attributes needed to succeed by industry, business function, job level, business challenge, strategy, or geographic market. |
| ◾ | World-class assessment tools deliver deep insights on how individuals and the enterprise-wide talent pipeline compare with best-in-class profiles. |
| ◾ | We draw on the full breadth of Korn Ferry’s people and organizational capabilities to close any gaps. |
Leadership Development: We develop leaders at every stage of the leadership journey, from first time manager to CEO, with leadership development experiences that are tightly aligned with succession and talent processes.
Our solutions are backed by world-class tools and techniques and delivered by hundreds of dedicated leadership development experts across the globe.
Organizational Strategy: Korn Ferry provides end-to-end support to organizations that want to transform their business. Strategy becomes operationalized by aligning the tangible elements of the organization—people, structure and process—and the intangible elements—motivations, relationships and culture.
Rewards and Benefits: We help organizations align reward with strategy, to pay their people fairly for doing the right things—with rewards they value—at a cost the organization can afford. Our advice is backed by the quality and quantity of our pay data and a robust and widely used job evaluation methodology.
Solutions consulting fee revenue was $540.5 million, $497.7 million and $351.2 million in fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Solutions consulting fee revenue represented 31%, 32% and 27% of the Company’s total fee revenue in fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Regions—As of April 30, 2018, we had Hay Group operations in 22 cities in North America, 36 in EMEA, 21 in Asia Pacific, and 9 in Latin America.
Client Base—During fiscal 2018, Hay Group partnered with approximately 11,000 clients across the globe and 16% of Hay Group’s fiscal 2018 fee revenue was referred from Korn Ferry’s Executive Search and Futurestep segments. Our clients come from the private, public and not-for-profit sectors, across every major industry and represent diverse business challenges.
Competition—Our main competitors include firms like Aon Hewitt, Willis Towers Watson, Deloitte, McKinsey, Boston Consulting Group, Development Dimensions International, Center for Creative Leadership, Right Management, Mercer and CEB. Although these firms are our largest competitors, we also compete with smaller boutique firms that specialize in specific regional, industry or functional aspects of leadership and organizational consulting services.
Futurestep
Overview—Korn Ferry Futurestep uses data-backed insight and IP, matched with strategic collaboration and innovative technology to deliver solutions spanning all aspects of RPO, Professional Search and Project Recruitment.
RPO: In fiscal 2018, Korn Ferry Futurestep was recognized as a top five RPO provider in the 2017 Baker’s Dozen list, marking its 11th consecutive year on the list. Through decades of experience, we have honed and refined our RPO solution to be as efficient as possible, keeping costs low and allowing clients to meet target time-to-hire goals without compromising on quality of candidate.
Through innovative sourcing and employer brand strategies, as well as the ability to leverage the Korn Ferry talent pool and comprehensive job market mapping, Korn Ferry Futurestep’s RPO solution is equipped to source candidates from a broader network. Combined with our best-in-class assessments and behavior interviewing
10
Table of Contents

techniques, we can then determine which qualified candidates will be a culture fit for an organization. Futurestep combines traditional recruitment expertise with a multi-tiered portfolio of talent acquisition solutions. Futurestep consultants, based in 30 countries, have access to our databases of pre-screened, mid-level professionals. Our global candidate pool complements our international presence and multi-channel sourcing strategy to provide speed, efficiency and quality service for clients worldwide.
Futurestep Professional Search: We are uniquely positioned to help organizations identify and attract professionals at the middle to upper levels of management in single-search engagements. We focus on:
|
◾ Consumer |
◾ Education/Not-for-Profit | |
| ◾ Financial Services |
◾ Finance & Accounting | |
| ◾ Industrial |
◾ Human Resources | |
| ◾ Life Sciences/Healthcare |
◾ Sales, Marketing & Digital | |
| ◾ Technology
|
◾ Supply Chain Management
|
Futurestep Project Recruitment: Korn Ferry Futurestep’s Project Recruitment Solution delivers the right talent in the right numbers through a process that is seamless, stress-free and aligned with the broader talent acquisition strategy. We work closely with the organization’s talent acquisition function to develop a recruitment strategy that is tailored to meet the needs of the business and designed to complement its culture. Our teams rely on proactive targeted sourcing, taking a direct approach with suitable candidates, and employing high-touch, in-depth candidate assessment and selection to deliver top talent on a timely basis, without compromising quality or efficiency.
Regions—As of April 30, 2018, we had Futurestep operations in 13 cities in North America, 13 in EMEA, 18 in Asia Pacific, and 9 in Latin America.
Client Base—During fiscal 2018, Futurestep partnered with 1,903 clients across the globe and 42% of Futurestep’s fiscal 2018 fee revenue was referred from Korn Ferry’s Executive Search and Hay Group segments.
Competition—Futurestep primarily competes for business with other RPO providers such as Cielo Talent, Alexander Mann Solutions, Hays, Kenexa, Spherion, KellyOCG and ADP, and competes for search assignments with regional contingency recruitment firms and large national retained recruitment firms.
Professional Staff and Employees
We have assembled a wealth of talent that is rewarded based on performance. Our Company brings together the best and brightest from a wide range of disciplines and professions—everything from academic research and technology development to executive recruiting, consulting, and business leadership. We are also a culturally diverse organization. Our people come from all over the world and speak a multitude of languages. For us, this diversity is a key source of strength. It means we have people who are able to challenge convention, offer unique perspectives, and generate innovative ideas. Equally important, it means we can think and act globally—just like our clients.
As of April 30, 2018, we had a total of 7,643 full-time employees. Of this, 1,865 were Executive Search employees consisting of 541 consultants and 1,324 associates, researchers, administrative and support staff. Hay Group had 3,454 employees as of April 30, 2018, consisting of 577 consultants and 2,877 associates, researchers, administrative and support staff. Futurestep had 2,188 employees as of April 30, 2018, consisting of 274 consultants and 1,914 administrative and support staff. Corporate had 136 professionals as of April 30, 2018. We are not party to a collective bargaining agreement and consider our relations with our employees to be good. Korn Ferry is an equal opportunity employer.
11
Table of Contents

The following table provides information relating to each of our business segments for fiscal 2018. Financial information regarding our business segments for fiscal 2017 and 2016 and additional information for fiscal 2018 is contained in Note 11—Business Segments, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, which is incorporated herein by reference.
| Fee Revenue | Operating Income (Loss) |
Number of Consultants as of April 30, 2018 |
||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Executive Search: |
||||||||||||
| North America |
$ | 408,098 | $ | 100,037 | 254 | |||||||
| EMEA |
173,725 | 26,768 | 163 | |||||||||
| Asia Pacific |
96,595 | 18,425 | 92 | |||||||||
| Latin America |
30,624 | 4,022 | 32 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Executive Search |
709,042 | 149,252 | 541 | |||||||||
| Hay Group |
785,013 | 100,939 | 577 | |||||||||
| Futurestep |
273,162 | 39,363 | 274 | |||||||||
| Corporate |
— | (85,670 | ) | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,767,217 | $ | 203,884 | 1,392 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following table provides information on fee revenues for each of the last three fiscal years attributable to the regions in which the Company operates:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 (1) | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Fee Revenue: |
||||||||||||
| United States |
$ | 778,470 | $ | 728,871 | $ | 669,585 | ||||||
| Canada |
69,699 | 57,640 | 40,401 | |||||||||
| EMEA |
537,654 | 445,681 | 343,460 | |||||||||
| Asia Pacific |
292,823 | 249,077 | 187,631 | |||||||||
| Latin America |
88,571 | 84,252 | 51,035 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,767,217 | $ | 1,565,521 | $ | 1,292,112 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Fee revenue from Legacy Hay was $186.8 million for the period from December 1, 2015, the effective date of the acquisition to April 30, 2016. |
Additional financial information regarding the regions in which the Company operates can be found in Note 11—Business Segments, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
KF Merger
As discussed above, in connection with the Plan, the Company intends to pursue a holding company reorganization (the “KF Merger”), after which a new public holding company, Korn Ferry, will own all of the stock of the Company. The Company will initially form Korn Ferry as a direct, wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company. Then, pursuant to the KF Merger, the Company will merge with and into another newly formed entity—Merger Sub, a Delaware corporation, and a direct, wholly-owned subsidiary of Korn Ferry and indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company—with the Company surviving as a direct, wholly-owned subsidiary of Korn Ferry and operating under the legal name “Korn Ferry US.” Each share of Company stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the KF Merger will be converted into an equivalent corresponding share of Korn Ferry stock, having the same designations, rights, powers and preferences and the qualifications, limitations and restrictions as the corresponding share of Company stock being converted. The Company’s current stockholders will become stockholders of Korn Ferry upon the consummation of the KF Merger and will not recognize gain or loss for U.S. federal income tax purposes upon the conversion of their shares.
12
Table of Contents

The Company plans to conduct the KF Merger pursuant to Section 251(g) of the Delaware General Corporation Law (“DGCL”), which permits the creation of a holding company through a merger with a direct or indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of the constituent corporation without stockholder approval, to create a parent company holding structure. The Company will adopt an amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws upon the consummation of the KF Merger, which will also reflect the change of the name of the corporation to Korn Ferry US, as permitted by Section 251(g) of the DGCL. Following the consummation of the KF Merger and as part of the Plan, the Company intends to merge certain of its subsidiaries organized in the U.S. with and into Korn Ferry US.
The risks described below are the material risks facing our Company. Additional risks not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also impair our business operations. Our business, financial condition or results of operations could be materially adversely affected by any of these risks.
Competition in our industries could result in our losing market share and/or require us to charge lower prices for services, which could reduce our revenue.
We compete for executive search business with numerous executive search firms and businesses that provide job placement services, including other large global executive search firms, smaller specialty firms and web-based firms. In recent years, we have also begun facing increased competition from sole proprietors and in-house human resource professionals whose ability to provide job placement services has been enhanced by professional profiles made available on the internet and enhanced social media-based search tools. The continued growth of the shared economy and related freelancing platform sites may also negatively impact demand for our services by allowing employers seeking services to connect with employees in real time and without any significant cost. Traditional executive search competitors include Egon Zehnder, Heidrick & Struggles International, Inc., Russell Reynolds Associates and Spencer Stuart. In each of our markets, one or more of our competitors may possess greater resources, greater name recognition, lower overhead or other costs and longer operating histories than we do, which may give them an advantage in obtaining future clients, capitalizing on new technology and attracting qualified professionals in these markets. Additionally, specialty firms can focus on regional or functional markets or on particular industries and executive search firms that have a smaller client base may be subject to fewer off-limits arrangements. There are no extensive barriers to entry into the executive search industry and new recruiting firms continue to enter the market. We believe the continuing development and increased availability of information technology will continue to attract new competitors, especially web-enabled professional and social networking website providers, and these providers may be facilitating a company’s ability to insource their recruiting capabilities. Competitors in these fields include SMASHFLY, iCIMS, Yello, Indeed, Google for Jobs and Jobvite. As these providers continue to evolve, they may develop offerings similar to or more expansive than ours, thereby increasing competition for our services or more broadly causing disruption in the executive search industry. Further, as technology continues to develop and the shared economy continues to grow, we expect that the use of freelancing platform sites will become more prevalent. As a result, companies may turn to such sites for their talent needs, which could negatively impact demand for the services we offer.
The human resource consulting business has been traditionally fragmented and a number of large consulting firms, such as Ernst and Young, McKinsey, Willis Towers Watson and Deloitte are building businesses in human resource management consulting to serve these needs. These companies are significantly larger than Korn Ferry and have considerable resources at their disposal, allowing for potentially significant investment to grow their human resource consulting business. Increased competition, whether as a result of professional and social networking website providers, traditional executive search firms, sole proprietors and in-house human resource professionals (as noted above) or larger consulting firms building human resources consulting businesses, may lead to pricing pressures that could negatively impact our business. For example, increased competition could require us to charge lower prices, and/or cause us to lose market share, each of which could reduce our fee revenue.
The talent acquisition business, including RPO, project recruitment, professional search, talent consulting and employee communications is a highly competitive and developing industry with numerous specialists. Our Futurestep division primarily competes for business with other RPO providers such as Cielo, Alexander Mann
13
Table of Contents

Solutions, Kenexa, Spherion, and Kelly Services, and competes for mid-level professional search assignments with regional contingency recruitment firms and large national retained recruitment firms. In addition, some organizations have developed or may develop internal solutions to address talent acquisition that may be competitive with our solutions. To compete successfully and achieve our growth targets for our talent acquisition business, we must continue to support and develop assessment and analytics solutions, maintain and grow our proprietary database, deliver demonstrable return on investment to clients, support our products and services globally, and continue to provide consulting and training to support our assessment products. Our failure to compete effectively with our competitors could adversely affect our operating results and future growth.
Consolidation in the industries that we serve could harm our business.
Companies in the industries that we serve may seek to achieve economies of scale and other synergies by combining with or acquiring other companies. If two or more of our clients merge or consolidate and combine their operations, we may experience a decrease in the amount of services we perform for these clients. If one of our clients merges or consolidates with a company that relies on another provider for its services, we may lose work from that client or lose the opportunity to gain additional work. The increased market power of larger companies could also increase pricing and competitive pressures on us. Any of these possible results of industry consolidation could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.
If we fail to attract and retain qualified and experienced consultants, our revenue could decline and our business could be harmed.
We compete with other executive and professional search and consulting firms for qualified and experienced consultants. These other firms may be able to offer greater compensation and benefits or more attractive lifestyle choices, career paths or geographic locations than we do. Attracting and retaining consultants in our industry is particularly important because, generally, a small number of consultants have primary responsibility for a client relationship. Because client responsibility is so concentrated, the loss of key consultants may lead to the loss of client relationships. In fiscal 2018, for example, our top three Executive Search and Hay Group consultants had primary responsibility for generating business equal to approximately 1% and 2% of our fee revenues, respectively, and our top ten Executive Search and Hay Group consultants had primary responsibility for generating business equal to approximately 3% and 4% of our fee revenues, respectively. This risk is heightened due to the general portability of a consultant’s business: consultants have in the past, and will in the future, terminate their employment with our Company. Any decrease in the quality of our reputation, reduction in our compensation levels relative to our peers or restructuring of our compensation program, whether as a result of insufficient revenue, a decline in the market price of our common stock or for any other reason, could impair our ability to retain existing consultants or attract additional qualified consultants with the requisite experience, skills and established client relationships. Our failure to retain our most productive consultants, whether in Executive Search, Hay Group or Futurestep, or maintain the quality of service to which our clients are accustomed as well as the ability of a departing consultant to move business to his or her new employer could result in a loss of clients, which could in turn cause our fee revenue to decline and our business to be harmed. We may also lose clients if the departing Executive Search, Hay Group or Futurestep consultant has widespread name recognition or a reputation as a specialist in his or her line of business in a specific industry or management function. We could also lose additional consultants if they choose to join the departing Executive Search, Hay Group or Futurestep consultant at another executive search or consulting firm. If we fail to limit departing consultants from moving business or recruiting our consultants to a competitor, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We may be limited in our ability to recruit candidates from our clients and we could lose those opportunities to our competition, which could harm our business.
Either by agreement with clients, or for client relations or marketing purposes, we sometimes refrain from, for a specified period of time, recruiting candidates from a client when conducting searches on behalf of other clients. These off-limit agreements can generally remain in effect for up to two years following the completion of an assignment. The duration and scope of the off-limit agreement, including whether it covers all operations of the client and its affiliates or only certain divisions of a client, generally are subject to negotiation or internal policies and may depend on factors such as the scope, size and complexity of the client’s business, the length of the client
14
Table of Contents

relationship and the frequency with which we have been engaged to perform executive searches for the client. If a prospective client believes that we are overly restricted by these off-limit agreements from recruiting employees of our existing clients, these prospective clients may not engage us to perform their executive searches. Therefore, our inability to recruit candidates from these clients may make it difficult for us to obtain search assignments from, or to fulfill search assignments for, other companies in that client’s industry. We cannot ensure that off-limit agreements will not impede our growth or our ability to attract and serve new clients, or otherwise harm our business.
We incur substantial costs to hire and retain our professionals, and we expect these costs to continue and to grow.
We may pay hiring bonuses and annual retention bonuses to secure the services of new hires and retain our professional employees. Those payments have taken the form of long-term deferred compensation, restricted stock, and unsecured cash payments in the form of promissory notes. The aggregate amount of these awards to employees is significant and we expect to continue issuing these types of long-term incentive awards.
If we are unable to retain our executive officers and key personnel or integrate new members of our senior management who are critical to our business, we may not be able to successfully manage our business in the future.
Our future success depends upon the continued service of our executive officers and other key management personnel. Competition for qualified personnel is intense, and we may compete with other companies that have greater financial and other resources than we do. If we lose the services of one or more of our executives or key employees, or if one or more of them decides to join a competitor or otherwise compete directly or indirectly with us, or if we are unable to integrate new members of our senior management who are critical to our business, we may not be able to successfully manage our business or achieve our business objectives.
If we are unable to maintain our professional reputation and brand name, our business will be harmed.
We depend on our overall reputation and brand name recognition to secure new engagements and to hire qualified professionals. Our success also depends on the individual reputations of our professionals. We obtain a majority of our new engagements from existing clients or from referrals by those clients. Any client who is dissatisfied with our services can adversely affect our ability to secure new engagements.
If any factor, including poor performance or negative publicity, whether or not true, hurts our reputation, we may experience difficulties in competing successfully for both new engagements and qualified consultants. Failing to maintain our professional reputation and the goodwill associated with our brand name could seriously harm our business.
As we develop new services, clients and practices, enter new lines of business, and focus more of our business on providing a full range of client solutions, the demands on our business and our operating risks may increase.
As part of our corporate strategy, we are attempting to leverage our research and advisory services to sell a full range of services across the life cycle of a policy, program, project or initiative, and we are regularly searching for ways to provide new services to clients. In addition, we plan to extend our services to new clients, into new lines of business, and into new geographic locations. As we focus on developing new services, clients, practice areas and lines of business; open new offices; and engage in business in new geographic locations, our operations may be exposed to additional as well as enhanced risks.
In particular, our growth efforts place substantial additional demands on our management and staff, as well as on our information, financial, administrative and operational systems. We may not be able to manage these demands successfully. Growth may require increased recruiting efforts, opening new offices, increased business development, selling, marketing and other actions that are expensive and entail increased risk. We may need to invest more in our people and systems, controls, compliance efforts, policies and procedures than we anticipate. Therefore, even if we do grow, the demands on our people and systems, controls, compliance efforts, policies and procedures may exceed the benefits of such growth, and our operating results may suffer, at least in the short-term, and perhaps in the long-term.
15
Table of Contents

Efforts involving a different focus, new services, new clients, new practice areas, new lines of business, new offices and new geographic locations entail inherent risks associated with our inexperience and competition from mature participants in those areas. Our inexperience may result in costly decisions that could harm our profit and operating results. In particular, new or improved services often relate to the development, implementation and improvement of critical infrastructure or operating systems that our clients may view as “mission critical,” and if we fail to satisfy the needs of our clients in providing these services, our clients could incur significant costs and losses for which they could seek compensation from us. Finally, as our business continues to evolve and we provide a wider range of services, we will become increasingly dependent upon our employees, particularly those operating in business environments less familiar to us. Failure to identify, hire, train and retain talented employees who share our values could have a negative effect on our reputation and our business.
Our rebranding plan may take a significant amount of time and involve substantial costs and may not be favorably received by our clients.
On June 12, 2018, the Company’s Board of Directors voted to approve a rebranding plan for the Company. This plan includes going to market under a single, master brand architecture, solely as Korn Ferry and sunsetting of all the Company’s sub-brands, including Futurestep, Hay Group and Lominger, among others. The Company is harmonizing under one brand to help accelerate the firm’s positioning as the preeminent organizational consultancy and bring more client awareness to its broad range of talent management solutions
We may incur substantial costs as a result of rebranding our products and services and may not be able to achieve or maintain brand name recognition or status that is comparable to the recognition and status previously enjoyed by certain of our sub-brands. The failure of our rebranding initiatives could adversely affect our ability to attract and retain clients, which could cause us not to realize some or all of the anticipated benefits contemplated by the rebranding.
We are subject to potential legal liability from clients, employees and candidates for employment. Insurance coverage may not be available to cover all of our potential liability and available coverage may not be sufficient to cover all claims that we may incur.
Our ability to obtain liability insurance, its coverage levels, deductibles and premiums, are all dependent on market factors, our loss history and insurers’ perception of our overall risk profile. We are exposed to potential claims with respect to the executive search process and the consulting services performed by Hay Group. For example, a client could assert a claim for matters such as breach of an off-limit agreement or recommending a candidate who subsequently proves to be unsuitable for the position filled. Further, the current employer of a candidate whom we placed could file a claim against us alleging interference with an employment contract; a candidate could assert an action against us for failure to maintain the confidentiality of the candidate’s employment search; and a candidate or employee could assert an action against us for alleged discrimination, violations of labor and employment law or other matters. Also, in various countries, we are subject to data protection laws impacting the processing of candidate information and other regulatory requirements that could give rise to liabilities/claims. The client may not be satisfied with the consulting services provided by our Hay Group consultants that may lead to claims against us.
Additionally, as part of our Hay Group services, we often send a team of leadership consultants to our clients’ workplaces. Such consultants generally have access to client information systems and confidential information. An inherent risk of such activity includes possible claims of misuse or misappropriation of client IP, confidential information, funds or other property, as well as harassment, criminal activity, torts, or other claims. Such claims may result in negative publicity, injunctive relief, criminal investigations and/or charges, payment by us of monetary damages or fines, or other material adverse effects on our business.
We cannot ensure that our insurance will cover all claims or that insurance coverage will be available at economically acceptable rates. Our insurance may also require us to meet a deductible. Significant uninsured liabilities could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be able to align our cost structure with our revenue level, which in turn may require additional financing in the future that may not be available at all or may be available only on unfavorable terms.
We continuously evaluate our cost base in relation to projected near to mid-term demand for our services in an effort to align our cost structure with the current realities of our markets. If actual or projected fee revenues are
16
Table of Contents

negatively impacted by weakening customer demand, we may find it necessary to take cost cutting measures so that we can minimize the impact on our profitability. There is, however, no guarantee that if we do take such measures that such measures will properly align our cost structure to our revenue level. Any failure to maintain a balance between our cost structure and our revenue could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations and lead to negative cash flows, which in turn might require us to obtain additional financing to meet our capital needs. If we are unable to secure such additional financing on favorable terms, or at all, our ability to fund our operations could be impaired, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our financial results could suffer if we are unable to achieve or maintain adequate utilization and suitable billing rates for our consultants.
Our profitability depends, to a large extent, on the utilization and billing rates of our professionals. Utilization of our professionals is affected by a number of factors, including:
| ◾ | the number and size of client engagements; |
| ◾ | the timing of the commencement, completion and termination of engagements (for example, the commencement or termination of multiple RPO engagements could have a significant impact on our business, including significant fluctuations in our fee revenue, since these types of engagements are generally larger, in terms of both staffing and fee revenue generated, than our other engagements); |
| ◾ | our ability to transition our consultants efficiently from completed engagements to new engagements; |
| ◾ | the hiring of additional consultants because there is generally a transition period for new consultants that results in a temporary drop in our utilization rate; |
| ◾ | unanticipated changes in the scope of client engagements; |
| ◾ | our ability to forecast demand for our services and thereby maintain an appropriate level of consultants; and |
| ◾ | conditions affecting the industries in which we practice as well as general economic conditions. |
The billing rates of our consultants that we are able to charge are also affected by a number of factors, including:
| ◾ | our clients’ perception of our ability to add value through our services; |
| ◾ | the market demand for the services we provide; |
| ◾ | an increase in the number of clients in the government sector in the industries we serve; |
| ◾ | the introduction of new services by us or our competitors; |
| ◾ | our competition and the pricing policies of our competitors; and |
| ◾ | current economic conditions. |
If we are unable to achieve and maintain adequate overall utilization, as well as maintain or increase the billing rates for our consultants, our financial results could materially suffer. In addition, our consultants oftentimes perform services at the physical locations of our clients. If there are natural disasters, disruptions to travel and transportation or problems with communications systems, our ability to perform services for, and interact with, our clients at their physical locations may be negatively impacted, which could have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
The profitability of our fixed-fee engagements with clients may not meet our expectations if we underestimate the cost of these engagements.
When making proposals for fixed-fee engagements, we estimate the costs and timing for completing the engagements. These estimates reflect our best judgment regarding the efficiencies of our methodologies and consultants as we plan to deploy them on engagements. Any increased or unexpected costs or unanticipated delays in connection with the performance of fixed-fee engagements, including delays caused by factors outside our control, could make these contracts less profitable or unprofitable, which would have an adverse effect on our profit margin. For the years ended April 30, 2018, 2017, and 2016, fixed-fee engagements represented 28%, 29%, and 24% of our revenues, respectively.
17
Table of Contents

Changes in our accounting estimates and assumptions could negatively affect our financial position and results of operations.
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). These accounting principles require us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of our financial statements. We are also required to make certain judgments that affect the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during each reporting period. We periodically evaluate our estimates and assumptions including those relating to revenue recognition, restructuring, deferred compensation, goodwill and other intangible assets, contingent consideration, annual performance-related bonuses, allowance for doubtful accounts, share-based payments and deferred income taxes. Actual results could differ from the estimates we make based on historical experience and various assumptions believed to be reasonable based on specific circumstances, and changes in accounting standards could have an adverse impact on our future financial position and results of operations.
Foreign currency exchange rate risks may adversely affect our results of operations.
A material portion of our revenue and expenses are generated by our operations in foreign countries, and we expect that our foreign operations will account for a material portion of our revenue and expenses in the future. Most of our international expenses and revenue are denominated in foreign currencies. As a result, our financial results could be affected by changes in foreign currency exchange rates or weak economic conditions in foreign markets in which we have operations, among other factors. Fluctuations in the value of those currencies in relation to the U.S. dollar have caused and will continue to cause dollar-translated amounts to vary from one period to another. Given the volatility of exchange rates, we may not be able to manage effectively our currency translation or transaction risks, which may adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Unfavorable tax laws, tax law changes and tax authority rulings may adversely affect results.
We are subject to income taxes in the U.S. and in various foreign jurisdictions. Domestic and international tax liabilities are subject to the allocation of income among various tax jurisdictions. Our effective tax rate could be adversely affected by changes in the mix of earnings among countries with differing statutory tax rates or changes in tax laws. The amount of income taxes and other taxes are subject to ongoing audits by U.S. federal, state and local tax authorities and by non-U.S. authorities. If these audits result in assessments different from estimated amounts recorded, future financial results may include unfavorable tax adjustments.
The effects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act on our business and our company have not yet been fully analyzed and the final impacts could be materially different from our current estimates.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Act”) was enacted into law, making significant changes to the taxation of U.S. business entities. The most significant impacts of the Tax Act on the Company include (1) a reduction in the U.S. corporate federal statutory income tax rate from 35.0% to 21.0% effective January 1, 2018, and (2) a one-time tax on accumulated foreign earnings (the “Transition Tax”), which is applicable at a rate of 15.5% on cash and other specified assets and 8% on other residual earnings. We have recorded in our consolidated financial statements provisional amounts based on our current estimates of the effects of the Tax Act in accordance with our current understanding of the Tax Act and currently available guidance. For additional information regarding the Tax Act and the provisional tax amounts recorded in our consolidated financial statements, see Note 8—Income Taxes. The final amounts may be significantly affected by regulations and interpretive guidance expected to be issued by the tax authorities, clarifications of the accounting treatment of various items, our additional analysis, and our refinement of our estimates of the effects of the Tax Act and, therefore, such final amounts could be materially different than our current provisional amounts, which could materially affect our tax obligations and effective tax rate.
We have deferred tax assets that we may not be able to use under certain circumstances.
If we are unable to generate sufficient future taxable income in certain jurisdictions, or if there is a significant change in the time period within which the underlying temporary differences become taxable or deductible, we could be required to increase our valuation allowances against our deferred tax assets. This would result in an increase in our effective tax rate, and an adverse effect on our future operating results. In addition, changes in
18
Table of Contents

statutory tax rates may also change our deferred tax assets or liability balances, with either a favorable or unfavorable impact on our effective tax rate. Our deferred tax assets may also be impacted by new legislation or regulation.
Our indebtedness could impair our financial condition and reduce funds available to us for other purposes and our failure to comply with the covenants contained in our debt instruments could result in an event of default that could adversely affect our operating results.
On June 15, 2016, the Company entered into a senior secured $400 million Credit Agreement with a syndicate of banks made up of a $275 million term loan and $125 million of secured revolving loans. As of April 30, 2018, $238.9 million was outstanding under the term loan, and there is no outstanding balance under the revolving loans.
If we do not generate sufficient cash flow from operations to satisfy our debt obligations, we may have to undertake alternative financing plans. We cannot ensure that we will be able to refinance our debt or enter into alternative financing plans in adequate amounts on commercially reasonable terms, terms acceptable to us or at all, or that such plans guarantee that we would be able to meet our debt obligations.
Our existing debt agreements contain financial and restrictive covenants that limit the total amount of debt that we may incur and may limit our ability to engage in other activities that we may believe are in our long-term best interests, including the disposition or acquisition of assets or other companies or the payment of dividends to our stockholders. Our failure to comply with these covenants may result in an event of default, which, if not cured or waived, could accelerate the maturity of our indebtedness or prevent us from accessing additional funds under our revolving credit facility. If the maturity of our indebtedness is accelerated, we may not have sufficient cash resources to satisfy our debt obligations, and we may not be able to continue our operations as planned.
The expansion of social media platforms presents new risks and challenges that can cause damage to our brand and reputation.
There has been a marked increase in the use of social media platforms, including weblogs (or blogs), social media websites and other forms of Internet-based communications, which allow individuals access to a broad audience of consumers and other interested persons. The inappropriate and/or unauthorized use of such media vehicles by our clients or employees could increase our costs, cause damage to our brand, lead to litigation or result in information leakage, including the improper collection and/or dissemination of personally identifiable information of candidates and clients. In addition, negative or inaccurate posts or comments about us on any social networking platforms could damage our reputation, brand image and goodwill.
Technological advances may significantly disrupt the labor market and weaken demand for human capital at a rapid rate.
Our success is directly dependent on our customers’ demands for talent. As technology continues to evolve, more tasks currently performed by people may be replaced by automation, robotics, machine learning, artificial intelligence and other technological advances outside of our control. This trend poses a risk to the human resource industry as a whole, particularly in lower-skill job categories that may be more susceptible to such replacement.
Limited protection of our intellectual property could harm our business, and we face the risk that our services or products may infringe upon the intellectual property rights of others.
We cannot guarantee that trade secrets, trademark and copyright law protections are adequate to deter misappropriation of our IP (which has become an important part of our business). Existing laws of some countries in which we provide services or products may offer only limited protection of our IP rights. Redressing infringements may consume significant management time and financial resources. Also, we may be unable to detect the unauthorized use of our IP and take the necessary steps to enforce our rights, which may have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations. We cannot be sure that our services and products, or the products of others that we offer to our clients, do not infringe on the IP rights of third parties, and we may have infringement claims asserted against us or our clients. These claims may harm our reputation, result in financial liability and prevent us from offering some services or products.
19
Table of Contents

We have invested in specialized technology and other intellectual property for which we may fail to fully recover our investment or which may become obsolete.
We have invested in developing specialized technology and IP, including proprietary systems, processes and methodologies, such as Searcher Express and KF Insight, that we believe provide us a competitive advantage in serving our current clients and winning new engagements. Many of our service and product offerings rely on specialized technology or IP that is subject to rapid change, and to the extent that this technology and IP is rendered obsolete and of no further use to us or our clients, our ability to continue offering these services, and grow our revenues, could be adversely affected. There is no assurance that we will be able to develop new, innovative or improved technology or IP or that our technology and IP will effectively compete with the IP developed by our competitors. If we are unable to develop new technology and IP or if our competitors develop better technology or IP, our revenues and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We rely heavily on our information systems and if we lose that technology, or fail to further develop our technology, our business could be harmed.
Our success depends in large part upon our ability to store, retrieve, process, manage and protect substantial amounts of information. To achieve our strategic objectives and to remain competitive, we must continue to develop and enhance our information systems. This may require the acquisition of equipment and software and the development of new proprietary software, either internally or through independent consultants. If we are unable to design, develop, implement and utilize, in a cost-effective manner, information systems that provide the capabilities necessary for us to compete effectively, or for any reason any interruption or loss of our information processing capabilities occurs, this could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition. We cannot be sure that our insurance against the effects of a disaster regarding our information technology or our disaster recovery procedures currently in place will continue to be available at reasonable prices, cover all our losses or compensate us for the possible loss of clients occurring during any period that we are unable to provide business services.
We are subject to risk as it relates to software that we license from third parties.
We license software from third parties, much of which is integral to our systems and our business. The licenses are generally terminable if we breach our obligations under the license agreements. If any of these relationships were terminated or if any of these parties were to cease doing business or cease to support the applications we currently utilize, we may be forced to spend significant time and money to replace the licensed software. However, we cannot assure you that the necessary replacements will be available on reasonable terms, if at all.
We are increasingly dependent on third parties for the execution of critical functions.
We do not maintain all of our technology infrastructure, and we have outsourced certain other critical applications or business processes to external providers, including cloud-based services. The failure or inability to perform on the part of one or more of these critical suppliers or partners could cause significant disruptions and increased costs.
Cyber security vulnerabilities and incidents could lead to the improper disclosure of information obtained from our clients, candidates and employees that could result in liability and harm to our reputation.
We use information technology and other computer resources to carry out operational and marketing activities and to maintain our business records. The continued occurrence of high-profile data breaches against various entities and organizations provides evidence of an external environment that is increasingly hostile to information security. This environment demands that we continuously improve our design and coordination of security controls across our business groups and geographies in order to protect information that we develop or that is obtained from our clients, candidates and employees. Despite these efforts, given the ongoing and increasingly sophisticated attempts to access the information of entities, our security controls over this information, our training of employees, and other practices we follow may not prevent the improper disclosure of such information. Our efforts and the costs incurred to bolster our security against attacks cannot provide absolute assurance that future data breaches will not occur. We depend on our overall reputation and brand name recognition to secure new engagements. Perceptions that we do not adequately protect the privacy of information could inhibit attaining new engagements, qualified consultants and could potentially damage currently existing client relationships.
20
Table of Contents

Data security, data privacy and data protection laws such as the European Union General Data Protection Regulation, and other evolving regulations and cross-border data transfer restrictions, may limit the use of our services and adversely affect our business.
We are or may become subject to a variety of laws and regulations in the European Union (the “E.U.”) (including the E.U. General Data Protection Act and the General Data Protection Regulation, which became effective in May 2018), U.S. and abroad regarding data privacy, protection and security. As these laws continue to evolve, we may be required to make changes to our services, solutions and/or products so as to enable the Company and/or our clients to meet the new legal requirements, including by taking on more onerous obligations in our contracts, limiting our storage, transfer and processing of data and, in some cases, limiting our service and/or solution offerings in certain locations. Changes in these laws may also increase our potential exposure through significantly higher potential penalties for non-compliance. The costs of compliance with, and other burdens imposed by, such laws and regulations and client demand in this area may limit the use of, or demand for, our services, solutions and/or products, make it more difficult and costly to meet client expectations, or lead to significant fines, penalties or liabilities for noncompliance, any of which could harm our business.
In addition, due to the uncertainty and potentially conflicting interpretations of these laws, it is possible that such laws and regulations may be interpreted and applied in a manner that is inconsistent from one jurisdiction to another and may conflict with other rules or our practices. Any failure or perceived failure by us to comply with applicable laws or satisfactorily protect personal information could result in governmental enforcement actions, litigation, or negative publicity, any of which could inhibit sales of our services, solutions and/or products.
Acquisitions, or our inability to effect acquisitions, may have an adverse effect on our business.
We have completed several strategic acquisitions of businesses in the last several years, including our acquisitions of Legacy Hay in fiscal 2016 and PDI and Global Novations in fiscal 2013. Targeted acquisitions have been part of our growth strategy, and we may in the future selectively acquire businesses that are complementary to our existing service offerings. However, we cannot be certain that we will be able to continue to identify appropriate acquisition candidates or acquire them on satisfactory terms. Our ability to consummate such acquisitions on satisfactory terms will depend on:
| ◾ | the extent to which acquisition opportunities become available; |
| ◾ | our success in bidding for the opportunities that do become available; |
| ◾ | negotiating terms that we believe are reasonable; and |
| ◾ | regulatory approval, if required. |
Our ability to make strategic acquisitions may also be conditioned on our ability to fund such acquisitions through the incurrence of debt or the issuance of equity. Our credit agreement dated as of June 15, 2016 limits us from consummating permitted acquisitions unless we are in compliance with our pro forma financial covenants, our pro forma leverage ratio is no greater than 2.50 to 1.00, and domestic liquidity after giving effect to the acquisition is at least $50.0 million. If we are required to incur substantial indebtedness in connection with an acquisition, and the results of the acquisition are not favorable, the increased indebtedness could decrease the value of our equity. In addition, if we need to issue additional equity to consummate an acquisition, doing so would cause dilution to existing stockholders.
If we are unable to make strategic acquisitions, or the acquisitions we do make are not on terms favorable to us or not effected in a timely manner, it may impede the growth of our business, which could adversely impact our profitability and our stock price.
We have provisions that make an acquisition of us more difficult and expensive.
Anti-takeover provisions in our Certificate of Incorporation, our Bylaws and under Delaware law make it more difficult and expensive for us to be acquired in a transaction that is not approved by our Board of Directors. Some of the provisions in our Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws include:
| ◾ | limitations on stockholder actions; |
21
Table of Contents

| ◾ | advance notification requirements for director nominations and actions to be taken at stockholder meetings; and |
| ◾ | the ability to issue one or more series of preferred stock by action of our Board of Directors. |
These provisions could discourage an acquisition attempt or other transaction in which stockholders could receive a premium over the current market price for the common stock.
We may not be able to successfully integrate or realize the expected benefits from our acquisitions.
Our future success may depend in part on our ability to complete the integration of acquisition targets successfully into our operations. The process of integrating an acquired business may subject us to a number of risks, including:
| ◾ | diversion of management attention; |
| ◾ | amortization of intangible assets, adversely affecting our reported results of operations; |
| ◾ | inability to retain and/or integrate the management, key personnel and other employees of the acquired business; |
| ◾ | inability to properly integrate businesses resulting in operating inefficiencies; |
| ◾ | inability to establish uniform standards, disclosure controls and procedures, internal control over financial reporting and other systems, procedures and policies in a timely manner; |
| ◾ | inability to retain the acquired company’s clients; |
| ◾ | exposure to legal claims for activities of the acquired business prior to acquisition; and |
| ◾ | incurrence of additional expenses in connection with the integration process. |
If our acquisitions are not successfully integrated, our business, financial condition and results of operations, as well as our professional reputation, could be materially adversely affected.
Further, we cannot assure that acquisitions will result in the financial, operational or other benefits that we anticipate. Some acquisitions may not be immediately accretive to earnings and some expansion may result in significant expenditures.
Businesses we acquire may have liabilities or adverse operating issues which could harm our operating results.
Businesses we acquire may have liabilities or adverse operating issues, or both, that we either fail to discover through due diligence or underestimate prior to the consummation of the acquisition. These liabilities and/or issues may include the acquired business’ failure to comply with, or other violations of, applicable laws, rules or regulations or contractual or other obligations or liabilities. As the successor owner, we may be financially responsible for, and may suffer harm to our reputation or otherwise be adversely affected by, such liabilities and/or issues. An acquired business also may have problems with internal controls over financial reporting, which could in turn cause us to have significant deficiencies or material weaknesses in our own internal controls over financial reporting. These and any other costs, liabilities, issues, and/or disruptions associated with any past or future acquisitions, and the related integration, could harm our operating results.
As a result of our acquisitions, we have substantial amounts of goodwill and intangible assets, and changes in business conditions could cause these assets to become impaired, requiring write-downs that would adversely affect our operating results.
All of our acquisitions have been accounted for as purchases and involved purchase prices well in excess of tangible asset values, resulting in the creation of a significant amount of goodwill and other intangible assets. As of April 30, 2018, goodwill and purchased intangibles accounted for approximately 26% and 9%, respectively, of our total assets. Under U.S. GAAP, we do not amortize goodwill and intangible assets acquired in a purchase business combination that are determined to have indefinite useful lives, but instead review them annually (or more frequently if impairment indicators arise) for impairment. As discussed above, in connection with the Plan, the Company intends to offer all of the Company’s current products and services using the “Korn Ferry” name, branding and trademarks, and sunset all sub-brands, including Futurestep, Hay Group and Lominger, among others. The Hay Group and Lominger brands came to the Company through acquisitions and, in connection with
22
Table of Contents

the accounting for those acquisitions, $106 million of the purchase price was allocated to indefinite lived tradename intangible assets. On June 12, 2018, the Company concluded that as a result of the decision to discontinue the use of such sub-brands in the near term, the Company will be required under U.S. generally accepted accounting principles to record in the first quarter of fiscal 2019 a one-time, non-cash intangible asset impairment charge of $106 million, or $79 million on an after-tax basis. The discontinuation of such brands and resulting impairment charge could adversely affect our business. Further, although we have to date determined that none of our other assets have been impaired, future events or changes in circumstances that result in an impairment of goodwill or other intangible assets would have a negative impact on our profitability and operating results.
An impairment in the carrying value of goodwill and other intangible assets could negatively impact our consolidated results of operations and net worth.
Goodwill is initially recorded as the excess of amounts paid over the fair value of net assets acquired. While goodwill is not amortized, it is reviewed for impairment at least annually or more frequently if impairment indicators are present. In assessing the carrying value of goodwill, we make qualitative and quantitative assumptions and estimates about revenues, operating margins, growth rates and discount rates based on our business plans, economic projections, anticipated future cash flows and marketplace data. There are inherent uncertainties related to these factors and management’s judgment in applying these factors. Goodwill valuations have been calculated using an income approach based on the present value of future cash flows of each reporting unit and a market approach. We could be required to evaluate the carrying value of goodwill prior to the annual assessment if we experience unexpected, significant declines in operating results or sustained market capitalization declines. These types of events and the resulting analyses could result in goodwill impairment charges in the future. Impairment charges, such as the impairment charge that we will be required to record in the first quarter of fiscal 2019 related to the discontinuation of the Hay Group and Lominger brands, could substantially affect our results of operations and net worth in the periods of such charges.
We are a cyclical Company whose performance is tied to local and global economic conditions.
Demand for our services is affected by global economic conditions and the general level of economic activity in the geographic regions and industries in which we operate. When conditions in the global economy, including the credit markets deteriorate, or economic activity slows, many companies hire fewer permanent employees and some companies, as a cost-saving measure, choose to rely on their own human resources departments rather than third-party search firms to find talent, and under these conditions, companies may cut back on human resource initiatives, all of which negatively affects our financial condition and results of operations. We may also experience more competitive pricing pressure during periods of economic decline. If the geopolitical uncertainties result in a reduction in business confidence, if the national or global economy or credit market conditions in general deteriorate, or if the unemployment rate increases, such uncertainty or changes could put negative pressure on demand for our services and our pricing, resulting in lower cash flows and a negative effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, some of our clients may experience reduced access to credit and lower revenues resulting in their inability to meet their payment obligations to us.
We face risks associated with social and political instability, legal requirements and economic conditions in our international operations.
We operate in 52 countries and, during the year ended April 30, 2018, generated 56% of our fee revenue from operations outside of the U.S. We are exposed to the risk of changes in social, political, legal and economic conditions inherent in international operations. Examples of risks inherent in transacting business worldwide that we are exposed to include:
| ◾ | uncertainties and instability in economic and market conditions caused by the United Kingdom’s (the “U.K.”) vote to exit the E.U. (“Brexit”); |
| ◾ | uncertainty regarding how the U.K.’s access to the E.U. Single Market and the wider trading, legal, regulatory and labor environments, especially in the U.K. and E.U., will be impacted by Brexit, including the resulting impact on our business and that of our clients; |
23
Table of Contents

| ◾ | changes in and compliance with applicable laws and regulatory requirements, including U.S. laws affecting the activities of U.S. companies abroad, including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977 and sanctions programs administered by the U.S. Department of the Treasury Office of Foreign Assets Control, and similar foreign laws such as the U.K. Bribery Act, as well as the fact that many countries have legal systems, local laws and trade practices that are unsettled and evolving, and/or commercial laws that are vague and/or inconsistently applied; |
| ◾ | difficulties in staffing and managing global operations, which could impact our ability to maintain an effective system of internal control; |
| ◾ | difficulties in building and maintaining a competitive presence in existing and new markets; |
| ◾ | social, economic and political instability; |
| ◾ | differences in cultures and business practices; |
| ◾ | statutory equity requirements; |
| ◾ | differences in accounting and reporting requirements; |
| ◾ | repatriation controls; |
| ◾ | differences in labor and market conditions; |
| ◾ | potential adverse tax consequences; |
| ◾ | multiple regulations concerning pay rates, benefits, vacation, statutory holiday pay, workers’ compensation, union membership, termination pay, the termination of employment, and other employment laws; and |
| ◾ | the introduction of greater uncertainty with respect to trade policies, tariffs and government regulation affecting trade between the U.S. and other countries. |
We cannot ensure that one or more of these factors will not harm our business, financial condition or results of operations.
You may not receive the level of dividends provided for in the dividend policy our Board of Directors has adopted or any dividends at all.
We are not obligated to pay dividends on our common stock. Our Board of Directors adopted a dividend policy on December 8, 2014, that reflects an intention to distribute to our stockholders a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.10 per share of common stock. Although the Company paid our first dividend under this program on April 9, 2015 and has declared a quarterly dividend every quarter since the adoption of the dividend policy, the declaration and payment of all future dividends to holders of our common stock are subject to the discretion of our Board of Directors, which may amend, revoke or suspend our dividend policy at any time and for any reason, including earnings, capital requirements, financial conditions and other factors our Board of Directors may deem relevant. The terms of our indebtedness may also restrict us from paying cash dividends on our common stock under certain circumstances. See below “—Our ability to pay dividends will be restricted by agreements governing our debt, including our credit agreement, and by Delaware law.”
Over time, our capital and other cash needs may change significantly from our current needs, which could affect whether we pay dividends and the level of any dividends we may pay in the future. If we were to use borrowings under our credit facility to fund our payment of dividends, we would have less cash and/or borrowing capacity available for future dividends and other purposes, which could negatively affect our financial condition, our results of operations, our liquidity and our ability to maintain and expand our business. Accordingly, you may not receive dividends in the intended amounts, or at all. Any reduction or elimination of dividends may negatively affect the market price of our common stock.
Our ability to pay dividends will be restricted by agreements governing our debt, including our credit agreement, and by Delaware law.
Our credit agreement restricts our ability to pay dividends. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources,” where we describe the terms of our indebtedness, including provisions limiting our ability to declare and pay dividends. As a result of such restrictions, we may be limited in our ability to pay dividends unless we amend our credit agreement or otherwise obtain a waiver from our lenders. In addition, as a result of general economic conditions, conditions in the lending markets, the results of our business or for any other reason, we may elect or be required to amend or refinance
24
Table of Contents

our senior credit facility, at or prior to maturity, or enter into additional agreements for indebtedness. Any such amendment, refinancing or additional agreement may contain covenants which could limit in a significant manner or entirely our ability to pay dividends to you.
Additionally, under the DGCL, our Board of Directors may not authorize payment of a dividend unless it is either paid out of surplus, as calculated in accordance with the DGCL, or if we do not have a surplus, out of net profits for the fiscal year in which the dividend is declared and/or the preceding fiscal year.
If, as a result of these restrictions, we are required to reduce or eliminate the payment of dividends, a decline in the market price or liquidity, or both, of our common stock could result. This may in turn result in losses by you.
Our dividend policy may limit our ability to pursue growth opportunities.
If we pay dividends at the level currently anticipated under our dividend policy, we may not retain a sufficient amount of cash to finance growth opportunities, meet any large unanticipated liquidity requirements or fund our operations in the event of a significant business downturn. In addition, because a portion of cash available will be distributed to holders of our common stock under our dividend policy, our ability to pursue any material expansion of our business, including through acquisitions, increased capital spending or other increases of our expenditures, will depend more than it otherwise would on our ability to obtain third party financing. We cannot assure you that such financing will be available to us at all, or at an acceptable cost. If we are unable to take timely advantage of growth opportunities, our future financial condition and competitive position may be harmed, which in turn may adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
We may be subject to the actions of activist shareholders.
Our Board of Directors and management team are committed to acting in the best interest of all of our shareholders. We value constructive input from investors and regularly engage in dialogue with our shareholders regarding strategy and performance. Activist shareholders who disagree with the composition of the Board of Directors, our strategy or the way the Company is managed may seek to effect change through various strategies and channels. Responding to shareholder activism can be costly and time-consuming, disrupt our operations, and divert the attention of management and our employees from our strategic initiatives. Activist campaigns can create perceived uncertainties as to our future direction, strategy, or leadership and may result in the loss of potential business opportunities, harm our ability to attract new employees, investors, and customers, and cause our stock price to experience periods of volatility or stagnation.
Our business could be disrupted as a result of actions of certain stockholders.
If any of our stockholders commence a proxy contest, advocate for change, make public statements critical of our performance or business, or engage in other similar activities, then our business could be adversely affected because we may have difficulty attracting and retaining clients due to perceived uncertainties as to our future direction and negative public statements about our business; responding to proxy contests and other similar actions by stockholders is likely to result in us incurring substantial additional costs and significantly divert the attention of management and our employees; and, if individuals are elected to our Board with a specific agenda, the execution of our strategic plan may be disrupted or a new strategic plan altogether may be implemented, which could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations. Further, any of these matters or any such actions by stockholders may impact and result in volatility of the price of our common stock.
Our inability to successfully recover should we experience a disaster or other business continuity problem could cause material financial loss, loss of human capital, regulatory actions, reputational harm or legal liability.
Should we experience a disaster or other business continuity problem, such as an earthquake, hurricane, terrorist attack, pandemic, security breach, power loss, telecommunications failure or other natural or man-made disaster, our continued success will depend, in part, on the availability of our personnel, our office facilities, and the proper functioning of our computer, telecommunication and other related systems and operations. In such an event, we
25
Table of Contents

could experience near-term operational challenges with regard to particular areas of our operations. In particular, our ability to recover from any disaster or other business continuity problem will depend on our ability to protect our technology infrastructure against damage from business continuity events that could have a significant disruptive effect on our operations. We could potentially lose client data or experience material adverse interruptions to our operations or delivery of services to our clients in a disaster. A disaster on a significant scale or affecting certain of our key operating areas within or across regions, or our inability to successfully recover should we experience a disaster or other business continuity problem, could materially interrupt our business operations and cause material financial loss, loss of human capital, regulatory actions, reputational harm, damaged client relationships or legal liability.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not applicable.
Our corporate office is located in Los Angeles, California. We lease our corporate office and all 105 of our Executive Search, Hay Group, and Futurestep offices located in North America, EMEA, Asia Pacific and Latin America. As of April 30, 2018, we leased an aggregate of approximately 1.3 million square feet of office space. The leases generally have remaining terms of one to 12 years and contain customary terms and conditions. We believe that our facilities are adequate for our current needs and we do not anticipate any difficulty replacing such facilities or locating additional facilities to accommodate any future growth.
From time to time, we are involved in litigation both as a plaintiff and a defendant, relating to claims arising out of our operations. As of the date of this report, we are not engaged in any legal proceedings that are expected, individually or in the aggregate, to have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
| Name
|
Age as of
|
Position
| ||
| Gary D. Burnison |
57 | President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Robert P. Rozek |
57 | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Corporate Officer | ||
| Mark Arian |
57 | Chief Executive Officer, Hay Group | ||
| Byrne Mulrooney
|
57
|
Chief Executive Officer, Futurestep
| ||
Our executive officers serve at the discretion of our Board of Directors. There is no family relationship between any executive officer or director. The following information sets forth the business experience for at least the past five years for each of our executive officers.
Gary D. Burnison has been President and Chief Executive Officer since July 2007. He was Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from March 2002 until June 30, 2007 and Chief Operating Officer from November 2003 until June 30, 2007. Prior to joining Korn Ferry, Mr. Burnison was Principal and Chief Financial Officer of Guidance Solutions, a privately held consulting firm, from 1999 to 2001. Prior to that, he served as an executive officer and a member of the Board of Directors of Jefferies and Company, Inc., the principal operating subsidiary of Jefferies Group, Inc. from 1995 to 1999. Earlier, Mr. Burnison was a Partner at KPMG Peat Marwick.
Robert P. Rozek joined the Company in February 2012 as our Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer and in December 2015 also became our Chief Corporate Officer. Prior to joining Korn Ferry, he served as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Cushman & Wakefield, Inc., a privately held commercial
26
Table of Contents

real estate services firm, from June 2008 to February 2012. Prior to joining Cushman & Wakefield, Inc., Mr. Rozek served as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Las Vegas Sands Corp., a leading global developer of destination properties (integrated resorts) that feature premium accommodations, world-class gaming and entertainment, convention and exhibition facilities and many other amenities, from 2006 to 2008. Prior to that, Mr. Rozek held senior leadership positions at Eastman Kodak, and spent five years as a Partner with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP.
Mark Arian joined the Company as Chief Executive Officer of Korn Ferry’s Hay Group segment in April 2017. Prior to Korn Ferry, Mr. Arian served as a Managing Principal at Ernst and Young LLP, a multinational professional services firm that provides audit, tax, business risk, technology and security risk services, and human capital services worldwide, from March 2014 until March of 2017. In that capacity, he led the People Advisory Services—Financial Services Sector, and his responsibilities included commercial, people and key account leadership. Between 2008 and 2014, Mr. Arian held various leadership positions at AON and AON Hewitt, a provider of insurance, reinsurance, human capital and management consulting services, serving as an Executive Vice President and leading its strategic Mergers and Acquisitions (“M&A”) and business transformation offering globally. Mr. Arian has also held various leadership positions at Towers Perrin (now Wills Towers Watson) including serving as the Global M&A and Global Change Management leader, and Hewitt Associates, where Mr. Arian built and led the Corporate Restructuring and Change Practice. Mr. Arian is a graduate of Duke University and holds a juris doctorate from Columbia University.
Byrne Mulrooney joined the Company in April 2010 as Chief Executive Officer of Futurestep. Prior to joining Korn Ferry, he was President and Chief Operating Officer of Flynn Transportation Services, a third-party logistics company, from 2007 to 2010. Prior to that, he led Spherion’s workforce solutions business in North America, which provides workforce solutions in professional services and general staffing, including recruitment process outsourcing and managed services, from 2003 to 2007. Mr. Mulrooney held executive positions for almost 20 years at EDS and IBM in client services, sales, marketing and operations. Mr. Mulrooney is a graduate of Villanova University in Pennsylvania. He holds a master’s degree in management from Northwestern University’s J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of Management.
27
Table of Contents

Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Common Stock
Our common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol ‘KFY’. The following table sets forth the high and low sales price per share of the common stock for the periods indicated, as reported on the New York Stock Exchange:
| High | Low | |||||||
| Fiscal Year Ended April 30, 2018 |
||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 36.07 | $ | 31.19 | ||||
| Second Quarter |
$ | 42.34 | $ | 31.53 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
$ | 45.26 | $ | 39.93 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter |
$ | 55.45 | $ | 38.53 | ||||
| Fiscal Year Ended April 30, 2017 |
||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 30.78 | $ | 18.57 | ||||
| Second Quarter |
$ | 24.85 | $ | 19.94 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
$ | 31.53 | $ | 19.95 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter |
$ | 33.14 | $ | 27.47 | ||||
On June 21, 2018, the last reported sales price on the New York Stock Exchange for the Company’s common stock, was $63.94 per share and there were approximately 18,525 beneficial stockholders of the Company’s common stock.
Performance Graph
We have presented below a graph comparing the cumulative total stockholder return on the Company’s shares with the cumulative total stockholder return on (1) the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index and (2) a company-established peer group. Cumulative total return for each of the periods shown in the performance graph is measured assuming an initial investment of $100 on April 30, 2013 and the reinvestment of any dividends paid by the Company and any company in the peer group on the date the dividends were paid.
Our peer group is comprised of a broad number of publicly traded companies, which are principally or in significant part involved in either professional staffing or consulting. The peer group is comprised of the following 14 companies: CBIZ, Inc. (CBZ), FTI Consulting, Inc. (FCN), Heidrick & Struggles International, Inc. (HSII), Huron Consulting Group Inc. (HURN), ICF International, Inc. (ICFI), Insperity, Inc. (NSP), Kelly Services, Inc. (KELYA), Kforce Inc. (KFRC), Navigant Consulting, Inc. (NCI), Resources Connection, Inc. (RECN), Robert Half International, Inc. (RHI), The Dun & Bradstreet Corporation (DNB), Willis Towers Watson (WLTW) and TrueBlue, Inc. (TBI). We believe this group of professional services firms, is reflective of similar sized companies in terms of our market capitalization, revenue or profitability, and therefore provides a more meaningful comparison of stock performance. The returns of each company have been weighted according to their respective stock market capitalization at the beginning of each measurement period for purposes of arriving at a peer group average.
The stock price performance depicted in this graph is not necessarily indicative of future price performance. This graph will not be deemed to be incorporated by reference by any general statement incorporating this Annual Report on Form 10-K into any filing by us under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, except to the extent we specifically incorporate this information by reference and shall not otherwise be deemed soliciting material or deemed filed under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
28
Table of Contents

COMPARISON OF 5 YEAR CUMULATIVE TOTAL RETURN(*)
Among Korn/Ferry International, the S&P 500 Index, and a Peer Group
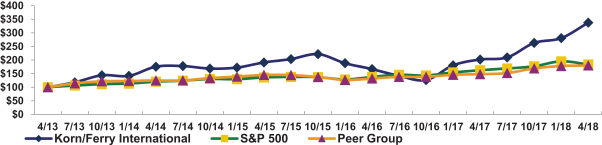
Copyright© 2018 Standard & Poor’s, a division of S&P Global. All rights reserved.
| (*) | $100 invested on April 30, 2013 in stock or index, including reinvestment of dividends. Fiscal year ended April 30, 2018. |
Capital Allocation Approach
The Company and its Board of Directors endorse a balanced approach to capital allocation. The Company’s first priority is to invest in growth initiatives, such as the hiring of consultants, the continued development of IP and derivative products and services, and the investment in synergistic accretive M&A transactions that earn a return superior to the Company’s cost of capital. Next, the Company’s capital allocation approach contemplates the planned return of a portion of excess capital to stockholders, in the form of a regular quarterly dividend, subject to the factors discussed below under “Dividends” and in more detail in the “Risk Factors” section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Additionally, the Company considers share repurchases on an opportunistic basis and subject to the terms of our credit agreement.
Dividends
On December 8, 2014, the Board of Directors adopted a dividend policy, reflecting an intention to distribute to our stockholders a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.10 per share. In fiscal 2017, the Board of Directors declared the following dividends:
| Declaration Date
|
Dividend Per Share
|
Record Date
|
Total Amount (in thousands)
|
Payment Date
| ||||
| June 15, 2016 |
$0.10 | June 27, 2016 | $5,909 | July 15, 2016 | ||||
| September 7, 2016 |
$0.10 | September 26, 2016 | $5,841 | October 14, 2016 | ||||
| December 6, 2016 |
$0.10 | December 20, 2016 | $5,796 | January 17, 2017 | ||||
| March 6, 2017 |
$0.10 | March 23, 2017 | $5,772 | April 14, 2017 | ||||
29
Table of Contents

In fiscal 2018, the Board of Directors declared the following dividends:
| Declaration Date
|
Dividend Per Share
|
Record Date
|
Total Amount (in thousands)
|
Payment Date
| ||||
| June 20, 2017 |
$0.10 | June 30, 2017 | $5,823 | July 14, 2017 | ||||
| September 5, 2017 |
$0.10 | September 27, 2017 | $5,714 | October 13, 2017 | ||||
| December 6, 2017 |
$0.10 | December 20, 2017 | $5,705 | January 12, 2018 | ||||
| March 5, 2018 |
$0.10 | March 26, 2018 | $5,713 | April 13, 2018 | ||||
The declaration and payment of future dividends under the quarterly dividend policy will be at the discretion of the Board of Directors and will depend upon many factors, including the Company’s earnings, capital requirements, financial conditions, the terms of the Company’s indebtedness and other factors that the Board of Directors may deem to be relevant. The Board of Directors may amend, revoke or suspend the dividend policy at any time and for any reason.
Our senior secured revolving credit agreement, dated June 15, 2016, permits us to pay dividends to our stockholders and make share repurchases so long as our pro forma leverage ratio, defined as, the ratio of consolidated funded indebtedness to consolidated Adjusted EBITDA, is no greater than 2.50 to 1.00, and our pro forma domestic liquidity is at least $50.0 million.
Stock Repurchase Program
On December 8, 2014, the Board of Directors approved an increase in the Company’s stock repurchase program to an aggregate of $150.0 million. Common stock may be repurchased from time to time in open market or privately negotiated transactions at the Company’s discretion subject to market conditions and other factors. During the second quarter of fiscal 2017, the Company began to repurchase shares through this program. The Company repurchased approximately $33.1 million and $28.8 million of the Company’s common stock during fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively. Any decision to execute on our stock repurchase program will depend on our earnings, capital requirements, financial condition and other factors considered relevant by our Board of Directors. Our credit agreement permits us to pay dividends to our stockholders and make share repurchases so long as our pro forma leverage ratio is no greater than 2.50 to 1.00, and our pro forma domestic liquidity is at least $50.0 million, including undrawn amounts on our revolving credit facility.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table summarizes common stock repurchased by us during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2018:
| Shares Purchased (1) |
Average Price Paid Per Share |
Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly- Announced Programs (2) |
Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet be Purchased under the Programs (2) |
|||||||||||||
| February 1, 2018 — February 28, 2018 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | 88.6 million | ||||||||||
| March 1, 2018 — March 31, 2018 |
2,168 | $ | 41.85 | — | $ | 88.6 million | ||||||||||
| April 1, 2018 — April 30, 2018 |
10,897 | $ | 50.46 | 10,000 | $ | 88.1 million | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total |
13,065 | $ | 49.04 | 10,000 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (1) | Represents withholding of a portion of restricted shares to cover taxes on vested restricted shares and shares purchased as part of our publicly announced programs. |
| (2) | On December 8, 2014, the Board of Directors approved an increase in the Company’s stock repurchase program to an aggregate of $150.0 million. The shares can be repurchased in open market transactions or privately negotiated transactions at the Company’s discretion. We repurchased approximately $0.5 million of the Company’s common stock under the program during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2018. |
30
Table of Contents

Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The following selected financial data are qualified by reference to, and should be read together with, our “Audited Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected statements of income data set forth below for the fiscal years ended April 30, 2018, 2017 and 2016 and the selected balance sheets data as of April 30, 2018 and 2017 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements, appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected balance sheets data as of April 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014 and the selected statements of income data set forth below for the fiscal years ended April 30, 2015 and 2014 are derived from audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto which are not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 (1) | 2015 (2) | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data and other operating data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Selected Consolidated Statements of Income Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 1,767,217 | $ | 1,565,521 | $ | 1,292,112 | $ | 1,028,152 | $ | 960,301 | ||||||||||
| Reimbursed out-of-pocket engagement expenses |
52,302 | 56,148 | 54,602 | 37,914 | 35,258 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total revenue |
1,819,519 | 1,621,669 | 1,346,714 | 1,066,066 | 995,559 | |||||||||||||||
| Compensation and benefits |
1,203,619 | 1,071,507 | 897,345 | 691,450 | 646,889 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses |
237,390 | 226,232 | 213,018 | 145,917 | 152,040 | |||||||||||||||
| Reimbursed expenses |
52,302 | 56,148 | 54,602 | 37,914 | 35,258 | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of services |
73,658 | 71,482 | 59,824 | 39,692 | 39,910 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
48,588 | 47,260 | 36,220 | 27,597 | 26,172 | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, net (3) |
78 | 34,600 | 33,013 | 9,468 | 3,682 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
1,615,635 | 1,507,229 | 1,294,022 | 952,038 | 903,951 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating income |
203,884 | 114,440 | 52,692 | 114,028 | 91,608 | |||||||||||||||
| Other income (loss), net |
11,525 | 11,820 | (4,167 | ) | 7,458 | 9,769 | ||||||||||||||
| Interest (expense) income, net |
(9,676 | ) | (10,251 | ) | 237 | (1,784 | ) | (2,363 | ) | |||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated subsidiaries, net |
297 | 333 | 1,631 | 2,181 | 2,169 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
70,133 | 29,104 | 18,960 | 33,526 | 28,492 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income |
135,897 | 87,238 | 31,433 | 88,357 | 72,691 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(2,118 | ) | (3,057 | ) | (520 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Korn/Ferry International |
$ | 133,779 | $ | 84,181 | $ | 30,913 | $ | 88,357 | $ | 72,691 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Basic earnings per share |
$ | 2.39 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 0.58 | $ | 1.78 | $ | 1.51 | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share |
$ | 2.35 | $ | 1.47 | $ | 0.58 | $ | 1.76 | $ | 1.48 | ||||||||||
| Basic weighted average common shares outstanding |
55,426 | 56,205 | 52,372 | 49,052 | 48,162 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding |
56,254 | 56,900 | 52,929 | 49,766 | 49,145 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared per common share |
$ | 0.40 | $ | 0.40 | $ | 0.40 | $ | 0.10 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Other Operating Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue by business segment: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive search: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
$ | 408,098 | $ | 356,625 | $ | 371,345 | $ | 330,634 | $ | 306,768 | ||||||||||
| EMEA |
173,725 | 146,506 | 144,319 | 153,465 | 147,917 | |||||||||||||||
| Asia Pacific |
96,595 | 80,169 | 80,506 | 84,148 | 84,816 | |||||||||||||||
| Latin America |
30,624 | 34,376 | 26,744 | 29,160 | 29,374 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total executive search |
709,042 | 617,676 | 622,914 | 597,407 | 568,875 | |||||||||||||||
| Hay Group |
785,013 | 724,186 | 471,145 | 267,018 | 254,636 | |||||||||||||||
| Futurestep |
273,162 | 223,659 | 198,053 | 163,727 | 136,790 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total fee revenue |
$ | 1,767,217 | $ | 1,565,521 | $ | 1,292,112 | $ | 1,028,152 | $ | 960,301 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
31
Table of Contents

| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 (1) | 2015 (2) | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data and other operating data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of offices (at period end) (4) |
106 | 114 | 150 | 78 | 84 | |||||||||||||||
| Number of consultants (at period end) |
1,392 | 1,330 | 1,164 | 694 | 646 | |||||||||||||||
| Number of new engagements opened |
9,307 | 8,126 | 7,430 | 6,755 | 6,483 | |||||||||||||||
| Number of full-time employees: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive search |
1,865 | 1,791 | 1,682 | 1,562 | 1,566 | |||||||||||||||
| Hay Group |
3,454 | 3,598 | 3,626 | 894 | 794 | |||||||||||||||
| Futurestep |
2,188 | 1,710 | 1,530 | 1,147 | 958 | |||||||||||||||
| Corporate |
136 | 133 | 109 | 84 | 78 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total full-time employees |
7,643 | 7,232 | 6,947 | 3,687 | 3,396 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Selected Consolidated Balance Sheets Data as of April 30: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 520,848 | $ | 410,882 | $ | 273,252 | $ | 380,838 | $ | 333,717 | ||||||||||
| Marketable securities (5) |
137,085 | 119,937 | 141,430 | 144,576 | 134,559 | |||||||||||||||
| Working capital |
455,799 | 385,095 | 188,010 | 331,148 | 270,535 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
2,287,914 | 2,062,898 | 1,898,600 | 1,317,801 | 1,233,666 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term obligations |
509,839 | 517,271 | 375,035 | 196,542 | 191,197 | |||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
1,219,615 | 1,087,048 | 1,047,301 | 815,249 | 755,536 | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | Due to the acquisition of Legacy Hay on December 1, 2015, which accounted for $186.8 million and $740.2 million of fee revenue and total assets, respectively, during fiscal 2016, financial data trends for fiscal 2016 are not comparable to prior periods. See Note 12—Acquisitions, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for discussion of fiscal 2016 acquisitions. |
| (2) | Due to the acquisition of Pivot Leadership on March 1, 2015, which accounted for $3.7 million and $20.0 million of fee revenue and total assets, respectively, during fiscal 2015, financial data trends for fiscal 2015 are not comparable to the prior period. |
| (3) | During fiscal 2018 and 2017, the Company continued to implement the fiscal 2016 restructuring plan in order to integrate the Hay Group entities that were acquired in fiscal 2016 by eliminating redundant positions and operational, general and administrative expenses and consolidating office space. This resulted in restructuring charges of $0.1 million and $34.6 million in fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively. Of the amount recorded in restructuring charges in fiscal 2017, $16.0 million related to severance and $18.6 million related to consolidation of office spaces. In fiscal 2016, the Company implemented a restructuring plan in order to rationalize its cost structure by eliminating redundant positions and consolidating office space due to the acquisition of Legacy Hay on December 1, 2015. As a result, we recorded $33.0 million in restructuring charges, of which $32.1 million related to severance and $0.9 million related to consolidation and abandonment of premises. In fiscal 2015, the Company took actions to rationalize its cost structure as a result of efficiencies obtained from prior year technology investments that enabled further integration of the legacy business and the acquisitions (PDI and Global Novations), as well as other cost saving initiatives. As a result, we recorded $9.2 million of severance and $0.3 million relating to the consolidation/abandonment of premises. In fiscal 2014, the Company continued the implementation of the fiscal 2013 restructuring plan in order to integrate the prior year acquisitions by consolidating and eliminating certain redundant office space around the world and by continuing to consolidate certain overhead functions. As a result, we recorded $0.8 million of severance and $2.9 million related to the consolidation of premises. |
| (4) | The number of offices decreased by eight as of April 30, 2018 compared to April 30, 2017 and 36 as of April 30, 2017 compared to April 30, 2016, due to the continued implementation of the 2016 restructuring plan. |
| (5) | As of April 30, 2018, 2017, 2016, 2015, and 2014, the Company’s marketable securities included $137.1 million, $119.9 million, $141.4 million, $131.4 million, and $116.2 million, respectively, held in trust for settlement of the Company’s obligations under certain of its deferred compensation plans. See Note 5—Financial Instruments in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Forward-looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K may contain certain statements that we believe are, or may be considered to be, “forward-looking” statements, within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). These forward-looking
32
Table of Contents

statements generally can be identified by use of statements that include phrases such as “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “plan,” “foresee,” “may,” “will,” “likely,” “estimates,” “potential,” “continue” or other similar words or phrases. Similarly, statements that describe our objectives, plans or goals also are forward-looking statements. All of these forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those contemplated by the relevant forward-looking statement. The principal risk factors that could cause actual performance and future actions to differ materially from the forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, changes in demand for our services as a result of automation, dependence on attracting and retaining qualified and experienced consultants, maintaining our relationships with customers and suppliers and retaining key employees, maintaining our brand name and professional reputation, the expected timing of the consummation of the Plan and the KF Merger, the impact of the rebranding on the Company’s products and services, the costs of the Plan and the KF Merger, potential legal liability and regulatory developments, portability of client relationships, global and local political or economic developments in or affecting countries where we have operations, currency fluctuations in our international operations, risks related to growth, restrictions imposed by off-limits agreements, competition, consolidation in industries, reliance on information processing systems, cyber security vulnerabilities, changes to data security, data privacy, and data protection laws, limited protection of our IP, our ability to enhance and develop new technology, our ability to successfully recover from a disaster or business continuity problems, employment liability risk, an impairment in the carrying value of goodwill and other intangible assets, the effects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Act”) on our business and our company, deferred tax assets that we may not be able to use, our ability to develop new products and services, changes in our accounting estimates and assumptions, alignment of our cost structure, risks related to the integration of recently acquired businesses, the utilization and billing rates of our consultants, seasonality and the matters disclosed under the heading “Risk Factors” in the Company’s Exchange Act reports, including Item 1A included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Readers are urged to consider these factors carefully in evaluating the forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are made only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and we undertake no obligation to publicly update these forward-looking statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances.
The following presentation of management’s discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read together with our consolidated financial statements and related notes included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Executive Summary
Korn/Ferry International (referred to herein as the “Company,” “Korn Ferry,” or in the first person notations “we,” “our,” and “us”) is a global organizational consulting firm. Our services include Executive Search, advisory solutions and products through Hay Group (formerly known as Leadership & Talent Consulting (“Legacy LTC”) which was combined with HG (Luxembourg) S.à.r.l (“Legacy Hay”) in December 2015) and recruitment for non-executive professionals and recruitment process outsourcing (“RPO”) through Futurestep. The Company also operates a Corporate segment to record global expenses of the Company. Approximately 69% of the executive searches we performed in fiscal 2018 were for board level, chief executive and other senior executive and general management positions. Our 3,773 search engagement clients in fiscal 2018 included many of the world’s largest and most prestigious public and private companies. We have built strong client loyalty, with 88% of assignments performed during fiscal 2018 having been on behalf of clients for whom we had conducted assignments in the previous three fiscal years. Approximately 62% of our revenues were generated from clients that utilize multiple lines of business.
33
Table of Contents

Superior performance comes from having the right conditions for success in two key areas—the organization and its people. Organizational conditions encourage people to put forth their best effort and invest their energy towards achieving the organization’s purpose. We can help operationalize a client’s complete strategy or address any combination of five broad categories:
|
Organizational Strategy |
We map talent strategy to business strategy by designing operating models and organizational structures that align to them, helping organizations put their plans into action. We make sure they have the right people, in the right roles, engaged and enabled to do the right things.
| |
|
Assessment and Succession |
We provide actionable, research-backed insights that allow organizations to understand the true capabilities of their people so they can make decisions that ensure the right leaders are ready—when and where they are needed—in the future.
| |
| Talent Acquisition |
From executive search to recruitment process outsourcing, we integrate scientific research with our practical experience and industry-specific expertise to recruit professionals of all levels and functions for client organizations.
| |
| Leadership Development |
We activate purpose, vision and strategy through leaders at all levels and organizations. We combine expertise, science and proven techniques with forward thinking and creativity to build leadership experiences that help entry- to senior-level leaders grow and deliver superior results.
| |
| Rewards and Benefits |
We help organizations align reward with strategy. We help them pay their people fairly for doing the right things—with rewards they value—at a cost the organization can afford.
| |
The Company currently operates through three business segments: Executive Search, Hay Group and Futurestep. See Note 11—Business Segments, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for discussion of the Company’s global business segments. The Company evaluates performance and allocates resources based on the chief operating decision maker’s review of (1) fee revenue and (2) adjusted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (“Adjusted EBITDA”). To the extent that such charges occur, Adjusted EBITDA excludes restructuring charges, integration/acquisition costs, certain separation costs and certain non-cash charges (goodwill, intangible asset and other than temporary impairment). For fiscal 2017 and 2016, Adjusted EBITDA includes a deferred revenue adjustment related to the Legacy Hay acquisition, reflecting revenue that Hay Group would have realized if not for business combination accounting that requires a company to record the acquisition balance sheet at fair value and write-off deferred revenue where no future services are required to be performed to earn that revenue. For fiscal 2018, management no longer has adjusted fee revenue.
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA are non-GAAP financial measures. They have limitations as analytical tools, should not be viewed as a substitute for financial information determined in accordance with United States (“U.S.”) generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and should not be considered in isolation or as a substitute for analysis of the Company’s results as reported under GAAP. In addition, they may not necessarily be comparable to non-GAAP performance measures that may be presented by other companies.
Management believes the presentation of these non-GAAP financial measures provides meaningful supplemental information regarding Korn Ferry’s performance by excluding certain charges, items of income and other items that may not be indicative of Korn Ferry’s ongoing operating results. The use of these non-GAAP financial measures facilitates comparisons to Korn Ferry’s historical performance and identification of operating trends that may otherwise be distorted by certain charges and other items that may not be indicative of Korn Ferry’s ongoing operating results. Korn Ferry includes these non-GAAP financial measures because management believes it is useful to investors in allowing for greater transparency with respect to supplemental information used by management in its evaluation of Korn Ferry’s ongoing operations and financial and operational decision-making. The accounting policies for the reportable segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies in the accompanying consolidated financial statements, except that the above noted items are excluded from EBITDA to arrive at Adjusted EBITDA. Management further believes that EBITDA is useful to investors because it is frequently used by investors and other interested parties to measure operating performance among companies with different capital structures, effective tax rates and tax attributes and capitalized asset values, all of which can vary substantially from company to company.
34
Table of Contents

Similarly, adjusted fee revenue, which includes revenue that Hay Group would have realized over the ensuing year after the acquisition if not for business combination accounting that requires a company to record the acquisition balance sheet at fair value and write-off deferred revenue where no future services are required to be performed to earn that revenue, is a non-GAAP financial measure. Adjusted fee revenue is not a measure that substitutes an individually tailored revenue recognition or measurement method for those of GAAP; rather, it is an adjustment for a short period of time that will provide better comparability in the current and future periods. Management believes the presentation of adjusted fee revenue assists management in its evaluation of ongoing operations and provides useful information to investors because it allows investors to make more meaningful period-to-period comparisons of the Company’s operating results, to better identify operating trends that may otherwise be distorted by write-offs required under business combination accounting and to perform related trend analysis and provides a higher degree of transparency of information used by management in its evaluation of Korn Ferry’s ongoing operations and financial and operational decision-making.
Fee revenue was $1,767.2 million during fiscal 2018, an increase of $201.7 million, or 13%, compared to $1,565.5 million in fiscal 2017, with increases in fee revenue in all business segments. During fiscal 2018, we recorded operating income of $203.9 million with Executive Search, Hay Group and Futurestep segments contributing $149.3 million, $100.9 million and $39.4 million, respectively, offset by Corporate expenses of $85.7 million. Net income attributable to Korn Ferry increased $49.6 million during fiscal 2018 to $133.8 million from $84.2 million in fiscal 2017. Adjusted EBITDA was $273.8 million, an increase of $38.8 million during fiscal 2018, from Adjusted EBITDA of $235.0 million in the year-ago period. During fiscal 2018, Executive Search, Hay Group and Futurestep segments contributed $158.9 million, $142.0 million and $42.6 million, respectively, offset by Corporate expenses net of other income of $69.7 million.
Our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities increased $127.1 million to $657.9 million at April 30, 2018, compared to $530.8 million at April 30, 2017. This increase was mainly due to cash provided by operating activities, offset by bonuses earned in fiscal 2017 and paid during fiscal 2018, sign-on and retention payments, stock repurchases in the open market, payments for the purchase of property and equipment, dividends paid during fiscal 2018 and principal payments on our term loan. As of April 30, 2018, we held marketable securities to settle obligations under our Executive Capital Accumulation Plan (“ECAP”) with a cost value of $127.1 million and a fair value of $137.1 million. Our vested obligations for which these assets were held in trust totaled $118.2 million as of April 30, 2018 and our unvested obligations totaled $29.5 million.
Our working capital increased by $70.7 million to $455.8 million in fiscal 2018. We believe that cash on hand and funds from operations and other forms of liquidity will be sufficient to meet our anticipated working capital, capital expenditures, general corporate requirements, repayment of the debt obligations incurred in connection with the Legacy Hay acquisition, the retention pool obligations pursuant to the Legacy Hay acquisition and dividend payments under our dividend policy in the next twelve months. We had no outstanding borrowings under our revolving credit facility at April 30, 2018 and 2017. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, there was $2.9 million and $3.0 million, respectively, of standby letters of credit issued under our long-term debt arrangements. We had a total of $7.4 million and $8.1 million of standby letters of credits with other financial institutions as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
On June 12, 2018, the Company’s Board of Directors approved a plan (the “Plan”) to go to market under a single, master brand architecture and to simplify the Company’s organizational structure by eliminating and/or consolidating certain of the Company’s legal entities and implementing a rebranding of the Company to offer the Company’s current products and services using the “Korn Ferry” name, branding and trademarks. In connection with the Plan, the Company intends to sunset all sub-brands, including Futurestep, Hay Group and Lominger, among others. The Company is harmonizing under one brand to help accelerate the firm’s positioning as the preeminent organizational consultancy and bring more client awareness to its broad range of talent management solutions. The Hay Group back office was fully integrated as of the beginning of fiscal 2018 and the Company then focused on its integrated go-to-market activities. This integrated go-to-market approach was a key driver in the 13% fee revenue growth in fiscal 2018, which led to the decision to further integrate our go-to-market activities under one master brand – Korn Ferry. In the near term the Company will discontinue the use of all sub-brands. While the rebranding will not impact the Company’s segment financial reporting, starting in the first quarter of fiscal
35
Table of Contents

2019, the Company will rename its Hay Group segment as “Korn Ferry Advisory“ and its Futurestep segment as “Korn Ferry RPO and Professional Search.” The Company’s Executive Search segment will remain unchanged. In connection with the Plan, the Company also intends to pursue a holding company reorganization which is discussed in further detail in Item 1. Business in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Critical Accounting Policies
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based on our consolidated financial statements. Preparation of our periodic filings requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amount of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of our financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions and changes in the estimates are reported in current operations as new information is learned or upon the amounts becoming fixed and determinable. In preparing our consolidated financial statements and accounting for the underlying transactions and balances, we apply our accounting policies as disclosed in the notes to our consolidated financial statements. We consider the policies discussed below as critical to an understanding of our consolidated financial statements because their application places the most significant demands on management’s judgment and estimates. Specific risks for these critical accounting policies are described in the following paragraphs. Senior management has discussed the development, selection and key assumptions of the critical accounting estimates with the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
Revenue Recognition. Substantially all fee revenue is derived from fees for professional services related to executive search performed on a retained basis, recruitment for non-executive professionals, recruitment process outsourcing, people and organizational advisory services and the sale of product services. Fee revenue from executive search activities and recruitment for non-executive professionals is generally one-third of the estimated first year compensation of the placed executive or non-executive professional, as applicable, plus a percentage of the fee to cover indirect engagement related expenses. We generally recognize such revenue on a straight-line basis over a three-month period, commencing upon client acceptance, as this is the period over which the recruitment services are performed. Fees earned in excess of the initial contract amount are recognized upon completion of the engagement, which reflect the difference between the final actual compensation of the placed executive and the estimate used for purposes of the previous billings. Since the initial contract fees are typically not contingent upon placement of a candidate, our assumptions primarily relate to establishing the period over which such service is performed. These assumptions determine the timing of revenue recognition and profitability for the reported period. Any revenues associated with services that are provided on a contingent basis are recognized once the contingency is resolved. In addition to recruitment for non-executive professionals, Futurestep provides recruitment process outsourcing services and fee revenue is recognized as services are rendered and/or as milestones are achieved. Fee revenue from Hay Group is recognized as services are rendered for consulting engagements and other time-based services, measured by total hours incurred to the total estimated hours at completion. It is possible that updated estimates for the consulting engagement may vary from initial estimates with such updates being recognized in the period of determination. Depending on the timing of billings and services rendered, we accrue or defer revenue as appropriate. Hay Group revenue is also derived from the sale of product services, which includes revenue from licenses and from the sale of products. Revenue from licenses is recognized using a straight-line method over the term of the contract (generally 12 months). Under the fixed term licenses, we are obligated to provide the licensee with access to any updates to the underlying intellectual property (“IP”) that are made by us during the term of the license. Once the term of the agreement expires, the client’s right to access or use the IP expires and we have no further obligations to the client under the license agreement. Revenue from perpetual licenses is recognized when the license is sold since our only obligation is to provide the client access to the IP but is not obligated to provide maintenance, support, updates or upgrades. Products sold by us mainly consist of books and automated services covering a variety of topics including performance management, team effectiveness, and coaching and development. We recognize revenue for products when the product has been sold or shipped in the case of books. Furthermore, a provision for doubtful accounts on recognized revenue is established with a charge to general and administrative expenses based on historical loss experience, assessment of the collectability of specific accounts, as well as expectations of future collections based upon trends and the type of work for which services are rendered.
36
Table of Contents

Annual Performance Related Bonuses. Each quarter, management makes its best estimate of its annual performance related bonuses, which requires management to, among other things, project annual consultant productivity (as measured by engagement fees billed and collected by executive search consultants and revenue and other performance/profitability metrics for Hay Group and Futurestep consultants), the level of engagements referred by a consultant in one line of business to a different line of business, our performance including profitability, competitive forces and future economic conditions and their impact on our results. At the end of each fiscal year, annual performance related bonuses take into account final individual consultant productivity (including referred work), Company/line of business results including profitability, the achievement of strategic objectives and the results of individual performance appraisals, and the current economic landscape. Accordingly, each quarter we reevaluate the assumptions used to estimate annual performance related bonus liability and adjust the carrying amount of the liability recorded on the consolidated balance sheets and report any changes in the estimate in current operations. Because annual performance-based bonuses are communicated and paid only after we report our full fiscal year results, actual performance-based bonus payments may differ from the prior year’s estimate. Such changes in the bonus estimate historically have been immaterial and are recorded in current operations in the period in which they are determined.
Deferred Compensation. Estimating deferred compensation requires assumptions regarding the timing and probability of payments of benefits to participants and the discount rate. Changes in these assumptions could significantly impact the liability and related cost on our consolidated balance sheets and statements of income, respectively. For certain deferred compensation plans, management engages an independent actuary to periodically review these assumptions in order to confirm that they reflect the population and economics of our deferred compensation plans in all material respects and to assist us in estimating our deferred compensation liability and the related cost. The actuarial assumptions we use may differ from actual results due to changing market conditions or changes in the participant population. These differences could have a significant impact on our deferred compensation liability and the related cost.
Carrying Values. Valuations are required under GAAP to determine the carrying value of various assets. Our most significant assets for which management is required to prepare valuations are carrying value of receivables, goodwill, intangible assets, fair value of contingent consideration and recoverability of deferred income taxes. Management must identify whether events have occurred that may impact the carrying value of these assets and make assumptions regarding future events, such as cash flows and profitability. Differences between the assumptions used to prepare these valuations and actual results could materially impact the carrying amount of these assets and our operating results.
Of the assets mentioned above, goodwill is the largest asset requiring a valuation. Fair value of goodwill for purposes of the goodwill impairment test is determined utilizing (1) a discounted cash flow analysis based on forecasted cash flows (including estimated underlying revenue and operating income growth rates) discounted using an estimated weighted-average cost of capital for market participants and (2) a market approach, utilizing observable market data such as comparable companies in similar lines of business that are publicly traded or which are part of a public or private transaction (to the extent available). We also reconcile the results of these analyses to its market capitalization. If the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its estimated fair value, goodwill is considered potentially impaired and further tests are performed to measure the amount of impairment loss, if any. We recorded no goodwill impairment in conjunction with our annual goodwill impairment assessment performed as of January 31, 2018. While historical performance and current expectations have resulted in fair values of goodwill in excess of carrying values, if our assumptions are not realized, it is possible that in the future an impairment charge may need to be recorded. However, it is not possible at this time to determine if an impairment charge would result or if such a charge would be material. Fair value determinations require considerable judgment and are sensitive to changes in underlying assumptions and factors. As a result, there can be no assurance that the estimates and assumptions made for purposes of the annual goodwill impairment test will prove to be accurate predictions of the future. As of our testing date, the fair value of each reporting unit exceeded its carrying amount and no reporting units were at risk of failing the impairment test. As a result, no impairment charge was recognized. There was also no indication of potential impairment during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2018 that would have required further testing.
37
Table of Contents

Examples of events or circumstances that could reasonably be expected to negatively affect the underlying key assumptions and ultimately impact the estimated fair value of the reporting units may include such items as follows:
| ◾ | A prolonged downturn in the business environment in which the reporting units operate; |
| ◾ | An economic climate that significantly differs from our future profitability assumptions in timing or degree; |
| ◾ | The deterioration of the labor markets; and |
| ◾ | Volatility in equity and debt markets. |
Results of Operations
The following table summarizes the results of our operations as a percentage of fee revenue:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Reimbursed out-of-pocket engagement expenses |
3.0 | 3.6 | 4.2 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total revenue |
103.0 | 103.6 | 104.2 | |||||||||||||
| Compensation and benefits |
68.1 | 68.4 | 69.4 | |||||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses |
13.4 | 14.5 | 16.5 | |||||||||||||
| Reimbursed expenses |
3.0 | 3.6 | 4.2 | |||||||||||||
| Cost of services |
4.2 | 4.6 | 4.6 | |||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
2.8 | 3.0 | 2.8 | |||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, net |
— | 2.2 | 2.6 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating income |
11.5 | 7.3 | 4.1 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income |
7.7 | % | 5.6 | % | 2.4 | % | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Korn/Ferry International |
7.6 | % | 5.4 | % | 2.4 | % | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
The following tables summarize the results of our operations by business segment:
(Numbers may not total exactly due to rounding)
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dollars | % | Dollars | % | Dollars | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Search: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
$ | 408,098 | 23.1 | % | $ | 356,625 | 22.8 | % | $ | 371,345 | 28.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| EMEA |
173,725 | 9.8 | 146,506 | 9.4 | 144,319 | 11.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Asia Pacific |
96,595 | 5.5 | 80,169 | 5.1 | 80,506 | 6.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Latin America |
30,624 | 1.7 | 34,376 | 2.2 | 26,744 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Total Executive Search |
709,042 | 40.1 | 617,676 | 39.5 | 622,914 | 48.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hay Group |
785,013 | 44.4 | 724,186 | 46.3 | 471,145 | 36.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Futurestep |
273,162 | 15.5 | 223,659 | 14.3 | 198,053 | 15.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Total fee revenue |
1,767,217 | 100.0 | % | 1,565,521 | 100.0 | % | 1,292,112 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reimbursed out-of-pocket engagement expense |
52,302 | 56,148 | 54,602 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 1,819,519 | $ | 1,621,669 | $ | 1,346,714 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
38
Table of Contents

| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dollars | Margin(1) | Dollars | Margin(1) | Dollars | Margin(1) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Search: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
$ | 100,037 | 24.5 | % | $ | 81,550 | 22.9 | % | $ | 100,381 | 27.0 | % | ||||||||||||||
| EMEA |
26,768 | 15.4 | 27,854 | 19.0 | 20,607 | 14.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Asia Pacific |
18,425 | 19.1 | 8,580 | 10.7 | 12,572 | 15.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Latin America |
4,022 | 13.1 | 6,268 | 18.2 | (1,854 | ) | (6.9 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Executive Search |
149,252 | 21.0 | 124,252 | 20.1 | 131,706 | 21.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hay Group |
100,939 | 12.9 | 47,302 | 6.5 | (3,415 | ) | (0.7 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Futurestep |
39,363 | 14.4 | 29,986 | 13.4 | 26,702 | 13.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate |
(85,670 | ) | (87,100 | ) | (102,301 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating income |
$ | 203,884 | 11.5 | % | $ | 114,440 | 7.3 | % | $ | 52,692 | 4.1 | % | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Margin calculated as a percentage of fee revenue by business segment. |
| Year Ended April 30, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
EMEA | Asia Pacific |
Latin America |
Subtotal | Hay Group | Futurestep | Corporate | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 408,098 | $ | 173,725 | $ | 96,595 | $ | 30,624 | $ | 709,042 | $ | 785,013 | $ | 273,162 | $ | — | $ | 1,767,217 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 421,260 | $ | 177,234 | $ | 98,062 | $ | 30,717 | $ | 727,273 | $ | 801,005 | $ | 291,241 | $ | — | $ | 1,819,519 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Korn/Ferry International |
$ | 133,779 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
2,118 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income, net |
(11,525 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense, net |
9,676 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated subsidiaries, net |
(297 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
70,133 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
$ | 100,037 | $ | 26,768 | $ | 18,425 | $ | 4,022 | $ | 149,252 | $ | 100,939 | $ | 39,363 | $ | (85,670 | ) | $ | 203,884 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
3,930 | 1,689 | 1,408 | 455 | 7,482 | 31,527 | 3,054 | 6,525 | 48,588 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income, net |
845 | 168 | 373 | 181 | 1,567 | 599 | 152 | 9,207 | 11,525 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated subsidiaries, net |
297 | — | — | — | 297 | — | — | — | 297 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA |
105,109 | 28,625 | 20,206 | 4,658 | 158,598 | 133,065 | 42,569 | (69,938 | ) | 264,294 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, net |
— | — | 313 | — | 313 | (241 | ) | 6 | — | 78 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Integration/acquisition costs |
— | — | — | — | — | 9,151 | — | 279 | 9,430 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 105,109 | $ | 28,625 | $ | 20,519 | $ | 4,658 | $ | 158,911 | $ | 141,975 | $ | 42,575 | $ | (69,659) | $ | 273,802 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating margin |
24.5 | % | 15.4 | % | 19.1 | % | 13.1 | % | 21.0 | % | 12.9 | % | 14.4 | % | 11.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA margin |
25.8 | % | 16.5 | % | 21.2 | % | 15.2 | % | 22.4 | % | 18.1 | % | 15.6 | % | 15.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
39
Table of Contents

| Year Ended April 30, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
EMEA | Asia Pacific |
Latin America |
Subtotal | Hay Group | Futurestep | Corporate | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 356,625 | $ | 146,506 | $ | 80,169 | $ | 34,376 | $ | 617,676 | $ | 724,186 | $ | 223,659 | $ | — | $ | 1,565,521 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | — | — | — | — | 3,535 | — | — | 3,535 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted fee revenue |
$ | 356,625 | $ | 146,506 | $ | 80,169 | $ | 34,376 | $ | 617,676 | $ | 727,721 | $ | 223,659 | $ | — | $ | 1,569,056 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 369,803 | $ | 150,113 | $ | 81,744 | $ | 34,533 | $ | 636,193 | $ | 741,533 | $ | 243,943 | $ | — | $ | 1,621,669 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable |
$ | 84,181 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable |
3,057 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income, net |
(11,820 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense, net |
10,251 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
(333 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
29,104 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
$ | 81,550 | $ | 27,854 | $ | 8,580 | $ | 6,268 | $ | 124,252 | $ | 47,302 | $ | 29,986 | $ | (87,100 | ) | $ | 114,440 | |||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and |
3,812 | 1,030 | 1,060 | 483 | 6,385 | 32,262 | 2,818 | 5,795 | 47,260 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (loss), net |
844 | (15 | ) | 300 | 684 | 1,813 | 341 | (91 | ) | 9,757 | 11,820 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
333 | — | — | — | 333 | — | — | — | 333 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA |
86,539 | 28,869 | 9,940 | 7,435 | 132,783 | 79,905 | 32,713 | (71,548 | ) | 173,853 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, |
1,719 | 629 | 1,495 | 773 | 4,616 | 29,663 | 101 | 220 | 34,600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Integration/acquisition |
— | — | — | — | — | 14,440 | — | 7,939 | 22,379 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | — | — | — | — | 3,535 | — | — | 3,535 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Separation costs |
— | — | — | — | — | 609 | — | — | 609 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 88,258 | $ | 29,498 | $ | 11,435 | $ | 8,208 | $ | 137,399 | $ | 128,152 | $ | 32,814 | $ | (63,389 | ) | $ | 234,976 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating margin |
22.9 | % | 19.0 | % | 10.7 | % | 18.2 | % | 20.1 | % | 6.5 | % | 13.4 | % | 7.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
24.7 | % | 20.1 | % | 14.3 | % | 23.9 | % | 22.2 | % | 17.6 | % | 14.7 | % | 15.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
40
Table of Contents

| Year Ended April 30, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
EMEA | Asia Pacific |
Latin America |
Subtotal | Hay Group | Futurestep | Corporate | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 371,345 | $ | 144,319 | $ | 80,506 | $ | 26,744 | $ | 622,914 | $ | 471,145 | $ | 198,053 | $ | — | $ | 1,292,112 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | — | — | — | — | 10,967 | — | — | 10,967 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted fee revenue |
$ | 371,345 | $ | 144,319 | $ | 80,506 | $ | 26,744 | $ | 622,914 | $ | 482,112 | $ | 198,053 | $ | — | $ | 1,303,079 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 386,256 | $ | 148,285 | $ | 83,206 | $ | 26,781 | $ | 644,528 | $ | 488,217 | $ | 213,969 | $ | — | $ | 1,346,714 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable |
$ | 30,913 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable |
520 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other loss, net |
4,167 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest income, net |
(237 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
(1,631 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
18,960 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
$ | 100,381 | $ | 20,607 | $ | 12,572 | $ | (1,854 | ) | $ | 131,706 | $ | (3,415 | ) | $ | 26,702 | $ | (102,301 | ) | $ | 52,692 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and |
3,267 | 1,029 | 941 | 312 | 5,549 | 21,854 | 2,386 | 6,431 | 36,220 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other (loss) income, net |
(147 | ) | 433 | 21 | 312 | 619 | (868 | ) | 364 | (4,282 | ) | (4,167 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
437 | — | — | — | 437 | — | — | 1,194 | 1,631 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA |
103,938 | 22,069 | 13,534 | (1,230 | ) | 138,311 | 17,571 | 29,452 | (98,958 | ) | 86,376 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, |
499 | 5,807 | 577 | 322 | 7,205 | 25,682 | 49 | 77 | 33,013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Integration/acquisition |
— | — | — | — | — | 17,607 | — | 27,802 | 45,409 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Venezuelan foreign |
— | — | — | 6,635 | 6,635 | 7,085 | — | — | 13,720 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | — | — | — | — | 10,967 | — | — | 10,967 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Separation costs |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 744 | 744 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 104,437 | $ | 27,876 | $ | 14,111 | $ | 5,727 | $ | 152,151 | $ | 78,912 | $ | 29,501 | $ | (70,335 | ) | $ | 190,229 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating margin |
27.0 | % | 14.3 | % | 15.6 | % | (6.9 | )% | 21.1 | % | (0.7 | )% | 13.5 | % | 4.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
28.1 | % | 19.3 | % | 17.5 | % | 21.4 | % | 24.4 | % | 16.4 | % | 14.9 | % | 14.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Fiscal 2018 Compared to Fiscal 2017
Fee Revenue
Fee Revenue. Fee revenue went up by $201.7 million, or 13%, to $1,767.2 million in fiscal 2018 compared to $1,565.5 million in fiscal 2017. Exchange rates favorably impacted fee revenue by $35.3 million, or 2%, in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. The higher fee revenue was attributable to organic growth in all lines of business.
Executive Search. Executive Search reported fee revenue of $709.0 million, an increase of $91.3 million, or 15%, in fiscal 2018 compared to $617.7 million in the year-ago period. As detailed below, Executive Search fee revenue was
41
Table of Contents

higher in North America, EMEA and Asia Pacific, partially offset by lower fee revenue in the Latin America region in fiscal 2018 as compared to fiscal 2017. The higher fee revenue in Executive Search was mainly due to a 9% increase in the number of engagements billed and a 3% increase in the weighted-average fees billed per engagement (calculated using local currency) during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. Exchange rates favorably impacted fee revenue by $12.3 million, or 2%, in fiscal 2018, compared to the year-ago period.
North America reported fee revenue of $408.1 million, an increase of $51.5 million, or 14%, in fiscal 2018 compared to $356.6 million in the year-ago period. North America’s fee revenue was higher due to an 11% increase in the number of engagements billed and a 3% increase in the weighted-average fees billed per engagement (calculated using local currency) during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. All business sectors contributed to the growth in fee revenue in fiscal 2018 as compared to fiscal 2017, with industrial, technology and financial services contributing the most. The effect of exchange rates on fee revenue was minimal in fiscal 2018, compared to the year-ago period.
EMEA reported fee revenue of $173.7 million, an increase of $27.2 million, or 19%, in fiscal 2018 compared to $146.5 million in fiscal 2017. The favorable effect of exchange rates on fee revenue was $8.8 million, or 6%, in fiscal 2018, compared to the year-ago period. The increase in fee revenue was due to a 10% increase in the number of engagements billed, partially offset by a 2% decrease in the weighted-average fees billed per engagement (calculated using local currency) during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. The performance in the United Kingdom, Germany, and France were the primary contributors to the increase in fee revenue in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. All business sectors contributed to the growth in fee revenue in fiscal 2018 as compared to the year-ago period, with industrial, financial services and consumer goods contributing the most.
Asia Pacific reported fee revenue of $96.6 million, an increase of $16.4 million, or 20%, in fiscal 2018 compared to $80.2 million in fiscal 2017. The increase in fee revenue was due to an 8% increase in the number of engagements billed and an 8% increase in the weighted-average fees billed per engagement (calculated using local currency) in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. The performance in China, Australia, Singapore, and Japan were the primary contributors to the increase in fee revenue in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period, partially offset by a decrease in fee revenue in New Zealand. All business sectors contributed to the growth in fee revenue in fiscal 2018 as compared to the year-ago period, with financial services, life sciences/healthcare, and technology contributing the most. The favorable effect of exchange rates on fee revenue was $2.3 million, or 3%, compared to the year-ago period.
Latin America reported fee revenue of $30.6 million, a decrease of $3.8 million, or 11%, in fiscal 2018 compared to $34.4 million in fiscal 2017. The decrease in fee revenue was due to lower fee revenue in Mexico in fiscal 2018, compared to the year-ago period, partially offset by higher fee revenue in Argentina. Financial services and consumer goods were the main sectors contributing to the decline in fee revenue in fiscal 2018, compared to the year-ago period. The effect of exchange rates on fee revenue was minimal.
Hay Group. Hay Group reported fee revenue of $785.0 million, an increase of $60.8 million, or 8%, in fiscal 2018 compared to $724.2 million in fiscal 2017. Exchange rates favorably impacted fee revenue by $17.4 million, or 2%, compared to the year-ago period. Fee revenue from consulting services was higher by $42.8 million in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period, with the remaining increase of $18.0 million generated by our products business.
Futurestep. Futurestep reported fee revenue of $273.2 million, an increase of $49.5 million, or 22%, in fiscal 2018 compared to $223.7 million in fiscal 2017. Higher fee revenues in RPO and professional search of $33.3 million and $18.1 million, respectively, drove the increase in fee revenue. Exchange rates favorably impacted fee revenue by $5.6 million, or 3%, compared to the year-ago period.
Compensation and Benefits
Compensation and benefits expense increased $132.1 million, or 12%, to $1,203.6 million in fiscal 2018 from $1,071.5 million in fiscal 2017. Exchange rates unfavorably impacted compensation and benefits expenses by $23.0 million, or 2%, in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. The increase in compensation and benefits was primarily due to a 9% increase in the average consultant headcount, which contributed $80.4 million in higher salaries and related payroll taxes, $8.1 million more in expenses associated with our deferred compensation and
42
Table of Contents

retirement plans (includes the increases in the fair value of participants’ accounts) and an increase of $5.8 million in employer insurance costs in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. The rest of the change was due to $40.8 million increase in performance-related bonus expense mainly due to the increase in fee revenue and $11.3 million increase in amortization of long term incentive awards, offset by a $9.8 million decrease in integration costs and $2.9 million from the change in the cash surrender value (“CSV”) of company owned life insurance (“COLI”) in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. The change in the CSV of COLI decreased compensation and benefits expense in fiscal 2018 compared to fiscal 2017 due to larger increases in the market value of the underlying investments due to market changes. COLI is held to fund other deferred compensation retirement plans (See Note 6—Deferred Compensation and Retirement Plans, included in the notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements). Compensation and benefits expense, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 68% in both fiscal 2018 and 2017.
Executive Search compensation and benefits expense increased by $60.0 million, or 15%, to $469.0 million in fiscal 2018 compared to $409.0 million in fiscal 2017. The increase was primarily due to higher salary cost and related payroll taxes of $24.8 million due to a 5% increase in average headcount reflecting our continued growth-related investment back into the business. Also contributing to the increase in compensation and benefits expense was a $17.1 million increase in performance related bonus expense compared to the year-ago period, an $8.4 million increase in amortization of long-term incentive awards, and an increase of $4.9 million in expenses associated with our deferred compensation and retirement plans (includes the increases in the fair value of participants’ accounts). The increase in performance related bonus expense was due to a 15% increase in fee revenue in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. Executive Search compensation and benefits expense, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 66% in both fiscal 2018 and 2017.
Hay Group compensation and benefits expense increased $34.8 million, or 8%, to $496.9 million in fiscal 2018 from $462.1 million in fiscal 2017. The change was primarily due to increases in salaries and related payroll taxes of $25.3 million and $4.1 million increase in expenses associated with our deferred compensation and retirement plans (includes the increases in the fair value of participants’ accounts). Also contributing to the increase in compensation and benefits expense was an increase of $10.5 million in performance related bonus expense and $2.8 million more in employer insurance costs, offset by a decrease in integration costs of $6.3 million compared to year-ago period. Hay Group compensation and benefits expense, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 63% in fiscal 2018 compared to 64% in the year-ago period.
Futurestep compensation and benefits expense increased $38.4 million, or 25%, to $193.2 million in fiscal 2018 from $154.8 million in fiscal 2017. The increase was due to higher salaries and related payroll taxes of $26.8 million due to a 20% increase in the average headcount in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. The higher average headcount was primarily driven by the need to service an increase in fee revenue in both the professional search and RPO businesses. Also contributing to the increase in compensation and benefits expense was an increase of $11.3 million in performance related bonus expense due to a 22% increase in fee revenue in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. Futurestep compensation and benefits expense, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 71% in fiscal 2018 compared to 69% in the year-ago period.
Corporate compensation and benefits expense decreased by $1.0 million, or 2%, to $44.6 million in fiscal 2018 from $45.6 million in fiscal 2017. This change was mainly due to a decrease of $3.5 million in integration costs in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period and $2.9 million from the change in the CSV of COLI that decreased compensation and benefits expense in fiscal 2018 compared to fiscal 2017 due to larger increases in the market value of the underlying investments due to market changes. These decreases in compensation and benefit expense were partially offset by $3.5 million in higher salaries and related taxes in order to support the overall growth in the entire business.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses increased $11.2 million, or 5%, to $237.4 million in fiscal 2018 compared to $226.2 million in fiscal 2017. The increase in general and administrative expenses was due to increases of $6.2 million and $2.2 million in legal and other professional fees and premise and office expenses, respectively, offset by a decline of $3.8 million in integration costs during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. The rest of the change was primarily due to generating foreign exchange loss of $3.3 million during fiscal 2018 compared to
43
Table of Contents

a foreign exchange gain of $0.3 million in fiscal 2017. General and administrative expenses, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 13% in fiscal 2018 compared to 14% in fiscal 2017. Exchange rates unfavorably impacted general and administrative expenses by $3.7 million, or 2%, during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period.
Executive Search general and administrative expenses increased $8.0 million, or 11%, to $77.7 million in fiscal 2018 from $69.7 million in fiscal 2017. General and administrative expenses increased due to generating foreign exchange losses of $1.2 million during fiscal 2018 compared to a foreign exchange gain of $1.3 million during the year-ago period and an increase in legal and other professional fees of $0.9 million. The rest of the change was due to an increase in $0.8 million in marketing and business development expenses to support the higher fee revenues generated in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period, $0.7 million increase in premise and office expenses, and an increase in bad debt expense of $0.6 million. Executive Search general and administrative expenses, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 11% in both fiscal 2018 and 2017.
Hay Group general and administrative expenses increased $1.3 million to $98.4 million in fiscal 2018 compared to $97.1 million in the year-ago period. General and administrative expenses increased due to a foreign exchange loss of $1.1 million during fiscal 2018 compared to a foreign exchange gain of $0.2 million in fiscal 2017. Hay Group general and administrative expenses, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 13% in both fiscal 2018 and 2017.
Futurestep general and administrative expenses increased $2.8 million, or 12%, to $26.7 million in fiscal 2018 from $23.9 million in fiscal 2017. The increase was due primarily to increases in premise and office expenses, bad debt expense and legal and other professional fees of $1.2 million, $1.0 million and $0.4 million, respectively, in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. Futurestep general and administrative expenses, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 10% in fiscal 2018 compared to 11% in fiscal 2017.
Corporate general and administrative expenses decreased $0.9 million, or 3%, to $34.6 million in fiscal 2018 compared to $35.5 million in fiscal 2017. The decrease in general and administrative expenses was due to a decrease of $4.2 million in integration costs associated with the Legacy Hay acquisition and $0.8 million in business development expenses, offset by an increase in legal and other professional fees of $4.3 million during fiscal 2018 compared to fiscal 2017.
Cost of Services Expense
Cost of services expense consists primarily of non-billable contractor and product costs related to the delivery of various services and products, primarily in Futurestep and Hay Group. Cost of services expense was $73.7 million in fiscal 2018 compared to $71.5 million in fiscal 2017. Cost of services expense, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 4% in fiscal 2018 as compared to 5% in the year-ago period.
Depreciation and Amortization Expenses
Depreciation and amortization expenses were $48.6 million, an increase of $1.3 million, in fiscal 2018 compared to $47.3 million in fiscal 2017. The increase relates primarily to technology investments made in the current and prior year in software and computer equipment, in addition to increases in leasehold improvements and furniture and fixtures.
Restructuring Charges, Net
The Company continued the implementation of the fiscal 2016 restructuring plan in fiscal 2017 in order to integrate the Hay Group entities that were acquired in fiscal 2016 by eliminating redundant positions and operational, general and administrative expenses and consolidating premises. This resulted in restructuring charges of $34.6 million in fiscal 2017, of which $16.0 million related to severance and $18.6 million related to consolidation of premises. Fiscal 2018 restructuring charges were minimal.
Operating Income
Operating income was $203.9 million, an increase of $89.5 million, in fiscal 2018 as compared to $114.4 million in fiscal 2017. This increase in operating income resulted from higher fee revenue of $201.7 million and a decrease in restructuring charges, net of $34.5 million, offset by increases of $132.1 million in compensation and benefits
44
Table of Contents

expense, $11.2 million in general and administrative expenses, $2.2 million in cost of services expense, and $1.3 million in depreciation and amortization expenses.
Executive Search operating income increased $25.0 million, or 20%, to $149.3 million in fiscal 2018 as compared to $124.3 million in fiscal 2017. The increase in Executive Search operating income was driven by increases in higher fee revenue of $91.3 million and a decrease in restructuring charges, net of $4.3 million, offset by increases in compensation and benefits expense, general and administrative expenses, cost of services expense and depreciation and amortization expenses of $60.0 million, $8.0 million, $1.6 million and $1.1 million, respectively. Executive Search operating income, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 21% in fiscal 2018 as compared to 20% in the year-ago period.
Hay Group operating income was $100.9 million, an increase of $53.6 million, or 113%, in fiscal 2018 as compared to operating income of $47.3 million in fiscal 2017. The increase was primarily driven by an increase in fee revenue of $60.8 million and a decrease in restructuring charges, net of $29.9 million, offset by an increase of $34.8 million in compensation and benefits expense, $1.8 million in cost of services expense, and $1.3 million in general and administrative expenses in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. Hay Group operating income, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 13% in fiscal 2018 compared to 7% in the year-ago period.
Futurestep operating income was $39.4 million, an increase of $9.4 million, in fiscal 2018 as compared to $30.0 million in fiscal 2017. The increase in operating income was driven by higher fee revenue of $49.5 million, offset by an increase in compensation and benefits expense of $38.4 million and general and administrative expenses of $2.8 million. Futurestep operating income, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 14% in fiscal 2018 compared to 13% in the year-ago period.
Net Income Attributable to Korn Ferry
Net income attributable to Korn Ferry increased by $49.6 million to $133.8 million in fiscal 2018 compared to $84.2 million in fiscal 2017. The increase was due to higher total revenue of $197.8 million, offset by higher operating expenses of $108.4 million and an increase in income tax provision of $41.0 million partially due to the enactment of the Tax Act compared to the year-ago period. Net income attributable to Korn Ferry, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 8% in fiscal 2018 as compared to 5% in the year-ago period.
Adjusted EBITDA
Adjusted EBITDA increased by $38.8 million, or 17% to $273.8 million in fiscal 2018 as compared to $235.0 million in fiscal 2017. This increase was driven by higher adjusted fee revenue of $198.1 million, offset by increases of $141.9 million in compensation and benefits expense (excluding integration costs), $14.9 million in general and administrative expenses (excluding integration costs) and $2.2 million in cost of services expense compared to the year-ago period. Adjusted EBITDA, as a percentage of adjusted fee revenue, was 15% in both fiscal 2018 and 2017.
Executive Search Adjusted EBITDA increased $21.5 million, or 16%, to $158.9 million in fiscal 2018 as compared to $137.4 million in fiscal 2017. The increase was driven by higher fee revenue of $91.3 million, offset by increases of $60.0 million in compensation and benefits expense, $8.0 million in general and administrative expenses, and an increase in cost of services expense of $1.6 million during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. Executive Search Adjusted EBITDA, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 22% in both fiscal 2018 and 2017.
Hay Group Adjusted EBITDA was $142.0 million, an increase of $13.8 million, or 11%, in fiscal 2018 as compared to $128.2 million in fiscal 2017. The increase was driven by higher adjusted fee revenue of $57.3 million, offset by increases of $41.1 million in compensation and benefits expense (excluding integration costs), $0.9 million in general and administrative expenses (excluding integration costs), and an increase in cost of services expense of $1.8 million during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. Hay Group Adjusted EBITDA, as a percentage of adjusted fee revenue, was 18% in both fiscal 2018 and 2017.
Futurestep Adjusted EBITDA was $42.6 million in fiscal 2018, an increase of $9.8 million, or 30%, as compared to $32.8 million in fiscal 2017. The increase was driven by higher fee revenue of $49.5 million, offset by increases of $38.4 million in compensation and benefits expense and $2.8 million in general and administrative expenses
45
Table of Contents

during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period. Futurestep Adjusted EBITDA, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 16% in fiscal 2018 compared to 15% in the year-ago period.
Other Income (Loss), Net
Other income, net was $11.5 million in fiscal 2018 as compared to $11.8 million in fiscal 2017. The decrease was primarily due to the change in the fair value of our marketable securities, where there was a smaller gain during fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period.
Interest (Expense) Income, Net
Interest (expense) income, net primarily relates to our term loan facility and borrowings under our COLI policies, which was partially offset by interest earned on cash and cash equivalent balances. Interest expense, net was $9.7 million in fiscal 2018 as compared to $10.3 million in fiscal 2017.
Income Tax Provision
The provision for income tax was $70.1 million in fiscal 2018 compared to $29.1 million in the year-ago period. This reflects a 34% and 25% effective tax rate for fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively. In fiscal 2018 the effective tax rate was significantly impacted by the December 22, 2017 enactment of the Tax Act as a result of which, Korn Ferry recorded a provisional tax charge of $18.4 million as a one-time tax on accumulated foreign earnings (the “Transition Tax”), and a provisional tax benefit of $5.9 million from the remeasurement of our U.S. federal deferred tax assets and liabilities. Korn Ferry will continue to appropriately refine these amounts within the measurement period allowed by SAB No.118, which will be completed no later than December 22, 2018.
Net Income Attributable to Noncontrolling Interest
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest represents the portion of a subsidiary’s net earnings that are attributable to shares of such subsidiary not held by Korn Ferry that are included in the consolidated results of operations. Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest for fiscal 2018 and 2017 was $2.1 million compared to $3.1 million, respectively.
Fiscal 2017 Compared to Fiscal 2016
Fee Revenue
Fee Revenue. Fee revenue increased $273.4 million, or 21%, to $1,565.5 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $1,292.1 million in fiscal 2016. Exchange rates unfavorably impacted fee revenue by $27.9 million, or 2%, in fiscal 2017. The higher fee revenue was attributable to growth in Hay Group and Futurestep, offset by a decrease in Executive Search. The increase in Hay Group was primarily due to the Legacy Hay acquisition that was completed on December 1, 2015.
Executive Search. Executive Search reported fee revenue of $617.7 million, a decrease of $5.2 million, or 1%, in fiscal 2017 compared to $622.9 million in fiscal 2016. As detailed below, Executive Search fee revenue was lower in North America and Asia Pacific regions, offset by higher fee revenue in the Latin America and EMEA regions in fiscal 2017 as compared to fiscal 2016. Exchange rates unfavorably impacted fee revenue by $12.3 million, or 2%, in fiscal 2017.
North America reported fee revenue of $356.6 million, a decrease of $14.8 million, or 4%, in fiscal 2017 compared to $371.4 million in fiscal 2016. North America’s decrease in fee revenue is primarily due a 3% decrease in the weighted-average fees billed per engagement (calculated using local currency) and 1% decrease in the number of engagements billed during fiscal 2017 as compared to fiscal 2016. The overall decrease in fee revenue was driven by a decline in the life sciences/healthcare, education/non-profit and financial services sectors as compared to the year-ago period, partially offset by an increase in the industrial sector. Exchange rates did not impact fee revenue in fiscal 2017 when compared to the year-ago period.
EMEA reported fee revenue of $146.5 million, an increase of $2.2 million, or 2%, in fiscal 2017 compared to $144.3 million in fiscal 2016. The increase in fee revenue was due to a 6% increase in the number of engagements billed and a 2% increase in the weighted-average fees billed per engagement (calculated using local
46
Table of Contents

currency) during fiscal 2017 as compared to fiscal 2016. This was offset by unfavorable exchange rates which impacted fee revenue by $10.0 million, or 7%, in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016. The performance in existing offices in Germany, United Arab Emirates and Denmark were the primary contributors to the increase in fee revenue in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016, offset by a decrease in fee revenue in United Kingdom, France and Switzerland. In terms of business sectors, the technology and industrial sectors had the largest increase in fee revenue in fiscal 2017 as compared to fiscal 2016, partially offset by a decrease in fee revenue in the financial services, consumer goods and life sciences/healthcare sectors.
Asia Pacific reported fee revenue of $80.2 million in fiscal 2017, essentially flat with the $80.5 million in fiscal 2016. Exchange rates unfavorably impacted fee revenue by $0.5 million in fiscal 2017 when compared to the year-ago period. There were decreases in Hong Kong and Australia which were offset by an increase in fee revenue in China and Taiwan. Fee revenue in the technology, financial services and education/non-profit sectors decreased in fiscal 2017 as compared to fiscal 2016, offset by an increase in fee revenue in the consumer goods and industrial sectors.
Latin America reported fee revenue of $34.4 million, an increase of $7.7 million, or 29%, in fiscal 2017 compared to $26.7 million in fiscal 2016. Exchange rates unfavorably impacted fee revenue in Latin America by $1.7 million, or 6%, in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016. The increase is due to $11.0 million in fee revenue from our Mexico subsidiary that we began consolidating in the fourth quarter of 2016 as a result of obtaining control of the entity. The rest of the change primarily relates to a decrease in fee revenue in Venezuela caused by currency devaluation, offset by higher fee revenues in Brazil in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016. Industrial, life sciences/healthcare and financial services were the main sectors contributing to the growth in fee revenue in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016, offset by a decrease in fee revenue in the consumer goods sector.
Hay Group. Hay Group reported fee revenue of $724.2 million, an increase of $253.1 million, or 54%, in fiscal 2017 compared to $471.1 million in fiscal 2016. Exchange rates unfavorably impacted fee revenue by $11.0 million, or 2%, in fiscal 2017. The increase in fee revenue was primarily due to the Legacy Hay acquisition that was completed on December 1, 2015. As a result of the Legacy Hay acquisition, consulting fee revenue was higher by $146.5 million in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016, with the remaining increase of $106.6 million generated by higher fee revenue from our products business.
Futurestep. Futurestep reported fee revenue of $223.7 million, an increase of $25.6 million, or 13%, in fiscal 2017 compared to $198.1 million in fiscal 2016. Exchange rates unfavorably impacted fee revenue by $4.6 million, or 2%, in fiscal 2017. Higher fee revenues in RPO and professional search of $13.6 million and $12.2 million, respectively, drove the increase in fee revenue.
Compensation and Benefits
Compensation and benefits expense increased $174.1 million, or 19%, to $1,071.5 million in fiscal 2017 from $897.4 million in fiscal 2016. Exchange rates favorably impacted compensation and benefits expense by $17.2 million, or 2%, during fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016. The Legacy Hay acquisition was the main factor that contributed to the increase in compensation and benefits expense. Given the size of the Legacy Hay acquisition, all components of compensation and benefits expense increased with salaries and related payroll taxes, insurance costs and deferred compensation seeing the largest increases. Compensation and benefits expense, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 68% in fiscal 2017 compared to 69% in fiscal 2016.
Executive Search compensation and benefits expense increased $8.1 million, or 2%, to $409.0 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $400.9 million in fiscal 2016. This increase was primarily due to an increase in the fair value of amounts owed under certain deferred compensation plans of $10.3 million and higher salaries and related payroll expense of $10.9 million due to a 7% increase in average consultant headcount reflecting our continued growth-related investments back into the business in fiscal 2017 compared to the year-ago period. The rest of the change was due to an increase of $6.7 million in the amortization of long-term incentive awards, offset by lower performance related bonus expense of $15.6 million during fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016. The decrease in performance related bonus expense was primarily due to lower fee revenue and profitability. Executive Search compensation and benefits expense as a percentage of fee revenue decreased to 66% in fiscal 2017 compared to 64% in fiscal 2016.
47
Table of Contents

Hay Group compensation and benefits expense increased $146.9 million, or 47%, to $462.1 million in fiscal 2017 from $315.2 million in fiscal 2016. The increase in compensation and benefits was primarily due to the Legacy Hay acquisition, which increased our average headcount during fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016, resulting in higher salaries and related payroll taxes, performance related bonus expense, insurance costs, retirement plans and recruiting costs of $101.8 million, $15.1 million, $6.7 million, $6.5 million and $4.2 million, respectively. Hay Group compensation and benefits expense, as a percentage of fee revenue, decreased to 64% in fiscal 2017 from 67% in the year-ago period.
Futurestep compensation and benefits expense increased $18.7 million, or 14%, to $154.8 million in fiscal 2017 from $136.1 million in fiscal 2016. The increase was due to a 21% increase in the average headcount in fiscal 2017 compared to the year-ago period that resulted in higher salaries and related payroll taxes and insurance costs of $19.8 million and $1.9 million, respectively, partially offset by lower performance related bonus expense. The higher average headcount was primarily driven by the need to service an increase in fee revenue in both the professional search and RPO businesses. Futurestep compensation and benefits expense as a percentage of fee revenue was 69% in both fiscal 2017 and 2016.
Corporate compensation and benefits expense increased $0.4 million, or 1%, to $45.6 million in fiscal 2017 from $45.2 million in fiscal 2016. This increase was mainly due to $1.6 million in higher outside contractor costs and a change in the fair value of vested amounts owed under certain deferred compensation plans of $1.5 million in fiscal 2017 compared to the year-ago period. Offsetting these increases in compensation and benefit expense was a decline in integration/acquisition costs and certain separation costs of $2.2 million in fiscal 2017 as compared to the year-ago period.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses increased $13.2 million, or 6%, to $226.2 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $213.0 million in fiscal 2016. Exchange rates favorably impacted general and administrative expenses by $5.2 million, or 2%, during fiscal 2017. The increase in general and administrative expenses was primarily due to the Legacy Hay acquisition that took place in fiscal 2016, partially offset by a decrease of $20.3 million in integration/acquisition costs and $13.7 million of Venezuelan foreign currency loss compared to the year-ago period. The Legacy Hay acquisition was the main factor that contributed to increases of $27.0 million, $8.4 million, $5.3 million and $4.4 million, in premise and office expenses, marketing and business development expenses, travel-related expenses, and bad debt expense, respectively. General and administration expenses as a percentage of fee revenue was 14% in fiscal 2017 compared to 16% in fiscal 2016.
Executive Search general and administrative expenses decreased $5.6 million, or 7%, to $69.7 million in fiscal 2017 from $75.3 million in fiscal 2016. The decrease was due to the $6.6 million in Venezuelan foreign currency loss incurred in fiscal 2016, offset by higher bad debt expense of $1.5 million in fiscal 2017 compared to the year-ago period. Executive Search general and administrative expenses as a percentage of fee revenue was 11% in fiscal 2017 compared to 12% in fiscal 2016.
Hay Group general and administrative expenses increased $31.5 million, or 48%, to $97.1 million in fiscal 2017 from $65.6 million in fiscal 2016. The increase in general and administrative expenses was primarily due to the Legacy Hay acquisition that took place in fiscal 2016, partially offset by a decrease of $1.8 million in integration/acquisition costs and $7.1 million of Venezuelan foreign currency loss compared to the year-ago period. The acquisition of Legacy Hay was the main factor for increases of $24.0 million, $4.7 million, $4.2 million, $2.5 million and $1.6 million in premise and office expenses, marketing and business development expenses, travel-related expenses, bad debt expense and legal and other professional fees, respectively. Hay Group general and administrative expenses as a percentage of fee revenue was 13% in fiscal 2017 compared to 14% in fiscal 2016.
Futurestep general and administrative expenses increased $2.5 million, or 12%, to $23.9 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $21.4 million in fiscal 2016. General and administrative expenses increased $1.4 million, $0.4 million and $0.4 million in premise and office expenses, marketing and business development expenses and bad debt expense, respectively, during fiscal 2017 compared to the year-ago period due in large part to an increase in fee revenue. Futurestep general and administrative expenses as a percentage of fee revenue was 11% in both fiscal 2017 and 2016.
48
Table of Contents

Corporate general and administrative expenses decreased $15.2 million, or 30%, to $35.5 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $50.7 million in fiscal 2016. General and administrative expenses decreased due to a decline of $18.4 million in integration/acquisition costs, offset by increases of $3.2 million in marketing and business development expenses in fiscal 2017 compared to the year-ago period.
Cost of Services Expense
Cost of services expense consist primarily of non-billable contractor and product costs related to the delivery of various services and products, primarily in Futurestep and Hay Group. Cost of services expense increased $11.7 million, or 20%, to $71.5 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $59.8 million in fiscal 2016. The increase is mainly due to higher fee revenue in Hay Group due to the Legacy Hay acquisition. Cost of services expense as a percentage of fee revenue was 5% in both fiscal 2017 and 2016.
Depreciation and Amortization Expenses
Depreciation and amortization expenses were $47.3 million in fiscal 2017, an increase of $11.1 million compared to $36.2 million in fiscal 2016. The increase is mainly due to the Legacy Hay acquisition. The increase relates primarily to technology investments that were made in the current and prior year in software and computer equipment, in addition to increases in leasehold improvements, furniture and fixtures (associated with our office co-location) and intangible assets.
Restructuring Charges, Net
We continued the implementation of the fiscal 2016 restructuring plan in order to integrate the Hay Group entities that were acquired in the prior year by eliminating redundant positions and operational, general and administrative expenses and consolidation of office space. As a result, we recorded $34.6 million of restructuring charges in fiscal 2017, of which $16.0 million related to severance costs and $18.6 million related to the consolidation of office space.
During fiscal 2016, we implemented a restructuring plan in order to rationalize our cost structure in order to eliminate redundant positions and consolidation of office space that were created due to the acquisition of Legacy Hay. As a result, we recorded $33.0 million of restructuring charges, with $32.1 million of severance and $0.9 million relating to the consolidation/abandonment of premises during fiscal 2016.
Operating Income
Operating income increased $61.7 million, or 117%, to $114.4 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $52.7 million in fiscal 2016. This increase in operating income resulted from $273.4 million in higher fee revenue, offset by an increase of $174.1 million in compensation and benefits expense. The rest of the change was due to increases of $13.2 million in general and administrative expenses, $11.7 million in cost of services expense, and $11.1 million of depreciation and amortization expenses during fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016. Operating income as a percentage of fee revenue was 7% in fiscal 2017 compared to 4% in fiscal 2016.
Executive Search operating income was $124.3 million, a decrease of $7.4 million, or 6%, in fiscal 2017 compared to $131.7 million in fiscal 2016. The decrease in Executive Search operating income was driven by lower fee revenue of $5.2 million and higher compensation and benefits expense of $8.1 million, offset by a decrease in general and administrative expenses of $5.6 million. Executive Search operating income as a percentage of fee revenue was 20% in fiscal 2017 compared to 21% in fiscal 2016.
Hay Group operating income increased by $50.7 million to $47.3 million in fiscal 2017 compared to operating loss of $3.4 million in fiscal 2016. The change was primarily driven by the Legacy Hay acquisition resulting in an increase in fee revenue of $253.1 million, offset by increases in compensation and benefits expense, general and administrative expenses, depreciation and amortization expenses, cost of services expense and restructuring charges, net of $146.9 million, $31.5 million, $10.4 million, $9.5 million and $4.0 million, respectively in fiscal 2017 compared to 2016. Hay Group operating income as a percentage of fee revenue was 7% in fiscal 2017 compared to operating loss as a percentage of fee revenue of 1% in fiscal 2016.
Futurestep operating income increased by $3.3 million to $30.0 million in fiscal 2017 from $26.7 million in fiscal 2016. The increase in Futurestep operating income was primarily due to higher fee revenues of $25.6 million,
49
Table of Contents

partially offset by increases of $18.7 million in compensation and benefits expense and $2.5 million in general and administrative expenses. Futurestep operating income, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 13% in both fiscal 2017 and 2016.
Net Income Attributable to Korn Ferry
Net income attributable to Korn Ferry increased $53.3 million, or 172%, to $84.2 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $30.9 million in fiscal 2016. The increase was due primarily to higher total revenue of $275.0 million, offset by higher operating expenses of $213.2 million and an increase in income tax provision of $10.1 million. Net income attributable to Korn Ferry, as a percentage of fee revenue, was 5% during fiscal 2017 as compared to 2% in the year-ago period.
Adjusted EBITDA
Adjusted EBITDA increased $44.8 million, or 24%, to $235.0 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $190.2 million in fiscal 2016. This increase was driven by higher adjusted fee revenue of $266.0 million, and an increase in other income, net due to the change in fair value of our marketable securities of $16.0 million in fiscal 2017 compared to the year-ago period, offset by increases of $177.0 million, $47.2 million and $11.7 million in compensation and benefits expense, general and administrative expenses and cost of services expense, respectively. Adjusted EBITDA as a percentage of fee revenue was 15% in both fiscal 2017 and 2016.
Executive Search Adjusted EBITDA was $137.4 million, a decrease of $14.8 million, or 10%, in fiscal 2017 compared to $152.2 million in fiscal 2016. This decrease was due to lower fee revenue of $5.2 million and higher compensation and benefits expense and general and administrative expenses of $8.1 million and $1.0 million, respectively. Executive Search Adjusted EBITDA as a percentage of fee revenue was 22% in fiscal 2017 as compared to 24% in fiscal 2016.
Hay Group Adjusted EBITDA increased by $49.3 million to $128.2 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $78.9 million in fiscal 2016. This increase was due to higher adjusted fee revenue of $245.6 million, offset by an increase in compensation and benefit expense, general and administrative expenses and cost of services expense of $147.6 million, $40.5 million and $9.5 million, respectively. The higher compensation and benefit expense was driven mainly by increases in salaries and related payroll taxes due to an increase in average headcount and an increase in performance related bonus expense. Hay Group Adjusted EBITDA as a percentage of fee revenue was 18% in fiscal 2017 compared to 16% in fiscal 2016.
Futurestep Adjusted EBITDA increased by $3.3 million to $32.8 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $29.5 million in fiscal 2016. The increase in Futurestep Adjusted EBITDA was primarily due to higher fee revenue of $25.6 million, offset by an increase in compensation and benefits expense and in general and administrative expenses of $18.7 million and $2.5 million, respectively, during fiscal 2017 as compared to fiscal 2016. The increase in compensation and benefits expense was primarily driven by higher salaries and related payroll taxes due to an increase in average headcount. Futurestep Adjusted EBITDA as a percentage of fee revenue was 15% in both fiscal 2017 and 2016.
Other Income (Loss), Net
Other income, net was $11.8 million in fiscal 2017 as compared to other loss, net of $4.2 million in fiscal 2016. The change in other income (loss), net is primarily due to the increase in the fair value of our marketable securities, held in trust for settlement of our obligations under certain deferred compensation plans, during fiscal 2017 compared to the decrease in the fair value of our marketable securities in the year-ago period.
Interest (Expense) Income, Net
Interest (expense) income, net primarily relates to our term loan facility that we entered into in the current fiscal year to provide enhanced financial flexibility and in recognition of the accelerated pace of the Legacy Hay integration. It also includes interest on our borrowings under our COLI policies and interest earned on cash and cash equivalent balances. Interest expense, net was $10.3 million in fiscal 2017 compared to interest income, net of $0.3 million in fiscal 2016.
50
Table of Contents

Equity in Earnings of Unconsolidated Subsidiaries
Equity in earnings of unconsolidated subsidiaries is comprised of our less than 50% interest in IGroup, LLC, which is engaged in organizing, planning and conducting conferences and training programs throughout the world for directors, chief executive officers, other senior level executives and also includes earnings of our Mexico subsidiary for the first nine months in fiscal 2016. In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2016, we obtained control of our Mexico subsidiary and began to consolidate the operations. Equity in earnings was $0.3 million in fiscal 2017 as compared to $1.6 million in fiscal 2016. The decrease is due to the consolidation of our Mexico subsidiary in fiscal 2017, which is now included in operations.
Income Tax Provision
The provision for income taxes was $29.1 million in fiscal 2017 compared to $19.0 million in fiscal 2016, reflecting a 25% and 39% effective tax rate, respectively. The lower effective tax rate in fiscal 2017 was due primarily to a higher percentage of taxable income arising in jurisdictions outside of the U.S. with lower statutory tax rates. The effective tax rate in fiscal 2016 was higher largely due to the impact of non-deductible expenses incurred in connection with the acquisition of Legacy Hay and non-deductible charges related to the devaluation of the Venezuelan currency.
Net Income Attributable to Noncontrolling Interest
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest represents the portion of a subsidiary’s net earnings that are attributable to shares of such subsidiary not held by Korn Ferry that are included in the consolidated results of operations. In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2016, we obtained control of our Mexico subsidiary and began to consolidate the operations. Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest in fiscal 2017 was $3.1 million compared to $0.5 million in fiscal 2016.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company and its Board of Directors endorse a balanced approach to capital allocation. The Company’s priority is to invest in growth initiatives, such as the hiring of consultants, the continued development of IP and derivative products and services, and the investment in synergistic, accretive merger and acquisition transactions that earn a return that is superior to the Company’s cost of capital. Next, the Company’s capital allocation approach contemplates the return of a portion of excess capital to stockholders, in the form of a regular quarterly dividend, subject to the factors discussed below and in the “Risk Factors” section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Additionally, the Company considers share repurchases on an opportunistic basis and subject to the terms of our credit agreement.
On June 15, 2016, we entered into a senior secured $400 million Credit Agreement with a syndicate of banks and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association as administrative agent, to provide for enhanced financial flexibility and in recognition of the accelerated pace of the Legacy Hay integration. See Note 10—Long-Term Debt for a description of the credit facility. In anticipation of the Plan, on June 8, 2018, we entered into an amendment (the “Amendment”) to the Credit Agreement. The Amendment permits the KF Merger, and will become effective when certain conditions set forth therein, including consummation of the KF Merger, are satisfied. We drew down $275 million on the term loan and used $140 million of the proceeds to pay-off the term loan that was outstanding as of April 30, 2016. We had $2.9 million and $3.0 million standby letters of credit issued under our long-term debt arrangements as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. We had a total of $7.4 million and $8.1 million of standby letters of credits with other financial institutions as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The standby letters of credits were generally issued as a result of entering into office premise leases.
As part of the Legacy Hay acquisition, the Company has committed to a $40 million retention pool (of which $23.5 million has been paid) for certain employees of Legacy Hay subject to certain circumstances. The remaining balance will be payable within 45 days after November 30, 2018.
On December 8, 2014, the Board of Directors adopted a dividend policy to distribute, to our stockholders, a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.10 per share. Every quarter since the adoption of the dividend policy, the Company has declared a quarterly dividend. The declaration and payment of future dividends under the quarterly dividend
51
Table of Contents

program will be at the discretion of the Board of Directors and will depend upon many factors, including our earnings, capital requirements, financial conditions, the terms of our indebtedness and other factors our Board of Directors may deem to be relevant. Our Board of Directors may, however, amend, revoke or suspend our dividend policy at any time and for any reason.
On December 8, 2014, the Board of Directors also approved an increase in the Company’s stock repurchase program to an aggregate of $150.0 million. Common stock may be repurchased from time to time in open market or privately negotiated transactions at the Company’s discretion subject to market conditions and other factors. We repurchased approximately $33.1 million and $28.8 million of the Company’s common stock during fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively. As of April 30, 2018, $88.1 million remained available for common stock repurchases under our stock repurchase program. Any decision to continue to execute our currently outstanding share repurchase program will depend on our earnings, capital requirements, financial condition and other factors considered relevant by our Board of Directors. Our senior secured credit agreement requires that our pro forma leverage ratio, defined as the ratio of consolidated funded indebtedness to consolidated Adjusted EBITDA, is no greater than 2.50 to 1.00, and our pro forma domestic liquidity is at least $50.0 million, including undrawn amounts on our revolving credit facility as a condition to consummating permitted acquisitions, paying dividends to our stockholders and share repurchases of our common stock.
Our performance is subject to the general level of economic activity in the geographic regions and the industries which we service. We believe, based on current economic conditions, that our cash on hand and funds from operations and the Credit Agreement we entered into on June 15, 2016 will be sufficient to meet anticipated working capital, capital expenditures, general corporate requirements, repayment of the debt incurred in connection with the Legacy Hay acquisition, the retention pool obligations in connection with the Legacy Hay acquisition, shares repurchases and dividend payments under our dividend policy during the next twelve months. However, if the national or global economy, credit market conditions and/or labor markets were to deteriorate in the future, such changes could put negative pressure on demand for our services and affect our operating cash flows. If these conditions were to persist over an extended period of time, we may incur negative cash flows and it might require us to access our existing credit facility to meet our capital needs and/or discontinue our share repurchases and dividend policy.
Cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities were $657.9 million and $530.8 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Net of amounts held in trust for deferred compensation plans and accrued bonuses, cash and marketable securities were $312.4 million and $245.1 million at April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, we held $207.6 million and $165.8 million, respectively of cash and cash equivalents in foreign locations, net of amounts held in trust for deferred compensation plans and to pay fiscal 2018 and 2017 annual bonuses. We have not provided deferred income taxes on approximately $492.3 million of undistributed earnings from our foreign subsidiaries as such earnings are intended to be reinvested indefinitely. If a distribution of these earnings was to be made, we may be subject to state income and foreign withholding taxes. An estimate of such taxes, however, is not practicable. Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash and highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less. Marketable securities consist of mutual funds. The primary objectives of our investment in mutual funds are to meet the obligations under certain of our deferred compensation plans.
As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, marketable securities of $137.1 million (net of gross unrealized gains of $11.0 million and gross unrealized losses of $1.0 million) and $119.9 million (net of gross unrealized gains of $6.7 million and gross unrealized losses of $0.6 million), respectively, were held in trust for settlement of our obligations under certain deferred compensation plans, of which $122.8 million and $115.6 million, respectively, are classified as non-current. These marketable securities were held to satisfy vested obligations totaling $118.2 million and $99.5 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Unvested obligations under the deferred compensation plans totaled $29.5 million and $37.6 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
The net increase in our working capital of $70.7 million as of April 30, 2018 compared to April 30, 2017 is primarily attributable to an increase in cash and cash equivalents and accounts receivable, offset by an increase in compensation and benefits payable. The increase in cash and cash equivalents is due to cash provided by operations. Accounts receivable and compensation and benefits payable increased due an increase in fee
52
Table of Contents

revenue and overall profitability of the Company. Cash provided by operating activities was $219.1 million in fiscal 2018, an increase of $113.0 million, compared to $106.1 million in fiscal 2017.
Cash used in investing activities was $44.8 million in fiscal 2018, an increase of $24.2 million, compared to $20.6 million in the year-ago period. Cash used in investing activities was higher due to a decrease in proceeds from sales/maturities of marketable securities, offset by less cash used for the purchases of property and equipment and higher proceeds from life insurance policies in fiscal 2018 compared to fiscal 2017.
Cash used in financing activities was $77.3 million in fiscal 2018 compared to cash provided by financing activities of $64.4 million in fiscal 2017. The change from cash provided by financing activities to cash used in financing activities was primarily due to a decrease of $135.0 million in proceeds from our term loan facility net of pay-off of the term loan that was outstanding as of April 30, 2016, and an increase of shares repurchased under the stock repurchase program of $4.3 million in fiscal 2018 compared to the year-ago period.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements and have not entered into any transactions involving unconsolidated, special purpose entities.
Contractual Obligations
Contractual obligations represent future cash commitments and liabilities under agreements with third parties and exclude contingent liabilities for which we cannot reasonably predict future payment. The following table represents our contractual obligations as of April 30, 2018:
| Payments Due in: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note (1) | Total | Less Than 1 Year |
1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | More Than 5 Years |
|||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating lease commitments |
14 | $ | 392,824 | $ | 66,071 | $ | 118,939 | $ | 91,628 | $ | 116,186 | |||||||||||||
| Accrued restructuring charges (2) |
7 | 3,760 | 2,436 | 1,324 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest payments on COLI loans (3) |
10 | 36,699 | 3,776 | 7,551 | 7,432 | 17,940 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Retention awards |
12 | 16,500 | 16,500 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Term loan |
10 | 238,906 | 25,781 | 55,000 | 158,125 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Estimated interest on term loan (4) |
— | 19,867 | 7,277 | 11,953 | 637 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 708,556 | $ | 121,841 | $ | 194,767 | $ | 257,822 | $ | 134,126 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| (1) | See Note in the accompanying consolidated financial statements in Item 15. |
| (2) | Represents rent payments, net of sublease income on an undiscounted basis and severance costs. |
| (3) | Assumes COLI loans remain outstanding until receipt of death benefits on COLI policies and applies current interest rates on COLI loans ranging from 4.76% to 8.00% with total death benefits payable, net of loans under COLI contracts of $226.0 million at April 30, 2018. |
| (4) | Interest rate used is the variable rate per the credit agreement as of April 30, 2018 for outstanding balance on the term loan. |
In addition to the contractual obligations above, we have liabilities related to certain employee benefit plans. These liabilities are recorded in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. The obligations related to these employee benefit plans are described in Note 6—Deferred Compensation and Retirement Plans, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Lastly, we have contingent commitments under certain employment agreements that are payable upon involuntary, termination without cause, as described in Note 14—Commitments and Contingencies, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Cash Surrender Value of Company Owned Life Insurance Policies, Net of Loans
The Company purchased COLI policies or contracts insuring the lives of certain employees eligible to participate in the deferred compensation and pension plans as a means of funding benefits under such plans. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, we held contracts with gross CSV of $186.8 million and $180.3 million, respectively. Total outstanding borrowings against the CSV of COLI contracts were $66.7 million and $67.2 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Such borrowings do not require annual principal repayments, bear interest primarily
53
Table of Contents

at variable rates and are secured by the CSV of COLI contracts. At April 30, 2018 and 2017, the net cash value of these policies was $120.1 million and $113.1 million, respectively. Total death benefits payable, net of loans under COLI contracts, were $226.0 million and $220.6 million at April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Long-Term Debt
On June 15, 2016, we entered into a senior secured $400 million Credit Agreement (the “Credit Agreement”) with a syndicate of banks and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association as administrative agent. On June 8, 2018, in anticipation of the Plan, we entered into an amendment (the “Amendment”) to the Credit Agreement. The Amendment permits the KF Merger, and will become effective when certain conditions set forth therein, including consummation of the KF Merger, are satisfied. The Credit Agreement provides for, among other things: (a) a senior secured term loan facility in an aggregate principal amount of $275 million (the “ Term Facility”), (b) a senior secured revolving credit facility (the “Revolver” and together with the Term Facility, the “Credit Facilities”) in an aggregate principal amount of $125 million, (c) annual term loan amortization of 7.5%, 7.5%, 10.0%, 10.0% and 10.0%, with the remaining principal due at maturity, (d) certain customary affirmative and negative covenants, including a maximum consolidated total leverage ratio (as defined below) and a minimum interest coverage ratio and (e) an expanded definition of permitted add-backs to Adjusted EBITDA in recognition of the accelerated integration actions. Our credit agreement permits payment of dividends to stockholders and share repurchases so long as the pro forma leverage ratio is no greater than 2.50 to 1.00, and the pro forma domestic liquidity is at least $50.0 million. We drew down $275 million on the term loan and used $140 million of the proceeds to pay-off the term loan that was outstanding as of April 30, 2016.
At our option, loans issued under the Credit Agreement will bear interest at either LIBOR or an alternate base rate, in each case plus the applicable interest rate margin. The interest rate applicable to loans outstanding under the Credit Facilities may fluctuate between LIBOR plus 1.25% per annum to LIBOR plus 2.00% per annum, in the case of LIBOR borrowings (or between the alternate base rate plus 0.25% per annum and the alternate base rate plus 1.00% per annum, in the alternative), based upon our total funded debt to Adjusted EBITDA ratio (as set forth in the Credit Agreement, the “consolidated leverage ratio”) at such time. In addition, we will be required to pay to the lenders a quarterly fee ranging from 0.20% to 0.35% per annum on the average daily unused amount of the Term Facility, based upon our consolidated leverage ratio at such time and fees relating to the issuance of letters of credit. During fiscal 2018 and 2017, the average rate on the Term Facility was 2.60% and 2.23%, respectively.
Both the Revolver and the Term Facility mature on June 15, 2021 and may be prepaid and terminated early by us at any time without premium or penalty (subject to customary LIBOR breakage fees). The Term Facility is payable in quarterly installments with principal payments totalling $20.6 million and $15.5 million made during fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, $238.9 million and $259.5 million were outstanding under the Term Facility, respectively. The current and long-term portion of unamortized debt issuance costs associated with the long-term debt, was $2.7 million and $3.5 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The fair value of our Term Facility is based on borrowing rates currently required of loans with similar terms, maturity and credit risk. The carrying amount of the Term Facility approximates fair value because the base interest rate charged varies with market conditions and the credit spread is commensurate with current market spreads for issuers of similar risk. The fair value of the Term Facility is classified as a Level 2 liability in the fair value hierarchy. As of April 30, 2018, we were in compliance with our debt covenants.
As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, we had no borrowings under the Revolver. The Company had a total of $122.1 million and $122.0 million available under the Revolver after $2.9 million and $3.0 million standby letters of credit were issued as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. We had a total of $7.4 million and $8.1 million of standby letters of credits with other financial institutions as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The standby letters of credits were generally issued as a result of entering into office premise leases.
We are not aware of any other trends, demands or commitments that would materially affect liquidity or those that relate to our resources.
54
Table of Contents

Accounting Developments
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
In March 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (the “FASB”) issued guidance on accounting for certain aspects of share-based payments to employees. The new guidance requires excess tax benefits and tax deficiencies to be recorded in the income statement when the awards vest or are settled. Furthermore, cash flows related to excess tax benefits will no longer be separately classified as a financing activity apart from other income tax cash flows. The guidance also allows companies to repurchase more of an employee’s shares for tax withholding purposes without triggering liability accounting, clarifying that all cash payments made on an employee’s behalf for withheld shares should be presented as a financing activity in the consolidated statements of cash flows and provides an accounting policy election to account for forfeitures as they occur. The provisions of the guidance are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016 and were adopted by us effective May 1, 2017. The primary impact of the adoption was the recognition of excess tax benefits in our provision for income taxes in the current year compared to recording it previously as a component of equity. Additional amendments to the accounting for income taxes and minimum statutory withholding tax requirements had no impact to retained earnings, where the cumulative effect of these changes are required to be recorded. We elected to apply the presentation for cash flows related to excess tax benefits retrospectively for all periods presented which resulted in an increase to cash provided by operations and decrease in cash provided by financing activities of $0.1 million and $4.9 million for fiscal 2017 and 2016, respectively. The presentation requirements for cash flows related to employee taxes paid for withheld shares had no impact on any of the periods presented on our consolidated cash flows statements since such cash flows have historically been presented as a financing activity. We elected to account for forfeitures as they occur, rather than estimating the expected forfeitures over the vesting period. This election did not have an impact on our financial statements.
In March 2018, the FASB issued guidance amending accounting for the tax effects of the Tax Act. The new guidance allows companies to complete the accounting under ASC 740 within a one-year measurement period from the Tax Act enactment date. This update was effective upon issuance. The amounts recorded as a result of the enactment of the Tax Act, specifically the impact of the Transition Tax and the remeasurement of deferred tax balances, are provisional estimates. We will continue to appropriately refine these amounts within the measurement period, which will be completed no later than December 22, 2018.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards—Not Yet Adopted
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, which superseded revenue recognition requirements regarding contracts with customers to transfer goods or services or for the transfer of nonfinancial assets. Under this new guidance, entities are required to recognize revenue that depicts the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The transfer is considered to occur when the customer obtains control of the goods or services delivered. The guidance provides a five-step analysis to be performed on transactions to determine when and how revenue is recognized. The new guidance is effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those annual years beginning after December 15, 2017. We will adopt this guidance in our fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018.
We organized a team and developed a project plan to guide the implementation. The project plan included working sessions to review, evaluate and document the arrangements with customers under our various reporting units to identify potential differences that would result from applying the requirements of the new standard.
We completed our evaluation of the impact of ASU 2014-09 for all our revenue streams and selected the modified retrospective method as the transition method, which will include a cumulative-effect adjustment as of the date of adoption. The impact to recruitment process outsourcing, advisory and products revenue is not material, although there will be minor process changes to comply with ASU 2014-09. As to executive search and recruitment for non-executive professionals, the implementation of ASU 2014-09 will result in timing differences in the recognition of uptick revenue (uptick revenue occurs when a placement’s actual compensation is higher than the original estimated compensation). Currently we recognize uptick revenue as the amount becomes fixed and determinable. Under ASU 2014-09, however, upticks are considered variable consideration and we will be required to estimate upticks at contract inception and recognize the revenue over the service period.
55
Table of Contents

In February 2016, the FASB issued guidance on accounting for leases that generally requires all leases to be recognized on the consolidated balance sheet. The provisions of the guidance are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018 and early adoption is permitted. We plan to adopt this guidance in fiscal year beginning May 1, 2019. The provisions of the guidance are to be applied using a modified retrospective approach. We are still evaluating the effect this guidance will have on the consolidated financial statements. Based on our initial assessment, we expect that upon adoption we will report an increase in assets and liabilities on our consolidated balance sheet as a result of recognizing right-of-use assets and lease liabilities related to lease agreements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued guidance on the classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments in the statement of cash flows. The new guidance provides clarification on specific cash flow issues regarding presentation and classification in the statement of cash flows with the objective of reducing the existing diversity in practice. The amendments in this update are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. We plan to adopt this guidance in our fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018. The provisions of the guidance are to be applied using a retrospective transition method. The adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued guidance that clarifies the definition of a business. The new guidance assists a company when evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions (disposals) of assets or businesses. The provisions of the guidance require that if the fair value of the gross assets acquired (or disposed of) is substantially concentrated in a single identifiable asset or a group of similar identifiable assets, then it is not a business. The provisions of the guidance are effective for annual years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods, with early adoption permitted. We plan to adopt this guidance in our fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018. The provisions of the guidance are to be applied prospectively. The adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued guidance simplifying the test for goodwill impairment. The new guidance simplifies the test for goodwill impairment by removing Step 2 from the goodwill impairment test. Companies will now perform the goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount, recognizing an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value not to exceed the total amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit. An entity still has the option to perform the qualitative assessment for a reporting unit to determine if the quantitative impairment test is necessary. The amendments of this standard are effective for goodwill impairment tests in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted for goodwill impairment tests performed after January 1, 2017. We are evaluating the adoption timeline and the effects that the standard will have on the consolidated financial statements.
In March 2017, the FASB issued guidance that changes the presentation of net periodic pension cost and net periodic postretirement benefit cost. The new guidance will change the presentation of net periodic benefit cost related to employer sponsored defined benefit plans and other postretirement benefits. Service cost will be included within the same income statement line item as other compensation costs arising from services rendered during the period, while other components of net periodic benefit pension cost will be presented separately outside of operating income. Additionally, only service costs may be capitalized in assets. The amendments of this standard are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those years. We will adopt this guidance in our fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018. The adoption of this standard is not anticipated to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In May 2017, the FASB issued guidance clarifying the scope of modification accounting for stock compensation. The new standard provides guidance about which changes to the terms or conditions of a share-based payment award require an entity to apply modification accounting in Topic 718. This pronouncement is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, but early adoption is permitted. We will adopt this guidance in our fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018. The adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In August 2017, the FASB issued guidance amending and simplifying accounting for hedging activities. The new guidance will refine and expand strategies that qualify for hedge accounting and simplify the application of hedge
56
Table of Contents

accounting in certain situations. The amendments of this standard are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018. We will adopt this guidance in our fiscal year beginning May 1, 2019. We are currently evaluating the impact of adopting this guidance.
In February 2018, the FASB issued guidance that provides companies the option to reclassify stranded tax effects within accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net to retained earnings resulting from the Tax Act. The new guidance requires companies to disclose whether they decided to reclassify the income tax effects of the Tax Act from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net to retained earnings and to disclose a policy for releasing the income tax effects from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net. The guidance is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018, but early adoption is permitted. If companies elect to reclassify the stranded tax effects the guidance allows it to be recorded in the period of adoption or retrospectively to each period in which the effect of the Tax Act is recognized. We are currently evaluating the impact of adopting this guidance.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
As a result of our global operating activities, we are exposed to certain market risks, including foreign currency exchange fluctuations and fluctuations in interest rates. We manage our exposure to these risks in the normal course of our business as described below.
Foreign Currency Risk
Substantially all our foreign subsidiaries’ operations are measured in their local currencies. Assets and liabilities are translated into U.S. dollars at the rates of exchange in effect at the end of each reporting period and revenue and expenses are translated at average rates of exchange during the reporting period. Resulting translation adjustments are reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive loss, net on our consolidated balance sheets.
Transactions denominated in a currency other than the reporting entity’s functional currency may give rise to foreign currency gains or losses that impact our results of operations. Historically, we have not realized significant foreign currency gains or losses on such transactions. Foreign currency losses, on an after-tax basis, included in net income were $2.2 million and $8.7 million in fiscal 2018 and 2016, respectively. Foreign currency gains, on an after-tax basis, included in net income were $0.2 million in fiscal 2017.
Our exposure to foreign currency exchange rates is primarily driven by fluctuations involving the following currencies—U.S. Dollar, Canadian Dollar, Euro, Pound Sterling, Swiss Franc, Korean Won, Brazilian Real, Singapore Dollar, Mexican Peso, Indonesian Rupiah and Indian Rupee. Based on balances exposed to fluctuation in exchange rates between these currencies as of April 30, 2018, a 10% increase or decrease equally in the value of these currencies could result in a foreign exchange gain or loss of $9.7 million. We have a program that primarily utilizes foreign currency forward contracts to offset the risks associated with the effects of certain foreign currency exposures. These foreign currency forward contracts are neither used for trading purposes nor are they designated as hedging instruments pursuant to Accounting Standards Codification 815, Derivatives and Hedging.
Interest Rate Risk
Our exposure to interest rate risk is limited to our Term Facility and borrowings against the CSV of COLI contracts. As of April 30, 2018, there was $238.9 million outstanding under the Term Facility. At our option, loans issued under the Credit Facilities bear interest at either LIBOR or an alternate base rate, in each case plus the applicable interest rate margin. The interest rate applicable to loans outstanding under the Credit Facilities may fluctuate between LIBOR plus 1.25% per annum to LIBOR plus 2.00% per annum, in the case of LIBOR borrowings (or between the alternate base rate plus 0.25% per annum and the alternate base rate plus 1.00% per annum, in the alternative), based upon our total funded debt to Adjusted EBITDA ratio (as set forth in the Credit Agreement, the “consolidated leverage ratio”) at such time. In addition, we are required to pay the lenders a quarterly fee ranging from 0.20% to 0.35% per annum on the average daily unused amount of the Term Facility, based upon our consolidated leverage ratio at such time and fees relating to the issuance of letters of credit. A 100 basis point increase in LIBOR rates would have increased our interest expense by approximately $2.5 million for fiscal 2018.
57
Table of Contents

During fiscal 2018, the average interest rate on the term loan was 2.60%. We had no borrowings under the Revolver as of April 30, 2018.
To mitigate the interest rate risk on our Term Facility, we entered into an interest rate swap contract with an initial notional amount of $129.8 million to hedge the variability to changes in cash flows attributable to interest rate risks caused by changes in interest rates related to our variable rate debt. We have designated the swap as a cash flow hedge. The notional amount is amortized so that the amount is always 50% of the principal balance of the debt outstanding. As of April 30, 2018, the notional amount was $119.5 million. The interest rate swap agreement matures on June 15, 2021 and locks the interest rates on 50% of our outstanding debt at 1.919%, exclusive of the credit spread on the debt.
We had $66.7 million and $67.2 million of borrowings against the CSV of COLI contracts as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively, bearing interest primarily at variable rates. The risk of fluctuations in these variable rates is minimized by the fact that we receive a corresponding adjustment to our borrowed funds crediting rate which has the effect of increasing the CSV on our COLI contracts.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
See Consolidated Financial Statements beginning on page F-1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Supplemental Financial Information regarding quarterly results is contained in Note 15—Quarterly Results, in the Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
Not applicable.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
| a) | Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures. |
As of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, management, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures and internal controls over financial reporting. Based on their evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures conducted as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”)) are effective.
| b) | Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting. |
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the fourth fiscal quarter that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting. See Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting and Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting on pages F-2 and F-3, respectively.
On June 25, 2018, Korn/Ferry International (the “Company”) filed a Certificate of Amendment to its Restated Certificate of Incorporation (the “Certificate of Amendment”) with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware to implement amendments approved at the Company’s 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders that remove the supermajority voting standard for future amendments to the Bylaws approved by the stockholders and the supermajority voting standard to amend action by written consent right. The Certificate of Amendment became effective immediately upon filing.
Upon the effectiveness of the Certificate of Amendment on June 25, 2018, the Restated Certificate of Incorporation (the “Restated Certificate”) was further restated to reflect the Certificate of Amendment, a conforming amendment to the Company’s Fourth Amended and Restated Bylaws (the “Bylaws”) became effective, and the
58
Table of Contents

Bylaws were restated as the Fifth Amended and Restated Bylaws to reflect the conforming amendment. The conforming amendment was to Article V, Section 7 of the Bylaws, and provides that in order for stockholders to alter, amend or repeal the Bylaws, such action must be approved by the affirmative vote of at least the majority vote standard set forth in Article VI of the Certificate, instead of two-thirds of the voting power of the Company’s outstanding shares.
59
Table of Contents

Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this Item will be included under the captions “The Board of Directors” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” and elsewhere in our 2018 Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference. The information under the heading “Executive Officers of the Registrant” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K is also incorporated by reference in this section.
We have adopted a “Code of Business Conduct and Ethics,” that applies to all of our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer (who is our Chief Executive Officer), principal financial officer, and principal accounting officer (who is our Chief Financial Officer) and senior financial officers, or persons performing similar functions. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available on the Investor Relations portion of our website at http://ir.kornferry.com. We intend to disclose future amendments to certain provisions of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and waivers of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics granted to executive officers and directors on our website within four business days following the date of the amendment or waiver.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item will be included under the captions “Compensation Discussion and Analysis” and “Compensation of Executive Officers and Directors” and elsewhere in our 2018 Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this Item will be included under the caption “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and elsewhere in our 2018 Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item will be included under the caption “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” and elsewhere in our 2018 Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information required by this Item will be included under the captions “Fees Paid to Ernst & Young LLP,” and “Audit Committee Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures,” and elsewhere in our 2018 Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
60
Table of Contents

Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
Financial Statements.
| (a) | The following documents are filed as part of this report: |
| 1. | Index to Financial Statements: | Page | ||||
| See Consolidated Financial Statements included as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and Schedule II — Valuation and Qualifying Accounts. Pursuant to Rule 7-05 of Regulation S-X, the other schedules have been omitted as the information to be set forth therein is included in the notes of the audited consolidated financial statements | F-1 | |||||
Exhibits:
61
Table of Contents

62
Table of Contents

63
Table of Contents

| * | Management contract, compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| ** | Schedules omitted pursuant to Item 601(b)(2) of Regulation S-K. The Company agrees to furnish supplementally a copy of any omitted schedule to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request. |
| ^ | Confidential treatment was granted for portions of this exhibit which have been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| + | Incorporated herein by reference. |
None
64
Table of Contents

Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| Korn/Ferry International | ||
| By: /s/ Robert P. Rozek | ||
| Robert P. Rozek | ||
Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Corporate Officer
Date: June 28, 2018
KNOW ALL MEN BY THESE PRESENTS, that each of the undersigned officers and directors of the registrant hereby constitutes and appoints Jonathan M. Kuai and Gary D. Burnison, and each of them, as lawful attorney-in-fact and agent for each of the undersigned (with full power of substitution and resubstitution, for and in the name, place and stead of each of the undersigned officers and directors), to sign and file with the Securities and Exchange Commission under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, any and all amendments, supplements and exhibits to this report and any and all other documents in connection therewith, hereby granting unto said attorneys-in-fact, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing necessary or desirable to be done in order to effectuate the same as fully and to all intents and purposes as each of the undersigned might or could do if personally present, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents, or any of them, or any of their substitutes, may do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||||||
| /s/ GEORGE T. SHAHEEN George T. Shaheen |
Chairman of the Board and Director | June 28, 2018 | ||||||
| /s/ GARY D. BURNISON Gary D. Burnison |
President & Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) and Director |
June 28, 2018 | ||||||
| /s/ ROBERT P. ROZEK Robert P. Rozek |
Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Corporate Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
June 28, 2018 | ||||||
| /s/ DOYLE N. BENEBY Doyle N. Beneby |
Director | June 28, 2018 | ||||||
| /s/ WILLIAM R. FLOYD William R. Floyd |
Director | June 28, 2018 | ||||||
| /s/ CHRISTINA A. GOLD Christina A. Gold |
Director | June 28, 2018 | ||||||
| /s/ JERRY LEAMON Jerry Leamon |
Director | June 28, 2018 | ||||||
| /s/ ANGEL MARTINEZ Angel Martinez |
Director | June 28, 2018 | ||||||
| /s/ DEBRA J. PERRY Debra J. Perry |
Director | June 28, 2018 | ||||||
65
Table of Contents

KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
APRIL 30, 2018
F-1
Table of Contents

INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Management of Korn/Ferry International (the “Company”) is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting and for the assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting. As defined by the Securities and Exchange Commission, internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or supervised by, the issuer’s principal executive and principal financial officers, and effected by the issuer’s board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is supported by written policies and procedures, that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the Company’s assets; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of the Company’s management and directors; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In connection with the preparation of the Company’s annual financial statements, management of the Company has undertaken an assessment of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of April 30, 2018 based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Management’s assessment included an evaluation of the design of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting and testing of the operational effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Based on this assessment, management did not identify any material weakness in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting, and management has concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of April 30, 2018.
Ernst & Young LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that audited the Company’s financial statements for the year ended April 30, 2018 included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has issued an audit report on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of April 30, 2018, a copy of which is included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
June 28, 2018
F-2
Table of Contents

REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors of Korn/Ferry International
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited Korn/Ferry International and subsidiaries’ internal control over financial reporting as of April 30, 2018, based on criteria established in Internal Control— Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Korn/Ferry International and subsidiaries (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of April 30, 2018, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended April 30, 2018 and the related notes and the financial statement schedule listed in the index at Item 15(a) and our report dated June 28, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/Ernst & Young LLP
Los Angeles, California
June 28, 2018
F-3
Table of Contents

REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED
PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors of Korn/Ferry International
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Korn/Ferry International and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended April 30, 2018 and the related notes and the financial statement schedule listed in the index at Item 15(a) (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at April 30, 2018 and 2017, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended April 30, 2018, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of April 30, 2018, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated June 28, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2002
Los Angeles, California
June 28, 2018
F-4
Table of Contents

KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES
| April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) |
||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 520,848 | $ | 410,882 | ||||
| Marketable securities |
14,293 | 4,363 | ||||||
| Receivables due from clients, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $17,845 and
$15,455, |
384,996 | 345,314 | ||||||
| Income taxes and other receivables |
29,089 | 31,573 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
65,033 | 51,542 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
1,014,259 | 843,674 | ||||||
| Marketable securities, non-current |
122,792 | 115,574 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
119,901 | 109,567 | ||||||
| Cash surrender value of company owned life insurance policies, net of loans |
120,087 | 113,067 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes, net |
25,520 | 20,175 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
584,222 | 576,865 | ||||||
| Intangible assets, net |
203,216 | 217,319 | ||||||
| Investments and other assets |
97,917 | 66,657 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 2,287,914 | $ | 2,062,898 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 35,196 | $ | 37,481 | ||||
| Income taxes payable |
23,034 | 4,526 | ||||||
| Compensation and benefits payable |
304,980 | 248,354 | ||||||
| Term loan |
24,911 | 19,754 | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
170,339 | 148,464 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
558,460 | 458,579 | ||||||
| Deferred compensation and other retirement plans |
227,729 | 219,905 | ||||||
| Term loan, non-current |
211,311 | 236,222 | ||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities |
9,105 | 7,014 | ||||||
| Other liabilities |
61,694 | 54,130 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
1,068,299 | 975,850 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Commitments and contingencies |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity: |
||||||||
| Common stock: $0.01 par value, 150,000 shares authorized, 71,631 and 70,811 shares issued at
April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively, and 56,517 and 56,938 shares outstanding |
683,942 | 692,527 | ||||||
| Retained earnings |
572,800 | 461,976 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net |
(40,135 | ) | (71,064 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Korn/Ferry International stockholders’ equity |
1,216,607 | 1,083,439 | ||||||
| Noncontrolling interest |
3,008 | 3,609 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
1,219,615 | 1,087,048 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 2,287,914 | $ | 2,062,898 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
Table of Contents

KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 1,767,217 | $ | 1,565,521 | $ | 1,292,112 | ||||||
| Reimbursed out-of-pocket engagement expenses |
52,302 | 56,148 | 54,602 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total revenue |
1,819,519 | 1,621,669 | 1,346,714 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Compensation and benefits |
1,203,619 | 1,071,507 | 897,345 | |||||||||
| General and administrative expenses |
237,390 | 226,232 | 213,018 | |||||||||
| Reimbursed expenses |
52,302 | 56,148 | 54,602 | |||||||||
| Cost of services |
73,658 | 71,482 | 59,824 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
48,588 | 47,260 | 36,220 | |||||||||
| Restructuring charges, net |
78 | 34,600 | 33,013 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
1,615,635 | 1,507,229 | 1,294,022 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating income |
203,884 | 114,440 | 52,692 | |||||||||
| Other income (loss), net |
11,525 | 11,820 | (4,167 | ) | ||||||||
| Interest (expense) income, net |
(9,676 | ) | (10,251 | ) | 237 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income before provision for income taxes and |
205,733 | 116,009 | 48,762 | |||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated subsidiaries, net |
297 | 333 | 1,631 | |||||||||
| Income tax provision |
70,133 | 29,104 | 18,960 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income |
135,897 | 87,238 | 31,433 | |||||||||
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(2,118 | ) | (3,057 | ) | (520 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income attributable to Korn/Ferry International |
$ | 133,779 | $ | 84,181 | $ | 30,913 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Earnings per common share attributable to Korn/Ferry International: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 2.39 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 0.58 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 2.35 | $ | 1.47 | $ | 0.58 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
55,426 | 56,205 | 52,372 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted |
56,254 | 56,900 | 52,929 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash dividends declared per share |
$ | 0.40 | $ | 0.40 | $ | 0.40 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
Table of Contents

KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 135,897 | $ | 87,238 | $ | 31,433 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments |
22,900 | (19,266 | ) | (15,428 | ) | |||||||
| Deferred compensation and pension plan adjustments, net of tax |
6,054 | 6,445 | (1,864 | ) | ||||||||
| Unrealized losses on marketable securities, net of tax |
— | — | (4 | ) | ||||||||
| Net unrealized gain (loss) on interest rate swap, net of tax |
1,915 | (578 | ) | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive income |
166,766 | 73,839 | 14,137 | |||||||||
| Less: comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(2,058 | ) | (2,811 | ) | (512 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to Korn/Ferry International |
$ | 164,708 | $ | 71,028 | $ | 13,625 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-7
Table of Contents

KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| Retained Earnings |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income, Net |
Total Korn/Ferry International Stockholders’ Equity |
Noncontrolling Interest |
Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at May 1, 2015 |
50,573 | $ | 463,839 | $ | 392,033 | $ | (40,623 | ) | $ | 815,249 | $ | — | $ | 815,249 | ||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of noncontrolling interest in Mexico |
— | — | — | — | — | 1,489 | 1,489 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income |
— | — | 30,913 | (17,288 | ) | 13,625 | 512 | 14,137 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to shareholders |
— | — | (21,833 | ) | — | (21,833 | ) | — | (21,833 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of stock |
(215 | ) | (7,410 | ) | — | — | (7,410 | ) | — | (7,410 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of stock |
6,914 | 222,456 | — | — | 222,456 | — | 222,456 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | 18,305 | — | — | 18,305 | — | 18,305 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise of stock options and vesting of restricted stock |
— | 4,908 | — | — | 4,908 | — | 4,908 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at April 30, 2016 |
57,272 | 702,098 | 401,113 | (57,911 | ) | 1,045,300 | 2,001 | 1,047,301 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income |
— | — | 84,181 | (13,153 | ) | 71,028 | 2,811 | 73,839 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to shareholders |
— | — | (23,318 | ) | — | (23,318 | ) | — | (23,318 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to noncontrolling interest |
— | — | — | — | — | (1,203 | ) | (1,203 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of stock |
(1,346 | ) | (33,579 | ) | — | — | (33,579 | ) | — | (33,579 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of stock |
1,012 | 5,886 | — | — | 5,886 | — | 5,886 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | 18,045 | — | — | 18,045 | — | 18,045 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise of stock options and vesting of restricted stock |
— | 77 | — | — | 77 | — | 77 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at April 30, 2017 |
56,938 | 692,527 | 461,976 | (71,064 | ) | 1,083,439 | 3,609 | 1,087,048 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income |
— | — | 133,779 | 30,929 | 164,708 | 2,058 | 166,766 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to shareholders |
— | — | (22,955 | ) | — | (22,955 | ) | — | (22,955 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to noncontrolling interest |
— | — | — | — | — | (2,659 | ) | (2,659 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of stock |
(1,092 | ) | (36,865 | ) | — | — | (36,865 | ) | — | (36,865 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of stock |
671 | 7,998 | — | — | 7,998 | — | 7,998 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | 20,282 | — | — | 20,282 | — | 20,282 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at April 30, 2018 |
56,517 | $ | 683,942 | $ | 572,800 | $ | (40,135 | ) | $ | 1,216,607 | $ | 3,008 | $ | 1,219,615 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-8
Table of Contents

KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 135,897 | $ | 87,238 | $ | 31,433 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
48,588 | 47,260 | 36,220 | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
21,469 | 18,958 | 18,895 | |||||||||
| Provision for doubtful accounts |
13,675 | 12,987 | 8,570 | |||||||||
| Gain on cash surrender value of life insurance policies |
(7,776 | ) | (4,918 | ) | (3,984 | ) | ||||||
| (Gain) loss on marketable securities |
(10,278 | ) | (10,842 | ) | 3,333 | |||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
(6,564 | ) | 6,589 | (13,792 | ) | |||||||
| Change in other assets and liabilities, net of effect of acquisitions: |
||||||||||||
| Deferred compensation |
27,660 | 6,868 | (4,605 | ) | ||||||||
| Receivables due from clients |
(53,357 | ) | (42,326 | ) | (16,622 | ) | ||||||
| Income taxes and other receivables |
2,093 | (10,177 | ) | (191 | ) | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
(13,491 | ) | (8,485 | ) | (6,310 | ) | ||||||
| Investment in unconsolidated subsidiaries |
(297 | ) | (333 | ) | (1,631 | ) | ||||||
| Income taxes payable |
32,439 | 205 | 686 | |||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
66,081 | 5,420 | 18,862 | |||||||||
| Other |
(37,014 | ) | (2,303 | ) | (1,875 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
219,125 | 106,141 | 68,989 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Purchase of property and equipment |
(42,000 | ) | (50,088 | ) | (26,144 | ) | ||||||
| Purchase of marketable securities |
(9,462 | ) | (10,536 | ) | (30,397 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from sales/maturities of marketable securities |
2,642 | 42,815 | 30,066 | |||||||||
| Cash paid for acquisitions, net of cash acquired and earnout |
— | (2,880 | ) | (256,082 | ) | |||||||
| Acquisition of Mexico subsidiary, net of cash acquired |
— | — | 3,973 | |||||||||
| Premiums on company-owned life insurance policies |
(1,614 | ) | (1,597 | ) | (1,623 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from life insurance policies |
5,355 | 1,117 | 3,256 | |||||||||
| Dividends received from unconsolidated subsidiaries |
240 | 564 | 2,373 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(44,839 | ) | (20,605 | ) | (274,578 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from term loan facility |
— | 275,000 | 150,000 | |||||||||
| Principal payment on term loan facility |
(20,625 | ) | (155,469 | ) | (10,000 | ) | ||||||
| Payment of contingent consideration from acquisition |
(485 | ) | (1,070 | ) | — | |||||||
| Repurchases of common stock |
(33,071 | ) | (28,821 | ) | — | |||||||
| Payment of tax withholdings on restricted stock |
(3,794 | ) | (4,758 | ) | (7,410 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock upon exercise of employee stock options and in connection with an employee stock purchase plan |
6,885 | 5,121 | 4,038 | |||||||||
| Dividends – noncontrolling interest |
(2,659 | ) | (1,203 | ) | — | |||||||
| Dividends paid to shareholders |
(22,955 | ) | (23,318 | ) | (21,833 | ) | ||||||
| Payments on life insurance policy loans |
(554 | ) | (1,117 | ) | (1,251 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities |
(77,258 | ) | 64,365 | 113,544 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents |
12,938 | (12,271 | ) | (15,541 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
109,966 | 137,630 | (107,586 | ) | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
410,882 | 273,252 | 380,838 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
$ | 520,848 | $ | 410,882 | $ | 273,252 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental cash flow information: |
||||||||||||
| Cash used to pay interest |
$ | 11,946 | $ | 10,882 | $ | 5,154 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash used to pay income taxes, net of refunds |
$ | 37,486 | $ | 32,458 | $ | 33,189 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-9
Table of Contents

KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
April 30, 2018
1. Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Nature of Business
Korn/Ferry International, a Delaware corporation (the “Company”), and its subsidiaries are engaged in the business of providing talent management solutions, including executive search on a retained basis, recruitment for non-executive professionals, recruitment process outsourcing (“RPO”) and leadership & talent consulting services.
Basis of Consolidation and Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly and majority owned/controlled domestic and international subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The preparation of the consolidated financial statements conform with United States (“U.S.”) generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The consolidated financial statements include all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring accruals and any other adjustments that management considers necessary for a fair presentation of the results for these periods.
Investments in affiliated companies, which are 50% or less owned and where the Company exercises significant influence over operations, are accounted for using the equity method. Dividends received from our unconsolidated subsidiaries were approximately $0.2 million, $0.6 million and $2.4 million during fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2016, we obtained control of our Mexico subsidiary and began to consolidate the operations. Noncontrolling interest in our Mexico subsidiary is reflected on the Company’s consolidated financial statements for fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016.
The Company considers events or transactions that occur after the balance sheet date but before the consolidated financial statements are issued to provide additional evidence relative to certain estimates or to identify matters that require additional disclosures.
Use of Estimates and Uncertainties
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from these estimates, and changes in estimates are reported in current operations as new information is learned or upon the amounts becoming fixed and determinable. The most significant areas that require management judgment are revenue recognition, restructuring, deferred compensation, annual performance related bonuses, evaluation of the carrying value of receivables, goodwill and other intangible assets, fair value of contingent consideration, share-based payments and the recoverability of deferred income taxes.
Revenue Recognition
Substantially all fee revenue is derived from fees for professional services related to executive search performed on a retained basis, recruitment for non-executive professionals, recruitment process outsourcing, people and organizational advisory services and the sale of product services. Fee revenue from executive search activities and recruitment for non-executive professionals is generally one-third of the estimated first year compensation of the placed executive or non-executive professional, as applicable, plus a percentage of the fee to cover indirect engagement related expenses. The Company generally recognizes such revenue on a straight-line basis over a three-month period, commencing upon client acceptance, as this is the period over which the recruitment services are performed. Fees earned in excess of the initial contract amount are recognized upon completion of the
F-10
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
engagement, which reflect the difference between the final actual compensation of the placed executive and the estimate used for purposes of the previous billings. Since the initial contract fees are typically not contingent upon placement of a candidate, our assumptions primarily relate to establishing the period over which such service is performed. These assumptions determine the timing of revenue recognition and profitability for the reported period. Any revenues associated with services that are provided on a contingent basis are recognized once the contingency is resolved. In addition to recruitment for non-executive professionals, Futurestep provides RPO services and fee revenue is recognized as services are rendered and/or as milestones are achieved. Fee revenue from Hay Group (formerly known as Leadership & Talent Consulting (“Legacy LTC”) which was combined with HG (Luxembourg) S.à.r.l (“Legacy Hay”) in December 2015) is recognized as services are rendered for consulting engagements and other time-based services, measured by total hours incurred to the total estimated hours at completion. It is possible that updated estimates for the consulting engagement may vary from initial estimates with such updates being recognized in the period of determination. Depending on the timing of billings and services rendered, the Company accrues or defers revenue as appropriate. Hay Group revenue is also derived from the sale of product services, which includes revenue from licenses and from the sale of products. Revenue from licenses is recognized using a straight-line method over the term of the contract (generally 12 months). Under the fixed term licenses, the Company is obligated to provide the licensee with access to any updates to the underlying intellectual property (“IP”) that are made by the Company during the term of the license. Once the term of the agreement expires, the client’s right to access or use the IP expires and the Company has no further obligations to the client under the license agreement. Revenue from perpetual licenses is recognized when the license is sold since the Company’s only obligation is to provide the client access to the IP but is not obligated to provide maintenance, support, updates or upgrades. Products sold by the Company mainly consist of books and automated services covering a variety of topics including performance management, team effectiveness, and coaching and development. The Company recognizes revenue for its products when the product has been sold or shipped in the case of books. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the Company included deferred revenue of $120.1 million and $95.8 million, respectively, in other accrued liabilities.
Reimbursements
The Company incurs certain out-of-pocket expenses that are reimbursed by its clients, which are accounted for as revenue in its consolidated statements of income.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
An allowance is established for doubtful accounts by taking a charge to general and administrative expenses. The amount of the allowance is based on historical loss experience, assessment of the collectability of specific accounts, as well as expectations of future collections based upon trends and the type of work for which services are rendered. After the Company exhausts all collection efforts, the amount of the allowance is reduced for balances identified as uncollectible.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the Company’s investments in cash equivalents, consist of money market funds for which market prices are readily available.
Marketable Securities
The Company currently has investments in mutual funds that are classified as trading securities based upon management’s intent and ability to hold, sell or trade such securities. The classification of the investments in mutual funds is assessed upon purchase and reassessed at each reporting period. The investments in mutual funds (for which market prices are readily available) are held in trust to satisfy obligations under the Company’s deferred compensation plans. Such investments are based upon the employees’ investment elections in their deemed accounts in the Executive Capital Accumulation Plan and similar plans in Asia Pacific and Canada (“ECAP”) from a pre-determined set of securities and the Company invests in marketable securities to mirror these elections. These investments are recorded at fair value and are classified as marketable securities in the
F-11
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The investments that the Company may sell within the next twelve months are carried as current assets. Realized gains (losses) on marketable securities are determined by specific identification. Interest is recognized on an accrual basis, dividends are recorded as earned on the ex-dividend date. Interest, dividend income and the changes in fair value in trading securities are recorded in the accompanying consolidated statements of income in other income (loss), net.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is the price the Company would receive to sell an asset or transfer a liability (exit price) in an orderly transaction between market participants. For those assets and liabilities recorded or disclosed at fair value, the Company determines the fair value based upon the quoted market price, if available. If a quoted market price is not available for identical assets, the fair value is based upon the quoted market price of similar assets. The fair values are assigned a level within the fair value hierarchy as defined below:
| ◾ | Level 1: Observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical, unrestricted assets or liabilities. |
| ◾ | Level 2: Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. These include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active. |
| ◾ | Level 3: Unobservable inputs that reflect the reporting entity’s own assumptions. |
As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the Company held certain assets that are required to be measured at fair value on a recurring basis. These included cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, marketable securities and foreign currency forward contracts and an interest rate swap. The carrying amount of cash, cash equivalents and accounts receivable approximates fair value due to the short maturity of these instruments. The fair values of marketable securities classified as trading are obtained from quoted market prices, and the fair values of foreign currency forward contracts or the interest rate swap are obtained from a third party, which are based on quoted prices or market prices for similar assets and financial instruments.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company is exposed to interest rate risk due to the outstanding senior secured credit agreement entered on June 15, 2016. The Company entered into an interest rate swap agreement to effectively convert its variable debt to a fixed-rate basis. The principal objective of this contract is to eliminate or reduce the variability of the cash flows in interest payments associated with the Company’s long-term debt, thus reducing the impact of interest rate changes on future interest payment cash flows. The Company has determined that the interest rate swap qualifies as a cash flow hedge in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification 815, Derivatives and Hedging. Changes in the fair value of an interest rate swap agreement designated as a cash flow hedge are recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (“AOCI”) within stockholders’ equity and are amortized to interest expense over the term of the related debt.
Foreign Currency Forward Contracts Not Designated as Hedges
The Company has established a program that primarily utilizes foreign currency forward contracts to offset the risks associated with the effects of certain foreign currency exposures primarily originating from intercompany balances due to cross border work performed in the ordinary course of business. These foreign currency forward contracts are neither used for trading purposes nor are they designated as hedging instruments pursuant to Accounting Standards Codification 815, Derivatives and Hedging. Accordingly, the fair value of these contracts is recorded as of the end of the reporting period in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets, while the change in fair value is recorded to the accompanying consolidated statements of income.
Business Acquisitions
Business acquisitions are accounted for under the acquisition method. The acquisition method requires the reporting entity to identify the acquirer, determine the acquisition date, recognize and measure the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed and any noncontrolling interest in the acquired entity, and recognize and
F-12
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
measure goodwill or a gain from the purchase. The acquiree’s results are included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements from the date of acquisition. Assets acquired and liabilities assumed are recorded at their fair values and the excess of the purchase price over the amounts assigned is recorded as goodwill, or if the fair value of the assets acquired exceeds the purchase price consideration, a bargain purchase gain is recorded. Adjustments to fair value assessments are generally recorded to goodwill over the measurement period (not longer than twelve months). The acquisition method also requires that acquisition-related transaction and post-acquisition restructuring costs be charged to expense as committed and requires the Company to recognize and measure certain assets and liabilities including those arising from contingencies and contingent consideration in a business combination.
Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment is carried at cost less accumulated depreciation. Leasehold improvements are amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of the asset, or the lease term, whichever is shorter. Software development costs incurred for internal use projects are capitalized and, once placed in service, amortized using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life, generally three to seven years. All other property and equipment is depreciated or amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of three to ten years.
The Company reviews long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of an asset may not be recoverable. In fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, there were no such impairment charges recorded.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of assets acquired. The goodwill impairment test compares the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill. If the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value, goodwill of the reporting unit would be considered impaired. To measure the amount of the impairment loss, the implied fair value of a reporting unit’s goodwill is compared to the carrying amount of that goodwill. The implied fair value of goodwill is determined in the same manner as the amount of goodwill recognized in a business combination. If the carrying amount of a reporting unit’s goodwill exceeds the implied fair value of that goodwill, an impairment loss is recognized in an amount equal to that excess. For each of these tests, the fair value of each of the Company’s reporting units is determined using a combination of valuation techniques, including a discounted cash flow methodology. To corroborate the discounted cash flow analysis performed at each reporting unit, a market approach is utilized using observable market data such as comparable companies in similar lines of business that are publicly traded or which are part of a public or private transaction (to the extent available). Results of the annual impairment test performed as of January 31, 2018, indicated that the fair value of each reporting unit exceeded its carrying amount and no reporting units were at risk of failing the impairment test. As a result, no impairment charge was recognized. There was also no indication of potential impairment during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2018 that would have required further testing.
Intangible assets primarily consist of customer lists, non-compete agreements, proprietary databases, IP and trademarks and are recorded at their estimated fair value at the date of acquisition and are amortized in a pattern in which the asset is consumed if that pattern can be reliably determined or using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives which range from one to 24 years. For intangible assets subject to amortization, an impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount of the intangible assets is not recoverable and exceeds fair value. The carrying amount of the intangible assets is considered not recoverable if it exceeds the sum of the undiscounted cash flows expected to result from use of the asset. Intangible assets with indefinite lives are not amortized but are reviewed annually for impairment or more frequently whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the fair value of the asset may be less than its carrying amount. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, there were no indicators of impairment with respect to the Company’s intangible assets.
Compensation and Benefits Expense
Compensation and benefits expense in the accompanying consolidated statements of income consist of compensation and benefits paid to consultants (employees who originate business), executive officers and
F-13
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
administrative and support personnel. The most significant portions of this expense are salaries and the amounts paid under the annual performance related bonus plan to employees. The portion of the expense applicable to salaries is comprised of amounts earned by employees during a reporting period. The portion of the expenses applicable to annual performance related bonuses refers to the Company’s annual employee performance related bonus with respect to a fiscal year, the amount of which is communicated and paid to each eligible employee following the completion of the fiscal year.
Each quarter, management makes its best estimate of its annual performance related bonuses, which requires management to, among other things, project annual consultant productivity (as measured by engagement fees billed and collected by executive search consultants and revenue and other performance/profitability metrics for Hay Group and Futurestep consultants), the level of engagements referred by a consultant in one line of business to a different line of business, Company performance including profitability, competitive forces and future economic conditions and their impact on the Company’s results. At the end of each fiscal year, annual performance related bonuses take into account final individual consultant productivity (including referred work), Company/line of business results including profitability, the achievement of strategic objectives and the results of individual performance appraisals, and the current economic landscape. Accordingly, each quarter the Company reevaluates the assumptions used to estimate annual performance related bonus liability and adjusts the carrying amount of the liability recorded on the consolidated balance sheet and reports any changes in the estimate in current operations.
Because annual performance-based bonuses are communicated and paid only after the Company reports its full fiscal year results, actual performance-based bonus payments may differ from the prior year’s estimate. Such changes in the bonus estimate historically have been immaterial and are recorded in current operations in the period in which they are determined. The performance related bonus expense was $220.4 million, $179.6 million and $186.5 million for the years ended April 30, 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively, included in compensation and benefits expense in the consolidated statements of income.
Other expenses included in compensation and benefits expense are due to changes in deferred compensation and pension plan liabilities, changes in cash surrender value (‘CSV’) of company owned life insurance (“COLI”) contracts, amortization of stock compensation awards, payroll taxes and employee insurance benefits. Investments and other assets include long-term retention awards that are generally amortized over four to five years.
Deferred Compensation and Pension Plans
For financial accounting purposes, the Company estimates the present value of the future benefits payable under the deferred compensation and pension plans as of the estimated payment commencement date. The Company also estimates the remaining number of years a participant will be employed by the Company. Then, each year during the period of estimated employment, the Company accrues a liability and recognizes expense for a portion of the future benefit using the unit credit cost method for Senior Executive Incentive Plan (“SEIP”), Wealth Accumulation Plan (“WAP”), Enhanced Wealth Accumulation Plan (“EWAP”) and the Worldwide Executive Benefit Plan (“WEB”) and the pension plan acquired under Legacy Hay, while the medical and life insurance plan and Long Term Performance Unit Plan (“LTPU Plan”) uses the projected unit credit cost method. The amounts charged to operations are made up of service and interest costs and the expected return on plan assets. Actuarial gains and losses are initially recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). The actuarial gains/losses included in accumulated other comprehensive income are amortized to the consolidated statements of income, if at the beginning of the year, the amount exceeds 10% of the greater of the projected benefit obligation and market-related plan assets. The amortization included in periodic benefit cost is divided by the average remaining service of inactive plan participants, or the period for which benefits will be paid, if shorter. The expected return on plan assets takes into account the current fair value of plan assets and reflects the Company’s estimate for trust asset returns given the current asset allocation and any expected changes to the asset allocation and current and future market conditions.
In calculating the accrual for future benefit payments, management has made assumptions regarding employee turnover, participant vesting, violation of non-competition provisions and the discount rate. Management
F-14
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
periodically reevaluates all assumptions. If assumptions change in future reporting periods, the changes may impact the measurement and recognition of benefit liabilities and related compensation expense.
Executive Capital Accumulation Plan
The Company, under the ECAP makes discretionary contributions and such contributions may be granted to key employees annually based on the employee’s performance. Certain key management may also receive Company contributions upon commencement of employment. The Company amortizes these contributions on a straight-line basis as they vest, generally over a four to five-year period. The amounts that are expected to be paid to employees over the next 12 months are classified as a current liability included in compensation and benefits payable in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
The ECAP is accounted for whereby the changes in the fair value of the vested amounts owed to the participants are adjusted with a corresponding charge (or credit) to compensation and benefits costs.
Cash Surrender Value of Life Insurance
The Company purchased COLI policies or contracts insuring the lives of certain employees eligible to participate in certain of the deferred compensation and pension plans as a means of funding benefits under such plans. The Company purchased both fixed and variable life insurance contracts and does not purchase “split-dollar” life insurance policy contracts. The Company historically has had both contracts or policies that provide for a fixed or guaranteed rate of return and a variable rate of return depending on the return of the policies’ investment in their underlying portfolio in equities and bonds. Beginning in fiscal 2017 the Company currently only holds contracts or policies that provide for a fixed or guaranteed rate of return. The CSV of these COLI contracts are carried at the amounts that would be realized if the contract were surrendered at the balance sheet date, net of the outstanding loans from the insurer. The Company has the intention and ability to continue to hold these COLI policies and contracts. Additionally, the loans secured by the policies do not have any scheduled payment terms and the Company also does not intend to repay the loans outstanding on these policies until death benefits under the policy have been realized. Accordingly, the investment in COLI is classified as long-term in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
The change in the CSV of COLI contracts, net of insurance premiums paid and gains realized, is reported in compensation and benefits expense. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the Company held contracts with gross CSV of $186.8 million and $180.3 million, offset by outstanding policy loans of $66.7 million and $67.2 million, respectively. If the issuing insurance companies were to become insolvent, the Company would be considered a general creditor for $120.1 million and $61.3 million of net CSV as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively; therefore, these assets are subject to credit risk. Management, together with its outside advisors, routinely monitors the claims paying abilities of these insurance companies.
Restructuring Charges, Net
The Company accounts for its restructuring charges as a liability when the obligations are incurred and records such charges at fair value. Such charges include one-time employee termination benefits and cost to terminate leases, including remaining lease payments. Changes in the estimates of the restructuring charges are recorded in the period the change is determined.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company has employee compensation plans under which various types of stock-based instruments are granted. These instruments principally include restricted stock units, restricted stock and an Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”). The Company recognizes compensation expense related to restricted stock units, restricted stock and the estimated fair value of stock purchases under the ESPP on a straight-line basis over the service period for the entire award.
Translation of Foreign Currencies
Generally, financial results of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries are measured in their local currencies. Assets and liabilities are translated into U.S. dollars at exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet date, while revenue
F-15
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
and expenses are translated at weighted-average exchange rates during the fiscal year. Resulting translation adjustments are recorded as a component of accumulated comprehensive income. Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries and the translation of the financial results of subsidiaries operating in highly inflationary economies are included in general and administrative expense in the period incurred. Foreign currency losses, on an after-tax basis, included in net income were $2.2 million and $8.7 million during fiscal 2018 and 2016, respectively. Foreign currency gains, on an after-tax basis, included in net income were $0.2 million during fiscal 2017.
On February 17, 2016, the Venezuelan government announced a devaluation of the Bolivar, from the official exchange rate of 6.3 Bolivars per USD to 10.0 Bolivars per USD and streamlined the previous three-tiered currency exchange mechanism into a dual currency exchange mechanism. The weaker of the two rates is a free-floating exchange rate that at the time of its introduction, sold dollars at approximately 200 Bolivars per USD. The economic and political environment in Venezuela has continued to deteriorate and the currency exchange restrictions have become more onerous. The Company had used the previously prevailing official exchange rate of 6.3 Bolivars per USD to re-measure our Venezuelan subsidiary’s financial statements in previous periods, but after careful consideration, at the time of the devaluation, the Company decided to adopt the free-floating exchange rate during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2016 as it more appropriately reflects the ability to convert Bolivars to U.S. dollars given the deteriorating environment in Venezuela. The devaluation of the Bolivar to approximately 260 Bolivars per USD resulted in a pre-tax charge of $13.7 million, or diluted loss per share of $0.26 during fiscal 2016. In fiscal 2018 and 2017, the Bolivar continued to weaken but did not materially impact our results of operations.
Income Taxes
There are two components of income tax expense: current and deferred. Current income tax expense (benefit) approximates taxes to be paid or refunded for the current period. Deferred income tax expense (benefit) results from changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities between periods. These gross deferred tax assets and liabilities represent decreases or increases in taxes expected to be paid in the future because of future reversals of temporary differences in the basis of assets and liabilities as measured by tax laws and their basis as reported in the consolidated financial statements. Deferred tax assets are also recognized for tax attributes such as net operating loss carryforwards and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are presented net on the consolidated balance sheets by tax jurisdiction. Valuation allowances are then recorded to reduce deferred tax assets to the amounts management concludes are more likely than not to be realized.
Income tax benefits are recognized and measured based upon a two-step model: (1) a tax position must be more-likely-than-not to be sustained based solely on its technical merits in order to be recognized and (2) the benefit is measured as the largest dollar amount of that position that is more-likely-than-not to be sustained upon settlement. The difference between the benefit recognized for a position and the tax benefit claimed on a tax return is referred to as an unrecognized tax benefit. The Company records income tax related interest and penalties within income tax expense.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments which potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of cash, cash equivalents, investments, foreign currency forward contracts, interest rate swap, receivables due from clients and net CSV due from insurance companies, which are discussed above. Cash equivalents include investments in money market securities while investments include mutual funds. Investments are diversified throughout many industries and geographic regions. The Company conducts periodic reviews of its customers’ financial condition and customer payment practices to minimize collection risk on accounts receivable. At April 30, 2018 and 2017, the Company had no other significant credit concentrations.
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
In March 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (the “FASB”) issued guidance on accounting for certain aspects of share-based payments to employees. The new guidance requires excess tax benefits and tax deficiencies to be recorded in the income statement when the awards vest or are settled. Furthermore, cash flows
F-16
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
related to excess tax benefits will no longer be separately classified as a financing activity apart from other income tax cash flows. The guidance also allows companies to repurchase more of an employee’s shares for tax withholding purposes without triggering liability accounting, clarifying that all cash payments made on an employee’s behalf for withheld shares should be presented as a financing activity in the consolidated statements of cash flows and provides an accounting policy election to account for forfeitures as they occur. The provisions of the guidance are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016 and were adopted by the Company effective May 1, 2017. The primary impact of the adoption was the recognition of excess tax benefits in our provision for income taxes in the current year compared to recording it previously as a component of equity. Additional amendments to the accounting for income taxes and minimum statutory withholding tax requirements had no impact to retained earnings, where the cumulative effect of these changes are required to be recorded. The Company elected to apply the presentation for cash flows related to excess tax benefits retrospectively for all periods presented which resulted in an increase to cash provided by operations and decrease in cash provided by financing activities of $0.1 million and $4.9 million for fiscal 2017 and 2016, respectively. The presentation requirements for cash flows related to employee taxes paid for withheld shares had no impact on any of the periods presented on our consolidated cash flows statements since such cash flows have historically been presented as a financing activity. The Company elected to account for forfeitures as they occur, rather than estimating the expected forfeitures over the vesting period. This election did not have an impact on the Company’s financial statements.
In March 2018, the FASB issued Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) No. 118 amending accounting for the tax effects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Act”). The new guidance allows companies to complete the accounting under ASC 740 within a one-year measurement period from the Tax Act enactment date. This update was effective upon issuance. The amounts recorded as a result of the enactment of the Tax Act, specifically the impact of the Transition Tax and the remeasurement of deferred tax balances, are provisional estimates. The Company will continue to appropriately refine these amounts within the measurement period, which will be completed no later than December 22, 2018.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards - Not Yet Adopted
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, which superseded revenue recognition requirements regarding contracts with customers to transfer goods or services or for the transfer of nonfinancial assets. Under this new guidance, entities are required to recognize revenue that depicts the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The transfer is considered to occur when the customer obtains control of the goods or services delivered. The guidance provides a five-step analysis to be performed on transactions to determine when and how revenue is recognized. The new guidance is effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those annual years beginning after December 15, 2017. The Company will adopt this guidance in its fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018.
The Company organized a team and developed a project plan to guide the implementation. The project plan included working sessions to review, evaluate and document the arrangements with customers under our various reporting units to identify potential differences that would result from applying the requirements of the new standard.
The Company completed its evaluation of the impact of ASU 2014-09 for all its revenue streams and selected the modified retrospective method as the transition method, which will include a cumulative-effect adjustment as of the date of adoption. The impact to recruitment process outsourcing, advisory and products revenue is not material, although there will be minor process changes to comply with ASU 2014-09. As to executive search and recruitment for non-executive professionals, the implementation of ASU 2014-09 will result in timing differences in the recognition of uptick revenue (uptick revenue occurs when a placement’s actual compensation is higher than the original estimated compensation). Currently the Company recognizes uptick revenue as the amount becomes fixed and determinable. Under ASU 2014-09, however, upticks are considered variable consideration and the Company will be required to estimate upticks at contract inception and recognize the revenue over the service period.
F-17
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
In February 2016, the FASB issued guidance on accounting for leases that generally requires all leases to be recognized on the consolidated balance sheet. The provisions of the guidance are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018 and early adoption is permitted. The Company plans to adopt this guidance in fiscal year beginning May 1, 2019. The provisions of the guidance are to be applied using a modified retrospective approach. The Company is still evaluating the effect this guidance will have on the consolidated financial statements. Based on our initial assessment, the Company expects that upon adoption it will report an increase in assets and liabilities on our consolidated balance sheet as a result of recognizing right-of-use assets and lease liabilities related to lease agreements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued guidance on the classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments in the statement of cash flows. The new guidance provides clarification on specific cash flow issues regarding presentation and classification in the statement of cash flows with the objective of reducing the existing diversity in practice. The amendments in this update are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. The Company plans to adopt this guidance in its fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018. The provisions of the guidance are to be applied using a retrospective transition method. The adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued guidance that clarifies the definition of a business. The new guidance assists a company when evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions (disposals) of assets or businesses. The provisions of the guidance require that if the fair value of the gross assets acquired (or disposed of) is substantially concentrated in a single identifiable asset or a group of similar identifiable assets, then it is not a business. The provisions of the guidance are effective for annual years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods, with early adoption permitted. The Company plans to adopt this guidance in its fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018. The provisions of the guidance are to be applied prospectively. The adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued guidance simplifying the test for goodwill impairment. The new guidance simplifies the test for goodwill impairment by removing Step 2 from the goodwill impairment test. Companies will now perform the goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount, recognizing an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value not to exceed the total amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit. An entity still has the option to perform the qualitative assessment for a reporting unit to determine if the quantitative impairment test is necessary. The amendments of this standard are effective for goodwill impairment tests in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted for goodwill impairment tests performed after January 1, 2017. The Company is evaluating the adoption timeline and the effects that the standard will have on the consolidated financial statements.
In March 2017, the FASB issued guidance that changes the presentation of net periodic pension cost and net periodic postretirement benefit cost. The new guidance will change the presentation of net periodic benefit cost related to employer sponsored defined benefit plans and other postretirement benefits. Service cost will be included within the same income statement line item as other compensation costs arising from services rendered during the period, while other components of net periodic benefit pension cost will be presented separately outside of operating income. Additionally, only service costs may be capitalized in assets. The amendments of this standard are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those years. The Company will adopt this guidance in its fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018. The adoption of this standard is not anticipated to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In May 2017, the FASB issued guidance clarifying the scope of modification accounting for stock compensation. The new standard provides guidance about which changes to the terms or conditions of a share-based payment award require an entity to apply modification accounting in Topic 718. This pronouncement is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, but early adoption is permitted. The Company will adopt this guidance in its fiscal year beginning May 1, 2018. The adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
F-18
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
In August 2017, the FASB issued guidance amending and simplifying accounting for hedging activities. The new guidance will refine and expand strategies that qualify for hedge accounting and simplify the application of hedge accounting in certain situations. The amendments of this standard are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018. The Company will adopt this guidance in its fiscal year beginning May 1, 2019. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting this guidance.
In February 2018, the FASB issued guidance that provides companies the option to reclassify stranded tax effects within accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net to retained earnings resulting from the Tax Act. The new guidance requires companies to disclose whether they decided to reclassify the income tax effects of the Tax Act from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net to retained earnings and to disclose a policy for releasing the income tax effects from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net. The guidance is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018, but early adoption is permitted. If companies elect to reclassify the stranded tax effects the guidance allows it to be recorded in the period of adoption or retrospectively to each period in which the effect of the Tax Act is recognized. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting this guidance.
2. Basic and Diluted Earnings Per Share
Accounting Standards Codification 260, Earnings Per Share, requires companies to treat unvested share-based payment awards that have non-forfeitable rights to dividends prior to vesting as a separate class of securities in calculating earnings per share. We have granted and expect to continue to grant to certain employees under our restricted stock agreements, grants that contain non-forfeitable rights to dividends. Such grants are considered participating securities. Therefore, we are required to apply the two-class method in calculating earnings per share. The two-class method of computing earnings per share is an earnings allocation formula that determines earnings per share for each class of common stock and participating security according to dividends declared (or accumulated) and participation rights in undistributed earnings. The dilutive effect of participating securities is calculated using the more dilutive of the treasury method or the two-class method.
Basic earnings per common share was computed using the two-class method by dividing basic net earnings attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted earnings per common share was computed using the two-class method by dividing diluted net earnings attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding plus dilutive common equivalent shares. Dilutive common equivalent shares include all in-the-money outstanding options or other contracts to issue common stock as if they were exercised or converted. Financial instruments that are not in the form of common stock, but when converted into common stock increase earnings per share, are anti-dilutive and are not included in the computation of diluted earnings per share.
During fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, restricted stock awards of 0.6 million shares, 0.5 million shares and 0.6 million shares, respectively, were outstanding but not included in the computation of diluted earnings per share because they were anti-dilutive.
F-19
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
The following table summarizes basic and diluted earnings per common share attributable to common stockholders:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Korn/Ferry International |
$ | 133,779 | $ | 84,181 | $ | 30,913 | ||||||
| Less: distributed and undistributed earnings to nonvested restricted stockholders |
1,426 | 765 | 280 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic net earnings attributable to common stockholders |
132,353 | 83,416 | 30,633 | |||||||||
| Add: undistributed earnings to nonvested restricted stockholders |
1,187 | 560 | 82 | |||||||||
| Less: reallocation of undistributed earnings to nonvested restricted stockholders |
1,169 | 553 | 81 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted net earnings attributable to common stockholders |
$ | 132,371 | $ | 83,423 | $ | 30,634 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||
| Basic weighted-average number of common shares outstanding |
55,426 | 56,205 | 52,372 | |||||||||
| Effect of dilutive securities: |
||||||||||||
| Restricted stock |
822 | 646 | 487 | |||||||||
| Stock options |
5 | 24 | 50 | |||||||||
| ESPP |
1 | 25 | 20 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted weighted-average number of common shares outstanding |
56,254 | 56,900 | 52,929 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net earnings per common share: |
||||||||||||
| Basic earnings per share |
$ | 2.39 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 0.58 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted earnings per share |
$ | 2.35 | $ | 1.47 | $ | 0.58 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
3. Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is comprised of net income and all changes to stockholders’ equity, except those changes resulting from investments by stockholders (changes in paid-in capital) and distributions to stockholders (dividends) and is reported in the accompanying consolidated statements of comprehensive income. Accumulated comprehensive loss, net of taxes, is recorded as a component of stockholders’ equity.
The components of accumulated other comprehensive loss were as follows:
| April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments |
$ | (32,399 | ) | $ | (55,359 | ) | ||
| Deferred compensation and pension plan adjustments, net of taxes |
(9,073 | ) | (15,127 | ) | ||||
| Interest rate swap unrealized gain (loss), net of taxes |
1,337 | (578 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net |
$ | (40,135 | ) | $ | (71,064 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
F-20
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
The following table summarizes the changes in each component of accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income:
| Foreign Currency Translation |
Deferred Compensation and Pension Plan (1) |
Unrealized Gains (Losses) on Marketable Securities |
Unrealized (losses) gains on interest rate swap (2) |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of May 1, 2015 |
$ | (20,919 | ) | $ | (19,708 | ) | $ | 4 | $ | — | $ | (40,623 | ) | |||||||
| Unrealized losses arising during the period |
(15,420 | ) | (3,653 | ) | (4 | ) | — | (19,077 | ) | |||||||||||
| Reclassification of realized net losses to net income |
— | 1,789 | — | — | 1,789 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Balance as of April 30, 2016 |
(36,339 | ) | (21,572 | ) | — | — | (57,911 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Unrealized (losses) gains arising during the period |
(19,020 | ) | 4,584 | — | (635 | ) | (15,071 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Reclassification of realized net losses to net income |
— | 1,861 | — | 57 | 1,918 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Balance as of April 30, 2017 |
(55,359 | ) | (15,127 | ) | — | (578 | ) | (71,064 | ) | |||||||||||
| Unrealized gains arising during the period |
22,960 | 4,813 | — | 1,465 | 29,238 | |||||||||||||||
| Reclassification of realized net losses to net income |
— | 1,241 | — | 450 | 1,691 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Balance as of April 30, 2018 |
$ | (32,399 | ) | $ | (9,073 | ) | $ | — | $ | 1,337 | $ | (40,135 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | The tax effects on unrealized gains (losses) were $2.5 million, $1.9 million and $(2.3) million as of April 30, 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively. The tax effects on reclassifications of realized net losses were $0.8 million, $1.2 million and $1.1 million as of April 30, 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively. |
| (2) | The tax effects on unrealized gains (losses) were $0.8 million and $(0.4) million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The tax effect on the reclassification of realized net losses to net income was $0.3 million as of April 30, 2018. |
4. Employee Stock Plans
Stock-Based Compensation
The following table summarizes the components of stock-based compensation expense recognized in the Company’s consolidated statements of income for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Restricted stock |
$ | 20,282 | $ | 18,045 | $ | 18,288 | ||||||
| ESPP |
1,187 | 913 | 590 | |||||||||
| Stock options |
— | — | 17 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total stock-based compensation expense, pre-tax |
21,469 | 18,958 | 18,895 | |||||||||
| Tax benefit from stock-based compensation expense |
(7,319 | ) | (4,756 | ) | (7,347 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total stock-based compensation expense, net of tax |
$ | 14,150 | $ | 14,202 | $ | 11,548 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Stock Incentive Plan
At the Company’s 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, held on October 6, 2016, the Company’s stockholders approved an amendment and restatement to the Korn/Ferry International Amended and Restated 2008 Stock Incentive Plan (the 2016 amendment and restatement being “The Third A&R 2008 Plan”), which among other things, increased the number of shares under the plan by 5,500,000, increasing the current maximum number of shares that may be issued under the plan to 11,200,000 shares, subject to certain changes in the Company’s capital structure and other extraordinary events. The Third A&R 2008 Plan provides for the grant of awards to eligible participants, designated as either nonqualified or incentive stock options, restricted stock and restricted stock units, any of which may be performance-based or market-based, and incentive bonuses, which may be paid in cash or stock or a combination thereof. Under the Third A&R 2008 Plan, the ability to issue full-value awards is limited by requiring full-value stock awards to count 2.3 times as much as stock options.
F-21
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Restricted Stock
The Company grants time-based restricted stock awards to executive officers and other senior employees generally vesting over a four-year period. In addition, certain key management members typically receive time-based restricted stock awards upon commencement of employment and may receive them annually in conjunction with the Company’s performance review. Time-based restricted stock awards are granted at a price equal to fair value, which is determined based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. The Company recognizes compensation expense for time-based restricted stock awards on a straight-line basis over the vesting period.
The Company also grants market-based and performance-based restricted stock units to executive officers and other senior employees. The market-based units vest after three years depending upon the Company’s total stockholder return over the three-year performance period relative to other companies in its selected peer group. The fair value of these market-based restricted stock units are determined by using extensive market data that is based on historical Company and peer group information. The Company recognizes compensation expense for market-based restricted stock units on a straight-line basis over the vesting period.
Performance-based restricted stock units vest after three years depending upon the Company meeting certain objectives that are set at the time the restricted stock unit is issued. Performance-based restricted stock units are granted at a price equal to fair value, which is determined based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. At the end of each reporting period, the Company estimates the number of restricted stock units expected to vest, based on the probability that certain performance objectives will be met, exceeded, or fall below target levels, and the Company takes into account these estimates when calculating the expense for the period.
Restricted stock activity is summarized below:
| April 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Shares | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Shares | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
|||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-vested, beginning of year |
1,581 | $ | 29.74 | 1,506 | $ | 34.12 | 1,560 | $ | 22.15 | |||||||||||||||
| Granted |
650 | $ | 37.60 | 852 | $ | 17.43 | 784 | $ | 39.19 | |||||||||||||||
| Vested |
(431 | ) | $ | 26.13 | (751 | ) | $ | 24.15 | (809 | ) | $ | 16.35 | ||||||||||||
| Forfeited. |
(70 | ) | $ | 33.26 | (26 | ) | $ | 26.80 | (29 | ) | $ | 23.38 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Non-vested, end of year |
1,730 | $ | 33.45 | 1,581 | $ | 29.74 | 1,506 | $ | 34.12 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
As of April 30, 2018, there were 0.7 million shares and 0.2 million non-vested shares outstanding relating to market-based and performance-based restricted stock units, respectively, with total unrecognized compensation totaling $8.3 million and $3.0 million, respectively.
As of April 30, 2018, there was $30.8 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to all non-vested awards of restricted stock, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.3 years. During fiscal 2018 and 2017, 108,089 shares and 205,440 shares of restricted stock totaling $3.8 million and $4.8 million, respectively, were repurchased by the Company, at the option of the employee, to pay for taxes related to vesting of restricted stock.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The Company has an ESPP that, in accordance with Section 423 of the Internal Revenue Code, allows eligible employees to authorize payroll deductions of up to 15% of their salary to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock at 85% of the fair market price of the common stock on the last day of the enrollment period. Employees may not purchase more than $25,000 in stock during any calendar year. The maximum number of shares that may be issued under the ESPP is 3.0 million shares. During fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, employees
F-22
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
purchased 198,749 shares at $31.77 per share, 207,141 shares at $20.93 per share and 95,135 shares at $28.83 per share, respectively. As of April 30, 2018, the ESPP had approximately 1.1 million shares remaining available for future issuance.
Common Stock
During fiscal 2018, 2017, and 2016, the Company issued 41,075 shares, 53,955 shares and 87,648 shares of common stock, respectively, as a result of the exercise of stock options, with cash proceeds from the exercise of $0.6 million, $0.8 million and $1.3 million, respectively.
During fiscal 2018 and 2017, the Company repurchased (on the open market) 984,079 shares and 1,140,576 shares, respectively, of the Company’s common stock for $33.1 million and $28.8 million, respectively. No shares were repurchased during fiscal 2016, other than to satisfy minimum tax withholding requirements upon the vesting of restricted stock as described above.
5. Financial Instruments
The following tables show the Company’s financial instruments and balance sheet classification as of April 30, 2018 and 2017:
| April 30, 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value Measurement | Balance Sheet Classification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost | Unrealized Gains |
Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Marketable Securities, Current |
Marketable Securities, Non-current |
Income Taxes & Other Receivables |
Other Accrued Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Level 1: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 519,818 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 519,818 | $ | 519,818 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Money market funds |
1,030 | — | — | 1,030 | 1,030 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mutual funds (1) |
127,077 | 11,040 | (1,032 | ) | 137,085 | — | 14,293 | 122,792 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 647,925 | $ | 11,040 | $ | (1,032 | ) | $ | 657,933 | $ | 520,848 | $ | 14,293 | $ | 122,792 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Level 2: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency |
$ | — | $ | 1,778 | $ | (1,025 | ) | $ | 753 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 753 | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
$ | — | $ | 2,076 | $ | — | $ | 2,076 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 2,076 | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| April 30, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value Measurement | Balance Sheet Classification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost | Unrealized Gains |
Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Marketable Securities, Current |
Marketable Securities, Non-current |
Income Taxes & Other Receivables |
Other Accrued Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Level 1: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 409,824 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 409,824 | $ | 409,824 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Money market funds |
1,058 | — | — | 1,058 | 1,058 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mutual funds (1) |
113,818 | 6,697 | (578 | ) | 119,937 | — | 4,363 | 115,574 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 524,700 | $ | 6,697 | $ | (578 | ) | $ | 530,819 | $ | 410,882 | $ | 4,363 | $ | 115,574 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Level 2: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency forward contracts |
$ | — | $ | 129 | $ | (846 | ) | $ | (717 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (717 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swap |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | (947 | ) | $ | (947 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (947 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
F-23
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
| (1) | These investments are held in trust for settlement of the Company’s vested obligations of $118.2 million and $99.5 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively, under the ECAP (see Note 6 — Deferred Compensation and Retirement Plans). During fiscal 2018 and 2017, the fair value of the investments increased; therefore, the Company recognized income of $10.3 million and $10.8 million, respectively which was recorded in other income (loss), net. During fiscal 2016, the fair value of the investments decreased; therefore, the Company recognized a loss of $3.3 million, which was recorded in other income (loss), net. |
Investments in marketable securities classified as trading are based upon employee elections from a pre-determined set of securities in the ECAP and the Company invests in marketable securities to mirror these elections. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the Company’s investments in marketable securities classified as trading consist of mutual funds for which market prices are readily available. Investments in marketable securities classified as available-for-sale securities are made based on the Company’s investment policy, which restricts the types of investments that can be made. As of April 30, 2018 and April 30, 2017, the Company does not hold marketable securities classified as available-for-sale. During fiscal 2016, the Company received $13.1 million in proceeds from maturities of available-for-sale marketable securities.
Designated Derivatives—Interest Rate Swap Agreement
In March 2017, the Company entered into an interest rate swap contract with a notional amount of $129.8 million to hedge the variability to changes in cash flows attributable to interest rate risks caused by changes in interest rates related to its variable rate debt. The Company has designated the swap as a cash flow hedge. The notional amount will be amortized so that the amount is always half of the principal balance of the debt outstanding. As of April 30, 2018, the notional amount was $119.5 million. The interest rate swap agreement matures on June 15, 2021 and locks the interest rates on half the debt outstanding at 1.919%, exclusive of the credit spread on the debt.
The fair value of the derivative designated as a cash flow hedge instrument is as follows:
| April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||
| Derivative asset: |
||||||||
| Interest rate swap contract |
$ | 2,076 | $ | — | ||||
| Derivative liability: |
||||||||
| Interest rate swap contract |
$ | — | $ | 947 | ||||
During fiscal 2018 and 2017, the Company recognized the following gains and losses on the interest rate swap:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||
| Gains (Losses) recognized in other comprehensive income (net of tax effects of $828 and ($406), respectively) | $ | 1,465 | $ | (635) | ||||
| Losses reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income into interest (expense) income, net | $ | (730 | ) | $ | (94) | |||
As the critical terms of the hedging instrument and the hedged forecasted transaction are the same, the Company has concluded the changes in the fair value or cash flows attributable to the risk being hedged are expected to completely offset at inception and on an ongoing basis.
We estimate that $0.4 million of derivative gains included in AOCI as of April 30, 2018 will be reclassified into interest (expense) income, net within the following 12 months. The cash flows related to interest rate swap contracts are included in net cash provided by operating activities.
F-24
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Foreign Currency Forward Contracts Not Designated as Hedges
The fair value of derivatives not designated as hedge instruments are as follows:
| April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Derivative assets: |
||||||||
| Foreign currency forward contracts |
$ | 1,778 | $ | 129 | ||||
| Derivative liabilities: |
||||||||
| Foreign currency forward contracts |
$ | 1,025 | $ | 846 | ||||
As of April 30, 2018, the total notional amounts of the forward contracts purchased and sold were $80.8 million and $78.5 million, respectively. As of April 30, 2017, the total notional amounts of the forward contracts purchased and sold were $19.4 million and $70.0 million, respectively. The Company recognizes forward contracts as a net asset or net liability on the consolidated balance sheets as such contracts are covered by master netting agreements. During fiscal 2018 and 2016, the Company incurred losses of $3.7 million and $1.8 million, respectively, related to forward contracts which is recorded in general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. These losses offset foreign currency gains that result from transactions denominated in a currency other than the Company’s functional currency. During fiscal 2017, the Company incurred gains of $0.6 million related to forward contracts which is recorded in general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. These gains offset foreign currency losses that result from transactions denominated in a currency other than the Company’s functional currency. The cash flows related to foreign currency forward contracts are included in cash flows from operating activities in the accompanying statements of cash flow.
6. Deferred Compensation and Retirement Plans
The Company has several deferred compensation and retirement plans for eligible consultants and vice presidents that provide defined benefits to participants based on the deferral of current compensation or contributions made by the Company subject to vesting and retirement or termination provisions.
The total benefit obligations for these plans were as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||
| Deferred compensation and pension plans |
$ | 100,404 | $ | 95,596 | ||||
| Medical and Life Insurance plan |
7,157 | 12,147 | ||||||
| International retirement plans |
13,729 | 12,021 | ||||||
| Executive Capital Accumulation Plan |
128,430 | 111,584 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total benefit obligation |
249,720 | 231,348 | ||||||
| Less: current portion of benefit obligation |
(21,991 | ) | (11,443 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Non-current benefit obligation |
$ | 227,729 | $ | 219,905 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Deferred Compensation and Pension Plans
The Enhanced Wealth Accumulation Plan (“EWAP”) was established in fiscal 1994, which replaced the Wealth Accumulation Plan (“WAP”). Certain vice presidents elected to participate in a “deferral unit” that required the participant to contribute a portion of their compensation for an eight year period, or in some cases, make an after-tax contribution, in return for defined benefit payments from the Company over a fifteen year period at retirement age of 65 or later. Participants were able to acquire additional “deferral units” every five years. Vice presidents who did not choose to roll over their WAP units into the EWAP continue to be covered under the earlier version in which participants generally vest and commence receipt of benefit payments at retirement age of 65. In
F-25
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
June 2003, the Company amended the EWAP and WAP, so as not to allow new participants or the purchase of additional deferral units by existing participants.
The Company also maintains a Senior Executive Incentive Plan (“SEIP”) for participants approved by the Board. Generally, to be eligible, the vice president must be participating in the EWAP. Participation in the SEIP required the participant to contribute a portion of their compensation during a four-year period, or in some cases make an after-tax contribution, in return for a defined benefit paid by the Company generally over a fifteen year period after ten years of participation in the plan or such later date as elected by the participant. In June 2003, the Company amended the SEIP, so as not to allow new participants or the purchase of additional deferral units by existing participants.
The Company has a defined benefit pension plan, referred to as the Worldwide Executive Benefit (“WEB”), covering certain executives in the U.S. and foreign countries. The WEB is designed to integrate with government sponsored and local benefits and provide a monthly benefit to vice presidents upon retirement from the Company. Each year a plan participant accrued and was fully vested in one-twentieth of the targeted benefits expressed as a percentage set by the Company for that year. Upon retirement, a participant receives a monthly benefit payment equal to the sum of the percentages accrued over such participant’s term of employment, up to a maximum of 20 years, multiplied by the participant’s highest average monthly salary during the 36 consecutive months in the final 72 months of active full-time employment through June 2003. In June 2003, the Company froze the WEB, so as to not allow new participants, future accruals and future salary increases.
In conjunction with the acquisition of Legacy Hay on December 1, 2015, the Company acquired multiple pension and savings plans covering certain of its employees worldwide. Among these plans is a defined benefit pension plan for certain employees in the United States. The assets of this plan are held separately from the assets of the sponsors in self-administered funds. The plan is funded consistent with local statutory requirements.
On July 8, 2016, the Company established the LTPU Plan in order to promote the success of the Company by providing a select group of management and highly compensated employees with nonqualified supplemental retirement benefits as an additional means to attract, motivate and retain such employee. A unit award has a base value of $50,000 for the purpose of determining the payment that would be made upon early termination for a partially vested unit awards. The units vest 25% on each anniversary date with the unit becoming fully vested on the fourth anniversary of the grant date, subject to the participant’s continued service as of each anniversary date. Each vested unit award will pay out an annual benefit of $25,000 for each of five years commencing on the seventh anniversary of the grant date.
F-26
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Deferred Compensation and Pension Plans
The following tables reconcile the benefit obligation for the deferred compensation plans:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||
| Change in benefit obligation: |
||||||||
| Benefit obligation, beginning of year |
$ | 121,042 | $ | 124,566 | ||||
| Service cost |
11,691 | 5,507 | ||||||
| Interest cost |
3,469 | 3,820 | ||||||
| Actuarial gain |
(1,574 | ) | (4,791 | ) | ||||
| Administrative expenses paid |
(166 | ) | — | |||||
| Benefits paid from plan assets |
(1,833 | ) | (1,884 | ) | ||||
| Benefits paid from cash |
(6,135 | ) | (6,176 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Benefit obligation, end of year |
126,494 | 121,042 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Change in fair value of plan assets: |
||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets, beginning of year |
25,446 | 24,867 | ||||||
| Actual return on plan assets |
2,425 | 2,463 | ||||||
| Benefits paid from plan assets |
(1,833 | ) | (1,884 | ) | ||||
| Administrative expenses paid |
(166 | ) | — | |||||
| Employer contributions |
218 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Fair value of plan assets, end of year |
26,090 | 25,446 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Funded status and balance, end of year (1) |
$ | (100,404) | $ | (95,596) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Current liability |
$ | 6,496 | $ | 6,182 | ||||
| Non-current liability |
93,908 | 89,414 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liability |
$ | 100,404 | $ | 95,596 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Plan Assets - weighted-average asset allocation: |
||||||||
| Debt securities |
55 | % | 46 | % | ||||
| Equity securities |
44 | % | 54 | % | ||||
| Other |
1 | % | — | % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
100 | % | 100 | % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | The Company purchased COLI contracts insuring the lives of certain employees eligible to participate in the deferred compensation and pension plans as a means of funding benefits under such plans. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the Company held contracts with gross CSV of $186.8 million and $180.3 million, offset by outstanding policy loans of $66.7 million and $67.2 million, respectively. |
The fair value measurements of the defined benefit plan assets fall within the following levels of the fair value hierarchy as of April 30, 2018 and 2017:
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||
| April 30, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||
| Mutual funds |
$ | — | $ | 25,899 | $ | — | $ | 25,899 | ||||||||
| Money market funds |
191 | — | — | 191 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 191 | $ | 25,899 | $ | — | $ | 26,090 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| April 30, 2017: |
||||||||||||||||
| Mutual funds |
$ | — | $ | 25,446 | $ | — | $ | 25,446 | ||||||||
| Money market funds |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | — | $ | 25,446 | $ | — | $ | 25,446 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
F-27
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Plan assets are invested in various asset classes that are expected to produce a sufficient level of diversification and investment return over the long term. The investment goal is a return on assets that is at least equal to the assumed actuarial rate of return over the long term within reasonable and prudent levels of risk. Investment policies reflect the unique circumstances of the respective plans and include requirements designed to mitigate risk including quality and diversification standards. Asset allocation targets are reviewed periodically with investment advisors to determine the appropriate investment strategies for acceptable risk levels. Our target allocation ranges are as follows: equity securities 40% to 50%, debt securities 45% to 55% and other assets of 5% to 10%. We establish our estimated long-term return on plan assets considering various factors including the targeted asset allocation percentages, historic returns and expected future returns. In fiscal 2017, the Company changed the method of achieving the target allocation by investing in mutual funds that are only available to institutional investors rather than owning specific equity and debt instruments as was done in previous years. The mutual funds are valued at fair value as determined by the net asset value of shares held at year-end.
The components of net periodic benefits costs are as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
| Service cost |
$ | 11,691 | $ | 5,507 | $ | — | ||||||
| Interest cost |
3,469 | 3,820 | 3,423 | |||||||||
| Amortization of actuarial loss |
2,308 | 3,051 | 2,924 | |||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
(1,594 | ) | (1,559 | ) | (682 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost |
$ | 15,874 | $ | 10,819 | $ | 5,665 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The weighted-average assumptions used in calculating the benefit obligations were as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| Discount rate, beginning of year |
3.57 | % | 3.18 | % | 3.28 | % | ||||||
| Discount rate, end of year |
3.93 | % | 3.57 | % | 3.18 | % | ||||||
| Rate of compensation increase |
0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | ||||||
| Expected long-term rates of return on plan assets |
6.25 | % | 6.50 | % | 6.50 | % | ||||||
At April 30, 2017, the Company elected to change the method it uses to estimate the interest and service components of net periodic cost for its defined benefit pension and supplemental benefit plans, which impacted the net periodic cost in fiscal 2018. The Company utilized a full yield curve approach in the estimation of these components by applying the specific spot rates along the yield curve used in the determination of the benefit obligation to the relevant projected cash flows. Previously, the Company estimated the interest and service cost components utilizing a single weighted-average discount rate derived from the yield curve used to measure the benefit obligation at the beginning of the period. This change compared to the previous method impacted the interest and service components of net periodic cost in future periods. The Company made this change to provide a more precise measurement of interest and service costs by improving the correlation between projected benefit cash flows to the corresponding spot yield curve rates. This change did not affect the measurement of the total benefit obligation as the change in the interest and service costs is offset in net actuarial gains and losses. The impact to interest and service costs is not significant. The Company accounted for this change prospectively as a change in accounting estimate.
F-28
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, as appropriate, are expected to be paid over the next ten years as follows:
| Year Ending April 30, |
Deferred Retirement Plans | |||
| (in thousands)
|
||||
| 2019 |
$ | 9,463 | ||
| 2020 |
9,552 | |||
| 2021 |
9,252 | |||
| 2022 |
9,179 | |||
| 2023 |
9,061 | |||
| 2024-2028 |
58,903 | |||
During fiscal 2019, the Company expects to recognize $1.8 million in net periodic benefit expense from deferred compensation and pension plans that will be transferred from accumulated other comprehensive income through the amortization of actuarial losses in the consolidated statements of income.
Medical and Life Insurance Plan
In conjunction with the acquisition of Legacy Hay on December 1, 2015, the Company inherited a benefit plan which offers medical and life insurance coverage to 128 participants. The Company amended the plan and required any active participants that were not yet eligible for benefits to retire within a short time frame in order to receive any benefits from the plan. As a result of the amendment, participants eligible to the plan declined and the Company reduced the benefit obligation by $4.0 million against other comprehensive income (loss) during fiscal 2018. Medical and life insurance benefit plans are unfunded.
The following table reconciles the benefit obligation for the medical and life insurance plan:
| Year End April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||
| Change in benefit obligation: |
||||||||
| Benefit obligation, beginning of year |
$ | 12,147 | $ | 13,006 | ||||
| Plan amendment |
(4,008 | ) | — | |||||
| Service cost |
94 | 155 | ||||||
| Interest cost |
366 | 426 | ||||||
| Actuarial gain |
(875 | ) | (833 | ) | ||||
| Benefits paid |
(567 | ) | (607 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Benefit obligation, end of year |
$ | 7,157 | $ | 12,147 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Current liability |
$ | 668 | $ | 765 | ||||
| Non-current liability |
6,489 | 11,382 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liability |
$ | 7,157 | $ | 12,147 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
F-29
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
The components of net periodic benefits costs are as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
| Service cost |
$ | 94 | $ | 155 | $ | 62 | ||||||
| Interest cost |
366 | 426 | 208 | |||||||||
| Net periodic service credit amortization |
(308 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost |
$ | 152 | $ | 581 | $ | 270 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
The weighted-average assumptions used in calculating the medical and life insurance plan were as follows:
|
| |||||||||||
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| Discount rate, beginning of year or acquisition date |
3.75 | % | 3.36 | % | 4.10 | % | ||||||
| Discount rate, end of year |
3.94 | % | 3.75 | % | 3.36 | % | ||||||
| Healthcare care cost trend rate |
7.00 | % | 7.00 | % | 7.00 | % | ||||||
We anticipate that the health care cost trend rate assumption will be 5.0% by fiscal 2022. Increasing the assumed health care cost trend rate by one-percentage point would increase the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation for the medical and life insurance plan by less than $0.1 million. Decreasing the assumed health care cost trend rate by one-percentage point would decrease the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation for the medical and life insurance plan by less than $0.1 million.
Benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, as appropriate, are expected to be paid over the next ten years as follows:
| Year Ending April 30, |
Medical and Life Insurance | |||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| 2019 |
$ | 676 | ||
| 2020 |
667 | |||
| 2021 |
643 | |||
| 2022 |
620 | |||
| 2023 |
601 | |||
| 2024-2028 |
2,555 | |||
During fiscal 2019, the Company expects to recognize $0.3 million in net periodic benefit income from the medical and life insurance plan that will be transferred from accumulated other comprehensive income through the amortization of prior service credit in the consolidated statements of income.
International Retirement Plans
The Company also maintains various retirement plans and other miscellaneous deferred compensation arrangements in 21 foreign jurisdictions. The aggregate of the long-term benefit obligation accrued at April 30, 2018 and 2017 is $13.7 million for 1,999 participants and $12.0 million for 1,710 participants, respectively. The Company’s contribution to these plans was $10.7 million and $9.3 million in fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Executive Capital Accumulation Plan
The Company’s ECAP is intended to provide certain employees an opportunity to defer salary and/or bonus on a pre-tax basis. In addition, the Company, as part of its compensation philosophy, makes discretionary contributions into the ECAP and such contributions may be granted to key employees annually based on the employee’s performance. Certain key management may also receive Company ECAP contributions upon commencement of employment. The Company amortizes these contributions on a straight-line basis over the service period,
F-30
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
generally a four to five year period. Participants have the ability to allocate their deferrals among a number of investment options and may receive their benefits at termination, retirement or ‘in service’ either in a lump sum or in quarterly installments over one to 15 years. The ECAP amounts that are expected to be paid to employees over the next 12 months are classified as a current liability included in compensation and benefits payable on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
The Company issued ECAP awards during fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016 of $6.2 million, $6.2 million and $23.2 million, respectively.
The ECAP is accounted for whereby the changes in the fair value of the vested amounts owed to the participants are adjusted with a corresponding charge (or credit) to compensation and benefits costs. During fiscal 2018 and 2017, the deferred compensation liability increased; therefore, the Company recognized compensation expense of $11.1 million and $10.6 million, respectively. Offsetting the increases in compensation and benefits liability was an increase in the fair value of marketable securities classified as trading (held in trust to satisfy obligations of the ECAP liabilities) of $10.3 million and $10.8 million in fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively, recorded in other income (loss), net on the consolidated statements of income. During fiscal 2016, the deferred compensation liability decreased; therefore, the Company recognized a credit to compensation expense of $1.7 million, offset by a decrease in the fair value of marketable securities classified as trading (held in trust to satisfy obligations of the ECAP liabilities) of $3.3 million, recorded in other income (loss), net on the consolidated statements of income.
Changes in the ECAP liability were as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year |
$ | 111,584 | $ | 105,676 | ||||
| Employee contributions |
5,036 | 5,349 | ||||||
| Amortization of employer contributions |
12,175 | 13,667 | ||||||
| Gain on investment |
11,095 | 10,565 | ||||||
| Employee distributions |
(11,923 | ) | (23,044 | ) | ||||
| Exchange rate fluctuations |
463 | (629 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Balance, end of year |
128,430 | 111,584 | ||||||
| Less: current portion |
(14,827 | ) | (4,496 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Non-current portion |
$ | 113,603 | $ | 107,088 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the unamortized portion of the Company contributions to the ECAP was $19.2 million and $25.5 million, respectively.
Defined Contribution Plan
The Company has a defined contribution plan (“401(k) plan”) for eligible employees. Participants may contribute up to 50% of their base compensation as defined in the plan agreement. In addition, the Company has the option to make matching contributions. The Company intends to make matching contributions related to fiscal 2018 in fiscal 2019. The Company made a $2.3 million matching contribution in fiscal 2018 related to contributions made by employees in fiscal 2017 and a $1.8 million matching contribution in fiscal 2017 related to contributions made by employees in fiscal 2016.
Company Owned Life Insurance
The Company purchased COLI contracts insuring the lives of certain employees eligible to participate in the deferred compensation and pension plans as a means of funding benefits under such plans. The gross CSV of these contracts of $186.8 million and $180.3 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively, is offset by outstanding policy loans of $66.7 million and $67.2 million in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Total death benefits payable, net of loans under COLI contracts, were $226.0 million and $220.6 million at April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Management intends to use the future
F-31
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
death benefits from these insurance contracts to fund the deferred compensation and pension arrangements; however, there may not be a direct correlation between the timing of the future cash receipts and disbursements under these arrangements. The CSV value of the underlying COLI investments increased by $7.8 million, $4.9 million and $4.0 million during fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively, recorded as a decrease in compensation and benefits expense. In addition, certain policies are held in trusts to provide additional benefit security for the deferred compensation and pension plans. As of April 30, 2018, COLI contracts with a net CSV of $81.5 million and death benefits, net of loans, of $150.4 million were held in trust for these purposes.
7. Restructuring Charges, Net
During fiscal 2016, the Company implemented a restructuring plan in order to rationalize its cost structure by eliminating redundant positions and consolidating office space due to the acquisition of Legacy Hay on December 1, 2015. This resulted in restructuring charges, net of $33.0 million in fiscal 2016, of which $32.1 million related to severance and $0.9 million, related to consolidation/abandonment of premises.
The Company continued the implementation of the fiscal 2016 restructuring plan in fiscal 2017 and 2018 in order to integrate the Hay Group entities that were acquired in fiscal 2016 by eliminating redundant positions and operational, general and administrative expenses and consolidating premises. This resulted in restructuring charges of $0.1 million in fiscal 2018 related to consolidation of premises and restructuring charges of $34.6 million in fiscal 2017, of which $16.0 million related to severance and $18.6 million related to consolidation of premises.
Changes in the restructuring liability were as follows:
| Severance | Facilities | Total | ||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
| Liability as of April 30, 2016 |
$ | 5,293 | $ | 669 | $ | 5,962 | ||||||
| Restructuring charges, net |
15,963 | 18,637 | 34,600 | |||||||||
| Reductions for cash payments |
(14,974 | ) | (8,703 | ) | (23,677 | ) | ||||||
| Non-cash items |
— | (2,024 | ) | (2,024 | ) | |||||||
| Exchange rate fluctuations |
(941 | ) | (225 | ) | (1,166 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Liability as of April 30, 2017 |
5,341 | 8,354 | 13,695 | |||||||||
| Restructuring charges, net |
— | 78 | 78 | |||||||||
| Reductions for cash payments |
(4,541 | ) | (6,050 | ) | (10,591 | ) | ||||||
| Exchange rate fluctuations |
251 | 563 | 814 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Liability as of April 30, 2018 |
$ | 1,051 | $ | 2,945 | $ | 3,996 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the restructuring liability is included in the current portion of other accrued liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets, except for $1.0 million and $4.6 million, respectively, of facilities costs which primarily relate to commitments under operating leases, net of estimated sublease income, which are included in other long-term liabilities.
The restructuring liability by segment is summarized below:
| April 30, 2018 | ||||||||||||
| Severance | Facilities | Total | ||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
| Executive Search |
||||||||||||
| North America |
$ | — | $ | 254 | $ | 254 | ||||||
| Asia Pacific |
— | 6 | 6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Executive Search |
— | 260 | 260 | |||||||||
| Hay Group |
1,051 | 2,602 | 3,653 | |||||||||
| Futurestep |
— | 83 | 83 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Liability as of April 30, 2018 |
$ | 1,051 | $ | 2,945 | $ | 3,996 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
F-32
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
| April 30, 2017 | ||||||||||||
| Severance | Facilities | Total | ||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
| Executive Search |
||||||||||||
| North America |
$ | 134 | $ | 250 | $ | 384 | ||||||
| Europe, Middle East and Africa (“EMEA”) |
393 | — | 393 | |||||||||
| Asia Pacific |
— | 6 | 6 | |||||||||
| Latin America |
— | 87 | 87 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Executive Search |
527 | 343 | 870 | |||||||||
| Hay Group |
4,814 | 7,879 | 12,693 | |||||||||
| Futurestep |
— | 132 | 132 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Liability as of April 30, 2017 |
$ | 5,341 | $ | 8,354 | $ | 13,695 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
8. Income Taxes
The provision for income taxes is based on reported income before income taxes. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities reflect the impact of temporary differences between the amounts of assets and liabilities recognized for financial reporting purposes and the amounts recognized for tax purposes, as measured by applying the currently enacted tax laws.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Act was enacted and contains significant changes to U.S. income tax law. The most significant impacts of the Tax Act on the Company’s current fiscal year include (1) a reduction in the U.S. corporate federal statutory income tax rate from 35.0% to 21.0% effective January 1, 2018, and (2) a one-time tax on accumulated foreign earnings (the “Transition Tax”), which is applicable at a rate of 15.5% on cash and other specified assets and 8% on other residual earnings. Because of our April 30 fiscal year end, the Company’s fiscal 2018 statutory federal tax rate is 30.4%.
As a result of the enactment of the Tax Act, the Company recorded a provisional tax charge of $18.4 million for the Transition Tax and a provisional tax benefit of $5.9 million from the remeasurement of our U.S. federal deferred tax assets and liabilities at the rate at which we expect these deferred tax balances to be realized. The amounts recorded as a result of the enactment of the Tax Act, specifically the impact of the Transition Tax and the remeasurement of deferred tax balances, are provisional estimates. Additional information and analysis are required to finalize the impact that the Tax Act will have on our financial results, including refinement of the computation of foreign subsidiaries earnings and the final determination of deferred tax balances subject to remeasurement. Additionally, anticipated future guidance from the Internal Revenue Service, state tax agencies, the Financial Accounting Standards Board and the Securities and Exchange Commission could result in changes to these provisional amounts. The Company will continue to appropriately refine these amounts within the measurement period allowed by SAB No.118, which will be completed no later than December 22, 2018.
F-33
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
The provision (benefit) for domestic and foreign income taxes was as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
| Current income taxes: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 29,400 | $ | (2,026 | ) | $ | 13,087 | |||||
| State |
2,863 | 1,207 | 3,271 | |||||||||
| Foreign |
44,434 | 23,334 | 16,394 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Current provision for income taxes |
76,697 | 22,515 | 32,752 | |||||||||
| Deferred income taxes: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
(3,530 | ) | 3,341 | (5,334 | ) | |||||||
| State |
(317 | ) | 341 | (1,838 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign |
(2,717 | ) | 2,907 | (6,620 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Deferred (benefit) provision for income taxes |
(6,564 | ) | 6,589 | (13,792 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total provision for income taxes |
$ | 70,133 | $ | 29,104 | $ | 18,960 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The domestic and foreign components of income from continuing operations before domestic and foreign income and other taxes and equity in earnings of unconsolidated subsidiaries were as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Domestic |
$ | 46,867 | $ | 5,539 | $ | 22,228 | ||||||
| Foreign |
158,866 | 110,470 | 26,534 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income before provision for income taxes and |
$ | 205,733 | $ | 116,009 | $ | 48,762 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate to the effective consolidated tax rate is as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| U.S. federal statutory income tax rate |
30.4 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| Non-deductible transaction costs |
— | — | 5.8 | |||||||||
| Foreign tax rates differential |
(2.3 | ) | (9.1 | ) | (2.8 | ) | ||||||
| COLI increase, net |
(1.2 | ) | (1.5 | ) | (2.9 | ) | ||||||
| Conclusion of U.S. federal tax audit |
— | — | (4.4 | ) | ||||||||
| Transition tax |
9.0 | — | — | |||||||||
| Deferred tax remeasurement |
(2.4 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Non-deductible operating expenses |
0.3 | 0.6 | 1.5 | |||||||||
| Devaluation of Venezuelan currency |
— | — | 7.4 | |||||||||
| Change in valuation allowance |
(2.3 | ) | (3.1 | ) | (6.2 | ) | ||||||
| Change in uncertain tax positions |
0.9 | — | 1.3 | |||||||||
| Foreign source income, net of credits generated |
(0.1 | ) | (0.1 | ) | 0.5 | |||||||
| Other |
1.8 | 3.3 | 3.7 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effective income tax rate |
34.1 | % | 25.1 | % | 38.9 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The higher effective tax rate in fiscal 2018 was due primarily to the enactment of the Tax Act. Korn Ferry will continue to appropriately refine these amounts within the measurement period allowed by SAB No.118, which will be completed no later than December 22, 2018. The lower effective tax rate in fiscal 2017 was due primarily to a higher percentage of taxable income arising in jurisdictions with lower statutory tax rates. In both fiscal 2018 and 2017, the Company recorded an income tax benefit from the reversal of valuation allowances previously recorded against deferred tax assets, including net operating losses, of certain foreign subsidiaries that have returned to profitability and are now more-likely-than-not to realize those deferred tax assets.
F-34
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Components of deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
| April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
| Deferred compensation |
$ | 67,852 | $ | 92,043 | ||||
| Loss and credit carryforwards |
22,297 | 32,854 | ||||||
| Reserves and accruals |
13,945 | 14,095 | ||||||
| Deferred rent |
6,827 | 9,797 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue |
1,793 | 2,434 | ||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
2,296 | 1,705 | ||||||
| Other |
982 | 3,041 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Gross deferred tax assets |
115,992 | 155,969 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
| Intangibles |
(57,046 | ) | (90,214 | ) | ||||
| Property and equipment |
(5,000 | ) | (11,507 | ) | ||||
| Prepaid expenses |
(19,123 | ) | (17,324 | ) | ||||
| Other |
(2,726 | ) | (2,485 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Gross deferred tax liabilities |
(83,895 | ) | (121,530 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Valuation allowances |
(15,682 | ) | (21,278 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax asset |
$ | 16,415 | $ | 13,161 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance if it is more-likely-than-not that some portion or all of the deferred tax asset will not be realized. Management believes uncertainty exists regarding the realizability of certain operating losses and has, therefore, established a valuation allowance for this portion of the deferred tax asset. Realization of the deferred tax asset is dependent on the Company generating sufficient taxable income of the appropriate nature in future years. Although realization is not assured, management believes that it is more likely than-not that the net deferred tax assets will be realized. Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are presented net on the consolidated balance sheets by tax jurisdiction.
As of April 30, 2018, the Company had U.S. federal net operating loss carryforwards of $3.2 million, which the Company anticipates will be fully utilized by fiscal 2028. The Company has state net operating loss carryforwards of $61.2 million, which, if unutilized, will begin to expire in fiscal 2019. The Company also has foreign net operating loss carryforwards of $87.8 million, which, if unutilized, will begin to expire in fiscal 2019.
The Company has not provided deferred income taxes on approximately $492.3 million of undistributed earnings of its foreign subsidiaries as such earnings are intended to be reinvested indefinitely. If a distribution of these earnings was to be made, the Company may be subject to state income and foreign withholding taxes. An estimate of such taxes, however, is not practicable.
The Company and its subsidiaries file federal and state income tax returns in the U.S. as well as in foreign jurisdictions. These income tax returns are subject to audit by the Internal Revenue Service (the ‘IRS’) and various state and foreign tax authorities. The IRS is currently auditing the fiscal year 2016 federal tax return. The States of California, Illinois, Minnesota, New York and the City of New York are currently auditing the Company’s state income tax returns for various fiscal years. Outside the United States, income tax returns of the Company’s subsidiaries are under audit in Canada, France and India. The Company’s income tax returns are not otherwise under examination in any material jurisdictions. The statute of limitations varies by jurisdiction in which the Company operates. With few exceptions, however, the Company’s tax returns for years prior to fiscal 2012 are no longer open to examination by tax authorities (including U.S. federal, state and foreign).
Unrecognized tax benefits are the differences between the amount of benefits of tax positions taken, or expected to be taken, on a tax return and the amount of benefits recognized for financial reporting purposes. As of April 30,
F-35
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
2018, the Company had a liability of $3.7 million for unrecognized tax benefits. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances of the unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits, beginning of year |
$ | 2,478 | $ | 2,095 | $ | 2,423 | ||||||
| Settlement with tax authority |
(708 | ) | — | (1,963 | ) | |||||||
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year |
1,116 | 383 | 1,305 | |||||||||
| Additions based on tax positions related to prior years |
788 | — | 330 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits, end of year |
$ | 3,674 | $ | 2,478 | $ | 2,095 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The liability for unrecognized tax benefits is included in income taxes payable in the consolidated balance sheets. The full amount of unrecognized tax benefits would impact the effective tax rate if recognized. In the next twelve months, it is reasonably possible that the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits could change due to resolution of certain tax matters either because the tax position are sustained on audit or the Company agrees to their disallowance. These resolutions could reduce the Company’s liability for unrecognized tax benefits by approximately $3.1 million. The Company does not expect a change in the amount of unrecognized tax benefits to have a material financial statement impact.
The Company classifies interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as a component of the provision for income taxes. The Company accrued approximately $0.3 million and no accrual for interest related to unrecognized tax benefits as of April 30, 2018 and April 30, 2017, respectively. The Company had no accrual for penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as of April 30, 2018 and April 30, 2017, respectively. The Company accrued approximately $0.3 million of interest related to unrecognized tax benefits over the last three fiscal years.
9. Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment include the following:
| April 30, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||
| Computer equipment and software (1) |
$ | 191,437 | $ | 160,399 | ||||
| Leasehold improvements |
82,467 | 75,921 | ||||||
| Furniture and fixtures |
42,889 | 39,848 | ||||||
| Automobiles |
1,305 | 1,956 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 318,098 | 278,124 | |||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(198,197 | ) | (168,557 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Property and equipment, net |
$ | 119,901 | $ | 109,567 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Depreciation expense for capitalized software was $12.8 million, $12.6 million and $11.3 million during fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively. The net book value of the Company’s computer software costs included in property and equipment, net was $46.4 million and $33.2 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. |
Depreciation expense for property and equipment was $33.8 million, $31.9 million and $24.5 million during fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
10. Long-Term Debt
On June 15, 2016, the Company entered into a senior secured $400 million Credit Agreement (the “Credit Agreement”) with a syndicate of banks and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association as administrative agent. On June 8, 2018, the Company entered into an amendment to the Credit Agreement. See Note 16—Subsequent Events. The Credit Agreement provides for, among other things: (a) a senior secured term loan facility in an aggregate principal amount of $275 million (the “ Term Facility”), (b) a senior secured revolving credit facility (the
F-36
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
“Revolver” and together with the Term Facility, the “Credit Facilities”) in an aggregate principal amount of $125 million, (c) annual term loan amortization of 7.5%, 7.5%, 10.0%, 10.0%, and 10.0%, with the remaining principal due at maturity, (d) certain customary affirmative and negative covenants, including a maximum consolidated total leverage ratio (as defined below) and a minimum interest coverage ratio, and (e) an expanded definition of permitted add-backs to Adjusted EBITDA in recognition of the accelerated integration actions. The Company’s credit agreement permits payment of dividends to stockholders and share repurchases so long as the pro forma leverage ratio is no greater than 2.50 to 1.00, and the pro forma domestic liquidity is at least $50.0 million. The Company drew down $275 million on the new term loan and used $140 million of the proceeds to pay-off the term loan that was outstanding as of April 30, 2016. Principal payments under the term facility are as follows:
| Year Ending April 30, |
Principal Payments on Term Loan |
|||
| (in thousands)
|
||||
| 2019 |
$ | 25,781 | ||
| 2020 |
27,500 | |||
| 2021 |
27,500 | |||
| 2022 |
158,125 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 238,906 | |||
|
|
|
|||
At the Company’s option, loans issued under the Credit Agreement will bear interest at either LIBOR or an alternate base rate, in each case plus the applicable interest rate margin. The interest rate applicable to loans outstanding under the Credit Facilities may fluctuate between LIBOR plus 1.25% per annum to LIBOR plus 2.00% per annum, in the case of LIBOR borrowings (or between the alternate base rate plus 0.25% per annum and the alternate base rate plus 1.00% per annum, in the alternative), based upon the Company’s total funded debt to Adjusted EBITDA ratio (as set forth in the Credit Agreement, the “consolidated leverage ratio”) at such time. In addition, the Company will be required to pay to the lenders a quarterly fee ranging from 0.20% to 0.35% per annum on the average daily unused amount of the Term Facility, based upon the Company’s consolidated leverage ratio at such time, and fees relating to the issuance of letters of credit. During fiscal 2018 and 2017, the average rate on the Term Facility was 2.60% and 2.23%, respectively.
Both the Revolver and the Term Facility mature on June 15, 2021 and may be prepaid and terminated early by the Company at any time without premium or penalty (subject to customary LIBOR breakage fees). The Term Facility is payable in quarterly installments with principal payments totaling $20.6 million and $15.5 million made during fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively. As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, $238.9 million and $259.5 million were outstanding under the Term Facility, respectively. The current and long-term portion of unamortized debt issuance costs associated with the long-term debt, was $2.7 million and $3.5 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The fair value of the Company’s Term Facility is based on borrowing rates currently required of loans with similar terms, maturity and credit risk. The carrying amount of the Term Facility approximates fair value because the base interest rate charged varies with market conditions and the credit spread is commensurate with current market spreads for issuers of similar risk. The fair value of the Term Facility is classified as a Level 2 liability in the fair value hierarchy. As of April 30, 2018, the Company was in compliance with its debt covenants.
As of April 30, 2018 and 2017, the Company had no borrowings under the Revolver. The Company had a total of $122.1 million and $122.0 million available under the Revolver after $2.9 million and $3.0 million standby letters of credit were issued as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The Company had a total of $7.4 million and $8.1 million of standby letters of credits with other financial institutions as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The standby letters of credits were generally issued as a result of entering into office premise leases.
The Company has outstanding borrowings against the CSV of COLI contracts of $66.7 million and $67.2 million at April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively. CSV reflected in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets is net of the outstanding borrowings, which are secured by the CSV of the life insurance policies. Principal payments are not scheduled and interest is payable at least annually at various fixed and variable rates ranging from 4.76% to 8.00%.
F-37
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
11. Business Segments
The Company currently operates through three business segments: Executive Search, Hay Group and Futurestep. The Executive Search segment focuses on recruiting Board of Director and C-level positions, in addition to research-based interviewing and onboarding solutions, for clients predominantly in the consumer, financial services, industrial, life sciences/healthcare and technology industries. Hay Group assists clients with ongoing assessment, compensation and development of their senior executives and management teams, and addresses four fundamental needs: Talent Strategy, Succession Management, Leadership Development, and Rewards, Motivation and Engagement, all underpinned by a comprehensive array of world-leading IP, products and tools. Futurestep is a global industry leader in high-impact talent acquisition solutions. Its portfolio of services includes global and regional RPO, project recruitment, individual professional search and consulting. The Executive Search business segment is managed by geographic regional leaders and Hay Group and Futurestep worldwide operations are managed by their Chief Executive Officers. The Executive Search geographic regional leaders and the Chief Executive Officers of Hay Group and Futurestep report directly to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company. The Company also operates a Corporate segment to record global expenses of the Company.
The Company evaluates performance and allocates resources based on the Company’s chief operating decision maker’s (“CODM”) review of (1) fee revenue and (2) adjusted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (“Adjusted EBITDA”). To the extent that such charges occur, Adjusted EBITDA excludes restructuring charges, integration/acquisition costs, certain separation costs and certain non-cash charges (goodwill, intangible asset and other than temporary impairment). The accounting policies for the reportable segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies, except the items described above are excluded from EBITDA to arrive at Adjusted EBITDA. For fiscal 2017 and 2016, Adjusted EBITDA includes deferred revenue adjustment related to the Legacy Hay acquisition, reflecting revenue that the Hay Group would have realized if not for business combination accounting that requires a company to record the acquisition balance sheet at fair value and write-off deferred revenue where no future services are required to be performed to earn that revenue. The accounting policies for the reportable segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies, except the items described above are excluded from EBITDA to arrive at Adjusted EBITDA.
F-38
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Financial highlights by business segment are as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
EMEA | Asia Pacific | Latin America |
Subtotal | Hay Group |
Futurestep | Corporate | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 408,098 | $ | 173,725 | $ | 96,595 | $ | 30,624 | $ | 709,042 | $ | 785,013 | $ | 273,162 | $ | — | $ | 1,767,217 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 421,260 | $ | 177,234 | $ | 98,062 | $ | 30,717 | $ | 727,273 | $ | 801,005 | $ | 291,241 | $ | — | $ | 1,819,519 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Korn/Ferry |
$ | 133,779 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
2,118 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income, net |
(11,525 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense, net |
9,676 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
(297 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
70,133 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
$ | 100,037 | $ | 26,768 | $ | 18,425 | $ | 4,022 | $ | 149,252 | $ | 100,939 | $ | 39,363 | $ | (85,670 | ) | $ | 203,884 | |||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and |
3,930 | 1,689 | 1,408 | 455 | 7,482 | 31,527 | 3,054 | 6,525 | 48,588 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income, net |
845 | 168 | 373 | 181 | 1,567 | 599 | 152 | 9,207 | 11,525 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
297 | — | — | — | 297 | — | — | — | 297 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA |
105,109 | 28,625 | 20,206 | 4,658 | 158,598 | 133,065 | 42,569 | (69,938 | ) | 264,294 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges |
— | — | 313 | — | 313 | (241 | ) | 6 | — | 78 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Integration/acquisition |
— | — | — | — | — | 9,151 | — | 279 | 9,430 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 105,109 | $ | 28,625 | $ | 20,519 | $ | 4,658 | $ | 158,911 | $ | 141,975 | $ | 42,575 | $ | (69,659 | ) | $ | 273,802 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiable assets (1) |
$ | 411,347 | $ | 198,815 | $ | 98,599 | $ | 23,832 | $ | 732,593 | $ | 1,092,474 | $ | 144,160 | $ | 318,687 | $ | 2,287,914 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Long-lived assets (1) |
$ | 22,813 | $ | 11,018 | $ | 10,834 | $ | 3,203 | $ | 47,868 | $ | 42,605 | $ | 6,390 | $ | 23,038 | $ | 119,901 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill (1) |
$ | 47,757 | $ | 47,501 | $ | 972 | $ | — | $ | 96,230 | $ | 458,169 | $ | 29,823 | $ | — | $ | 584,222 | ||||||||||||||||||
F-39
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
| Year Ended April 30, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
EMEA | Asia Pacific | Latin America |
Subtotal | Hay Group |
Futurestep | Corporate | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 356,625 | $ | 146,506 | $ | 80,169 | $ | 34,376 | $ | 617,676 | $ | 724,186 | $ | 223,659 | $ | — | $ | 1,565,521 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | — | — | — | — | 3,535 | — | — | 3,535 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted fee revenue |
$ | 356,625 | $ | 146,506 | $ | 80,169 | $ | 34,376 | $ | 617,676 | $ | 727,721 | $ | 223,659 | $ | — | $ | 1,569,056 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 369,803 | $ | 150,113 | $ | 81,744 | $ | 34,533 | $ | 636,193 | $ | 741,533 | $ | 243,943 | $ | — | $ | 1,621,669 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to |
$ | 84,181 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to |
3,057 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income, net |
(11,820 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense, net |
10,251 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
(333 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
29,104 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
$ | 81,550 | $ | 27,854 | $ | 8,580 | $ | 6,268 | $ | 124,252 | $ | 47,302 | $ | 29,986 | $ | (87,100 | ) | $ | 114,440 | |||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and |
3,812 | 1,030 | 1,060 | 483 | 6,385 | 32,262 | 2,818 | 5,795 | 47,260 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (loss), net |
844 | (15 | ) | 300 | 684 | 1,813 | 341 | (91 | ) | 9,757 | 11,820 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
333 | — | — | — | 333 | — | — | — | 333 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA |
86,539 | 28,869 | 9,940 | 7,435 | 132,783 | 79,905 | 32,713 | (71,548 | ) | 173,853 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, |
1,719 | 629 | 1,495 | 773 | 4,616 | 29,663 | 101 | 220 | 34,600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Integration/acquisition |
— | — | — | — | — | 14,440 | — | 7,939 | 22,379 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | — | — | — | — | 3,535 | — | — | 3,535 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Separation costs |
— | — | — | — | — | 609 | — | — | 609 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 88,258 | $ | 29,498 | $ | 11,435 | $ | 8,208 | $ | 137,399 | $ | 128,152 | $ | 32,814 | $ | (63,389 | ) | $ | 234,976 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiable assets (1) |
$ | 340,069 | $ | 158,927 | $ | 87,845 | $ | 26,897 | $ | 613,738 | $ | 1,057,611 | $ | 116,717 | $ | 274,832 | $ | 2,062,898 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Long-lived assets (1) |
$ | 23,746 | $ | 11,089 | $ | 8,371 | $ | 3,262 | $ | 46,468 | $ | 37,846 | $ | 6,693 | $ | 18,560 | $ | 109,567 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill (1) |
$ | 46,201 | $ | 44,976 | $ | 972 | $ | — | $ | 92,149 | $ | 457,241 | $ | 27,475 | $ | — | $ | 576,865 | ||||||||||||||||||
F-40
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
| Year Ended April 30, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
EMEA | Asia Pacific | Latin America |
Subtotal | Hay Group |
Futurestep | Corporate | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 371,345 | $ | 144,319 | $ | 80,506 | $ | 26,744 | $ | 622,914 | $ | 471,145 | $ | 198,053 | $ | — | $ | 1,292,112 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | — | — | — | — | 10,967 | — | — | 10,967 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted fee revenue |
$ | 371,345 | $ | 144,319 | $ | 80,506 | $ | 26,744 | $ | 622,914 | $ | 482,112 | $ | 198,053 | $ | — | $ | 1,303,079 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 386,256 | $ | 148,285 | $ | 83,206 | $ | 26,781 | $ | 644,528 | $ | 488,217 | $ | 213,969 | $ | — | $ | 1,346,714 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to |
$ | 30,913 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to |
520 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other loss, net |
4,167 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest income, net |
(237 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
(1,631 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
18,960 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
$ | 100,381 | $ | 20,607 | $ | 12,572 | $ | (1,854 | ) | $ | 131,706 | $ | (3,415 | ) | $ | 26,702 | $ | (102,301 | ) | $ | 52,692 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and |
3,267 | 1,029 | 941 | 312 | 5,549 | 21,854 | 2,386 | 6,431 | 36,220 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other (loss) income, net |
(147 | ) | 433 | 21 | 312 | 619 | (868 | ) | 364 | (4,282 | ) | (4,167 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of |
437 | — | — | — | 437 | — | — | 1,194 | 1,631 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| EBITDA |
103,938 | 22,069 | 13,534 | (1,230 | ) | 138,311 | 17,571 | 29,452 | (98,958 | ) | 86,376 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restructuring charges, |
499 | 5,807 | 577 | 322 | 7,205 | 25,682 | 49 | 77 | 33,013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Integration/acquisition |
— | — | — | — | — | 17,607 | — | 27,802 | 45,409 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Venezuelan foreign |
— | — | — | 6,635 | 6,635 | 7,085 | — | — | 13,720 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | — | — | — | — | 10,967 | — | — | 10,967 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Separation costs |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 744 | 744 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 104,437 | $ | 27,876 | $ | 14,111 | $ | 5,727 | $ | 152,151 | $ | 78,912 | $ | 29,501 | $ | (70,335 | ) | $ | 190,229 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiable assets (1) |
$ | 227,228 | $ | 150,516 | $ | 86,394 | $ | 24,273 | $ | 488,411 | $ | 1,005,457 | $ | 104,396 | $ | 300,336 | $ | 1,898,600 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Long-lived assets (1) |
$ | 19,044 | $ | 4,817 | $ | 3,708 | $ | 1,479 | $ | 29,048 | $ | 42,974 | $ | 4,635 | $ | 18,779 | $ | 95,436 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill (1) |
$ | 48,320 | $ | 46,193 | $ | 972 | $ | — | $ | 95,485 | $ | 465,937 | $ | 28,650 | $ | — | $ | 590,072 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | As of the end of the fiscal year. |
F-41
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Fee revenue attributed to an individual customer or country, other than the U.S., did not account for more than 10% of the total fee revenue in fiscal 2018, 2017 or 2016. Fee revenue classified by country in which the Company derives revenues are as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
| U.S. |
$ | 778,470 | $ | 728,871 | $ | 669,585 | ||||||
| Other countries |
988,747 | 836,650 | 622,527 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total fee revenue |
$ | 1,767,217 | $ | 1,565,521 | $ | 1,292,112 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Other than the U.S., no single country controlled over 10% of the total long-lived assets, excluding financial instruments and tax assets. Long-lived assets, excluding financial instruments and tax assets, classified by controlling country are as follows:
| Year Ended April 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| U.S. (1) |
$ | 80,424 | $ | 70,949 | $ | 64,525 | ||||||
| Other countries |
39,477 | 38,618 | 30,911 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total long-lived assets |
$ | 119,901 | $ | 109,567 | $ | 95,436 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Includes Corporate long-lived assets |
12. Acquisitions
The following is a summary of acquisitions the Company completed during the periods indicated (no acquisitions were completed in fiscal 2018 or 2017:
| Year Ended April 30, 2016 (1) |
||||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| Receivables due from clients |
$ | 116,509 | ||
| Other current assets |
15,587 | |||
| Property and equipment |
29,428 | |||
| Intangible assets |
196,400 | |||
| Other non-current assets |
7,345 | |||
| Current liabilities |
125,640 | |||
| Deferred compensation and other retirement plans |
31,400 | |||
| Deferred tax liabilities |
58,729 | |||
| Other liabilities |
8,536 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Net assets acquired |
140,964 | |||
| Purchase price |
476,885 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Goodwill |
$ | 335,921 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Integration/acquisition costs |
$ | 45,409 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Goodwill by segment – Hay Group |
$ | 335,921 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| (1) | On December 1, 2015, the Company completed its acquisition of Legacy Hay, a global leader in people strategy and organizational performance, for $476.9 million, net of cash acquired. The purchase price consisted of $259.0 million in cash ($54 million from foreign locations), net of estimated cash acquired and 5,922,136 shares of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.01 per share (the “Consideration Shares”), representing an aggregate value of $217.9 million based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on The New York Stock Exchange on November 30, 2015. On November 23, 2015, the Company borrowed |
F-42
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
| $150 million from the Term Facility, to finance a portion of the Legacy Hay acquisition purchase price. As part of the acquisition, the Company has committed to a $40 million retention pool (of which $14.5 million and $9.0 million were paid in fiscal 2018 and 2017, respectively) for certain employees of Legacy Hay subject to certain circumstances. The remaining balance will be payable within 45 days after November 30, 2018. |
The acquisition strengthens the Company’s IP, enhances our geographical presence, adds complimentary capabilities to further leverage search relationships and broadens capabilities for assessment and development. It improves our ability to support the global business community not only in attracting top talent and designing compensation and reward incentives, but also with an integrated approach to the entire leadership and people continuum. Actual results of operations of Legacy Hay are included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements from December 1, 2015, the effective date of the acquisition, and includes $186.8 million, $740.2 million and $28.5 million in fee revenue, total assets and Adjusted EBITDA, respectively, with an Adjusted EBITDA margin of 14.4%, during fiscal 2016. Legacy Hay is included in the Hay Group segment.
The aggregate purchase price for Legacy Hay was allocated on a preliminary basis to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed on their estimated fair values at the date of acquisition. During fiscal 2017, the Company finalized the purchase price allocation by recording a decrease to goodwill of $8.2 million primarily as a result of tax returns filed for periods prior to the acquisition and an increase in other assets.
Pro forma financial information (unaudited)
Unaudited pro forma consolidated fee revenue and unaudited pro forma net income for fiscal 2016 were $1.6 billion and $23 million, respectively, as though the acquisition of Legacy Hay had occurred as of the beginning of fiscal 2016. The unaudited pro forma financial information is for illustrative purposes and is not indicative of the results of operations that would have been realized if the acquisition had been completed on the date indicated, nor is it indicative of future operating results.
The unaudited pro forma results primarily include adjustments for amortization charges for acquired intangible assets and property and equipment, compensation expense for retention awards and imputed interest expense on Term Facility and the related tax effect on the aforementioned items.
13. Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Changes in the carrying value of goodwill by reportable segment were as follows. Also see Note 16—Subsequent Events for information regarding an impairment charge that the Company will record in the first quarter of fiscal 2019:
| Executive Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
EMEA | Asia Pacific | Subtotal | Hay Group | Futurestep | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of May 1, 2016. |
$ | 48,320 | $ | 46,193 | $ | 972 | $ | 95,485 | $ | 465,937 | $ | 28,650 | $ | 590,072 | ||||||||||||||
| Adjustments |
— | — | — | — | (8,179 | ) | — | (8,179 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Exchange rate fluctuations. |
(2,119 | ) | (1,217 | ) | — | (3,336 | ) | (517 | ) | (1,175 | ) | (5,028 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance as of April 30, 2017. |
46,201 | 44,976 | 972 | 92,149 | 457,241 | 27,475 | 576,865 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Exchange rate fluctuations. |
1,556 | 2,525 | — | 4,081 | 928 | 2,348 | 7,357 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance as of April 30, 2018. |
$ | 47,757 | $ | 47,501 | $ | 972 | $ | 96,230 | $ | 458,169 | $ | 29,823 | $ | 584,222 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Tax deductible goodwill from the PIVOT Leadership acquisition was $7.0 million and $7.4 million as of April 30, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
F-43
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Intangible assets include the following:
| April 30, 2018 | April 30, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortized intangible assets: | Gross | Accumulated Amortization |
Net | Gross | Accumulated Amortization |
Net | ||||||||||||||||||
| Customer lists |
$ | 125,099 | $ | (42,248 | ) | $ | 82,851 | $ | 125,099 | $ | (31,094 | ) | $ | 94,005 | ||||||||||
| Intellectual property |
33,100 | (20,112 | ) | 12,988 | 33,100 | (16,994 | ) | 16,106 | ||||||||||||||||
| Proprietary databases |
4,256 | (3,628 | ) | 628 | 4,256 | (3,202 | ) | 1,054 | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-compete agreements |
910 | (873 | ) | 37 | 910 | (833 | ) | 77 | ||||||||||||||||
| Trademarks |
3,986 | (3,986 | ) | — | 3,986 | (3,986 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 167,351 | $ | (70,847 | ) | 96,504 | $ | 167,351 | $ | (56,109 | ) | 111,242 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Unamortized intangible assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trademarks |
|
106,000 | 106,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Exchange rate fluctuations |
|
712 | 77 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Intangible assets |
|
$ | 203,216 | $ | 217,319 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Amortization expense for amortized intangible assets was $14.7 million, $15.4 million and $11.7 million during fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Estimated annual amortization expense related to amortizing intangible assets is as follows:
| Year Ending April 30, |
Estimated Annual Amortization Expense |
|||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| 2019 |
$ | 13,487 | ||
| 2020 |
13,204 | |||
| 2021 |
13,071 | |||
| 2022 |
13,060 | |||
| 2023 |
11,208 | |||
| Thereafter |
32,474 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 96,504 | |||
|
|
|
|||
All amortizable intangible assets will be fully amortized by the end of fiscal 2032.
14. Commitments and Contingencies
Lease Commitments
The Company leases office premises and certain office equipment under leases expiring at various dates through 2030. Total rental expense during fiscal 2018, 2017 and 2016 amounted to $57.6 million, $56.8 million and $45.5 million, respectively.
Future minimum commitments under non-cancelable operating leases with lease terms in excess of one year excluding commitments accrued in the restructuring liability are as follows:
| Year Ending April 30, |
Lease Commitments |
|||
| (in thousands)
|
||||
| 2019 |
$ | 66,071 | ||
| 2020 |
62,305 | |||
| 2021 |
56,634 | |||
| 2022 |
49,322 | |||
| 2023 |
42,306 | |||
| Thereafter |
116,186 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 392,824 | |||
|
|
|
|||
F-44
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Employment Agreements
The Company has a policy of entering into offer letters of employment or letters of promotion with vice presidents which provide for an annual base salary and discretionary and incentive bonus payments. Certain key vice presidents who typically have been employed by the Company for several years may also have a standard form employment agreement. Upon termination without cause, the Company is required to pay the amount of severance due under the employment agreement, if any. The Company also requires its vice presidents to agree in their employment letters and their employment agreement, if applicable, not to compete with the Company during the term of their employment, and for a certain period after their employment ends.
Litigation
From time to time, the Company has been and is involved in litigation incidental to its business. The Company is currently not a party to any litigation which, if resolved adversely against the Company, would, in the opinion of management, after consultation with legal counsel, have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial position or results of operations.
15. Quarterly Results (Unaudited)
The following table sets forth certain unaudited consolidated statements of income data for the quarters in fiscal 2018 and 2017. The unaudited quarterly information has been prepared on the same basis as the annual financial statements and, in management’s opinion, includes all adjustments necessary to present fairly the information for the quarters presented.
| Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal 2018 | Fiscal 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| April 30 | January 31 | October 31 | July 31 | April 30 | January 31 | October 31 | July 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fee revenue |
$ | 475,364 | $ | 447,581 | $ | 443,018 | $ | 401,254 | $ | 406,065 | $ | 381,918 | $ | 401,917 | $ | 375,621 | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating income |
$ | 63,281 | $ | 48,622 | $ | 51,244 | $ | 40,737 | $ | 32,834 | $ | 30,542 | $ | 46,548 | $ | 4,516 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 42,309 | $ | 27,427 | $ | 36,732 | $ | 29,429 | $ | 27,736 | $ | 24,378 | $ | 31,056 | $ | 4,068 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Korn/Ferry International |
$ | 41,160 | $ | 27,247 | $ | 36,331 | $ | 29,041 | $ | 26,924 | $ | 23,897 | $ | 30,152 | $ | 3,208 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings per common share: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic. |
$ | 0.74 | $ | 0.49 | $ | 0.65 | $ | 0.52 | $ | 0.48 | $ | 0.42 | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||
| Diluted.
|
$
|
0.73
|
|
$
|
0.48
|
|
$
|
0.64
|
|
$
|
0.51
|
|
$
|
0.47
|
|
$
|
0.42
|
|
$
|
0.52
|
|
$
|
0.06
|
| ||||||||
16. Subsequent Events
Credit Agreement Amendment
On June 8, 2018, in anticipation of the approval by the Board of Directors of the Company of a rebranding and restructuring plan (which plan was approved on June 12, 2018), as discussed under “Impairment of Intangible Asset”, the Company entered into an amendment to its Credit Agreement. The Amendment permits a holding company reorganization (the “KF Merger”), after which a new public holding company, Korn Ferry, will own all of the stock of the Company, and will become effective when certain conditions set forth therein, including consummation of the KF Merger, are satisfied.
Quarterly Dividend Declaration
On June 12, 2018, the Board of Directors of the Company declared a cash dividend of $0.10 per share that will be paid on July 13, 2018 to holders of the Company’s common stock of record at the close of business on June 26, 2018. The declaration and payment of future dividends under the quarterly dividend policy will be at the discretion of the Board of Directors and will depend upon many factors, including the Company’s earnings, capital requirements, financial conditions, the terms of the Company’s indebtedness and other factors that the Board of Directors may deem to be relevant. The Board may amend, revoke or suspend the dividend policy at any time and for any reason.
F-45
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS April 30, 2018 (continued) |
Impairment of Intangible Asset
On June 12, 2018, the Company’s Board of Directors voted to approve a rebranding plan for the Company. This plan includes going to market under a single, master brand architecture, solely as Korn Ferry and sunsetting of all the Company’s sub-brands, including Futurestep, Hay Group and Lominger, among others. The Company is harmonizing under one brand to help accelerate the firm’s positioning as the preeminent organizational consultancy and bring more client awareness to its broad range of talent management solutions. The Hay Group back office was fully integrated as of the beginning of FY’18 and the Company then focused on its integrated go-to-market activities. This integrated go-to-market approach was a key driver in the 13% fee revenue growth in FY’18, which led to the decision to further integrate our go-to-market activities under one master brand – Korn Ferry. In the near term, the Company will discontinue the use of all sub-brands. Two of the Company’s sub-brands, Hay Group and Lominger came to Korn Ferry through acquisitions. In connection with the accounting for these acquisitions, $106 million of the purchase price was allocated to indefinite lived tradename intangible assets. As a result of the decision to discontinue their use, the Company will take a one-time, non-cash intangible asset impairment charge of $106 million, or $79 million on an after-tax basis in Q1 FY’19.
F-46
Table of Contents
|
|
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL AND SUBSIDIARIES
SCHEDULE II – VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
April 30, 2018
| Column A |
Column B | Column C | Column D | Column E | ||||||||||||||||
| Additions | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
Balance at Beginning of Period |
Charges to Cost and Expenses |
Recoveries (Charges) to Other Accounts (1) |
Deductions (2) | Balance at End of Period |
|||||||||||||||
| (in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended April 30, 2018 |
$ | 15,455 | $ | 13,675 | $ | 551 | $ | (11,836 | ) | $ | 17,845 | |||||||||
| Year Ended April 30, 2017 |
$ | 11,292 | $ | 12,987 | $ | (415 | ) | $ | (8,409 | ) | $ | 15,455 | ||||||||
| Year Ended April 30, 2016 |
$ | 9,958 | $ | 8,570 | $ | (270 | ) | $ | (6,966 | ) | $ | 11,292 | ||||||||
| Deferred tax asset valuation allowance: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended April 30, 2018 |
$ | 21,278 | $ | 3,421 | $ | — | $ | (9,017 | ) | $ | 15,682 | |||||||||
| Year Ended April 30, 2017 |
$ | 22,030 | $ | 7,931 | $ | — | $ | (8,683 | ) | $ | 21,278 | |||||||||
| Year Ended April 30, 2016
|
$
|
21,608
|
|
$
|
18,993
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
$
|
(18,571
|
)
|
$
|
22,030
|
| |||||
| (1) | Exchange rate fluctuations. |
| (2) | Allowance for doubtful accounts represents accounts written-off, net of recoveries and deferred tax asset valuation represents release of prior valuation allowances. |
F-47

EXHIBIT 2.4
EXECUTION VERSION
April 19, 2018
VIA EMAIL
Korn/Ferry International
1900 Avenue of the Stars, Suite 2600 Los Angeles,
California 90067
Attention: Mr. Brian Suh, Senior Vice President-Corporate Development
Cc: Jonathan M. Kuai Korn/Ferry
International
1900 Avenue of the Stars Suite 2600 Los Angeles, California
90067 [email protected]
Blank Rome LLP
2049 Century Park East 6th Floor
Los Angeles, California 90067
| Attention: | Michael C. Cohen |
| Email: | [email protected] |
Re: Letter Agreement--Extension of the Resolution Period
Mr. Suh:
Reference is hereby made to (a) that certain Stock Purchase Agreement, dated as of September 23, 2015 (the “Original Execution Date”) (as amended, modified or supplemented from time to time in accordance with its terms, the “Purchase Agreement”), entered into by and between HG (Bermuda) Limited, an exempted company incorporated with limited liability under the laws of Bermuda, and Korn/Ferry International, a Delaware corporation.
Capitalized terms used but not defined herein shall have the same meanings given to them in the Purchase Agreement, unless context otherwise requires.
This letter agreement (this “Letter Agreement”), effective as of the date first written above (the “Effective Date”), reflects the desire of Seller and Buyer to extend the period of time that comprises the Resolution Period and memorializes the agreement of Seller and Buyer with respect to the foregoing and such other matters contemplated by the Purchase Agreement, in each case as more particularly set forth herein.
1. Extension of Resolution Period. Each of Seller and Buyer hereby agree that, effective as of the Effective Date, the “Resolution Period” shall end on the five-year anniversary of the Closing, rather on the three-year anniversary of the Closing.
2. Continuation. Each of Seller and Buyer hereby agree that, effective as of the Effective Date, the first sentence of Section 5.19(a) of the Purchase Agreement shall be deleted in its entirety and replaced with the following:
“(a) Seller agrees that for the period commencing on the Closing Date and expiring on the five-year anniversary thereof, Seller shall continuously maintain its existence as an exempted company incorporated with limited liability under the laws of Bermuda (or such other legal entity) and shall not dissolve, liquidate or permit its dissolution or liquidation or take any other action to terminate its existence; provided, however, that in the event (i) the Pending Disputes have not been settled or otherwise subject to a Final Determination pursuant to clauses (i) and (ii) of Section 5.26(a) prior to the end of the Resolution Period or (ii) the acquisition or transfer of the Designated Interests shall have not been completed prior to the Resolution Period, Seller’s obligations to so maintain its existence shall continue for so long as reasonably necessary to sufficiently satisfy its obligations expressly contemplated by Sections 5.26 and 5.27 of the Purchase Agreement, as applicable (but in no event shall such obligations continue for more than three months from and following the Resolution Period, such time period, as applicable, the “Continuation Stub Period”).”
1

3. Information; Access and Books and Records.
(a) From and after the date hereof, and for a period (the “Reporting Period”) of no longer than the earlier of (i) the date of the settlement of or Final Determination with respect to the Pending Disputes and the completion of the acquisitions or transfers of the Designated Interests and (ii) the end of the Continuation Stub Period, on or within five days prior to each July 20, October 20, January 20 and April 20 arising during the Reporting Period, Seller shall deliver to Buyer a written “Schedule of Budget of Future Liabilities” (the “Liabilities Budget”), which shall be substantially in the form of the Liabilities Budget delivered to Buyer on the date hereof, reflecting as of the date of each such Liabilities Budget substantially the same information as is set forth in the “Liabilities Budget” delivered to the Buyer on the date hereof, together with a written statement from Seller setting forth a good faith accounting of the amount of all cash and cash equivalents (exclusive of the securities of the Buyer) being held by Seller as of the date of each such Liabilities Budget (it being understood that any immaterial errors with respect to such good faith accounting shall not be considered a breach of such obligation). Seller hereby covenants that during the Reporting Period, it shall use its best efforts to maintain and retain cash and cash equivalents (exclusive of the securities of the Buyer) in an aggregate amount in excess of the total amount of liabilities set forth in the “Worst Case” scenario reflected in the most recent Liabilities Budget.
(b) From and after the date hereof, and for a period of no longer than the earlier of
(i) six months following the settlement of or Final Determination with respect to the Pending Disputes and the completion of the acquisitions or transfers of the Designated Interests and
(ii) the end of the Continuation Stub Period, in connection with any reasonable business purpose, subject to any applicable Law and any applicable privileges (including attorney-client privilege) and contractual confidentiality obligations, upon reasonable prior notice, Seller shall (A) afford Buyer and its Representatives reasonable access, during normal business hours, to the offices, properties, books and records and other information and documents of Seller in respect of the Pending Disputes and/or the Designated Interests and (B) make available to Buyer and its Representatives the employees and other personnel of Seller whose assistance, expertise, testimony, notes and recollections or presence is necessary to assist Buyer or its Representatives in connection with Buyer and its Representatives’ inquiries for any of the purposes referred to in this Paragraph 3(a); provided, however, that such access or request shall not unreasonably interfere with the business or operations of Seller and its personnel. In no event shall the auditors and independent accountants of Seller be obligated to make any work papers available to any Person unless and until such Person has signed, if requested by such auditors or independent accountants, a customary confidentiality and hold harmless agreement relating to such access to work papers in form and substance reasonably acceptable to such auditors or independent accountants. If so reasonably requested by Seller, Buyer shall enter into a customary joint defense agreement with any one or more of Buyer and its Affiliates with respect to any information to be provided to Seller or any of its Representatives pursuant to this Paragraph 3(a). Seller shall be reimbursed promptly by Buyer (but in no event later than five Business Days from the date on which any request for reimbursement is made) for any reasonable and documented out-of-pocket expenses incurred by Seller in complying with any request by Buyer and/or its Representatives pursuant to this Paragraph 3(a).
(c) From and after the date hereof, Seller shall preserve and keep through the earlier of (i) the six-month anniversary of the settlement of or Final Determination with respect to the Pending Disputes and the completion of the acquisitions or transfers of the Designated Interests and (ii) the end of the end of the Continuation Stub Period, all books and records in respect of the Pending Disputes and/or the Designated Interests. After such period of time, before Seller may dispose of any of such books and records, Seller shall give Buyer at least ten days’ prior written notice of such intent, and Buyer shall be given an opportunity, at its own cost and expense, to remove and retain copies of all or any part of such books and records as Buyer may select.
4. Each of Seller and Buyer hereby agree that, effective as of the Effective Date that Section 1.1 of the Purchase Agreement shall be amended by inserting the following definition in alphabetical order with respect to the other defined terms: ““Continuation Stub Period” has the meaning set forth in Section 5.19(a).”
5. Amendment to Section 9.1. Seller and Buyer agree that Section 9.1 of the Purchase Agreement is hereby amended by changing the person to whom notices, requests, instructions, consents, claims, demands, waivers and other communications are to be given to Buyer, as follows:
2

If to Buyer:
Korn/Ferry International
1900 Avenue of the Stars Suite 2600 Los Angeles, California 90067
Attention: Brian Suh, Senior Vice President-Corporate Development
Telephone: (310) 843-4101
Email: [email protected]
with a copy to (which shall not constitute notice):
Korn/Ferry International
1900 Avenue of the Stars Suite 2600 Los Angeles, California 90067
Attention: Jonathan Kuai, General Counsel
Telephone: (310) 226-2654
Email: [email protected]
and
Blank Rome LLP
2029 Century Park East, 6th Floor Los Angeles,
California 90067 Attention: Michael C. Cohen
Telephone: (424) 239-3455 Email:
Email: [email protected]
6. Further Assurances. Seller and Buyer shall execute and deliver, or shall cause to be executed and delivered, such documents and other instruments and shall take, or shall cause to be taken, such further actions as may be reasonably required to carry out the provisions of this Letter Agreement.
7. Effect of this Letter Agreement. This Letter Agreement shall not constitute an amendment or waiver of any provision of the Purchase Agreement except as expressly stated herein and except as expressly amended or otherwise modified hereby, the provisions of the Purchase Agreement shall remain unchanged and shall continue to be, and shall remain, in full force and effect in accordance with its terms and for the avoidance of doubt, (a) all references in the Purchase Agreement to “the date hereof”, “herein” or “the date of this Agreement” and words or concepts of similar import shall refer to the Original Execution Date and (b) any representations and warranties set forth in the Purchase Agreement made by either the Seller or the Buyer shall not change as a result of the execution of this Letter Agreement and shall be made as of the Original Execution Date.
8. Expenses. All costs and expenses incurred in connection with this Letter Agreement shall be paid by the party incurring such costs and expenses.
9. General Provisions. Sections 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 9.2, 9.4, 9.5, 9.6, 9.8, 9.9, 9.10, 9.12, 9.13 and 9.14 of the Purchase Agreement shall apply to this Letter Agreement, mutatis mutandis.
[Signature Page Follows]
3

If you are in agreement with the foregoing, please so indicate by signing and returning one copy of this Letter Agreement, whereupon this Letter Agreement will constitute our agreement with respect to the subject matter hereof.
| Very truly yours, | ||
| HG (BERMUDA) LIMITED | ||
| By |
| |
| Name: | Chris R. Matthews | |
| Title: | Chief Executive Officer |
| CONFIRMED AND AGREED TO: | ||
| KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL | ||
| By |
| |
| Name: | Brian Suh | |
| Title: | Senior Vice President- | |
| Corporate Development |
[Signature Page to Letter Agreement Regarding Extension of the Resolution Period]
4

If you are in agreement with the foregoing, please so indicate by signing and returning one copy of this Letter Agreement, whereupon this Letter Agreement will constitute our agreement with respect to the subject matter hereof.
| Very truly yours, | ||
| HG (BERMUDA) LIMITED | ||
| By |
| |
| Name: | Chris R. Matthews | |
| Title: | Chief Executive Officer |
| CONFIRMED AND AGREED TO: | ||
| KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL | ||
| By |

| |
| Name: | Brian Suh | |
| Title: | Senior Vice President- | |
| Corporate Development |
[Signature Page to Letter Agreement Regarding Extension of the Resolution Period]
5

EXHIBIT 3.2
CERTIFICATE OF AMENDMENT
OF
RESTATED CERTIFICATE OF INCORPORATION
OF
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL, a corporation organized and existing under and by the virtue of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware (the “Company”), DOES HEREBY CERTIFY as follows:
FIRST: The Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Company (as amended theretofore from time to time and in effect on such date) (the “Certificate”) is hereby amended such that Article VI is amended and restated in its entirety to read as set forth below:
In furtherance and not in limitation of the powers conferred by the laws of the State of Delaware, the Board of Directors is expressly authorized to adopt, alter, amend and repeal the Bylaws of the Corporation, subject to the power of the stockholders of the Corporation to alter or repeal any bylaw whether adopted by them or otherwise; provided, however, that the affirmative vote of the majority of the voting power of the then outstanding voting stock of the Corporation shall be required for stockholders to adopt, amend, alter or repeal any provision of the Bylaws of the Corporation.
SECOND: The Certificate is hereby amended such that first paragraph of Article XIV is amended and restated in its entirety to read as set forth below:
No action that is required or permitted to be taken by the stockholders of the Corporation at any annual or special meeting of the stockholders may be effected by written consent of the stockholders in lieu of a meeting of the stockholders, unless the action to be effected by written consent of stockholders and the taking of such action by such written consent have expressly been approved in advance by the Board of Directors of the Corporation.
THIRD: The foregoing amendments to the Restated Certificate of Incorporation were duly adopted in accordance with the terms of Section 242 of the General Corporation Law.
[Signature page follows]
1

IN WITNESS WHEREOF, KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL has caused this certificate to be signed by its duly authorized officer on this 25 day of June, 2018.
| KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL | ||
| By: | /s/ Jonathan Kuai | |
| Name: | Jonathan Kuai | |
| Title: | Corporate Secretary | |
2

EXHIBIT 3.3
RESTATED CERTIFICATE OF INCORPORATION
OF
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL
Korn/Ferry International, a corporation organized and existing under the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware (the “Corporation”), DOES HEREBY CERTIFY AS FOLLOWS:
FIRST: The Corporation filed its original Certificate of Incorporation with the Secretary of State of Delaware on September 13, 1999.
SECOND: The Board of Directors of the Corporation duly adopted, pursuant to Sections 242 and 245 of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware, a Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Corporation.
THIRD: The Restated Certificate of Incorporation, as adopted by the Board of Directors of the Corporation, is as follows:
Article I: Name
The name of the corporation is Korn/Ferry International (the “Corporation”).
Article II: Registered Office
The address of the registered office of the Corporation in the State of Delaware is 251 Little Falls Drive, Wilmington, County of New Castle 19808. The name of its registered agent at such address is Corporation Service Company.
Article III: Purpose
The purpose of the Corporation is to engage in any lawful act or activity for which corporations may be organized under the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware.
Article IV: Stock
Section 1. Authorized Shares. The total number of shares of all classes which the Corporation shall have the authority to issue shall be 200,000,000, which shall be divided into two classes, one to be designated “Common Stock,” which shall consist of 150,000,000 authorized shares, $0.01 par value per share, and a second class to be designated as “Preferred Stock,” which shall consist of 50,000,000 authorized shares, $0.01 par value per share.
Section 2. Preferred Stock of the Corporation. The Preferred Stock may be issued in one or more series, from time to time, each series to be appropriately designated by a distinguishing number, letter or title, prior to the issuance of any shares thereof. The first series of Preferred Stock shall initially consist of 10,000 shares and shall be designated “7.5% Convertible Series A Preferred Stock” (“Series A Preferred Stock”).
Section 3. Authority of Board of Directors to Issue Stock. Each series of Preferred Stock shall consist of such number of shares and have such voting powers, full or limited, or no voting powers, and such designations, preferences and relative, participating, optional or other special rights, and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions thereof, as shall be stated in the resolutions or resolutions providing for the issuance of such series adopted by the Board of Directors of the Corporation (the “Board of Directors”), and the Board of Directors is hereby expressly vested with authority, to the full extent now or hereafter provided by law, to adopt any such resolution or resolutions. The authority of the Board of Directors with respect to each series shall include, but not be limited to, determination of the following:
(a) The number of shares constituting the series and the distinctive designation of that series;
1

(b) The dividend rate on the shares of that series, whether dividends shall be cumulative, and, if so, from which date or dates, and the relative rights of priority, if any, of payment of dividends on shares of that series;
(c) Whether that series shall have voting rights, in addition to the voting rights provided by law, and, if so, the terms of such voting rights;
(d) Whether that series shall have conversion privileges, and, if so, the terms and conditions of such conversion, including provision for adjustment of the conversion rate in such events as the Board of Directors shall determine;
(e) Whether or not the shares of that series shall be redeemable, and, if so, the terms and conditions of such redemption, including the date or date upon or after which they shall be redeemable, and the amount per share payable in case of redemption, which amount may vary under different conditions and at different redemption dates;
(f) Whether that series shall have a sinking fund for the redemption or purchase of shares of that series, and, if so, the terms and amount of such sinking fund;
(g) The rights of the shares of that series in the event of voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of the Corporation, and the relative rights of priority, if any, of payment of shares of that series; and
(h) Any other relative rights, preferences and limitations of that series.
Section 4. No Preemptive or Preferential Rights. No holders of shares of the Corporation of any class, now or hereafter authorized, shall have any preferential or preemptive rights to subscribe for, purchase or receive any shares of the Corporation of any class, now or hereafter authorized, or any options or warrants to subscribe for such shares, or any rights to subscribe for, purchase or receive any securities convertible to or exchangeable for such shares, which may at any time be issued, sold or offered for sale by the Corporation.
Section 5. Series A Preferred Stock.
(a) Designation. Each share of Series A Preferred Stock shall be identical in all respects to every other share of Series A Preferred Stock. The shares of Series A Preferred Stock are subject to subordination in the manner, and to the extent, set forth in that certain Subordination Agreement, dated as of June 13, 2002, made by the Corporation and certain other persons in favor of Bank of America and certain senior creditors.
(b) Number of Shares. The number of shares of Series A Preferred Stock shall initially be 10,000. Such number may from time to time be increased (but not in excess of the total number of authorized shares of Preferred Stock) or decreased (but not below the number of shares of Series A Preferred Stock then outstanding) by the Board of Directors. Shares of Series A Preferred Stock that are redeemed, purchased or otherwise acquired by the Corporation or converted into Common Stock shall be cancelled and shall revert to authorized but unissued shares of Preferred Stock undesignated as to series.
(c) Definitions. As used herein with respect to Series A Preferred Stock:
(i) “Accrued Dividends,” with respect to any share of Series A Preferred Stock, means an amount computed at the annual dividend rate for Series A Preferred Stock, from the Closing Date or the Accrual Date, as applicable, to and including the date to which such dividends are to be accrued (whether or not such dividends have been declared), less the aggregate amount of all dividends previously paid on such share whether in cash or stock.
(ii) “Average Closing Price” with respect to any period shall be calculated on a volume-weighted average basis. Specifically, it shall be computed by (x) multiplying the Closing Price on each Trading Day within the period by a fraction, the numerator of which is the trading volume of the Common Stock for such Trading Day on the New York Stock Exchange or within the relevant trading market if not the New York Stock Exchange, and the denominator of which is the aggregate trading volume for the trading period, and (y) adding together the products thus derived.
2

(iii) “Business Day” means each Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday or Friday on which banking institutions in New York, New York or Los Angeles, California are not authorized or obligated by law, regulation or executive order to close.
(iv) “Closing Date” means June 13, 2002.
(v) “Closing Price” on any Trading Day means the last reported sales price regular way or, in case no such reported sale takes place on such Trading Day, the average of the reported closing bid and asked prices regular way, in each case on the New York Stock Exchange or, if the Common Stock is not listed or admitted to trading on the New York Stock Exchange, on the principal national securities exchange, market or quotation system on which the Common Stock is listed or admitted to trading, or, if such prices are not available, Closing Price shall mean the price per share of the Common Stock determined by the Board of Directors on a reasonable basis and in good faith.
(vi) “Fair Market Value” on any day means the Closing Price.
(vii) “Fundamental Change” means any transaction (including any merger, consolidation, recapitalization or other reorganization) or a series of related transactions as a result of which all or substantially all of the outstanding Common Stock is converted into or exchanged for stock, other securities, cash or assets.
(viii) “Junior Stock” means the Common Stock and any other class or series of stock of the Corporation hereafter authorized over which Series A Preferred Stock has preference or priority in the payment of dividends or in the distribution of assets on any liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation.
(ix) “Note” means the 7.5% Convertible Subordinated Note Due 2010 of the Corporation.
(x) “Parity Stock” means any other class or series of stock of the Corporation that ranks on a parity with Series A Preferred Stock in the payment of dividends or in the distribution of assets on any liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation.
(xi) “Redemption Date” means the date fixed for redemption by or pursuant to this Certificate of Designations.
(xii) “Trading Day” means a day on which the principal national securities exchange, market or quotation system on which the Common Stock is listed or admitted to trading is open for the transaction of business or, if the Common Stock is not listed or admitted to trading, a Business Day.
(xiii) “Warrants” means the eight-year warrants issued pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, dated as of June 13, 2002, by and between the Corporation and the other parties thereto.
(d) Dividends.
(i) Rate. Holders of Series A Preferred Stock shall be entitled to receive, when, as and if declared by the Board of Directors, but only out of funds legally available therefor, cumulative dividends per share of Series A Preferred Stock at the annual rate of 7.5% (or as such rate may be modified pursuant to the next paragraph) of the Issuance Price. The Issuance Price means $1000 per share of Series A Preferred Stock, as adjusted to reflect the occurrence of any stock split, stock dividend, stock combination, stock subdivision or similar recapitalization affecting such share.
In the event that any Registration Default (as such term is defined in the Investor Rights Agreement, entered into as of the Closing Date by and between the Corporation and the other parties thereto, hereinafter the “Investor Rights Agreement”) exists and is continuing, then the annual rate of 7.5% referred to in the foregoing paragraph shall be increased by one percentage point per quarter, up to a maximum of 14%, until such time as the Registration Default ceases to continue (as set forth in the Investor Rights Agreement) at which point the annual rate shall immediately be reduced to 7.5%.
(ii) Payment. Dividends are payable semi-annually on the thirteenth day of June and December in each year (or, if any such date is not a Business Day, on the next succeeding Business Day), beginning December 13, 2002, to holders of record on the Business Day preceding such dividend payment date, fixed for that
3

purpose by the Board of Directors in advance of payment of each particular dividend. The amount of dividends payable for the initial dividend period and any period shorter than a full semi-annual period during which shares are outstanding shall be computed on the basis of a 360-day year of twelve 30-day months and the actual number of days elapsed in the period which is payable. The dividend payable per share of Series A Preferred Stock for each full dividend period shall be computed by dividing the annual dividend rate by two. No interest, or sum of money in lieu of interest, shall be payable in respect of any dividend payments on shares of Series A Preferred Stock which may be in arrears; provided, however, that to the extent that the Corporation does not declare and pay the amounts specified in Section 5(d)(i) above on the dividend payment date on which such dividend is payable, the holders of the Series A Preferred Stock thus affected shall also receive, but only out of funds legally available for the payment of dividends, additional dividends in an amount equal to 2.0% per annum of such overdue amount for each day (beginning with the first day following such dividend payment date) for which such failure to declare and pay such dividends continues.
Dividends payable on shares of Series A Preferred Stock shall be paid in additional shares of Series A Preferred Stock; provided, however, that on any dividend payment date occurring on or before the second anniversary of the Closing Date, dividends equal to 1% of the Issuance Price shall be paid in cash and equal to 6.5% of the Issuance Price shall be paid in additional shares of Series A Preferred Stock, and provided, further, at the option of the Corporation, dividends payable on shares of Series A Preferred Stock on any dividend payment date occurring after the second anniversary of the Closing Date may be paid entirely in cash or in additional shares of Series A Preferred Stock. To the extent that dividends are paid in additional shares of Series A Preferred Stock, such shares shall be valued at the Issuance Price, and such additional shares shall be entitled to receive cumulative dividends beginning from the date of issuance (such date an “Accrual Date”).
(iii) Priority of Dividends. So long as any share of Series A Preferred Stock remains outstanding, no dividend whatsoever shall be paid or declared and no distribution shall be made on any Junior Stock, other than a dividend or distribution payable solely in Junior Stock, and no shares of Junior Stock shall be purchased, redeemed or otherwise acquired for consideration by the Corporation, directly or indirectly (other than as a result of (A) a reclassification of Junior Stock for or into Junior Stock, (B) the exchange or conversion of one share of Junior Stock for or into another share of Junior Stock, or (C) the repurchase of Common Stock from the Corporation’s employees up to an aggregate amount of up to $1,000,000 of Common Stock per year) provided, however, that dividends may be paid on Junior Stock if (i) all Accrued Dividends on all outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock for all past dividend periods have been paid in full and (ii) in the case of a dividend or distribution, there shall contemporaneously have been declared and paid or made on each outstanding share of Series A Preferred Stock a dividend or distribution in the same amount as the Corporation would have paid on such share if such share had been converted into Common Stock on the record date for the payment of such dividend or distribution and had received the dividend or distribution payable on such Common Stock. Subject to the foregoing, such dividends and distributions (payable in cash, stock or otherwise) as may be determined by the Board of Directors may be declared and paid on any Junior Stock from time to time out of any funds legally available therefor.
(e) Liquidation Rights.
(i) Voluntary or Involuntary Liquidation. In the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the affairs of the Corporation, holders of Series A Preferred Stock shall be entitled, before any distribution or payment out of the assets of the Corporation may be made to the holders of any Junior Stock, to receive in full an amount per share equal to the greater of (i) the Issuance Price, together with an amount equal to all Accrued Dividends to the date of payment and (ii) the amount that a holder of one share of Series A Preferred Stock would be entitled to receive if such shares were converted into Common Stock immediately prior to such liquidation, dissolution or winding up. Such greater amount per share shall be the “Liquidation Preference Amount”.
(ii) Partial Payment. If the assets of the Corporation are not sufficient to pay the Liquidation Preference Amount in full to all holders of Series A Preferred Stock and all holders of any Parity Stock, the amounts paid to the holders of Series A Preferred Stock and to the holders of all Parity Stock shall be pro rata in accordance with the respective aggregate Liquidation Preference Amounts of Series A Preferred Stock and all such Parity Stock.
(iii) Residual Distributions. If the Liquidation Preference Amount has been paid in full to all holders of Series A Preferred Stock and all holders of any Parity Stock, the holders of Junior Stock shall be entitled to receive all remaining assets of the Corporation according to their respective rights and preferences.
(iv) Merger, Consolidation and Sale of Assets Not Liquidation. For purposes of this Section 5(e), the merger or consolidation of the Corporation with any other corporation, including a merger in which the holders of Series A Preferred Stock receive cash or property for their shares, or the sale of all or substantially all of the assets of the Corporation, shall not constitute a liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation.
4

(f) Redemption.
(i) Optional Redemption by the Corporation. Any time after the third anniversary of the Closing Date, the Corporation, at the option of the Board of Directors, may redeem in whole or in part the shares of Series A Preferred Stock at the time outstanding, at any time or from time to time, upon notice given as provided in Section 5(f)(vi), at the redemption price in effect at the notice date as provided in this Section 5(f), provided, however, that (A) no shares of Series A Preferred Stock may be redeemed pursuant to this Section 5(f)(i) if at any time during the 135 days prior to the Redemption Date the Shelf Registration Statement (as defined in the Investor Rights Agreement) with respect to the Common Stock into which any shares of Series A Preferred Stock are convertible shall not be effective, (B) optional redemption may only be made if the Corporation certifies to the holders in the redemption notice sent in accordance with Section 5(f)(vi) that it is able, financially and otherwise, to make the redemption payment, and there has been no default (as set forth in Section 5(f)(ix)) by the Corporation on an obligation to pay for shares of Series A Preferred Stock duly called for redemption in accordance with this Section 5(f) within the 12 months prior to the date of such notice, (C) optional redemption may only be made pursuant to this Section 5(f)(i) if, after giving effect to such redemption (and any simultaneous redemption of Notes), the ratio of (a) the aggregate outstanding principal amount of the Notes and (b) the product of (x) the number of issued and outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock and (y) the Issuance Price, is equal to 4:1, and (D) the Corporation shall not be permitted to redeem shares of Series A Preferred Stock pursuant to this Section 5(f)(i) if, after giving effect to such redemption (and any simultaneous redemption of Notes), the sum of (a) the aggregate outstanding principal amount of the Notes and (b) the product of (x) the number of issued and outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock and (y) the Issuance Price, does not exceed $15,000,000.00. The foregoing clauses (C) and (D) shall not limit the Corporation’s right pursuant to this Section 5(f)(i) to redeem all of the outstanding principal amount of the Notes and all of the outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock in one redemption.
(ii) Redemption Price. The redemption price for shares of Series A Preferred Stock redeemed pursuant to Section 5(f)(i) hereof shall be set by the Corporation in its discretion pursuant to any available redemption price calculation methodology set forth below.
The Corporation may in its discretion set the redemption price for each share of Series A Preferred Stock at 100% of the Issuance Price together with an amount equal to all Accrued Dividends to the date of redemption, provided, however, that the Corporation may not set the redemption price using this methodology unless the Average Closing Price of the Common Stock over the 20 Trading Day period immediately preceding the Redemption Date is equal to or greater than the price that is the result of dividing (i) the price specified in the following schedule by (ii) the number of shares of Common Stock into which such share of Series A Preferred Stock would be convertible on the notice date (such price, the “Minimum Share Purchase Price”).
| Redemption Date
|
Basis of Minimum Share Purchase Price Calculation
| |
| After the third and through and including the fourth anniversary of the Closing Date
|
2.0 x Issuance Price
| |
| After the fourth and through and including the fifth anniversary of the Closing Date
|
2.25 x Issuance Price | |
| After the fifth anniversary of the Closing Date
|
25 x Issuance Price
|
The Corporation may in its discretion set the redemption price for each share of Series A Preferred Stock at the product of (i) the number of shares of Common Stock into which such share of Series A Preferred Stock would be convertible on the notice date and (ii) the greater of (x) the Average Closing Price over the 20 Trading Day period immediately preceding the notice date and (y) the Minimum Share Purchase Price.
(iii) Mandatory Redemption. The Corporation shall, on the eighth anniversary of the Closing Date, redeem all of the outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock at a redemption price per share equal to (i) 101% of the Issuance Price plus (ii) an amount equal to all Accrued Dividends to such Redemption Date.
5

(iv) Optional Redemption by the Holders. After the sixth anniversary of the Closing Date, all (or a portion) of the shares of Series A Preferred Stock shall be subject to redemption at the option of the holders thereof at a redemption price per share equal to (i) 101% of the Issuance Price plus (ii) an amount equal to all Accrued Dividends to the Redemption Date. In addition, if a Registration Default exists and is continuing, and either (a) the Shelf Registration Statement has not been declared effective by the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) on or before the 365th calendar day after the date of filing of the Shelf Registration Statement or (b) the Shelf Registration Statement is declared effective by the SEC but the Shelf Registration Statement thereafter ceases to be effective and such failure to be effective continues for a period of 90 consecutive calendar days, or more than 120 days in any 365 day period, then all of the shares of Series A Preferred Stock shall be subject to redemption at the option of the holders thereof, beginning on such 365th or 91st or 121st day, as the case may be, until such time as the Registration Default ceases to continue (as set forth in the Investor Rights Agreement) at a redemption price equal to the greater of (y) 100% of the Issuance Price plus an amount equal to all Accrued Dividends to the Redemption Date or (z) the product of the number of shares of Common Stock into which such share of Series A Preferred Stock would be convertible on the date of the exercise of such option by the holder and the Average Closing Price over the 20 Trading Day period immediately preceding such date.
Any holder of Series A Preferred Stock electing to redeem shares of Series A Preferred Stock pursuant to this Section 5(f)(iv) shall give notice in writing of such election to the Corporation (or its successor, if the Corporation is no longer in existence) at its principal office, which notice shall set forth the name of the holder and the number of shares of Series A Preferred Stock to be redeemed. Such written notice of election shall be irrevocable without the consent of the Corporation, in its sole discretion. The Corporation shall forthwith give notice to all other holders of Series A Preferred Stock of any such notice of redemption, specifying the date fixed by the Corporation for redemption of such shares of Series A Preferred Stock, such date to be not more than 45 days nor less than 30 days from the notice date. Such other holders of Series A Preferred Stock may elect to sell to the Corporation all or a portion of their shares of Series A Preferred Stock by delivering written notice to the Corporation within 15 days after the distribution of the notice regarding optional redemption by the Corporation. Each holder of shares of Series A Preferred Stock that has given timely notice to the Corporation shall be entitled to receive the redemption price thereof as described in this Section 5(f)(iv), without interest, after surrender to the principal office of the Corporation of the certificate or certificates for the shares to be surrendered.
(v) Change Of Control. For the purposes of this Section 5(f): (1) a sale, conveyance or disposition of all or substantially all of the assets of the Corporation, (ii) the effectuation of a transaction (including a merger, consolidation, recapitalization or other reorganization) or series of related transactions as a result of which 50% or more of the issued and outstanding voting securities of the resulting entity are beneficially owned by a person, corporation, entity or group other than the stockholders of the Corporation immediately prior to such transactions, or (iii) the effectuation of a transaction (including a merger, consolidation, recapitalization or other reorganization) or series of related transactions as a result of which any person or “group” (within the meaning of Section 13(d)(3) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) shall succeed in having a sufficient number of its nominees elected to the Corporation’s Board of Directors such that such nominees will constitute a majority of the Board of Directors, shall be a “Change of Control Event.” In the event of a Change of Control Event, each holder of a share of Series A Preferred Stock shall have the right to receive, at the option of the holder, (i) 101% of the Issuance Price plus an amount equal to all Accrued Dividends to the date of the Change of Control Event, or (ii) the per share consideration to be received by a holder of the Common Stock into which such share of Series A Preferred Stock is convertible as of such Change of Control Event. Upon the consummation of a Change of Control Event that is a Fundamental Change, each share of Series A shall automatically be converted into the right to receive, at the election of the holder in accordance with the third paragraph of this Section 5(f)(v), one of the two forms of consideration described above.
On or before the 30th calendar day after a Change of Control Event (or the 30th calendar day prior to such Change of Control Event that is a Fundamental Change), the Corporation shall give notice in accordance with this Section 5(f)(v) of the redemption right or other right to receive consideration set forth herein arising as a result thereof to each holder. To exercise a redemption right, a Holder shall deliver to the Corporation (or an agent designated by the Corporation for such purposes in the notice referred to above) on or before the 90th calendar day after such Change of Control Event (or if such Change of Control Event is a Fundamental Change then on or before such date of such Fundamental Change) (a) written notice of the holder’s exercise of such right, which notice shall set forth the name of the holder, the number of shares of Series A Preferred Stock to be redeemed, and a statement that the option to exercise the redemption right or receive the consideration is being made thereby, and (b) the certificates for the shares of Series A Preferred Stock with respect to which the redemption right is being exercised, duly endorsed for transfer to the Corporation. Such written notice shall be irrevocable without the consent of the Corporation, in its sole discretion.
6

(vi) Notice of Redemption. Each notice of a redemption of shares of Series A Preferred Stock or otherwise to be provided by the Corporation under this Section 5(f) shall be made by hand delivery or delivered by overnight courier, addressed to the holders of record of the shares to be redeemed at their respective addresses appearing on the books of the Corporation. Each such notice shall state, as appropriate, the following and may contain such other information as the Corporation deems advisable: (a) the Redemption Date, (b) the number of such shares of Series A Preferred Stock held by such holder to be redeemed, (c) the redemption price, (d) the place or places where one or more certificates for such shares of Series A Preferred Stock are to be surrendered for redemption and (e) such items as are required to be stated in a notice of an optional redemption by the Corporation pursuant to Section 5(f)(i) above. The “notice date” shall be the date such notice is mailed. Such mailing shall be at least 30 days and not more than 45 days before the date fixed for redemption. Any notice mailed as provided in this Section 5(f)(vi) shall be conclusively presumed to have been duly given upon receipt, but failure duly to give such notice by overnight mail, or any defect in such notice or in the mailing thereof, to any holder of shares of Series A Preferred Stock designated for redemption shall not affect the validity of the proceedings for the redemption of any other shares of Series A Preferred Stock Upon duly delivering notice to a holder of Series A Preferred Stock, the Corporation may not thereafter rescind such notice of redemption or the Company’s obligation to pay the redemption price.
(vii) Partial Redemption. In case of any optional redemption of only part of the shares of Series A Preferred Stock at the time outstanding (other than in the case of optional redemption by the holders pursuant to Section 5(f)(iv), the shares to be redeemed shall be selected either pro rata or by lot or in such other mariner as the Board of Directors may determine to be equitable.
(viii) Effectiveness of Redemption. If notice of redemption has been duly given and if on or before the Redemption Date specified in the notice all funds necessary for the redemption have been set aside by the Corporation, separate and apart from its other funds, in trust for the pro rata benefit of the holders of the shares of Series A Preferred Stock called for redemption (or to be redeemed pursuant to Section 5(f)(iv)), so as to be and continue to be available therefor, then, notwithstanding that any certificate (or an affidavit of loss and indemnification in lieu thereof has been provided to the Corporation as provided below) for any share of Series A Preferred Stock so called for redemption (or to be redeemed pursuant to Section 5(f)(iv)) has not been surrendered for cancellation, on and after the Redemption Date all shares of Series A Preferred Stock so called for redemption (or to be redeemed pursuant to Section 5(f)(iv)) shall cease to be outstanding and all rights with respect to such shares of Series A Preferred Stock shall forthwith on such Redemption Date cease and terminate, except only the right of the holders thereof to receive the amount payable on such redemption without interest. In the event any certificate shall have been lost, stolen or destroyed, upon the making of an affidavit of that fact by the holder certifying to the satisfaction of the Corporation that such certificate has been lost, stolen or destroyed and entering into an indemnity agreement against any claim that may be made against it with respect to such certificate, the Corporation will deliver any redemption price in respect thereof issuable and/or payable in exchange for such lost, stolen or destroyed certificate pursuant to the terms of this Section 5(f). Any funds unclaimed at the end of one year from the Redemption Date shall, to the extent permitted by law, be released to the Corporation, after which time the holders of the shares of Series A Preferred Stock so called for redemption (or to be redeemed pursuant to Section 5(f)(iv)) shall look only to the Corporation for payment of the redemption price of such shares of Series A Preferred Stock.
(ix) Redemption Default. If the Corporation defaults on an obligation incurred hereunder to pay a redemption price payable pursuant to the terms of this Section 5(f), the holder of any share of Series A Preferred Stock subject to such default (a) shall receive additional dividends in an amount equal to 2.0% per annum for each day for which such default continues, and (b) may at its option either (A) enforce its right to receive such redemption price and receive the additional interest due thereon pursuant to clause (b) or (B) terminate or rescind such attempted redemption.
(g) Conversion Rights. Each share of Series A Preferred Stock shall be convertible at the option of the holder thereof at any time into fully paid and non-assessable shares of Common Stock of the Corporation (calculated as to each conversion to the nearest 1/100th of a share) on and subject to the following terms and conditions:
(i) Conversion Price. The conversion price at which shares of Series A Preferred Stock shall be convertible into Common Stock (the “Conversion Price”) shall initially be $10.25 per share and shall be adjusted in certain events as provided in Section 5(g)(v). Each share of Series A Preferred Stock shall be taken at the Issuance Price and any Accrued Dividends for the purpose of conversion.
(ii) Surrender of Certificates. In order to convert shares of Series A Preferred Stock into Common Stock the holder must surrender, at the office of any transfer agent for the Common Stock or at such other office as the Board of Directors may designate, the certificate or certificates for the shares to be converted, duly
7

endorsed or assigned either to the Corporation or in blank, together with irrevocable written notice that such holder elects to convert such shares. Such shares shall be deemed to be converted immediately before the close of business on the date of such surrender, and the person or persons entitled to receive the Common Stock issuable upon such conversion shall be treated for all purposes as the record holder or holders of such Common Stock at such time. As promptly as practicable on or after such date, and in any event within 3 Business Days, the Corporation shall issue and deliver at such office to the person or persons entitled to receive the same a certificate or certificates for the number of full shares of Common Stock issuable upon such conversion, together with payment in lieu of any fraction of a share as provided in Section 5(g)(iv).
(iii) Shares Called for Redemption. In case shares of Series A Preferred Stock are called for redemption, the right to convert such shares shall cease and terminate at the close of business on the Business Day before the date fixed for redemption’ provided, however, that such right may be reinstated in case of a default in payment of the redemption price as set forth in Section 5(f)(ix).
(iv) Fractional Shares. No fractional shares of Common Stock shall be issued upon conversion of shares of Series A Preferred Stock, but, instead of any fraction of a share that would otherwise be issuable, the Corporation shall pay cash in an amount equal to the same fraction of the Closing Price on the date of surrender of the certificate or certificates for such shares for conversion, or, if such date is not a Trading Day, on the next Trading Day.
(v) Adjustment of Conversion Price Anti-Dilution. The Conversion Price and the number and kind of shares of capital stock or other property issuable on conversion shall be adjusted from time to time as follows.
(A) Sales of Common Stock Below Fair Market Value. In case the Corporation shall issue or grant to any person (whether directly or by assumption in a merger or otherwise, other than upon a Fundamental Change to which Section 5(g)(v)(E) applies) (a) rights, warrants, options, exchangeable securities or convertible securities (each referred to herein as “Rights”) entitling such person to subscribe for or purchase shares of Common Stock at a price per share less than the Fair Market Value or (b) shares of Common Stock at a price per share less than the Fair Market Value, on the record date fixed for the determination of persons entitled to receive such Rights or such shares, the Conversion Price in effect immediately before the close of business on the record date fixed for such determination shall be reduced by multiplying such Conversion Price by a fraction, of which (i) the numerator is the number of shares of Common Stock outstanding (including all shares of Common Stock issued or issuable upon conversion of any convertible security or upon the exercise of any rights, warrants or options) on such record date plus the number of shares of Common Stock which the aggregate of the offering price of the total number of shares of Common Stock so offered for subscription or purchase pursuant to such Rights, or so issued, would purchase at the Fair Market Value on such record date and (ii) the denominator shall be the number of shares of Common Stock outstanding (including all shares of Common Stock issued or issuable upon conversion of any convertible security or upon the exercise of any rights, warrants or options) at the close of business on such record date plus the number of shares of Common Stock so offered for subscription or purchase pursuant to such Rights, or so issued. If, after any such record date, any such Rights or shares are not in fact issued, or are not exercised prior to the expiration thereof, the Conversion Price shall be immediately readjusted, effective as of the date such Rights or shares expire, or the date the Board of Directors determines not to issue such Rights or shares, to the Conversion Price that would have been in effect if the unexercised Rights had never been granted or such record date had not been fixed, as the case may be. Such adjustment shall be made successively whenever any such event shall occur. For the purposes of this paragraph, the aggregate of the offering price received or to be received by the Corporation shall include the maximum aggregate amount (if any) payable upon exercise or conversion of such Rights. The value of any consideration received or to be received by the Corporation, if other than cash, is to be determined by the Board of Directors on a reasonable basis and in good faith.
(B) Stock Splits and Combinations. In case the Corporation shall subdivide its outstanding Common Stock into a greater number of shares or combine its outstanding Common Stock into a smaller number of shares, the Conversion Price in effect immediately before the time when such subdivision or combination becomes effective shall be adjusted so that the holder of each share of Series A Preferred Stock converted thereafter shall be entitled to receive the number of shares of Common Stock that such holder would have received if such shares of Series A Preferred Stock had been converted immediately prior thereto at the Conversion Price then in effect. Such adjustment shall be made successively whenever any such event shall occur.
(C) Stock Dividends in Common Stock. In case the Corporation shall pay a dividend or make a distribution in shares of Common Stock on any class of capital stock of the Corporation, the Conversion Price in effect immediately before the close of business on the record date fixed for determination of stockholders entitled to receive such dividend or distribution shall be reduced by multiplying such Conversion Price by a fraction, of
8

which the numerator is the number of shares of Common Stock outstanding (including all shares of Common Stock issued or issuable upon conversion of any convertible security or upon the exercise of any rights, warrants or options) on such record date and the denominator is the sum of such number of shares and the total number of shares of Common Stock issued in such dividend or distribution. Such adjustment shall be made successively whenever any such event shall occur.
(D) Distributions of Indebtedness, Securities or Assets. In case the Corporation shall distribute to all holders of Common Stock (whether by dividend or in a merger or consolidation or otherwise) evidences of indebtedness, shares of capital stock of any class or series, other securities, cash or assets (other than Common Stock or a dividend or distribution payable exclusively in cash and other than as a result of a Fundamental Change), the Conversion Price in effect immediately before the close of business on the record date fixed for determination of stockholders entitled to receive such distribution shall be reduced by multiplying such Conversion Price by a fraction, of which the numerator is the Fair Market Value on such record date less the fair market value (as determined by the Board of Directors, whose determination in good faith shall be conclusive) of the portion of such evidences of indebtedness, shares of capital stock, other securities, cash and assets so distributed applicable to one share of Common Stock and the denominator is such Fair Market Value. Such adjustment shall be made successively whenever any such event shall occur. In case such distribution is not made after such a record date has been fixed, the Conversion Price shall be readjusted to the Conversion Price that would have been in effect if such record date had not been fixed.
(E) Fundamental Changes. In case any Fundamental Change shall occur, the holder of each share of Series A Preferred Stock outstanding immediately before such Fundamental Change shall have, in addition to all other rights hereunder, the right to receive the kind and amount of stock, other securities, cash and assets that such holder would have received if such share of Series A Preferred Stock had been converted immediately prior thereto. The Corporation agrees that it will not be a party to or permit any Fundamental Change to occur unless the foregoing provisions are included in the terms thereof, and unless the holders of Series A Preferred Stock shall continue to have all of its rights and privileges hereunder in an equivalent manner after giving effect to the Fundamental Change.
(F) Exempted Issuances. Notwithstanding any other provision in this Section 5(g)(v), the foregoing provisions of this Section 5(g)(v) shall not apply to, and no adjustment shall be made to the Conversion Price for:
(1) shares of Common Stock issuable upon the exercise of options or other convertible securities to be issued pursuant to the Company’s stock option, performance award or employee benefit plans; provided, however, that this exemption shall be limited to 7,000,000 shares of Common Stock issuable upon and an additional 1,574,501 shares of Common Stock issuable upon the exercise of options reserved for grant in September 2002 pursuant to the Company’s option exchange program;
(2) shares of Common Stock issuable upon the exercise of options or other convertible securities previously issued pursuant to the Corporation’s stock option, performance award or employee benefit plan;
(3) shares of Common Stock issuable upon conversion of shares of Series A Preferred Stock, the Note or exercise of outstanding Warrants, or pay-in-kind dividends paid on the Series A Preferred Stock or the Note;
(4) securities that have been approved for issuance or grant by the holders of at least two-thirds of the outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock; or
(5) securities that are issued in conjunction with an acquisition or a non-financing strategic transaction approved by the Board of Directors; provided, however, that the number of shares of Common Stock or securities convertible into Common Stock issued by the Corporation in conjunction with non-financing strategic transactions that are exempt from the foregoing provisions of this Section 5(g)(v) shall be limited to 20% of the shares of Common Stock outstanding (including all shares of Common Stock issued or issuable upon conversion of any convertible security or upon the exercise of any rights, warrants or options) immediately prior to the Closing Date.
(G) No Adjustment for Participating Distributions. Notwithstanding any of the provisions of this Section 5(g)(v), no adjustment to the Conversion Price shall be made pursuant to a distribution by the Corporation in which the holders of Series A Preferred Stock shares have participated on an as-converted to Common Stock basis in accordance with Section 5(d)(iii).
9

(H) Deferral of Certain Conversions Requiring Adjustment. In any case in which this Section 5(g)(v) requires that an adjustment as a result of any event become effective from and after a record date, the Corporation may elect to defer until after the occurrence of such event (A) issuing to the holder of any shares of Series A Preferred Stock converted after such record date and before the occurrence of such event the additional shares of Common Stock issuable upon such conversion over and above the shares issuable on the basis of the Conversion Price in effect immediately before adjustment and (B) paying to such holder any amount in cash in lieu of a fractional share of Common Stock pursuant to Section 5(g)(iv) above. In any such case the Corporation shall issue or cause a transfer agent to issue due bills or other appropriate evidence of the right to receive the shares the issuance of which is so deferred.
(I) Deferral of Small Adjustments. Any adjustment in the Conversion Price otherwise required by this Section 5(g) may be postponed until the date of the next adjustment (or the date of conversion, if earlier) otherwise required to be made if such adjustment (together with any other adjustments postponed pursuant to this paragraph (ix) and not theretofore made) would not require an increase or decrease of more than 0.5% in such Conversion Price. All calculations under this Section 5(g)(v) shall be made to the nearest cent or to the nearest 1/100th of a share, as the case may be.
(J) Voluntary Reduction in Conversion Price. The Board of Directors may make such reductions in the Conversion Price, in addition to those required by this Section 5(g)(v), as it shall deem necessary to avoid taxation of any dividend or distribution of stock or rights to acquire stock or any event treated as a deemed dividend or distribution for Federal income tax purposes to the recipients.
(vi) Notice of Conversion Price Adjustments. Whenever the Conversion Price is adjusted as herein provided:
(A) The Corporation shall compute and file with each transfer agent for the shares of Series A Preferred Stock the adjusted Conversion Price in accordance with this Section 5(g) and shall prepare a certificate signed by the Corporation’s chief financial officer setting forth the adjusted Conversion Price and showing in reasonable detail the facts upon which such adjustment is based; and
(B) A notice stating that the Conversion Price has been adjusted and setting forth the adjusted Conversion Price shall be made by hand delivery or delivered by overnight courier, as soon as practicable to the holders of record of outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock at their respective addresses appearing on the books of the Corporation.
(vii) Notice of Certain Events. In case:
(A) The Corporation declares a dividend or other distribution on its Common Stock;
(B) The Corporation authorizes the issuance to the holders of its Common Stock of rights or warrants entitling them to subscribe for or purchase any shares of capital stock of any class or any other subscription rights or warrants; or
(C) Of any reclassification of the capital stock of the Corporation (other than a subdivision or combination of its outstanding shares of Common Stock), or of any consolidation or merger to which the Corporation is a party and for which approval of any stockholders of the Corporation is required, or of any sale, transfer or other disposition of all or substantially all of the assets of the Corporation or of any other transaction or event that would constitute or result in a Fundamental Change or a Change in Control; or
(D) Of the voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation;
then the Corporation shall file with each transfer agent for the shares of Series A Preferred Stock and shall deliver by hand delivery or by overnight courier to the holders of record of outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock, at their respective addresses appearing on the books of the Corporation, at least 5 days before the applicable record or effective date hereinafter specified, a notice stating (x) the date as of which the holders of record of Common Stock to be entitled to such dividend, distribution, rights or warrants are to be determined, or (y) the date
10

on which such reclassification, consolidation, merger, sale, transfer, disposition, liquidation, dissolution or winding up or Fundamental Change is expected to become effective, and the date as of which it is expected that holders of record of Common Stock shall be entitled to exchange their shares for securities, cash or other property deliverable upon such reclassification, consolidation, merger, sale, transfer, disposition, liquidation, dissolution or winding up or Fundamental Change. Failure to give notice as required by this Section 5(g)(vii), or any defect in such notice, shall not affect the validity of any such dividend, distribution, right, warrant, reclassification, consolidation, merger, sale, transfer, disposition, liquidation, dissolution or winding up or Fundamental Change, or the vote on any action authorizing such.
(viii) Reservation of Shares. The Corporation shall at all times reserve and keep available, free from preemptive rights, out of its authorized but unissued Common Stock, solely for the purpose of issuance upon conversion of shares of Series A Preferred Stock, the full number of shares of Common Stock then deliverable upon conversion of all shares of Series A Preferred Stock outstanding.
(h) Voting Rights.
(i) General. The holders of Series A Preferred Stock shall be entitled to vote and, except as hereinafter provided, shall vote together with the holders of Common Stock (and of any other class or series that may similarly be entitled to vote with the holders of Common Stock) as a single class on all matters on which holders of Common Stock are entitled to vote.
In so voting, the holders of Series A Preferred Stock shall be entitled to cast such number of votes as such holders would have been entitled to cast if the Series A Preferred Stock and the Note had been converted into Common Stock on the record date for the determination of holders entitled to vote. Each share of Series A Preferred Stock shall be entitled to cast a pro rata portion of such number of votes.
(ii) Other Voting Rights. So long as the sum of (a) the aggregate outstanding principal amount of the Notes and (b) the product of (x) the number of issued and outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock and (y) the Issuance Price, exceeds $15,000,000.00, the Corporation will not, without the prior written consent of the holders of two thirds of the Series A Preferred Stock at the time outstanding, permit the taking of the following actions or take any action that has the effect of:
(A) waiving, amending, altering, repealing or changing the rights, preferences or privileges of the Series A Preferred Stock, as provided herein or in the certificate of incorporation, whether by merger, consolidation or otherwise;
(B) authorizing or issuing any other equity security, including any other security convertible into or exercisable for any equity security, having a preference over the Series A Preferred Stock with respect to voting, the payment of dividends or in the distribution of assets on any liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation;
(C) reclassifying any outstanding shares of equity securities, including any security convertible into or exercisable for any such equity security, into equity securities having a preference over, or being on a parity with, the Series A Preferred Stock with respect to voting, the payment of dividends or in the distribution of assets on any liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation;
(D) authorizing or paying any dividend or distribution with respect to Common Stock or any other class or series of Junior Stock;
(E) increasing the authorized number of shares of Series A Preferred Stock other than in connection with the payment of dividends on the Series A Preferred Stock;
(F) altering or changing the business of the Corporation in any fundamental respect; or
(G) effecting a voluntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation;
provided, however, that the amendment of the certificate of incorporation so as to authorize or create, or to increase the authorized amount of, any Junior Stock or any shares of any class or series or any securities convertible
11

into shares of any class or series of capital stock of the Corporation ranking on a parity with Series A Preferred Stock in the payment of dividends or in the distribution of assets on any liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Corporation shall not be deemed to affect adversely the rights, preferences or privileges of the Series A Preferred Stock; provided, further, that no such vote or consent of the holders of Series A Preferred Stock shall be required if provision is made for the redemption pursuant to Section 5(f) of all shares of Series A Preferred Stock at the time outstanding at or before the time when such amendment, alteration or repeal is to take effect or when such authorization, creation or increase in the authorized amount of any shares or convertible securities is to be made, as the case may be.
(i) Other Rights. The shares of Series A Preferred Stock shall not have any voting powers, preferences or relative, participating, optional or other special rights, or qualifications, limitations or restrictions thereof, other than as set forth herein or in the certificate of incorporation of the Corporation.
Article V: Incorporator
The name and mailing address of the incorporator are as follows: Peter L. Dunn, Korn/Ferry International, 1800 Century Park East, Suite 900, Los Angeles, California 90067.
Article VI: Bylaws
In furtherance and not in limitation of the powers conferred by the laws of the State of Delaware, the Board of Directors is expressly authorized to adopt, alter, amend and repeal the Bylaws of the Corporation, subject to the power of the stockholders of the Corporation to alter or repeal any bylaw whether adopted by them or otherwise; provided, however, that the affirmative vote of the majority of the voting power of the then outstanding voting stock of the Corporation shall be required for stockholders to adopt, amend, alter or repeal any provision of the Bylaws of the Corporation.
Article VII: Election of Directors
Unless and except to the extent that the Bylaws of the Corporation shall so require, the election of directors of the Corporation need not be by written ballot.
Article VIII: Number of Directors
Except as otherwise provided for or fixed by or pursuant to the provisions of Article IV of this Certificate of Incorporation or any resolution or resolutions of the Board of Directors providing the issuance of any class or series of stock having a preference over the Common Stock as to dividends or upon liquidation to elect additional directors under specified circumstances, the Board of Directors shall consist of not fewer than 8 nor more than 15 directors, the exact number of directors within such limits to be determined solely by the Board of Directors in the manner set forth in the Bylaws of the Corporation. Commencing with the 2013 annual meeting of stockholders, directors shall be elected for a term ending on the date of the next annual meeting of stockholders following their election and until their successors shall have been duly elected and qualified, or until their earlier death, resignation or removal.
Article IX: Director Liability
A director of the Corporation shall not be liable to the Corporation or its stockholders for monetary damages for breach of fiduciary duty as a director, except to the extent such exemption from liability or limitation thereof is not permitted under the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware as the same exists or may hereafter be amended. Any amendment, modification or repeal of the foregoing sentence shall not adversely affect any right or protection of a director of the Corporation hereunder in respect of any act or omission occurring prior to the time of such amendment, modification or repeal.
Article X: Removal of Directors
Any or all directors may be removed with or without cause by the holders of a majority of the shares entitled to vote at an election of directors.
Article XI: Reservation of Rights by the Corporation
The Corporation hereby reserves the right at any time and from time to time to amend, alter, change or
12

repeal any provisions contained in this Certificate of Incorporation, and other provisions authorized by the laws of the State of Delaware at the time in force may be added or inserted, in the manner now or hereafter prescribed by law, and all rights, preferences and privileges of whatsoever nature conferred upon stockholders, directors or any other persons whomsoever by or pursuant to this Certificate of Incorporation in its present form or as hereafter amended are granted subject to the right reserved in this Article XI.
Article XII: Meetings of the Stockholders
Section 1. Place of Meetings. Meetings of the stockholders may be held within or without the State of Delaware, as the Bylaws of the Corporation may provide.
Section 2. Ability to Call Special Meetings. Special meetings of the stockholders may be called only by the Board of Directors, the Chair of the Board of Directors, the Chief Executive Officer or the President of the Corporation, and may not be called by any other person or persons.
Article XIII: Books of the Corporation
The books of the Corporation may be kept (subject to any provision contained in the laws of the State of Delaware) outside of the State of Delaware at such place or places as may be designated from time to time by the Board of Directors or in the Bylaws of the Corporation.
Article XIV: Action by Written Consent of Stockholders Prohibited
No action that is required or permitted to be taken by the stockholders of the Corporation at any annual or special meeting of the stockholders may be effected by written consent of the stockholders in lieu of a meeting of the stockholders, unless the action to be effected by written consent of stockholders and the taking of such action by such written consent have expressly been approved in advance by the Board of Directors of the Corporation.
[Remainder of Page Intentionally Left Blank]
13

IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the Corporation has caused this Restated Certificate of Incorporation to be executed on its behalf by its Corporate Secretary on this 25 day of June, 2018.
| KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL |
| By: /s/ Jonathan Kuai |
| Name: Jonathan Kuai |
| Title: Corporate Secretary |
14

EXHIBIT 3.4
FIFTH AMENDED AND RESTATED BYLAWS
of
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL,
a Delaware corporation
(effective June 25, 2018)
1

INDEX
| Page | |||||||
| ARTICLE I OFFICES. |
5 | ||||||
| Section 1 |
REGISTERED OFFICE. |
5 | |||||
| Section 2 |
PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICE. |
5 | |||||
| Section 3 |
OTHER OFFICES. |
5 | |||||
| ARTICLE II STOCKHOLDERS. |
5 | ||||||
| Section 1 |
PLACE OF MEETINGS. |
5 | |||||
| Section 2 |
ANNUAL MEETINGS. |
5 | |||||
| Section 3 |
BUSINESS WHICH MAY BE CONDUCTED AT MEETINGS OF THE STOCKHOLDERS. |
5 | |||||
| Section 4 |
SPECIAL MEETINGS. |
8 | |||||
| Section 5 |
NOTICE OF ANNUAL OR SPECIAL MEETINGS. |
9 | |||||
| Section 6 |
QUORUM—REQUIRED VOTES. |
9 | |||||
| Section 7 |
ADJOURNED OR RECESSED MEETINGS AND NOTICE THEREOF. |
9 | |||||
| Section 8 |
VOTING. |
9 | |||||
| Section 9 |
RECORD DATE. |
10 | |||||
| Section 10 |
PROXIES. |
10 | |||||
| Section 11 |
INSPECTORS OF ELECTION. |
11 | |||||
| Section 12 |
CONDUCT OF MEETING. |
11 | |||||
| Section 13 |
LIST OF STOCKHOLDERS ENTITLED TO VOTE. |
12 | |||||
| Section 14 |
CONSENT OF STOCKHOLDERS IN LIEU OF MEETING. |
12 | |||||
| ARTICLE III DIRECTORS. |
13 | ||||||
| Section 1 |
POWERS. |
13 | |||||
| Section 2 |
NUMBER OF DIRECTORS. |
14 | |||||
| Section 3 |
NOMINATION, ELECTION, QUALIFICATION AND TERM OF OFFICE. |
14 | |||||
| Section 4 |
VACANCIES. |
14 | |||||
| Section 5 |
PLACE OF MEETING. |
14 | |||||
| Section 6 |
REGULAR MEETINGS. |
14 | |||||
| Section 7 |
SPECIAL MEETINGS. |
15 | |||||
2

| Section 8 |
QUORUM. |
15 | |||||
| Section 9 |
PARTICIPATION IN MEETINGS BY COMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT. |
15 | |||||
| Section 10 |
WAIVER OF NOTICE. |
15 | |||||
| Section 11 |
ADJOURNMENT. |
15 | |||||
| Section 12 |
FEES AND COMPENSATION. |
16 | |||||
| Section 13 |
ACTION WITHOUT MEETING. |
16 | |||||
| Section 14 |
RIGHTS OF INSPECTION. |
16 | |||||
| Section 15 |
COMMITTEES. |
16 | |||||
| Section 16 |
CHAIR OF THE BOARD. |
16 | |||||
| ARTICLE IV OFFICERS. |
17 | ||||||
| Section 1 |
OFFICERS. |
17 | |||||
| Section 2 |
ELECTION OR APPOINTMENT. |
17 | |||||
| Section 3 |
ELECTED SENIOR OFFICERS. |
17 | |||||
| Section 4 |
REMOVAL AND RESIGNATION. |
18 | |||||
| Section 5 |
VACANCIES. |
18 | |||||
| ARTICLE V OTHER PROVISIONS. |
18 | ||||||
| Section 1 |
INSPECTION OF BYLAWS. |
18 | |||||
| Section 2 |
ENDORSEMENT OF DOCUMENTS; CONTRACTS. |
18 | |||||
| Section 3 |
CERTIFICATES OF STOCK. |
18 | |||||
| Section 4 |
REPRESENTATION OF SHARES OF OTHER CORPORATIONS. |
19 | |||||
| Section 5 |
ELECTION OF FISCAL YEAR. |
19 | |||||
| Section 6 |
CONSTRUCTION AND DEFINITIONS. |
19 | |||||
| Section 7 |
AMENDMENTS. |
19 | |||||
| Section 8 |
EMERGENCY BYLAWS. |
19 | |||||
| ARTICLE VI INDEMNIFICATION. |
19 | ||||||
| Section 1 |
RIGHT TO INDEMNIFICATION. |
19 | |||||
| Section 2 |
PREPAYMENT OF EXPENSES. |
19 | |||||
| Section 3 |
CLAIMS. |
20 | |||||
| Section 4 |
NON-EXCLUSIVITY OF RIGHTS. |
20 | |||||
3

| Section 5 |
OTHER SOURCES. |
20 | |||||
| Section 6 |
AMENDMENT OR REPEAL. |
20 | |||||
| Section 7 |
NATURE OF RIGHTS; SEVERABILITY. |
20 | |||||
| Section 8 |
OTHER INDEMNIFICATION AND PREPAYMENT OF EXPENSES. |
20 | |||||
4

FIFTH AMENDED AND RESTATED BYLAWS
for the regulation, except
as otherwise provided by statute or
its Certificate of Incorporation,
of
KORN/FERRY INTERNATIONAL
(effective June 25, 2018)
ARTICLE I OFFICES.
| Section 1 | REGISTERED OFFICE. |
The registered office of the corporation in the State of Delaware shall be fixed in the Certificate of Incorporation (as defined below) of the corporation.
Section 2 PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICE.
The corporation’s principal executive office shall be fixed and located at such place, either within or without the State of Delaware, as the Board of Directors of the corporation (the “Board”) shall determine. The Board is granted full power and authority to change said principal executive office from one location to another.
| Section 3 | OTHER OFFICES. |
The corporation may have such other offices, either within or without the State of Delaware, as the Board may designate or the business of the corporation may from time to time require.
ARTICLE II STOCKHOLDERS.
| Section 1 | PLACE OF MEETINGS. |
Meetings of the stockholders shall be held at the principal executive office of the corporation or at another place, if any, within or without the State of Delaware as may be designated by the Board and filed with the Secretary of the corporation.
| Section 2 | ANNUAL MEETINGS. |
The annual meetings of the stockholders shall be held at such time, date, and place, if any, either within or without the State of Delaware, as may be fixed by the Board. At such meetings, directors shall stand for election and any other proper business may be transacted. The Board may postpone, reschedule, or cancel any annual meeting of the stockholders previously scheduled by the Board.
| Section 3 | BUSINESS WHICH MAY BE CONDUCTED AT MEETINGS OF THE STOCKHOLDERS. |
| (a) | Annual Meetings of the Stockholders. |
| (i) | Nominations of persons for election to the Board and the proposal of business to be considered by the stockholders may be made at an annual meeting of the stockholders only (A) pursuant to the corporation’s notice of meeting (or any supplement thereto), (B) by or at the direction of the Board, or (C) by any stockholder of the corporation who was a stockholder of record of the corporation at the time the notice provided for in this Section 3 is delivered to the Secretary of the corporation, who is entitled to vote at the meeting, and who complies with the notice procedures set forth in this Section 3. For the avoidance of doubt, the foregoing clause (C) shall be the exclusive means for a stockholder to make nominations or propose other business |
5

| (other than a proposal included in the corporation’s proxy statement pursuant to and in compliance with Rule 14a-8 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)) at an annual meeting of stockholders. |
| (ii) | For nominations or other business to be properly brought before an annual meeting by a stockholder pursuant to clause (C) of paragraph (a)(i) of this Section 3, the stockholder must have given timely notice thereof in writing to the Secretary of the corporation and any such proposed business, other than the nominations of persons for election to the Board, must constitute a proper matter for stockholder action. To be timely, a stockholder’s notice shall be delivered to the Secretary at the principal executive office of the corporation not later than the close of business (as defined in paragraph (c)(ii) of this Section 3) on the 90th day nor earlier than the close of business on the 120th day prior to the first anniversary of the preceding year’s annual meeting (provided, however, that in the event that the date of the annual meeting is more than 30 days before or more than 70 days after such anniversary date, or if no annual meeting was held in the preceding year, notice by the stockholder must be so delivered not earlier than the close of business on the 120th day prior to such annual meeting and not later than the close of business on the later of the 90th day prior to such annual meeting or the 10th day following the day on which public announcement (as defined in paragraph (c)(ii) of this Section 3) of the date of such meeting is first made by the corporation). In no event shall an adjournment, recess, or postponement of an annual meeting commence a new time period (or extend any time period) for the giving of a stockholder’s notice as described above. Such stockholder’s notice shall set forth (A) as to each person whom the stockholder proposes to nominate for election as a director, all information relating to such person that is required to be disclosed in solicitations of proxies for election of directors in an election contest, or is otherwise required, in each case pursuant to Regulation 14A under Exchange Act (and such person’s written consent to being named in the proxy statement as a nominee and to serving as a director if elected); provided, however, that, in addition to the information required in the stockholder’s notice pursuant to this paragraph (a)(ii), the corporation may require each such person to furnish such other information as may reasonably be required by the corporation to determine the eligibility of such person to serve as a director of the corporation, including information relevant to a determination whether such person can be considered an independent director, (B) as to any other business that the stockholder proposes to bring before the meeting, a brief description of the business desired to be brought before the meeting, the text of the proposal or business (including the text of any resolutions proposed for consideration and, in the event that such business includes a proposal to amend the bylaws of the corporation, the language of the proposed amendment), the reasons for conducting such business at the meeting, and any substantial interest (within the meaning of Item 5 of Schedule 14A under the Exchange Act) in such business of such stockholder and the beneficial owner (within the meaning of Section 13(d) of the Exchange Act), if any, on whose behalf the proposal is made, (C) as to the stockholder giving the notice and the beneficial owner, if any, on whose behalf the nomination or proposal is made (1) the name and address of such stockholder, as they appear on the corporation’s books, and of such beneficial owner, (2) the class and number of shares of stock of the corporation which are owned of record by such stockholder and such beneficial owner, and a representation that the stockholder will notify the corporation in writing within 5 business days after the record date for such meeting of the class and number of shares of stock of the corporation owned of record by the stockholder and such beneficial owner as of the record date for the meeting (except as otherwise provided in paragraph (a)(iv) of this Section 3), and (3) a representation that the stockholder is a holder of record of stock of the corporation entitled to vote at such meeting and intends to appear in person or by proxy at such meeting to propose such business or nomination, and (D) as to the stockholder giving the notice or, if the notice is given on behalf of a beneficial owner on whose behalf the business is proposed or the nomination is made, as to such beneficial owner, and if such stockholder or beneficial owner is an entity, as to each director, executive, managing member or control person of such entity (any such individual or control person, a “control person”) (1) the class and number of shares of stock of the corporation which are beneficially owned (as defined in paragraph (c)(ii) of this Section 3) by such stockholder or beneficial owner and by any control person as of the date of the notice, and a representation that the stockholder will notify the corporation in writing within 5 business days after the record date for such meeting of the class and number of shares of stock of the corporation beneficially owned by such stockholder or beneficial owner and by any control person as of the record date for the meeting (except as otherwise provided in paragraph (a)(iv) of this Section 3), (2) a description of any agreement, arrangement, or understanding with respect to the nomination or other business between or among such stockholder, beneficial owner, or control person and any other person, including without limitation any agreements that |
6

| would be required to be disclosed pursuant to Item 5 or Item 6 of Exchange Act Schedule 13D (regardless of whether the requirement to file a Schedule 13D is applicable) and a representation that the stockholder will notify the corporation in writing within 5 business days after the record date for such meeting of any such agreement, arrangement, or understanding in effect as of the record date for the meeting (except as otherwise provided in paragraph (a)(iv) of this Section 3), (3) a description of any agreement, arrangement, or understanding (including without limitation any derivative or short positions, profit interests, options, hedging transactions, and borrowed or loaned shares) that has been entered into as of the date of the stockholder’s notice by, or on behalf of, such stockholder, beneficial owner, or control person, the effect or intent of which is to mitigate loss, manage risk or benefit from changes in the share price of any class or series of the corporation’s stock, or maintain, increase, or decrease the voting power of the stockholder, beneficial owner, or control person with respect to securities of the corporation, and a representation that the stockholder will notify the corporation in writing within 5 business days after the record date for such meeting of any such agreement, arrangement, or understanding in effect as of the record date for the meeting (except as otherwise provided in paragraph (a)(iv) of this Section 3), and (4) a representation whether the stockholder or beneficial owner, if any, intends or is part of a group which intends (x) to solicit proxies from stockholders in support of such proposal or nomination, and/or (y) to deliver a proxy statement and/or form of proxy to holders of at least the percentage of the corporation’s outstanding stock required to approve or adopt the proposal. |
| (iii) | Notwithstanding anything in the second sentence of paragraph (a)(ii) of this Section 3 to the contrary, in the event that the number of directors to be elected to the Board of the corporation at the annual meeting is increased and there is no public announcement by the corporation naming the nominees for the additional directorships at least 10 days prior to the last day a stockholder may deliver a notice in accordance with paragraph (a)(ii) of this Section 3, a stockholder’s notice required by this Section 3 shall also be considered timely, but only with respect to nominees for the additional directorships, if it shall be delivered to the Secretary of the corporation at the principal executive office of the corporation not later than the close of business on the 10th day following the day on which such public announcement is first made by the corporation. |
| (iv) | Notwithstanding anything in paragraphs (a) and (b) of this Section 3 to the contrary, if the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to vote at any meeting of stockholders is different from the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to notice of the meeting, a stockholder’s notice required by this Section 3 shall set forth a representation that the stockholder will notify the corporation in writing within 5 business days after the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to vote at the meeting, or by the opening of business on the date of the meeting (whichever is earlier), of the information required under clauses (C)(2) and (D)(1) – (3) of paragraph (a)(ii) of this Section 3, and such information when provided to the corporation shall be current as of the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to vote at the meeting. |
(b) Special Meetings of the Stockholders. Only such business shall be conducted at a special meeting of the stockholders as shall have been brought before the meeting pursuant to the corporation’s notice of meeting. Nominations of persons for election to the Board may be made at a special meeting of the stockholders at which directors are to be elected pursuant to the corporation’s notice of meeting (i) by or at the direction of the Board, or (ii) provided that the Board has determined that directors shall be elected at such meeting, by any stockholder of the corporation who is a stockholder of record at the time the notice provided for in this Section 3 is delivered to the Secretary of the corporation, who is entitled to vote at the meeting and upon such election, and who complies with the notice procedures set forth in this Section 3. In the event the corporation calls a special meeting of the stockholders for the purpose of electing one or more directors to the Board, any stockholder entitled to vote in such election of directors may nominate a person or persons (as the case may be) for election to such position(s) as specified in the corporation’s notice of meeting, if the stockholder’s notice required by this paragraph shall be delivered to the Secretary at the principal executive office of the corporation not earlier than the close of business on the 120th day prior to such special meeting and not later than the close of business on the later of the 90th day prior to such special meeting or the 10th day following the day on which public announcement is first made of the date of the special meeting and of the nominees proposed by the Board to be elected at such meeting. In no event shall an adjournment, recess, or postponement of a special meeting commence a new time period (or extend any time period) for the giving of a stockholder’s notice as described above.
(c) General.
7

| (i) | Only persons who are nominated in accordance with the procedures set forth in this Section 3 shall be eligible to be elected at an annual or special meeting of the stockholders of the corporation to serve as directors, and only such business shall be conducted at a meeting of the stockholders as shall have been brought before the meeting in accordance with the procedures set forth in this Section 3. Except as otherwise provided by law, the Board, the Chair of the Board, or the chair of the meeting, shall have the power and duty (A) to determine whether a nomination or any business proposed to be brought before the meeting was made or proposed, as the case may be, in accordance with the procedures set forth in this Section 3 (including whether the stockholder or beneficial owner, if any, on whose behalf the nomination or proposal is made or solicited (or is part of a group which solicited) or did not so solicit, as the case may be, proxies in support of such stockholder’s nominee or proposal in compliance with such stockholder’s representation as required by clause (D)(4) of paragraph (a)(ii) of this Section 3), and (B) if any proposed nomination or business was not made or proposed in compliance with this Section 3, to declare that such nomination shall be disregarded or that such proposed business shall not be transacted. Notwithstanding the foregoing provisions of this Section 3, unless otherwise required by law, if the stockholder does not provide the information required under clauses (C)(2) and (D)(1) – (3) of paragraph (a)(ii) of this Section 3 to the corporation within the time frames specified herein, or if the stockholder (or a qualified representative of the stockholder) does not appear at the annual or special meeting of stockholders of the corporation to present a nomination or other business, such nomination shall be disregarded and such other business shall not be transacted, notwithstanding that proxies in respect of such vote may have been received by the corporation. For purposes of this Section 3, to be considered a qualified representative of a stockholder, a person must be a duly authorized officer, manager, or partner of such stockholder or authorized by a writing executed by such stockholder (or a reliable reproduction or electronic transmission of the writing) delivered to the corporation prior to the making of such nomination or proposal at such meeting by such stockholder stating that such person is authorized to act for such stockholder as proxy at the meeting of stockholders. |
| (ii) | For purposes of this Section 3, the “close of business” shall mean 6:00 p.m. local time at the principal executive office of the corporation on any calendar day, whether or not the day is a business day, and a “public announcement” shall include disclosure in a press release reported by the Dow Jones News Service, Associated Press, or comparable national news service or in a document publicly filed or furnished by the corporation with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Section 13, 14, or 15(d) of the Exchange Act. For purposes of clause (D)(1) of paragraph (a)(ii) of this Section 3, shares shall be treated as “beneficially owned” by a person if the person beneficially owns such shares, directly or indirectly, for purposes of Section 13(d) of the Exchange Act and Regulations 13D and 13G thereunder or has or shares pursuant to any agreement, arrangement, or understanding (whether or not in writing) (A) the right to acquire such shares (whether such right is exercisable immediately or only after the passage of time or the fulfillment of a condition or both), (B) the right to vote such shares, alone or in concert with others, and/or (C) investment power with respect to such shares, including the power to dispose of, or to direct the disposition of, such shares. |
| (iii) | Notwithstanding the foregoing provisions of this Section 3, a stockholder shall also comply with all applicable requirements of the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations thereunder with respect to the matters set forth in this Section 3. Nothing in this Section 3 shall be deemed to affect any rights (A) of stockholders to request inclusion of proposals in the corporation’s proxy statement pursuant to Rule 14a-8 under the Exchange Act, or (B) of the holders of any series of Preferred Stock to elect directors pursuant to any applicable provisions of the certificate of incorporation of the corporation, including any certificate of designations relating to any series of Preferred Stock, as any such documents may be amended and restated from time to time (collectively, the “Certificate of Incorporation”). |
| Section 4 | SPECIAL MEETINGS. |
Special meetings of the stockholders may be called only by the Board, the Chair of the Board, the Chief Executive Officer, or the President, and may not be called by any other person or persons. Subject to the provisions of applicable law, only such business shall be considered at a special meeting of the stockholders as shall have been stated in the notice for such meeting. The Board may postpone, reschedule, or cancel any special meeting of the stockholders previously scheduled pursuant to this Section 4.
8

| Section 5 | NOTICE OF ANNUAL OR SPECIAL MEETINGS. |
(a) Time Periods. Notice of each annual or special meeting of the stockholders shall be given not less than 10 nor more than 60 days before the date of the meeting to each stockholder entitled to vote at such meeting as of the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to notice of the meeting. Such notice shall state the place, if any, date, and hour of the meeting, the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to vote at the meeting (if such date is different from the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to notice of the meeting), the means of remote communications, if any, by which stockholders may be deemed present in person or represented by proxy and vote at the meeting, and (i) in the case of the annual meeting, those matters which the Board, at the time of the mailing of the notice, intends to present for action by the stockholders (but, subject to Section 3 of this Article II and the provisions of applicable law, any other matters properly brought may be presented at the meeting for action), or (ii) in the case of a special meeting, the purpose or purposes for which the meeting was called. The notice of any meeting at which directors are to stand for election shall include the names of nominees intended at the time of the notice to be presented by the Board for election.
(b) Method. Notice of a stockholders’ meeting shall be given (i) in writing, (ii) by United States mail, addressed to the stockholder at the address of such stockholder appearing on the books of the corporation or given by the stockholder to the corporation for the purpose of notice, or (iii) by electronic transmission in accordance with Section 232 of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware. Notice by mail shall be deemed to have been given at the time written notice is deposited in the United States mail, postage prepaid. Any other written notice shall be deemed to have been given at the time it is personally delivered to the recipient or delivered to a common carrier for transmission. Notice by electronic transmission shall be deemed given as provided in Section 232 of the Corporation Law of the State of Delaware. An affidavit that notice has been given, executed by the Secretary, any Assistant Secretary or any transfer agent or other agent of the corporation, shall be prima facie evidence of the facts stated in the notice in the absence of fraud. Notice shall be deemed to have been given to all stockholders who share an address if notice is given in accordance with the “householding” rules set forth in Rule 14a-3(e) under the Exchange Act and Section 233 of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware.
| Section 6 | QUORUM—REQUIRED VOTES. |
Except as otherwise provided by law, the Certificate of Incorporation, or these bylaws, at each meeting of the stockholders the presence in person or by proxy of the holders of a majority in voting power of the outstanding shares of stock entitled to vote at the meeting shall be necessary and sufficient to constitute a quorum. In the absence of a quorum, the chair of the meeting, or the stockholders so present, by a majority in voting power thereof, may adjourn the meeting from time to time in the manner provided in Section 7 of this Article II until a quorum shall attend. Subject to applicable law, if a quorum initially is present at any meeting of stockholders, the stockholders may continue to transact business until adjournment or recess, notwithstanding the withdrawal of enough stockholders to leave less than a quorum, but if a quorum is not present at least initially, no business other than adjournment or recess may be transacted.
| Section 7 | ADJOURNED OR RECESSED MEETINGS AND NOTICE THEREOF. |
Any meeting of the stockholders, annual or special, may be adjourned or recessed for any reason from time to time by the chair of the meeting, subject to any rules and regulations adopted by the Board pursuant to Section 12 of this Article II, and may be adjourned for any reason from time to time by the stockholders so present, by a majority in voting power thereof. Notice need not be given of any adjourned meeting if the time and place, if any, thereof, and the means of remote communications, if any, by which stockholders and proxy holders may be deemed to be present in person and vote at such adjourned meeting are announced at the meeting at which the adjournment is taken. At the adjourned meeting the corporation may transact any business which might have been transacted at the original meeting. If the adjournment is for more than 30 days, or if after the adjournment a new record date for stockholders entitled to vote is fixed for the adjourned meeting, the Board shall fix a new record date for notice of such adjourned meeting in accordance with Section 9 of this Article II and notice of the adjourned meeting shall be given to each stockholder of record entitled to vote at the adjourned meeting as of the record date fixed for notice of such adjourned meeting.
| Section 8 | VOTING. |
Except as otherwise provided by law, the stockholders entitled to notice of any meeting or to vote at any such meeting shall be only those persons in whose name shares stand on the stock records of the corporation on the record date determined in accordance with Section 9 of this Article II.
Voting at meetings of the stockholders need not be by written ballot. At any meeting of the stockholders for the election of directors, each nominee for election as a director in an uncontested election shall be elected if the number of votes cast for the nominee’s election exceeds the number of votes cast against the nominee’s election. In all director elections other than uncontested elections, the nominees for election as a director shall be elected by a plurality of the votes cast. For purposes of this Section 8, an “uncontested election” means any meeting of the stockholders at which the
9

number of candidates does not exceed the number of directors to be elected and with respect to which (a) no stockholder has submitted notice of an intent to nominate a candidate for election at such meeting in accordance with Section 3 of this Article II, or (b) such a notice has been submitted, and on or before the 5th business day prior to the date that the corporation files its definitive proxy statement relating to such meeting with the Securities and Exchange Commission (regardless of whether thereafter revised or supplemented), the notice has been (i) withdrawn in writing to the Secretary of the corporation, (ii) determined not to be a valid notice of nomination, with such determination to be made by the Board (or a committee thereof) pursuant to Section 3 of this Article II, or if challenged in court, by a final court order, or (iii) determined by the Board (or a committee thereof) not to create a bona fide election contest.
All other matters shall, unless otherwise provided by the Certificate of Incorporation, these bylaws, the rules or regulations of any stock exchange applicable to the corporation, or as otherwise provided by law or pursuant to any regulation applicable to the corporation, be decided by the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority in voting power of the shares of stock of the corporation which are present in person or by proxy and entitled to vote thereon.
| Section 9 | RECORD DATE. |
In order that the corporation may determine the stockholders entitled to notice of or to vote at any meeting of the stockholders or any adjournment thereof, or entitled to receive payment of any dividend or other distribution or allotment of any rights, or entitled to exercise any rights in respect of any change, conversion, or exchange of stock, or for the purpose of any other lawful action, the Board may fix a record date, which record date shall not precede the date upon which the resolution fixing the record date is adopted by the Board, and which record date (a) in the case of determination of stockholders entitled to notice of any meeting of stockholders or adjournment thereof, shall, unless otherwise required by law, not be more than 60 nor less than 10 days before the date of such meeting, which shall also be the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to vote at such meeting unless the Board determines, at the time it fixes such record date, that a later date on or before the date of the meeting shall be the date for making such determination, and (b) subject to Section 14 of this Article II, in the case of any other action, shall not be more than 60 days prior to such other action. If no record date is fixed (a) the record date for determining stockholders entitled to notice of or to vote at a meeting of stockholders shall be at the close of business on the day next preceding the day on which notice is given, or, if notice is waived, at the close of business on the day next preceding the day on which the meeting is held, and (b) subject to Section 14 of this Article II, the record date for determining stockholders for any other purpose shall be at the close of business on the day on which the Board adopts the resolution relating thereto. A determination of stockholders of record entitled to notice of or to vote at a meeting of stockholders shall apply to any adjournment of the meeting; provided, however, that the Board may fix a new record date for the adjourned meeting.
| Section 10 | PROXIES. |
Each stockholder entitled to vote for directors, or on any other matter, may authorize another person or persons to act for such stockholder by proxy, but no such proxy shall be voted or acted upon after three years from its date, unless the proxy provides for a longer period. A proxy shall be irrevocable if it states that it is irrevocable and if, and only as long as, it is coupled with an interest sufficient in law to support an irrevocable power. A stockholder may revoke any proxy which is not irrevocable by attending the meeting and voting in person or by delivering a revocation of the proxy or a proxy bearing a later date to the Secretary of the corporation.
A proxy validly delivered to the corporation shall mean any written authorization which is signed by the person executing the proxy, as well as any electronic transmission (to include without limitation transmissions by facsimile and by computer messaging systems), which is authorized by a stockholder or the stockholder’s attorney in fact, which gives another person or persons power to vote with respect to the shares of such stockholder. A stockholder may authorize another person or persons to act for such stockholder as proxy by transmitting or authorizing the transmission of an electronic transmission to the person who will be the holder of the proxy or to a proxy solicitation firm, proxy support service organization or like agent duly authorized by the person who will be the holder of the proxy to receive such transmission, provided that any such electronic transmission must either set forth or be submitted with information from which it can be determined that the electronic transmission was authorized by the stockholder. If it is determined that such electronic transmissions are valid, the inspectors or, if there are no inspectors, such other persons making that determination shall specify the information upon which they relied. Any copy, facsimile telecommunication or other reliable reproduction of the writing or transmission created pursuant to this Section 10 may be substituted or used in lieu of the original writing or transmission for any and all purposes for which the original writing or transmission could be used, provided that such copy, facsimile telecommunication or other reproduction shall be a complete reproduction of the entire original writing or transmission.
10

| Section 11 | INSPECTORS OF ELECTION. |
(a) Appointment of Inspectors. In advance of any meeting of the stockholders, the Board shall appoint inspectors of election to act at such meeting. If inspectors of election are not so appointed, or if any persons so appointed fail to appear or refuse to act, the chair of the meeting may, and on the request of any stockholder or stockholder’s proxy shall, make such appointment at the meeting. The number of inspectors shall be either one or three. If appointed at a meeting on the request of one or more stockholders’ proxies, the majority of shares present shall determine whether one or three inspectors are to be appointed.
(b) Duties of Inspectors. The duties of such inspectors shall include: determining the number of shares outstanding and the voting power of each; determining the shares represented at the meeting; determining the existence of a quorum; determining the authenticity, validity, and effect of proxies; receiving votes and ballots; counting and tabulating all votes and ballots; certifying the results; and doing such acts as may be proper to conduct the election or vote with fairness to all stockholders. If there are three inspectors, the decision, act or certificate of a majority is in all respects the decision, act or certificate of all. Each inspector, before entering upon the discharge of his or her duties, shall take and sign an oath to execute faithfully the duties of inspector with strict impartiality and according to the best of his or her ability. Inspectors need not be stockholders. No director or nominee for the office of director at an election shall be appointed as an inspector at such election.
| Section 12 | CONDUCT OF MEETING. |
(a) Chair of Meeting. The Chair of the Board shall preside at all meetings of the stockholders, or, in his or her absence, another person designated by the Board. The chair of the meeting shall conduct each such meeting in a businesslike and fair manner, but shall not be obligated to follow any technical, formal, or parliamentary rules or principles of procedure. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, the chair of the meeting shall have all of the powers usually vested in the chair of a meeting of stockholders, in addition to specific powers relating to the matters addressed in paragraph (b) of this Section 12. (b) Organization. The date and time of the opening and the closing of the polls for each matter upon which the stockholders shall vote at a meeting of stockholders shall be announced at the meeting. The Board may adopt such rules and regulations for the conduct of any meeting of stockholders as it shall deem appropriate. Except to the extent inconsistent with such rules and regulations as adopted by the Board, the chair of the meeting shall have the authority to adopt and enforce such rules and regulations for the conduct of any meeting of stockholders and the safety of those in attendance as, in the judgment of the chair, are necessary, appropriate, or convenient for the conduct of the meeting. Rules and regulations for the conduct of meetings of stockholders, whether adopted by the Board or by the chair of the meeting, may include without limitation, establishing (i) an agenda or order of business for the meeting, (ii) rules and procedures for maintaining order at the meeting and the safety of those present, (iii) limitations on attendance at or participation in the meeting to stockholders entitled to vote at the meeting, their duly authorized and constituted proxies, and such other persons as the chair of the meeting shall permit, (iv) restrictions on entry to the meeting after the time fixed for the commencement thereof, (v) limitations on the time allotted for consideration of each agenda item and for questions and comments by participants, (vi) regulations for the opening and closing of the polls for balloting and matters which are to be voted on by ballot (if any), and (vii) procedures (if any) requiring attendees to provide the corporation advance notice of their intent to attend the meeting. Subject to any rules and regulations adopted by the Board, the chair of the meeting may convene and, for any or no reason, from time to time, adjourn, and/or recess any meeting of stockholders pursuant to Section 7 of this Article II. The chair of the meeting, in addition to making any other determinations that may be appropriate to the conduct of the meeting, shall have the power and duty to declare that a nomination or other business was not properly brought before the meeting if the facts warrant (including if a determination is made, pursuant to Section 3 of this Article II, that a nomination or other business was not made or proposed, as the case may be, in accordance with Section 3 of this Article II), and if such chair should so declare, such nomination shall be disregarded or such other business shall not be transacted. The Secretary of the corporation, or in his or her absence, an Assistant Secretary, or in the absence of the Secretary and all Assistant Secretaries, a person whom the chair of the meeting shall appoint, shall act as secretary of the meeting and keep a record of the proceedings thereof. (c) Meetings by Remote Communications. The Board may, in its sole discretion, determine that a meeting of stockholders shall not be held at any place, but may instead be held solely by means of remote communication in accordance with Section 211(a)(2) of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware. If authorized by the Board in its sole discretion, and subject to such guidelines and procedures as the Board may adopt, stockholders not physically present or represented by proxy at a meeting of stockholders may, by means of remote communication (i) participate in a meeting of stockholders, and (ii) be deemed present in person and vote at a meeting of stockholders whether such meeting is to be held at a designated place or solely by means of remote communication, provided that (A) the corporation shall implement reasonable measures to verify that each person deemed present and permitted to vote at the meeting by means of remote communication is a stockholder or a person representing a stockholder by proxy, (B) the corporation shall implement reasonable measures to provide such stockholders and persons representing stockholders by proxy a reasonable opportunity to participate in the meeting and to vote on matters submitted to the stockholders, including an opportunity to read or hear the proceedings of the meeting substantially concurrently with such proceedings, and (C) if any stockholder or person representing a stockholder by proxy votes or takes other action at the meeting by means of remote communication, a record of such vote or other action shall be maintained by the corporation.
11

Section 13 LIST OF STOCKHOLDERS ENTITLED TO VOTE.
The Secretary of the corporation shall prepare and make, at least 10 days before every meeting of the stockholders, a complete list of the stockholders entitled to vote at the meeting; provided, however, that if the record date for determining the stockholders entitled to vote is less than 10 days before the date of the meeting, the list shall reflect the stockholders entitled to vote as of the 10th day before the meeting date. Such list shall be arranged in alphabetical order, and showing the address of each stockholder and the number of shares registered in the name of each stockholder, provided that nothing in this Section 13 shall require the corporation to include electronic mail addresses or other electronic contact information on such list. Such list shall be open to the examination of any stockholder, for any purpose germane to the meeting, during ordinary business hours, for a period of at least 10 days prior to the meeting (a) on a reasonably accessible electronic network, provided that the information required to gain access to such list is provided with the notice of meeting, or (b) during ordinary business hours, at the corporation’s principal place of business. In the event that the corporation determines to make the list available on an electronic network, the corporation may take reasonable steps to ensure that such information is available only to stockholders. If the meeting is to be held at a place, then the list shall also be produced and kept at the time and place of the meeting during the whole time thereof and may be examined by any stockholder who is present. If the meeting is to be held solely by means of remote communication, then the list shall also be open to the examination of any stockholder during the whole time of the meeting on a reasonably accessible electronic network, and the information required to access such list shall be provided with the notice of the meeting. Except as otherwise provided by law, the stock ledger shall be the only evidence as to who are the stockholders entitled to examine the stock ledger, or the list of stockholders or the books of the corporation, or to vote in person or by proxy at any meeting of the stockholders.
| Section 14 | CONSENT OF STOCKHOLDERS IN LIEU OF MEETING. |
(a) Pursuant to the Certificate of Incorporation, any action required to be taken at any annual or special meeting of the stockholders of the corporation, or any action which may be taken at any annual or special meeting of the stockholders duly called in accordance with the Certificate of Incorporation or these bylaws, may be effected by written consent of the stockholders in lieu of a meeting only if the action to be effected by written consent of the stockholders and the taking of such action by such written consent have expressly been approved in advance by the Board, and only if a consent or consents in writing, setting forth the action so taken, shall be signed by the holders of outstanding stock having not less than the minimum number of votes that would be necessary to authorize or take such action at a meeting at which all shares entitled to vote thereon were present and voted, and delivered to the corporation by delivery to its registered office in Delaware, its principal place of business, or an officer or agent of the corporation having custody of the book in which proceedings of meetings of the stockholders are recorded. Delivery made to the corporation’s registered office shall be made by hand or by certified or registered mail, return receipt requested. Any person executing a consent may provide, whether through instruction to an agent or otherwise, that such a consent will be effective at a future time (including a time determined upon the happening of an event), no later than 60 days after such instruction is given or such provision is made and if evidence of such instruction or provision is provided to the corporation, such later effective time shall serve as the date of signature so long as such person did not revoke the consent prior to such time. Any such consent shall be revocable prior to its becoming effective.
(b) Every written consent shall bear the date of signature of each stockholder who signs the consent and no written consent shall be effective to take the corporate action referred to therein unless, within 60 days of the date the earliest dated consent is delivered to the corporation, a written consent or consents signed by a sufficient number of holders to take action are delivered to the corporation in the manner prescribed in paragraph (c) of this Section 14.
(c) In order that the corporation may determine the stockholders entitled to consent to corporate action in writing without a meeting, the Board may fix a record date, which record date shall not precede the date upon which the resolution fixing the record date is adopted by the Board, and which date shall not be more than 10 days after the date upon which the resolution fixing the record date is adopted by the Board. Any stockholder of record seeking to have the stockholders authorize or take corporate action by written consent in writing without a meeting shall, by written notice to the Secretary of the corporation, request that the Board approve the action to be effected by written consent of the stockholders and the taking of such action by such written consent. The Board shall promptly, but in all events within 10 days after the date on which such a request is received, decide whether to grant such approval. Following the receipt of such approval, the stockholder shall, by written notice to the Secretary, request the Board to fix a record date. The Board shall promptly, but in all events within 10 days after the date on which the request for a record date is received, adopt a resolution fixing the record date. If no record date has been fixed by the Board within 10 days of the date on which such a request is received, the record date for determining stockholders entitled to consent to corporate action in writing without a meeting, when no prior action by the Board is required by applicable law, shall be the first date on which a signed written
12

consent setting forth the action taken or proposed to be taken is delivered to the corporation in accordance with paragraphs (a) and (b) of this Section 14. If no record date has been fixed by the Board and prior action by the Board is required by applicable law, the record date for determining stockholders entitled to consent to corporate action in writing without a meeting shall be at the close of business on the date on which the Board adopts the resolution taking such prior action.
(d) Within 5 business days after receipt of the earliest dated consent delivered to the corporation in the manner provided in this Section 14, the corporation, shall retain nationally recognized independent inspectors of elections for the purposes of performing a review of the validity of consents and any revocations thereof. The cost of retaining inspectors of election shall be borne by the corporation.
(e) At any time that stockholders soliciting consents in writing to corporate action have a good faith belief that the requisite number of valid and unrevoked consents to authorize or take the action specified has been received by them, the consents shall be delivered by the soliciting stockholders to the corporation’s registered office in the State of Delaware, or principal place of business, or to the Secretary of the corporation, together with a certificate stating their belief that the requisite number of valid and unrevoked consents has been received as of a specific date, which date shall be identified in the certificate. In the event that delivery shall be made to the corporation’s registered office in Delaware, such delivery shall be made by hand or by certified or registered mail, return receipt requested. Upon receipt of such consents, the corporation shall cause the consents to be delivered promptly to the inspectors of election. The corporation also shall deliver promptly to the inspectors of election any revocations of consents in its possession, custody, or control as of the time of receipt of the consents.
(f) The corporation shall give prompt notice to the stockholders of the results of any consent solicitation or the taking of corporate action without a meeting by less than unanimous written consent.
(g) This Section 14 shall in no way impair or diminish the right of any stockholder or director, or any officer whose title to office is contested, to contest the validity of any consent or revocation thereof, or to take any other action with respect thereto.
ARTICLE III OFFICES.
| Section 1 | POWERS. |
Subject to limitations of the Certificate of Incorporation, of these bylaws, and of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware relating to action required to be approved by the stockholders or by the outstanding shares, the business and affairs of the corporation shall be managed by or under the direction of the Board and it shall have the final authority in matters of strategy and policy matters for the corporation.
The Board may delegate management duties for the operation of the business of the corporation to those persons to whom authority is properly delegated by the Board, including officers of the corporation, provided that the business and affairs of the corporation shall be managed and all corporate powers shall be exercised under the ultimate direction of the Board. Without prejudice to such general powers, but subject to the same limitations, it is hereby expressly declared that the Board shall have the following powers in addition to the other powers enumerated in these bylaws
(a) To select and remove officers (in accordance with the provisions of these bylaws), prescribe the powers and duties for them as may not be inconsistent with law, the Certificate of Incorporation, or these bylaws, and fix their compensation.
(b) To conduct, manage, and control the affairs and business of the corporation and to make such rules and regulations therefor not inconsistent with law, the Certificate of Incorporation, or these bylaws, as the Board may deem best.
(c) To adopt, alter, amend, and repeal these bylaws from time to time as the Board may deem best.
(d) To adopt, make, and use a corporate seal, and to prescribe the forms of any certificates of stock, and to alter the form of such seal and of such certificates from time to time as the Board may deem best.
(e) To authorize the issuance of shares of stock of the corporation from time to time, upon such terms and for such consideration as may be lawful.
13

(f) To borrow money and incur indebtedness for the purposes of the corporation, and to cause to be executed and delivered, in the corporate name, promissory notes, bonds, debentures, deeds of trust, mortgages, pledges, hypothecations, or other evidences of debt and securities therefor.
(g) To adopt such rules and regulations for the conduct of its meetings as the Board may deem best.
| Section 2 | NUMBER OF DIRECTORS. |
The authorized number of directors shall be as set forth in the Certificate of Incorporation. The Board shall fix the exact number of directors by resolution duly adopted by the Board.
| Section 3 | NOMINATION, ELECTION, QUALIFICATION AND TERM OF OFFICE. |
(a) Eligibility for Election as Director. Only persons who are nominated by, or at the direction of the Board, or by a stockholder who has given timely written notice to the Secretary of the corporation in accordance with Section 3 of Article II of these bylaws, will be eligible for election as directors of the corporation. (b) Meetings at which Directors May Be Elected. The directors shall stand for election at each annual meeting of the stockholders, but if any such annual meeting is not held or the directors are not elected thereat, the directors may be elected at any special meeting of the stockholders called for that purpose. (c) Qualified Directors. For a person to be qualified to serve as a director of the corporation, such person need not be an employee or stockholder of the corporation during his or her directorship. (d) Length of Term for Directors. Each director shall hold office until the next annual meeting of stockholders and until his or her successor is duly elected and qualified or until his or her earlier death, resignation or removal. (e) Removal of Directors. Any director, or the entire Board, may be removed with our without cause, by the holders of a majority of the shares then entitled to vote at the election of directors.
| Section 4 | VACANCIES. |
Any director may resign, to be effective upon delivery, by giving notice in writing or by electronic transmission to the Board or to the Chair of the Board, President, or Secretary of the corporation, unless the notice specifies a later time for the effectiveness of such resignation or an effective time determined upon the happening of an event or events. Unless otherwise specified therein, the acceptance of such resignation shall not be necessary to make it effective. If the resignation is effective at a future time or upon the happening of a future event or events, a successor may be elected to take office when the resignation becomes effective.
Any newly-created directorship resulting from an increase in the authorized number of directors or any vacancies in the Board occurring by reason of death, resignation, retirement, disqualification, or removal may be filled by a majority of the remaining directors, though less than a quorum, or by a sole remaining director, and each director so elected shall hold office until the next annual meeting and until such director’s successor has been elected and qualified.
The stockholders may elect a director or directors at any time to fill any vacancy or vacancies not filled by the directors.
No reduction of the authorized number of directors shall have the effect of removing any director prior to the expiration of the director’s term of office.
| Section 5 | PLACE OF MEETING. |
Regular or special meetings of the Board shall be held at any place within or without the State of Delaware which has been designated from time to time by the Board. In the absence of such designation, regular meetings shall be held at the principal executive office of the corporation.
| Section 6 | REGULAR MEETINGS. |
The Board shall hold a regular meeting annually or at such other intervals as the Board deems appropriate for the purpose of organization, election of officers and the transaction of other business.
Other regular meetings of the Board shall be held without call on such dates and at such times as may be fixed by the Board. Call and notice of all regular meetings of the Board are hereby dispensed with.
14

| Section 7 | SPECIAL MEETINGS. |
Special meetings of the Board for any purpose or purposes may be called at any time by the Chair, the Chief Executive Officer, the President, the Secretary of the corporation, or by a majority of the directors then in office.
Special meetings of the Board shall be held upon four days’ written notice or at least twenty-four hours’ notice given personally or by telephone or electronic transmission, including a voice messaging system or other system or technology designed to record and communicate messages, facsimile, electronic mail, or other electronic means of communication. Any written notice shall be addressed or delivered to each director at such director’s address as it is shown upon the records of the corporation or as may have been given to the corporation by the director for purposes of notice or, if such address is not shown on such records or is not readily ascertainable, at the place in which the meetings of the directors are regularly held.
Notice by mail shall be deemed to have been given at the time a written notice is deposited in the United States mails, postage prepaid. Any other written notice shall be deemed to have been given at the time it is personally delivered to the recipient or is delivered to a common carrier for transmission. Oral notice shall be deemed to have been given at the time it is communicated, in person or by telephone, to the recipient or to a person at the office of the recipient who the person giving the notice has reason to believe will promptly communicate it to the recipient.
| Section 8 | QUORUM. |
A majority of the total number of directors then authorized constitutes a quorum of the Board for the transaction of business, except to adjourn as provided in Section 11 of this Article III. Every act or decision done or made by a majority of the directors present at a meeting duly held at which a quorum is present shall be regarded as the act of the Board, unless a greater number is required by law or by the Certificate of Incorporation.
| Section 9 | PARTICIPATION IN MEETINGS BY COMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT. |
Members of the Board, or any committee thereof, may participate in a meeting through the use of conference telephones, electronic video screen equipment, or other similar communications equipment. Participation in such a meeting shall constitute presence in person at that meeting by a member of the Board if all of the following apply
| (i) | each member participating in the meeting can hear and communicate with all of the other members concurrently, |
| (ii) | each member is provided the means of participating in all matters before the Board, including, without limitation, the capacity to propose, or to interpose an objection to, a specific action to be taken by the corporation, and |
| (iii) | the corporation is able to verify both of the following (x) a person participating in the meeting is a director or other person entitled to participate in the Board meeting, and (y) all actions of, or votes by, the Board are taken or cast only by the directors and not by persons who are not directors. |
| Section 10 | WAIVER OF NOTICE. |
Notice of a meeting need not be given to any director who signs, or provides by electronic transmission, a waiver of notice or a consent to holding the meeting or an approval of the minutes thereof, whether before or after the meeting, or who attends the meeting without protesting, prior thereto or at its commencement, the lack of notice to such director. All such waivers, consents, and approvals shall be filed with the corporate records or made a part of the minutes of the meeting. Such filing shall be in paper form if the minutes are maintained in paper form and shall be in electronic form if the minutes are maintained in electronic form.
| Section 11 | ADJOURNMENT. |
A majority of the directors present, whether or not a quorum is present, or the chair of the meeting may adjourn any directors’ meeting to another time and place.
15

| Section 12 | FEES AND COMPENSATION. |
Directors and members of committees may receive such compensation, if any, for their services, and such reimbursement for expenses, as may be fixed or determined by the Board. The corporation shall not compensate directors who are also employees of the corporation.
| Section 13 | ACTION WITHOUT MEETING. |
Any action required or permitted to be taken by the Board, or any committee thereof, may be taken without a meeting if all members of the Board or committee shall consent in writing or by electronic transmission to such action. Such consent or consents shall have the same effect as a unanimous vote of the Board or committee and shall be filed with the minutes of the proceedings of the Board or committee. Such filing shall be in paper form if the minutes are maintained in paper form and shall be in electronic form if the minutes are maintained in electronic form. Any person (whether or not then a director) may provide, whether through instruction to an agent or otherwise, that a consent will be effective at a future time (including a time determined upon the happening of an event), no later than 60 days after such instruction is given or such provision is made and such consent shall be deemed to have been given at such effective time so long as such person is then a director and did not revoke the consent prior to such time. Any such consent shall be revocable prior to its becoming effective.
| Section 14 | RIGHTS OF INSPECTION. |
Every director shall have the right at any reasonable time to examine the corporation’s stock ledger, a list of the stockholders of the corporation, and the corporation’s other books and records for any purpose reasonably related to such director’s position as a director.
| Section 15 | COMMITTEES. |
The Board may appoint one or more committees, each consisting of one or more directors, and delegate to such committees such powers and authority of the Board as determined by the Board, except no such committee shall have power or authority in reference to the following
(a) Approving, adopting or recommending to the stockholders any action or matter expressly required by the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware to be submitted to the stockholders for approval, or
(b) Adopting, altering, amending, or repealing these bylaws or any of them.
Any such committee must be designated, and the members or alternate members thereof appointed, by resolution adopted by a majority of the total number of directors then authorized and any such committee may be designated by such name as the Board shall specify. In the absence or disqualification of a member of a committee, the member or members present at any meeting and not disqualified from voting, whether or not a quorum, may unanimously appoint another member of the Board to act at the meeting in the place of any absent or disqualified member. Alternate members of a committee may replace any absent member at any meeting of the committee. The Board shall have the power to prescribe the manner in which proceedings of any such committee shall be conducted. In the absence of any such prescription, such committee shall have the power to prescribe the manner in which its proceedings shall be conducted. Unless the Board or such committee shall otherwise provide, the regular and special meetings and other action of any such committee shall be governed by the provisions of this Article III applicable to meetings and actions of the Board. Minutes shall be kept of each meeting of each committee.
| Section 16 | CHAIR OF THE BOARD. |
The Board shall elect one of its members to be Chair of the Board and shall fill any vacancy in the position of Chair of the Board at such time and in such manner as the Board shall determine. The Chair of the Board shall preside at all meetings of stockholders and directors, and shall perform such other and further duties as may from time to time be required by the Board. If the Chair of the Board is not present at a meeting of the Board, another director chosen by the Board shall preside.
16

ARTICLE IV OFFICERS.
| Section 1 | OFFICERS. |
The senior officers of the corporation shall be a Chief Executive Officer, a Chief Operating Officer, a Chief Financial Officer, and a Secretary. The corporation may also have, at the discretion of the Board, a President, a Chief Administrative Officer, one or more Vice Presidents, one or more Assistant Secretaries, Treasurers, Assistant Treasurers, and such other officers as may be elected or appointed in accordance with the provisions of Section 2 of this Article IV.
| Section 2 | ELECTION OR APPOINTMENT. |
The senior officers of the corporation shall be elected by the Board annually or at such other intervals as the Board deems appropriate. In addition, other officers may be elected or appointed in accordance with the provisions of Section 5 of this Article IV. All officers, whether elected or appointed, shall serve at the pleasure of the Board, and shall hold their respective offices until their resignation, removal, or other disqualification from service, or until their respective successors shall be elected.
The Board may elect, and may empower the Chief Executive Officer to appoint, such other subordinate officers as the business of the corporation may require, each of whom shall hold office for such period and shall have such authority and perform such duties as are provided in these bylaws or as the Board may from time to time determine.
| Section 3 | ELECTED SENIOR OFFICERS. |
The elected senior officers of the corporation shall have those positions and those duties named below in this Section 3. Further, in each case, the named officer also shall have the general powers and duties of governance or management usually vested in that office and such other powers and duties as may be prescribed by the Board.
The Chief Executive Officer shall be the senior executive officer of the corporation. The President, if any, shall have the general powers and duties of management of the corporation. The Chief Operating Officer shall have the general powers and duties to carry out general administrative and financial management of the corporation.
The Secretary shall keep or cause to be kept, at the principal executive office and such other place as the Board may order, a book of minutes of all meetings of stockholders, the Board and its committees, with the time and place of holding, whether regular or special, and if special, how authorized, the notice thereof given, the names of those present at Board and committee meetings, the number of shares present or represented at stockholders’ meetings, and the proceedings thereof. The Secretary shall keep, or cause to be kept, a copy of these bylaws of the corporation at the principal executive office or such other place as the Board may order.
The Secretary shall keep, or cause to be kept, at the principal executive office or at the office of the corporation’s transfer agent or registrar, if one has been appointed, a share register, or a duplicate share register, showing the names of the stockholders and their addresses, the number and classes of shares held by each, and, if such shares are represented by certificates, the number and date of certificates issued for the same, and the number and date of cancellation of every certificate surrendered for cancellation.
The Secretary shall give, or cause to be given, notice of all meetings of the stockholders and of the Board and any committees thereof required by these bylaws or by law to be given, shall keep the seal of the corporation in safe custody, and shall have such other powers and perform such other duties as may be prescribed by the Board or the Chief Executive Officer.
The Chief Financial Officer shall keep and maintain, or cause to be kept and maintained, adequate and correct accounts of the properties and business transactions of the corporation, and shall send or cause to be sent to the stockholders of the corporation such financial statements and reports as are by law or these bylaws required to be sent to them.
The Chief Financial Officer shall deposit, or cause to be deposited, all moneys and other valuables in the name and to the credit of the corporation in depositaries of the corporation. The Chief Financial Officer shall disburse, or cause to be disbursed, the funds of the corporation as may be ordered by the Board, the Chief Executive Officer or the President, shall render to the Chief Executive Officer, the President, and the directors, whenever they request it, an account of all transactions as Chief Financial Officer and of the financial condition of the corporation, and shall have such other powers and perform such other duties as may be prescribed by the Board, the Chief Executive Officer or the President.
17

| Section 4 | REMOVAL AND RESIGNATION. |
Any officer elected by the Board may be removed only by the Board, either with or without cause, at any time. In the case of an officer not elected by the Board, such an officer may be removed by another officer upon whom such power of removal may be conferred by the Board. Any removal shall be without prejudice to the rights, if any, of the officer under any contract of employment of the officer.
Any officer may resign at any time by giving notice to the corporation in writing or by electronic transmission, subject to the rights of the corporation under any contract between the corporation and the officer. Any such resignation shall take effect at the date of delivery of such notice or at any later time specified therein, including upon the happening of a future event or events, and, unless otherwise specified therein, the acceptance of such resignation shall not be necessary to make it effective.
| Section 5 | VACANCIES. |
A vacancy in any office because of death, resignation, removal, disqualification, or any other cause shall be filled in the manner prescribed in these bylaws for regular election or appointment to such office.
ARTICLE V OTHER PROVISIONS.
| Section 1 | INSPECTION OF BYLAWS. |
The corporation shall keep in its principal executive office in the State of California, or if its principal executive office is not in such State at its principal business office in such State, the original or a copy of these bylaws as amended to date, which shall be open to inspection by stockholders at all reasonable times during office hours. If the principal executive office of the corporation is located outside the State of California and the corporation has no principal business office in such state, it shall upon the written request of any stockholder furnish to such stockholder a copy of these bylaws as amended to date.
| Section 2 | ENDORSEMENT OF DOCUMENTS; CONTRACTS. |
Subject to the provisions of applicable law unless otherwise specifically determined by the Board or pursuant to authority delegated by the Board, any note, mortgage, evidence of indebtedness, contract, conveyance, or other instrument in writing and any assignment or endorsements thereat executed or entered into between the corporation and any other person, may be signed by (a) any two of the Chief Executive Officer, the President, the Chief Financial Officer, and the General Counsel, or (b) any Executive Vice President, any senior vice president, the Secretary, any Assistant Secretary, or any Assistant Treasurer of the corporation, in each case only with regard to such instruments or documents that pertain to or relate to such person’s duties or business functions, and when so signed shall be valid and binding on the corporation in the absence of actual knowledge on the part of the other person that the signing officers had no authority to execute the same. Any such instruments may be signed by any other person or persons and in such manner as from time to time shall be determined by the Board or pursuant to authority delegated by the Board, and, unless so authorized, no officer, agent, or employee shall have any power or authority to bind the corporation by any contract or engagement, or to pledge its credit or to render it liable for any purpose or amount.
| Section 3 | CERTIFICATES OF STOCK. |
The shares of the corporation shall be represented by certificates; provided, however, that the Board may provide by resolution or resolutions that some or all of any or all classes or series of stock shall be uncertificated shares. Any such resolution shall not apply to shares represented by a certificate until such certificate is surrendered to the corporation. Every holder of shares of the corporation represented by certificates shall be entitled to have a certificate signed in the name of the corporation by the Chair of the Board, or the Chief Executive Officer, the President, or a Vice President, and by the Chief Financial Officer or an Assistant Treasurer or the Secretary or an Assistant Secretary, representing the number of shares and the class or series of shares registered in certificate form. Any or all of the signatures on the certificate may be facsimile. If any officer, transfer agent, or registrar who has signed or whose facsimile signature has been placed upon a certificate shall have ceased to be such officer, transfer agent, or registrar before such certificate is issued, it may be issued by the corporation with the same effect as if such person were an officer, transfer agent, or registrar at the date of issue.
Except as provided in this Section 3, no new share certificate or uncertificated shares shall be issued in lieu of any certificate theretofore issued by the corporation unless the latter is surrendered and cancelled at the same time. The Board may, however, if any certificate for shares is alleged to have been lost, stolen, or destroyed, authorize the issuance
18

of a new certificate or uncertificated shares in lieu thereof, and the corporation may require that the corporation be given a bond or other adequate security sufficient to indemnify it against any claim that may be made against it (including expense or liability) on account of the alleged loss, theft, or destruction of such certificate or the issuance of such new certificate or uncertificated shares.
| Section 4 | REPRESENTATION OF SHARES OF OTHER CORPORATIONS. |
Any officer or officers authorized by the Board are each authorized to vote, represent, and exercise on behalf of the corporation all rights incident to any and all shares or other equity interests of any other corporation or entity or corporations or entities, standing in the name of the corporation. The authority herein granted may be exercised either by any such officer in person or by any other person authorized so to do by proxy or power of attorney duly executed by said officer.
| Section 5 | ELECTION OF FISCAL YEAR. |
The Fiscal Year of the corporation shall be fixed by resolution of the Board.
| Section 6 | CONSTRUCTION AND DEFINITIONS. |
Unless the context otherwise requires, the general provisions, rules of construction, and definitions contained in the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware shall govern the construction of these bylaws.
| Section 7 | AMENDMENTS. |
These bylaws may be altered, amended, or repealed either by the approval of the majority of the voting power of the then outstanding voting stock of the corporation or, subject to the provisions of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware, by the approval of the Board.
| Section 8 | EMERGENCY BYLAWS. |
In the event of any emergency, disaster, or catastrophe, as referred to in Section 110 of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware, or other similar emergency condition, as a result of which a quorum of the Board or a standing committee of the Board cannot readily be convened for action, then the director or directors in attendance at the meeting shall constitute a quorum. Such director or directors in attendance may further take action to appoint one or more of themselves or other directors to membership on any standing or temporary committees of the Board as they shall deem necessary and appropriate.
ARTICLE VI INDEMNIFICATION.
| Section 1 | RIGHT TO INDEMNIFICATION. |
The corporation shall indemnify and hold harmless, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law as it presently exists or may hereafter be amended, any person (an “Indemnitee”) who was or is made or is threatened to be made a party to or is otherwise involved in any action, suit, or proceeding, whether of a civil, criminal, administrative, investigative, or other nature (a “proceeding”), by reason of the fact that he or she, is or was a director or officer of the corporation or, while a director or officer of the corporation, is or was serving at the written request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee, or agent of another corporation or of a partnership, joint venture, trust, non-profit entity, or other enterprise, including service with respect to employee benefit plans, against all liability and loss suffered and expenses (including attorneys’ fees) actually and reasonably incurred by such Indemnitee. Notwithstanding the preceding sentence, except as otherwise provided in Section 3 of this Article VI, the corporation shall be required to indemnify or advance expenses to an Indemnitee in connection with a proceeding (or part thereof) commenced by such Indemnitee only if the commencement of such proceeding (or part thereof) by the Indemnitee was authorized by the Board.
| Section 2 | PREPAYMENT OF EXPENSES. |
The corporation shall pay the expenses (including attorneys’ fees) incurred by an Indemnitee in defending any proceeding in advance of its final disposition, provided, however, that, a payment of expenses in advance of the final disposition of the proceeding shall be made only upon receipt by the corporation of an undertaking by the Indemnitee to repay all amounts advanced if it should be ultimately determined that the Indemnitee is not entitled to be indemnified under this Article VI or otherwise.
19

| Section 3 | CLAIMS. |
If a claim for indemnification or advancement of expenses under this Article VI is not paid in full within 60 days after a written claim for indemnification or 20 days after a written claim for advancement by the Indemnitee has been received by the corporation, the Indemnitee may file suit to recover the unpaid amount of such claim and, if successful in whole or in part, shall be entitled to be paid the expense of prosecuting such claim. In any such action the corporation shall have the burden of proving that the Indemnitee is not entitled to the requested indemnification or advancement of expenses under applicable law.
| Section 4 | NON-EXCLUSIVITY OF RIGHTS. |
The rights conferred on any Indemnitee by this Article VI shall not be exclusive of any other rights which such Indemnitee may have or hereafter acquire under any statute, provision of a certificate of incorporation, bylaws, agreement, or vote of the stockholders or disinterested directors or otherwise.
| Section 5 | OTHER SOURCES. |
The corporation’s obligation, if any, to indemnify or to advance expenses to any Indemnitee who was or is serving at its request as a director, officer, employee, or agent of another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust, non-profit entity, or other enterprise shall be reduced by any amount such Indemnitee may collect as indemnification or advancement of expenses from such other corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust, non-profit entity, or other enterprise.
| Section 6 | AMENDMENT OR REPEAL. |
Any repeal or modification of the foregoing provisions of this Article VI shall not adversely affect any right or protection hereunder of any Indemnitee in respect of any act or omission occurring prior to the time of such repeal or modification.
| Section 7 | NATURE OF RIGHTS; SEVERABILITY. |
The rights conferred upon Indemnitees in this Article VI shall be contract rights and such rights shall continue as to an Indemnitee who has ceased to be a director or officer and shall inure to the benefit of the Indemnitee’s heirs, executors, and administrators.
If any provision or provisions of this Article VI shall be held to be invalid, illegal or unenforceable for any reason whatsoever (a) the validity, legality, and enforceability of the remaining provisions of this Article VI (including, without limitation, all portions of any paragraph of this Article VI containing any such provision held to be invalid, illegal, or unenforceable, that are not by themselves invalid, illegal, or unenforceable) shall not in any way be affected or impaired thereby, and (b) to the fullest extent possible, the provisions of this Article VI (including, without limitation, all portions of any paragraph of this Article VI containing any such provision held to be invalid, illegal, or unenforceable, that are not themselves invalid, illegal, or unenforceable) shall be construed so as to give effect to the intent of the parties that the corporation provide protection to the indemnitee to the fullest enforceable extent.
| Section 8 | OTHER INDEMNIFICATION AND PREPAYMENT OF EXPENSES. |
This Article VI shall not limit the right of the corporation, to the extent and in the manner permitted by law, to indemnify and to advance expenses to persons other than Indemnitees when and as authorized by appropriate corporate action.
20

EXHIBIT 21.1
Note: Korn/Ferry International or one of its Subsidiaries has 100% ownership of the Subsidiaries listed below, except for Korn/Ferry International (M) Sdn. Bhd. (49%), Korn/Ferry Mexico, S.C. (49%), Hay Group S.A. de C.V. and Hay Group, S.R.L. are wholly owned subsidiaries of Korn/Ferry Mexico, S.C.
| Subsidiaries
|
Jurisdiction
| |||
| 1. | Korn Ferry International S.A. | Argentina | ||
| 2. | Korn Ferry Futurestep Argentina S.R.L. | Argentina | ||
| 3. | Korn/Ferry International Pty Limited | Australia | ||
| 4. | Futurestep (Australia) Pty Ltd | Australia | ||
| 5. | Korn/Ferry International GmbH | Austria | ||
| 6. | Korn/Ferry International Futurestep (Belgium) BVBA | Belgium | ||
| 7. | Korn/Ferry International Consultoria Ltda. | Brazil | ||
| 8. | Korn/Ferry Canada, Inc. | Canada | ||
| 9. | Korn/Ferry International Futurestep (Canada) Inc. | Canada | ||
| 10. | Korn/Ferry International S.A. | Chile | ||
| 11. | Korn/Ferry International Human Capital Consulting (Beijing) Limited | Beijing, China | ||
| 12. | Guangzhou Korn/Ferry Human Capital Company Ltd. | Guangzhou, China | ||
| 13. | Korn/Ferry (Shanghai) Human Capital Consulting Co., Ltd. | Shanghai, China | ||
| 14. | PuDe Management Consulting Co. Ltd. | Shanghai, China | ||
| 15. | Futurestep (Shanghai) Talent Consulting Company Limited | China | ||
| 16. | Korn/Ferry International – Colombia | Colombia | ||
| 17. | Korn/Ferry International A/B | Denmark | ||
| 18. | Korn/Ferry International SAS | France | ||
| 19. | Korn/Ferry International Futurestep (France) SARL | France | ||
| 20. | Korn/Ferry International GmbH | Germany | ||
| 21. | Futurestep Germany GmbH | Germany | ||
| 22. | Korn/Ferry International SA | Greece | ||
| 23. | Korn/Ferry International (H.K.) Limited | Hong Kong | ||
| 24. | Futurestep (Hong Kong) Ltd. | Hong Kong | ||
| 25. | Korn/Ferry International Budapest Personnel Consulting and Service Ltd. | Hungary | ||
| 26. | PDI Hungary, Kft. | Hungary | ||
| 27. | Korn/Ferry International Private Limited | India | ||
| 28. | Futurestep Recruitment Services Private Limited. | India | ||
| 29. | Personnel Decisions International India Pvt. Limited | India | ||
| 30. | PT. Korn/Ferry International | Indonesia | ||
| 31. | Korn/Ferry International S.R.L. | Italy | ||
| 32. | Futurestep (Italia) S.r.l. | Italy | ||
| 33. | Nihon Korn/Ferry International K.K. | Japan | ||
| 34. | Futurestep (Japan) K.K. | Japan | ||
| 35. | Korn/Ferry International (Korea) Limited | Korea | ||
| 36. | Agensi Pekerjaan Futurestep Worldwide (M) Sdn. Bhd. | Malaysia | ||
| 37. | Korn/Ferry International (M) Sdn. Bhd. | Malaysia | ||
| 38. | Korn/Ferry Investment India Limited (Mauritius OCB) | Mauritius | ||
1

| Subsidiaries
|
Jurisdiction
| |||
| 39. | Korn/Ferry Mexico, S.C. | Mexico | ||
| 40. | Korn Ferry International B.V. | Netherlands | ||
| 41. | Korn/Ferry International Futurestep (Holdings) B.V. | Netherlands | ||
| 42. | Korn Ferry International NZ Limited | New Zealand | ||
| 43. | Futurestep (New Zealand) Ltd. | New Zealand | ||
| 44. | Korn/Ferry International A/S | Norway | ||
| 45. | Korn/Ferry International – Peru S.A. | Peru | ||
| 46. | Korn/Ferry International Sp.z.o.o. | Poland | ||
| 47. | Korn/Ferry International Futurestep (POLSKA) Sp.z.o.o. | Poland | ||
| 48. | Korn/Ferry International Pte. Ltd. | Singapore | ||
| 49. | Futurestep (Singapore) Pte Limited | Singapore | ||
| 50. | PDI Slovensko, sro | Slovakia | ||
| 51. | Korn/Ferry International S.A. | Spain | ||
| 52. | Futurestep (Espana), S.L. | Spain | ||
| 53. | Korn/Ferry International AB | Sweden | ||
| 54. | Personnel Decisions International Scandinavia A.B. | Sweden | ||
| 55. | Korn Ferry (Schweiz) GmbH | Switzerland | ||
| 56. | Korn/Ferry International (Taiwan) Co. Limited | Taiwan | ||
| 57. | Korn/Ferry International Musavirlik Limited Sirketi | Turkey | ||
| 58. | Futurestep (UK) Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 59. | Korn/Ferry International Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 60. | KFI (UK) Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 61. | The Whitehead Mann Partnership LLP | United Kingdom | ||
| 62. | Whitehead Mann Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 63. | Personnel Decisions International, Europe Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 64. | Personnel Decisions International UK Ltd | United Kingdom | ||
| 65. | Korn Ferry Global Holdings (UK) Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 66. | Korn Ferry GH1 Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 67. | Continental American Management Corp. | United States, California | ||
| 68. | Korn/Ferry International Holding India | United States, California | ||
| 69. | Korn/Ferry International Futurestep, Inc. | United States, Delaware | ||
| 70. | Korn/Ferry International Futurestep (Holdings) Inc. | United States, Delaware | ||
| 71. | Korn/Ferry International Worldwide, Inc. | United States, Delaware | ||
| 72. | K/FI Canada Holdings, LLC | United States, Delaware | ||
| 73. | Korn Ferry Hay Group, Inc. | United States, Delaware | ||
| 74. | Ninth House, Inc. | United States, Delaware | ||
| 75. | Korn Ferry Global Holdings, Inc. | United States, Delaware | ||
| 76. | Personnel Decisions International Singapore Corporation | United States, Minnesota | ||
| 77. | Sensa Solutions, Inc. | United States, Virginia | ||
| 78. | Korn/Ferry International Consultores Asociados, C.A. | Venezuela | ||
| 79. | Hay Group International, Inc. | United States, Delaware | ||
| 80. | Korn Ferry Hay Group Ltd. / Korn Ferry Hay Group Ltée | Canada | ||
2

| Subsidiaries
|
Jurisdiction
| |||
| 81. | Korn Ferry Hay Group N.V./S.A. | Belgium | ||
| 82. | Korn Ferry s.r.o. | Czech Republic | ||
| 83. | Hay Group Oy | Finland | ||
| 84. | Hay France S.A. | France | ||
| 85. | Korn Ferry Hay Group S.A. | France | ||
| 86. | Hay Group GmbH | Germany | ||
| 87. | Hay Group S.A. | Greece | ||
| 88. | Hay Group Management Consultants Ltd. | Hungary | ||
| 89. | Korn Ferry Limited | Ireland | ||
| 90. | Hay Management Consultants Ireland Ltd. | Ireland | ||
| 91. | Hay Group S.r.l. | Italy | ||
| 92. | Hay Group UAB | Lithuania | ||
| 93. | HG (Luxembourg) S.a.r.l. | Luxembourg | ||
| 94. | Talent Q International Ltd. | Malta | ||
| 95. | Talent Q Distribution Ltd. | Malta | ||
| 96. | Hay Group B.V. | Netherlands | ||
| 97. | Hay Group Investment Holding B.V. | Netherlands | ||
| 98. | Hay Management International B.V. | Netherlands | ||
| 99. | Hay Group Partners Holding B.V. | Netherlands | ||
| 100. | Hay Group AS | Norway | ||
| 101. | Hay Group Sp.Z o.o | Poland | ||
| 102. | Korn Ferry S.A. | Portugal | ||
| 103. | Hay Group LLC | Qatar | ||
| 104. | Korn Ferry SRL | Romania | ||
| 105. | OOO Hay Group (Hay Group Ltd.) | Russia | ||
| 106. | Hay Group Saudi Arabia Ltd. | Saudi Arabia | ||
| 107. | Hay Group s.r.o. | Slovakia | ||
| 108. | Korn Ferry (Pty) Ltd. | South Africa | ||
| 109. | Hay Group S.A. | Spain | ||
| 110. | Hay Group AB | Sweden | ||
| 111. | Hay Group Danismanlik Limited Sirketi | Turkey | ||
| 112. | Hay Group LLC | Ukraine | ||
| 113. | Korn Ferry Hay Group Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 114. | Hay Group UK Holdings Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 115. | Hay Group Intermediary Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 116. | Talent Q Services Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 117. | Talent Q Limited | United Kingdom | ||
| 118. | Korn Ferry Hay Group Pty. Limited | Australia | ||
| 119. | Hay Group Co., Ltd. | China | ||
| 120. | Hay Group Limited | Hong Kong | ||
| 121. | Hay Consultants India Private Ltd. | India | ||
| 122. | Talent Q India Private Ltd. | India | ||
3

| Subsidiaries
|
Jurisdiction
| |||
| 123. | PT Hay Group | Indonesia | ||
| 124. | Korn Ferry Hay Group K.K. | Japan | ||
| 125. | Hay Group Sdn. Bhd. | Malaysia | ||
| 126. | Korn Ferry Hay Group Limited | New Zealand | ||
| 127. | Korn Ferry Hay Group Pte Ltd. | Singapore | ||
| 128. | Hay Group Ltd. | South Korea | ||
| 129. | Hay Group Limited | Thailand | ||
| 130. | Hay Group Consulting Limited Liability | Vietnam | ||
| 131. | Hay Argentina S.A. | Argentina | ||
| 132. | Hay do Brasil Consultores Ltda. | Brazil | ||
| 133. | Hay Group Limitada | Chile | ||
| 134. | Hay Group Ltda | Colombia | ||
| 135. | Hay Group, S.R.L. | Costa Rica | ||
| 136. | Hay Financial Corporation N.V. | Curacao | ||
| 137. | Hay Group S.A. de C.V. | Mexico | ||
| 138. | Hay Group S.A. | Peru | ||
| 139. | Hay Group Venezuela, S.A. | Venezuela | ||
| 140. | Hay Management Consultants Limited | Bermuda | ||
| 141. | HG (Bermuda) Holding Limited | Bermuda | ||
| 142. | Korn Ferry GP Ventures LLC | United States, Delaware | ||
| 143. | Korn Ferry Global Ventures LP | United Kingdom | ||
| 144. | Korn/Ferry International Futurestep (the Netherlands) BV | Netherlands | ||
| 145. | Korn Ferry Global Ventures 2 LP | United Kingdom | ||
| 146. | Korn Ferry GP Ventures 2 LLC | United States | ||
| 147. | Korn Ferry NL91 B.V. | Netherlands | ||
| 148. | Korn Ferry Futurestep (The Philippines) Inc. | Philippines | ||
| 149. | Korn/Ferry (Thailand) Limited | Thailand | ||
| 150. | Personnel Decisions International India Corporation | United States. Minnesota | ||
| 151. | Inversiones Korn/Ferry International, C.A. | Venezuela | ||
4

EXHIBIT 23.1
CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
We consent to the incorporation by reference in the following Registration Statements:
| (1) | Registration Statement (Form S-3 No. 333-99429) of Korn/Ferry International and related Prospectus, |
| (2) | Registration Statement (Form S-8 Nos. 333-161844, 333-159900, 333-158632, 333-49580, 333-73147, 333-111038, 333-146346, 333-108696, 333-185438, 333-200840 and 333-214123) pertaining to the employee benefit plans of Korn/Ferry International; |
of our reports dated June 28, 2018, with respect to the consolidated financial statements and schedule of Korn/Ferry International and subsidiaries and the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting of Korn/Ferry International and subsidiaries included in this Annual Report (Form 10-K) of Korn/Ferry International and subsidiaries for the year ended April 30, 2018.
Los Angeles, California
June 28, 2018
1

EXHIBIT 31.1
CERTIFICATIONS
I, Gary D. Burnison, certify that:
| 1. | I have reviewed this annual report on Form 10-K of Korn/Ferry International; |
| 2. | Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report; |
| 3. | Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report; |
| 4. | The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15(d)-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15(d)-15(f)) for the registrant and have: |
| a. | Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
| b. | Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
| c. | Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and |
| d. | Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and |
| 5. | The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): |
| a. | All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and |
| b. | Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. |
| By: | /s/ GARY D. BURNISON | |
| Name: | Gary D. Burnison | |
| Title: | Chief Executive Officer and President |
Date: June 28, 2018
1

EXHIBIT 31.2
CERTIFICATIONS
I, Robert P. Rozek, certify that:
| 1. | I have reviewed this annual report on Form 10-K of Korn/Ferry International; |
| 2. | Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report; |
| 3. | Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the registrant as of, and for, the periods presented in this report; |
| 4. | The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the registrant and have: |
| a. | Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the registrant, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared; |
| b. | Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; |
| c. | Evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and |
| d. | Disclosed in this report any change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s most recent fiscal quarter (the registrant’s fourth fiscal quarter in the case of an annual report) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting; and |
| 5. | The registrant’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the registrant’s auditors and the audit committee of the registrant’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions): |
| a. | All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the registrant’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and |
| b. | Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. |
| By: | /s/ ROBERT P. ROZEK | |
| Name: | Robert P. Rozek | |
| Title: | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, and Chief Corporate Officer |
Date: June 28, 2018
1

EXHIBIT 32.1
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350 SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
Pursuant to section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (subsections (a) and (b) of section 1350, chapter 63 of title 18, United States Code), the undersigned officers of Korn/Ferry International, a Delaware corporation (the ‘Company’), hereby certify that, to the best of their knowledge:
| (a) | the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended April 30, 2018 (the ‘Report’) of the Company fully complies with the requirements of section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and |
| (b) | information contained in the Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company. |
Dated: June 28, 2018
| By: | /s/ GARY D. BURNISON | |
| Name: | Gary D. Burnison | |
| Title: | Chief Executive Officer and President | |
| By: | /s/ ROBERT P. ROZEK | |
| Name: | Robert P. Rozek | |
| Title: | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, and Chief Corporate Officer | |
1
