Form 497K BLACKROCK SERIES, INC.
SEPTEMBER 28, 2022
 |
Summary Prospectus |
BlackRock Series,
Inc. | Class K Shares
| • | BlackRock International Fund |
| Class K: MKILX |
Before you invest, you may
want to review the Fund’s prospectus, which contains more information about the Fund and its risks. You can find the Fund’s prospectus (including amendments and supplements), reports to shareholders and other information about the Fund,
including the Fund’s statement of additional information, online at http://www.blackrock.com/prospectus. You can also get this information at no cost by calling (800) 537-4942 or by sending an e-mail request to
[email protected], or from your financial professional. The Fund’s prospectus and
statement of additional information, both dated September 28, 2022, as amended and supplemented from time to time, are incorporated by reference into (legally made a part of) this Summary Prospectus.
This
Summary Prospectus contains information you should know before investing, including information about risks. Please read it before you invest and keep it for future reference.
The Securities and Exchange Commission has not approved or
disapproved these securities or passed upon the adequacy of this Summary Prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
Not FDIC Insured • May Lose Value • No Bank
Guarantee
Summary Prospectus
Key Facts About BlackRock International Fund
Investment Objective
The investment objective of BlackRock International Fund (the
“Fund”), a series of BlackRock Series, Inc. (the “Corporation”), is to seek long-term capital growth through investments primarily in a diversified portfolio of equity securities of companies located outside the United
States.
Fees and Expenses of the Fund
This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if
you buy, hold and sell Class K Shares of the Fund. You may pay other fees, such as brokerage commissions and other fees to your financial professional or your selected securities dealer, broker, investment adviser,
service provider or industry professional (including BlackRock Advisors, LLC (“BlackRock”) and its affiliates) (each, a “Financial Intermediary”), which are not reflected in the table and example below.
| Annual
Fund Operating Expenses (expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the value of your investment) |
Class
K Shares |
| Management Fee1 | 0.58% |
| Distribution and/or Service (12b-1) Fees | None |
| Other Expenses | 0.05% |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses | 0.63% |
| Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements1,2 | (0.03)% |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements1,2 | 0.60% |
| 1 | As described in the “Management of the Fund” section of the Fund’s prospectus beginning on page 33, BlackRock has contractually agreed to waive the management fee with respect to any portion of the Fund’s assets estimated to be attributable to investments in other equity and fixed-income mutual funds and exchange-traded funds managed by BlackRock or its affiliates that have a contractual management fee, through June 30, 2024. In addition, BlackRock has contractually agreed to waive its management fees by the amount of investment advisory fees the Fund pays to BlackRock indirectly through its investment in money market funds managed by BlackRock or its affiliates, through June 30, 2024. The contractual agreements may be terminated upon 90 days’ notice by a majority of the non-interested directors of the Corporation or by a vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the Fund. |
| 2 | As described in the “Management of the Fund” section of the Fund’s prospectus beginning on page 33, BlackRock has contractually agreed to waive and/or reimburse fees or expenses in order to limit Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waivers and/or Expense Reimbursements (excluding Dividend Expense, Interest Expense, Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses and certain other Fund expenses) to 0.60% of average daily net assets through June 30, 2024. The contractual agreement may be terminated upon 90 days’ notice by a majority of the non-interested directors of the Corporation or by a vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the Fund. |
Example:
This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the
Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your
investment has a 5% return each year and that the Fund’s operating expenses remain the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be:
| 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years | |
| Class K Shares | $61 | $199 | $348 | $783 |
Portfolio Turnover:
The Fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells
securities (or “turns over” its portfolio). A higher portfolio turnover rate may indicate higher transaction costs and may result in higher taxes when shares are held in a taxable account. These costs, which are not reflected in annual
fund operating expenses or in the Example, affect the Fund’s performance. For the most recent fiscal year, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate was 103% of the average value of its portfolio.
2
Principal Investment Strategies of the Fund
The Fund invests primarily in stocks of companies located
outside the United States. The Fund may purchase common stock, preferred stock, convertible securities and other instruments.
The Fund will invest at least 75% of its total assets in
global equity securities of any market capitalization, selected for their above average return potential. The Fund may invest in securities issued by companies of all sizes but will focus mainly on medium and large capitalization companies.
Companies will be located in developed countries of Europe and the Far East, and in countries with emerging capital markets anywhere in the world. The Fund may invest up to 25% of its total assets in global fixed income securities, including
corporate bonds, U.S. Government debt securities, non-U.S. Government and supranational debt securities, asset-backed securities, mortgage-backed securities, emerging market debt securities and non-investment grade debt securities (high yield or
junk bonds).
Fund management selects companies that it
believes are undervalued or have good prospects for earnings growth. The Fund chooses investments predominantly using a “bottom up” investment style using a global sector-based investment process. The Fund’s allocations to
particular countries are based on Fund management’s evaluation of individual companies.
Under normal circumstances, the Fund will allocate a
substantial amount (approximately 40% or more — unless market conditions are not deemed favorable by Fund management, in which case the Fund would invest at least 30%) of its total assets in securities (i) of foreign government issuers, (ii)
of issuers organized or located outside the United States, (iii) of issuers which primarily trade in a market located outside the United States, or (iv) of issuers doing a substantial amount of business outside the United States, which the Fund
considers to be companies that derive at least 50% of their revenue or profits from business outside the United States or have at least 50% of their sales or assets outside the United States. The Fund will allocate its assets among various regions
and countries, including the United States (but in no less than three different countries). For temporary defensive purposes the Fund may deviate very substantially from the allocation described above.
Fund management may, when consistent with the Fund’s
investment objective, buy or sell options or futures on a security or an index of securities, or enter into interest rate or foreign currency transactions, including swaps (collectively, commonly known as derivatives).
Principal Risks of Investing in the Fund
Risk is inherent in all investing. The value of your
investment in the Fund, as well as the amount of return you receive on your investment, may fluctuate significantly from day to day and over time. You may lose part or all of your investment in the Fund or your investment may not perform as well as
other similar investments. The following is a summary description of the principal risks of investing in the Fund. The relative significance of each risk factor below may change over time and you should review each risk factor carefully.
| ■ | Equity Securities Risk — Stock markets are volatile. The price of equity securities fluctuates based on changes in a company’s financial condition and overall market and economic conditions. |
| ■ | Foreign Securities Risk — Foreign investments often involve special risks not present in U.S. investments that can increase the chances that the Fund will lose money. These risks include: |
| ■ | The Fund generally holds its foreign securities and cash in foreign banks and securities depositories, which may be recently organized or new to the foreign custody business and may be subject to only limited or no regulatory oversight. |
| ■ | Changes in foreign currency exchange rates can affect the value of the Fund’s portfolio. |
| ■ | The economies of certain foreign markets may not compare favorably with the economy of the United States with respect to such issues as growth of gross national product, reinvestment of capital, resources and balance of payments position. |
| ■ | The governments of certain countries, or the U.S. Government with respect to certain countries, may prohibit or impose substantial restrictions through capital controls and/or sanctions on foreign investments in the capital markets or certain industries in those countries, which may prohibit or restrict the ability to own or transfer currency, securities, derivatives or other assets. |
| ■ | Many foreign governments do not supervise and regulate stock exchanges, brokers and the sale of securities to the same extent as does the United States and may not have laws to protect investors that are comparable to U.S. securities laws. |
| ■ | Settlement and clearance procedures in certain foreign markets may result in delays in payment for or delivery of securities not typically associated with settlement and clearance of U.S. investments. |
3
| ■ | The Fund’s claims to recover foreign withholding taxes may not be successful, and if the likelihood of recovery of foreign withholding taxes materially decreases, due to, for example, a change in tax regulation or approach in the foreign country, accruals in the Fund’s net asset value for such refunds may be written down partially or in full, which will adversely affect the Fund’s net asset value. |
| ■ | The European financial markets have recently experienced volatility and adverse trends due to concerns about economic downturns in, or rising government debt levels of, several European countries as well as acts of war in the region. These events may spread to other countries in Europe and may affect the value and liquidity of certain of the Fund’s investments. |
| ■ | Debt Securities Risk — Debt securities, such as bonds, involve interest rate risk, credit risk, extension risk, and prepayment risk, among other things. |
| Interest Rate Risk — The market value of bonds and other fixed-income securities changes in response to interest rate changes and other factors. Interest rate risk is the risk that prices of bonds and other fixed-income securities will increase as interest rates fall and decrease as interest rates rise. | |
| The Fund may be subject to a greater risk of rising interest rates due to the recent period of historically low interest rates. For example, if interest rates increase by 1%, assuming a current portfolio duration of ten years, and all other factors being equal, the value of the Fund’s investments would be expected to decrease by 10%. (Duration is a measure of the price sensitivity of a debt security of portfolio of debt securities to relative changes in interest rates.) The magnitude of these fluctuations in the market price of bonds and other fixed-income securities is generally greater for those securities with longer maturities. Fluctuations in the market price of the Fund’s investments will not affect interest income derived from instruments already owned by the Fund, but will be reflected in the Fund’s net asset value. The Fund may lose money if short-term or long-term interest rates rise sharply in a manner not anticipated by Fund management. | |
| To the extent the Fund invests in debt securities that may be prepaid at the option of the obligor (such as mortgage-backed securities), the sensitivity of such securities to changes in interest rates may increase (to the detriment of the Fund) when interest rates rise. Moreover, because rates on certain floating rate debt securities typically reset only periodically, changes in prevailing interest rates (and particularly sudden and significant changes) can be expected to cause some fluctuations in the net asset value of the Fund to the extent that it invests in floating rate debt securities. | |
| These basic principles of bond prices also apply to U.S. Government securities. A security backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. Government is guaranteed only as to its stated interest rate and face value at maturity, not its current market price. Just like other fixed-income securities, government-guaranteed securities will fluctuate in value when interest rates change. | |
| A general rise in interest rates has the potential to cause investors to move out of fixed-income securities on a large scale, which may increase redemptions from funds that hold large amounts of fixed-income securities. Heavy redemptions could cause the Fund to sell assets at inopportune times or at a loss or depressed value and could hurt the Fund’s performance. | |
| Credit Risk — Credit risk refers to the possibility that the issuer of a debt security (i.e., the borrower) will not be able to make payments of interest and principal when due. Changes in an issuer’s credit rating or the market’s perception of an issuer’s creditworthiness may also affect the value of the Fund’s investment in that issuer. The degree of credit risk depends on both the financial condition of the issuer and the terms of the obligation. | |
| Extension Risk — When interest rates rise, certain obligations will be paid off by the obligor more slowly than anticipated, causing the value of these obligations to fall. | |
| Prepayment Risk — When interest rates fall, certain obligations will be paid off by the obligor more quickly than originally anticipated, and the Fund may have to invest the proceeds in securities with lower yields. | |
| ■ | Convertible Securities Risk — The market value of a convertible security performs like that of a regular debt security; that is, if market interest rates rise, the value of a convertible security usually falls. In addition, convertible securities are subject to the risk that the issuer will not be able to pay interest or dividends when due, and their market value may change based on changes in the issuer’s credit rating or the market’s perception of the issuer’s creditworthiness. Since it derives a portion of its value from the common stock into which it may be converted, a convertible security is also subject to the same types of market and issuer risks that apply to the underlying common stock. |
| ■ | Derivatives Risk — The Fund’s use of derivatives may increase its costs, reduce the Fund’s returns and/or increase volatility. Derivatives involve significant risks, including: |
4
| Leverage Risk — The Fund’s use of derivatives can magnify the Fund’s gains and losses. Relatively small market movements may result in large changes in the value of a derivatives position and can result in losses that greatly exceed the amount originally invested. | |
| Market Risk — Some derivatives are more sensitive to interest rate changes and market price fluctuations than other securities. The Fund could also suffer losses related to its derivatives positions as a result of unanticipated market movements, which losses are potentially unlimited. Finally, BlackRock may not be able to predict correctly the direction of securities prices, interest rates and other economic factors, which could cause the Fund’s derivatives positions to lose value. | |
| Counterparty Risk — Derivatives are also subject to counterparty risk, which is the risk that the other party in the transaction will be unable or unwilling to fulfill its contractual obligation, and the related risks of having concentrated exposure to such a counterparty. | |
| Illiquidity Risk — The possible lack of a liquid secondary market for derivatives and the resulting inability of the Fund to sell or otherwise close a derivatives position could expose the Fund to losses and could make derivatives more difficult for the Fund to value accurately. | |
| Operational Risk — The use of derivatives includes the risk of potential operational issues, including documentation issues, settlement issues, systems failures, inadequate controls and human error. | |
| Legal Risk — The risk of insufficient documentation, insufficient capacity or authority of counterparty, or legality or enforceability of a contract. | |
| Volatility and Correlation Risk — Volatility is defined as the characteristic of a security, an index or a market to fluctuate significantly in price within a short time period. A risk of the Fund’s use of derivatives is that the fluctuations in their values may not correlate with the overall securities markets. | |
| Valuation Risk — Valuation for derivatives may not be readily available in the market. Valuation may be more difficult in times of market turmoil since many investors and market makers may be reluctant to purchase complex instruments or quote prices for them. | |
| Hedging Risk — Hedges are sometimes subject to imperfect matching between the derivative and the underlying security, and there can be no assurance that the Fund’s hedging transactions will be effective. The use of hedging may result in certain adverse tax consequences. | |
| Tax Risk — Certain aspects of the tax treatment of derivative instruments, including swap agreements and commodity-linked derivative instruments, are currently unclear and may be affected by changes in legislation, regulations or other legally binding authority. Such treatment may be less favorable than that given to a direct investment in an underlying asset and may adversely affect the timing, character and amount of income the Fund realizes from its investments. | |
| Regulatory Risk — Derivative contracts are subject to regulation under the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”) in the United States and under comparable regimes in Europe, Asia and other non-U.S. jurisdictions. Under the Dodd-Frank Act, with respect to uncleared swaps, swap dealers are required to collect variation margin from the Fund and may be required by applicable regulations to collect initial margin from the Fund. Both initial and variation margin may be comprised of cash and/or securities, subject to applicable regulatory haircuts. Shares of investment companies (other than certain money market funds) may not be posted as collateral under applicable regulations. In addition, regulations adopted by global prudential regulators that are now in effect require certain bank-regulated counterparties and certain of their affiliates to include in certain financial contracts, including many derivatives contracts, terms that delay or restrict the rights of counterparties, such as the Fund, to terminate such contracts, foreclose upon collateral, exercise other default rights or restrict transfers of credit support in the event that the counterparty and/or its affiliates are subject to certain types of resolution or insolvency proceedings. The implementation of these requirements with respect to derivatives, as well as regulations under the Dodd-Frank Act regarding clearing, mandatory trading and margining of other derivatives, may increase the costs and risks to the Fund of trading in these instruments and, as a result, may affect returns to investors in the Fund. | |
| ■ | Emerging Markets Risk — Emerging markets are riskier than more developed markets because they tend to develop unevenly and may never fully develop. Investments in emerging markets may be considered speculative. Emerging markets are more likely to experience hyperinflation and currency devaluations, which adversely affect returns to U.S. investors. In addition, many emerging securities markets have far lower trading volumes and less liquidity than developed markets. |
| ■ | Focus Risk — Under normal circumstances, the Fund focuses its investments in the securities of a limited number of issuers. This may subject the Fund to greater issuer-specific risk and potential losses than a fund that invests in the securities of a greater number of issuers. |
5
| ■ | Geographic Concentration Risk — From time to time the Fund may invest a substantial amount of its assets in issuers located in a single country or a limited number of countries. If the Fund concentrates its investments in this manner, it assumes the risk that economic, political and social conditions in those countries will have a significant impact on its investment performance. The Fund’s investment performance may also be more volatile if it concentrates its investments in certain countries, especially emerging market countries. |
| ■ | High Portfolio Turnover Risk — The Fund may engage in active and frequent trading of its portfolio securities. High portfolio turnover (more than 100%) may result in increased transaction costs to the Fund, including brokerage commissions, dealer mark-ups and other transaction costs on the sale of the securities and on reinvestment in other securities. The sale of Fund portfolio securities may result in the realization and/or distribution to shareholders of higher capital gains or losses as compared to a fund with less active trading policies. These effects of higher than normal portfolio turnover may adversely affect Fund performance. |
| ■ | Junk Bonds Risk — Although junk bonds generally pay higher rates of interest than investment grade bonds, junk bonds are high risk investments that are considered speculative and may cause income and principal losses for the Fund. |
| ■ | Leverage Risk — Some transactions may give rise to a form of economic leverage. These transactions may include, among others, derivatives, and may expose the Fund to greater risk and increase its costs. The use of leverage may cause the Fund to liquidate portfolio positions when it may not be advantageous to do so to satisfy its obligations or to meet the applicable requirements of the Investment Company Act, and the rules thereunder. Increases and decreases in the value of the Fund’s portfolio will be magnified when the Fund uses leverage. |
| ■ | Market Risk and Selection Risk — Market risk is the risk that one or more markets in which the Fund invests will go down in value, including the possibility that the markets will go down sharply and unpredictably. The value of a security or other asset may decline due to changes in general market conditions, economic trends or events that are not specifically related to the issuer of the security or other asset, or factors that affect a particular issuer or issuers, exchange, country, group of countries, region, market, industry, group of industries, sector or asset class. Local, regional or global events such as war, acts of terrorism, the spread of infectious illness or other public health issues like pandemics or epidemics, recessions, or other events could have a significant impact on the Fund and its investments. Selection risk is the risk that the securities selected by Fund management will underperform the markets, the relevant indices or the securities selected by other funds with similar investment objectives and investment strategies. This means you may lose money. |
| An outbreak of an infectious coronavirus (COVID-19) that was first detected in December 2019 developed into a global pandemic that has resulted in numerous disruptions in the market and has had significant economic impact leaving general concern and uncertainty. Although vaccines have been developed and approved for use by various governments, the duration of the pandemic and its effects cannot be predicted with certainty. The impact of this coronavirus, and other epidemics and pandemics that may arise in the future, could affect the economies of many nations, individual companies and the market in general ways that cannot necessarily be foreseen at the present time. | |
| ■ | Mid Cap Securities Risk — The securities of mid cap companies generally trade in lower volumes and are generally subject to greater and less predictable price changes than the securities of larger capitalization companies. |
| ■ | Mortgage- and Asset-Backed Securities Risks — Mortgage- and asset-backed securities represent interests in “pools” of mortgages or other assets, including consumer loans or receivables held in trust. Mortgage- and asset-backed securities are subject to credit, interest rate, prepayment and extension risks. These securities also are subject to risk of default on the underlying mortgage or asset, particularly during periods of economic downturn. Small movements in interest rates (both increases and decreases) may quickly and significantly reduce the value of certain mortgage-backed securities. |
| ■ | Preferred Securities Risk — Preferred securities may pay fixed or adjustable rates of return. Preferred securities are subject to issuer-specific and market risks applicable generally to equity securities. In addition, a company’s preferred securities generally pay dividends only after the company makes required payments to holders of its bonds and other debt. For this reason, the value of preferred securities will usually react more strongly than bonds and other debt to actual or perceived changes in the company’s financial condition or prospects. Preferred securities of smaller companies may be more vulnerable to adverse developments than preferred securities of larger companies. |
| ■ | Supranational Entities Risk — The Fund may invest in obligations issued or guaranteed by the World Bank. The government members, or “stockholders,” usually make initial capital contributions to the World Bank and in many cases are committed to make additional capital contributions if the World Bank is unable to repay its borrowings. There is no guarantee that one or more stockholders of the World Bank will continue to make any necessary additional capital contributions. If such contributions are not made, the entity may be unable to pay interest or repay principal on its debt securities, and the Fund may lose money on such investments. |
6
Performance Information
The information shows you how the Fund’s performance has
varied year by year and provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund. Class K Shares commenced operations on January 25, 2018. As a result, the returns shown below for Class K Shares prior to January 25, 2018 are those of the
Fund’s Institutional Shares, which are not offered in this prospectus. The performance of Class K Shares would be substantially similar to Institutional Shares because Class K Shares and Institutional Shares are invested in the same portfolio
of securities and performance would differ only to the extent that Institutional Shares and Class K Shares have different expenses. The actual returns of Class K Shares would have been higher than those of the Institutional Shares because Class K
Shares have lower expenses than the Institutional Shares. The table compares the Fund’s performance to that of the MSCI All Country World Index ex-USA. To the extent that dividends and distributions have been paid by the Fund, the performance
information for the Fund in the chart and table assumes reinvestment of the dividends and distributions. As with all such investments, past performance (before and after taxes) is not an indication of future results. The table includes all
applicable fees. If BlackRock and its affiliates had not waived or reimbursed certain Fund expenses during these periods, the Fund’s returns would have been lower. Updated information on the Fund’s performance, including its current net
asset value, can be obtained by visiting http://www.blackrock.com or can be obtained by phone at (800) 882-0052.
Class K Shares
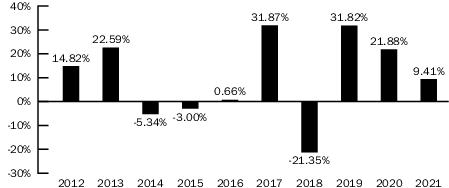
ANNUAL TOTAL RETURNS1
BlackRock International Fund
As of 12/31
As of 12/31
During the ten-year
period shown in the bar chart, the highest return for a quarter was 26.76% (quarter ended June 30, 2020) and the lowest return for a quarter was -25.08% (quarter ended March 31, 2020). The year-to-date return as of June 30, 2022 was -27.42%.
| For
the periods ended 12/31/21 Average Annual Total Returns |
1 Year | 5 Years | 10 Years1 |
| BlackRock International Fund — Class K Shares | |||
| Return Before Taxes | 9.41% | 12.76% | 9.02% |
| Return After Taxes on Distributions | 7.10% | 12.19% | 8.63% |
| Return After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 6.32% | 10.20% | 7.42% |
| MSCI
All Country World Index ex-USA (Reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) |
7.82% | 9.61% | 7.28% |
| 1 | For the fiscal year ended October 31, 2013, a portion of the Fund’s return for each share class consisted of a payment from an affiliate to compensate for foregone securities lending revenue. |
After-tax returns are calculated using the historical highest
individual federal marginal income tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on the investor’s tax situation and may differ from those shown, and the after-tax returns shown are not
relevant to investors who hold their shares through tax-deferred arrangements, such as 401(k) plans or individual retirement accounts.
Investment Manager
The Fund’s investment manager is BlackRock Advisors, LLC
(previously defined as “BlackRock”). The Fund’s sub-adviser is BlackRock International Limited (the “Sub-Adviser”). Where applicable, “BlackRock” refers also to the Sub-Adviser.
7
Portfolio Managers
| Name | Portfolio
Manager of the Fund Since |
Title |
| James Bristow, CFA | 2007 | Managing Director of BlackRock, Inc. |
| Gareth Williams, CFA | 2011 | Director of BlackRock, Inc. |
Purchase and Sale of Fund Shares
Class K Shares of the Fund are available only to (i) certain
employee benefit plans, such as health savings accounts, and certain employer-sponsored retirement plans (not including SEP IRAs, SIMPLE IRAs and SARSEPs) (collectively, “Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans”), (ii) collective trust
funds, investment companies and other pooled investment vehicles, each of which may purchase shares of the Fund through a Financial Intermediary (as defined below) that has entered into an agreement with the Fund’s distributor to purchase such
shares, (iii) “Institutional Investors,” which include, but are not limited to, endowments, foundations, family offices, banks and bank trusts, local, city, and state governmental institutions, corporations and insurance company separate
accounts, each of which may purchase shares of the Fund through a Financial Intermediary that has entered into an agreement with the Fund’s distributor to purchase such shares, (iv) clients of private banks that purchase shares of the Fund
through a Financial Intermediary that has entered into an agreement with the Fund’s distributor to sell such shares, (v) fee-based advisory platforms of a Financial Intermediary that (a) has specifically acknowledged in a written agreement
with the Fund’s distributor and/or its affiliate(s) that the Financial Intermediary shall offer such shares to fee-based advisory clients through an omnibus account held at the Fund or (b) transacts in the Fund’s shares through another
intermediary that has executed such an agreement and (vi) any other investors who met the eligibility criteria for BlackRock Shares or Class K Shares prior to August 15, 2016 and have continually held Class K Shares of the Fund in the same account
since August 15, 2016.
You may purchase or redeem shares
of the Fund each day the New York Stock Exchange is open. Purchase orders may also be placed by calling (800) 537-4942, by mail (c/o BlackRock, P.O. Box 9819, Providence, Rhode Island 02940-8019), or online at www.blackrock.com. Institutional
Investors are subject to a $5 million minimum initial investment requirement. Other investors, including Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans, have no minimum initial investment requirement. There is no minimum investment amount for additional
purchases.
Tax Information
Different income tax rules apply depending on whether you are
invested through a qualified tax-exempt plan described in section 401(a) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended. If you are invested through such a plan (and Fund shares are not “debt-financed property” to the plan), then the
dividends paid by the Fund and the gain realized from a redemption or exchange of Fund shares will generally not be subject to U.S. federal income taxes until you withdraw or receive distributions from the plan. If you are not invested through such
a plan, then the Fund’s dividends and gain from a redemption or exchange may be subject to U.S. federal income taxes and may be taxed as ordinary income or capital gains, unless you are a tax-exempt investor.
Payments to Broker/Dealers and Other Financial
Intermediaries
If you purchase shares of the Fund through a Financial
Intermediary, the Fund and BlackRock Investments, LLC, the Fund’s distributor, or its affiliates may pay the Financial Intermediary for the sale of Fund shares and related services. These payments may create a conflict of interest by
influencing the Financial Intermediary and your individual financial professional to recommend the Fund over another investment.
Class K Shares are only available through a Financial
Intermediary if the Financial Intermediary will not receive from Fund assets, or the Fund’s distributor’s or an affiliate’s resources, any commission payments, shareholder servicing fees (including sub-transfer agent and networking
fees), or distribution fees (including Rule 12b-1 fees) with respect to assets invested in Class K Shares.
Ask your individual financial professional or visit your
Financial Intermediary’s website for more information.
8
[This page intentionally left blank]
[This page intentionally left blank]
[This page intentionally left blank]
INVESTMENT COMPANY ACT FILE # 811-08797
SPRO-IF-K-0922
Serious News for Serious Traders! Try StreetInsider.com Premium Free!
You May Also Be Interested In
- Banxso Partners with TipRanks to Elevate Retail Investment Experience with Professional-Grade Tools
- A new prize for the Monaco Energy Boat Challenge to encourage sustainable yachting
- Major shareholder announcement
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share