Form 497K LORD ABBETT SERIES FUND

SUMMARY PROSPECTUS
Lord
Abbett Series Fund
Short Duration Income Portfolio
May 1, 2022
CLASS/TICKER | |||
CLASS VC | NO TICKER | ||
Before you invest, you may want to review the Fund’s prospectus and statement of additional information, which contain more information about the Fund and its risks. You can find the Fund’s prospectus, statement of additional information and other information about the Fund at www.lordabbett.com/seriesfunds. You can also get this information at no cost by calling 888-522-2388 (Option #2) or by sending an email request to [email protected]. The current prospectus and statement of additional information dated May 1, 2022, as may be supplemented from time to time, are incorporated by reference into this summary prospectus.
INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE
The Fund’s investment objective is to seek a high level of income consistent with preservation of capital.
FEES AND EXPENSES
This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy, hold, and sell shares of the Fund. You may pay other fees, such as brokerage commissions and other fees to financial intermediaries, which are not reflected in the table and examples below. The table does not reflect the fees and expenses of variable annuity contracts or variable life insurance policies (together, “Variable Contracts”). If such fees and expenses were reflected, expenses shown would be higher.
Annual Fund Operating Expenses | ||
(Expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the value of your investment) | ||
Class | VC Shares | |
Management Fees | 0.35% | |
Other Expenses | 0.48% | |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses | 0.83% | |
Example
This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and that the Fund’s operating expenses remain the same. The Example does not reflect Variable Contract expenses, fees, and charges. If these expenses, fees, and charges were included, your costs would be higher. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be:
Class | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| ||||
VC Shares | $ | 85 | $ | 265 | $ | 460 | $ | 1,025 |
|
Portfolio Turnover. The Fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells securities (or “turns over” its portfolio). A higher portfolio turnover rate may indicate higher transaction costs. These costs, which are not reflected in the annual fund operating expenses or in the example, affect the Fund’s performance. During the most recent fiscal year, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate was 66% of the average value of its portfolio.
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
2
PRINCIPAL INVESTMENT STRATEGIES
The Fund invests in various types of short duration debt (or fixed income) securities. Under normal conditions, the Fund pursues its investment objective by investing at least 65% of its net assets in investment grade debt securities of various types. Such investments include:
· corporate debt securities of U.S. issuers;
· corporate debt securities of non-U.S. (including emerging market) issuers that are denominated in U.S. dollars;
· mortgage-backed, mortgage-related, and other asset-backed securities, including privately issued mortgage-related securities and commercial mortgage-backed securities (“CMBS”);
· securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies and instrumentalities; and
· inflation-linked investments.
The Fund may invest in Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (“TIPS”), which are U.S. Government bonds whose principal automatically is adjusted for inflation as measured by the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (“CPI-U”), and other inflation-indexed securities issued by the U.S. Department of Treasury.
The Fund may invest up to 35% of its net assets in any one or a combination of the following types of fixed income securities and other instruments:
· high-yield debt securities (commonly referred to as “lower-rated” or “junk” bonds);
· debt securities of non-U.S. (including emerging market) issuers that are denominated in foreign currencies;
· loans, including bridge loans, novations, assignments, and participations;
· convertible securities, including convertible bonds and preferred stocks; and
· structured securities and other hybrid instruments, including collateralized loan obligations (“CLOs”).
The Fund will not invest more than 25% of its total assets in any industry; however, this limitation does not apply to mortgage-backed securities, privately issued mortgage-related securities, or securities issued by the U.S. Government, its agencies and instrumentalities. The Fund may, and typically does, invest substantially in CMBS, including lower-rated CMBS.
The Fund seeks to manage interest rate risk through its management of the average duration of the securities it holds in its portfolio. Under normal conditions, the Fund will maintain its average dollar-weighted duration range between one and three years. The duration of a security takes into account the pattern of all expected
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
3
payments of interest and principal on the security over time, including how these payments are affected by changes in interest rates.
The Fund may use derivatives to hedge against risk or to gain investment exposure. Currently, the Fund expects to invest in derivatives consisting principally of futures, forwards, options, and swaps. The Fund may use derivatives to seek to enhance returns, to attempt to hedge some of its investment risk, to manage portfolio duration, as a substitute for holding the underlying asset on which the derivative instrument is based, or for cash management purposes. For example, the Fund may invest in or sell short U.S. Treasury futures, securities index futures, other futures, and/or currency forwards to adjust the Fund’s exposure to the direction of interest rates, or for other portfolio management reasons.
The portfolio management team buys and sells securities using a relative value-oriented investment process, meaning the portfolio management team generally seeks more investment exposure to securities believed to be undervalued and less investment exposure to securities believed to be overvalued. The portfolio management team combines top-down and bottom-up analysis to construct its portfolio, using a blend of quantitative and fundamental research. As part of its top-down analysis, the portfolio management team evaluates global economic conditions, including monetary, fiscal, and regulatory policy, as well as the political and geopolitical environment, in order to identify and assess opportunities and risks across different segments of the fixed income market. The portfolio management team employs bottom-up analysis to identify and select securities for investment by the Fund based on in-depth company, industry, and market research and analysis. The portfolio management team may actively rotate sector exposure based on its assessment of relative value. The investment team may also consider the risks and return potential presented by environmental, social, and governance (“ESG”) factors in investment decisions. The Fund may engage in active and frequent trading of its portfolio securities.
The Fund may sell a security when the Fund believes the security is less likely to benefit from the current market and economic environment, or shows signs of deteriorating fundamentals, among other reasons. The Fund may deviate from the investment strategy described above for temporary defensive purposes. The Fund may miss certain investment opportunities if defensive strategies are used and thus may not achieve its investment objective.
PRINCIPAL RISKS
As with any investment in a mutual fund, investing in the Fund involves risk, including the risk that you may receive little or no return on your investment. When you redeem your shares, they may be worth more or less than what you paid for them, which means that you may lose a portion or all of the money you invested in the Fund. The principal risks of investing in the Fund, which could adversely affect its performance, include:
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
4
· Portfolio Management Risk: If the strategies used and investments selected by the Fund’s portfolio management team fail to produce the intended result, the Fund may suffer losses or underperform other funds with the same investment objective or strategies, even in a favorable market.
· Market Risk: The market values of securities will fluctuate, sometimes sharply and unpredictably, based on overall economic conditions, governmental actions or intervention, market disruptions caused by trade disputes or other factors, political developments, and other factors. Prices of equity securities tend to rise and fall more dramatically than those of debt securities.
· Fixed Income Securities Risk: The Fund is subject to the general risks and considerations associated with investing in debt securities, including the risk that issuers will fail to make timely payments of principal or interest or default altogether. Lower-rated securities in which the Fund may invest may be more volatile and may decline more in price in response to negative issuer developments or general economic news than higher rated securities. In addition, as interest rates rise, the Fund’s investments typically will lose value.
· Foreign Currency Risk: Investments in securities denominated in foreign currencies are subject to the risk that those currencies will decline in value relative to the U.S. dollar, or, in the case of hedged positions, that the U.S. dollar will decline in value relative to the currency being hedged. Foreign currency exchange rates may fluctuate significantly over short periods of time.
· High Yield Securities Risk: High yield securities (commonly referred to as “junk” bonds) typically pay a higher yield than investment grade securities, but may have greater price fluctuations and have a higher risk of default than investment grade securities. The market for high yield securities may be less liquid due to such factors as interest rate sensitivity, negative perceptions of the junk bond markets generally, and less secondary market liquidity. This may make such securities more difficult to sell at an acceptable price, especially during periods of financial distress, increased market volatility, or significant market decline.
· Credit Risk: Debt securities are subject to the risk that the issuer or guarantor of a security may not make interest and principal payments as they become due or may default altogether. In addition, if the market perceives a deterioration in the creditworthiness of an issuer, the value and liquidity of securities issued by that issuer may decline. To the extent that the Fund holds below investment grade securities, these risks may be heightened. Insured debt securities have the credit risk of the insurer in addition to the credit risk of the underlying investment being insured.
· Interest Rate Risk: As interest rates rise, prices of bonds (including tax-exempt bonds) generally fall, typically causing the Fund’s investments to lose value. Additionally, rising interest rates or lack of market participants may lead to decreased liquidity in fixed income markets. Interest rate changes generally
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
5
have a more pronounced effect on the market value of fixed-rate instruments, such as corporate bonds, than they have on floating rate instruments, and typically have a greater effect on the price of fixed income securities with longer durations. A wide variety of market factors can cause interest rates to rise, including central bank monetary policy, rising inflation, and changes in general economic conditions. To the extent the Fund invests in floating rate instruments, changes in short-term market interest rates may affect the yield on those investments. If short-term market interest rates fall, the yield on the Fund’s shares will also fall. Conversely, when short-term market interest rates rise, because of the lag between changes in such short- term rates and the resetting of the floating rates on the floating rate debt in the Fund’s portfolio, the impact of rising rates may be delayed. To the extent the Fund invests in fixed rate instruments, fluctuations in the market price of such investments may not affect interest income derived from those instruments, but may nonetheless affect the Fund’s net asset value (“NAV”), especially if the instrument has a longer maturity. Substantial increases in interest rates may cause an increase in issuer defaults, as issuers may lack resources to meet higher debt service requirements. In recent years, the U.S. has experienced historically low interest rates, increasing the exposure of bond investors to the risks associated with rising interest rates.
· Liquidity/Redemption Risk: The Fund may lose money when selling securities at inopportune times to fulfill shareholder redemption requests. The risk of loss may increase depending on the size and frequency of redemption requests, whether the redemption requests occur in times of overall market turmoil or declining prices, and whether the securities the Fund intends to sell have decreased in value or are illiquid. The Fund may be less able to sell illiquid securities at its desired time or price. It may be more difficult for the Fund to value its investments in illiquid securities than more liquid securities.
· Government Securities Risk: The Fund invests in securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies and instrumentalities (such as the Government National Mortgage Association (“Ginnie Mae”), the Federal National Mortgage Association (“Fannie Mae”), or the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“Freddie Mac”)). Unlike Ginnie Mae securities, securities issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government-related organizations, such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, are not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government and no assurance can be given that the U.S. Government would provide financial support.
· Mortgage-Related and Other Asset-Backed Securities Risk: Mortgage-related securities, including commercial mortgage-backed securities (“CMBS”) and other privately issued mortgage-related securities, and other asset-backed securities may be particularly sensitive to changes in prevailing interest rates and economic conditions, including delinquencies and defaults. The prices of mortgage-related and other asset-backed securities, depending on their structure and the rate of payments, can be volatile. They are subject to prepayment risk
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
6
(higher than expected prepayment rates of mortgage obligations due to a fall in market interest rates) and extension risk (lower than expected prepayment rates of mortgage obligations due to a rise in market interest rates). These risks increase the Fund’s overall interest rate risk. Some mortgage-related securities receive government or private support, but there is no assurance that such support will remain in place.
· Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities Risk: CMBS include securities that reflect an interest in, and are secured by, mortgage loans on commercial real property. Many of the risks of investing in CMBS reflect the risks of investing in the real estate securing the underlying mortgage loans. These risks reflect the effects of local and other economic conditions on real estate markets, the ability of tenants to make loan payments, and the ability of a property to attract and retain tenants. CMBS may be less liquid and exhibit greater price volatility than other types of mortgage- or asset-backed securities.
· Convertible Securities Risk: Convertible securities are subject to the risks affecting both equity and fixed income securities, including market, credit, liquidity, and interest rate risk. Convertible securities tend to be more volatile than other fixed income securities, and the markets for convertible securities may be less liquid than markets for common stocks or bonds. To the extent that the Fund invests in convertible securities and the investment value of the convertible security is greater than its conversion value, its price will likely increase when interest rates fall and decrease when interest rates rise. If the conversion value exceeds the investment value, the price of the convertible security will tend to fluctuate directly with the price of the underlying equity security. A significant portion of convertible securities have below investment grade credit ratings and are subject to increased credit and liquidity risks.
· Inflation-Linked Investments Risk: Unlike traditional fixed income securities, the principal and interest payments of inflation-linked investments are adjusted periodically based on the inflation rate. The value of the Fund’s inflation-linked investments may be vulnerable to changes in expectations of inflation or interest rates and there is no guarantee that the Fund’s use of these instruments will be successful.
· Foreign and Emerging Market Company Risk: Investments in foreign companies and in U.S. companies with economic ties to foreign markets generally involve special risks that can increase the likelihood that the Fund will lose money. For example, as compared with companies organized and operated in the U.S., these companies may be more vulnerable to economic, political, and social instability and subject to less government supervision, lack of transparency, inadequate regulatory and accounting standards, and foreign taxes. In addition, the securities of foreign companies also may be subject to inadequate exchange control regulations, the imposition of economic sanctions or other government restrictions, higher transaction and other costs, reduced liquidity, and delays in settlement to the extent they are traded on non-U.S.
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
7
exchanges or markets. Foreign company securities also include American Depositary Receipts (“ADRs”). ADRs may be less liquid than the underlying shares in their primary trading market. Foreign securities also may subject the Fund’s investments to changes in currency exchange rates. Emerging market securities generally are more volatile than other foreign securities, and are subject to greater liquidity, regulatory, and political risks. Investments in emerging markets may be considered speculative and generally are riskier than investments in more developed markets because such markets tend to develop unevenly and may never fully develop. Emerging markets are more likely to experience hyperinflation and currency devaluations. Securities of emerging market companies may have far lower trading volumes and less liquidity than securities of issuers in developed markets. Companies with economic ties to emerging markets may be susceptible to the same risks as companies organized in emerging markets.
· Loan Risk: Investments in floating or adjustable rate loans are subject to increased credit and liquidity risks. Loan prices also may be adversely affected by supply-demand imbalances caused by conditions in the loan market or related markets. Below investment grade loans, like high-yield debt securities, or junk bonds, usually are more credit sensitive than interest rate sensitive, although the value of these instruments may be affected by interest rate swings in the overall fixed income market. Loans may be subject to structural subordination and may be subordinated to other obligations of the borrower or its subsidiaries.
· Collateralized Loan Obligations and Other Collateralized Obligations Risk: An investment in a CLO can be viewed as investing in (or through) another investment adviser and is subject to the layering of fees associated with such an investment. The risks of an investment in a CLO depend largely on the type of the collateral held in the CLO portfolio and the tranche of securities in which the Fund invests. The risks of investing in a CLO can be generally summarized as a combination of economic risks of the underlying loans combined with the risks associated with the CLO structure governing the priority of payments, and include interest rate risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, prepayment risk, and the risk of default of the underlying asset, among others.
· LIBOR Risk: Certain instruments in which the Fund may invest rely in some fashion upon the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”). On March 5, 2021, the United Kingdom Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and LIBOR’s administrator, ICE Benchmark Administration (IBA), announced that most LIBOR settings will no longer be published after the end of 2021 and a majority of U.S. dollar LIBOR settings will no longer be published after June 30, 2023. Abandonment of or modifications to LIBOR could have adverse impacts on newly issued financial instruments and existing financial instruments which reference LIBOR and lead to significant short-term and long-term uncertainty and market instability.
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
8
· Derivatives Risk: The risks associated with derivatives may be different from and greater than the risks associated with directly investing in securities and other investments. Derivatives may increase the Fund’s volatility and reduce its returns. The risks associated with derivatives include, among other things, the following:
· The risk that the value of a derivative may not correlate with the value of the underlying asset, rate, or index in the manner anticipated by the portfolio management team and may be more sensitive to changes in economic or market conditions than anticipated.
· Derivatives may be difficult to value, especially under stressed or unforeseen market conditions.
· The risk that the counterparty may fail to fulfill its contractual obligations under the derivative contract. Central clearing of derivatives is intended to decrease counterparty risk but does not eliminate it.
· The Fund may be required to segregate permissible liquid assets to cover its obligations under these transactions and may have to liquidate positions before it is desirable to do so to fulfill its segregation requirements.
· The risk that there may not be a liquid secondary trading market for the derivative, or that the Fund may otherwise be unable to sell or otherwise close a derivatives position when desired, exposing the Fund to additional losses.
· Because derivatives generally involve a small initial investment relative to the risk assumed (known as leverage), derivatives can magnify the Fund’s losses and increase its volatility.
· The Fund’s use of derivatives may affect the amount, timing, and character of distributions, and may cause the Fund to realize more short-term capital gain and ordinary income than if the Fund did not use derivatives.
Derivatives may not perform as expected and the Fund may not realize the intended benefits. Whether the Fund’s use of derivatives is successful will depend on, among other things, the portfolio managers’ ability to correctly forecast market movements and other factors. If the portfolio managers incorrectly forecast these and other factors, the Fund’s performance could suffer. In addition, given their complexity, derivatives are subject to the risk that improper or misunderstood documentation may expose the Fund to losses.
· High Portfolio Turnover Risk: High portfolio turnover may result in increased transaction costs and reduced investment performance.
An investment in the Fund is not a deposit of any bank and is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency. For more information on the principal risks of the Fund, please see the “More Information About the Fund – Principal Risks” section in the prospectus.
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
9
PERFORMANCE
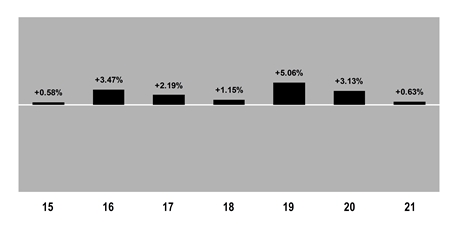
The bar chart and table below provide some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund by illustrating the variability of the Fund’s returns. Each assumes reinvestment of dividends and distributions. The Fund’s past performance is not necessarily an indication of how the Fund will perform in the future.
The bar chart shows changes in the performance of the Fund’s Class VC shares from calendar year to calendar year. This chart does not reflect the sales charges or other expenses of Variable Contracts. If those sales charges and expenses were reflected, returns would be lower.
Bar Chart (per calendar year) - Class VC Shares
Best Quarter 2nd Q 2020 +5.92% Worst Quarter 1st Q 2020 -5.33% |
The table below shows how the Fund’s average annual total returns compare to the returns of a securities market index with investment characteristics similar to those of the Fund.
Average Annual Total Returns |
| ||||
(for the periods ended December 31, 2021) |
| ||||
Class | 1 Year | 5 Years | Life of Class | Inception
|
|
Class VC Shares | 0.63% | 2.42% | 2.12% | 4/14/2014 |
|
Index |
|
|
|
|
|
ICE BofA U.S. Corporate 1-3 Year Index | -0.01% | 2.60% | 2.18% | 4/14/2014 |
|
(reflects no deduction for fees, expenses, or taxes) |
| ||||
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
10
MANAGEMENT
Investment Adviser. The Fund’s investment adviser is Lord, Abbett & Co. LLC (“Lord Abbett”).
Portfolio Managers.
Portfolio Managers/Title | Member of |
Andrew H. O’Brien, Partner and Portfolio Manager | 2014 |
Robert A. Lee, Partner and Co-Head of Taxable Fixed Income | 2014 |
Kewjin Yuoh, Partner and Portfolio Manager | 2014 |
Steven F. Rocco, Partner and Co-Head of Taxable Fixed Income | 2014 |
Adam C. Castle, Managing Director and Portfolio Manager | 2021 |
Harris A. Trifon, Managing Director and Portfolio Manager | 2021 |
Yoana N. Koleva, Managing Director and Portfolio Manager | 2022 |
PURCHASE AND SALE OF FUND SHARES
Because the Fund serves as an underlying investment vehicle for Variable Contracts, Fund shares currently are available only to certain insurance company separate accounts at NAV.
TAX INFORMATION
For information about the federal income tax treatment of Fund distributions to the insurance company separate accounts that hold shares in the Fund, please refer to the prospectus provided by the insurance company for your Variable Contract. Because of the unique tax status of Variable Contracts, you should consult your tax adviser regarding treatment under the federal, state, and local tax rules that apply to you.
PAYMENTS TO INSURANCE COMPANIES AND OTHER FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES
The Fund and its related companies may make payments to the sponsoring insurance company, its affiliates, or other financial intermediaries for distribution and/or other services. These payments may create a conflict of interest by influencing the insurance company or other financial intermediary to recommend the Fund over another investment. Ask your individual financial professional or visit your insurance company’s or financial intermediary’s website for more information.
SUMMARY – Short Duration Income Portfolio
11
Investment Company Act File Number: 811-05876 |
| ||
| SF-SDIP-7 | ||
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsRelated Entities
Lord, Abbett & CompanySign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share