Form 497 Putnam Target Date Funds
| Prospectus Supplement | July 1, 2022 |
| Putnam RetirementReady® Funds | |
| Prospectus dated November 30, 2021 | |
This
supplement replaces in its entirety the supplement to the Funds’ prospectus dated May 26, 2022.
Putnam Investment Management, LLC (“Putnam Management”), the investment adviser of the Putnam RetirementReady® Funds (each, a “Fund,” and each Fund a series of Putnam Target Date Funds (the “Trust”)), has recommended, and the Trust’s Board of Trustees has approved, changes to each Fund’s name and principal investment strategies (collectively, the “Repositioning”). The investment goal of each Fund will remain unchanged following the Repositioning. Putnam Management currently anticipates that the Repositioning will become effective in the fourth quarter of 2022 or the first quarter of 2023 (the effective date of the Repositioning hereinafter referred to as the “Effective Date”). On the Effective Date, each Fund’s name will change as follows:
| Current Fund | Repositioned Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2065 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2065 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2060 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2060 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2055 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2055 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2050 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2050 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2045 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2045 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2040 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2040 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2035 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2035 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2030 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2030 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady 2025 Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement 2025 Fund |
| Putnam RetirementReady Maturity Fund | Putnam Sustainable Retirement Maturity Fund |
Information
Concerning the Funds’ Investment Strategies and Risks Following the Repositioning:
In addition to the name change, on the Effective Date each Fund’s principal investment strategies will change, and it will pursue its investment objective by investing in Putnam Management-sponsored exchange-traded funds that focus on investments with positive sustainability or environmental, social, and governance (“ESG”) characteristics (hereinafter referred to as “Underlying ETFs”). Putnam Management will serve as investment adviser to each Underlying ETF, and, for two of the Underlying ETFs, PanAgora Asset Management, Inc. (“PanAgora”), an affiliate of Putnam Management, will serve as the sub-adviser responsible for the day-to-day management of the Underlying ETF’s portfolio. On the Effective Date, each Fund will have a policy to invest, under normal circumstances, in Underlying ETFs such that, in the aggregate, the Fund has indirect exposure to investments that meet Putnam Management’s or PanAgora’s, as applicable, sustainability or ESG criteria and that represent at least 80% of the value of its net assets. After the Effective Date, this policy may be changed only after 60 days’ notice to shareholders.

| 330410 – 7/22 |
The following table displays each Fund’s expected, initial approximate allocations to each asset class and Underlying ETF:
| Underlying ETF* | Year |
2065
|
2060 | 2055 | 2050 | 2045 | 2040 | 2035 | 2030 | 2025 | SR Maturity |
| Putnam Sustainable Leaders ETF | 2022 |
47.6% |
46.8% | 44.7% | 42.2% | 39.6% | 37.0% | 33.3% | 25.2% | 16.4% | 14.1% |
| 2023 |
47.6% |
46.5% | 44.2% | 41.6% | 39.1% | 36.3% | 32.4% | 22.8% | 15.6% | 14.1% | |
| Putnam Sustainable Future ETF | 2022 |
23.8% |
23.4% | 22.3% | 21.1% | 19.8% | 18.5% | 16.6% | 12.6% | 8.2% | 7.1% |
| 2023 |
23.8% |
23.2% | 22.1% | 20.8% | 19.5% | 18.2% | 16.2% | 11.4% | 7.8% | 7.1% | |
| Putnam PanAgora ESG International Equity ETF | 2022 |
17.8% |
17.6% | 16.8% | 15.8% | 14.8% | 13.2% | 10.6% | 7.6% | 4.9% | 4.2% |
| 2023 |
17.8% |
17.4% | 16.6% | 15.6% | 14.6% | 12.7% | 10.0% | 6.8% | 4.7% | 4.2% | |
| Putnam PanAgora ESG Emerging Markets Equity ETF | 2022 |
5.9% |
5.9% | 5.6% | 5.3% | 4.9% | 3.5% | 1.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 2023 |
5.9% |
5.8% | 5.5% | 5.2% | 4.8% | 3.0% | 0.4% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |
| Putnam ESG Core Bond ETF | 2022 |
3.2% |
4.4% | 7.6% | 11.4% | 14.3% | 20.0% | 29.8% | 43.3% | 54.9% | 51.7% |
| 2023 |
3.2% |
4.9% | 8.3% | 12.0% | 14.9% | 21.7% | 32.0% | 46.9% | 52.7% | 51.7% | |
| Putnam ESG High Yield ETF | 2022 |
1.1% |
1.5% | 2.5% | 3.8% | 4.8% | 4.9% | 4.8% | 6.1% | 9.6% | 16.9% |
| 2023 |
1.1% |
1.6% | 2.8% | 4.0% | 4.9% | 4.8% | 4.8% | 6.5% | 13.3% | 16.9% | |
| Putnam ESG Ultra Short ETF | 2022 |
0.5% |
0.5% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 1.8% | 3.0% | 4.0% | 5.2% | 6.0% | 6.0% |
| 2023 |
0.5% |
0.5% | 0.5% | 0.7% | 2.1% | 3.2% | 4.3% | 5.5% | 6.0% | 6.0% | |
| Equity** | 2022 |
95.2% |
93.7% | 89.4% | 84.3% | 79.1% | 72.2% | 61.4% | 45.4% | 29.5% | 25.4% |
| 2023 |
95.2% |
92.9% | 88.4% | 83.3% | 78.1% | 70.2% | 59.0% | 41.1% | 28.0% | 25.4% | |
| Fixed Income** | 2022 |
4.8% |
6.3% | 10.6% | 15.7% | 20.9% | 27.8% | 38.6% | 54.6% | 70.5% | 74.6% |
| 2023 |
4.8% |
7.1% | 11.6% | 16.7% | 21.9% | 29.8% | 41.0% | 58.9% | 72.0% | 74.6% |
* Due to rounding, allocations shown in the table above may not total 100%. In addition, because of rounding in the calculation of allocations among Underlying ETFs and market fluctuations, actual allocations might be more or less than these percentages.
** Equity and fixed income allocations are hypothetical estimates
based on an assumption that each of Putnam Sustainable Leaders ETF, Putnam Sustainable Future ETF, Putnam PanAgora ESG International Equity
ETF, and Putnam PanAgora ESG Emerging Markets Equity ETF is equivalent to an equity investment and each of Putnam ESG Core Bond ETF, Putnam
ESG High Yield ETF and Putnam ESG Ultra Short ETF is equivalent to a fixed income investment. Actual allocations will vary.
Each
Fund’s target allocations may differ from the allocations shown in the table above. For each Fund other than Putnam Sustainable
Retirement Maturity Fund (“Maturity Fund”), Putnam Management may change the glide path, the Fund’s target allocations,
and the Underlying ETFs in which it invests at any time, although Putnam Management generally expects these changes (other than the tactical
adjustments described below) to be infrequent and generally in response to longer-term structural changes (i.e., in the average
retirement age or life expectancy) that lead the Fund’s portfolio managers to determine that a change is advisable. Putnam Management
may also make tactical adjustments from time to time in a Fund’s (other than Maturity Fund’s) allocations to Underlying ETFs
in response to market conditions within a range of +/- 15% from the allocations to fixed-income and equity asset classes as presented
in the Fund’s
| -2- |
glide path (provided below). For Maturity Fund, Putnam Management may change the Fund’s target allocations and the Underlying ETFs in which it invests at any time, although Putnam Management generally expects these changes to be infrequent and generally in response to longer-term structural changes that lead the Fund’s portfolio managers to determine that a change is advisable.
On the Effective Date, each Fund, through its investments in Underlying ETFs, will make use of a range of ESG- and sustainability-oriented investment strategies and will invest across a variety of asset classes. For example, Putnam Management’s sustainability criteria for the investments of Putnam Sustainable Leaders ETF and Putnam Sustainable Future ETF (two of the Underlying ETFs that invest primarily in equities) are expected to differ from the ESG approach used by Putnam Management for the fixed-income Underlying ETFs, and from PanAgora’s quantitatively-oriented ESG equity approach for the Underlying ETFs that it subadvises. These differences may arise both from differences in the Underlying ETFs’ asset classes (such as the characteristics of non-U.S. versus U.S. issuers, or the structural differences (i.e., position in the capital structure) between equity and fixed-income investments) as well as from different managers’ styles. In implementing an Underlying ETF’s investment strategy, the portfolio managers of the Underlying ETF may apply and weigh different ESG factors differently than the portfolio managers of the other Underlying ETFs. There are also expected to be differences in how the portfolio managers of the Underlying ETFs source ESG-related or sustainability-oriented research (e.g., proprietary versus third-party research) and/or their approach to selecting companies based on ESG or sustainability criteria.
On the Effective Date, each Fund will be subject to the investment risks associated with the Underlying ETFs, which are identified below. The relative significance of these risks will vary over time based on the Fund’s target allocations to the Underlying ETFs and to equity and fixed income asset classes, which may change from time to time as discussed above.
Investment Strategy-Related Risks of the Underlying ETFs
Sustainability and ESG Investing risk. Investing in Underlying ETFs with an ESG or sustainability focus may result in the fund having exposure to Underlying ETFs that invest in certain types of companies, industries or sectors that the market may not favor. In evaluating an investment opportunity for the Underlying ETFs, Putnam Management or PanAgora may make investment decisions based on information and data that is incomplete or inaccurate. Sustainability and ESG metrics are not uniformly defined, and applying such metrics involves subjective assessments. Sustainability and ESG scorings and assessments of issuers can vary across third-party data providers and may change over time. Putnam Management and PanAgora do not rely exclusively on third-party data providers in evaluating sustainability and ESG factors for the Underlying ETFs. In addition, the business practices, products or services of issuers in which an Underlying ETF invests may change over time. As a result of these possibilities, among others, an Underlying ETF may temporarily hold securities that are inconsistent with the Underlying ETF’s ESG or sustainability investment criteria. Regulatory changes or interpretations regarding the definitions and/or use of ESG and/or sustainability criteria could have a material adverse effect on the Underlying ETF’s ability to invest in accordance with its investment policies and/or achieve its investment objective. The Underlying ETFs do not restrict investments based solely on “negative screens”, and the fixed income Underlying ETFs do not restrict their fixed-income investments to “green bonds” (i.e., U.S. dollar-denominated bonds designated as “green” by the Climate Bonds Initiative). For the Underlying ETFs that pursue fixed-income investment strategies, because fixed-income investments generally represent a promise to pay principal and interest by an issuer, and not an ownership interest, and may involve complex structures, ESG-related investment considerations may have a more limited impact on risk and return (or may have an impact over a different investment time horizon) relative to other asset classes, and this may be particularly true for shorter-term investments. In addition, holders of fixed-income investments do not typically have voting rights, unlike holders of equity investments who have the right to vote on issuer proposals, including ESG-related proposals, which limits the opportunity to provide input on fixed-income issuer proposals.
Market Risk. The value of investments in the Underlying ETFs’ portfolios may fall or fail to rise over extended periods of time for a variety of reasons, including general economic, political or financial market conditions, investor sentiment and market perceptions, government actions, geopolitical events or changes,
| -3- |
and factors related to a specific issuer, geography, industry or sector. These and other factors may lead to increased volatility and reduced liquidity in the Underlying ETFs’ portfolio holdings. The novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and efforts to contain its spread are likely to negatively affect the value, volatility, and liquidity of the securities and other assets in which the Underlying ETFs invest and exacerbate other risks that apply to the Underlying ETFs. These effects could negatively impact the Fund’s performance and lead to losses on your investment in the Fund.
Common stock risk. Common stock represents an ownership interest in a company. The value of a company’s stock may fall or fail to rise as a result of factors directly relating to that company, such as decisions made by its management or lower demand for the company’s products or services. A stock’s value may also fall because of factors affecting not just the company, but also other companies in the same industry or in a number of different industries, such as increases in production costs.
Growth investing risk. Growth stocks may be more susceptible to earnings disappointments, and the market may not favor growth-style investing.
Value investing risk. Value stocks may fail to rebound, and the market may not favor value-style investing. Companies whose stocks we believe are undervalued by the market may have experienced adverse business developments or may be subject to special risks that have caused their stocks to be out of favor.
Small and midsize companies risk. Stocks of small and midsize companies often trade in smaller volumes, and their prices may fluctuate more than stocks of larger companies. Stocks of these companies may therefore be more vulnerable to adverse developments than those of larger companies.
Industry or sector concentration risk. From time to time, an Underlying ETF may invest a significant portion of its assets in companies in one or more related industries or sectors, which would make the Underlying ETF more vulnerable to adverse developments affecting those industries or sectors.
Model Risk. If the quantitative models or data that are used in managing an Underlying ETF prove to be incorrect or incomplete, investment decisions made in reliance on the models or data may not produce the desired results, and the Underlying ETF may realize losses. Additionally, market movements are likely to change the risk levels and risk allocations of the Underlying ETF. Investments made based on quantitative models may perform differently from the market as a whole.
Foreign investment risk. The value of international investments traded in foreign currencies may be adversely impacted by fluctuations in exchange rates. International investments, particularly investments in emerging markets, may carry risks associated with potentially less stable economies or governments (such as the risk of seizure by a foreign government, the imposition of currency or other restrictions, or high levels of inflation), and may be or become illiquid.
Geographic focus risk. From time to time, an Underlying ETF may invest a significant portion of its assets in companies in one or more related geographic regions, industries or sectors, such as European and Asian countries, which would make the fund more vulnerable to adverse developments affecting those geographic regions, industries or sectors.
Fixed-income investments risk. The risks associated with fixed-income investments include interest rate risk, which is the risk that the value of an Underlying ETF’s investments is likely to fall if interest rates rise. Fixed-income investments are also subject to credit risk, which is the risk that the issuer of a fixed-income investment may default on payment of interest or principal. Credit risk is generally greater for debt not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government, and interest rate risk is generally greater for longer-term debt. Fixed-income investments may be more susceptible to downgrades or defaults during
| -4- |
economic downturns or other periods of economic stress.
Mortgage-backed investments, unlike traditional debt investments, are also subject to prepayment risk, which means that they may increase
in value less than other bonds when interest rates decline and decline in value more than other bonds when interest rates rise. The Underlying
ETF may have to invest the proceeds from prepaid investments, including mortgage-backed investments, in other investments with less attractive
terms and yields. The Underlying ETF’s investments in mortgage-backed securities, and in certain other securities and derivatives,
may be or become illiquid. The Underlying ETF’s investments in mortgage-backed securities may make the Underlying ETF’s net
asset value more susceptible to economic, market, political and other developments affecting the residential and commercial real estate
markets and the servicing of mortgage loans secured by real estate properties. During periods of difficult economic conditions, delinquencies
and losses on commercial mortgage-backed investments in particular generally increase, including as a result of the effects of those conditions
on commercial real estate markets, the ability of commercial tenants to make loan payments, and the ability of a property to attract and
retain commercial tenants.
Derivatives risk. An Underlying ETF’s use of derivatives may increase the risks of investing in the Underlying ETF by increasing investment exposure (which may be considered leverage) or, in the case of many over-the-counter instruments, because of the potential inability to terminate or sell derivatives positions and the potential failure of the other party to the instrument to meet its obligations. The value of derivatives may move in unexpected ways due to the use of leverage or other factors, especially in unusual market conditions, and may result in increased volatility.
Floating rate loan risk. To the extent an Underlying ETF holds floating rate loans, interest rate risk may be reduced but will not be eliminated. While floating rate loans are normally secured by specific collateral or assets of the issuer (so that holders of the loans, such as the Underlying ETF, will have a priority claim on those assets in the event of default or bankruptcy of the issuer), the value of collateral may be insufficient to meet the issuer’s obligations, and the Underlying ETF’s access to collateral may be limited by bankruptcy or other insolvency laws. The settlement period (the period between the execution of the trade and the delivery of cash to the purchaser) for floating rate loan transactions is typically longer than seven days, and it is possible that sale proceeds from floating rate loan transactions will not be available to meet redemption obligations.
Portfolio turnover rate risk. From time to time an Underlying ETF may engage in frequent trading. Funds with high turnover may be more likely to realize capital gains that must be distributed to shareholders as taxable income. High turnover may also cause a fund to pay more brokerage commissions and to incur other transaction costs (including imputed transaction costs), which may detract from performance. A fund’s portfolio turnover rate and the amount of brokerage commissions it pays and transaction costs it incurs will vary over time based on market conditions.
Management and Operational Risk. There is no guarantee that the investment techniques, analyses, or judgments that Putnam Management or PanAgora, as applicable, applies in making investment decisions for the Underlying ETFs will produce the intended outcome or that the investments they select for the Underlying ETFs will perform as well as other securities that were not selected for the Underlying ETFs. Putnam Management, PanAgora, or the Underlying ETFs’ other service providers, may experience disruptions or operating errors that could negatively impact the Underlying ETFs.
Risks Related to Investing in Exchange-Traded Funds (“ETFs”)
As ETFs, shares of the Underlying ETFs are traded in the secondary market. Prior to trading in the secondary market, shares of the Underlying ETFs are “created” at NAV by market makers, large investors and institutions (collectively, “authorized participants”) only in creation units. A creation transaction generally takes place when an authorized participant deposits into an underlying fund a designated portfolio of securities, assets or other positions, and an amount of cash (including any cash representing the value of substituted securities, assets or other positions), if any, in exchange for a specified number of creation units. Similarly, shares of an Underlying ETF can be redeemed only in creation units, generally for a designated
| -5- |
portfolio of securities, assets or other positions
held by the Underlying ETF and an amount of cash (including any portion of such securities for which cash may be substituted), if any.
Fluctuation of net asset value (“NAV”) and share price risk. Shares of the Underlying ETFs may trade at a larger premium or discount to their NAV than shares of other ETFs. The NAV of an Underlying ETF will generally fluctuate with changes in the market value of the Underlying ETF’s holdings. Underlying ETF shares can be bought and sold in the secondary market at market prices. Disruptions to creations and redemptions, the existence of extreme market volatility or potential lack of an active trading market for an Underlying ETF’s shares may result in the Underlying ETF’s shares trading significantly above (at a premium) or below (at a discount) to NAV or to the intraday value of the Underlying ETF’s holdings. In addition, in stressed market conditions or periods of market disruption or volatility, the market for shares of the Underlying ETFs may become less liquid in response to deteriorating liquidity in the markets for the Underlying ETFs’ portfolio holdings.
Authorized participant concentration risk. Only an authorized participant may engage in creation and redemption transactions directly with an Underlying ETF. The Fund is not an authorized participant and can only purchase and sell Underlying ETF shares in the secondary market at market prices or through an authorized participant. The Underlying ETF has a limited number of financial institutions that act as authorized participants, none of which are obligated to engage in creation and/ or redemption transactions. To the extent that those authorized participants do not engage in creation and redemption orders, there may be a significantly diminished trading market for Underlying ETF shares, or Underlying ETF shares may trade at a discount (or premium) to NAV and possibly face trading halts and/or de-listing.
Trading issues risk. The Underlying ETFs have a limited public trading history. Putnam Sustainable Leaders ETF and Putnam Sustainable Future ETF began trading publicly in May 2021, while Putnam PanAgora ESG International Equity ETF, Putnam PanAgora ESG Emerging Markets Equity ETF, Putnam ESG Core Bond ETF, Putnam ESG High Yield ETF, and Putnam ESG Ultra Short ETF have not yet commenced trading publicly .There can be no assurance that an active trading market will develop or be maintained or that the market for Underlying ETF shares will operate as intended, which could lead to the Underlying ETFs’ shares trading at wider spreads and larger premiums and discounts to NAV than other actively managed ETFs, particularly during periods of market disruption or volatility. As a result, it may cost the Fund more to trade Underlying ETF shares than shares of other ETFs. There is no guarantee that the Underlying ETF will be able to attract market makers and authorized participants. Market makers and authorized participants are not obligated to make a market in the Underlying ETF’s shares or to submit purchase and redemption orders for creation units.
The market prices of an Underlying ETF’s shares are expected to fluctuate, in some cases materially, in response to changes in the Underlying ETF’s NAV, the intraday value of the Underlying ETF’s holdings and supply and demand for the Underlying ETF’s shares. Putnam Management cannot predict whether an Underlying ETF’s shares will trade above, below or at their NAV or the intraday value of the Underlying ETF’s holdings. During periods when an Underlying ETF is trading below its NAV, the Fund may incur significant losses if it sells its Underlying ETF shares.
The securities held by an Underlying ETF may be traded in markets that close at a different time than the exchange on which the Underlying ETF’s shares are listed. Liquidity in those securities may be reduced after the applicable closing times. Accordingly, during the time when the exchange is open but after the applicable market closing, fixing or settlement times, bid-ask spreads on the exchange and the corresponding premium or discount to the NAV of the Underlying ETFs’ shares may widen.
Large shareholder risk. Certain accounts or affiliates of Putnam Management, including other funds advised by Putnam Management (including the Funds) or third parties, will from time to time own (beneficially or of record) or control a substantial amount of an Underlying ETF’s shares, including through seed capital arrangements. Such shareholders may at times be considered to control the Underlying ETF. Dispositions of a large number of shares by these shareholders may adversely affect the Underlying ETF’s liquidity and net assets to the extent such transactions are executed directly with the Underlying ETF in the
| -6- |
form of redemptions through an authorized participant,
rather than executed in the secondary market. These redemptions may also force the Underlying ETF to sell securities, which may increase
the Underlying ETF’s brokerage costs. To the extent these large shareholders transact in shares of the Underlying ETF on the secondary
market, such transactions may account for a large percentage of the trading volume on the exchange and may, therefore, have a material
effect (upward or downward) on the market price of the Underlying ETF’s shares.
Cash transactions risk. Some of the Underlying ETFs may effect creations and redemptions in cash or partially in cash. Therefore, an Underlying ETF may be required to sell portfolio securities, incur transaction costs, and subsequently recognize gains on such sales that the Underlying ETF might not have recognized if it were to distribute portfolio securities in-kind. As such, investments by a Fund in an Underlying ETF’s shares may be less tax-efficient than an investment in an ETF that distributes portfolio securities entirely in-kind. An Underlying ETF may also incur transaction costs in connection with creations effected in cash (in whole or in part).
Semi-transparent ETF risk. Two of the Underlying ETFs, Putnam Sustainable Leaders ETF and Putnam Sustainable Future ETF (the “Semi-Transparent ETFs”), are different from traditional ETFs, including the other Underlying ETFs. Traditional ETFs disclose to the public what assets they hold each day. However, the Semi-Transparent ETFs do not. This may create additional risks for an investment in the Semi-Transparent ETFs, including that an investor may have to pay more money to trade the Semi-Transparent ETF’s shares in light of the fact that the Semi-Transparent ETF will provide less information to traders, who tend to charge more for trades when they have less information. The price an investor pays to buy or sell an ETF’s shares on an exchange may not match the value of the ETF’s portfolio, and these price differences may be greater for the Semi-Transparent ETFs compared to other ETFs because they provide less information to traders. These additional risks may be even greater in adverse or uncertain market conditions.
The differences between the Semi-Transparent ETFs and other ETFs may also have advantages. By keeping certain information about the Semi-Transparent ETFs secret, a Semi-Transparent ETF may face less risk that other traders can predict or copy its investment strategy. This may improve the Semi-Transparent ETF’s performance. If other traders are able to copy or predict the Semi-Transparent ETF’s investment strategy, however, this may hurt the Semi-Transparent ETF’s performance.
Tracking basket structure risk. The Semi-Transparent ETFs are actively managed ETFs that operate pursuant to an exemptive order from the Securities and Exchange Commission and do not publicly disclose their complete portfolio holdings each business day. Instead, each Semi-Transparent ETF publishes each business day on its website a “Tracking Basket,” which is designed to closely track the daily performance of the Semi-Transparent ETF but is not the Semi-Transparent ETF’s actual portfolio. The Tracking Basket is comprised of: (1) select recently disclosed portfolio holdings and/or select securities from the universe from which the Semi-Transparent ETF’s investments are selected (“Strategy Components”); (2) liquid ETFs that convey information about the types of instruments (that are not otherwise fully represented by the Strategy Components) in which the Semi-Transparent ETF invests; and (3) cash and cash equivalents.
A Semi-Transparent ETF’s Tracking Basket structure may affect the price at which shares of the Semi-Transparent ETF trade in the secondary market. Although the Tracking Basket is intended to provide investors with enough information to allow for an effective arbitrage mechanism that will keep the market price of each Semi-Transparent ETF at or close to its NAV per share, there is a risk that market prices will vary significantly from NAV. The Semi-Transparent ETFs, which trade on the basis of a published Tracking Basket, may trade at a wider bid/ask spread than ETFs that publish their portfolios on a daily basis, and therefore, may cost investors more to trade. These risks may increase during periods of market disruption or volatility. In addition, although each Semi-Transparent ETF seeks to benefit from keeping its portfolio information secret, market participants may attempt to use the Tracking Basket to identify the Semi-Transparent ETF’s trading strategy. If successful, this could result in such market participants engaging in certain predatory trading practices that may have the potential to harm the Semi-Transparent ETF and its shareholders, such as front running the Semi-Transparent ETF’s trades of portfolio securities.
| -7- |
Arbitrage risk. Unlike ETFs that publicly disclose their complete portfolio holdings each business day, each Semi-Transparent ETF provides certain other information intended to allow market participants to estimate the value of positions in the Semi-Transparent ETF’s shares. Although this information is designed to facilitate arbitrage opportunities in the Semi-Transparent ETF’s shares to reduce bid/ask spreads and minimize discounts or premiums between the market price and NAV of the Semi-Transparent ETF shares, there is no guarantee the Semi-Transparent ETF’s arbitrage mechanism will operate as intended and that the Semi-Transparent ETF will not experience wide bid/ask spreads and/or large discount or premiums to NAV. In addition, market participants may attempt to use the disclosed information to “reverse engineer” the Semi-Transparent ETF’s trading strategy, which, if successful, could increase opportunities for predatory trading practices that may have the potential to negatively impact the Semi-Transparent ETF’s performance.
Trading halt risk. There may be circumstances where a security held in a Semi-Transparent ETF’s portfolio but not in the Tracking Basket does not have readily available market quotations. If Putnam Management determines that such circumstance may affect the reliability of the Tracking Basket as an arbitrage vehicle, that information, along with the identity and weighting of that security in the Semi-Transparent ETF’s portfolio, will be publicly disclosed on the Semi-Transparent ETF’s website, and Putnam Management will assess appropriate remedial measures. In these circumstances, market participants may use this information to engage in certain predatory trading practices that may have the potential to harm the Semi-Transparent ETF and its shareholders. In addition, if securities representing 10% or more of the Semi-Transparent ETF’s portfolio do not have readily available market quotations, Putnam Management would promptly request the exchange to halt trading of the Semi-Transparent ETF, meaning that investors (including the Fund) would not be able to trade their shares. Trading may also be halted in other circumstances, for example, due to market conditions.
Putnam Sustainable Retirement Funds’ Glide Path
For each Fund other than Maturity Fund, target allocations among asset classes and Underlying ETFs will increasingly emphasize capital preservation and income over time and will change gradually based on the number of remaining years until the Fund’s target date, as shown in the following predetermined “glide path” below. Putnam Management will adjust these Funds’ allocations at the end of each calendar quarter based on the glide path. Over a five-year period, each of these Fund’s allocations will gradually change to resemble the allocations of the Fund with the next earliest target date. For Maturity Fund, target allocations among asset classes and Underlying ETFs are not expected to change over time. Putnam Management will rebalance Maturity Fund’s investments towards its target allocations on a quarterly basis.
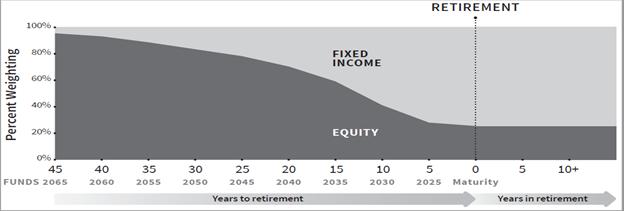
Asset class weightings are hypothetical estimates based on an assumption that each of Putnam Sustainable Leaders ETF, Putnam Sustainable Future ETF, Putnam PanAgora ESG International Equity ETF, and Putnam PanAgora ESG Emerging Markets Equity ETF is equivalent to an equity investment and each of Putnam ESG Core Bond ETF, Putnam ESG High Yield ETF, and Putnam ESG Ultra Short ETF is equivalent to a fixed-income investment. The managers of the Underlying ETFs may adjust those funds’ allocations among asset classes from time to time consistent with their
| -8- |
investment goals, and, consequently, actual allocations will vary. Because of rounding in the calculation of allocations among Underlying ETFs and of asset class weighting, actual allocations may be more or less than these percentages.
Additional Information Concerning the Repositioning:
In connection with the Repositioning, the Trust’s Board of Trustees also approved an amendment to the expense limitation agreement between Putnam Management and the Trust that would lower the current total expense cap on each class of each Fund (exclusive of payments under the Fund’s distribution plans, brokerage, interest, taxes, investment-related expenses, and extraordinary expenses) by 0.05%, effective as of the Effective Date.
Each Fund currently invests its assets in other Putnam funds (the “Current Underlying Funds”). In order to effect the Repositioning, shortly before the Effective Date the Funds will redeem their entire investment in the Current Underlying Funds and invest those proceeds in the Underlying ETFs. The redemption of the Funds’ investments in the Current Underlying Funds will result in transaction costs and, depending on market conditions at the time, could also result in the realization of capital gains that will be distributed to taxable Fund shareholders as taxable distributions. Shareholder approval of the Repositioning is not required.
The information provided above regarding the Funds, including, without limitation, the Funds’ investment strategies and risks following the Repositioning, the risks of investing in the Underlying ETFs, and the Funds’ allocations to the Underlying ETFs and asset classes, is subject to change.
This supplement is not an offer to sell the Underlying ETFs’ securities and is not soliciting an offer to buy the Underlying ETFs’ securities. The registration statement for each of Putnam PanAgora ESG International Equity ETF, Putnam PanAgora ESG Emerging Markets Equity ETF, Putnam ESG Core Bond ETF, Putnam ESG High Yield ETF, and Putnam ESG Ultra Short ETF has been filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission but is not yet effective, and the securities of these Underlying ETFs are, therefore, not available for sale.
Shareholders should retain this Supplement for future reference.
| -9- |
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsRelated Entities
Putnam InvestmentsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share