Form 8-K VYNE Therapeutics Inc. For: May 17
Exhibit 99.1

KOL Event: Update on the BET InhiBET Platform and VYN201 May 17, 2022

Forward Looking Statements This presentation includes forward - looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 , including, but not limited to statements regarding the development of VYNE’s product candidates, the timing of its clinical trials and regulatory filings and other statements regarding the future expectations, plans and prospects of VYNE . All statements in this presentation which are not historical facts are forward - looking statements . Any forward - looking statements are based on VYNE’s current knowledge and its present beliefs and expectations regarding possible future events and are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions that could cause actual results to differ materially and adversely from those set forth or implied by such forward - looking statements . These risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to : VYNE’s ability to successfully develop its product candidates ; the timing of commencement of future non - clinical studies and clinical trials ; VYNE’s ability to enroll patients and successfully progress, complete, and receive favorable results in, clinical trials for its product candidates ; VYNE’s ability to exercise its exclusive option with respect to VYN 202 pursuant to the terms of the option agreement with In 4 Derm Limited ; VYNE’s intentions and its ability to obtain additional funding, either through equity or debt financing transactions or collaboration arrangements ; disruptions related to COVID - 19 or another pandemic, epidemic or outbreak of a contagious disease, on the ability of VYNE’s suppliers to manufacture and provide materials for our product candidates, initiating and retaining patients in clinical trials, operating results, liquidity and financial condition ; the regulatory approval process for VYNE’s product candidates, including any delay or failure in obtaining requisite approvals ; the potential market size of treatments for any diseases and market adoption of products, if approved or cleared for commercial use, by physicians and patients ; developments and projections relating to competitors and the pharmaceuticals industry, including competing drugs and therapies ; the timing or likelihood of regulatory filings and approvals or clearances for product candidates ; VYNE’s ability to comply with various regulations applicable to its business, including Nasdaq continued listing rules ; VYNE’s ability to create intellectual property and the scope of protection it is able to establish and maintain for intellectual property rights covering its product candidates, including the projected terms of patent protection ; risks that any of VYNE’s patents may be held to be narrowed, invalid or unenforceable or one or more of VYNE’s patent applications may not be granted and potential competitors may also seek to design around VYNE’s granted patents or patent applications ; the timing, costs or results of litigation, including litigation to protect its intellectual property ; VYNE’s ability to successfully challenge intellectual property claimed by others ; estimates of VYNE’s expenses, capital requirements, its needs for additional financing and its ability to obtain additional capital on acceptable terms or at all ; VYNE’s ability to attract and retain key scientific or management personnel ; VYNE’s defense of any litigation that may be initiated against it ; VYNE’s expectations regarding licensing, business transactions and strategic operations ; VYNE’s future financial performance and liquidity ; and volatility in VYNE’s stock price may result in rapid and substantial increases or decreases in the stock price that may or may not be related to the company’s operating performance or prospects . For a discussion of other risks and uncertainties, and other important factors, any of which could cause VYNE’s actual results to differ from those contained in the forward - looking statements, see the section titled “Risk Factors” in VYNE’s annual report on Form 10 - K for the year ended December 31 , 2021 as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties, and other important factors in VYNE’s subsequent filings with the U . S . Securities and Exchange Commission . Although VYNE believes these forward - looking statements are reasonable, they speak only as of the date of this presentation and VYNE undertakes no obligation to update publicly such forward - looking statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances, except as otherwise required by law . Given these risks and uncertainties, you should not rely upon forward - looking statements as predictions of future events . The trademarks included herein are the property of the owners thereof and are used for reference purposes only . This presentation concerns product candidates that are under clinical investigation . None of such product candidates have been approved for marketing by the FDA or the EMA, and such product candidates are currently limited to investigational use, and no representation is made as to their safety or effectiveness for the purposes for which they are being investigated . 2

3 Provide insight into the continued unmet medical need and necessity for multiple treatments options for vitiligo patients Provide investors with a background on BET inhibition and its applicability to address multiple immuno - inflammatory - mediated diseases Purpose Impact Potential 2022 KOL Event – InhiBET Ρ BET Inhibitor Platform for Immunology and Inflammatory Diseases and Clinical Development Plan for VYN201 Review the preclinical data for VYN201 and reveal the initial clinical indication of vitiligo and supporting preclinical data

4 Today’s Agenda KOL Event Focused on the InhiBET Œ Platform and VYN201 Topic Presenter Time Overview of VYNE David Domzalski President and CEO 10:05 – 10:15 Introduction to BET proteins Professor Gerald V. Denis, Ph.D. Boston University School of Medicine 10:15 – 10:30 Overview of VYN201 Iain Stuart, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer 10:30 – 10:55 Overview of Vitiligo Professor Thierry Passeron, MD, Ph.D. University of Nice 10:55 – 11:10 Q&A All Panelists 11:10 – 11:25 Future milestones/Wrap - up David Domzalski President and CEO 11:25 – 11:30

5 Investment Highlights (NASDAQ: VYNE) VYNE is focused on developing proprietary, innovative, and differentiated therapies for the treatment of immuno - inflammatory conditions Innovative Pipeline • Pipeline focused on major markets (Atopic Dermatitis and I&I) and rare skin diseases with high unmet medical need • Key Targets: JAK/ sphingosine - 1 receptor modulator combo & BET inhibitors InhiBET Œ Platform • New platform, based on a novel class of targets called BET inhibitors • Pursuing locally administered (VYN201) and oral therapies (VYN202) • Exclusive global access to a NCE library for any indication • Substantial progress since August 2021 in - license Proven Development Capabilities and Leading Advisory Infrastructure Multiple Near - term Catalysts • Seasoned R&D team with proven product development track record • Strong network of discovery and preclinical science partners • Well respected SAB provide strong advisory input to pipeline development activities • Developed and received FDA approval for the first and only topical formulations of minocycline for acne and rosacea; Products were divested in January 2022 • Numerous near - term catalysts across FMX114, VYN201 and VYN202 with potentially significant long - term value creation AMZEEQ and ZILXI are registered trademarks owned by Journey Medical Corporation

VYNE: Developing differentiated therapies for the treatment of I&I conditions 6 FMX114: Combination therapy to address both the source & cause of inflammation associated with Atopic Dermatitis (AD) InhiBET TM BET Inhibitor Platform: Global rights to library of NCE BET inhibitors for any indication Target Market: Mild - to - moderate atopic dermatitis ~19 million people (U.S.) Combination Mechanism: • Tofacitinib (JAK - 1/3): to inhibit cytokine release • Fingolimod (sphingosine 1 - phosphate receptor modulator): to inhibit inflammatory cell migration Phase 1b Safety & Efficacy: • Well - tolerated, with no serious adverse events recorded; Systemic bioavailability of tofacitinib and fingolimod substantially lower compared to oral equivalents • FMX114 demonstrated a statistically significant improvement of the signs and symptoms of AD at 2 weeks Next Milestone: Topline results of Phase 2a trial:Q2 2022 VYN201: Locally administered pan - BD BET inhibitor • Target Market: Indications benefiting from local administration and “soft drug” approach • Preclinical Proof - of - Concept Data: Data suggests potential “pipeline in a product” with broad utility of VYN201 across multiple routes of administration VYN202: Oral, highly - selective BD2 BET inhibitor for major immuno - inflammatory diseases BD1 BD2 Oral VYN202 selectively binds to BD2 VYN201 binds to both BD1 and BD2 BRD4 BET Protein

Preclinical Proof - of - Concept Data Summary for VYN201 Based on established models, compared to active control and vehicle/placebo 7 VYN201 Potential “pipeline in a product” with broad utility across multiple routes of administration 1. Idiopathic pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) 2. Data on file TH7 Inflammation Model • Reduced composite score of inflammation severity • Dose - dependent reduction in pro - inflammatory cytokines Fibrotic Tissue & IPF 1 Models • Significantly lower fibrosis v. vehicle and negative control • Preliminary IPF model data suggests VYN201 could have promising impact on IPF - related fibrosis and biomarkers Rheumatoid Arthritis Model • Two highest doses demonstrated statistically significant improvement in treatment response, measured by paw thickening and arthritis score • Superior to locally - dosed active dexamethasone control Vitiligo Model • Highest doses demonstrated statistically significant improvement in reducing melanocyte loss & lowering key inflammatory biomarkers vs. vehicle • Numerically superior to active control, ruxolitinib cream, 1.5%

8 Improved inflammation scores Reduction in inflammatory biomarker levels Good tolerability in animals Good local pharmacology Limited systemic drug accumulation Potential to address high unmet medical need Attractive market opportunity Summary of Locally Administered Pan - BD BETi Candidate Selection Criteria Based on an assessment of preclinical data, market research and SAB/KOL input

VYN201 Lead Indication Vitiligo 9

Large Market 10 • Treatment is dominated by non - specific therapeutic options • VYN201 is a topically applied “soft” drug, designed to maximize target engagement in the skin and minimize systemic exposure The Vitiligo Opportunity A disabling disease and major unmet medical need • 0.5 to 2.0% of worldwide population • Non - segmental sub - type represents ~90% of patients • Est. U.S. prevalence is between 1.9 and 3.2 million cases (diagnosed/undiagnosed) Unmet Need • Vitiligo is a disabling disease impacting social, sexual and professional life. Resemblance to leprosy impacts QOL in some countries • Treatments need to impact both pigmentation and Quality of Life Preclinical Data Map to Clinical Plan • Melanocyte histology metrics and in vitro biomarkers ( TNF - α and IFN - ɣ , MMP9 and E - cadherin) translate well to clinical endpoints Differentiated Characteristics Sources: Bergqvist. Dermatol. 2020;236:571 - 592; JAMA Dermatology , “Prevalence of Vitiligo Among Adults in the United States”; 2022; 158(1):43 - 50 (published online Nov. 17, 2021); Rangu S, McKenzie PL, Castelo - Soccio L (2021) Therapy Utilization among Children with Vitiligo at an Urban Tertiary Care Center J Clin Dermatol Ther 7: 070.

Vitiligo – Disease Overview An acquired disorder of dermatologic pigmentation with high impact on self - esteem 11 Pathophysiology & Clinical Presentation • Vitiligo is a depigmenting skin disorder characterized by the loss of melanocytes, which causes typical non - scaly, chalky - white macules • Pathogenesis is classified as autoimmune in nature ; the disease is associated with a culmination of genetic and environmental factors with metabolic, oxidative stress, and cell detachment abnormalities • Vitiligo can be classified as segmental or non - segmental; segmental presentation appears unilaterally , while non - segmental presents bilaterally and occasionally mucosally (i.e., around the mouth) • Characteristic amelanotic lesions, while physically harmless, tend to be psychologically devastating Source: UptoDate ; Bergqvist. Dermatol. 2020;236:571 - 592; Karagaiah . Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2020;25(1):7 - 24

Vitiligo – Treatment Paradigm Current vitiligo treatment is dominated by non - specific therapeutic options 12 Current Treatment Paradigm and Unmet Need 1L Corticosteroids Phototherapy Topical Calcineurin Inhib . Excimer Laser 2L Phototherapy + Combo Agent(s) 3L+ Surgery Depigmentation Therapy Treatment modality is dependent on disease area (segmental vs. non - segmental) as well as activity (controlled vs. uncontrolled); patients typically receive NBUVB phototherapy, excimer laser procedure, or an oral / topical anti - inflammatory agent in the 1L 1L agents are often used in combination in the 2L to enhance disease control Surgeries include skin tissue / cellular grafting and hair follicle transplant, often technically challenging and costly ; depigmentation therapy is a less common FDA - approved modality for cosmetic improvement Vitiligo Key Unmet Need Current vitiligo treatment is dominated by non - specific therapeutics; a targeted, more efficacious treatment option is needed that lowers the disease recurrence rate and is effective for all skin tones / scar types Source: UptoDate ; Bergqvist. Dermatol. 2020;236:571 - 592; Karagaiah . Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2020;25(1):7 - 24 NBUVB: Narrow - band ultraviolet - B light; 1L = 1st line, 2L = 2nd line, 3L+ = 3rd line or greater

Vitiligo – Epidemiology Large market with high unmet need and lack of approved prescription treatment options 13 3.2 M 1.9 M 0 1 2 3 4 U.S. Vitiligo Patients U.S. Diagnosed (Dx) Vitiligo Patients U.S. Addressable Patients Literature suggests ~60% of patients are diagnosed • Large U.S. market between 1.9 (diagnosed) and 3.2 million (diagnosed/undiagnosed) with no approved treatments • Prevalence generally consistent across regions of the world with a range of 0.5% to 2.0% of the worldwide population • Literature suggests that many patients do not seek treatment due to lack of approved and effective treatment options Sources: JAMA Dermatology , “Prevalence of Vitiligo Among Adults in the United States”; 2022; 158(1):43 - 50 (published online Nov. 17, 2021); Rangu S, McKe nzie PL, Castelo - Soccio L (2021) Therapy Utilization among Children with Vitiligo at an Urban Tertiary Care Center J Clin Dermatol Ther 7: 070. Bergqvist. Dermatol. 2020;236:571 - 592; Kreuger (2012)

InhiBET ΠBET Inhibitor Platform Panel 14

2022 KOL Event: BET Inhibition for I&I Diseases & Clinical Development of VYN201 • Professor, Boston University School of Medicine - molecular oncologist with experience in chromatin control of transcription in cancer • Pioneered studies of the BET bromodomains proteins, a family comprised of BRD2 (originally named RING3), BRD3 and BRD4 in somatic cells • First to report a function for a BET protein, and to link these co - regulators to human cancer • Established that BET bromodomain proteins provide a functional link between abnormal metabolism, inflammation and breast cancer progression in post - menopausal African American women • Now exploring how BET proteins regulate cytokine/chemokine production in the immune cells that infiltrate the breast cancer microenvironment, which are important for immune exhaustion, chemoresistance and metastasis Gerald V. Denis, PhD • Professor of Dermatology at the University Hospital of Nice • Heads the laboratory INSERM U1065 team 12, C3M, dedicated to the study of molecular mechanisms involved in pigmentation and melanoma • President of the Department of Clinical Research and Innovation of Nice University hospital • Vice - president of Côte d’Azur University • Seven international patents and more than 220 publications in scientific journals • Co - founder of YUKIN therapeutics • Fields of research include pigmentary disorders (including vitiligo and melasma), melanoma, hidradenitis suppurativa, alopecia areata and lasers Thierry Passeron, MD, PhD Note : Professor Gerald V . Denis, Ph . D . and Professor Thierry Passeron, MD, Ph . D . are consultants for VYNE and are receiving compensation for their presentations at today‘s event . 15

Target Candidate Selection Preclinical Clinical Trials Near - Term Catalysts FMX114 Mild - to - moderate Atopic Dermatitis Phase 1b: completed Phase 2a: TLR Q2 VYN201 Locally administered Pan - BD BET inhibitor 2H 2022: FPI Phase 1 for Vitiligo 2023: Clinic - ready VYN202 Oral BD2 BET inhibitor 1 2022: Candidate Selection 1. Initial indications for VYN202 to be communicated following completion of requisite pre - clinical evaluations TLR = Top Line Results; FPI = First Patient In/Enrolled 16 Exclusive Access to Library of NCE BET Inhibitors for Any Indication Worldwide Targeted Clinical Milestones through 2023 Driving Pipeline to Proof - of - Concept Phase 1b/2a Vitiligo (topical administration) IND - enabling studies underway Candidate Selection process underway Undisclosed indication (non - topical administration)

Gerald V. Denis, PhD Boston University School of Medicine Department of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics BET proteins, through their bromodomain motifs, control transcription of cytokine genes critical for inflammatory diseases Boston University

Shi & Vakoc , Mol. Cell 2014 Domain structure of human BET proteins • The bromodomain family (“ Brd ” or “BD”) is comprises of 4 members (BRD2 - 4, BRDT) and have two shared domains, bromodomain 1 and 2 (BD1 and BD2) with an extra - terminal domain • The Brd family is different from other BD domain classes (i.e. acetylases/transcriptional co - regulators) so inhibitors do not tend to have a broad activity outside the Brd family

Shi & Vakoc , Mol. Cell 2014 Domain structure of human BET proteins • BD1 and BD2 primarily recognize acetylated lysines on histone termini of chromatin • Both BD1 and BD2 are recognized as druggable small molecule inhibitor targets • The difficulty in developing selective small molecule BET inhibitors ( BETi ) has been the high amino acid homology between BD1 and BD2 chromatin interaction chromatin interaction enzyme complex binding interaction P-TEFb cyclin T1 cdk9 interaction P-TEFb cyclin T1 cdk9

Shi & Vakoc , Mol. Cell 2014 Domain structure of human BET proteins • Remaining structure involved in recruiting/binding additional transcriptional factors that promote chromatin remodeling, which facilitates the initiation of gene transcription chromatin interaction chromatin interaction enzyme complex binding interaction P-TEFb cyclin T1 cdk9 interaction P-TEFb cyclin T1 cdk9

Cheung, … & Ming - Ming Zhou, Mol Cell 2017 BET proteins bind to histones in chromatin and recruit co - regulator complexes • Targeted loops is where all the “action” happens as transcription is a group effort among several recruited factors • Inhibiting BET proteins prevents transcriptional complex formation, thereby inhibiting the whole pathway • This targeting is different from drugs that inhibit a specific receptor (e.g. blocking the active site of tyrosine kinases such as JAKs) to prevent a specific downstream action/consequence from happening Transcriptional complex
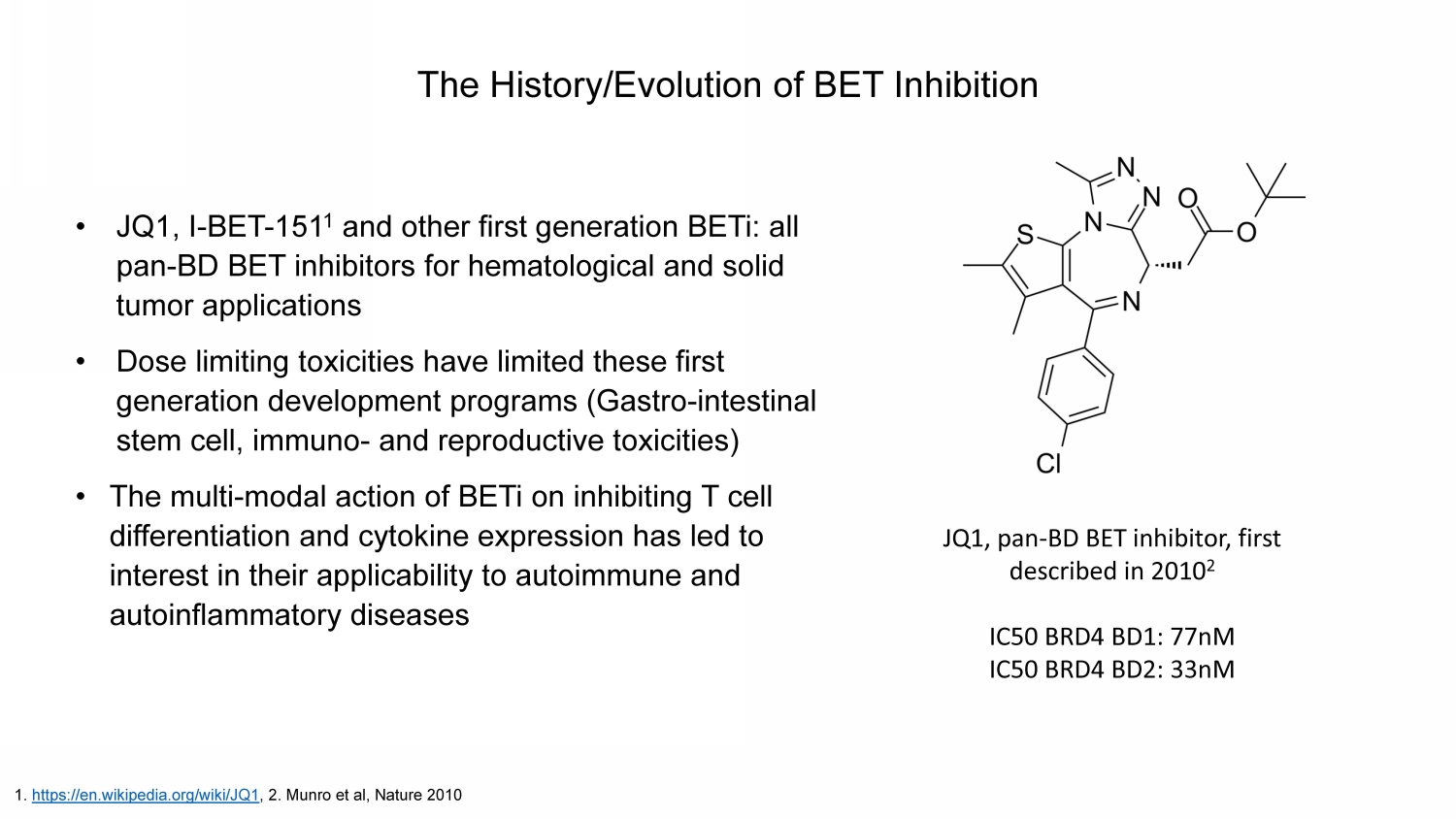
The History/Evolution of BET Inhibition • JQ1, I - BET - 151 1 and other first generation BETi : all pan - BD BET inhibitors for hematological and solid tumor applications • Dose limiting toxicities have limited these first generation development programs (Gastro - intestinal stem cell, immuno - and reproductive toxicities) • The multi - modal action of BETi on inhibiting T cell differentiation and cytokine expression has led to interest in their applicability to autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases 1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JQ1 , 2. Munro et al, Nature 2010 JQ1, pan - BD BET inhibitor, first described in 2010 2 IC50 BRD4 BD1: 77nM IC50 BRD4 BD2: 33nM
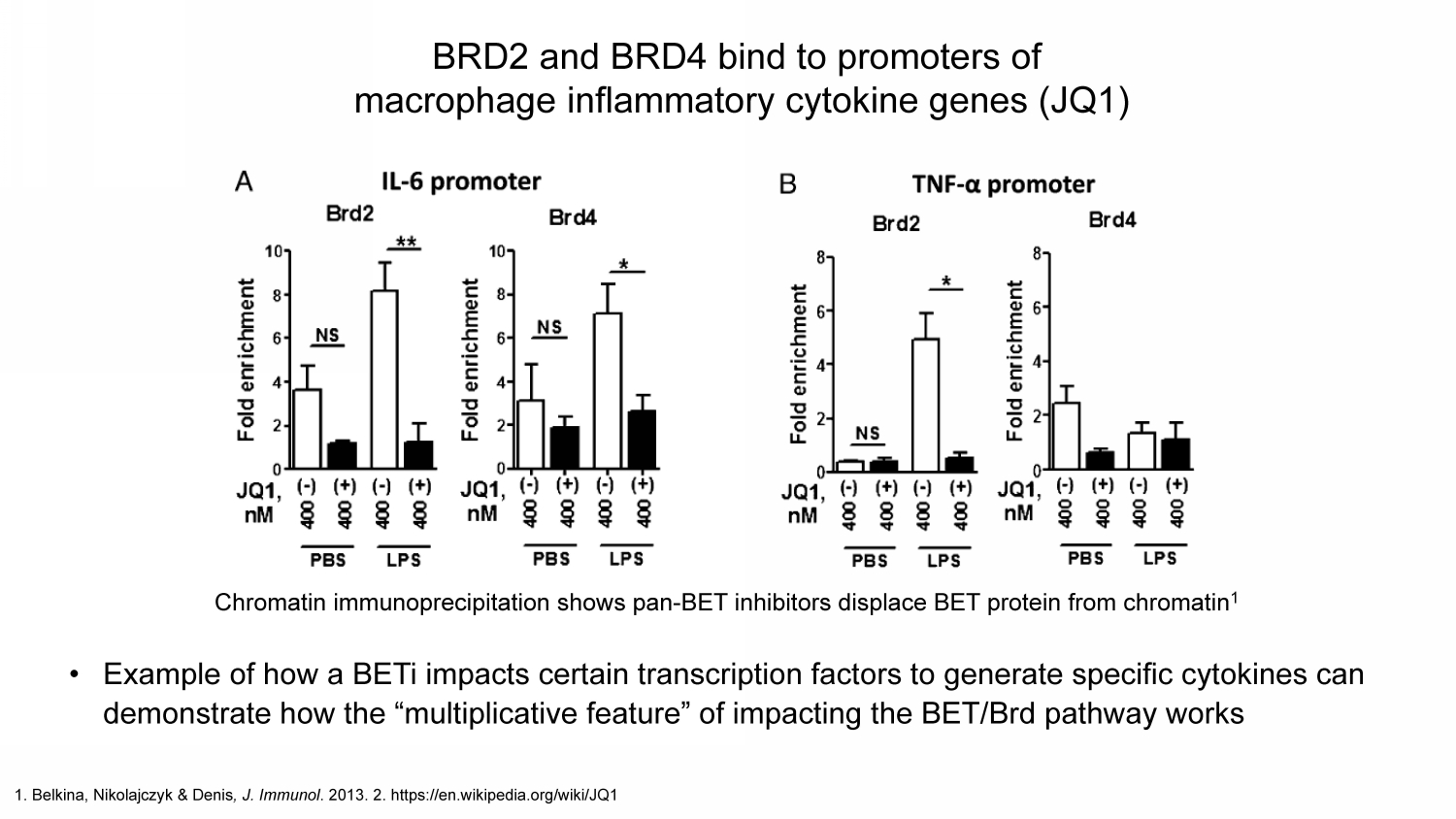
1. Belkina , Nikolajczyk & Denis , J. Immunol . 2013. 2. https:// en.wikipedia.org /wiki/JQ1 BRD2 and BRD4 bind to promoters of macrophage inflammatory cytokine genes (JQ1) Chromatin immunoprecipitation shows pan - BET inhibitors displace BET protein from chromatin 1 • Example of how a BETi impacts certain transcription factors to generate specific cytokines can demonstrate how the “multiplicative feature” of impacting the BET/ Brd pathway works

Knockdown of each BET protein in primary macrophages reduces cytokine production Belkina, Nikolajczyk & Denis , J. Immunol . 2013 CXCL1 CCL2 IL - 6 TNF α • Example shows that not all cytokines are regulated by BETis (CXCL1 is not regulated) • Disease applications have to be targetable by BETis and specificity is possible • The key question is how to ensure that the mechanism of action connects to the targeted indications

Pan - BET inhibition blocks Th17 differentiation in human naïve T cells (JQ1) Note: The canonical paper showing Th17 regulation by BET proteins: Mele et al, J. Exp Med. 2013 • Blocking Th17 with JQ1: this mechanism introduced the relevance of BETi for Th17 - mediated diseases • Th17 - relevant diseases include: rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, ulcerative colitis/Crohn’s disease

Pan - BET inhibition protects mice from autoimmunity (JQ1) Mele et al , J. Exp Med . 2013 collagen - induced arthritis model experimental autoimmune encephalitis model Th17 cytokine • Potent anti - inflammatory effects seen in in vitro T cell differentiation studies was shown to translate in several in vivo animal models of inflammatory disease with JQ1

The Future of BETi’s • Improved medicinal chemistry efforts have enabled gains on on - target potency, with differentiated BD1/2 selectivity profiles being achievable for new BETis • There is a greater (yet evolving) understanding of the role of bromodomain selectivity on both pharmacological/disease relevance and safety e.g BD1 v’s BD2 selectivity 1 • Newer approaches available to improve on benefit/risk for pan - BD BETi : ₋ Specific tissue targeting (local effect) ₋ Reduce or mitigate toxicities/systemic exposure through: o High on - target potency and BD selectivity (BD1 v. BD2 and vice versa) o Controlled release/modified release formulations o “Soft” and pro - drug approaches, as applicable 1. Galen et al, Science 2021

• The science of BET protein inhibition in immuno - inflammatory and oncology applications continues to evolve • Work continues to elucidate the impact of BD selectivity on both oncogene and cytokine expression “signatures” • Broad inhibitory networks have value because many inflammatory cytokines function in networks, not as single factors • Equally, clinical relevance requires knowledge of specific cytokines involved, as not all cytokines are inhibited, even by a pan - BETi approach ( e.g ., CXCL1) • Targeting both BD1 and BD2 bromodomains using less - selective small molecules ( e.g ., JQ1) has potent anti - inflammatory benefits, but also has undesirable toxicities that will necessitate more targeted therapies for pan - BD BETis • There is a continuing need to understand the interplay between BETi potency and selectivity relating to the intended clinical application to optimize benefit/risk Summary

InhiBET ΠBET Inhibitor Platform Bromodomain & Extra - Terminal Domain (BET) Inhibition for Immunology and Inflammatory Diseases 29
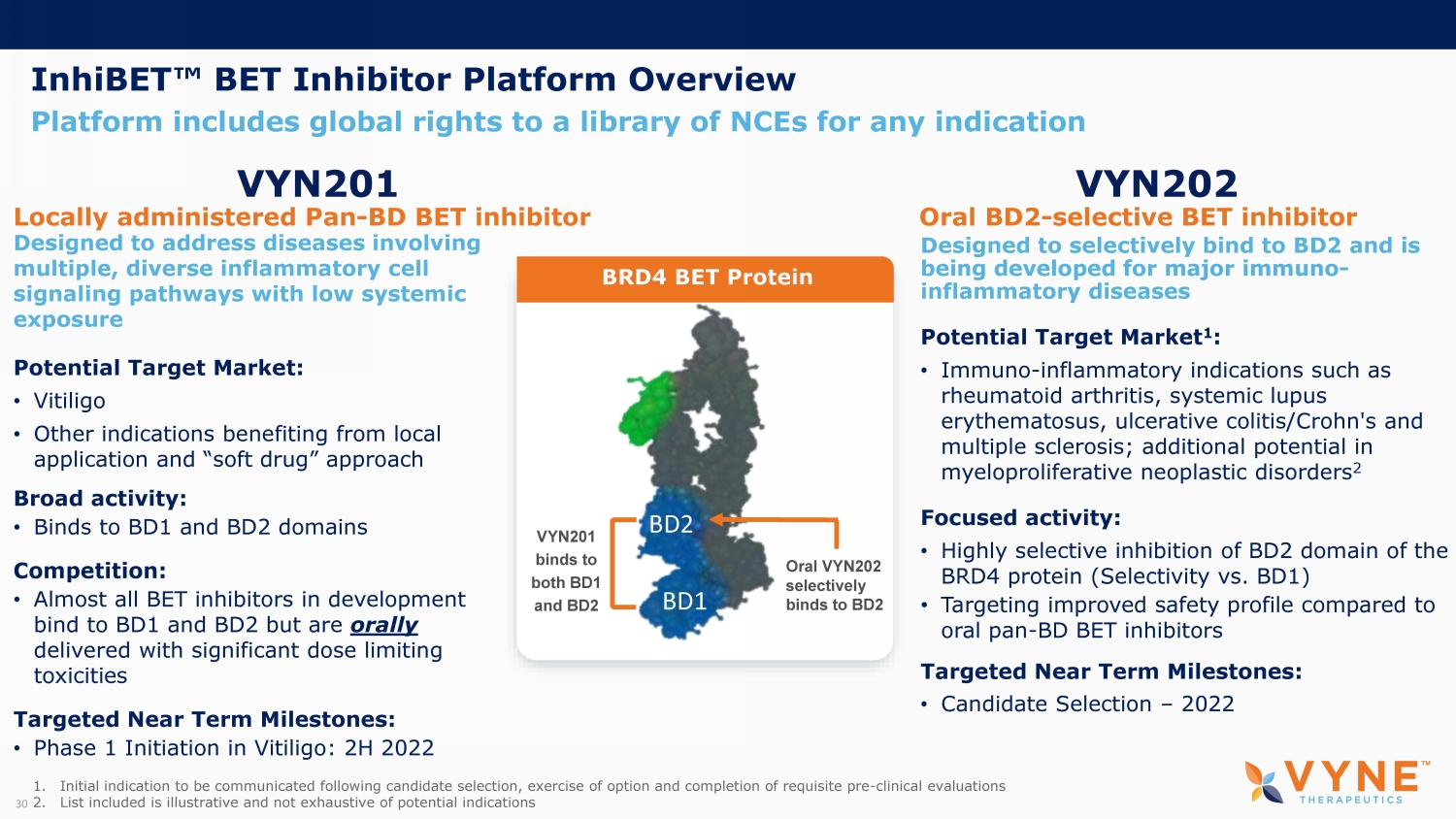
InhiBET Œ BET Inhibitor Platform Overview Platform includes global rights to a library of NCEs for any indication 30 VYN201 Locally administered Pan - BD BET inhibitor VYN202 Oral BD2 - selective BET inhibitor BD1 BD2 Designed to selectively bind to BD2 and is being developed for major immuno - inflammatory diseases Potential Target Market 1 : • Immuno - inflammatory indications such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, ulcerative colitis/Crohn's and multiple sclerosis; additional potential in myeloproliferative neoplastic disorders 2 Focused activity: • Highly selective inhibition of BD2 domain of the BRD4 protein (Selectivity vs. BD1) • Targeting improved safety profile compared to oral pan - BD BET inhibitors Targeted Near Term Milestones: • Candidate Selection – 2022 Oral VYN202 selectively binds to BD2 Designed to address diseases involving multiple, diverse inflammatory cell signaling pathways with low systemic exposure Potential Target Market: • Vitiligo • Other indications benefiting from local application and “soft drug” approach Broad activity: • Binds to BD1 and BD2 domains Competition: • Almost all BET inhibitors in development bind to BD1 and BD2 but are orally delivered with significant dose limiting toxicities Targeted Near Term Milestones: • Phase 1 Initiation in Vitiligo: 2H 2022 VYN201 binds to both BD1 and BD2 BRD4 BET Protein 1. Initial indication to be communicated following candidate selection, exercise of option and completion of requisite pre - clinical evaluations 2. List included is illustrative and not exhaustive of potential indications
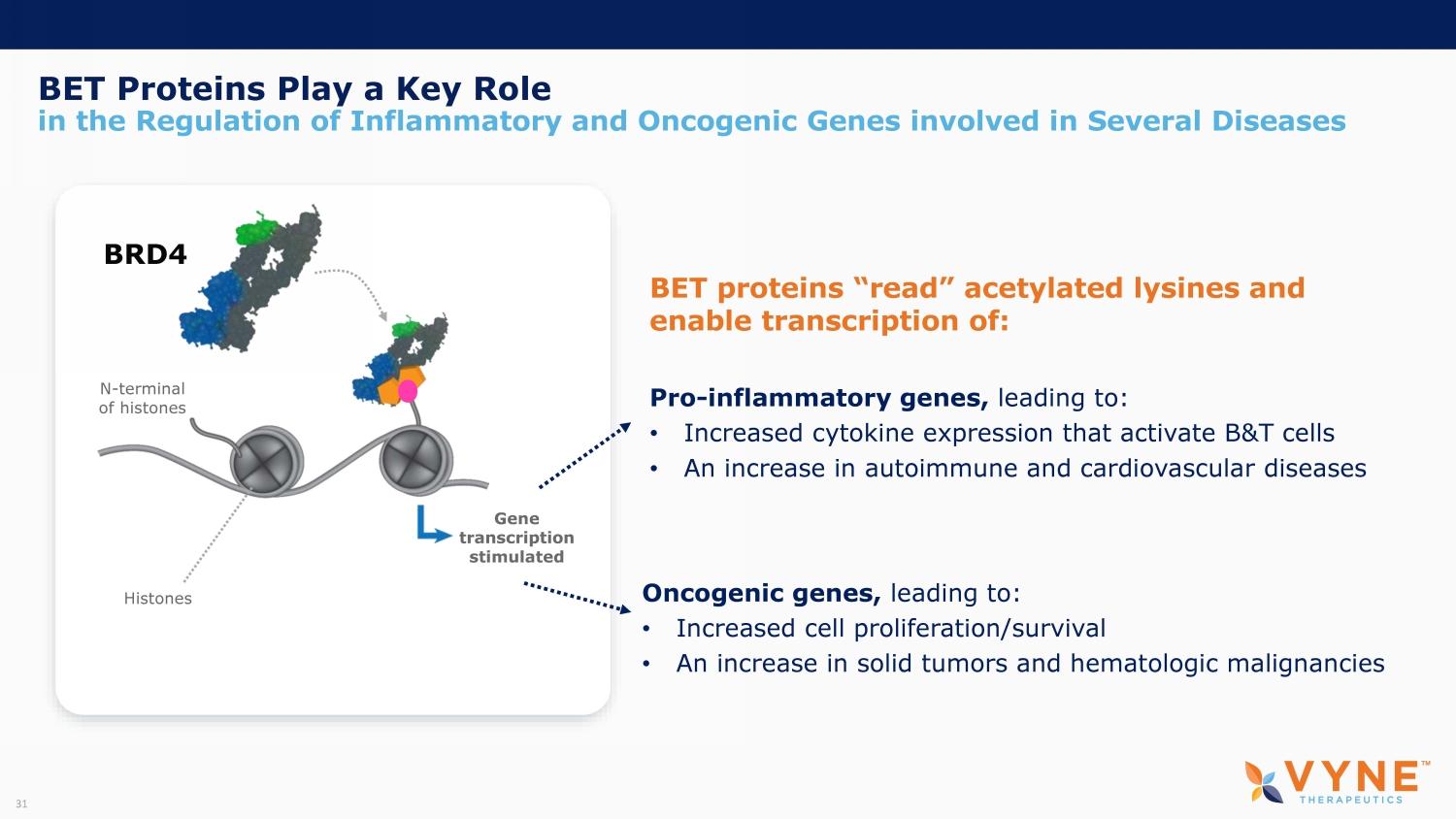
BET Proteins Play a Key Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory and Oncogenic Genes involved in Several Diseases Gene transcription stimulated Histones N - terminal of histones BRD4 Oncogenic genes, leading to: • Increased cell proliferation/survival • An increase in solid tumors and hematologic malignancies Pro - inflammatory genes, leading to: • Increased cytokine expression that activate B&T cells • An increase in autoimmune and cardiovascular diseases BET proteins “read” acetylated lysines and enable transcription of: 31

How BET Proteins Fuel the “Vicious Cycle” of Pro - Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Autoimmune Diseases Pro - inflammatory cytokines Cytokines bind to cytokine receptors 1 Activation of NF - kb kinase complex 2 Nuclear translocation 3 Recruitment of transcription factors 4 5 6 BRD4 active cytokine gene cytokine transcription cytokine translation NF - B = Nuclear Factor Kappa B 32

cytokine transcription BET Inhibitors Block BD1/BD2 Binding to Acetylated Lysines and Stall Pro - inflammatory Protein Transcription BET INHIBITOR Binds BD1 and/or BD2 of BRD4 protein making it unable recognize acetylated histones, recruit transcription factors and release pro - inflammatory cytokines Pro - inflammatory cytokines inactive gene cytokine translation cytokines BRD4 BD1 BD2 1 2 3 4 5 Pro - inflammatory cytokines 33

VYN201 Locally administered pan - BET inhibitor

VYN201 Pre - Clinical Efficacy Model Evaluations 35 Indication/area Model Administration Route Status Th17 autoimmune diseases IMI - induction mouse model Topical Complete Th2 autoimmune diseases DNCB - induction mouse model Topical Complete Fibrosis Wound healing outcomes mouse model Topical Complete Vitiligo Reconstituted human epithelial skin TNF α /IFN γ induction model Topical Complete Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Bleomycin - induction mouse model Intra - nasal Complete Rheumatoid arthritis Intra - articular cytokine cocktail mouse model Intra - articular Complete Macular degeneration Choroidal neovascularization rat model Intra - orbital/vitreous Complete Colitis (gut restricted) DSS - induction mouse model Oral Complete Oncology (AML/melanoma) Human cell line screening and biomarker discovery In - vitro On - going Program designed to investigate the targeted administration of a “soft drug” pan - BD BET inhibitor to maximize local effect and minimize systemic exposure

VYN201: Th17 autoimmune diseases

IMI – Imiquimod. *Composite Inflammation Severity Score is a composite mean score of erythema and peeling severity scored on a 4 - point ordinal sc ale per domain (0=none, 1=mild, 2=moderate and 3=severe for a maximum score of 6), data expressed as a mean percentage change from initiation of treatment phase. Dorsal depilated BALB - C mice were dosed topically for 14 days with 100mg topical IMI cream (Day 1 - 7: induction phase, Day 8 - 14: treatment phase). N=4 animals were assigned to each treatment group with each group receiving 100mg of allocated treatment on Day 8 - 14 once daily • Dose dependent response was observed over the VYN201 concentration range 0.001% to 0.1% • There was a 94% reduction in composite score for VYN201 0.1% relative to vehicle control group at Day 7 • VYN201 0.1% had comparable efficacy to clobetasol propionate 0.05% cream - 94 % -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean percent change in body weight Post - Induction Treatment Day VYN201 Vehicle (HC) VYN201 Vehicle VYN201 0.1% Clobetasol Cream 0.05% 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean percent change in Composite Inflammation Severity Score Post - Induction Treatment Day VYN201 Vehicle VYN201 0.001% VYN201 0.01% VYN201 0.1% Clobetasol Cream 0.05% • Animals treated with VYN201 0.1% continued to gain body weight in a similar manner to healthy control group treated with vehicle • Clobetasol cream 0.05% group had a 17% reduction in body weight compared to the VYN201 0.1% group at treatment day 7 - 17 % VYN201: Comparable Efficacy to Superpotent Steroid Clobetasol in a TH17 - Mediated Murine Inflammation Model; Potential for Greater Tolerability 37

IMI – Imiquimod. Dorsal depilated BALB - C mice were dosed topically for 14 days with 100mg topical IMI cream (Day 1 - 7: induction phase, Day 8 - 14: treatment phase). N=4 animals were assigned to each treatment group with each group receiving 100mg of allocated treatment on Day 8 - 14 once daily • Strong correlation between improvement in clinical severity scores and reduction in many pro - inflammatory biomarkers relevant to Th17 - mediated autoimmune diseases • Dose - dependent reduction in biomarker expression was observed with VYN201 0.1% as having the greatest effect • IL1 β , IL - 6 and IL - 23 precipitate the differentiation of naïve Th0 immune cells to Th17 cells • Th17 cells produce a range of cytokines that drive inflammation in autoimmune diseases. These include IL17, IL36 and TNF α 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 IL - 1 β IL-6 IL-17 IL-23 IL-36 TNF - α pmol/cytokine VYN201 Vehicle VYN201 0.001% VYN201 0.01% VYN201 0.1% VYN201: Dose - Dependent Reduction in Pro - Inflammatory Biomarkers in TH17 - Mediated Murine Inflammation Model Indicates Target Engagement 38

VYN201 0.1% VYN201 Vehicle Clobetasol Cream 0.05% • No appreciable improvement in clinical signs • Substantial resolution of clinical signs • Skin presents with normal physiology with no evidence of striae rubrae or atrophy • No evidence suggestive of intolerance • Substantial resolution of clinical signs • Significant evidence of dermal atrophy (clear presence of both rhytides/fine wrinkles and deep wrinkles) • Marked dermal translucency and elastolysis VYN201: Normal Skin Physiology in TH17 - Mediated Murine Inflammation Model Suggests VYN201 Well Tolerated (Day 7) 39
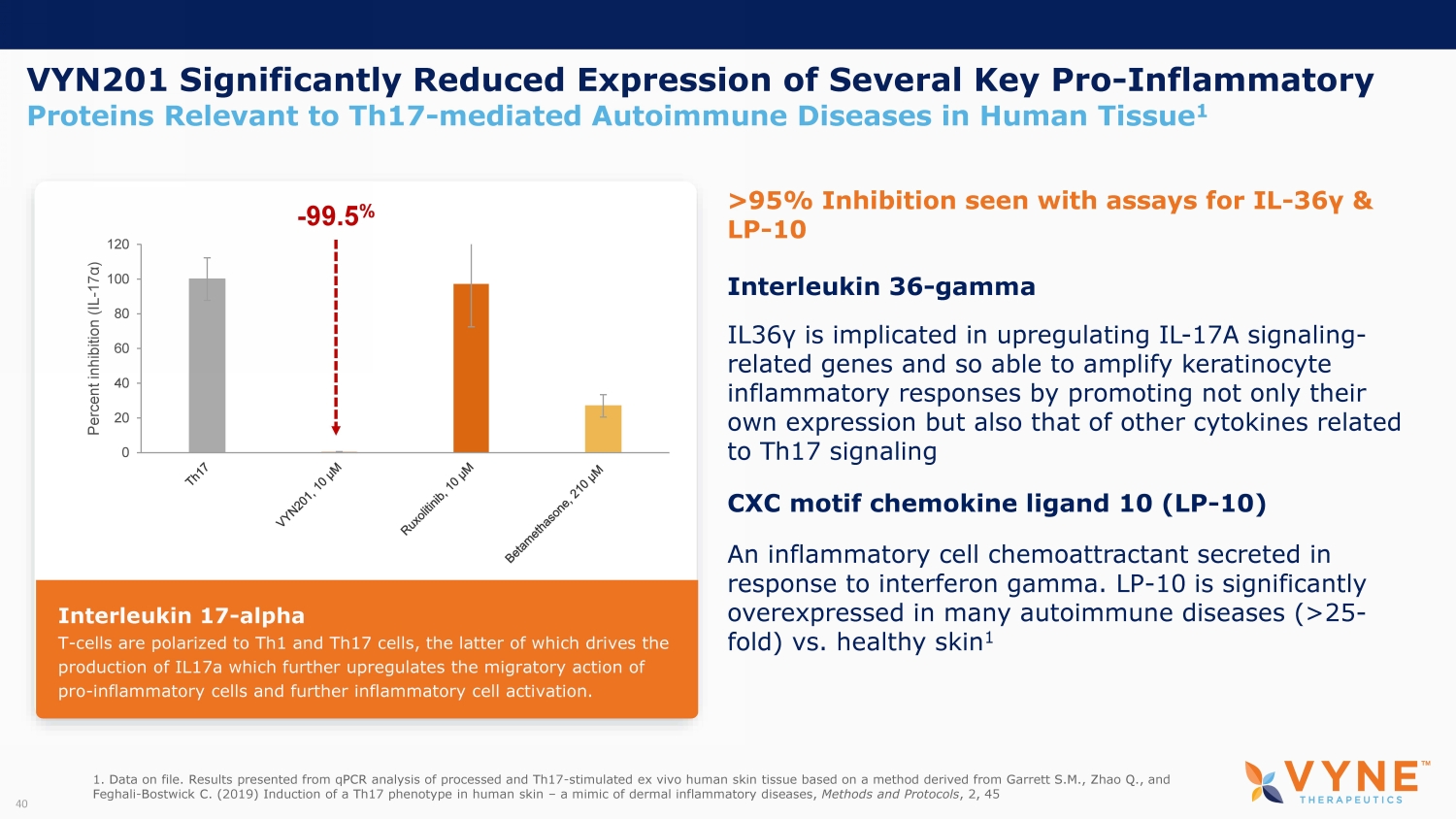
VYN201 Significantly Reduced Expression of Several Key Pro - Inflammatory Proteins Relevant to Th17 - mediated Autoimmune Diseases in Human Tissue 1 Interleukin 36 - gamma IL36 γ is implicated in upregulating IL - 17A signaling - related genes and so able to amplify keratinocyte inflammatory responses by promoting not only their own expression but also that of other cytokines related to Th17 signaling CXC motif chemokine ligand 10 (LP - 10) An inflammatory cell chemoattractant secreted in response to interferon gamma. LP - 10 is significantly overexpressed in many autoimmune diseases (>25 - fold) vs. healthy skin 1 >95% Inhibition seen with assays for IL - 36 γ & LP - 10 1. Data on file. Results presented from qPCR analysis of processed and Th17 - stimulated ex vivo human skin tissue based on a meth od derived from Garrett S.M., Zhao Q., and Feghali - Bostwick C. (2019) Induction of a Th17 phenotype in human skin – a mimic of dermal inflammatory diseases, Methods and Protocols , 2, 45 40 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Percent inhibition (IL - 17 α ) - 99.5 % Interleukin 17 - alpha T - cells are polarized to Th1 and Th17 cells, the latter of which drives the production of IL17a which further upregulates the migratory action of pro - inflammatory cells and further inflammatory cell activation.

VYN201: Dermal and Lung Fibrosis

Female hairless mice (n=4/group) had two identical 10mm incisions made either side of the flank. Animals were topically dosed 1X daily with 100mg VYN201 vehicle, VYN201 1% or a Hydroalcoholic gel* until each wound had completely healed • Statistically significant difference (p<0.05) in composite global external healing score for VYN201 1% compared to Hydroalcoholic gel from Day 8 • Complete healing occurred for VYN201 1% and VYN201 vehicle approximately 5 days earlier compared to Hydroalcoholic gel (Mean day to heal:15.5 vs. 21 days) *A negative control known to delay wound healing Global External Lesion Score is a composite severity score of lesion length, width, swelling and visibility Fibrotic tissue mass is scored on a 4 - point severity scale: 0=No tissue mass; 1=small tissue mass; 2=moderate tissue mass; 3=la rge tissue mass • Animals treated with VYN201 1% had statistically significant less tissue mass/fibrosis compared to VYN201 vehicle or Hydroalcoholic gel, indicative of the known anti - fibrotic mechanism for BET inhibition ( P <0.05 for VYN201 1% compared to VYN201 vehicle and Hydroalcoholic gel) VYN201: Demonstrated Anti - Fibrotic Activity without Delay in Healing Time in Murine Skin Healing Model 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Global External Lesion Healing Score Treatment Day VYN201 Vehicle VYN201 1% Hydroalcoholic gel 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 VYN201 1% VYN201 Vehicle Hydroalcoholic gel Fibrotic Tissue Mass Score

VYN201 1% VYN201 Vehicle Hydroalcoholic gel • Still evidence of minor swelling around incision sites • Little evidence of residual swelling • Wound appears more macular in nature compared to VYN201 vehicle or the Hydroalcoholic gel • Incision sites appear less distinct and leave a more aesthetic outcome compared to other treatments • Moderate swelling clearly evident at end of treatment • Although healed, residual scabbing still remains • Incision sites clearly visible VYN201: Little Evidence of Residual Swelling and Macular Wound Appearance in Murine Skin Healing Model 3
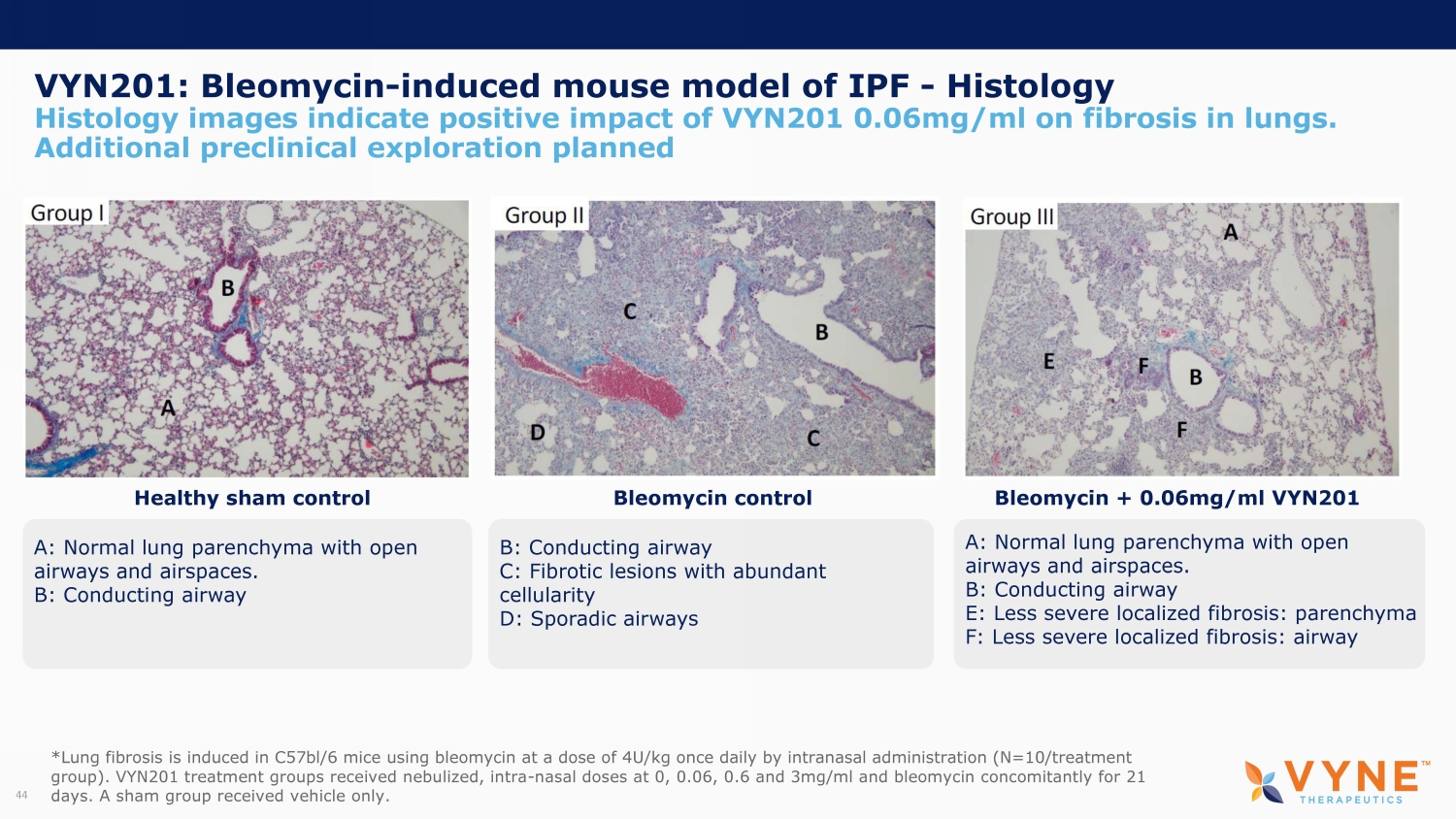
VYN201: Bleomycin - induced mouse model of IPF - Histology Histology images indicate positive impact of VYN201 0.06mg/ml on fibrosis in lungs. Additional preclinical exploration planned 4 Healthy sham control Bleomycin control Bleomycin + 0.06mg/ml VYN201 A : N ormal lung parenchyma with open airways and airspaces. B: C onducting airway B: C onducting airway C : F ibrotic lesions with abundant cellularity D: Sporadic airways A: Normal lung parenchyma with open airways and airspaces. B : C onducting airway E: Less severe localized fibrosis: parenchyma F: Less severe localized fibrosis: airway *Lung fibrosis is induced in C57bl/6 mice using bleomycin at a dose of 4U/kg once daily by intranasal administration (N=10/tr eat ment group). VYN201 treatment groups received nebulized, intra - nasal doses at 0, 0.06, 0.6 and 3mg/ml and bleomycin concomitantly for 21 days. A sham group received vehicle only.

VYN201: Rheumatoid Arthritis

VYN201: CAIA Mouse Model of Arthritis – Paw Thickness Marked inhibition of paw thickening/swelling CAIA = Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis; IA = Intra - articular; IP = Intraperitoneal 1.75 2.00 2.25 2.50 2.75 3.00 3.25 3.50 Baseline Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 10 Day 12 Paw thickness treated leg (mm) VYN201 Vehicle IA VYN201 10mg/kg IA VYN201 1mg/kg IA VYN201 0.1mg/kg IA VYN201 0.01 mg/kg IA Dexamethasone 1mg/kg IP Dexamethasone 1mg/kg IA Inflammatory arthritis was induced in BALB/C mice using a mixture of four arthritogenic MAbs by IV injection at Day 0 and was further challenged with an LPS IV injection at Day 4 (N=7/treatment group). VYN201 treatment groups received 50µl intra - articular (IA) doses of VYN201 at 0, 0.01, 0.1, 1 or 10mg/kg on Days 0, 3, 6 and 9. Dexamethasone control animals received 50 µl of 10mg/kg IA on Days 0, 3, 6 and 9 or 1mg/kg intraperitoneal (IP) on each treatment day (Day 0 - 11). Treatment response was evaluated based on an assessment of paw thickening/swelling. Paw thickening commences at study days 5/6 (expected) Both VYN201 1 & 10mg/kg superior to dexamethasone IA 10mg/kg Marked inhibition of paw thickening for the VYN201 1 & 10mg/kg dose levels and in line with 1mg/kg dexamethasone systemic dose 6

VYN201: CAIA Mouse Model of Arthritis – Arthritis Score Demonstrated dose dependent reduction in disease severity *Scoring based on a five - point composite severity scale of redness, swelling of the ankles and wrists, and paw thickness. Scorin g ranges from 0 (normal) to 4 (extensive signs and symptoms of arthritis); CAIA = Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis; IA = Intra - articular; IP = Intraperitoneal 0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 Baseline Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 10 Day 12 Arthritis scoring treated leg VYN201 Vehicle IA VYN201 10mg/kg IA VYN201 1mg/kg IA VYN201 0.1mg/kg IA VYN201 0.01 mg/kg IA Dexamethasone 1mg/kg IP Dexamethasone 1mg/kg IA Inflammatory arthritis was induced in BALB/C mice using a mixture of four arthritogenic MAbs by IV injection at Day 0 and was further challenged with an LPS IV injection at Day 4 (N=7/treatment group). VYN201 treatment groups received 50µl intra - articular (IA) doses of VYN201 at 0, 0.01, 0.1, 1 or 10mg/kg on Days 0, 3, 6 and 9. Dexamethasone control animals received 50 µl of 10mg/kg IA on Days 0, 3, 6 and 9 or 1mg/kg intraperitoneal (IP) on each treatment day (Day 0 - 11). Treatment response was evaluated based on an assessment of arthritis score* Arthritis severity quantifiable at study days 5/6 (expected) Marked inhibition of arthritis signs and symptoms for VYN201 at 1 & 10mg/kg dose levels with severity scores approaching “normal” (mean severity score <1) Both VYN201 1 & 10mg/kg superior to dexamethasone IA 10mg/kg 7

VYN201 1 & 10mg/kg results demonstrated the highest localized effect in the treated limb when compared to the untreated limbs (largest delta between treated and untreated limbs) Each animal treated with the intra - articular injections received the injection in the ankle of one rear paw. The untreated rear paw was assessed to evaluate any potential anti - inflammatory systemic effect. Anti - inflammatory systemic effect was evaluated based on an assessment vs. untreated paw VYN201: CAIA Mouse Model of Arthritis – Systemic Impact Demonstrated localized dose - dependent effect -0.50 0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 Baseline Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 10 Day 12 Paw thickness (mm) Δ untreated - treated leg VYN201 Vehicle IA VYN201 10mg/kg IA VYN201 1mg/kg IA VYN201 0.1mg/kg IA VYN201 0.01 mg/kg IA Dexamethasone 1mg/kg IP Dexamethasone 1mg/kg IA Paw Thickness -1.50 -0.50 0.50 1.50 2.50 3.50 Baseline Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 10 Day 12 Arthritis scoring Δ untreated - treated leg VYN201 Vehicle IA VYN201 10mg/kg IA VYN201 1mg/kg IA VYN201 0.1mg/kg IA VYN201 0.01 mg/kg IA Dexamethasone 1mg/kg IP Dexamethasone 1mg/kg IA Arthritis Score *Scoring based on a five - point composite severity scale of redness, swelling of the ankles and wrists, and paw thickness. Scorin g ranges from 0 (normal) to 4 (extensive signs and symptoms of arthritis); CAIA = Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis; IA = I ntr a - articular; IP = Intraperitoneal Treatment effect for VYN201 treated animals was dose - dependent over the dose range 0.01 to 10mg/kg For the VYN201 10mg/kg dose: o The average paw thickness at day 12 was 3.48 mm in the untreated paw versus 2.17 mm in the treated paw (p<0.01) o The average arthritis score was 0.67 in the treated paw versus 3.33 in the untreated paw (p<0.05) For the VYN201 1mg/kg dose: o The average paw thickness at day 12 was 2.98 mm in the untreated paw versus 2.18 mm in the treated paw (p<0.01) o The average arthritis score was 0.57 in the treated paw versus 2.43 in the untreated paw (p<0.05) 8

VYN201: Vitiligo

10 • Stimulated and vehicle treated RHE demonstrated a significant upregulation of MMP9, relative to unstimulated and untreated control • VYN201 markedly reduced the expression of MMP9 in a dose - dependent manner with a maximal effect at the 1% concentration • VYN201 1% reduced the secretion of MMP9 by 94.7%, relative to stimulated vehicle, and numerically superior to ruxolitinib 1.5% VYN201: Human Tissue Model of Vitiligo – Demonstrated Inhibition of MMP9 100 894 34 63 725 880 73 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 Untreated CTL Vehicle VYN201 - 1% VYN201 - 0.1% VYN201 - 0.01% VYN201 - 0.001% Rux 1.5% Ø TNF - α/ IFN - γ TNF - α 12 ng/ml/IFN - γ 12 ng/ml MMP - 9 secretion (% untreated unstimulated CTL) Reconstituted human epithelial (RHE) skin cultures were treated with a TNF - α and IFN - ɣ cytokine cocktail to induce a vitiligo phenotype ( melanocytorrhagy (loss of melanocyte), upregulation of MMP9 and soluble E - cadherin). 24hr prior to stimulation, RHE samples were topically treatment with VYN201 at varying concentrations and topical ruxolitinib 1.5% cream at 3 mg/cm 2 94.7 %

VYN201: Human Tissue Model of Vitiligo – Reduction of Soluble E - cadherin • Stimulated and vehicle - treated RHE demonstrated a significant upregulation of soluble E - cadherin, relative to unstimulated control • VYN201 affects a dose - dependent reduction in solubilized E - cadherin • VYN201 was numerically superior to topical ruxolitinib cream 1.5% 100 328 221 181 359 422 488 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 Untreated CTL Vehicle VYN201 - 1% VYN201 - 0.1% VYN201 - 0.01% VYN201 - 0.001% Rux 1.5% Ø TNF - α/ IFN - γ 12ng/ml TNF - α/ 12 ng/ml IFN - γ Soluble E - cadherin (% untreated unstimulated CTL) 11 Reconstituted human epithelial (RHE) skin cultures were treated with a TNF - α and IFN - ɣ cytokine cocktail to induce a vitiligo phenotype (melanocytorrhagy (loss of melanocyte), upregulation of MMP9 and soluble E - cadherin). 24hr prior to stimulation, RHE samples were topically treatment with VYN201 at varying concentrations and topical ruxolitinib 1.5% cream at 3 mg/cm 2

VYN201: Human Tissue Model of Vitiligo – Effect on Melanocyte Retention 12 • Stimulated and vehicle - treated RHE demonstrated a significant loss in melanin content, relative to unstimulated control • VYN201 substantially prevents the loss of melanin pigment in the basal layers of skin in a dose dependent manner • Residual melanin levels for VYN201 1% was approximately 10 - fold higher than vehicle, retaining approximately 75% of melanin relative to unstimulated control 498 100 35 367 290 36 9 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 Unstimulated control Stimulated control Stimulated + Vehicle Stimulated + VYN201 1% Stimulated + VYN201 0.1% Stimulated + VYN201 0.01% Stimulated + VYN201 0.001% Relative melanin content in basal layers (% relative to the stimulated control) Reconstituted human epithelial (RHE) skin cultures were treated with a TNF - α and IFN - ɣ cytokine cocktail to induce a vitiligo phenotype (melanocytorrhagy (loss of melanocyte), upregulation of MMP9 and soluble E - cadherin). 24hr prior to stimulation, RHE samples were topically treatment with VYN201 at varying concentrations and topical ruxolitinib 1.5% cream at 3 mg/cm 2

TRV: tyrosinase - related protein 1 (important enabler of melanogenesis) Keratinocytes (blue), melanocytes (green) Basal layer Melanocyte migration Retention of melanocytes at the basal layer Stimulated and Vehicle treated Unstimulated and untreated control Stimulated and VYN201 1% treated Melanocytes remain at or close to the basal layer implying that E - cadherin adhesion is still functional Clear evidence of melanocyte adhesion disruption, melanocyte detachment and migration through the skin VYN201 1% prevents detachment and subsequent loss of melanocytes from the basal layer implying that E - cadherin adhesion is still functional VYN201: Human Tissue Model of Vitiligo - Histology Micrographic images of TRV immuno - stained induced RHE specimens demonstrating the preservation of melanocytes in the basal layer of samples treated with VYN201 1% 13

Stimulated control Stimulated and VYN201 1% treated Preliminary data suggest that VYN201 regulates genes relevant to Vitiligo including impacting WNT pathway which is believed to play a key role in melanocyte regeneration Significant upregulation of cytokines IL6, IL1A and IL1B and TNF Melanocyte migration VYN201: Human Tissue Model of Vitiligo – Gene regulation Significant downregulation of cytokines IL6, IL1A and ILB and TNF and upregulation of the WNT pathway 14 Transcriptome volcano plots of genes relevant to vitiligo (preliminary findings):

Phase 1b Portion (n=up to 20) Treatment on the face and target lesion(s) on trunk of vitiligo patients for 8 weeks of once - daily treatment with planned extension. Primary objective: Evaluation of the safety and pharmacokinetics of VYN201 in vitiligo patients • Dose level(s) will be selected based on findings from the Phase 1a portion of the study. • Assessments will include TEAEs, pharmacokinetics, local skin tolerance, efficacy (F - VASI), biomarkers, photography Phase 1a/b initiation planned for 2H 2022 VYN201: Planned Phase 1 Study Design in Vitiligo Phase 1a Portion (n=6) A single ascending / multiple ascending dose cohort in healthy volunteer participants for up to 2 weeks of once - daily treatment. Primary objective: To identify safe starting doses for vitiligo patients in Phase 1b portion of the study • Assessments will include TEAEs, pharmacokinetics and local skin tolerance Vitiligo Phase 1a/b design comprising of: 15 TEAE = Treatment Emergent Adverse Events; F - VASI = Facial Vitiligo A rea S coring I ndex

VYN202: BD2 selective BET inhibitor

Potential Target Market 1 : • Immuno - inflammatory indications such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, ulcerative colitis/Crohn's and multiple sclerosis; additional potential in myeloproliferative neoplastic disorders 2 Focused activity: • Highly selective inhibition of BD2 domain of the BRD4 protein • Targeting improved safety profile compared to oral pan - BD BET inhibitors Targeted Near Term Milestones: • Candidate Selection – 2022 VYN202 Program Highlights & Molecular Profile VYN202 is an oral BET inhibitor designed to selectively bind to BD2 and is being developed for major immuno - inflammatory diseases 1. Initial indication to be communicated following candidate selection, exercise of option, IND - enabling studies and completion of requisite pre - clinical evaluations 2. List included is not exhaustive of potential indications 17 Potency vs. BD2 Selectivity BD2:BD1 Oral Bioavailability VYN202

Thierry Passeron, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology & INSERM U1065, C3M CHU Nice, France How addressing the pathophysiology of vitiligo is providing new therapeutic approaches 18

Disclosures • Almirall • Abbvie • Amgen • Astellas • BMS • Celgene • Galderma • GSK • Incyte • Janssen • LEO Pharma • Lilly • MSD • Novartis • Pfizer • Sanofi - Genzyme • SUN pharma • UCB pharma • Vyne therapeutics 19

Vitiligo • Acquired depigmentation of the skin and the hair • Acquired loss of melanocytes • 0.5 to 2% of worldwide population • (Non segmental) vitiligo : 85 to 95% of vitiligo cases Vitiligo Segmental vitiligo Mixed vitiligo 20 Image credit T . Passeron . Bergqvist C, Ezzedine K, 2020;236;571 - 592.

• Affect social, sexual and professional life (comparable at least to depression or even some cancers) • Difficulty to find a job • Major impact in some countries due to resemblance with leprosy • In Western countries more than half of the affected patients are willing to pay more than 5000 euros to treat their vitiligo Br J Dermatol. 2009;161:134 - 9 J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol . 2022 Apr 2. doi : 10.1111/jdv.18129 Major impact on affected patients 21

Rheumatoid arthritis Type 1 diabetes Celiac disease AutoImmune Thyroiditis Inflammatory bowel disease Alopecia Areata Multiple sclerosis Myasthenia gravis Auto - Immune Hepatitis Psoriasis Pigmentation phenotypes Melanoma Immune - related genes associated with vitiligo 1 – 4 * * Genes involved in immunity Genes involved in pigmentation Diseases frequently associated with vitiligo * * * 22 1. Jin Y, al. Nat Genet . 2016;48(11):1418 - 1424; 2. Jin Y, et al. Genet . 2012;44(6):676 - 680; 3. Birlea SA, et al. J Invest Dermatol . 2011;131(2):371 - 381; 4. Jin Y, Birlea SA, et al. Nat Genet . 2010;42(7):576 - 578.

Skin intrinsic abnormalities in vitiligo 1 • Involvement of melanocytes, keratinocytes and fibroblasts • Increased susceptibility to oxidative stress • Increased production of ROS • SAPS secretion • Mitochondrial alteration • Increase ECM protein release 23 α - SMA, alpha smooth muscle actin; ECM, extracellular matrix; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SAPS, senescence - associated secretory phenotype; SCF, stem cell factor; TNFα, tumour necrosis factor alpha. 1. Seneschal J, et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res . 2021;34:236 - 243.

Melanocytorragy • Detachment of melanocytes in vitiligo skin 1 • Altered e - cadherin levels and distribution precede clinical manifestation of vitiligo 2,3 • IFN g and TNF a induce melanocyte detachment through E - cadherin disruption by the increase of MMP9 4 MMP9 immuno - staining 24 MMP9: metalloproteinase 9 1. Gauthier Y, et al. Pigment Cell Res. 2003;16(4):322 - 32 2. Wagner RY, et al. J Invest Dermatol . 2015;135(7):1810 - 1819 3. Grill C, et al. Br J Dermatol . 2018;178(5):1204 - 1206 4. Boukhedouni N, et al. JCI Insight. 2020;5(11):e133772

Innate and adaptive immunity Innate response is the link between stressors and the adaptive anti - melanocytic response 25 1. Boniface K, et al. Front Immunol . 2021; 12:613056.

Healthy skin Vitiligo lesional skin WNT LEF Epidermis Dermis Differentiation & migration Keratinocyte Melanocyte Stem cell Oxidative stress Immune system Melanocyte detachment and melanocyte death LEF WNT Decreased renewal of melanocyte Differentiation & migration Keratinocyte Melanocyte Normal renewal of melanocyte Stem cell CXCL10 Antigen release Cell adhesion Melanocyte Regeneration: Key Role of The WNT Pathway • The WNT pathway has been demonstrated to be important enabler of melanocyte differentiation • Agonists of the WNT pathway can support melanocyte renewal and melanogenesis 26 1. Regazzetti C, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:3105 – 3114.

Three Objectives in Vitiligo Treatment To halt the melanocytic loss To induce the differentiation and the proliferation of melanocytes (long process that usually takes 6 to 24 months) To prevent relapses 27
To Halt the Depigmentation 28

Evolution of Vitiligo • The course of vitiligo is unpredictable • Lack of prognosis factors except clinical signs • Hypochromic borders under Wood’s lamp examination 1,3 • Confetti - like depigmentation 2 • Development of Vitiligo Signs of Activity Score (VSAS) 3 When vitiligo is active, it must be treated as a matter of urgency After 16 weeks 29 Top image adapted from van Geel , N et al.; 3 bottom images adapted from Sosa JJ, et al 2015. 2 VSAS=Vitiligo Signs of Activity Score. 1. Benzekri L, et al. Brit J Dermatol 2013; 168:265 - 71; 2. Sosa JJ, et al. J Am Acad Dermatol . 2015;73(2):272 - 275; 3. Van Geel N, et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:801 - 802.

How To Treat an Active Form of Vitiligo • Data strongly suggest the usefulness of Oral Mini - Pulse therapy (OMP) for halting vitiligo progression • MTX, cyclosporine and minocycline also seem to be effective (not indicated for treatment) • But Nb - UVB appears more important for halting disease progression and has the main advantage of also promoting more efficient repigmentation of vitiligo lesions • Interest of combining Nb - UVB and OMP in very active forms 30 MTX=methotrexate; Nb=narrow band; OMP=oral mini - pulse therapy. 1. Kubelis - Lopez DE, et al. Br J Dermatol . 2019;180:193 - 194
To Induce Repigmentation 31

Combination of Phototherapy and Topical Treatments • Interest of combining topical calcineurin inhibitors (off - label use) or potent topical steroids with sun exposure or Nb - UVB 1,2 • Confirmed by meta - analyses • Combination approaches are today the gold standard treatment for vitiligo • Better results on the face 3 • Optimal repigmentation requires 6 to 24 months 4 • No FDA or EMA approved treatment for repigmenting vitiligo 5 • High unmet need 32 Nb - UVB= narrow band ultraviolet B 1. Dang YP, et al. Dermatol Ther . 2016;29(2):126 - 133; 2. Li R, et al. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed . 2017;33(1):22 - 31; 3. Passeron T, et al. Lancet . 2020;396:74 - 75; 4 Taieb A, al. BJD. 2013;168(1):5 - 19; 5. Rodrigues M, et al. J Am Acad Dermatol . 2017;77(1):17 - 29.

To Prevent The Relapses 33

• >40% of lesions have new depigmentation in the year following the treatments » For localized vitiligo : » Tacrolimus 0.1% 2/ wk » Decreases the risk of relapse from 40% to 9.7% 1 » Potent topical steroids appears as effective but no demonstration in prospective randomized trials » For widespread vitiligo: » UVB 2 to 4 times / month » Expert opinion (no study available) 1 Cavalié, M, et al. J Invest Dermatol 2015 ; 135(4):970 - 4. Preventing Vitiligo Relapses 34

Adapted from Passeron T. Lancet 2020 ; 396(10244):74 - 5 and JEADV 2021, 35, 2305 – 2307 . Perspectives 35

Treatments today: • Cumbersome, poly - pharmacy regimen involving both Rx and Dx • Onset of efficacy can take quite some time to meaningfully develop • Some new treatments in development e.g. JAK inhibitors, anti - IL15 and WNT agonists (preclinical stage) but many more needed to provide treatment options Attributes of a drug to meet the vitiligo market need: • Works quickly with an enduring effect - greater time to relapse • No challenging safety signals (“without baggage”) • Promote melanocyte differentiation/proliferation What the market needs from new Vitiligo therapies 36

Thank you for your attention! 37

Target Candidate Selection Preclinical Clinical Trials Near - Term Catalysts FMX114 Mild - to - moderate Atopic Dermatitis Phase 1b: completed Phase 2a: TLR Q2 VYN201 Locally administered Pan - BD BET inhibitor 2H 2022: FPI Phase 1 for Vitiligo 2023: Clinic - ready VYN202 Oral BD2 BET inhibitor 1 2022: Candidate Selection 1. Initial indications for VYN202 to be communicated following completion of requisite pre - clinical evaluations TLR = Top Line Results; FPI = First Patient In/Enrolled 38 Exclusive Access to Library of NCE BET Inhibitors for Any Indication Worldwide Targeted Clinical Milestones through 2023 Driving Pipeline to Proof - of - Concept Phase 1b/2a Vitiligo (topical administration) IND - enabling studies underway Candidate Selection process underway Undisclosed indication (non - topical administration)
Serious News for Serious Traders! Try StreetInsider.com Premium Free!
You May Also Be Interested In
- Formlabs Launches Form 4, The Fastest, Most Reliable 3D Printer for Prototyping through Production
- Partslion Launches New Software to Streamline Access to Quality Car Parts
- Raynes & Lawn Law Firm Nationally Recognized for Its Work on Medical Malpractice and Birth Injuries
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share