Form 497K AQR Funds

AQR Macro Opportunities Fund
Fund Summary — May 1, 2022 (as Amended August 19, 2022)
Ticker: Class N/QGMNX — Class I/QGMIX — CLASS R6/QGMRX
Before you invest, you may want to review the Fund’s prospectus, which contains more information about the Fund and its risks. You can find the Fund’s prospectus, reports to shareholders, and other information about the Fund, including the statement of additional information, online at https://funds.aqr.com/fund-documents. You can also get this information at no cost by calling (866) 290-2688 or by sending an email to [email protected]. The Fund’s
prospectus and
statement of additional information, each dated May 1, 2022, as amended and supplemented from time to time, and the Fund’s most recent
shareholder report, dated December 31, 2021, are all incorporated by reference to this summary prospectus.
Investment Objective
The AQR
Macro Opportunities Fund (the “Fund”) seeks positive absolute returns.
As
further described under “Details About the AQR Macro Opportunities Fund” in the Fund’s prospectus, a “positive absolute return” seeks to earn a
positive total return over a reasonable period of time regardless of market conditions or
general market direction.
Fees and Expenses of the Fund
This
table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy and hold shares of the Fund.
Annual Fund Operating Expenses (expenses that you pay each year as a percentage of the
value of your investment)
| |
Class N |
Class I |
Class R6 |
| Management Fee |
1.00% |
1.00% |
1.00% |
| Distribution (12b-1) Fee |
0.25% |
None |
None |
| Other Expenses |
|
|
|
| Interest expense |
0.01% |
0.01% |
0.01% |
| All other expenses1,2 |
1.08% |
1.04%
|
0.96% |
| Total Other Expenses |
1.09% |
1.05% |
0.97% |
| Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses3
|
0.01% |
0.01% |
0.01% |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses2
|
2.35% |
2.06% |
1.98% |
| Less: Expense Reimbursements4
|
0.88% |
0.84% |
0.86% |
| Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses after Expense Reimbursements2,5 |
1.47% |
1.22% |
1.12% |
1 All other expenses have been restated to reflect the exclusion of certain non-recurring expenses that
occurred during the fiscal year-ended December 31, 2021.
2 The Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses and Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses after Expense
Reimbursements do not correlate to the Ratio to Average Net Assets of Expenses, Before Reimbursements and/or Waivers given in the Fund’s most recent annual report which does
not include the restatement of all other expenses.
3 Acquired Fund Fees and Expenses reflect the expenses incurred indirectly by the Fund as a result of the
Fund's investments in underlying money market mutual funds, exchange-traded funds or other pooled investment vehicles.
4 The
Adviser has contractually agreed to reimburse operating expenses of the Fund in an amount
sufficient to limit certain Specified Expenses at no more than 0.20% for Class N Shares and Class I Shares and 0.10% for Class R6 Shares. "Specified Expenses" for this purpose
include all Fund operating expenses other than management fees and 12b-1 fees and exclude interest, taxes, dividends on short sales, borrowing costs, acquired fund fees and expenses, interest expense relating to short sales, expenses related to class action claims, contingent expenses related to tax reclaim receipts and extraordinary expenses. This agreement (the “Expense Limitation Agreement”) will continue at least through April 30, 2023. The Expense Limitation Agreement may be
terminated with the consent of the Board of Trustees, including a majority of the Non-Interested Trustees of the Trust. The Adviser is entitled to recapture any expenses reimbursed during the thirty-six month period following the
end of the month during which the Adviser reimbursed expenses, provided that the amount
recaptured may not cause the Specified Expenses attributable to a share class of the Fund during a year in which a repayment is made to exceed either of (i) the applicable limits in
effect at the time of the reimbursement and (ii) the applicable limits in effect at the time of recapture.
AQR Funds–Summary Prospectus2
5 Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses after Expense Reimbursements are 1.46% for Class N Shares, 1.21%
for Class I Shares and 1.11% for Class R6 Shares if interest expense is not included.
Example: This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with
the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in
the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and
that the Fund’s operating expenses remain the same and takes into account the effect of the Expense Limitation Agreement through April 30, 2023, as discussed in Footnote No. 4 to the Fee Table. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower,
based on these assumptions your costs would be:
| |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years |
| Class N Shares |
$150 |
$649 |
$1,176 |
$2,619 |
| Class I Shares |
$124 |
$565 |
$1,031 |
$2,323 |
| Class R6 Shares |
$114 |
$538 |
$988 |
$2,237 |
Portfolio Turnover: The Fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells
securities (or “turns over” its portfolio). A higher portfolio turnover may indicate higher transaction costs and may result in higher taxes when shares are held in a taxable account. These costs, which are not reflected in annual fund operating expenses or in the
example, affect the Fund’s performance. During the most recent fiscal year, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate was 0% of the average value of its portfolio. In accordance
with industry practice, derivative instruments and instruments with a maturity of one year or less at the time of acquisition are excluded from the calculation of the portfolio
turnover rate which leads to the 0% portfolio turnover rate reported above. If these instruments were included in the calculation, the Fund would have a high portfolio turnover rate (as discussed below under “Principal Investment Strategies of the Fund”).
Principal Investment Strategies of the Fund
The Fund pursues its investment objective by investing globally across a wide range of asset classes, including equities, fixed income, currencies and commodities, and may take both long and short positions in each of the asset classes or
Instruments (as defined below). The Fund has the flexibility to shift its allocation across asset classes and markets around the world, including emerging markets, based on the Adviser’s assessment of their relative attractiveness.
The Adviser uses a bottom up process
that considers several primary indicators of attractiveness in determining whether to take a long and/or short position in an Instrument or asset class: macroeconomic data, value,
deep value, momentum, carry and defensive. The Adviser may utilize more idiosyncratic indicators of attractiveness beyond these broad themes.
Macroeconomic Data: The Adviser seeks to evaluate the impact of macroeconomic news and macroeconomic momentum on the attractiveness of Instruments and asset classes around the world. Macroeconomic themes considered include, but are
not limited to, business cycles, international trade, monetary policy, investor sentiment and asset-specific fundamentals.
The evaluation of macroeconomic attractiveness includes both quantitative and qualitative components.
•Quantitative analysis
measures an Instrument’s attractiveness based on the current level and historical evolution of key macroeconomic measures. These measures include, but are not limited to,
growth and inflation forecasts, demand for exports, central bank actions and equity market performance.
•Qualitative input adds a
perspective not available through quantitative analysis. These considerations include, but are not limited to, the Adviser’s assessment of fiscal and monetary policy, trade policy, geo-political risks and
supply-and-demand conditions.
Value: Value strategies favor investments that appear cheap over those that appear expensive based on
fundamental measures related to price, seeking to capture the tendency for relatively cheap assets to outperform relatively expensive assets. The Fund will seek to buy assets that are cheap and sell those that are expensive relative to similar investments
globally and relative to their historical averages. Examples of value measures include using price-to-earnings and price-to-book ratios for selecting equities.
Deep Value: Deep value strategies favor investments that exhibit extreme market dislocations based on price
moves and valuation signals that appear extreme relative to history. Once an investment opportunity is identified, the Adviser evaluates qualitative factors
to determine whether the opportunity represents a true dislocation. By combining a systematic screening process with discretionary oversight, the attractiveness of an
investment’s over/under valuation is determined using both quantitative and qualitative processes. Contrasted with value opportunities, deep value opportunities are typically
more idiosyncratic with availability varying over time and may require looking broadly across many different markets to uncover. Examples of deep value quantitative measures include extreme dislocations in price-to-earnings and price-to-book ratios for
selected equities. Examples of deep value qualitative considerations include fiscal and monetary policy, geo-political risks, and supply-and-demand dynamics, among others.
Momentum: Momentum strategies favor investments that have performed relatively well over those that have
underperformed over the medium-term, seeking to capture the tendency that an asset’s recent performance will continue in the near future. The Fund will seek to buy assets that recently outperformed and sell those that recently underperformed
relative to similar investments globally and relative to their historical averages. Examples of momentum measures include simple price momentum for selecting equities and price- and yield-based momentum for selecting bonds.
AQR Funds–Summary Prospectus3
Carry: Carry
strategies favor investments with higher yields over those with lower yields, seeking to capture the tendency for higher yielding assets to provide higher returns than
lower-yielding assets. The Fund will seek to buy high-yielding assets and sell low-yielding assets relative to similar investments globally and relative to their historical
averages. An example of carry measures includes using interest rates to select currencies and bonds.
Defensive:
Defensive strategies favor investments with low-risk characteristics over those with high-risk characteristics, seeking to capture the tendency for lower risk and higher-quality
assets to generate higher risk-adjusted returns than higher risk and lower-quality assets. The Fund will seek to buy low-risk, high-quality assets and sell high-risk, low-quality
assets. An example of a defensive measure includes the profitability of companies in an index.
Portfolio Construction
Each of the primary indicators of attractiveness (macroeconomic data, value, deep value, momentum, carry and defensive) is
taken into consideration in determining whether the Fund’s position in the Instrument in question should be long or short. The owner of a long position in an Instrument will
benefit from an increase in the price of the underlying instrument. The owner of a short position in an Instrument will benefit from a decrease in the price of the underlying
instrument. The Fund goes long Instruments deemed overall attractive, and short Instruments deemed overall unattractive. When there is strong agreement among the indicators, the long or short position in an Instrument or asset class will be given a greater weighting
in the portfolio, while conflicting indicators will result in a lesser weighting. Individual investments are bought or sold in accordance with periodic re-ranking and rebalancing, the frequency of which is expected to vary depending on the Adviser’s
assessment of the investment’s attractiveness and global market conditions.
The Adviser allocates among the
different asset classes based on their contribution to the Fund’s risk budget — i.e., the targeted level of risk or
volatility. The allocation process allows the Adviser to make tactical risk adjustments while maintaining long-term strategic risk weights. Within each asset class, a portion of the Fund’s target risk is allocated based on the macroeconomic indicators, with the remainder allocated based on the value, deep value, momentum, carry and defensive
indicators. These relative weights, and the relative weights to each of the value, deep value, momentum, carry and defensive indicators, can vary depending on market
conditions.
The Adviser generally expects that the Fund’s performance will have a low correlation to the performance
of the general global equity, fixed income, currency and commodity markets over any given market cycle; however, the Fund’s performance may correlate to the performance of any one or more of those markets over short-term periods.
The Adviser, on average, will target
an annualized volatility level for the Fund of 10%. Volatility is a statistical measurement
of the dispersion of returns of a security or fund or index, as measured by the annualized standard deviation of its returns. The Adviser expects that the
Fund’s targeted annualized forecasted volatility will typically range between 5% and
15%; however, the actual or realized volatility level for longer or shorter periods may be materially higher or lower depending on market conditions. Higher volatility generally indicates higher risk. Actual or realized volatility can and will differ from the forecasted or target volatility described above.
Instruments
In seeking to achieve its investment objective, the Fund will enter into both long and short positions
using derivative instruments. The Adviser generally expects that the Fund will have exposure in long and short positions across all four major asset classes
(commodities, currencies, fixed income and equities), but at any one time the Fund may emphasize one or two of the asset classes or a limited number of exposures within an asset
class.
The Fund invests primarily in a portfolio of futures contracts, futures-related
instruments, forwards, swaps, equity securities and government bonds, including, but not limited to, global developed and emerging market equity index futures, swaps on equity index futures, equity swaps and options on equity indices, global developed and emerging market currency forwards,
commodity futures, forwards and swaps, global developed fixed income futures, bond and interest rate futures and swaps and credit default index swaps, global developed and emerging market common stocks, preferred stocks, depositary receipts
and shares or interests in real estate investment trusts (“REITs”) or REIT-like entities and global developed and emerging market foreign government bonds (including
inflation-linked bonds, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (“TIPS”)) (collectively, the “Instruments”). The Fund will either invest directly in
the Instruments or indirectly by investing in the Subsidiary (as described below) that invests in the Instruments. The Fund may invest in or have exposure to issuers of any size. The
Fund may invest in or have exposure to U.S. or non-U.S. issuers, including in developed and emerging markets. The Fund may also invest in exchange-traded funds and exchange-traded
notes.
Futures and forward contracts are contractual agreements to buy or sell a particular
currency, commodity or financial instrument at a pre-determined price in the future. The Fund’s use of futures contracts, forward contracts, swaps and certain other Instruments will have the economic effect of financial leverage. Financial leverage magnifies exposure to the swings in
prices of an asset class underlying an Instrument and results in increased volatility, which means the Fund will have the potential for greater gains, as well as the potential for greater losses, than if the
Fund did not use Instruments that have a leveraging effect. For example, if the
Adviser seeks to gain enhanced exposure to a specific asset class through an Instrument providing leveraged exposure to the class and that Instrument increases in value, the gain to the Fund will be
magnified. If that investment decreases in value, however, the loss to the Fund will be magnified. As a result of the Fund’s strategy, the Fund may have highly leveraged exposure to one or more asset classes at times. A decline in the Fund’s assets
AQR
Funds–Summary Prospectus4
due to losses magnified by the Instruments providing leveraged exposure may require the Fund to liquidate
portfolio positions to satisfy its obligations or to meet redemption requests when it may not be advantageous to do so. There is no assurance that the Fund’s use of Instruments providing enhanced exposure will enable the Fund to achieve its investment
objective.
The
Fund’s strategy engages in frequent portfolio trading which may result in a higher portfolio turnover rate than a fund with less frequent trading, and correspondingly greater
brokerage commissions and other transactional expenses, which are borne by the Fund, and may have adverse tax consequences. The Adviser utilizes portfolio optimization techniques to determine the frequency of trading, taking into account the transaction costs associated with trading each Instrument, and
employs sophisticated proprietary trading techniques in an effort to mitigate trading costs and execution impact on the Fund.
A significant portion of the assets of the Fund may be invested directly or indirectly in money market
instruments, which may include, but are not limited to, U.S. Government securities, U.S. Government agency securities, short-term fixed income securities, overnight and/or fixed term repurchase agreements, money market fund shares, interests in short-term investment
funds, short-term bond fund shares, and cash and cash equivalents with one year or less term to maturity. These cash or cash equivalent holdings serve as collateral for the
positions the Fund takes and also earn income for the Fund. The Fund may also enter into repurchase and reverse repurchase agreements. Under a repurchase agreement the Fund buys
securities that the seller has agreed to buy back at a specified time and at a set price. Under a reverse repurchase agreement, the Fund sells securities to another party and agrees to repurchase them at a particular date and price. Leverage
may be created when the Fund enters into reverse repurchase agreements, engages in futures and swap transactions or uses certain other derivative instruments. While the Fund
normally does not engage in any direct borrowing, leverage is implicit in the futures and other derivatives it trades.
The Fund intends to make investments through the Subsidiary and may invest up to 25% of its total assets in the Subsidiary. The Subsidiary is a wholly-owned and controlled subsidiary of the Fund, organized under the laws of the Cayman
Islands as an exempted company. Generally, the Subsidiary will invest primarily in commodity futures, commodity forwards, commodity swaps, swaps on commodity futures and other
commodity-linked derivative Instruments but it may also invest in financial futures, option and swap contracts, fixed income securities, pooled investment vehicles, including those
that are not registered pursuant to the 1940 Act, and other investments intended to serve as margin or collateral for the Subsidiary’s derivative positions. The Fund will invest in the Subsidiary in order to gain exposure to the commodities markets within the limitations of the federal tax laws, rules and regulations that apply to registered investment companies. Unlike the Fund, the Subsidiary may invest without limitation in commodity-linked derivatives, however, the Fund and the
Subsidiary will comply
with Rule 18f-4 on a
consolidated basis with respect to investments in derivatives. In addition, the Fund and the Subsidiary will be subject to the same fundamental investment restrictions on a consolidated basis and, to the
extent applicable to the investment activities of the Subsidiary, the Subsidiary will follow the same
compliance policies and procedures as the Fund. Unlike the Fund, the Subsidiary will not seek to qualify as a regulated investment company under Subchapter M of the Code. The Fund is the sole shareholder of the Subsidiary and does not expect shares of the Subsidiary to be offered or sold to
other investors.
Principal Risks of Investing in the Fund
Risk is inherent in all investing. The value of your investment in the Fund, as well as the amount of return you receive on your investment, may fluctuate significantly from day to day and over time. You may lose part or all of your investment in
the Fund or your investment may not perform as well as other similar investments. The Fund is not a complete investment program and
should be considered only as one part of an investment portfolio. The Fund is more appropriate for long-term investors who can bear the risk of
short-term NAV fluctuations, which at times, may be significant and rapid, however, all investments long- or short-term are subject to risk of
loss. The following is a summary description of certain risks of investing in the Fund. The order of the below
risk factors does not indicate the significance of any particular risk factor.
Commodities Risk: Exposure to the commodities markets may subject the Fund to greater volatility than investments in
traditional securities. The value of commodity-linked derivative investments may be affected by changes in overall market movements, commodity index
volatility, changes in interest rates, or factors affecting a particular industry or
commodity, such as drought, floods, weather, embargoes, tariffs and international economic, political and regulatory developments. Additionally, the Fund may gain exposure to the commodities markets through investments in exchange-traded notes, the value
of which may be influenced by, among other things, time to maturity, level of supply and demand for the exchange-traded note, volatility and lack of liquidity in underlying markets, the performance of the reference instrument,
changes in the issuer’s credit rating and economic, legal, political or geographic events that affect the reference instrument.
Common Stock Risk:
The Fund may invest in, or have exposure to, common stocks. Common stocks are subject to greater fluctuations in market value than certain other asset classes as a result of such
factors as a company’s business performance, investor perceptions, stock market trends and general economic conditions.
Counterparty Risk:
The Fund may enter into various types of derivative contracts. Many of these derivative contracts will be privately negotiated in the over-the-counter market. These contracts also
involve exposure to credit risk, since contract performance depends in part on the financial condition of the counterparty. If a privately negotiated over-the-counter contract
calls for payments by the Fund, the Fund must be prepared to make such payments when due. In addition, if a
counterparty’s creditworthiness declines, the Fund may not receive payments owed under the contract, or such payments may be delayed under such circumstances and the value of agreements with such counterparty can be expected to decline,
potentially resulting in losses to the Fund.
AQR Funds–Summary Prospectus5
Credit Default Index Swap Agreements Risk: The Fund may enter into credit default index swap agreements as a “buyer” or “seller” of credit
protection. Credit default index swap agreements involve special risks because they may be difficult to value, are highly susceptible to liquidity and credit risk, and
generally pay a return to the party that has paid the premium only in the event of an actual default by the issuer of the underlying obligation (as opposed to a credit downgrade or
other indication of financial difficulty).
Credit Risk: Credit risk refers to the possibility that the issuer of a security or the issuer of the
reference asset of a derivative instrument will not be able to make principal and interest payments when due. Changes in an issuer’s credit rating or the market’s perception of an issuer’s creditworthiness may also affect the value of the Fund’s investment in that issuer. Securities rated in the four highest categories by the rating agencies are considered investment grade but they may also
have some speculative characteristics. Investment grade ratings do not guarantee that the issuer will not default on its payment obligations or that bonds will not otherwise lose value.
Currency Risk: Currency risk is the risk that changes in currency exchange rates will negatively affect
securities denominated in, and/or receiving revenues in, foreign currencies. The liquidity and trading value of foreign currencies could be affected by global economic factors, such as inflation, interest rate levels, and trade balances among countries, as well as the actions of sovereign governments and central banks. Adverse changes in currency exchange rates (relative to the U.S.
dollar) may erode or reverse any potential gains from the Fund’s investments in securities denominated in a foreign currency or may widen existing losses.
Derivatives Risk: In general, a derivative instrument typically involves leverage, i.e., it provides exposure to potential gain or loss from a change in the level of the market price of the underlying security, currency or commodity (or a basket or index) in a notional amount that exceeds the amount of cash or assets required to establish or maintain the derivative instrument.
Adverse changes in the value or level of the underlying asset or index, which the Fund may not directly own, can result in a loss to the Fund substantially greater than the amount invested in the derivative itself. The use of derivative instruments also exposes the Fund to additional risks and transaction costs. These instruments come in many varieties and have a wide range
of potential risks and rewards, and may include, as further described in the section entitled “Principal Investment Strategies of the Fund,” futures contracts, forward
contracts, options and swaps. A risk of the Fund’s use of derivatives is that the fluctuations in their values may not correlate perfectly with the overall securities
markets.
Emerging Market Risk: The Fund intends to have exposure to emerging markets. Emerging markets are riskier than more developed markets because
they tend to develop unevenly and may never fully develop. Investments in emerging markets may be considered speculative. Emerging markets are more likely to experience
hyperinflation and currency devaluations, which adversely affect returns to U.S. investors. In addition, many emerging securities markets have far lower trading volumes and less liquidity than developed markets. Emerging markets generally have less stable political systems, less
developed securities settlement procedures and may require the establishment of special custody arrangements. Emerging securities markets generally do not have the level of market efficiency and strict standards in accounting and securities
regulation as developed markets, which could impact the Adviser's ability to evaluate these securities and/or impact Fund performance.
Foreign Investments Risk: Foreign investments often involve special risks not present in U.S. investments that can increase the chances that the Fund
will lose money. These risks include:
•The Fund generally holds its foreign instruments and cash in foreign banks and securities depositories, which may be
recently organized or new to the foreign custody business and may be subject to only limited or no regulatory oversight.
•Changes in foreign currency
exchange rates can affect the value of the Fund’s portfolio.
•The economies of certain foreign markets may not compare favorably with the economy of the United States with respect to
such issues as growth of gross national product, reinvestment of capital, resources and balance of payments position.
•The governments of certain countries may prohibit or impose substantial restrictions on foreign investments in their
capital markets or in certain industries.
•Many foreign governments do not supervise and regulate stock exchanges, brokers and the sale of securities to the
same extent as does the United States and may not have laws to protect investors that are comparable to U.S. securities laws.
•Settlement and clearance procedures in certain foreign markets may result in delays in payment for or delivery of securities
not typically associated with settlement and clearance of U.S. investments.
•The regulatory, financial reporting, accounting, recordkeeping and auditing standards of foreign countries may differ, in
some cases significantly, from U.S. standards.
Forward and Futures Contract Risk: The successful use of forward and futures contracts draws upon the Adviser’s skill and experience with respect to such instruments and is subject to special risk considerations. The primary
risks associated with the use of forward and futures contracts, which may adversely affect the Fund’s NAV and total
return, are (a) the imperfect correlation between the change in market value of the instruments held by
the Fund and the price of the forward or futures contract; (b) possible lack of a liquid secondary market for a forward or futures contract and the resulting inability to
close a forward or futures contract when desired; (c) losses caused by unanticipated market movements, which are potentially unlimited; (d) the Adviser’s inability to predict correctly the direction of securities prices, interest rates, currency exchange rates and other
economic factors; (e) the possibility that the counterparty will default in the performance of its obligations; and (f) if the Fund has insufficient cash, it may have to
sell securities from its portfolio to meet daily variation margin requirements, and the Fund may have to sell securities at a time when it may be disadvantageous to do
so.
AQR Funds–Summary Prospectus6
Hedging Transactions Risk: The Adviser from time to time employs various hedging techniques. The success of the Fund’s hedging strategy will be subject to the Adviser’s ability to correctly assess the degree of correlation between the performance of the instruments used in the hedging
strategy and the performance of the investments in the portfolio being hedged. Since the characteristics of many securities change as markets change or time passes, the success of
the Fund’s hedging strategy will also be subject to the Adviser’s ability to continually recalculate, readjust, and execute hedges in an efficient and timely manner. For a variety of
reasons, the Adviser may not seek to establish a perfect correlation between such hedging instruments and the portfolio holdings being hedged. Such imperfect correlation may prevent the Fund from
achieving the intended hedge or expose the Fund to risk of loss. In addition, it is not possible to hedge fully or perfectly against any risk, and hedging entails its own costs (such as trading commissions and fees).
High Portfolio Turnover Risk: The investment techniques and strategies utilized by the Fund, including
investments made on a shorter-term basis or in derivative instruments or instruments with a maturity of one year or less at the time of acquisition, may result in frequent portfolio trading and high portfolio turnover. High portfolio turnover rates will cause the Fund to incur higher levels of brokerage fees and commissions, which may reduce performance, and may cause higher levels of
current tax liability to shareholders in the Fund.
Interest Rate
Risk: Interest rate risk is the risk that prices of fixed income securities generally increase when interest rates decline and decrease when interest rates increase. The Fund may lose money if short-term or long-term interest rates rise
sharply or otherwise change in a manner not anticipated by the Adviser.
Investment in
Other Investment Companies Risk: As with other investments, investments in other investment companies,
including exchange-traded funds (“ETFs”), are subject to market and manager risk. In addition, if the Fund acquires shares of investment companies, shareholders bear both their proportionate share of expenses in the Fund (including management and
advisory fees) and, indirectly, the expenses of the investment companies. The Fund may invest in money market mutual funds. An investment in a money market mutual fund is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency. Although money market mutual funds that invest in U.S. government securities seek to preserve the value of the Fund’s investment at $1.00 per share, it
is possible to lose money by investing in a stable NAV money market mutual fund. Moreover, prime money market mutual funds are required to use floating NAVs that do not preserve the value
of the Fund’s investment at $1.00 per share.
Leverage Risk: As part of the Fund’s principal investment strategy, the Fund will make investments in
futures contracts, forward contracts, options, swaps and other derivative instruments. These derivative instruments provide the economic effect of financial leverage by creating additional investment exposure to the underlying instrument, as well as the potential
for greater loss. If the Fund uses leverage through activities such as purchasing derivative
instruments, the Fund has the risk that losses may exceed the net assets of the Fund. The net
asset value of the Fund while employing leverage will be more volatile and sensitive to market movements.
Manager Risk: If
the Adviser makes poor investment decisions, it will negatively affect the Fund’s
investment performance.
Market Risk: Market risk is the risk that the markets on which the Fund’s investments trade will increase or decrease in value.
Prices may fluctuate widely over short or extended periods in response to company, market or economic news. Markets also tend to move in cycles, with periods of rising and falling
prices. If there is a general decline in the securities and other markets, your investment in the Fund may lose value, regardless of the individual results of the securities and
other instruments in which the Fund invests.
Mid-Cap Securities Risk: The Fund may invest in, or have exposure to, the securities of mid-cap companies.
The prices of securities of mid-cap companies generally are more volatile than those of large capitalization companies and are more likely to be adversely affected than large-cap companies by changes in earnings results and investor expectations or poor economic
or market conditions, including those experienced during a recession.
Model and Data
Risk: Given the complexity of the investments and strategies of the Fund, the Adviser relies heavily on quantitative models and information and data supplied or made available by third parties (“Models
and Data”). Models and Data are used to construct sets of transactions and investments, to provide risk management insights, and to assist in hedging the Fund’s investments.
When Models and Data prove to be incorrect or incomplete, including because data is stale, missing or
unavailable, any decisions made in reliance thereon expose the Fund to potential risks. Similarly, any hedging based on faulty Models and Data may prove to be unsuccessful. Some of the models used by the Adviser for the Fund are predictive in nature. The use of predictive models has inherent risks. Because predictive models are
usually constructed based on historical data supplied by third parties or otherwise, the success of relying on such models may depend on the accuracy and reliability of the supplied historical data. The Fund bears the risk that the quantitative models used by the Adviser will not be successful in selecting investments or in determining the weighting of investment positions that will enable
the Fund to achieve its investment objective.
All models rely on correct data inputs. If incorrect data is entered into even a well-founded model, the resulting information
will be incorrect. However, even if data is inputted correctly, “model prices” will often differ substantially from market prices, especially for instruments with complex characteristics, such as derivative instruments.
AQR Funds–Summary Prospectus7
The Fund is unlikely to be successful unless the assumptions underlying the models are realistic and either
remain realistic and relevant in the future or are adjusted to account for changes in the overall market environment. If such assumptions are inaccurate or become inaccurate and are not promptly adjusted, it is likely that profitable trading signals will not be
generated, and major losses may result.
The
Adviser, in its sole discretion, will continue to test, evaluate and add new models, which
may result in the modification of existing models from time to time. There can be no assurance that model modifications will enable the Fund to achieve its investment objective.
Momentum Style Risk: Investing in or having exposure to securities with positive momentum entails investing
in securities that have had above-average recent returns. These securities may be more volatile than a broad cross-section of securities. In addition, there may be periods during which the investment performance of the Fund while using a momentum strategy may
suffer.
Non-Diversified Status Risk: The Fund is a non-diversified fund. Because the Fund may invest in securities of a smaller number of issuers, the Fund may
be more exposed to the risks associated with and developments affecting an individual issuer than a fund that invests more widely, which may, therefore, have a greater impact on
the Fund’s performance.
Options Risk: An option is an agreement that, for a premium payment or fee, gives the option holder (the purchaser) the right but not the
obligation to buy (a “call option”) or sell (a “put option”) the underlying asset (or settle for cash an amount based on an underlying asset, rate, or
index) at a specified price (the “exercise price”) during a period of time or on a specified date. Investments in options are considered speculative. When the Fund
purchases an option, it may lose the premium paid for it if the price of the underlying security or other assets decreased or remained the same (in the case of a call option) or increased or remained the same (in the case of a put option). If a put or call option purchased by the Fund
were permitted to expire without being sold or exercised, its premium would represent a loss to the Fund.
Repurchase Agreements Risk: The Fund may invest in repurchase agreements. When entering into a repurchase agreement, the Fund essentially makes a
short-term loan to a qualified bank or broker-dealer. The Fund buys securities that the seller has agreed to buy back at a specified time and at a set price that includes interest.
There is a risk that the seller will be unable to buy back the securities at the time required and the Fund could experience delays in recovering amounts owed to it.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements Risk: Reverse repurchase agreements involve the sale of securities held by the Fund with an agreement to repurchase the securities
at an agreed-upon price, date and interest payment. Reverse repurchase agreements involve the risk that the other party may fail to return the securities in a timely manner or at
all. The Fund could lose money if it is unable to recover the securities and the value of the collateral held by the Fund, including the value of the investments made with cash collateral, is less than the value of securities. These events could also trigger adverse tax
consequences to the Fund. Furthermore, reverse repurchase agreements involve the risks that (i) the interest income earned in the investment of the proceeds will be less than the interest expense, (ii) the market value of the securities
retained in lieu of sale by the Fund may decline below the price of the securities the Fund has sold but is obligated to repurchase, and (iii) the market value of the securities sold will decline below the price at which the Fund is required to repurchase them. In addition, the use of reverse repurchase agreements may be regarded as leveraging.
Short Sale Risk:
The Fund may take a short position in a derivative instrument, such as a future, forward or swap. A short position in a derivative instrument involves the risk of a theoretically
unlimited increase in the value of the underlying instrument, which could cause the Fund to suffer a (potentially unlimited) loss. Short sales also involve transaction and financing costs that will reduce potential Fund gains and increase potential Fund losses.
Small-Cap Securities Risk: Investments in or exposure to the securities of companies with smaller market
capitalizations involve higher risks in some respects than do investments in securities of larger companies. For example, prices of such securities are often more volatile than prices of large capitalization securities. In addition, due to thin trading in some such securities, an investment in these securities may be less liquid (i.e., harder to sell) than that of larger capitalization securities. Smaller capitalization companies also fail more often than
larger companies and may have more limited management and financial resources than larger companies.
Sovereign Debt
Risk: The Fund may invest in, or have exposure to, sovereign debt instruments. These investments are subject to
the risk that a governmental entity may delay or refuse to pay interest or repay principal on its sovereign debt, due, for example, to cash flow problems, insufficient foreign
currency reserves, political considerations, the relative size of the governmental entity’s debt position in relation to the economy or the failure to put in place economic
reforms required by the International Monetary Fund or other multilateral agencies. If a governmental entity defaults, it may ask for more time in which to pay or for further loans. There is no legal process for collecting sovereign debt that a government does not pay nor
are there bankruptcy proceedings through which all or part of the sovereign debt that a governmental entity has not repaid may be collected.
Subsidiary Risk:
By investing in the Subsidiary, the Fund is indirectly exposed to the risks associated with
the Subsidiary’s investments. The commodity-related instruments held by the Subsidiary are generally similar to those that are permitted to be held by the Fund and are subject to the same risks that apply to
similar investments if held directly by the Fund. There can be no assurance that the investment objective of the Subsidiary will be achieved. The Subsidiary is not registered under
the 1940 Act, and,
unless otherwise noted in this prospectus, is not subject to all the investor protections of the 1940 Act. However, the Fund wholly owns and controls the Subsidiary, and the Fund and the Subsidiary are both managed by the Adviser, making it unlikely that the Subsidiary will take action contrary to the interests of the Fund and its shareholders. The
AQR Funds–Summary Prospectus8
Board of Trustees has oversight responsibility for the investment activities of the Fund, including its
investment in the Subsidiary, and the Fund’s role as sole shareholder of the Subsidiary. The Fund and the Subsidiary will be subject to the
same investment restrictions and limitations on a consolidated basis, and to the extent applicable to the investment activities of the Subsidiary, the Subsidiary will follow the same compliance policies and procedures as the Fund. Unlike the Fund, the
Subsidiary will not seek to qualify as a regulated investment company under Subchapter M of
the Code. Changes in the laws of the United States and/or the Cayman Islands could result in the inability of the Fund and/or the
Subsidiary to operate as
described in this prospectus and the SAI and could adversely affect the Fund.
Swap Agreements Risk: Swap agreements involve the risk that the party with whom the Fund has entered into
the swap will default on its obligation to pay the Fund. Additionally, certain unexpected market events or significant adverse market movements could result in the Fund not holding enough assets to be able to meet its obligations under the agreement. Such
occurrences may negatively impact the Fund’s ability to implement its principal investment strategies and could result in losses to the Fund.
Tax Risk: In order
for the Fund to qualify as a regulated investment company under Subchapter M of the Code, the
Fund must derive at least 90 percent of its gross income each taxable year from qualifying income, which is described in more detail in the SAI. Income from certain commodity-linked derivative instruments in which the Fund invests is not considered
qualifying income. The Fund will therefore restrict its income from direct investments in commodity-linked derivative instruments that do not generate qualifying income, such as commodity-linked swaps, to a maximum of 10 percent of its gross
income.
The Fund’s investment in the Subsidiary is expected to provide the Fund with exposure to the commodities markets within the limitations of the federal tax requirements of Subchapter M. Changes in the laws of the United States and/or the Cayman
Islands could result in the inability of the Fund and/or the Subsidiary to operate as described in this prospectus and the SAI and could adversely affect the Fund. For example, the Cayman Islands
does not currently impose any income, corporate or capital gains tax, estate duty, inheritance tax, gift tax or withholding tax on the Subsidiary. If Cayman Islands law changes such that the Subsidiary must pay
Cayman Islands taxes, Fund shareholders would likely suffer decreased investment returns.
TIPS and Inflation-Linked Bonds Risk: The value of inflation-protected securities generally fluctuates in response to changes in real interest rates, which are in
turn tied to the relationship between nominal interest rates and the rate of inflation. Therefore, if inflation were to rise at a faster rate than nominal interest rates, real
interest rates might decline, leading to an increase in the value of inflation-protected securities. In contrast, if nominal interest rates increased at a faster rate than inflation, real interest rates might rise, leading to a decrease in the value of inflation-protected securities. If the Fund purchases inflation-protected securities in the secondary market whose principal values have been adjusted upward due
to inflation since issuance, the Fund may experience a loss if there is a subsequent period of deflation. The inflation-protected securities markets are generally much smaller and
less liquid than the nominal bonds from the same issuers and as such can suffer losses during times of economic stress or illiquidity.
U.S. Government Securities Risk: Treasury obligations may differ in their interest rates, maturities, times of issuance and other characteristics.
Obligations of U.S. Government agencies and authorities are supported by varying degrees of credit but generally are not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government.
No assurance can be given that the U.S. Government will provide financial support to its agencies and authorities if it is not obligated by law to do so. Certain of the government agency securities the Fund may purchase are backed only by the credit of the government agency and not by
full faith and credit of the United States.
Value Style Risk: Investing in or having exposure to “value” securities (including those identified by the Adviser as having "deep value"),
as described in the section titled "Principal Investment Strategies of the Fund," presents the risk that the securities may never reach what the Adviser believes are their full market values, either because the market fails to recognize what the Adviser considers
to be the security’s true value or because the Adviser misjudged that value. In addition, there may be periods during which the investment performance of the Fund while using a value or deep
value strategy may suffer.
Volatility Risk: The Fund may have investments that appreciate or decrease significantly in value over
short periods of time. This may cause the Fund’s net asset value per share to experience significant increases or declines in value over short periods of time, however, all investments long- or short-term are subject to risk of loss.
Performance Information
The performance information below shows summary performance information for the Fund in a bar chart and an average annual total returns table. The
information shows you how the Fund’s performance has varied year by year and provides some indication of the risks of investing in the Fund. The Fund's returns prior to
October 19, 2021 as reflected in the bar chart and the table are those of the Fund when it followed different investment strategies under the name "AQR Global Macro Fund."
The
Fund’s past performance (before and after taxes), as provided by the bar chart and performance table that follows, is not an indication of future
results. Updated information on the Fund’s performance, including its current
NAV
per share, can be obtained by visiting https://funds.aqr.com.
AQR Funds–Summary Prospectus9
Class I Shares—Total Returns
The bar chart below provides an illustration of how the Fund’s performance has varied in each of
the indicated calendar years.
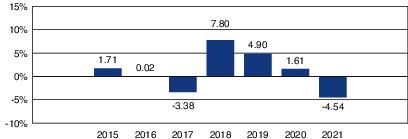
| Highest Quarterly Return |
Lowest Quarterly Return | ||
| 6.40% |
3/31/18 |
-4.62% |
9/30/21 |
Average Annual Total Returns as of December 31, 2021
The following table compares the Fund’s average annual total returns for Class I Shares, Class N Shares and Class R6 Shares for the periods ended December 31, 2021 to the ICE BofAML US 3-Month Treasury Bill Index. You cannot invest directly in an index. The table includes all applicable fees and sales charges.
| |
One
Year |
Five
Year |
Since
Inception |
Share Class
Inception
Date |
| AQR Macro Opportunities Fund—Class I |
|
|
|
|
| Return Before Taxes |
-4.54% |
1.17% |
0.92% |
04/08/2014 |
| Return After Taxes on Distributions |
-5.12% |
0.71% |
0.24% |
|
| Return After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares |
-2.69% |
0.74% |
0.55% |
|
| ICE BofAML US 3-Month Treasury Bill Index
(reflects no deductions for fees, expenses or
taxes) |
0.05% |
1.14% |
0.79% |
|
| AQR Macro Opportunities Fund—Class N |
|
|
|
|
| Return Before Taxes |
-4.82% |
0.93% |
0.68% |
04/08/2014 |
| ICE BofAML US 3-Month Treasury Bill Index
(reflects no deductions for fees, expenses or
taxes) |
0.05% |
1.14% |
0.79% |
|
| AQR Macro Opportunities Fund—Class R6 |
|
|
|
|
| Return Before Taxes |
-4.51% |
1.24% |
1.43% |
09/02/2014 |
| ICE BofAML US 3-Month Treasury Bill Index
(reflects no deductions for fees, expenses or
taxes) |
0.05% |
1.14% |
0.83% |
|
After-tax returns are calculated using the historical highest individual marginal tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. In some
cases, the return after taxes on distributions and sale of Fund shares may exceed the return before taxes and the return after taxes on distributions due to an assumed benefit from
any losses on a sale of Fund shares at the end of the measurement period. Actual after-tax returns depend on an investor’s tax situation and may differ from those shown, and after-tax returns
are not relevant to investors who hold their Fund shares through tax-deferred arrangements such as 401(k) plans or individual retirement accounts. After-tax returns are for Class I Shares only. After-tax returns for other classes will vary.
Investment Manager
The Fund’s investment manager is AQR Capital Management, LLC.
Portfolio Managers
| Name |
Portfolio Manager
of the Fund Since |
Title |
| John M. Liew, Ph.D., M.B.A. |
April 8, 2014 |
Founding Principal of the Adviser |
| Jordan Brooks, Ph.D., M.A. |
April 8, 2014 |
Principal of the Adviser |
| Yao Hua Ooi |
January 1, 2020 |
Principal of the Adviser |
| Ashwin Thapar |
March 31, 2021 |
Principal of the Adviser |
| Jonathan Fader |
March 31, 2021 |
Managing Director of the Adviser |
| Erik Stamelos |
January 1, 2022 |
Managing Director of the Adviser |
AQR Funds–Summary Prospectus10
Important Additional Information
Purchase and Sale of Fund Shares
You may purchase or redeem Class N Shares, Class I Shares and Class R6 Shares of the Fund, as applicable,
each day the NYSE is open. To purchase or redeem shares you should contact your financial
intermediary, or, if you hold your shares through the Fund, you should contact the Fund by phone at (866) 290-2688 or by mail (c/o AQR Funds, P.O. Box 2248, Denver, CO 80201-2248). The Fund’s initial and subsequent investment minimums for Class N Shares, Class I Shares and
Class R6 Shares, as applicable, generally are as follows.
| |
Class N Shares |
Class I Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
| Minimum Initial Investment |
$1,000,0001
|
$5,000,0001
|
$50,000,0001 |
| Minimum Subsequent Investment |
None |
None |
None |
1 Reductions apply to certain eligibility groups. See “Investing With the AQR Funds” in the
Fund’s prospectus.
Tax Information
The Fund’s dividends and distributions may be subject to federal income taxes and may be taxed as ordinary income or
capital gains, unless you are a tax-exempt investor or are investing through a retirement plan, in which case you may be subject to federal income tax upon withdrawal from such tax deferred arrangements.
Payments to Broker/Dealers and other Financial Intermediaries
If you purchase shares of the Fund through a broker-dealer or other financial intermediary, the Fund
and/or the Adviser or its
affiliates may pay the intermediary for the sale of Fund shares and other services. These payments may create a conflict of interest by influencing the broker-dealer or other financial intermediary and your individual financial professional to
recommend the Fund over another investment. Ask your individual financial professional or visit your financial intermediary’s website for more information.
Serious News for Serious Traders! Try StreetInsider.com Premium Free!
You May Also Be Interested In
- Three-quarters of New Jerseyans Familiar With Proper Guidelines to Store and Dispose of Medications, Opioids and Edibles
- More Preparation, Communication and Control: Hyatt Reveals Survey Findings on the Hotel Stay Needs of Neurodivergent Travelers
- Mapping Global Flash Drought Trends for Disaster Preparedness
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share