Form 8-K AVROBIO, Inc. For: May 24

MAY 2022 Corporate Presentation Exhibit 99.1

Disclaimer This presentation has been prepared by AVROBIO, Inc. (“AVROBIO”) for informational purposes only and not for any other purpose. Certain information contained in this presentation and statements made orally during this presentation relate to or are based on studies, publications, surveys and other data obtained from third-party sources and AVROBIO’s own internal estimates and research. While AVROBIO believes these third-party sources to be reliable as of the date of this presentation, it has not independently verified, and AVROBIO makes no representation as to the adequacy, fairness, accuracy or completeness of any information obtained from third-party sources. While AVROBIO believes its internal research is reliable, such research has not been verified by any independent source. This presentation may contain forward-looking statements made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements may be identified by words and phrases such as “aims,” “anticipates,” “believes,” “could,” “designed to,” “estimates,” “expects,” “forecasts,” “goal,” “intends,” “may,” “plans,” “possible,” “potential,” “seeks,” “will,” and variations of these words and phrases or similar expressions that are intended to identify forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements include, without limitation, statements regarding our business strategy for and the potential therapeutic benefits of our current and prospective product candidates; the design, commencement, enrollment and timing of ongoing or planned clinical trials and regulatory pathways; our plans and expectations with respect to the development of our clinical and preclinical product candidates, including timing, design and initiation of our potential clinical and registration trials and anticipated interactions with regulatory agencies; the timing of anticipated clinical and regulatory updates; the timing of patient recruitment and enrollment activities, clinical trial results, and product approvals; the timing and results of our ongoing preclinical studies; the anticipated benefits of our gene therapy platform including the potential impact on our commercialization activities, timing and likelihood of success; the expected benefits and results of our manufacturing technology, including the implementation of our plato® platform in our clinical trials and gene therapy programs; the expected safety profile of our investigational gene therapies; and our financial position and cash runway expectations. Any such statements in this presentation that are not statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. Any forward-looking statements in this presentation are based on our current expectations, estimates and projections about our industry as well as management’s current beliefs and expectations of future events only as of today and are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially and adversely from those set forth in or implied by such forward-looking statements. These risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to, the risk that any one or more of our product candidates will not be successfully developed or commercialized; the risk that regulatory agencies may disagree with our anticipated development approach for any one or more of our product candidates; the risk of cessation or delay of any ongoing or planned clinical trials of AVROBIO or our collaborators; the risk that we may not successfully recruit or enroll a sufficient number of patients for our clinical trials; the risk that we may not realize the intended benefits of our gene therapy platform, including the features of our plato® platform; the risk that our product candidates or procedures in connection with the administration thereof, including our use of busulfan as a conditioning agent or potential use of monoclonal antibody conditioning agents, will not have the safety or efficacy profile that we anticipate; the risk that prior results, such as signals of safety, activity or durability of effect, observed from preclinical or clinical trials, will not be replicated or will not continue in ongoing or future studies or trials involving our product candidates; the risk that we will be unable to obtain and maintain regulatory approval for our product candidates; the risk that the size and growth potential of the market for our product candidates will not materialize as expected; risks associated with our dependence on third-party suppliers and manufacturers; risks regarding the accuracy of our estimates of expenses and future revenue; risks relating to our capital requirements and needs for additional financing; risks relating to clinical trial and business interruptions resulting from the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic or similar public health crises, including that such interruptions may materially delay our development timeline and/or increase our development costs or that data collection efforts may be impaired or otherwise impacted by such crises; and risks relating to our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection for our product candidates. For a discussion of these and other risks and uncertainties, and other important factors, any of which could cause AVROBIO’s actual results to differ from those contained in the forward-looking statements, see the section entitled “Risk Factors” in AVROBIO’s most recent Quarterly Report, as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties and other important factors in AVROBIO’s subsequent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. AVROBIO explicitly disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements except to the extent required by law. Note regarding trademarks: plato® is a registered trademark of AVROBIO. Other trademarks referenced in this presentation are the property of their respective owners. Copyright© 2022 AVROBIO, Inc. All rights reserved.
Vision Bring personalized gene therapy to the world. Purpose Freedom from a lifetime of genetic disease.

Leading hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) gene therapy company Targeting lysosomal disorders representing a multi-billion revenue opportunity Strong efficacy and safety profile to date across two clinical-stage programs Regulatory discussions planned for 2H 2022 to frame approval pathways for multiple indications Strong balance sheet with cash runway into Q1 2024 Investment highlights 4

Leading lysosomal disorder gene therapy pipeline Gaucher type 1 AVR-RD-02 Cystinosis AVR-RD-04 Hunter AVR-RD-05 Gaucher type 3 AVR-RD-06 Pompe AVR-RD-03 IND-Enabling Phase 1/2 Indication WHOLLY-OWNED/LICENSED Planned regulatory milestones subject to regulatory agency clearance; *Collaborator-sponsored Phase 1/2 clinical trial of AVR-RD-04 is funded in part by grants to UCSD from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), Cystinosis Research Foundation (CRF) and National Institutes of Health (NIH). Gaucher
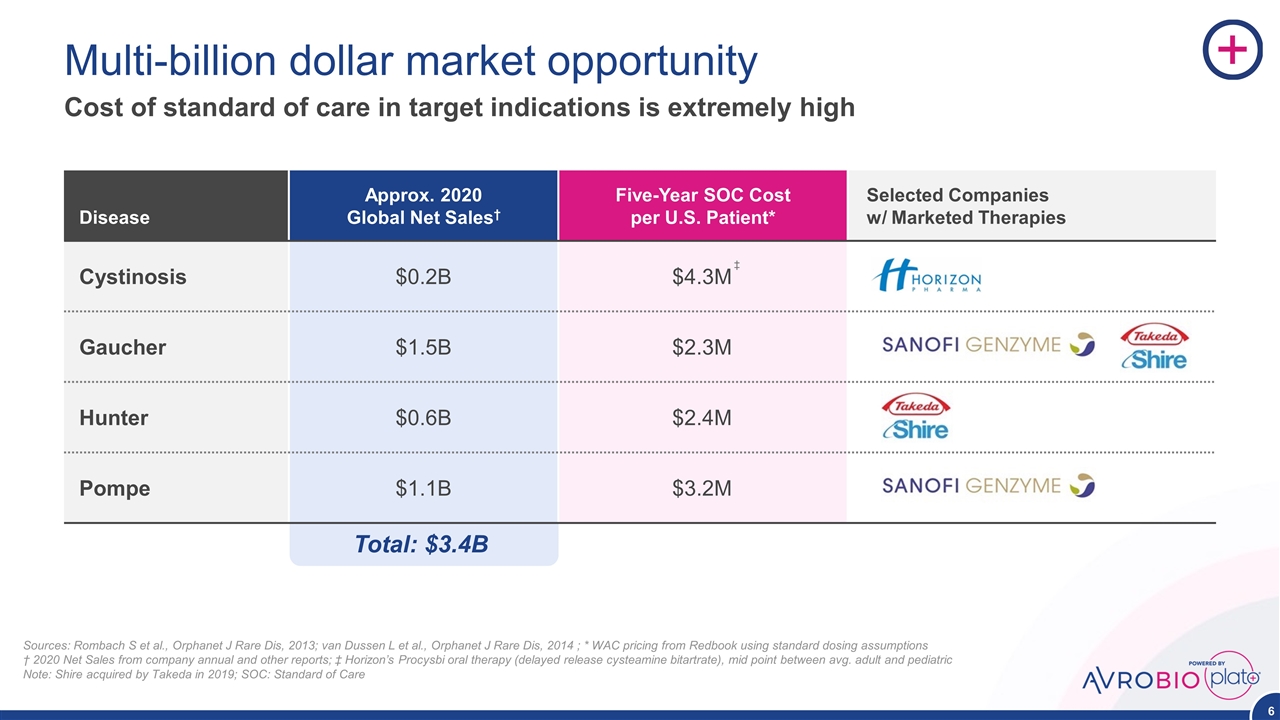
Disease Approx. 2020 Global Net Sales† Five-Year SOC Cost per U.S. Patient* Selected Companies w/ Marketed Therapies Cystinosis $0.2B $4.3M Gaucher $1.5B $2.3M Hunter $0.6B $2.4M Pompe $1.1B $3.2M Multi-billion dollar market opportunity Cost of standard of care in target indications is extremely high Sources: Rombach S et al., Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2013; van Dussen L et al., Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2014 ; * WAC pricing from Redbook using standard dosing assumptions † 2020 Net Sales from company annual and other reports; ‡ Horizon’s Procysbi oral therapy (delayed release cysteamine bitartrate), mid point between avg. adult and pediatric Note: Shire acquired by Takeda in 2019; SOC: Standard of Care Total: $3.4B ‡
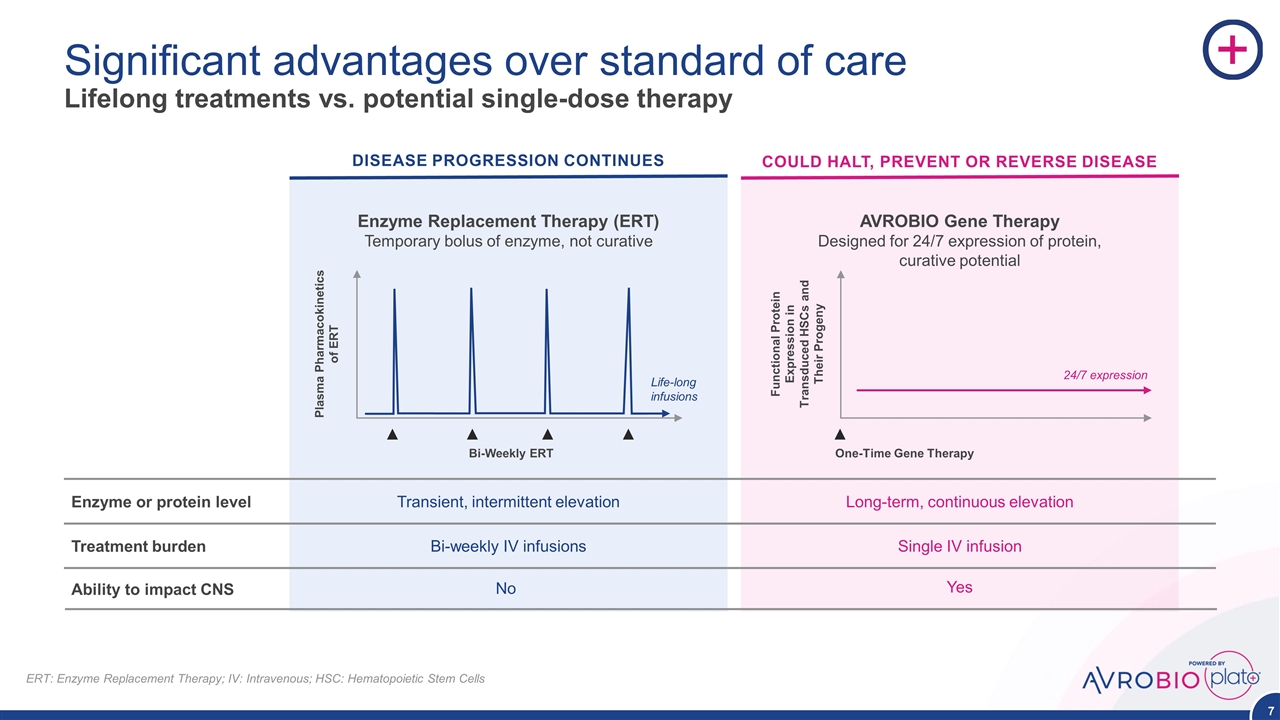
Significant advantages over standard of care Lifelong treatments vs. potential single-dose therapy Treatment burden Enzyme or protein level DISEASE PROGRESSION CONTINUES COULD HALT, PREVENT OR REVERSE DISEASE Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) Temporary bolus of enzyme, not curative Bi-Weekly ERT Plasma Pharmacokinetics of ERT Life-long infusions Transient, intermittent elevation Bi-weekly IV infusions AVROBIO Gene Therapy Designed for 24/7 expression of protein, curative potential Functional Protein Expression in Transduced HSCs and Their Progeny 24/7 expression One-Time Gene Therapy Long-term, continuous elevation Single IV infusion ERT: Enzyme Replacement Therapy; IV: Intravenous; HSC: Hematopoietic Stem Cells Ability to impact CNS No Yes
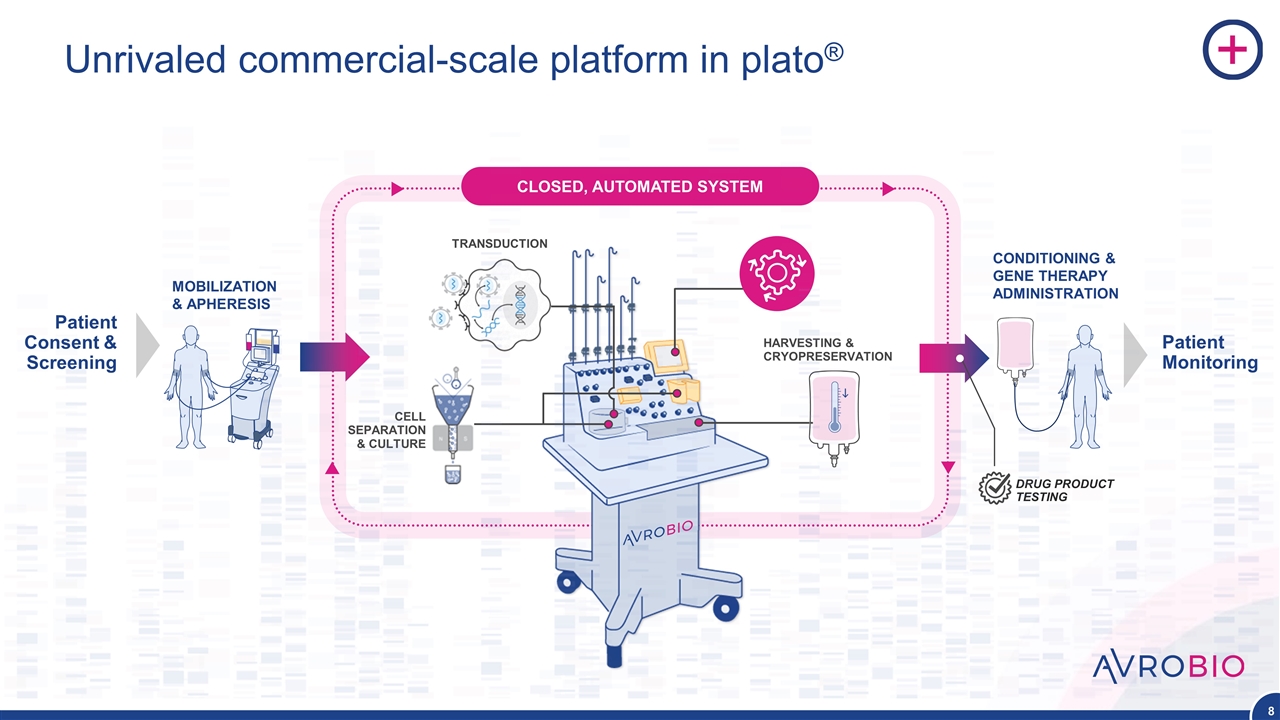
Unrivaled commercial-scale platform in plato® MOBILIZATION & APHERESIS Patient Consent & Screening Patient Monitoring CONDITIONING & GENE THERAPY ADMINISTRATION CELL SEPARATION & CULTURE TRANSDUCTION CLOSED, AUTOMATED SYSTEM HARVESTING & CRYOPRESERVATION DRUG PRODUCT TESTING

Cystinosis
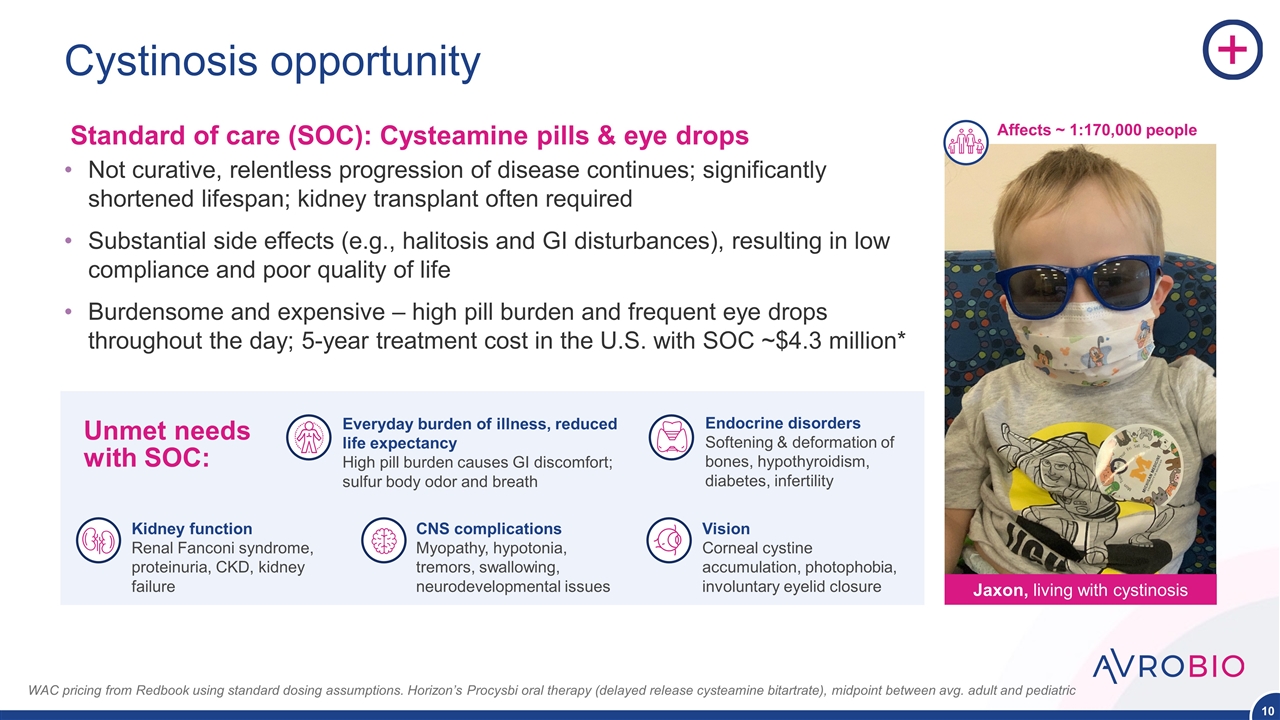
Cystinosis opportunity Not curative, relentless progression of disease continues; significantly shortened lifespan; kidney transplant often required Substantial side effects (e.g., halitosis and GI disturbances), resulting in low compliance and poor quality of life Burdensome and expensive – high pill burden and frequent eye drops throughout the day; 5-year treatment cost in the U.S. with SOC ~$4.3 million* WAC pricing from Redbook using standard dosing assumptions. Horizon’s Procysbi oral therapy (delayed release cysteamine bitartrate), midpoint between avg. adult and pediatric Unmet needs with SOC: Vision Corneal cystine accumulation, photophobia, involuntary eyelid closure Endocrine disorders Softening & deformation of bones, hypothyroidism, diabetes, infertility Everyday burden of illness, reduced life expectancy High pill burden causes GI discomfort; sulfur body odor and breath CNS complications Myopathy, hypotonia, tremors, swallowing, neurodevelopmental issues Kidney function Renal Fanconi syndrome, proteinuria, CKD, kidney failure Jaxon, living with cystinosis Affects ~ 1:170,000 people Standard of care (SOC): Cysteamine pills & eye drops
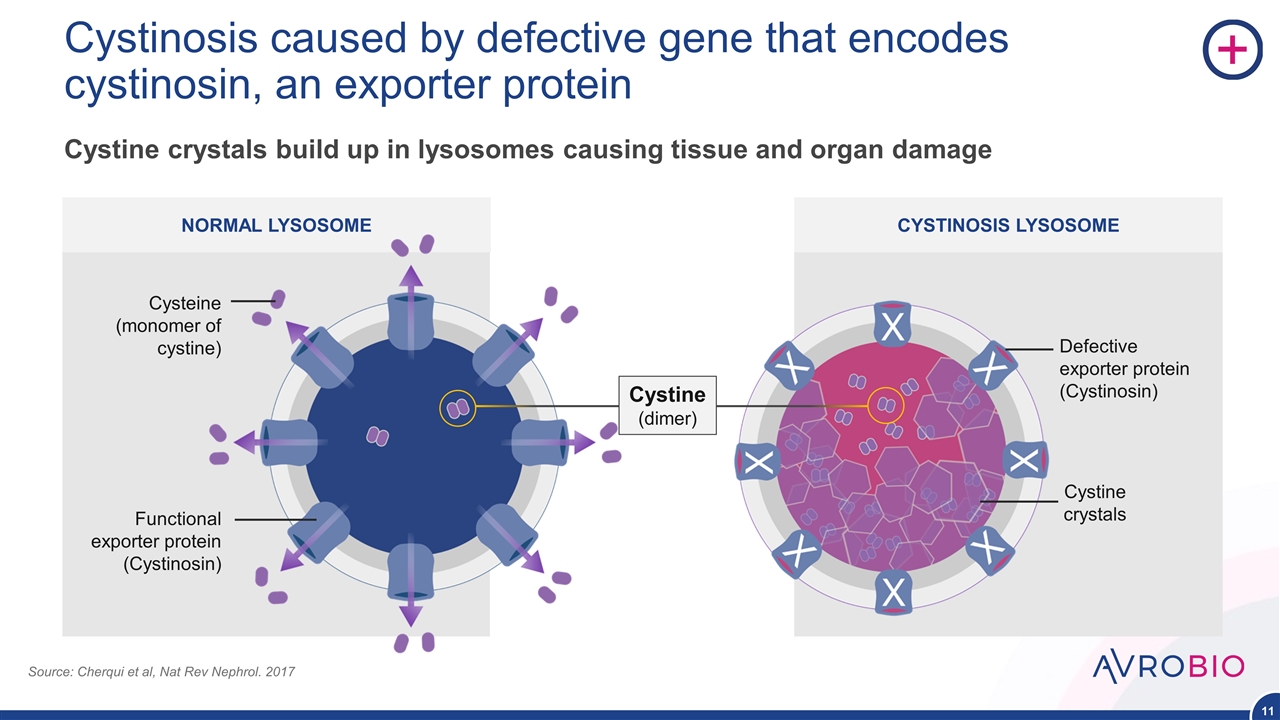
NORMAL LYSOSOME CYSTINOSIS LYSOSOME Cystinosis caused by defective gene that encodes cystinosin, an exporter protein Cysteine (monomer of cystine) Functional exporter protein (Cystinosin) Defective exporter protein (Cystinosin) Cystine crystals Cystine crystals build up in lysosomes causing tissue and organ damage Source: Cherqui et al, Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Cystine (dimer)
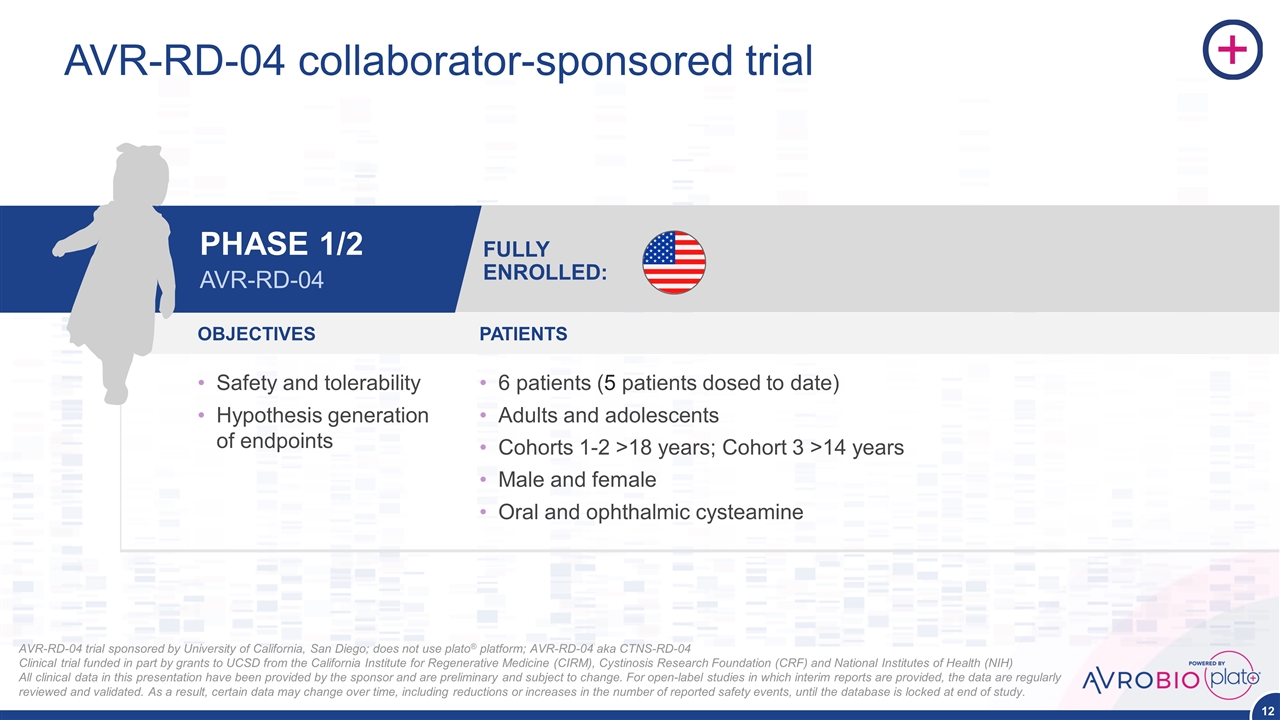
AVR-RD-04 collaborator-sponsored trial AVR-RD-04 trial sponsored by University of California, San Diego; does not use plato® platform; AVR-RD-04 aka CTNS-RD-04 Clinical trial funded in part by grants to UCSD from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), Cystinosis Research Foundation (CRF) and National Institutes of Health (NIH) All clinical data in this presentation have been provided by the sponsor and are preliminary and subject to change. For open-label studies in which interim reports are provided, the data are regularly reviewed and validated. As a result, certain data may change over time, including reductions or increases in the number of reported safety events, until the database is locked at end of study. OBJECTIVES PATIENTS Safety and tolerability Hypothesis generation of endpoints 6 patients (5 patients dosed to date) Adults and adolescents Cohorts 1-2 >18 years; Cohort 3 >14 years Male and female Oral and ophthalmic cysteamine FULLY ENROLLED: PHASE 1/2 AVR-RD-04
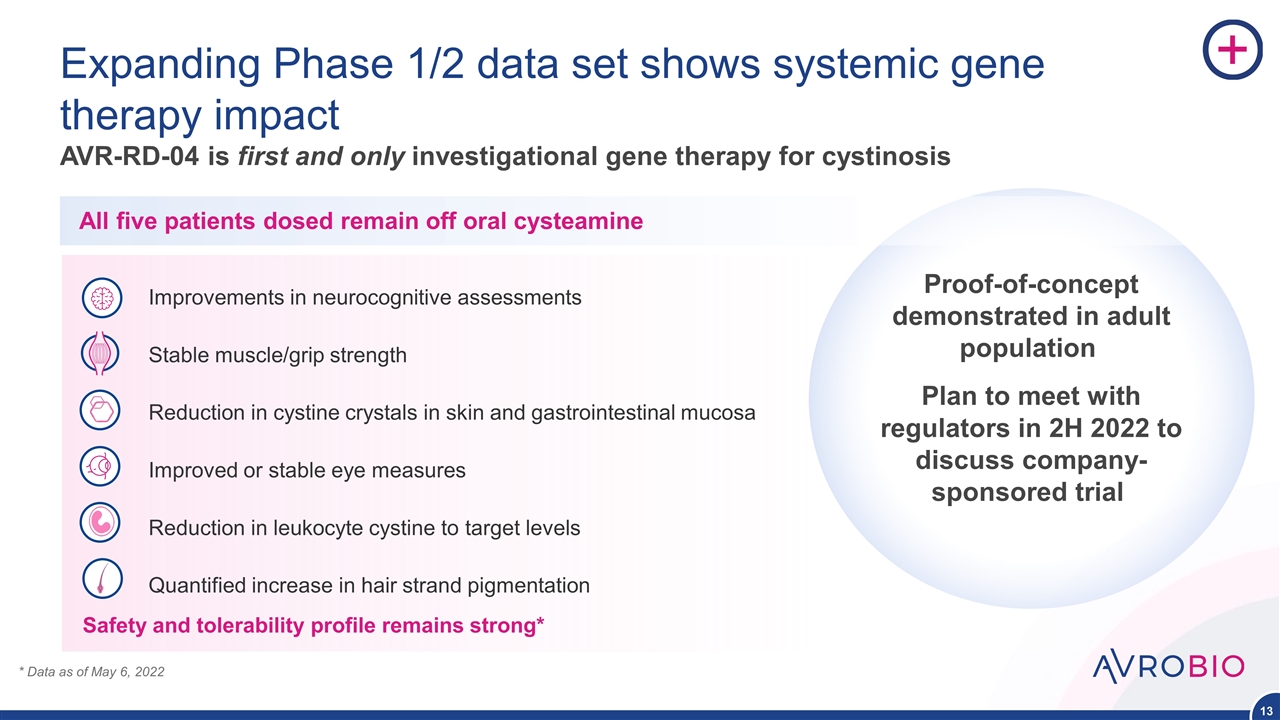
Expanding Phase 1/2 data set shows systemic gene therapy impact AVR-RD-04 is first and only investigational gene therapy for cystinosis Improvements in neurocognitive assessments Stable muscle/grip strength Reduction in cystine crystals in skin and gastrointestinal mucosa Improved or stable eye measures Reduction in leukocyte cystine to target levels Quantified increase in hair strand pigmentation * Data as of May 6, 2022 Proof-of-concept demonstrated in adult population Plan to meet with regulators in 2H 2022 to discuss company-sponsored trial Safety and tolerability profile remains strong* All five patients dosed remain off oral cysteamine
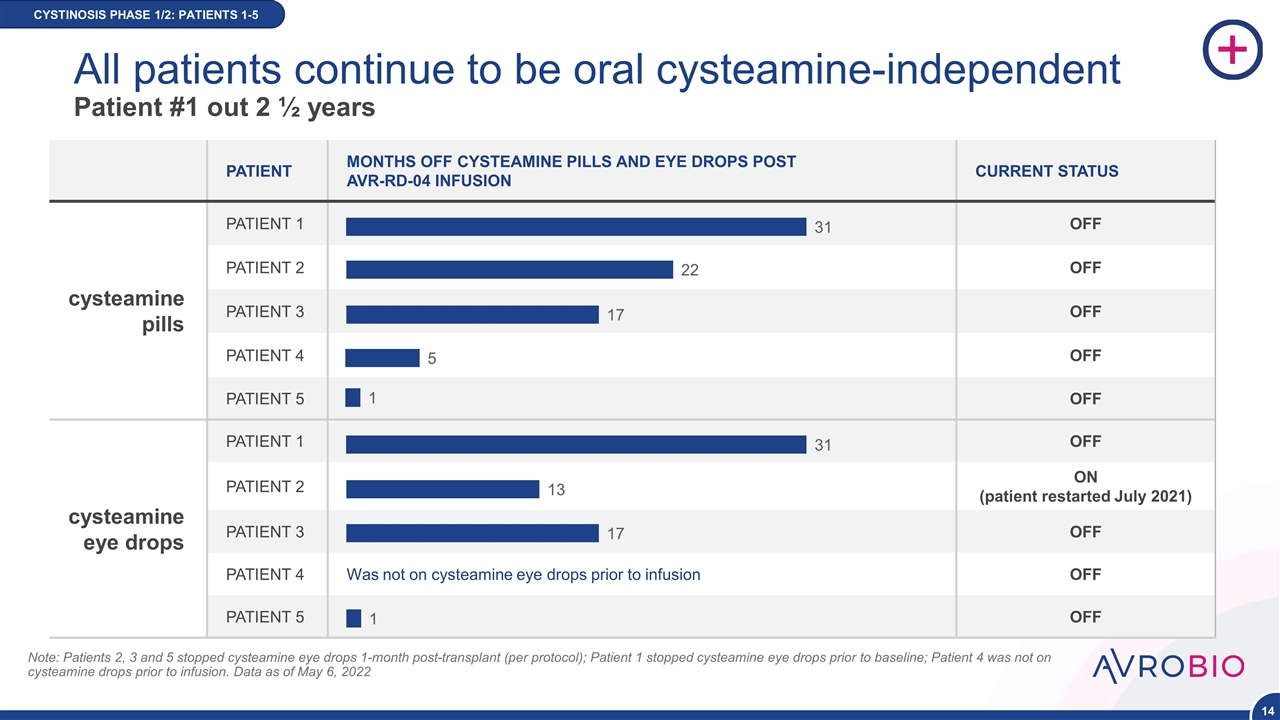
PATIENT MONTHS OFF CYSTEAMINE PILLS AND EYE DROPS POST AVR-RD-04 INFUSION CURRENT STATUS cysteamine pills PATIENT 1 OFF PATIENT 2 OFF PATIENT 3 OFF PATIENT 4 OFF PATIENT 5 OFF cysteamine eye drops PATIENT 1 OFF PATIENT 2 ON (patient restarted July 2021) PATIENT 3 OFF PATIENT 4 Was not on cysteamine eye drops prior to infusion OFF PATIENT 5 OFF CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2 Note: Patients 2, 3 and 5 stopped cysteamine eye drops 1-month post-transplant (per protocol); Patient 1 stopped cysteamine eye drops prior to baseline; Patient 4 was not on cysteamine drops prior to infusion. Data as of May 6, 2022 CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENTS 1-5 All patients continue to be oral cysteamine-independent Patient #1 out 2 ½ years NEW DATA
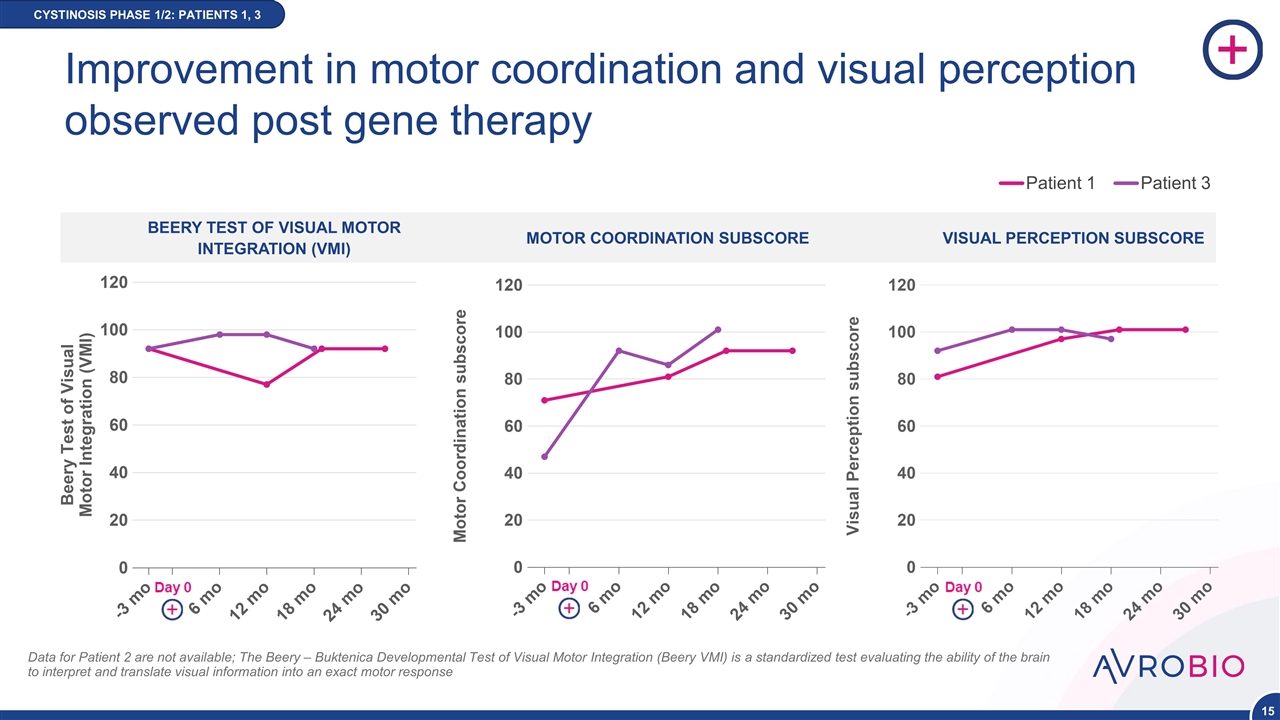
BEERY TEST OF VISUAL MOTOR INTEGRATION (VMI) Improvement in motor coordination and visual perception observed post gene therapy CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENTS 1, 3 MOTOR COORDINATION SUBSCORE VISUAL PERCEPTION SUBSCORE NEW DATA Patient 1 Patient 3 Data for Patient 2 are not available; The Beery – Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual Motor Integration (Beery VMI) is a standardized test evaluating the ability of the brain to interpret and translate visual information into an exact motor response
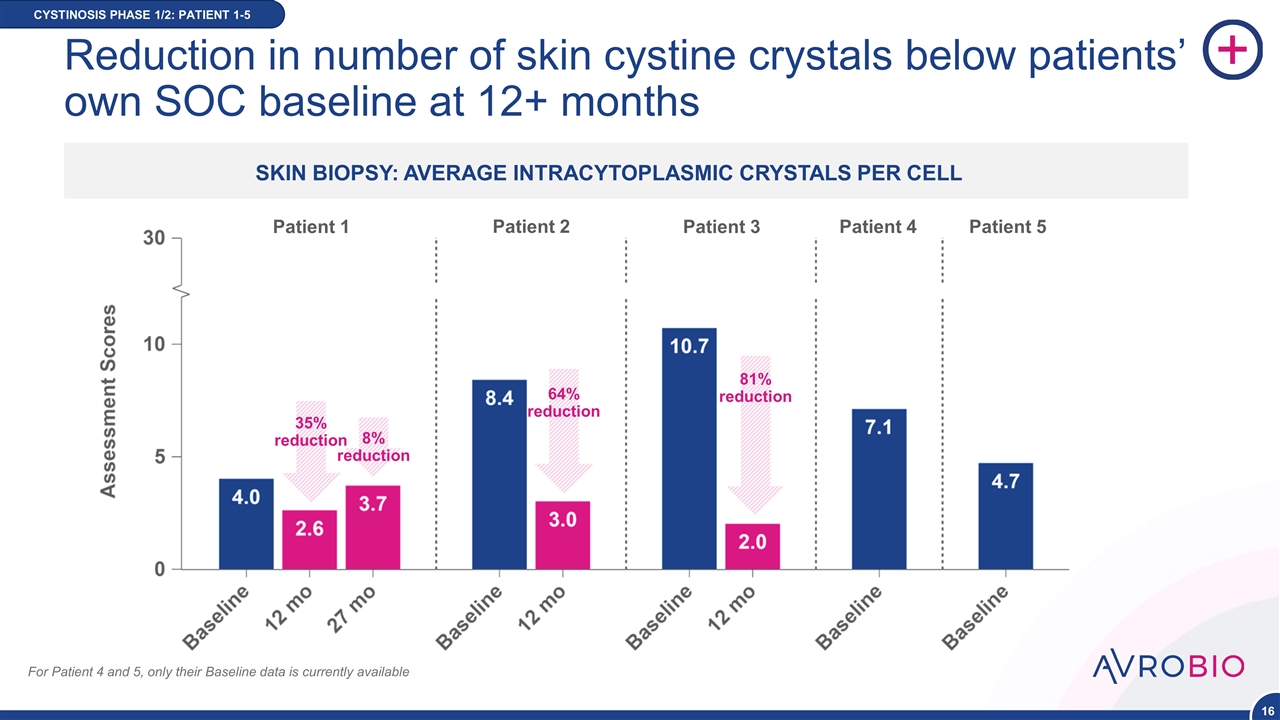
Reduction in number of skin cystine crystals below patients’ own SOC baseline at 12+ months CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENT 1-5 SKIN BIOPSY: AVERAGE INTRACYTOPLASMIC CRYSTALS PER CELL Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Patient 5 35% reduction 8% reduction 64% reduction 81% reduction For Patient 4 and 5, only their Baseline data is currently available
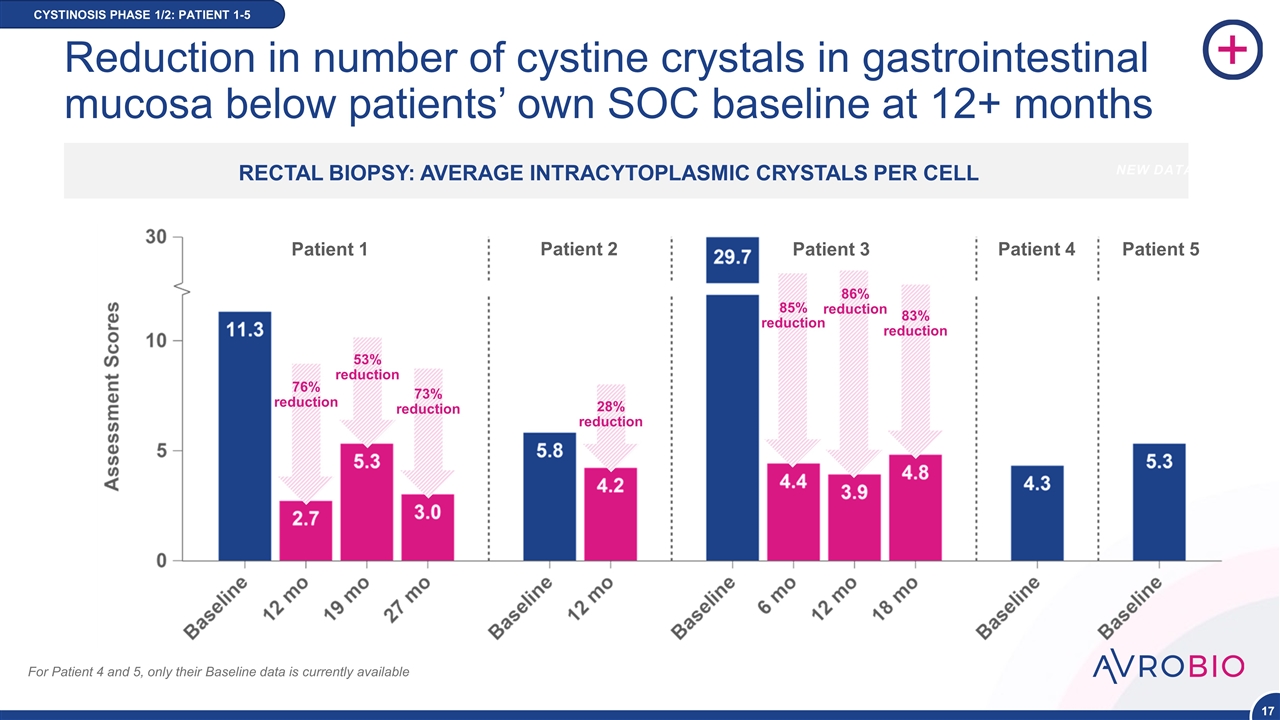
Reduction in number of cystine crystals in gastrointestinal mucosa below patients’ own SOC baseline at 12+ months CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENT 1-5 Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Patient 5 76% reduction 73% reduction 53% reduction 28% reduction 86% reduction 85% reduction 83% reduction For Patient 4 and 5, only their Baseline data is currently available RECTAL BIOPSY: AVERAGE INTRACYTOPLASMIC CRYSTALS PER CELL NEW DATA POIN
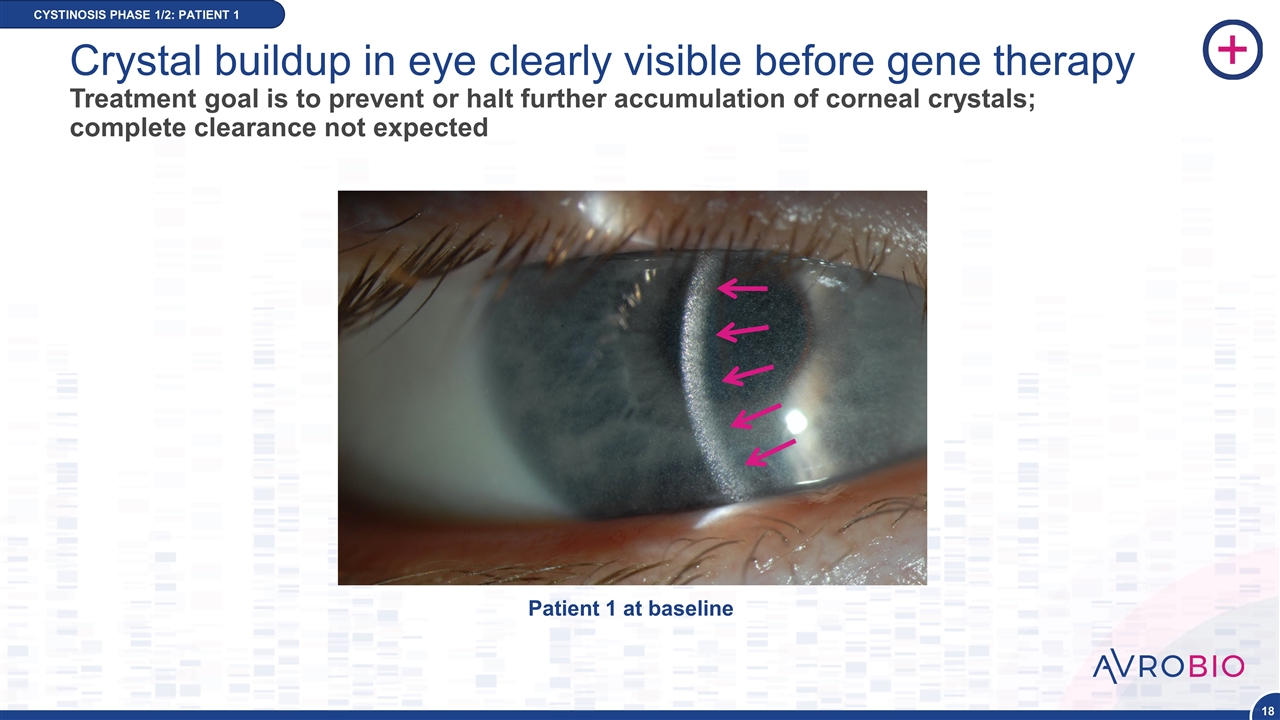
Crystal buildup in eye clearly visible before gene therapy Treatment goal is to prevent or halt further accumulation of corneal crystals; complete clearance not expected CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENT 1 Patient 1 at baseline
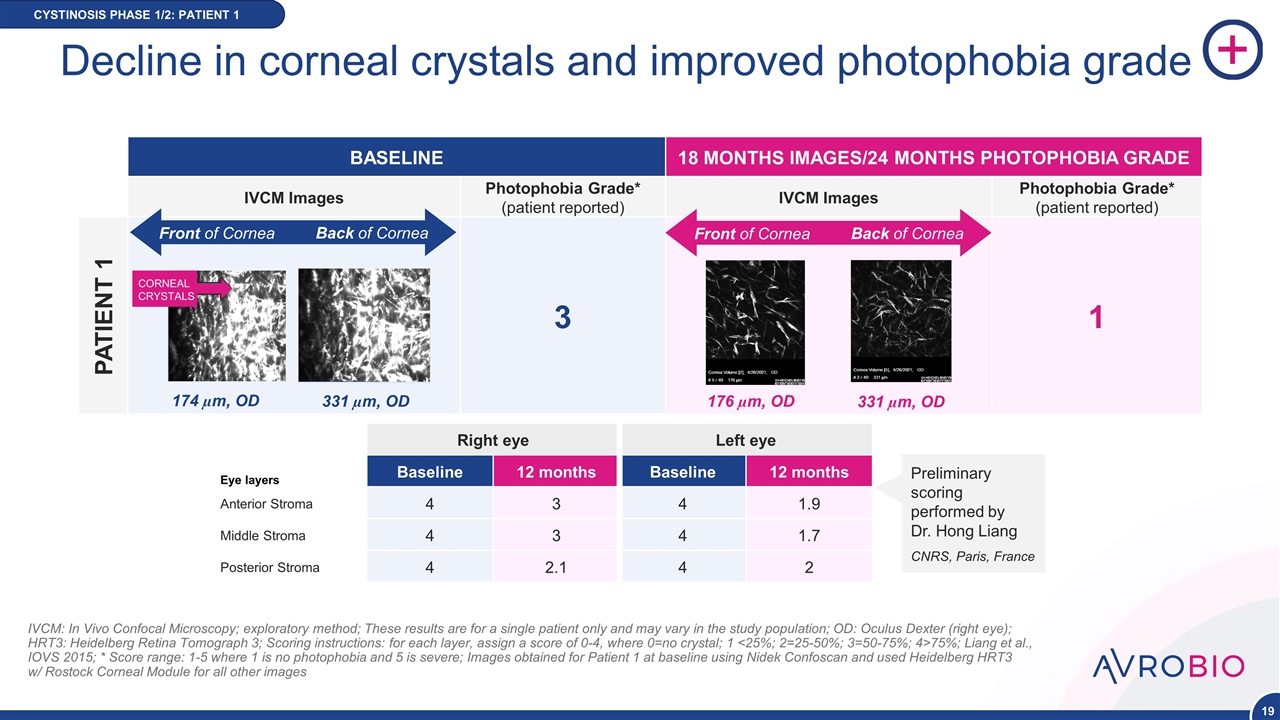
Decline in corneal crystals and improved photophobia grade CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENT 1 IVCM: In Vivo Confocal Microscopy; exploratory method; These results are for a single patient only and may vary in the study population; OD: Oculus Dexter (right eye); HRT3: Heidelberg Retina Tomograph 3; Scoring instructions: for each layer, assign a score of 0-4, where 0=no crystal; 1 <25%; 2=25-50%; 3=50-75%; 4>75%; Liang et al., IOVS 2015; * Score range: 1-5 where 1 is no photophobia and 5 is severe; Images obtained for Patient 1 at baseline using Nidek Confoscan and used Heidelberg HRT3 w/ Rostock Corneal Module for all other images BASELINE 18 MONTHS IMAGES/24 MONTHS PHOTOPHOBIA GRADE IVCM Images Photophobia Grade* (patient reported) IVCM Images Photophobia Grade* (patient reported) PATIENT 1 3 1 CORNEAL CRYSTALS 174 µm, OD 331 µm, OD Front of Cornea Back of Cornea 176 µm, OD 331 µm, OD Front of Cornea Back of Cornea Eye layers Right eye Left eye Baseline 12 months Baseline 12 months Anterior Stroma 4 3 4 1.9 Middle Stroma 4 3 4 1.7 Posterior Stroma 4 2.1 4 2 Preliminary scoring performed by Dr. Hong Liang CNRS, Paris, France NEW DATA POINT
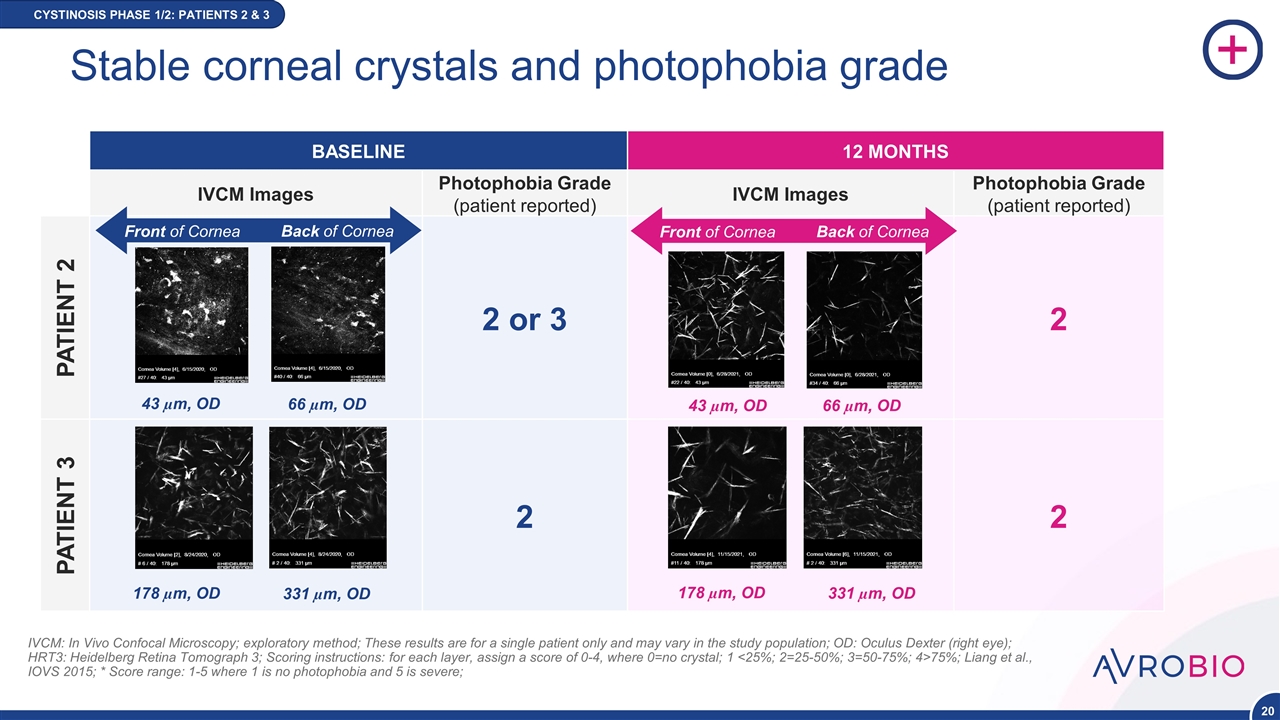
Stable corneal crystals and photophobia grade CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENTS 2 & 3 IVCM: In Vivo Confocal Microscopy; exploratory method; These results are for a single patient only and may vary in the study population; OD: Oculus Dexter (right eye); HRT3: Heidelberg Retina Tomograph 3; Scoring instructions: for each layer, assign a score of 0-4, where 0=no crystal; 1 <25%; 2=25-50%; 3=50-75%; 4>75%; Liang et al., IOVS 2015; * Score range: 1-5 where 1 is no photophobia and 5 is severe; BASELINE 12 MONTHS IVCM Images Photophobia Grade (patient reported) IVCM Images Photophobia Grade (patient reported) PATIENT 2 2 or 3 2 PATIENT 3 2 2 Front of Cornea Back of Cornea Front of Cornea Back of Cornea 43 µm, OD 66 µm, OD 43 µm, OD 66 µm, OD 178 µm, OD 331 µm, OD 178 µm, OD 331 µm, OD
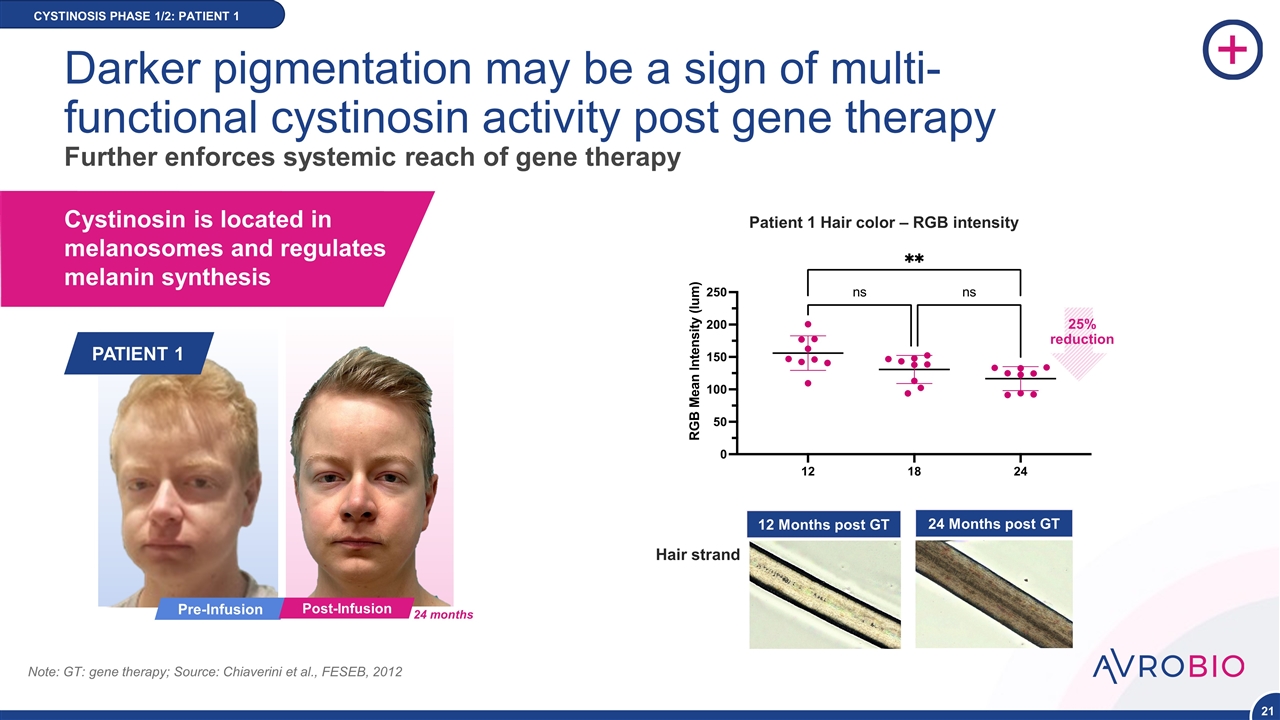
CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENT 1 Cystinosin is located in melanosomes and regulates melanin synthesis Note: GT: gene therapy; Source: Chiaverini et al., FESEB, 2012 Pre-Infusion PATIENT 1 Post-Infusion 24 months 12 Months post GT 24 Months post GT Patient 1 Hair color – RGB intensity NEW DATA Hair strand Darker pigmentation may be a sign of multi- functional cystinosin activity post gene therapy Further enforces systemic reach of gene therapy 25% reduction
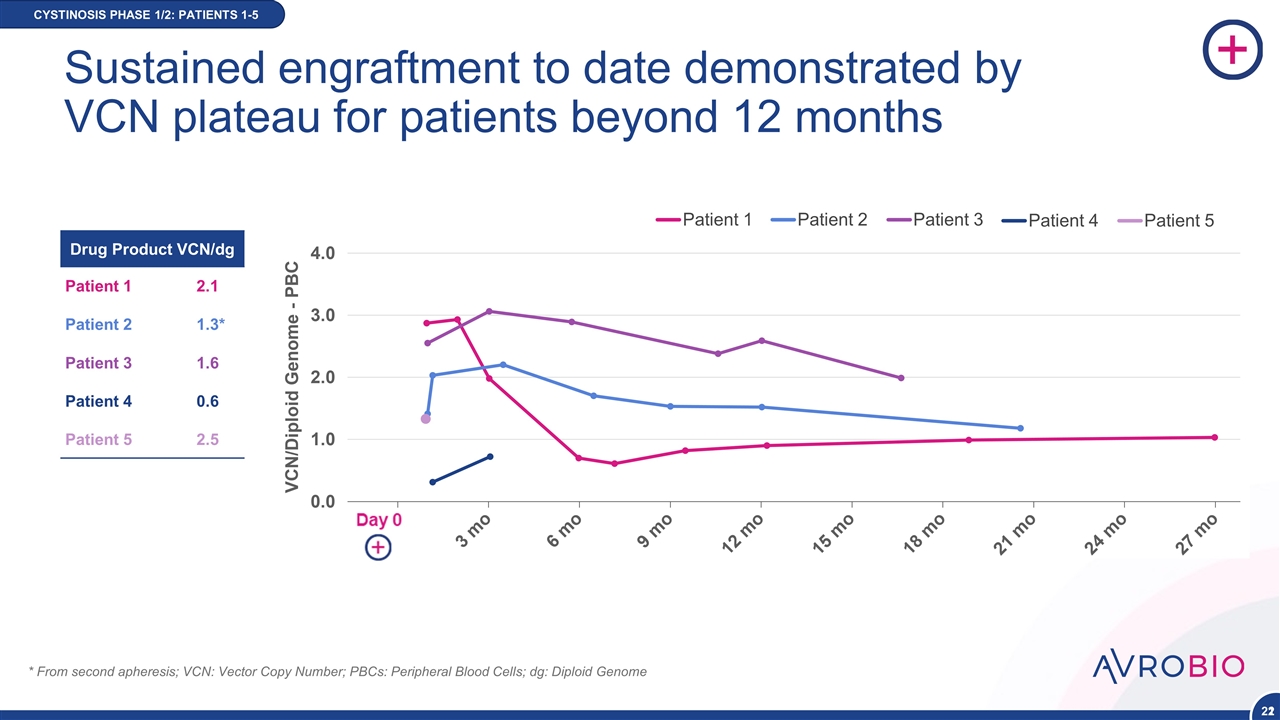
Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Patient 5 * From second apheresis; VCN: Vector Copy Number; PBCs: Peripheral Blood Cells; dg: Diploid Genome Drug Product VCN/dg Patient 1 2.1 Patient 2 1.3* Patient 3 1.6 Patient 4 0.6 Patient 5 2.5 CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENTS 1-5 22 Sustained engraftment to date demonstrated by VCN plateau for patients beyond 12 months
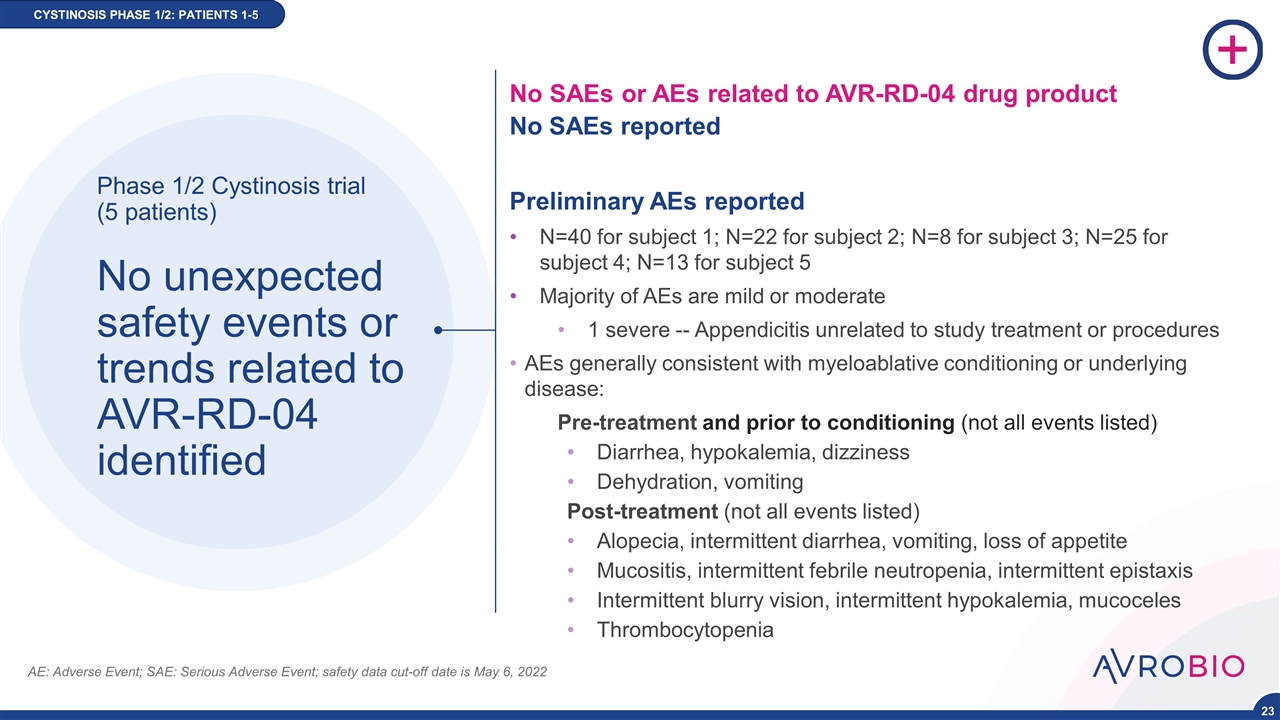
Phase 1/2 Cystinosis trial (5 patients) No unexpected safety events or trends related to AVR-RD-04 identified No SAEs or AEs related to AVR-RD-04 drug product No SAEs reported Preliminary AEs reported N=40 for subject 1; N=22 for subject 2; N=8 for subject 3; N=25 for subject 4; N=13 for subject 5 Majority of AEs are mild or moderate 1 severe -- Appendicitis unrelated to study treatment or procedures AEs generally consistent with myeloablative conditioning or underlying disease: Pre-treatment and prior to conditioning (not all events listed) Diarrhea, hypokalemia, dizziness Dehydration, vomiting Post-treatment (not all events listed) Alopecia, intermittent diarrhea, vomiting, loss of appetite Mucositis, intermittent febrile neutropenia, intermittent epistaxis Intermittent blurry vision, intermittent hypokalemia, mucoceles Thrombocytopenia AE: Adverse Event; SAE: Serious Adverse Event; safety data cut-off date is May 6, 2022 CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2 CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENTS 1-5
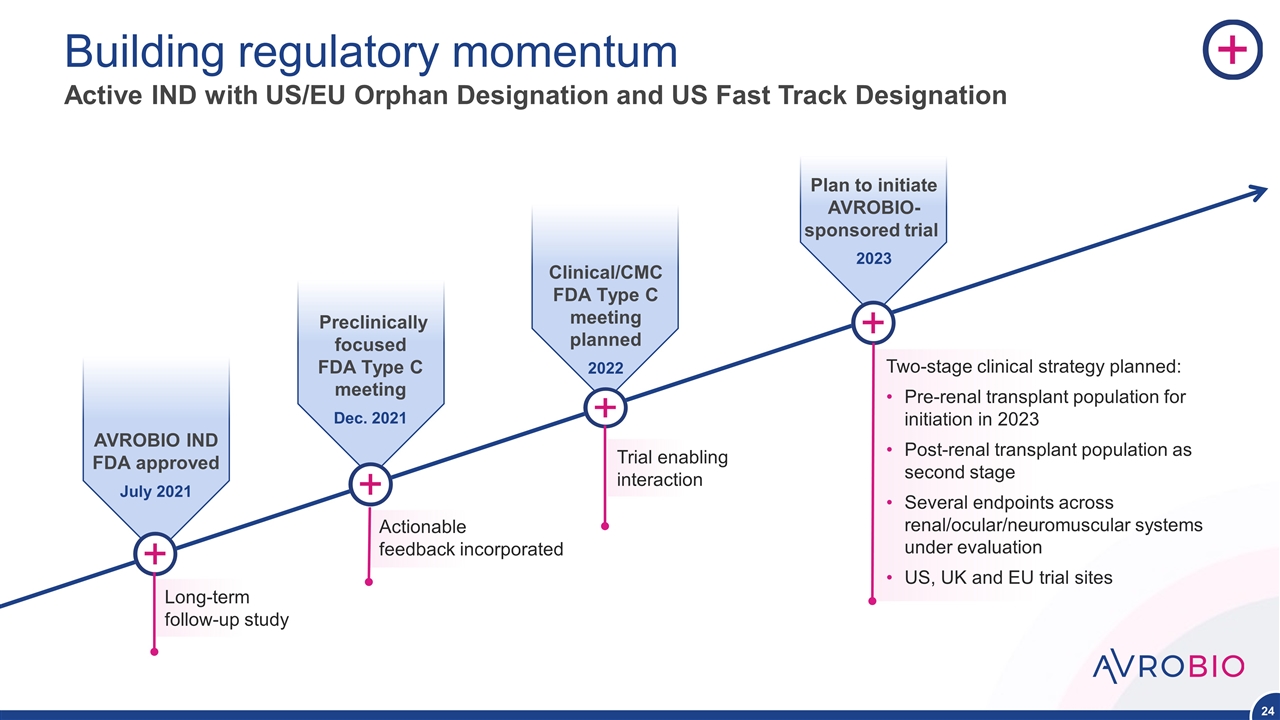
AVROBIO IND FDA approved July 2021 Building regulatory momentum Active IND with US/EU Orphan Designation and US Fast Track Designation Preclinically focused FDA Type C meeting Dec. 2021 Clinical/CMC FDA Type C meeting planned 2022 Plan to initiate AVROBIO-sponsored trial 2023 Two-stage clinical strategy planned: Pre-renal transplant population for initiation in 2023 Post-renal transplant population as second stage Several endpoints across renal/ocular/neuromuscular systems under evaluation US, UK and EU trial sites Trial enabling interaction Actionable feedback incorporated Long-term follow-up study

Gaucher disease franchise
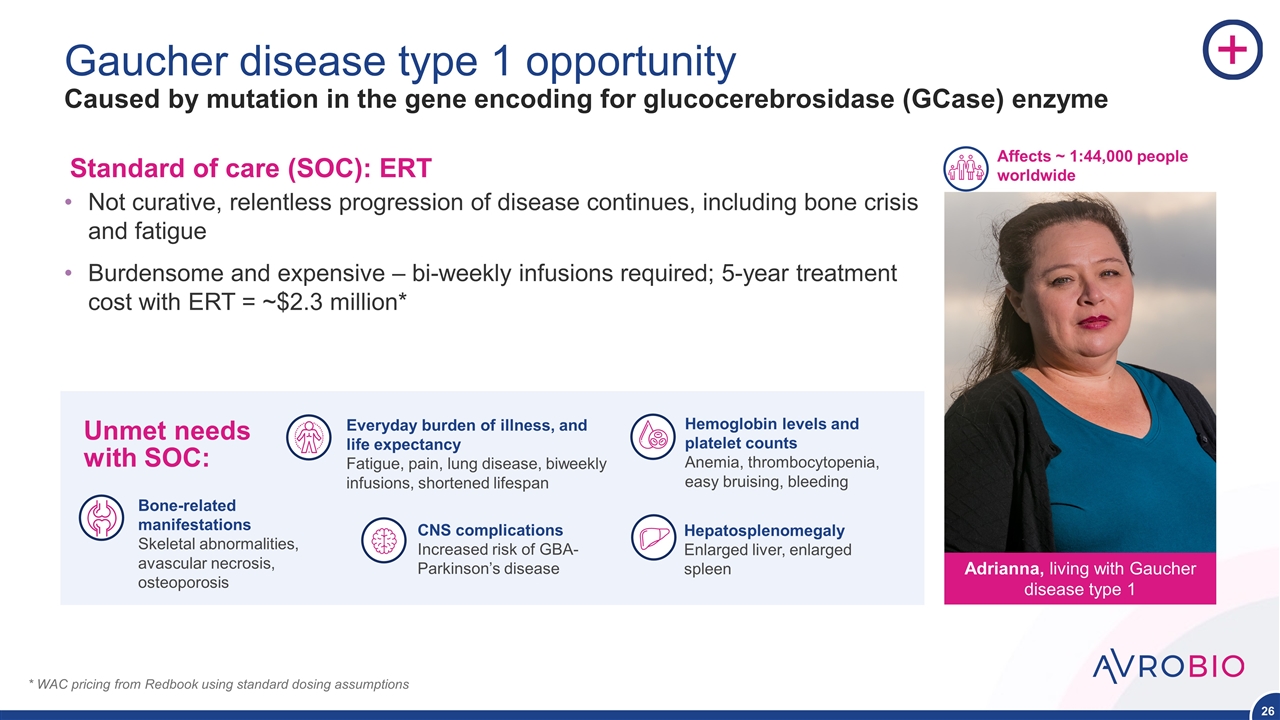
Gaucher disease type 1 opportunity Caused by mutation in the gene encoding for glucocerebrosidase (GCase) enzyme Not curative, relentless progression of disease continues, including bone crisis and fatigue Burdensome and expensive – bi-weekly infusions required; 5-year treatment cost with ERT = ~$2.3 million* * WAC pricing from Redbook using standard dosing assumptions Bone-related manifestations Skeletal abnormalities, avascular necrosis, osteoporosis Hemoglobin levels and platelet counts Anemia, thrombocytopenia, easy bruising, bleeding Hepatosplenomegaly Enlarged liver, enlarged spleen Everyday burden of illness, and life expectancy Fatigue, pain, lung disease, biweekly infusions, shortened lifespan CNS complications Increased risk of GBA-Parkinson’s disease Adrianna, living with Gaucher disease type 1 Affects ~ 1:44,000 people worldwide Standard of care (SOC): ERT Unmet needs with SOC:
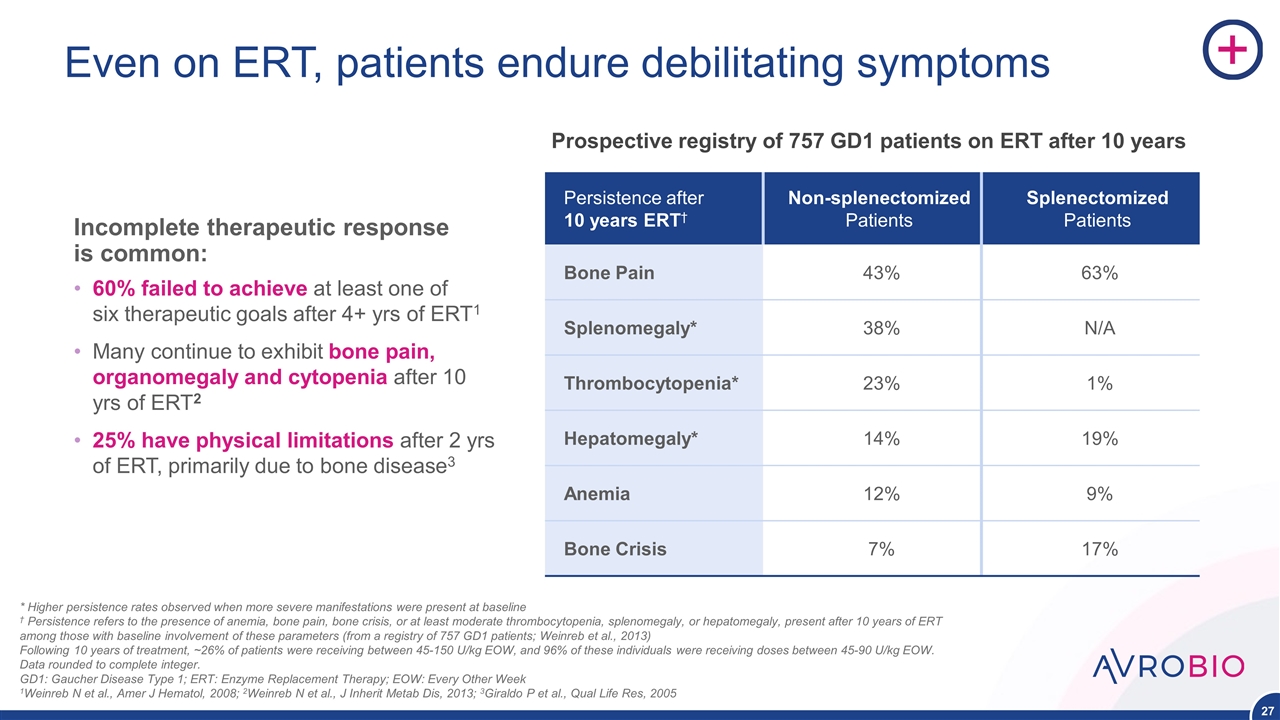
Even on ERT, patients endure debilitating symptoms Persistence after 10 years ERT† Non-splenectomized Patients Splenectomized Patients Bone Pain 43% 63% Splenomegaly* 38% N/A Thrombocytopenia* 23% 1% Hepatomegaly* 14% 19% Anemia 12% 9% Bone Crisis 7% 17% * Higher persistence rates observed when more severe manifestations were present at baseline † Persistence refers to the presence of anemia, bone pain, bone crisis, or at least moderate thrombocytopenia, splenomegaly, or hepatomegaly, present after 10 years of ERT among those with baseline involvement of these parameters (from a registry of 757 GD1 patients; Weinreb et al., 2013) Following 10 years of treatment, ~26% of patients were receiving between 45-150 U/kg EOW, and 96% of these individuals were receiving doses between 45-90 U/kg EOW. Data rounded to complete integer. GD1: Gaucher Disease Type 1; ERT: Enzyme Replacement Therapy; EOW: Every Other Week 1Weinreb N et al., Amer J Hematol, 2008; 2Weinreb N et al., J Inherit Metab Dis, 2013; 3Giraldo P et al., Qual Life Res, 2005 Prospective registry of 757 GD1 patients on ERT after 10 years Incomplete therapeutic response is common: 60% failed to achieve at least one of six therapeutic goals after 4+ yrs of ERT1 Many continue to exhibit bone pain, organomegaly and cytopenia after 10 yrs of ERT2 25% have physical limitations after 2 yrs of ERT, primarily due to bone disease3
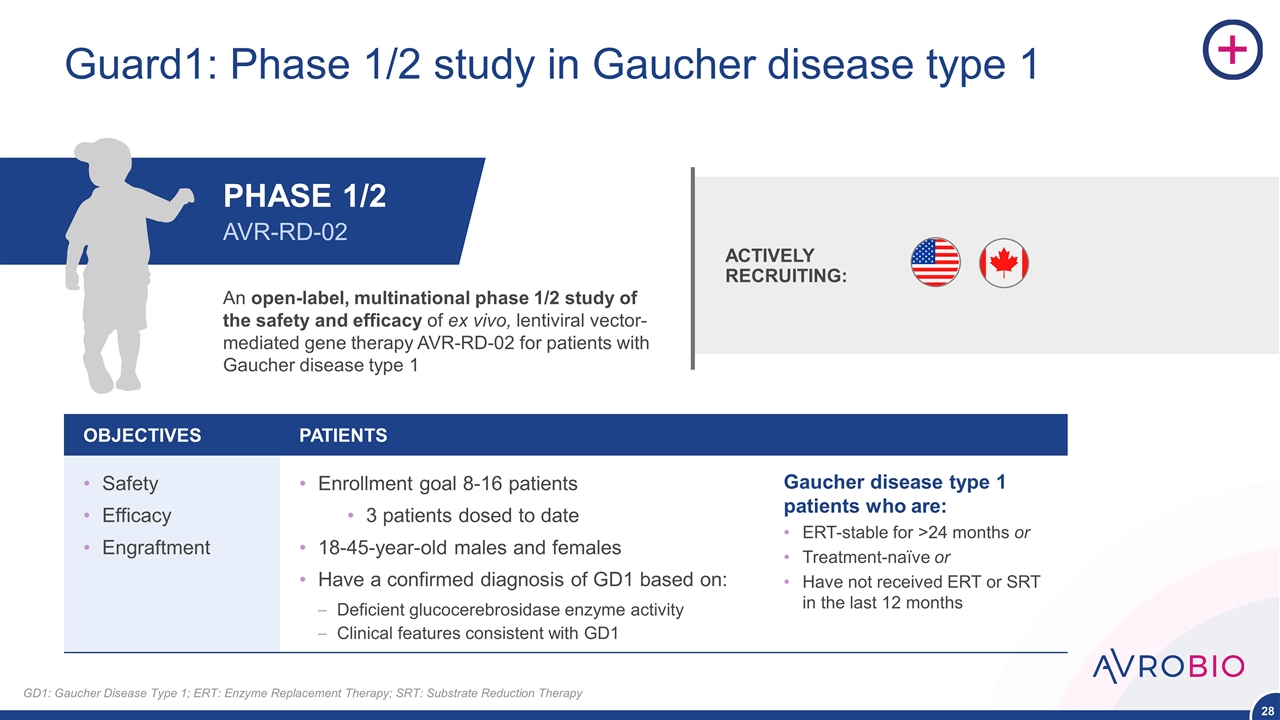
Guard1: Phase 1/2 study in Gaucher disease type 1 OBJECTIVES PATIENTS Safety Efficacy Engraftment Enrollment goal 8-16 patients 3 patients dosed to date 18-45-year-old males and females Have a confirmed diagnosis of GD1 based on: Deficient glucocerebrosidase enzyme activity Clinical features consistent with GD1 An open-label, multinational phase 1/2 study of the safety and efficacy of ex vivo, lentiviral vector-mediated gene therapy AVR-RD-02 for patients with Gaucher disease type 1 ACTIVELY RECRUITING: PHASE 1/2 AVR-RD-02 Gaucher disease type 1 patients who are: ERT-stable for >24 months or Treatment-naïve or Have not received ERT or SRT in the last 12 months GD1: Gaucher Disease Type 1; ERT: Enzyme Replacement Therapy; SRT: Substrate Reduction Therapy
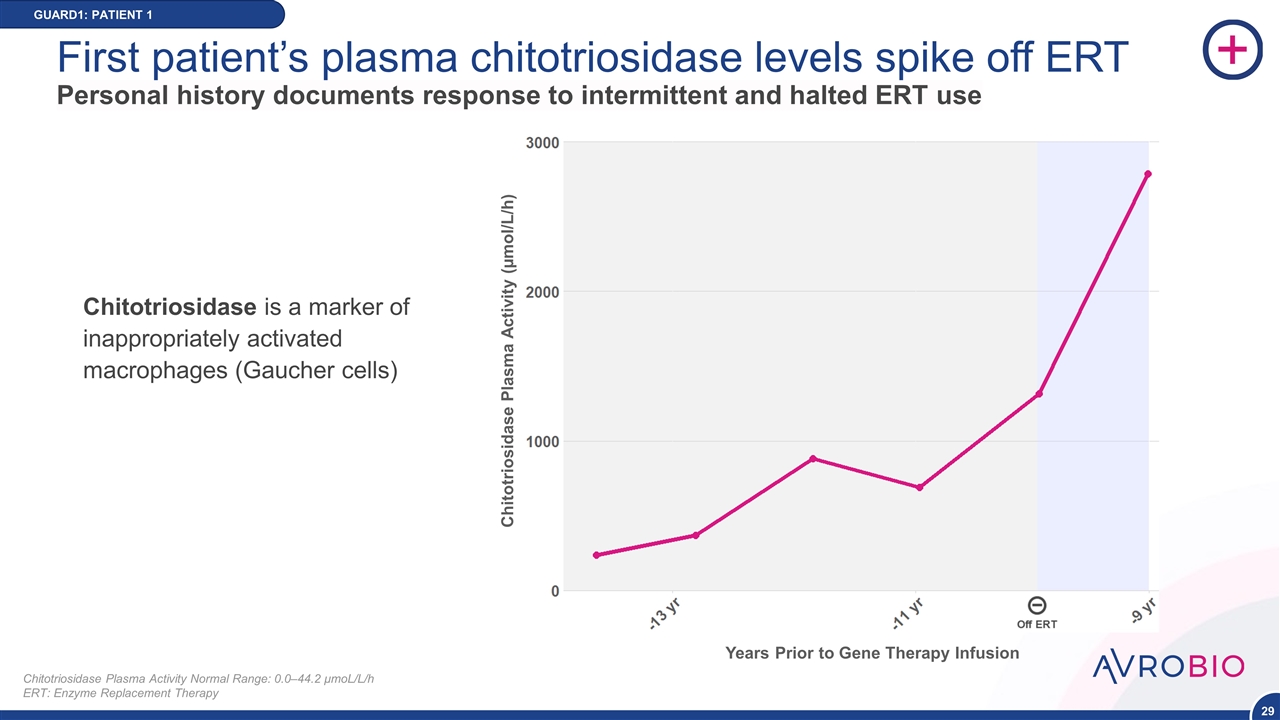
First patient’s plasma chitotriosidase levels spike off ERT Personal history documents response to intermittent and halted ERT use GUARD1: PATIENT 1 Chitotriosidase Plasma Activity Normal Range: 0.0–44.2 μmoL/L/h ERT: Enzyme Replacement Therapy Chitotriosidase is a marker of inappropriately activated macrophages (Gaucher cells) Chitotriosidase Plasma Activity (µmol/L/h) Years Prior to Gene Therapy Infusion
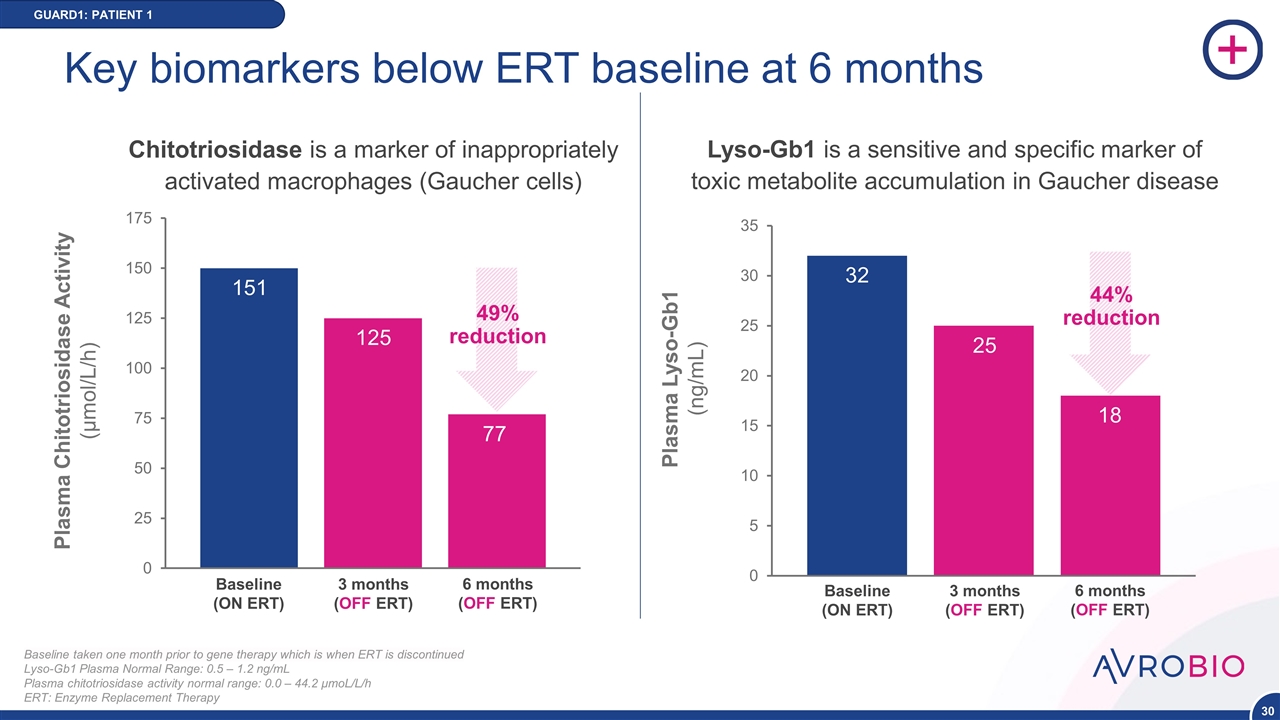
Plasma Chitotriosidase Activity (μmol/L/h) Baseline (ON ERT) 3 months (OFF ERT) 6 months (OFF ERT) 151 125 GUARD1: PATIENT 1 Baseline taken one month prior to gene therapy which is when ERT is discontinued Lyso-Gb1 Plasma Normal Range: 0.5 – 1.2 ng/mL Plasma chitotriosidase activity normal range: 0.0 – 44.2 μmoL/L/h ERT: Enzyme Replacement Therapy Key biomarkers below ERT baseline at 6 months 77 Chitotriosidase is a marker of inappropriately activated macrophages (Gaucher cells) 49% reduction NEW DATA 18 25 32 Plasma Lyso-Gb1 (ng/mL) Baseline (ON ERT) 3 months (OFF ERT) 6 months (OFF ERT) 44% reduction Lyso-Gb1 is a sensitive and specific marker of toxic metabolite accumulation in Gaucher disease
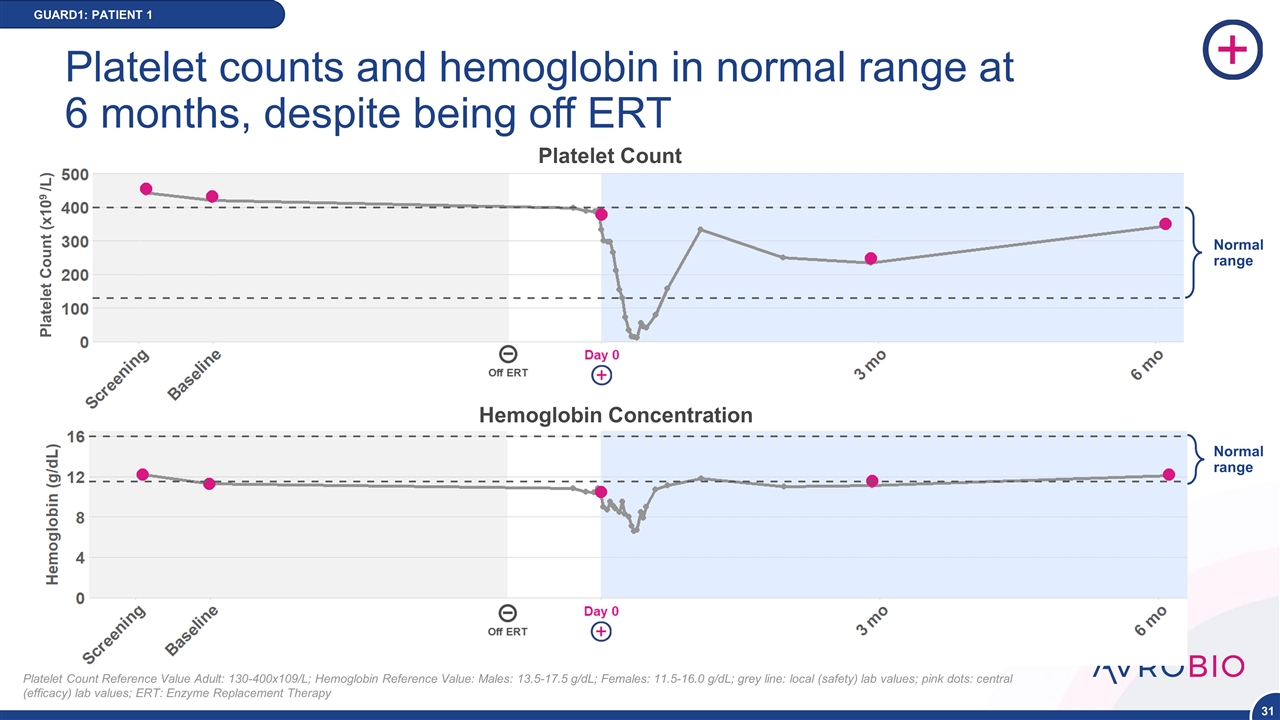
Platelet counts and hemoglobin in normal range at 6 months, despite being off ERT GUARD1: PATIENT 1 Platelet Count Reference Value Adult: 130-400x109/L; Hemoglobin Reference Value: Males: 13.5-17.5 g/dL; Females: 11.5-16.0 g/dL; grey line: local (safety) lab values; pink dots: central (efficacy) lab values; ERT: Enzyme Replacement Therapy Platelet Count (x109 /L) Platelet Count Normal range Hemoglobin Concentration Normal range
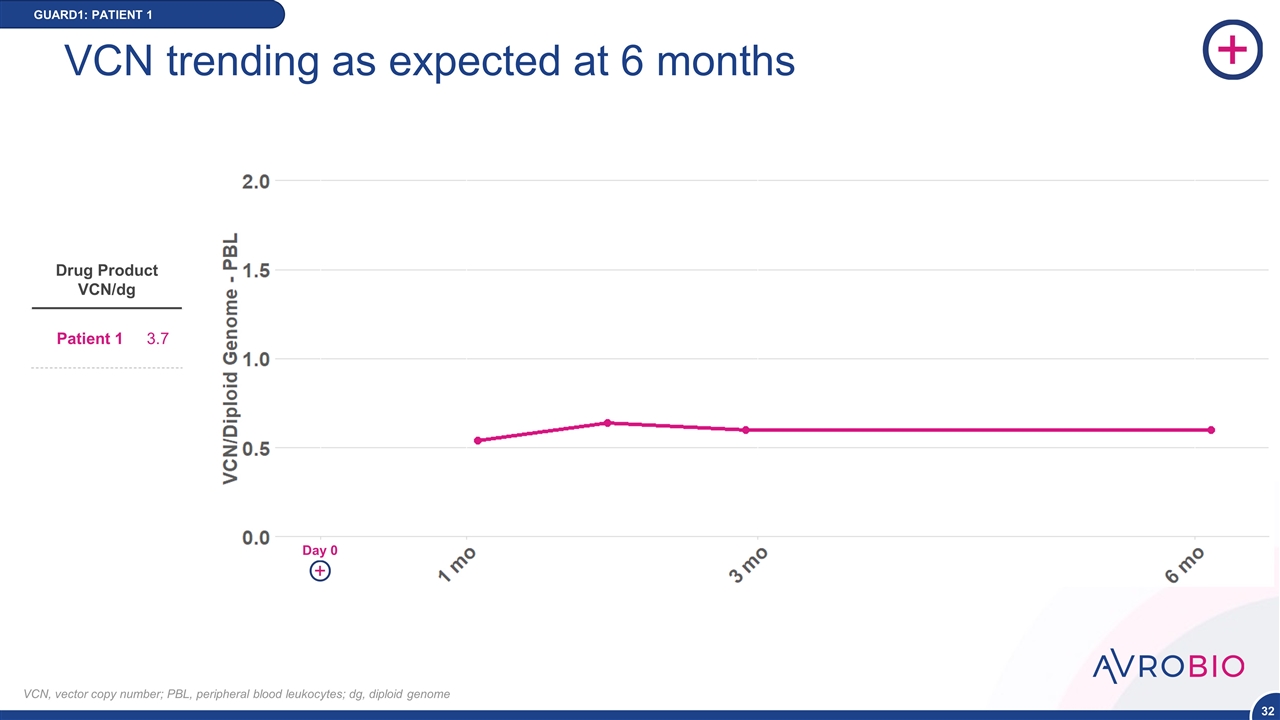
GUARD1: PATIENT 1 VCN trending as expected at 6 months VCN, vector copy number; PBL, peripheral blood leukocytes; dg, diploid genome Drug Product VCN/dg Patient 1 3.7 Day 0

No unexpected safety events 12+ months post dosing AVR-RD-02 has not been approved by the FDA or by any other regulatory body and its safety and efficacy has not been established Note: Safety database cut as of August 31, 2021 AE, adverse event; SAE, serious adverse event; G-CSF, granulocyte colony stimulating factor * Unresolved and ongoing as of the safety database cut of August 31, 2021 **Two of the AEs, dehydration and decreased appetite, are noted as related to both G-CSF and busulfan administrations AEs are consistent with myeloablative conditioning, drugs mandated by protocol or study procedures, underlying disease and pre-existing conditions No SAEs reported No SAEs or AEs related to drug product AEs reported, n= 37 GUARD1: PATIENT 1 Event severity assessment 26 AEs were Grade 1 or Grade 2 11 AEs were Grade 3 or 4 Anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, eye pain, decreased appetite, dehydration, headache, hypophosphatemia, amenorrhea* Event causality assessment 21 AEs definitely, probably or possibly related to busulfan (N= 1 patient dosed) 8 AEs definitely, probably or possibly related to G-CSF** (N= 2 patients enrolled) 1 AE definitely, probably or possibly related to Plerixafor (N= 2 patients enrolled)
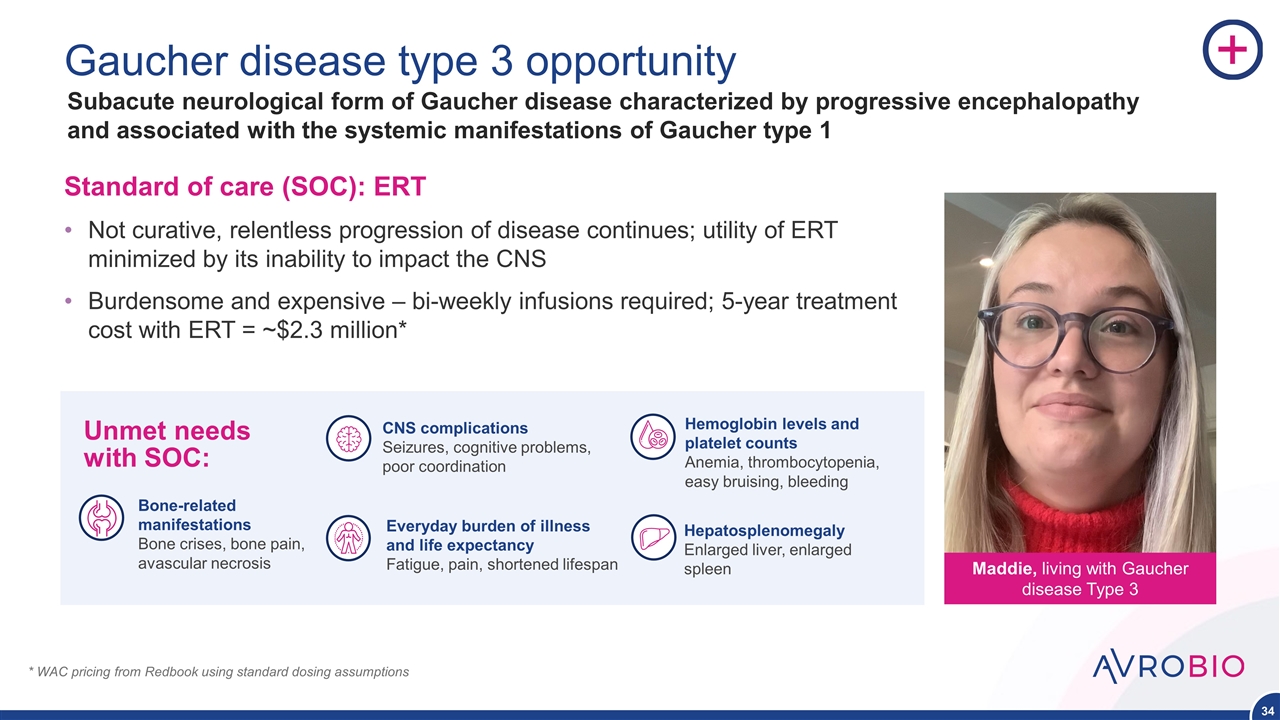
Gaucher disease type 3 opportunity Standard of care (SOC): ERT Not curative, relentless progression of disease continues; utility of ERT minimized by its inability to impact the CNS Burdensome and expensive – bi-weekly infusions required; 5-year treatment cost with ERT = ~$2.3 million* * WAC pricing from Redbook using standard dosing assumptions Subacute neurological form of Gaucher disease characterized by progressive encephalopathy and associated with the systemic manifestations of Gaucher type 1 Maddie, living with Gaucher disease Type 3 Bone-related manifestations Bone crises, bone pain, avascular necrosis Hemoglobin levels and platelet counts Anemia, thrombocytopenia, easy bruising, bleeding Hepatosplenomegaly Enlarged liver, enlarged spleen Everyday burden of illness and life expectancy Fatigue, pain, shortened lifespan CNS complications Seizures, cognitive problems, poor coordination Unmet needs with SOC:

Second wave programs

Advancing Pompe and Hunter programs to the clinic Regulatory meetings planned for 2H 2022 Figure adapted from Gleitz H et al., EMBO Mol Med, 2018 Fig 3A; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001; LV GT: Lentiviral Gene Therapy LV GT w/ Tag LV GT Pompe Mouse Normal Mouse Neurological complications Unmet needs with SOC: Skeletal and connective tissue Respiratory and cardiac system Burden of illness and life expectancy Pulmonary function Physical endurance and strength CNS complications GI complications Unmet needs with SOC: GT + Tag normalizes heparan sulfate in brain * * * * * * * * * * * * 0 5 10 Normal Mouse Hunter Mouse LV GT LV GT w/ Tag Fold Total Heparan Sulfate over Normal Mouse Hunter syndrome GT + Tag normalizes glycogen substrate in brain Pompe disease * * * * PRE-CLINICAL DATA
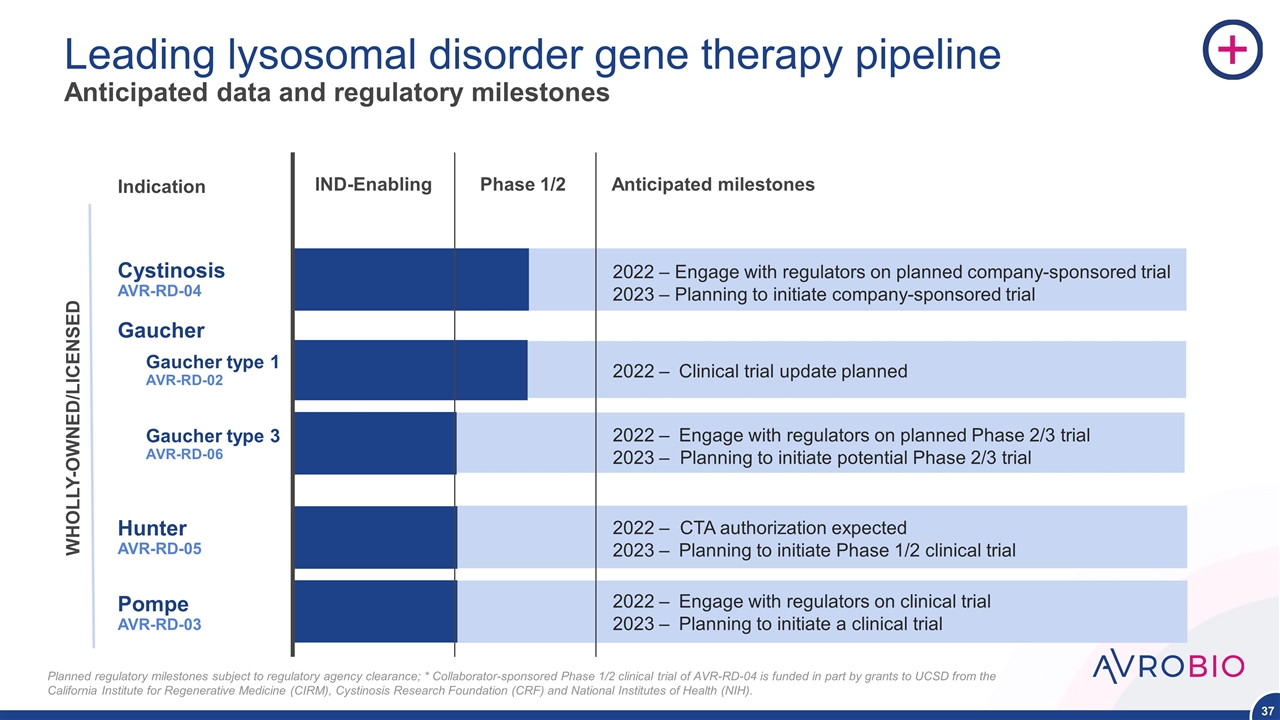
Leading lysosomal disorder gene therapy pipeline Anticipated data and regulatory milestones Gaucher type 1 AVR-RD-02 Cystinosis AVR-RD-04 Hunter AVR-RD-05 Gaucher type 3 AVR-RD-06 Pompe AVR-RD-03 IND-Enabling Phase 1/2 Anticipated milestones 2022 – Clinical trial update planned – Engage with regulators on planned company-sponsored trial 2023 – Planning to initiate company-sponsored trial 2022 – CTA authorization expected 2023 – Planning to initiate Phase 1/2 clinical trial 2022 – Engage with regulators on planned Phase 2/3 trial 2023 – Planning to initiate potential Phase 2/3 trial 2022 – Engage with regulators on clinical trial 2023 – Planning to initiate a clinical trial Indication WHOLLY-OWNED/LICENSED Planned regulatory milestones subject to regulatory agency clearance; * Collaborator-sponsored Phase 1/2 clinical trial of AVR-RD-04 is funded in part by grants to UCSD from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), Cystinosis Research Foundation (CRF) and National Institutes of Health (NIH). Gaucher

Thank you

Appendix
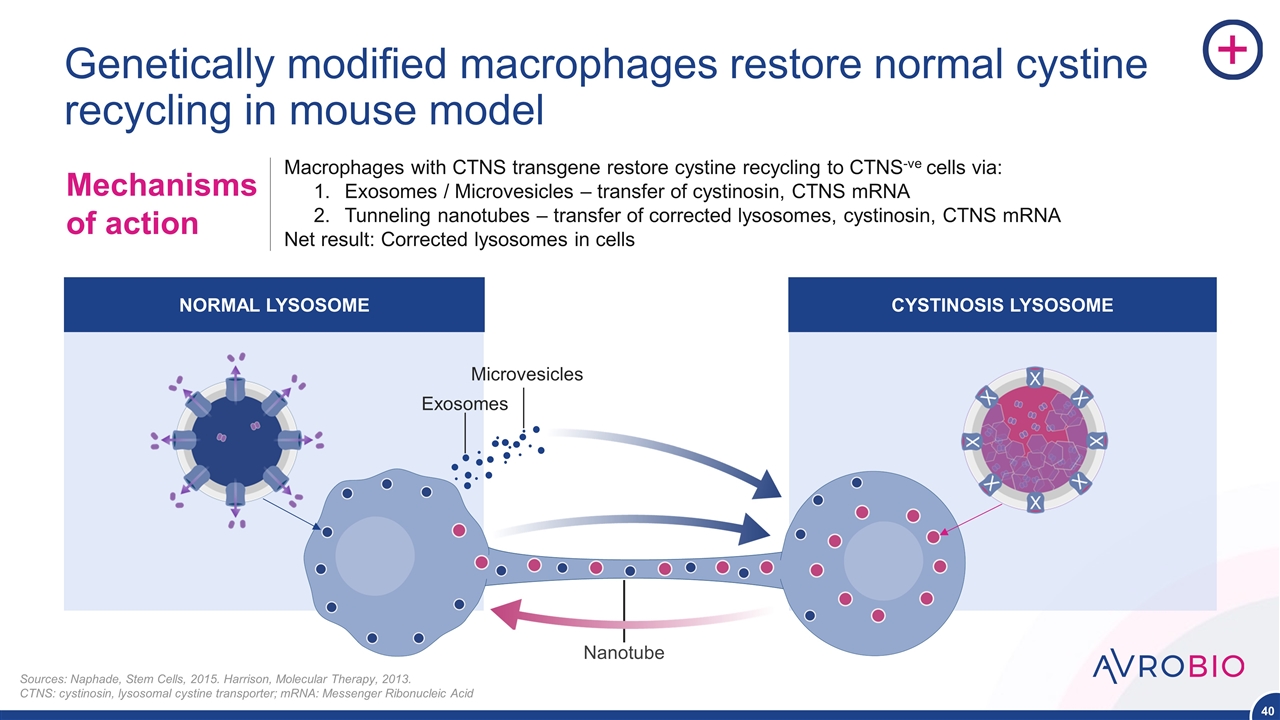
Macrophages with CTNS transgene restore cystine recycling to CTNS-ve cells via: Exosomes / Microvesicles – transfer of cystinosin, CTNS mRNA Tunneling nanotubes – transfer of corrected lysosomes, cystinosin, CTNS mRNA Net result: Corrected lysosomes in cells Mechanisms of action Genetically modified macrophages restore normal cystine recycling in mouse model NORMAL LYSOSOME CYSTINOSIS LYSOSOME Nanotube Sources: Naphade, Stem Cells, 2015. Harrison, Molecular Therapy, 2013. CTNS: cystinosin, lysosomal cystine transporter; mRNA: Messenger Ribonucleic Acid Exosomes Microvesicles

Cystinosis is an attractive commercial market * SOC: standard of care; WAC pricing from Redbook using standard dosing assumptions. Horizon’s Procysbi oral therapy (delayed release cysteamine bitartrate), midpoint between avg. adult and pediatric 5-year cystinosis SOC treatment cost ~$4.3 million* in U.S. ~1,600 patients in U.S., Europe and Japan alone Most severe form, infantile nephropathic cystinosis, affects ~95% of cystinosis population Billion-dollar revenue opportunity SOC does not stop disease progression Vision Corneal cystine accumulation, photophobia Endocrine disorders Softening & deformation of bones, hypothyroidism, diabetes, infertility CNS and muscular complications Myopathy, hypotonia, neurodevelopmental issues Kidney function Frequently require multiple kidney transplants Shortcomings of cysteamine pills often lead to poor patient compliance: Cause sulfur odor on body and breath High daily pill burden can lead to GI discomfort and vomiting SOC is burdensome Disease symptoms persist despite SOC:
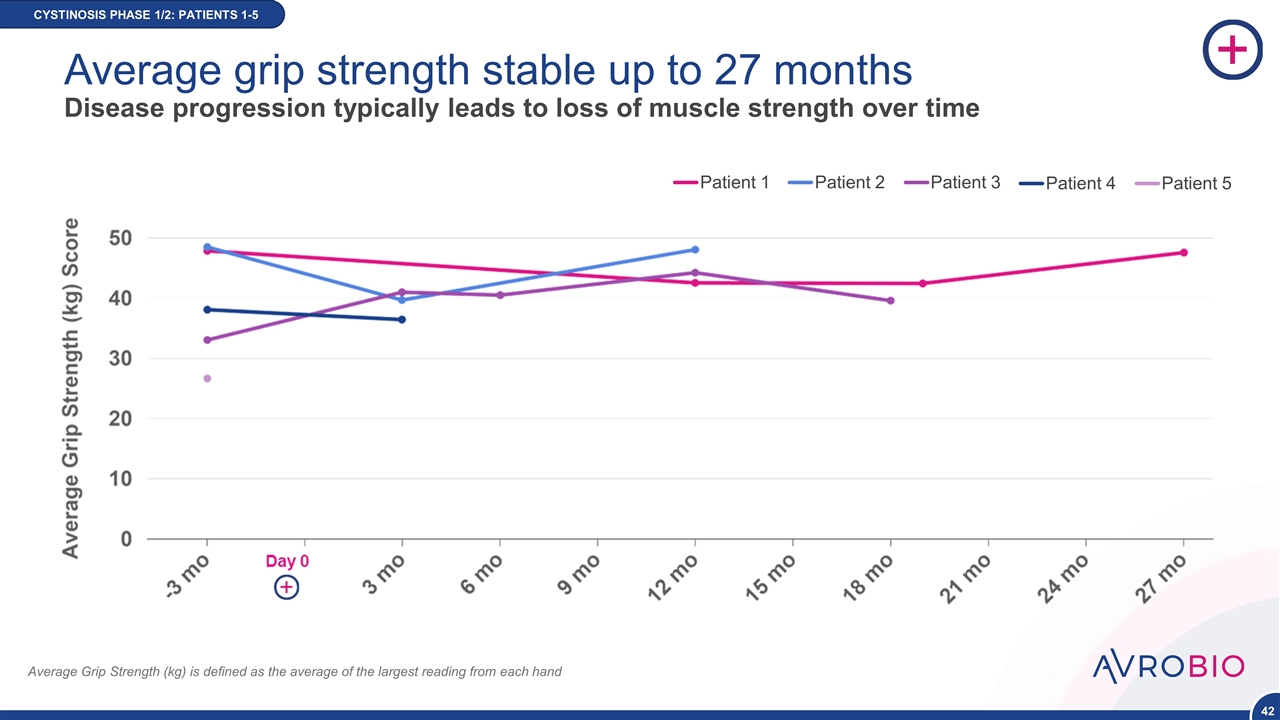
Average Grip Strength (kg) is defined as the average of the largest reading from each hand Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Patient 5 CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENTS 1-5 Average grip strength stable up to 27 months Disease progression typically leads to loss of muscle strength over time NEW DATA
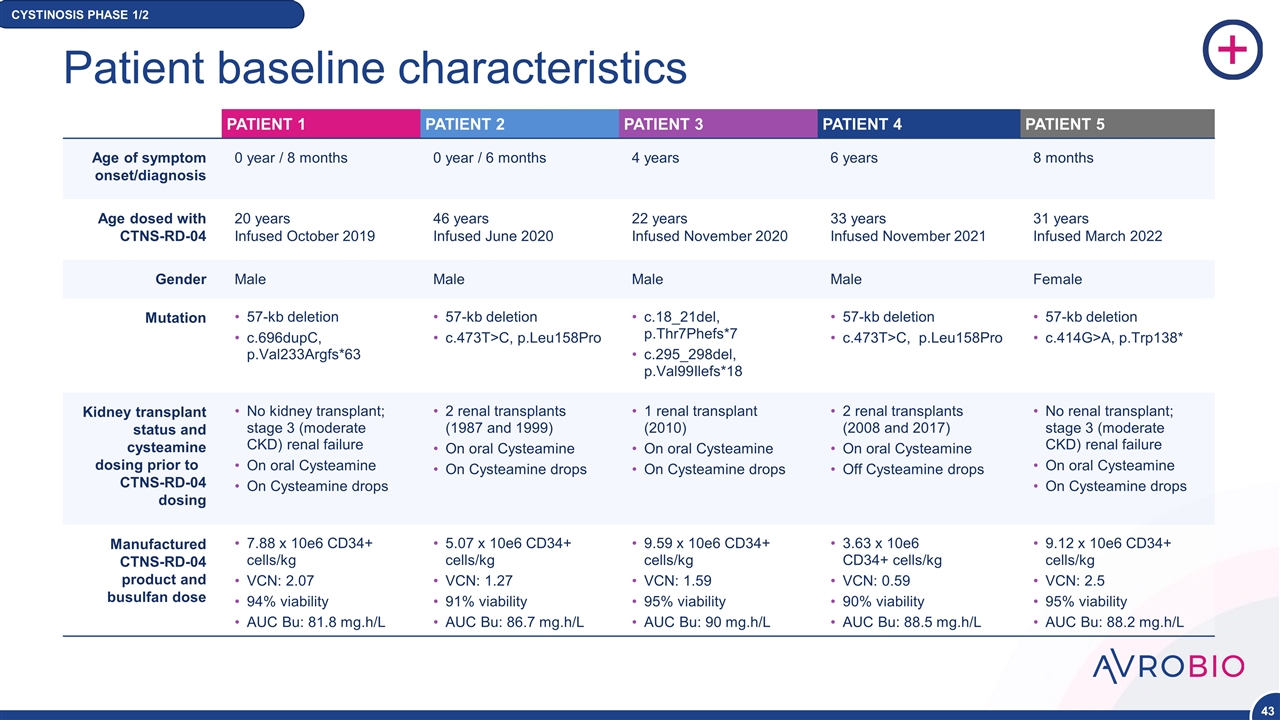
PATIENT 1 PATIENT 2 PATIENT 3 PATIENT 4 PATIENT 5 Patient baseline characteristics Age of symptom onset/diagnosis 0 year / 8 months 0 year / 6 months 4 years 6 years 8 months Age dosed with CTNS-RD-04 20 years Infused October 2019 46 years Infused June 2020 22 years Infused November 2020 33 years Infused November 2021 31 years Infused March 2022 Gender Male Male Male Male Female Mutation 57-kb deletion c.696dupC, p.Val233Argfs*63 57-kb deletion c.473T>C, p.Leu158Pro c.18_21del, p.Thr7Phefs*7 c.295_298del, p.Val99Ilefs*18 57-kb deletion c.473T>C, p.Leu158Pro 57-kb deletion c.414G>A, p.Trp138* Kidney transplant status and cysteamine dosing prior to CTNS-RD-04 dosing No kidney transplant; stage 3 (moderate CKD) renal failure On oral Cysteamine On Cysteamine drops 2 renal transplants (1987 and 1999) On oral Cysteamine On Cysteamine drops 1 renal transplant (2010) On oral Cysteamine On Cysteamine drops 2 renal transplants (2008 and 2017) On oral Cysteamine Off Cysteamine drops No renal transplant; stage 3 (moderate CKD) renal failure On oral Cysteamine On Cysteamine drops Manufactured CTNS-RD-04 product and busulfan dose 7.88 x 10e6 CD34+ cells/kg VCN: 2.07 94% viability AUC Bu: 81.8 mg.h/L 5.07 x 10e6 CD34+ cells/kg VCN: 1.27 91% viability AUC Bu: 86.7 mg.h/L 9.59 x 10e6 CD34+ cells/kg VCN: 1.59 95% viability AUC Bu: 90 mg.h/L 3.63 x 10e6 CD34+ cells/kg VCN: 0.59 90% viability AUC Bu: 88.5 mg.h/L 9.12 x 10e6 CD34+ cells/kg VCN: 2.5 95% viability AUC Bu: 88.2 mg.h/L CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2
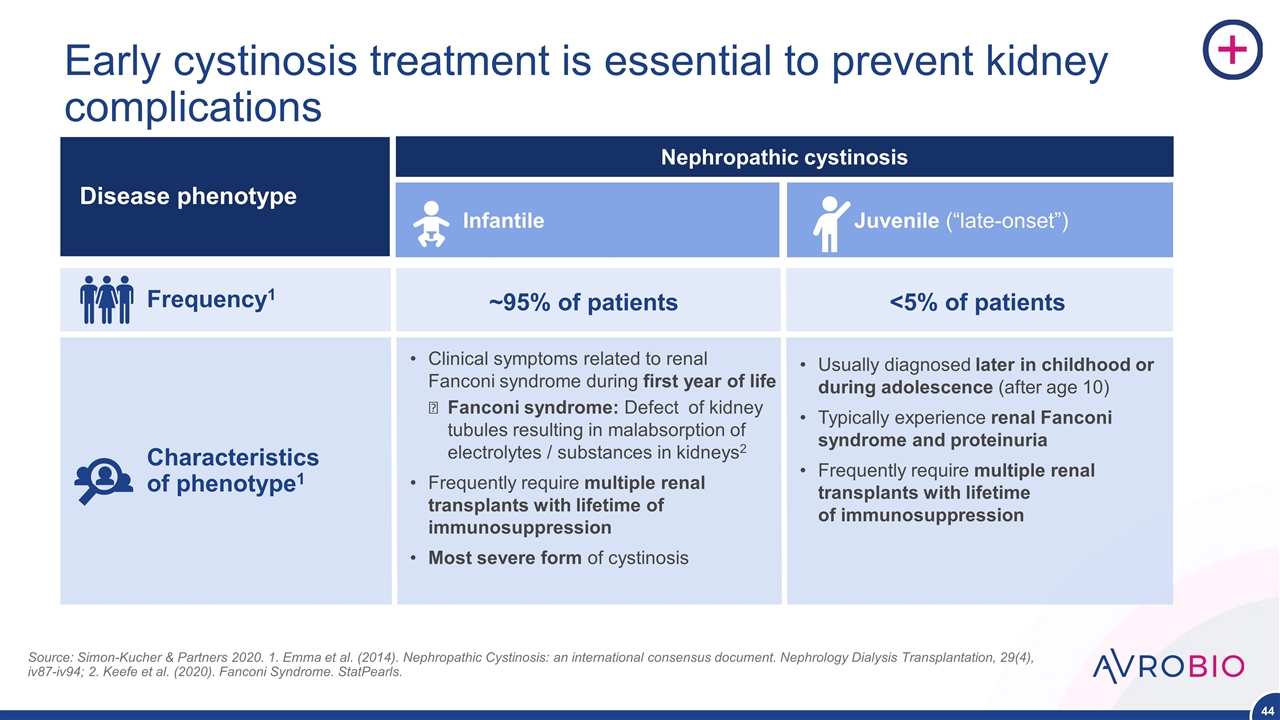
Early cystinosis treatment is essential to prevent kidney complications Frequency1 Characteristics of phenotype1 Disease phenotype Nephropathic cystinosis ~95% of patients Clinical symptoms related to renal Fanconi syndrome during first year of life Fanconi syndrome: Defect of kidney tubules resulting in malabsorption of electrolytes / substances in kidneys2 Frequently require multiple renal transplants with lifetime of immunosuppression Most severe form of cystinosis Infantile Juvenile (“late-onset”) <5% of patients Usually diagnosed later in childhood or during adolescence (after age 10) Typically experience renal Fanconi syndrome and proteinuria Frequently require multiple renal transplants with lifetime of immunosuppression Source: Simon-Kucher & Partners 2020. 1. Emma et al. (2014). Nephropathic Cystinosis: an international consensus document. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 29(4), iv87-iv94; 2. Keefe et al. (2020). Fanconi Syndrome. StatPearls.
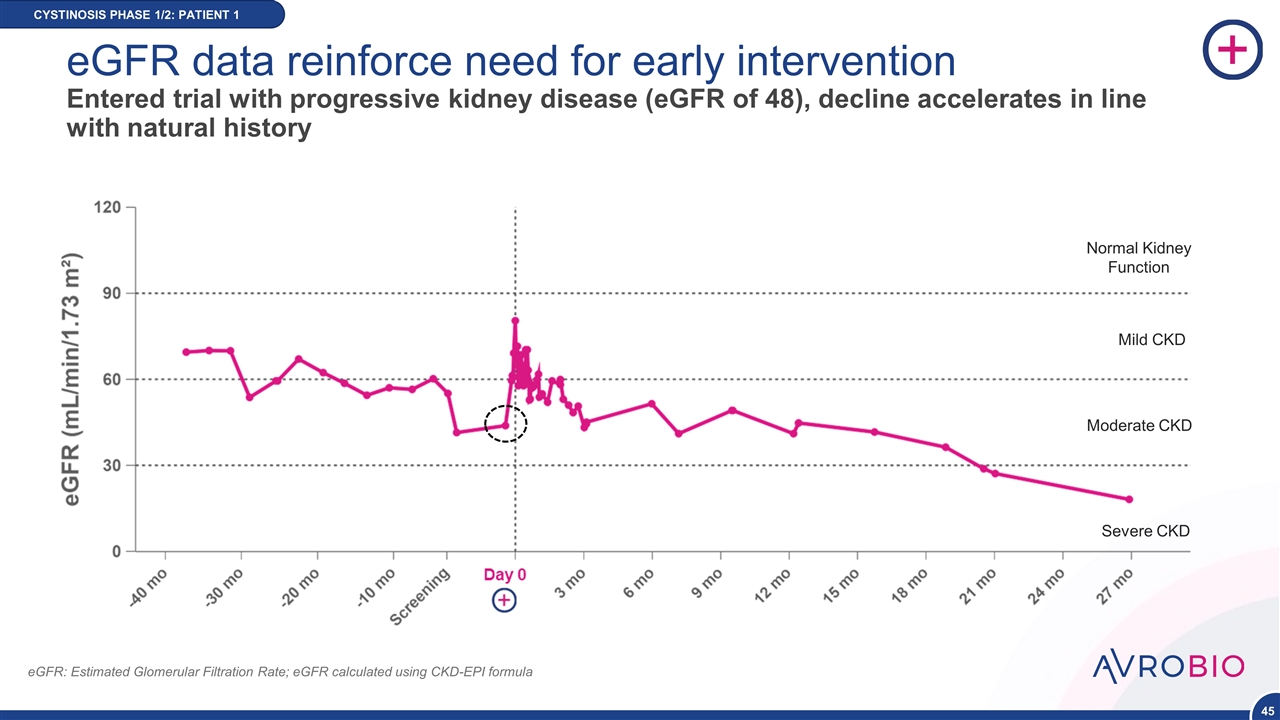
eGFR data reinforce need for early intervention Entered trial with progressive kidney disease (eGFR of 48), decline accelerates in line with natural history CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENT 1 eGFR: Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate; eGFR calculated using CKD-EPI formula Normal Kidney Function Mild CKD Moderate CKD Severe CKD
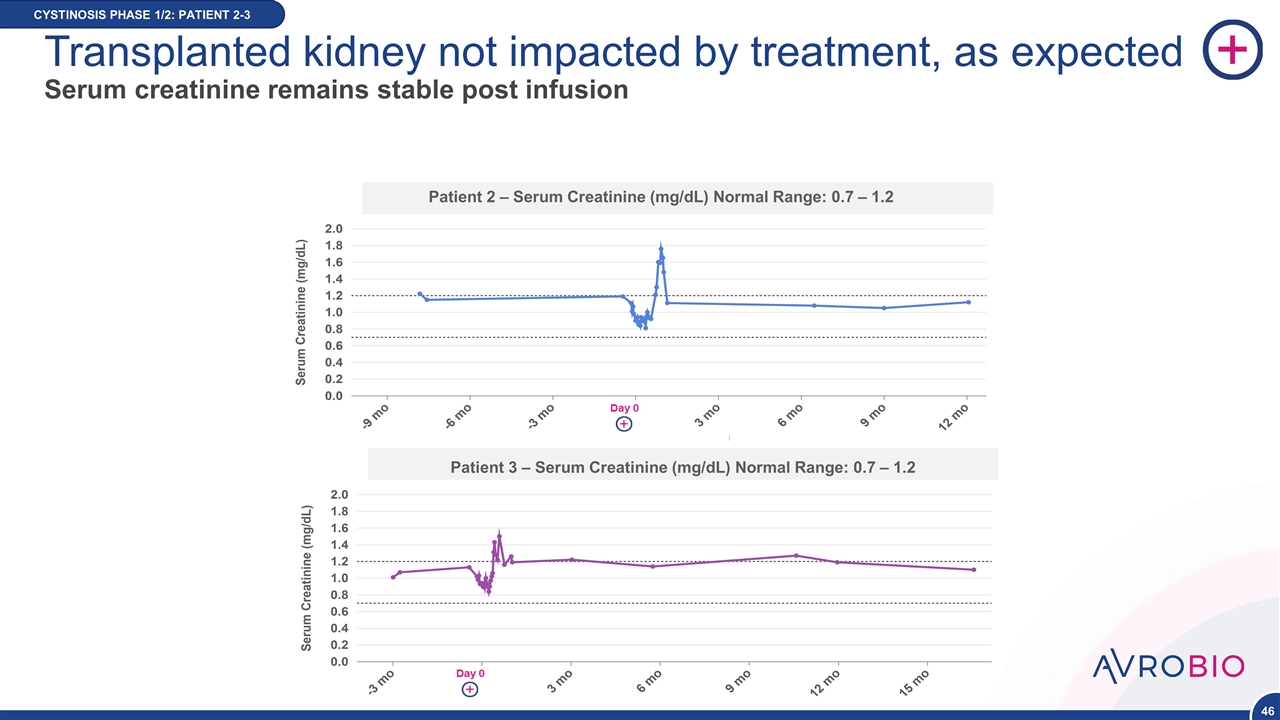
12 Month CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENT 2-3 Transplanted kidney not impacted by treatment, as expected Serum creatinine remains stable post infusion NEW DATA POINT NEW DATA Patient 2 – Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) Normal Range: 0.7 – 1.2 Patient 3 – Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) Normal Range: 0.7 – 1.2
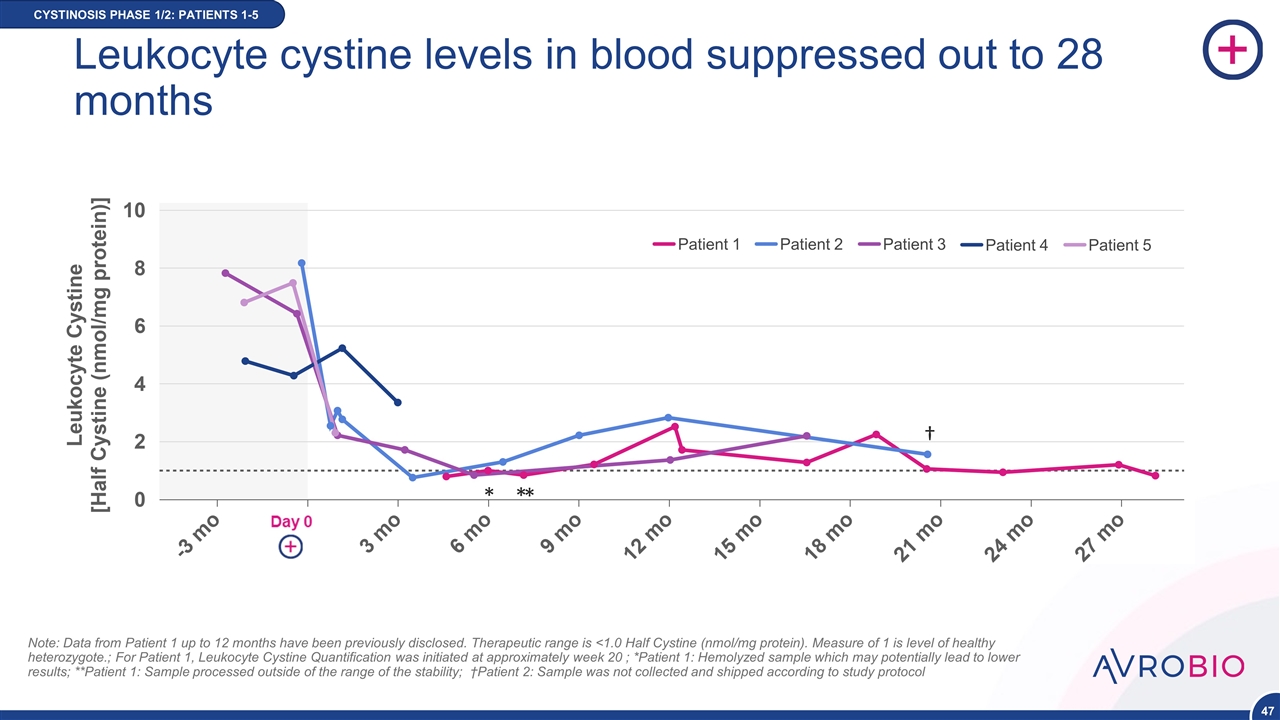
Note: Data from Patient 1 up to 12 months have been previously disclosed. Therapeutic range is <1.0 Half Cystine (nmol/mg protein). Measure of 1 is level of healthy heterozygote.; For Patient 1, Leukocyte Cystine Quantification was initiated at approximately week 20 ; *Patient 1: Hemolyzed sample which may potentially lead to lower results; **Patient 1: Sample processed outside of the range of the stability; †Patient 2: Sample was not collected and shipped according to study protocol CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENTS 1-5 NEW DATA Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Patient 5 † * * * Leukocyte cystine levels in blood suppressed out to 28 months
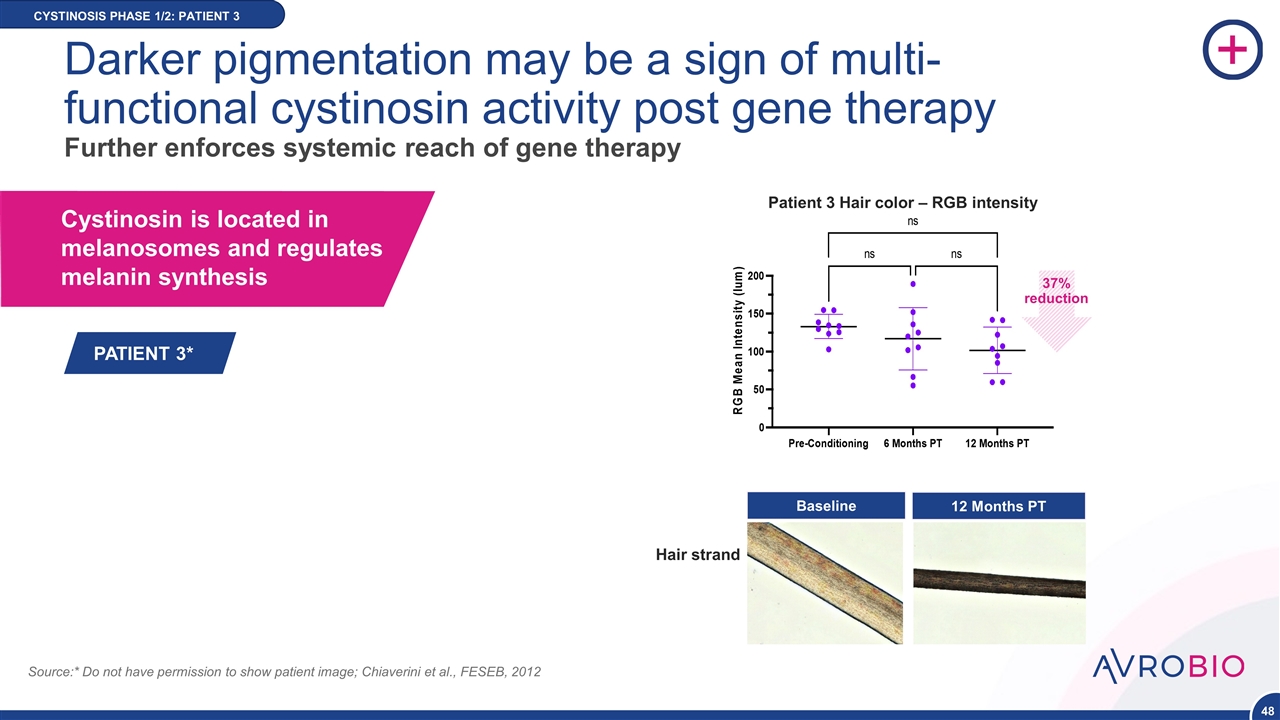
CYSTINOSIS PHASE 1/2: PATIENT 3 Cystinosin is located in melanosomes and regulates melanin synthesis Source:* Do not have permission to show patient image; Chiaverini et al., FESEB, 2012 12 Months PT Baseline Patient 3 Hair color – RGB intensity NE DATA Darker pigmentation may be a sign of multi-functional cystinosin activity post gene therapy Further enforces systemic reach of gene therapy Hair strand PATIENT 3* 37% reduction
Serious News for Serious Traders! Try StreetInsider.com Premium Free!
You May Also Be Interested In
- Jesper and Jesse Will Work Together Again at rabbit!
- TANDEM ALERT: Bragar Eagel & Squire, P.C. is Investigating Tandem Diabetes Care, Inc. on Behalf of Long-Term Stockholders and Encourages Investors to Contact the Firm
- Final Week of Containing Luxury's StartEngine Crowdfunding Campaign
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share