Form 8-K Ovid Therapeutics Inc. For: Aug 15
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 8-K
CURRENT REPORT
Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d)
of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
Date of Report (Date of earliest event reported): August 15, 2017
OVID THERAPEUTICS INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 001-38085 | 46-5270895 | ||
| (state or other jurisdiction of incorporation) |
(Commission File Number) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| 1460 Broadway, Suite 15044 New York, New York |
10036 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (646) 661-7661
(Former name or former address, if changed since last report.)
Check the appropriate box below if the Form 8-K filing is intended to simultaneously satisfy the filing obligation of the registrant under any of the following provisions (see General Instruction A.2. below):
| ☐ | Written communications pursuant to Rule 425 under the Securities Act (17 CFR 230.425) |
| ☐ | Soliciting material pursuant to Rule 14a-12 under the Exchange Act (17 CFR 240.14a-12) |
| ☐ | Pre-commencement communications pursuant to Rule 14d-2(b) under the Exchange Act (17 CFR 240.14d-2(b)) |
| ☐ | Pre-commencement communications pursuant to Rule 13e-4(c) under the Exchange Act (17 CFR 240.13e-4(c)) |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is an emerging growth company as defined in as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act of 1933 (§ 230.405 of this chapter) or Rule 12b–2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (§ 240.12b–2 of this chapter).
Emerging growth company ☒
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☒
Item 7.01. Regulation FD Disclosure.
On August 15, 2017, Ovid Therapeutics Inc. (the “Company”) posted its corporate presentation, dated August 15, 2017, to the “Events & Presentations” subsection of the “Investors & Media” tab on the Company’s website at www.ovidrx.com. A copy of the corporate presentation is attached hereto as Exhibit 99.1 and is incorporated by reference into this Item 7.01.
This information, including the Exhibit 99.1 referenced herein, is “furnished” and shall not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or otherwise subject to the liabilities of that section. It may only be incorporated by reference in another filing under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, only if and to the extent such subsequent filing specifically references the information herein as being incorporated by reference in such filing.
Cautionary Statements
This Current Report on Form 8-K and the corporate presentation include “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, including, but not limited to, whether or not any patents issue and the scope of future patent or other intellectual property protection, the risk of third-party challenges to the Company’s intellectual property, the likelihood, timing and scope of any future collaborations, the initiation, timing, progress and results of the Company’s current and future preclinical studies and clinical trials, uncertainties related to drug development results, costs and timelines and regulatory risks. Other factors that may cause the Company’s actual results to differ from current expectations are discussed under the caption “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in the Company’s filings and reports with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), including the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, which was filed with the SEC on August 10, 2017. Except as required by law, the Company assumes no obligation to update any forward-looking statements contained in the corporate presentation to reflect any change in expectations, even as new information becomes available.
Item 9.01. Financial Statements and Exhibits.
| (d) | Exhibits. |
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 99.1 | Corporate Presentation, dated August 15, 2017 | |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned hereunto duly authorized.
| OVID THERAPEUTICS INC. | ||
| By: | /s/ Yaron Werber | |
| Yaron Werber | ||
| Chief Business and Financial Officer | ||
Dated: August 15, 2017
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 99.1 | Corporate Presentation, dated August 15, 2017 | |

Corporate Presentation August 15, 2017 Exhibit 99.1

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains projections for Ovid Therapeutics Inc. (“Ovid”) and other forward-looking information. Such projections and information are based on assumptions as to future events that are inherently uncertain and subjective. Ovid, its officers, directors or stockholders make no representations or warranties as to the reasonableness of such assumptions or as to whether the future results will occur as projected. It must be recognized that Ovid is an early-stage company and that projections of its future performance are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty, that actual results can be expected to vary from the results projected, and that such variances may be material and adverse. You should and are expected to conduct your own investigation and review of Ovid before determining whether or not to pursue this transaction. Statements made by Ovid in this presentation may contain certain statements that are forward-looking and involve risks and uncertainties. Words such as “expects,” “anticipates,” “projects,” “estimates,” “intends,” “plans,” “believes,” variations of such words and similar expressions are intended to identify such forward-looking statements. These statements are based on current expectations and projections made by management and are not guarantees of future performance. Therefore, actual events, outcomes and results may differ materially from what is expressed or forecast in such forward-looking statements. Factors that may cause actual results to differ materially from these forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to: whether or not any patents issue and the scope of future patent or other intellectual property protection, the risk of third-party challenges to Ovid’s intellectual property, the likelihood, timing and scope of any future collaborations, the initiation, timing, progress and results of our current and future preclinical studies and clinical trials, uncertainties related to drug development results, costs and timelines and regulatory risks. Except as otherwise required under federal securities laws, we do not have any intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events, changes in assumptions or otherwise. This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and growth and other data about our industry. This data involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates.

To become a leading neurological disorder company Develop innovative therapies addressing to transform the lives of patients and families Built on core pillars of value Rare disorders with a genetic basis & novel MOA Driven by Business Development Scalable model Compelling growth opportunities Substantial unmet need Few effective medicines Track record of success Deep expertise in translational science, drug evaluation and orphan clinical drug development Significant biotech and pharma experience Multiple ongoing clinical programs Topline Phase 2 OV101 STARS trial data (2018) Phase 1 OV101 PK trial data in adolescents (H2:17) Phase 1b/2a OV935 in dEE ongoing OVIDAPPROACH FOCUSED MISSION CLEAR STRATEGY COMPELLING OPPORTUNITY WORLD CLASS TEAM ROBUST PIPELINE ~100 different disorders ~1 million patients in the US alone
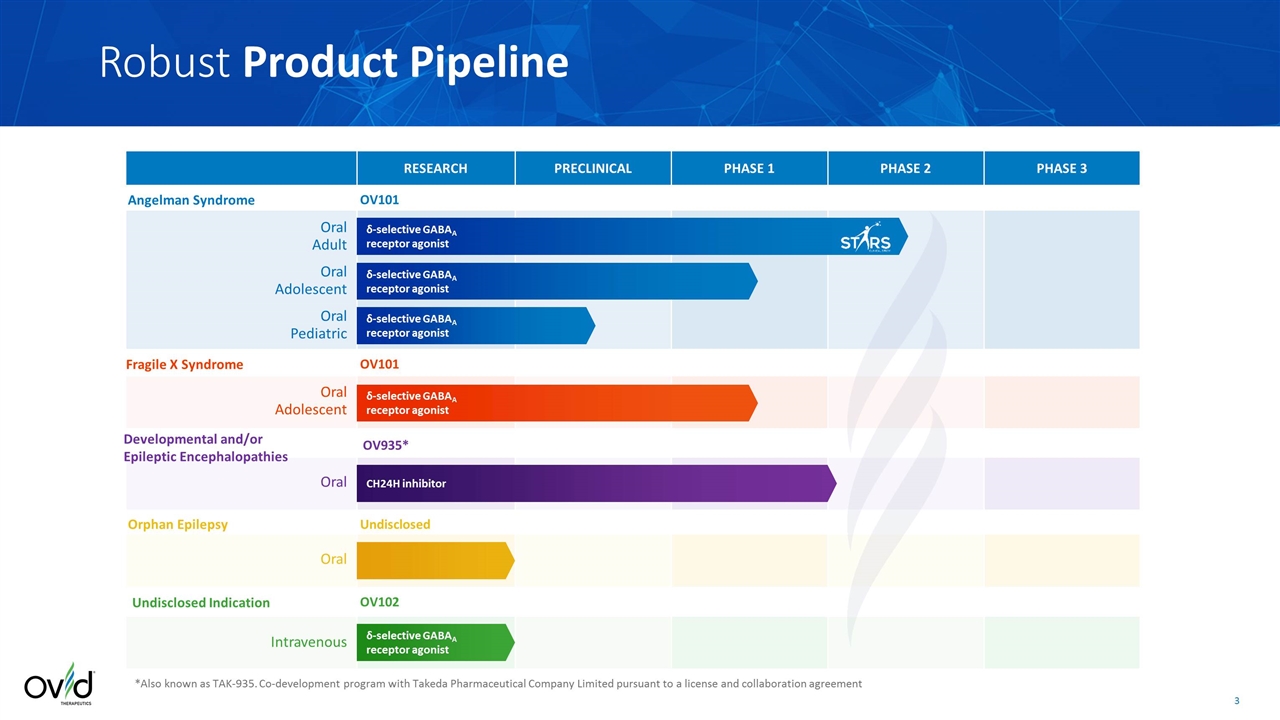
δ-selective GABAA receptor agonist Angelman Syndrome RESEARCH PRECLINICAL PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3 Fragile X Syndrome δ-selective GABAA receptor agonist δ-selective GABAA receptor agonist δ-selective GABAA receptor agonist Oral Adolescent Oral Pediatric Oral Adolescent Oral Adult OV101 OV101 Undisclosed Indication Intravenous δ-selective GABAA receptor agonist OV102 *Also known as TAK-935. Co-development program with Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited pursuant to a license and collaboration agreement Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathies CH24H inhibitor Oral OV935* Undisclosed Oral Orphan Epilepsy Robust Product Pipeline
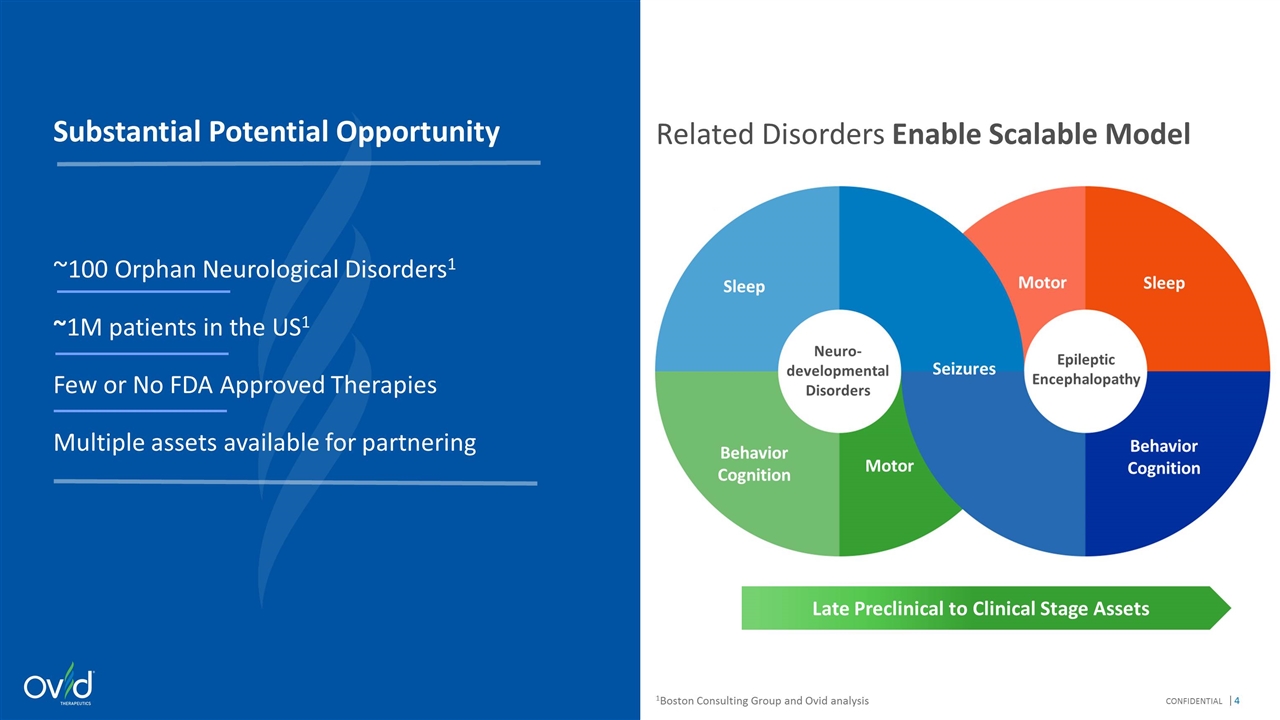
Substantial Potential Opportunity ~100 Orphan Neurological Disorders1 ~1M patients in the US1 Few or No FDA Approved Therapies Multiple assets available for partnering Late Preclinical to Clinical Stage Assets Related Disorders Enable Scalable Model 1Boston Consulting Group and Ovid analysis
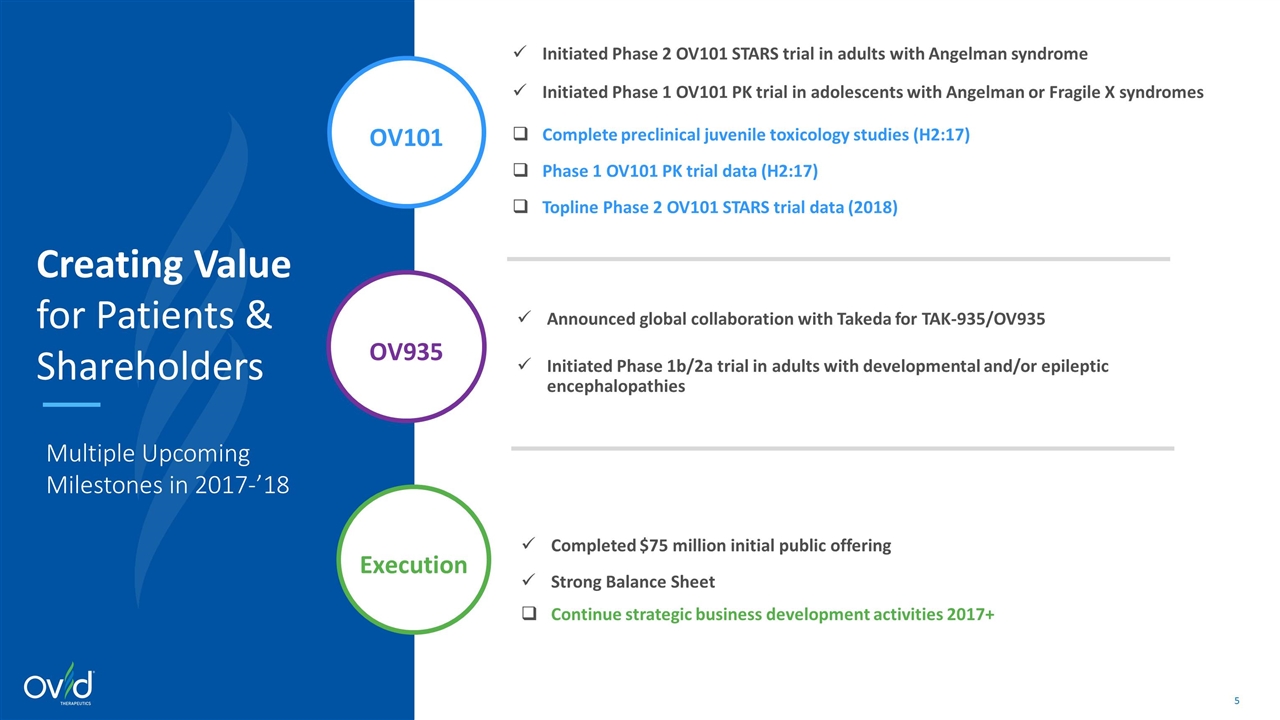
OV935 Execution OV101 Announced global collaboration with Takeda for TAK-935/OV935 Initiated Phase 1b/2a trial in adults with developmental and/or epileptic encephalopathies Initiated Phase 2 OV101 STARS trial in adults with Angelman syndrome Initiated Phase 1 OV101 PK trial in adolescents with Angelman or Fragile X syndromes Complete preclinical juvenile toxicology studies (H2:17) Phase 1 OV101 PK trial data (H2:17) Topline Phase 2 OV101 STARS trial data (2018) Completed $75 million initial public offering Strong Balance Sheet Continue strategic business development activities 2017+ Creating Value for Patients & Shareholders Multiple Upcoming Milestones in 2017-’18

OUR TEAM Jeremy Levin, DPhil, MB BChir Chairman & CEO Matthew During, MD, DSc Director, Founder, President & CSO Yaron Werber, MD, MBA Chief Business and Financial Officer & Secretary Amit Rakhit, MD, MBA Chief Medical and Portfolio Management Officer Dirk Haasner, PhD, MPM Senior Vice President, Global Regulatory Affairs Claude Nicaise, MD Head, Strategic Orphan Regulatory Affairs Suzanne Wakamoto, SPHR, SHRM-SCP Senior Vice President, Human Resources President & CEO, Teva Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Senior Vice President of Strategy, Alliances and Transactions, Bristol-Myers Squibb & Co. Global Head of Strategic Alliances, Novartis AG Co-Founder, NightstaRx Limited Professor of Neurosurgery, Yale University Professor, Cornell University Adjunct Professor, Ohio State University Managing Director & Head of U.S. Healthcare and Biotech Equity Research Teams, Citigroup Global Markets Inc. Vice President & Senior Biotech Analyst, Cowen & Co. Senior Vice President, Worldwide Medical, Biogen Inc. Vice president, Program Leadership & Management, Biogen Inc. Vice President, Intercontinental Medical, Bristol-Myers Squibb & Co. Vice President Regulatory and Medical Affairs, and Vice president Regulatory Strategy and Policy, Lundbeck USA Global Life-Cycle Leader, Roche AG Global Project Leader, Roche AG Head of HR, Blue Man Group Director of HR, Cadus Pharmaceuticals Corporation Senior Vice President, Strategic Product Development and Global Regulatory Affairs, Alexion Pharmaceuticals Vice President of Development and Worldwide Regulatory Sciences and Strategy, Bristol-Myers Squibb & Co.

OV101 Potential First-in-Class Therapeutic for Angelman & Fragile X Syndromes

Angelman Syndrome A Significant Unmet Need Epidemiology and Treatments Prevalence ~1/12,000 to ~ 1/20,000 ~16,000-27,000 patients in the US Treatment No FDA-approved therapies available Current treatment options limited to symptomatic agents and anti-seizure medications Monogenetic disorder that results in loss of UBE3A gene expression Developmental delay and behavioral disturbances Impaired motor coordination Seizures/abnormal EEG Sleep disturbances Severe speech impairments Genetics and Clinical Manifestation AS No FDA-approved therapies available Presents in early childhood and is a lifelong disorder

Epidemiology and Treatments Prevalence ~1/3,600-4,000 males ~1/4,000-6,000 females ~ 68,000 to 85,000 patients in the US Treatment No FDA-approved therapies available Limited to physical, communication, behavior and symptomatic therapy Genetics and Clinical Manifestations Monogenetic trinucleotide (CGG) repeat disorder in the FMR1 gene Intellectual disability Behavioral disturbances (e.g., anxiety, aggression) Language impairment No FDA-approved therapies available Presents in early childhood and is a lifelong disorder Fragile X Syndrome A Significant Unmet Need

Potential first-in-class, potent, δ-selective, extrasynaptic GABAA receptor agonist (δSEGA) Demonstrated ability to restore tonic inhibition and improve several key phenotypes in preclinical models of Angelman syndrome (AS) and Fragile X syndrome (FXS) Drug profile validated by clinical data in >4,000 adults with insomnia (approximately 950 patient-years of exposure) Phase 2 STARS trial in adult AS patients; data in 2018 Phase 1 PK trial in adolescents with AS/FXS; data in H2:17 Preclinical juvenile toxicology data in H2:17 to support pediatric studies Protected by two U.S. patents for methods of use for treating AS until 2035 Orphan drug designation for OV101 for the treatment of AS NOVEL MECHANISM OF ACTION ONGOING CLINICAL STUDIES ROBUST DATA PACKAGE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OVERVIEW OV101: Impacts Tonic Inhibition Restores Key Mechanism Underlying Neurodevelopmental Disorders In-licensed based on data package supporting mechanism of action in Angelman and Fragile X syndromes
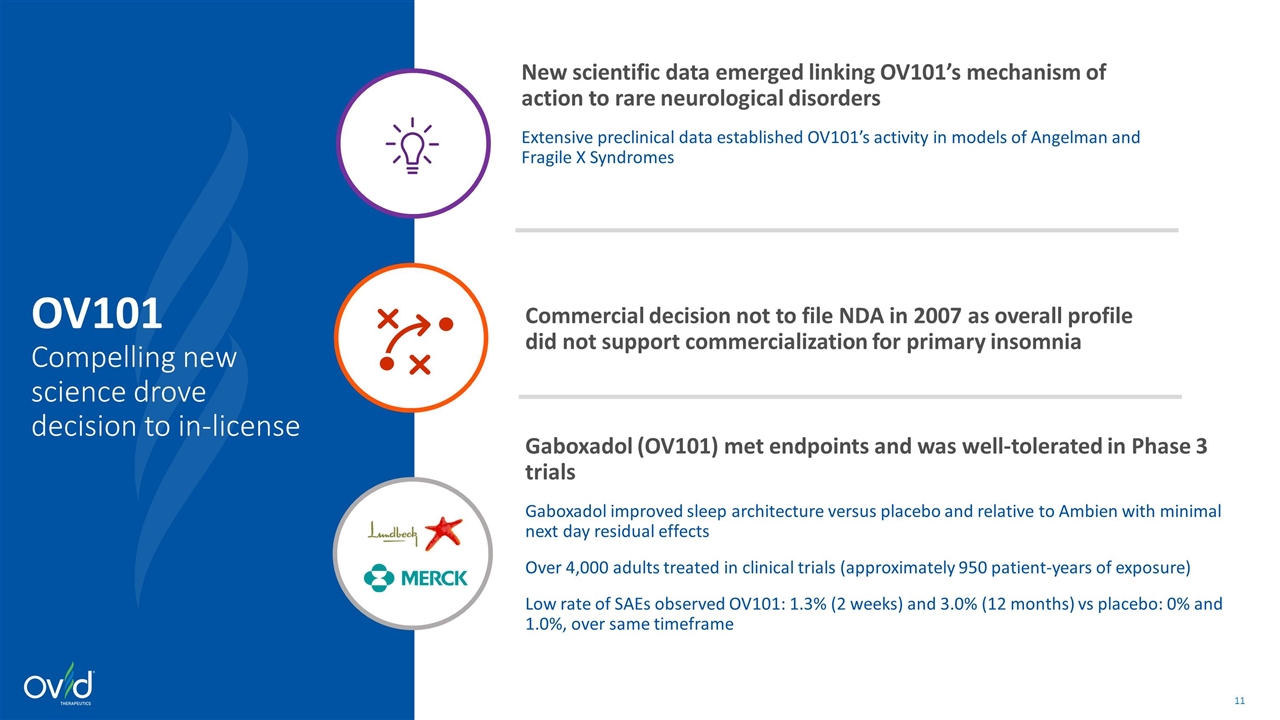
OV101 Compelling new science drove decision to in-license Gaboxadol (OV101) met endpoints and was well-tolerated in Phase 3 trials Gaboxadol improved sleep architecture versus placebo and relative to Ambien with minimal next day residual effects Over 4,000 adults treated in clinical trials (approximately 950 patient-years of exposure) Low rate of SAEs observed OV101: 1.3% (2 weeks) and 3.0% (12 months) vs placebo: 0% and 1.0%, over same timeframe Commercial decision not to file NDA in 2007 as overall profile did not support commercialization for primary insomnia New scientific data emerged linking OV101’s mechanism of action to rare neurological disorders Extensive preclinical data established OV101’s activity in models of Angelman and Fragile X Syndromes
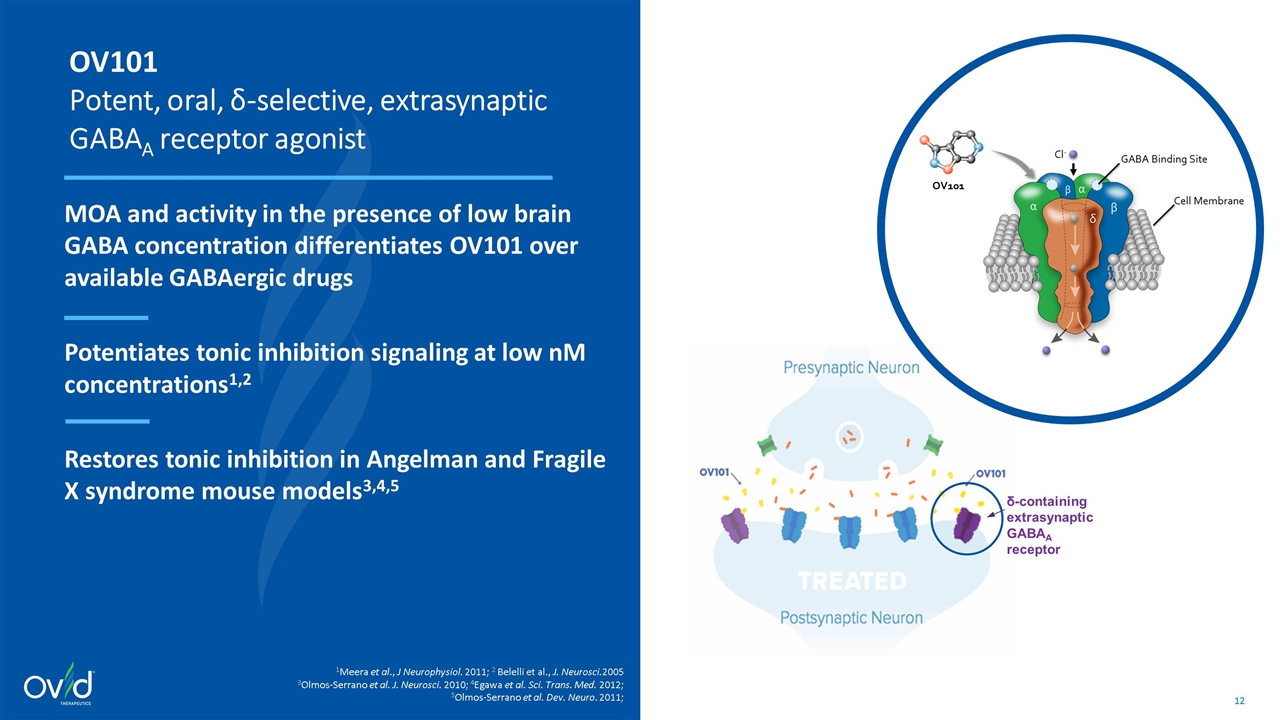
δ-containing extrasynaptic GABAA receptor OV101 Potent, oral, δ-selective, extrasynaptic GABAA receptor agonist MOA and activity in the presence of low brain GABA concentration differentiates OV101 over available GABAergic drugs Potentiates tonic inhibition signaling at low nM concentrations1,2 Restores tonic inhibition in Angelman and Fragile X syndrome mouse models3,4,5 1Meera et al., J Neurophysiol. 2011; 2 Belelli et al., J. Neurosci.2005 3Olmos-Serrano et al. J. Neurosci. 2010; 4Egawa et al. Sci. Trans. Med. 2012; 5Olmos-Serrano et al. Dev. Neuro. 2011;
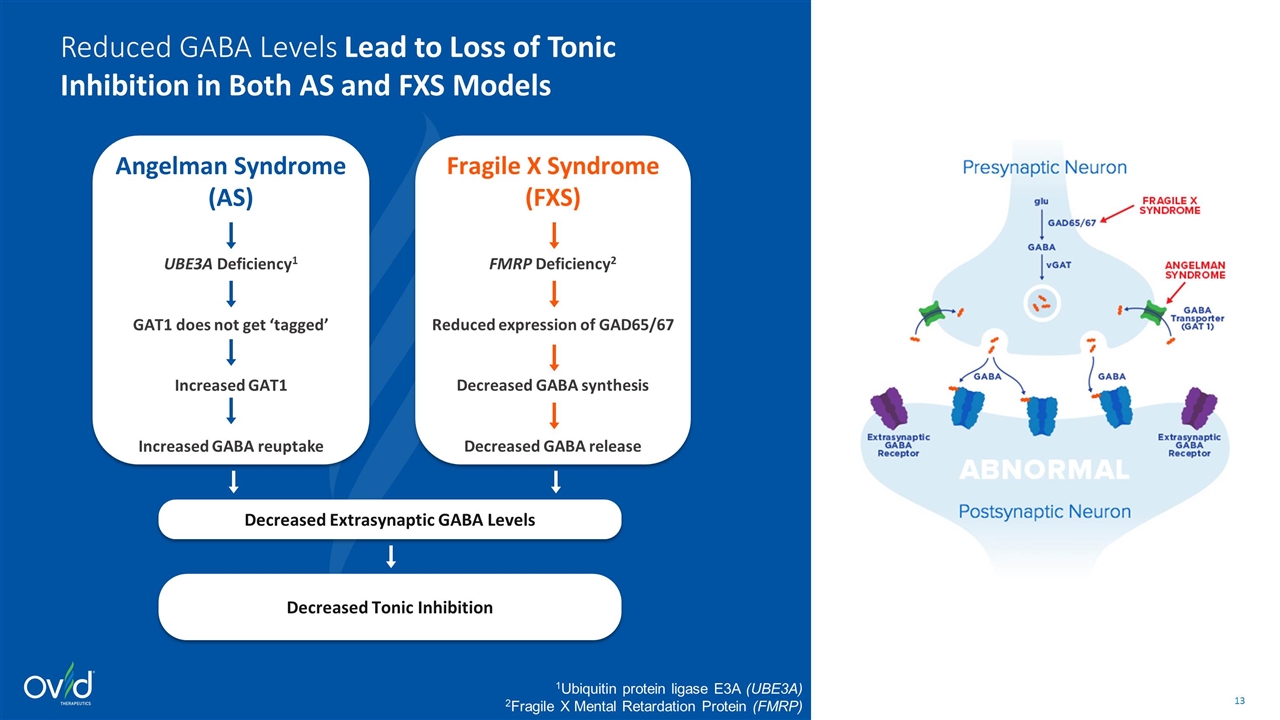
Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) FMRP Deficiency2 Reduced expression of GAD65/67 Decreased GABA synthesis Decreased GABA release 1Ubiquitin protein ligase E3A (UBE3A) 2Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein (FMRP) Angelman Syndrome (AS) UBE3A Deficiency1 GAT1 does not get ‘tagged’ Increased GAT1 Increased GABA reuptake Decreased Extrasynaptic GABA Levels Decreased Tonic Inhibition Reduced GABA Levels Lead to Loss of Tonic Inhibition in Both AS and FXS Models
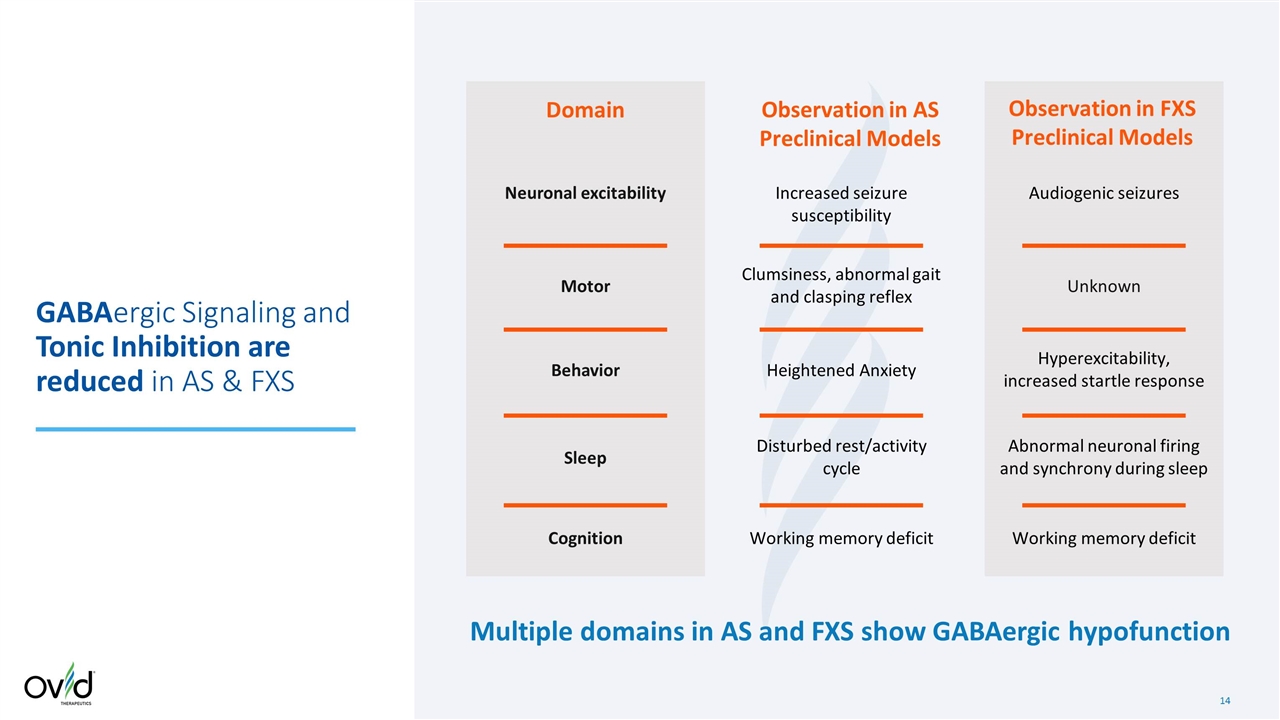
Increased seizure susceptibility Domain Observation in AS Preclinical Models GABAergic Signaling and Tonic Inhibition are reduced in AS & FXS Observation in FXS Preclinical Models Audiogenic seizures Hyperexcitability, increased startle response Working memory deficit Abnormal neuronal firing and synchrony during sleep Neuronal excitability Motor Behavior Sleep Cognition Unknown Working memory deficit Clumsiness, abnormal gait and clasping reflex Heightened Anxiety Disturbed rest/activity cycle Multiple domains in AS and FXS show GABAergic hypofunction
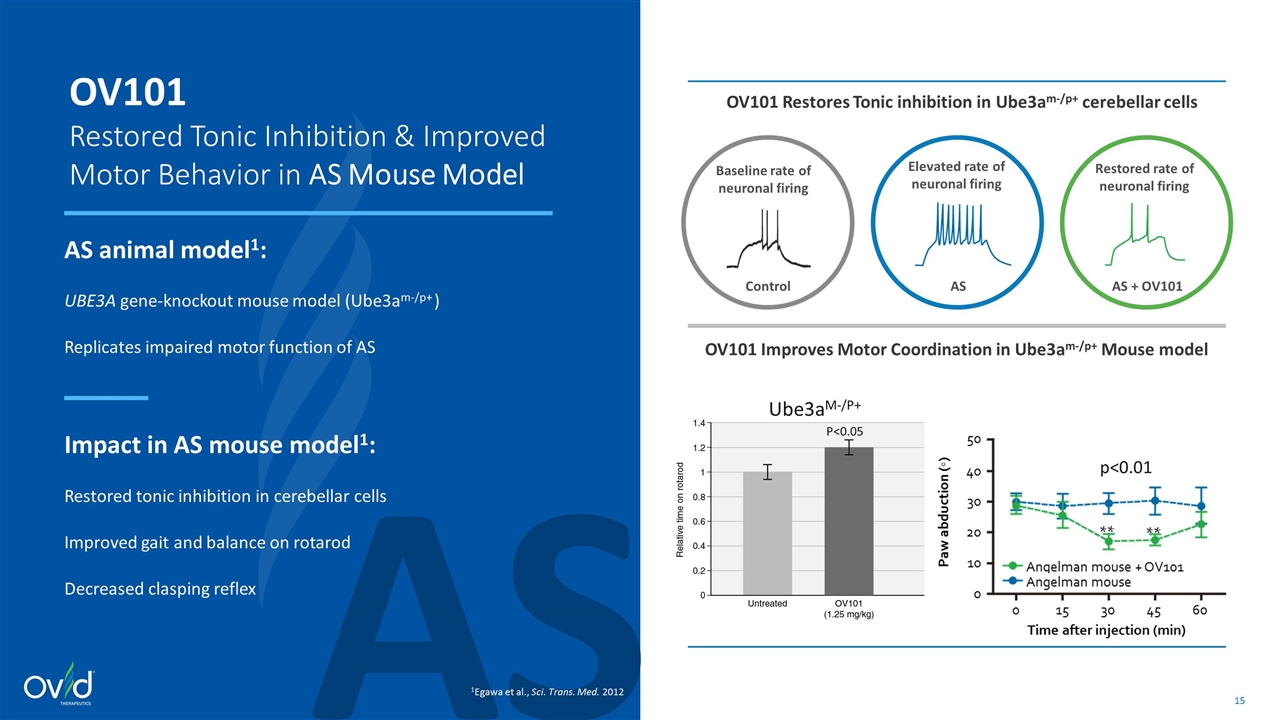
AS OV101 Restored Tonic Inhibition & Improved Motor Behavior in AS Mouse Model AS animal model1: UBE3A gene-knockout mouse model (Ube3am-/p+ ) Replicates impaired motor function of AS Impact in AS mouse model1: Restored tonic inhibition in cerebellar cells Improved gait and balance on rotarod Decreased clasping reflex 1Egawa et al., Sci. Trans. Med. 2012 Elevated rate of neuronal firing Restored rate of neuronal firing AS AS + OV101 Baseline rate of neuronal firing Control OV101 Restores Tonic inhibition in Ube3am-/p+ cerebellar cells OV101 Improves Motor Coordination in Ube3am-/p+ Mouse model P<0.05 Ube3am-/p+ p<0.01
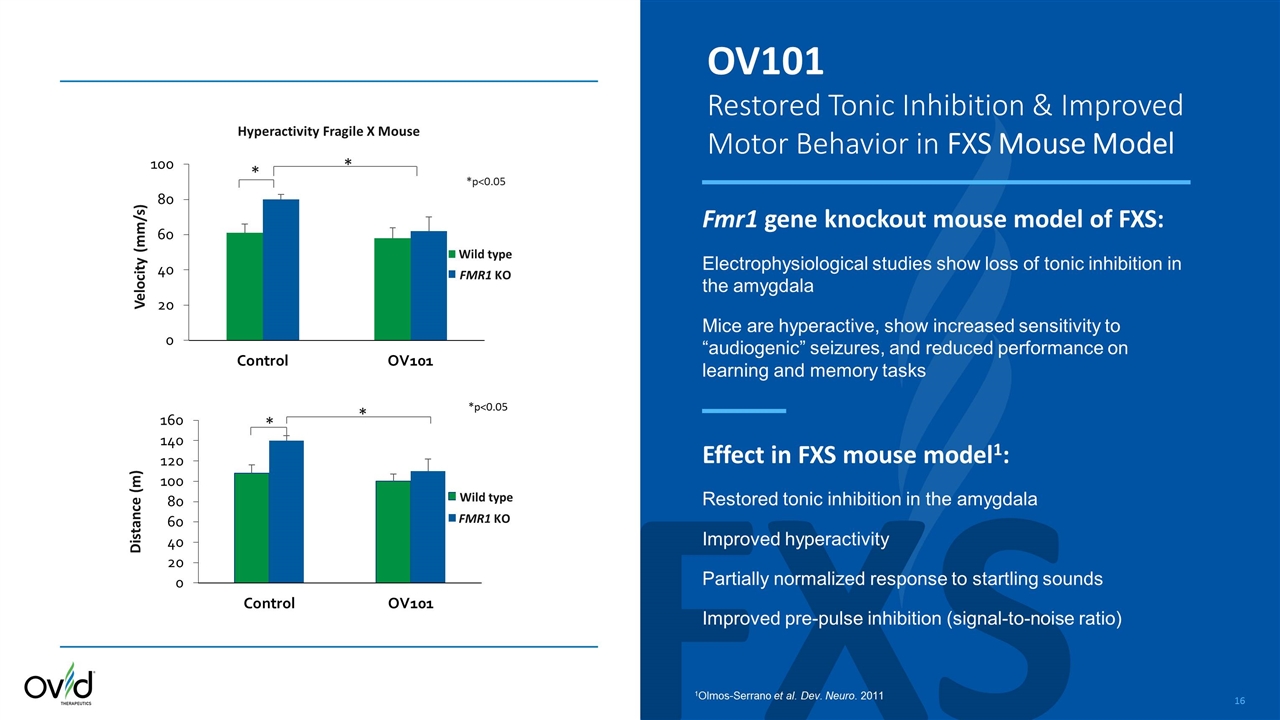
FXS OV101 Restored Tonic Inhibition & Improved Motor Behavior in FXS Mouse Model Fmr1 gene knockout mouse model of FXS: Electrophysiological studies show loss of tonic inhibition in the amygdala Mice are hyperactive, show increased sensitivity to “audiogenic” seizures, and reduced performance on learning and memory tasks Effect in FXS mouse model1: Restored tonic inhibition in the amygdala Improved hyperactivity Partially normalized response to startling sounds Improved pre-pulse inhibition (signal-to-noise ratio) 1Olmos-Serrano et al. Dev. Neuro. 2011 Distance (m) * * * * Hyperactivity Fragile X Mouse Velocity (mm/s) *p<0.05 FMR1 KO Wild type Wild type FMR1 KO

OV101 Clinical Development in Angelman and Fragile X Syndromes Phase 2 Data (Expected 2018) Adult Angelman Syndrome Clinical Trial: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Safety and Efficacy Trial of OV101 Inclusion N=75, age 18-49 years Diagnosis of AS Exclusion Poorly controlled seizures Concomitant disease that would limit participation Baseline Week 12 Randomization Placebo twice daily OV101 twice daily OV101 once daily 15 mg night, 10 mg day 15 mg night Primary endpoint Incidence of adverse events Exploratory secondary endpoints Clinical Global Impression, Motor Function, Sleep, Behavior, Quality of Life Phase 1 Data (Expected H2:17) PK Trial in Adolescent Subjects with AS/FXS n=12 Age: 13-17 years Single dose, open label, PK trial Designed to select dosing for future trials

OV935 New Approach to Potentially Treat Rare Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathies
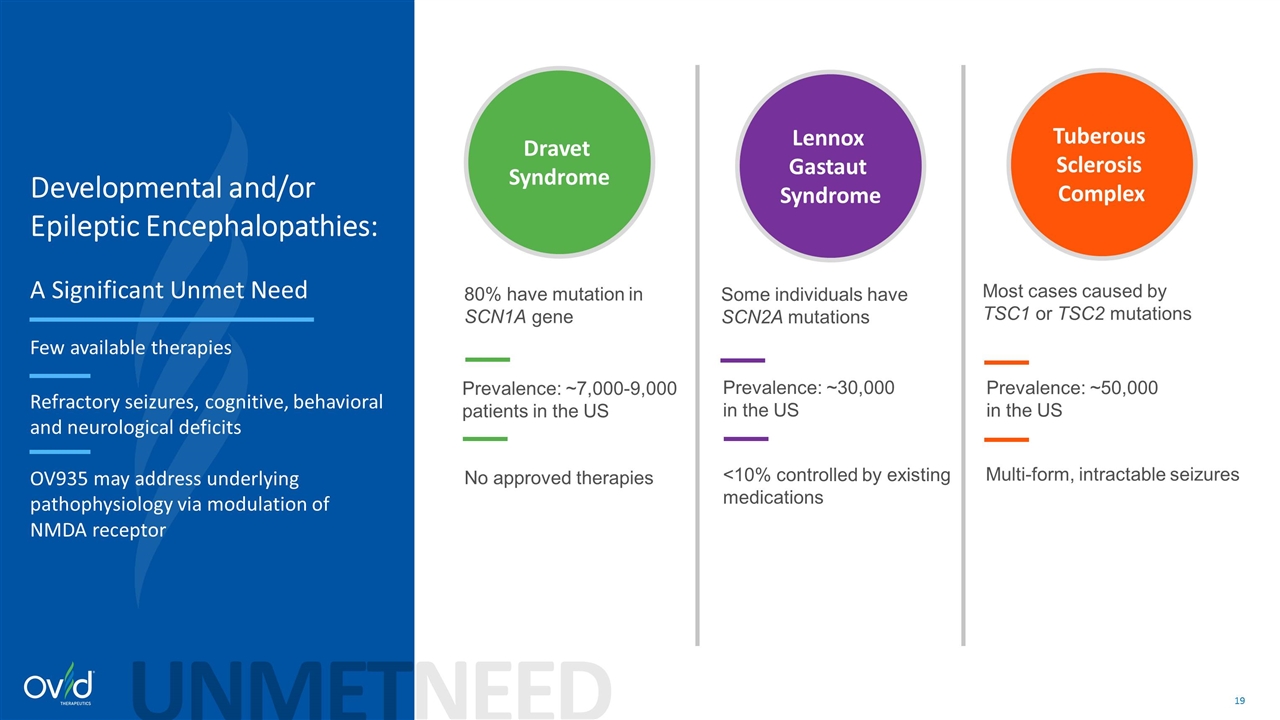
Some individuals have SCN2A mutations Most cases caused by TSC1 or TSC2 mutations Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathies: A Significant Unmet Need Few available therapies Refractory seizures, cognitive, behavioral and neurological deficits OV935 may address underlying pathophysiology via modulation of NMDA receptor Dravet Syndrome Lennox Gastaut Syndrome Tuberous Sclerosis Complex UNMETNEED Prevalence: ~7,000-9,000 patients in the US Prevalence: ~30,000 in the US Prevalence: ~50,000 in the US 80% have mutation in SCN1A gene No approved therapies <10% controlled by existing medications Multi-form, intractable seizures

OV935: A Novel Approach for Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathies (dEE) Potential first-in-class CH24H inhibitor Differentiated mechanism over available anti-seizure drugs Broad activity in preclinical seizure models, including genetic refractory models Commence studies in adults with a focus to move to adolescent and pediatric patients Potent (nM), highly selective, cholesterol 24-hydroxylase inhibitor (CH24H) Encouraging anti-seizure activity across several epileptic animal models Phase 1b/2a trial ongoing in adult patients with dEE including, Dravet syndrome, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Portfolio of issued U.S. and international patents directed to composition-of-matter expiring in 2032 NOVEL MECHANISM OF ACTION ONGOING CLINICAL STUDY ROBUST DATA PACKAGE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY OVERVIEW Plasma-based 24HC biomarker
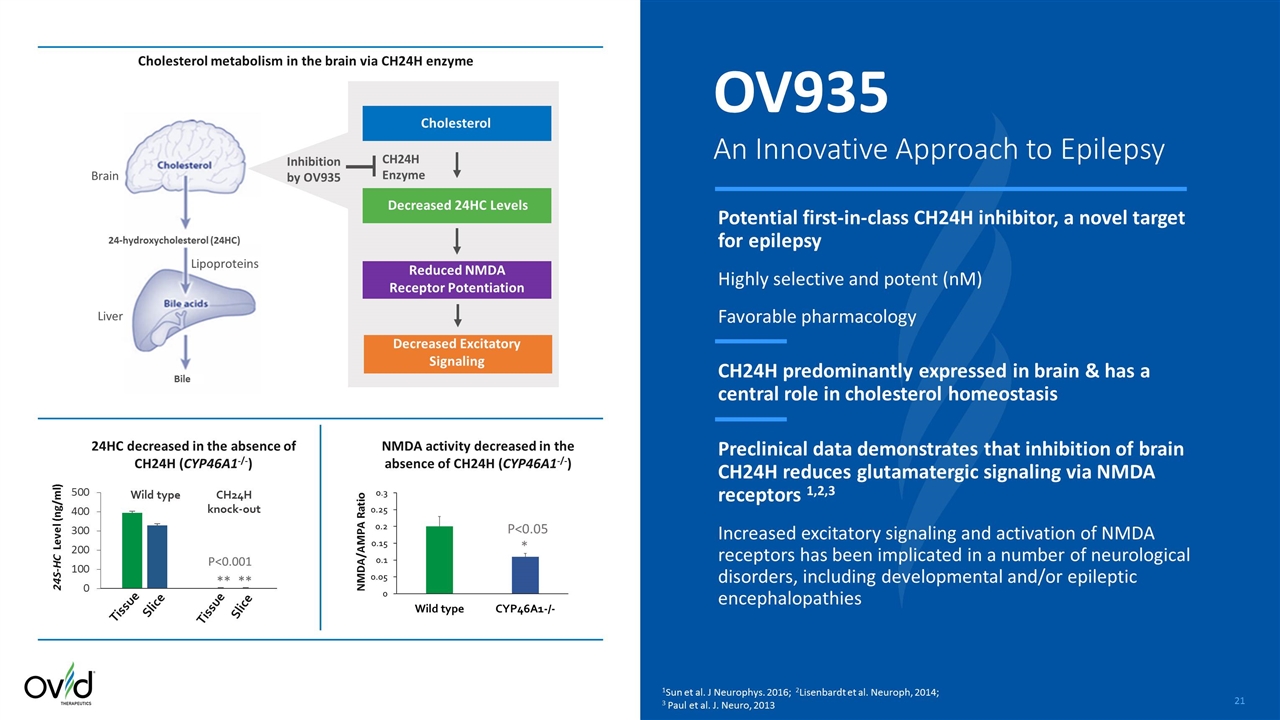
Tissue Slice Slice Tissue CH24H knock-out Wild type Potential first-in-class CH24H inhibitor, a novel target for epilepsy Highly selective and potent (nM) Favorable pharmacology CH24H predominantly expressed in brain & has a central role in cholesterol homeostasis Preclinical data demonstrates that inhibition of brain CH24H reduces glutamatergic signaling via NMDA receptors 1,2,3 Increased excitatory signaling and activation of NMDA receptors has been implicated in a number of neurological disorders, including developmental and/or epileptic encephalopathies CH24H Enzyme Inhibition by OV935 Brain Liver Lipoproteins 24-hydroxycholesterol (24HC) Bile Cholesterol Reduced NMDA Receptor Potentiation Decreased Excitatory Signaling Decreased 24HC Levels OV935 An Innovative Approach to Epilepsy 1Sun et al. J Neurophys. 2016; 2Lisenbardt et al. Neuroph, 2014; 3 Paul et al. J. Neuro, 2013 P<0.05 * 24S-HC Level (ng/ml) ** ** P<0.001 24HC decreased in the absence of CH24H (CYP46A1-/-) NMDA activity decreased in the absence of CH24H (CYP46A1-/-) NMDA/AMPA Ratio Cholesterol metabolism in the brain via CH24H enzyme
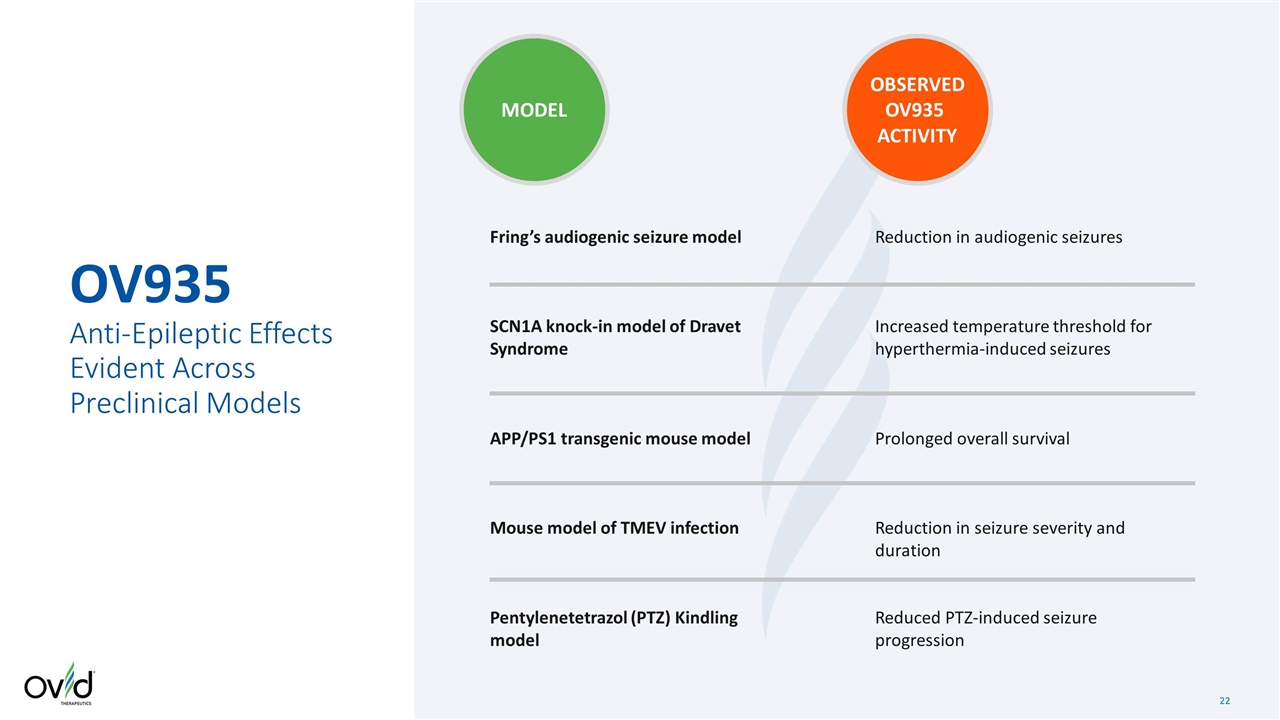
OV935 Anti-Epileptic Effects Evident Across Preclinical Models Fring’s audiogenic seizure model SCN1A knock-in model of Dravet Syndrome APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model Mouse model of TMEV infection Pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) Kindling model Reduction in audiogenic seizures Increased temperature threshold for hyperthermia-induced seizures Prolonged overall survival Reduction in seizure severity and duration Reduced PTZ-induced seizure progression MODEL OBSERVED OV935 ACTIVITY
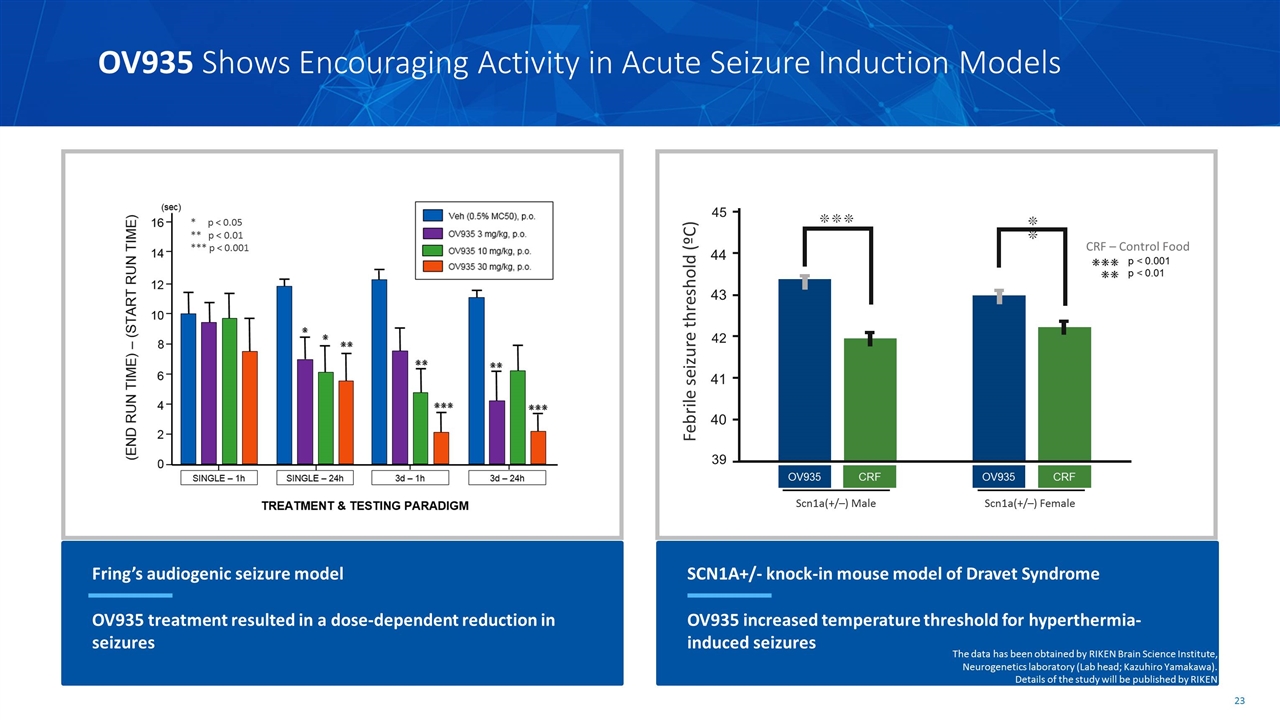
OV935 Shows Encouraging Activity in Acute Seizure Induction Models Fring’s audiogenic seizure model OV935 treatment resulted in a dose-dependent reduction in seizures * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01 *** p < 0.001 SCN1A+/- knock-in mouse model of Dravet Syndrome OV935 increased temperature threshold for hyperthermia-induced seizures CRF – Control Food The data has been obtained by RIKEN Brain Science Institute, Neurogenetics laboratory (Lab head; Kazuhiro Yamakawa). Details of the study will be published by RIKEN ❊❊❊ 40 42 44 41 43 45 39 OV935 OV935 CRF CRF Scn1a(+/–) Male Scn1a(+/–) Female ❊❊ Febrile seizure threshold (ºC)
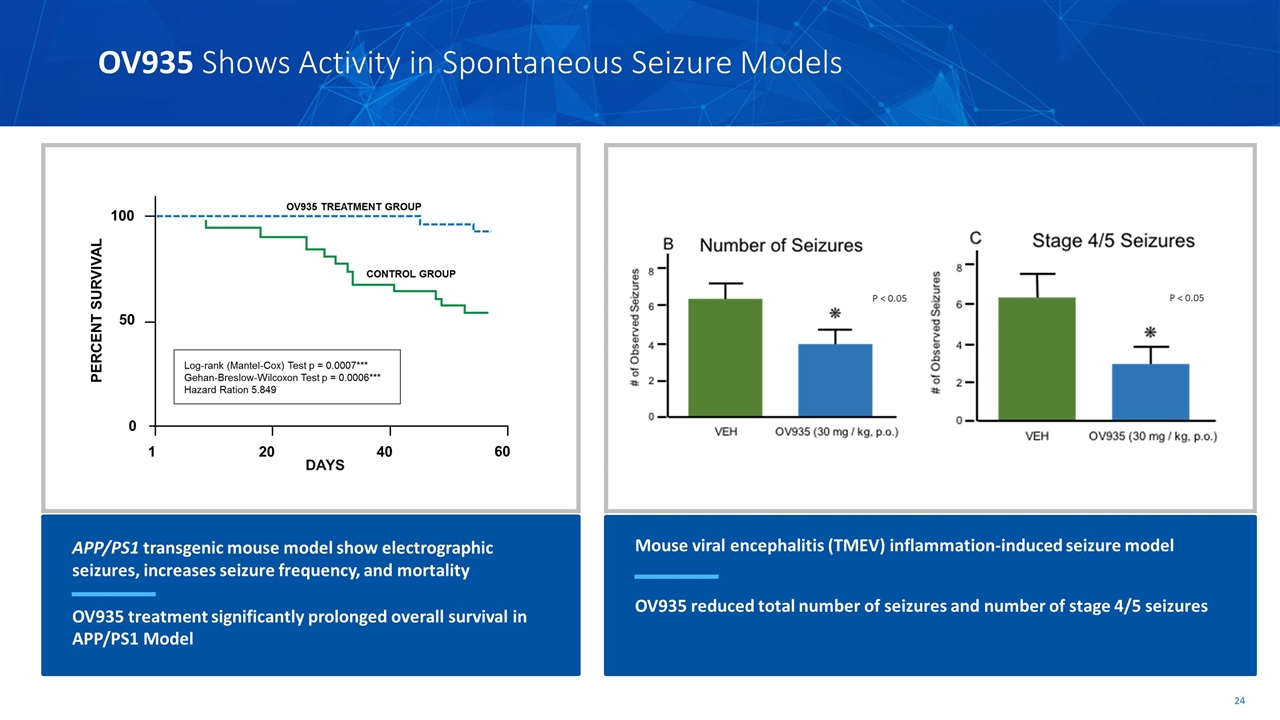
P < 0.05 P < 0.05 OV935 Shows Activity in Spontaneous Seizure Models Mouse viral encephalitis (TMEV) inflammation-induced seizure model OV935 reduced total number of seizures and number of stage 4/5 seizures APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model show electrographic seizures, increases seizure frequency, and mortality OV935 treatment significantly prolonged overall survival in APP/PS1 Model DAYS
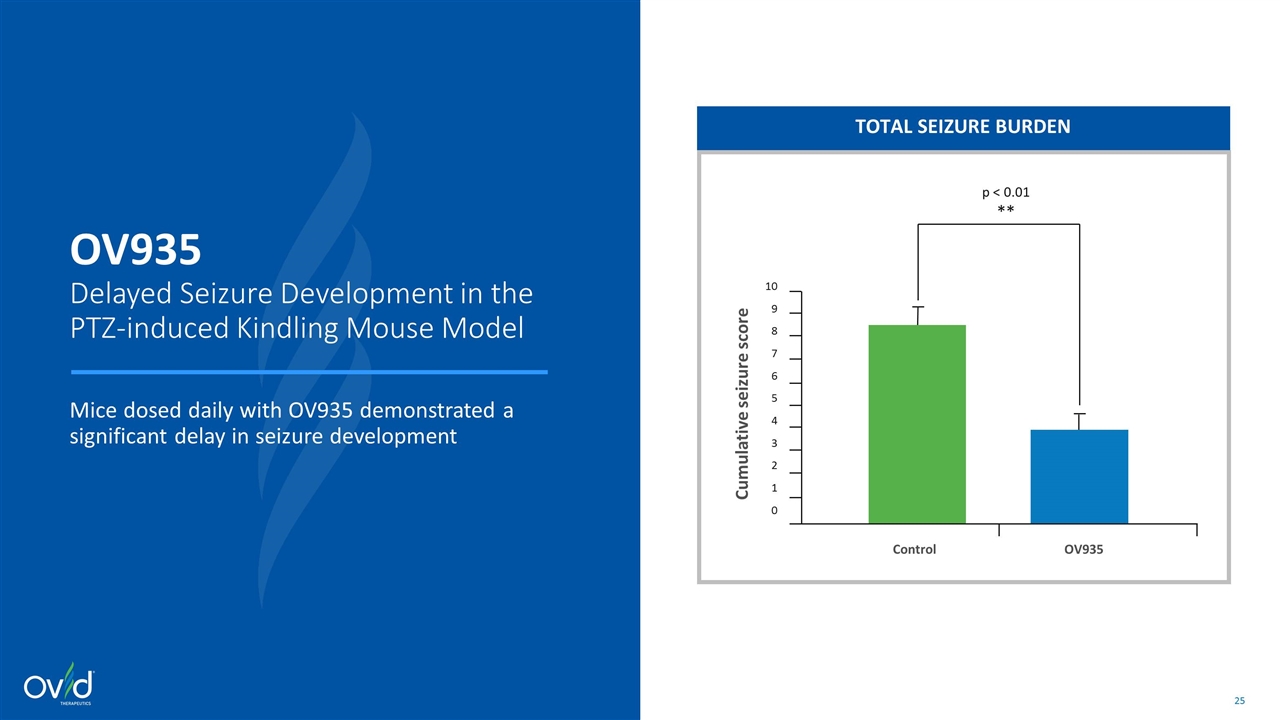
TOTAL SEIZURE BURDEN OV935 Delayed Seizure Development in the PTZ-induced Kindling Mouse Model Mice dosed daily with OV935 demonstrated a significant delay in seizure development Control OV935 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Cumulative seizure score p < 0.01 **

Design Phase 1, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, single ascending dose Subjects 48 Dosage 15-1,350mg QD Design Phase 1, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, multiple ascending dose Subjects 40 Dosage 100-600mg QD, and 300mg BID; 14 days Design Open-label, non-randomized Subjects 11 Dosage 50-600mg QD Design Phase 1, randomized, open-label, single dose trial Subjects 9 Dosage 300mg (tab.) QD; 300mg (sol.) QD Safety and tolerability Safety and tolerability Brain CH24H enzyme occupancy using PET Relative bioavailability (tablet vs. solution); effect of food Four Phase 1 Trials Completed 86 Healthy Subjects Dosed Single doses of up to 1,350mg of OV935 were well tolerated In 14-day MAD trial, doses of 100mg, 300mg and 400mg QD were well tolerated One volunteer at 600mg QD experienced acute psychosis One volunteer at 300mg BID experienced an event of confusional state One placebo volunteer reported events of nightmares, spatial disorientation, insomnia and dizziness All TEAEs resolved with continued dosing through day 15 Overall no safety issues of concern were identified; no SAEs reported
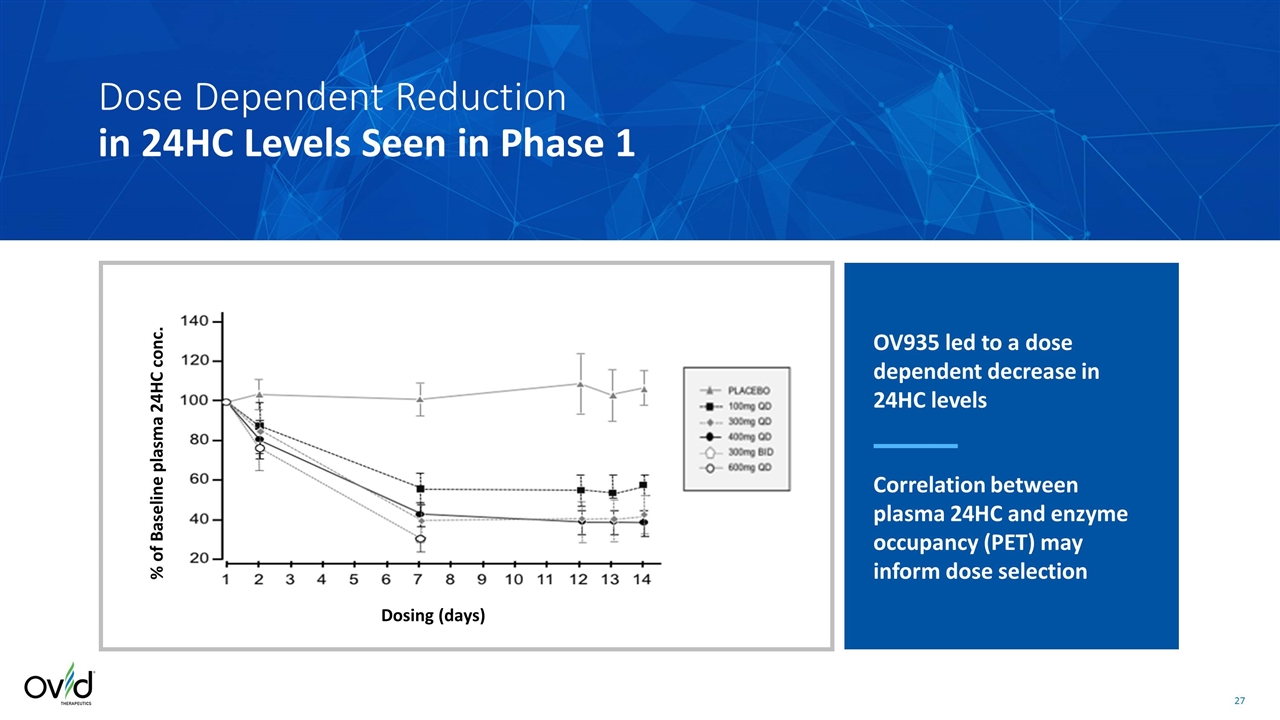
Dosing (days) % of Baseline plasma 24HC conc. Dose Dependent Reduction in 24HC Levels Seen in Phase 1 OV935 led to a dose dependent decrease in 24HC levels Correlation between plasma 24HC and enzyme occupancy (PET) may inform dose selection
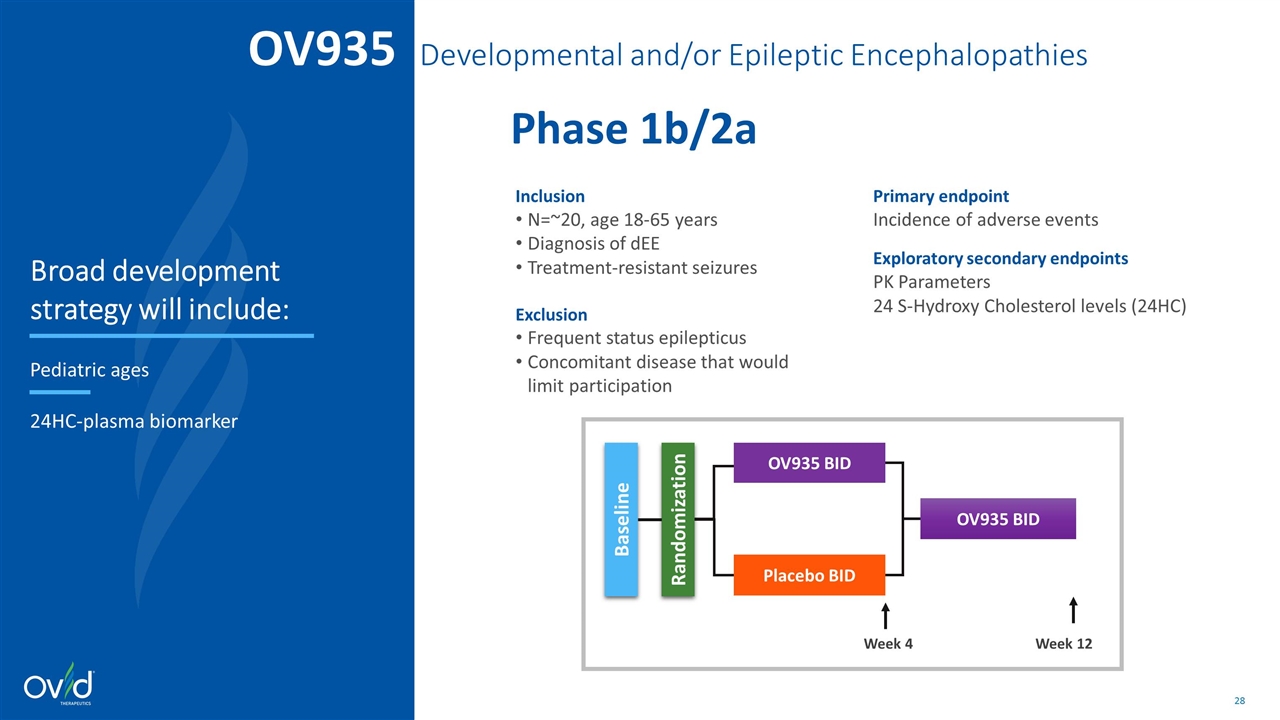
Inclusion N=~20, age 18-65 years Diagnosis of dEE Treatment-resistant seizures Exclusion Frequent status epilepticus Concomitant disease that would limit participation Primary endpoint Incidence of adverse events Exploratory secondary endpoints PK Parameters 24 S-Hydroxy Cholesterol levels (24HC) Week 12 Week 4 Randomization OV935 BID Placebo BID Baseline OV935 BID OV935 Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathies Phase 1b/2a Broad development strategy will include: Pediatric ages 24HC-plasma biomarker

FINANCE & BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT Comprehensive Approach to Secure Early to Late Stage Assets
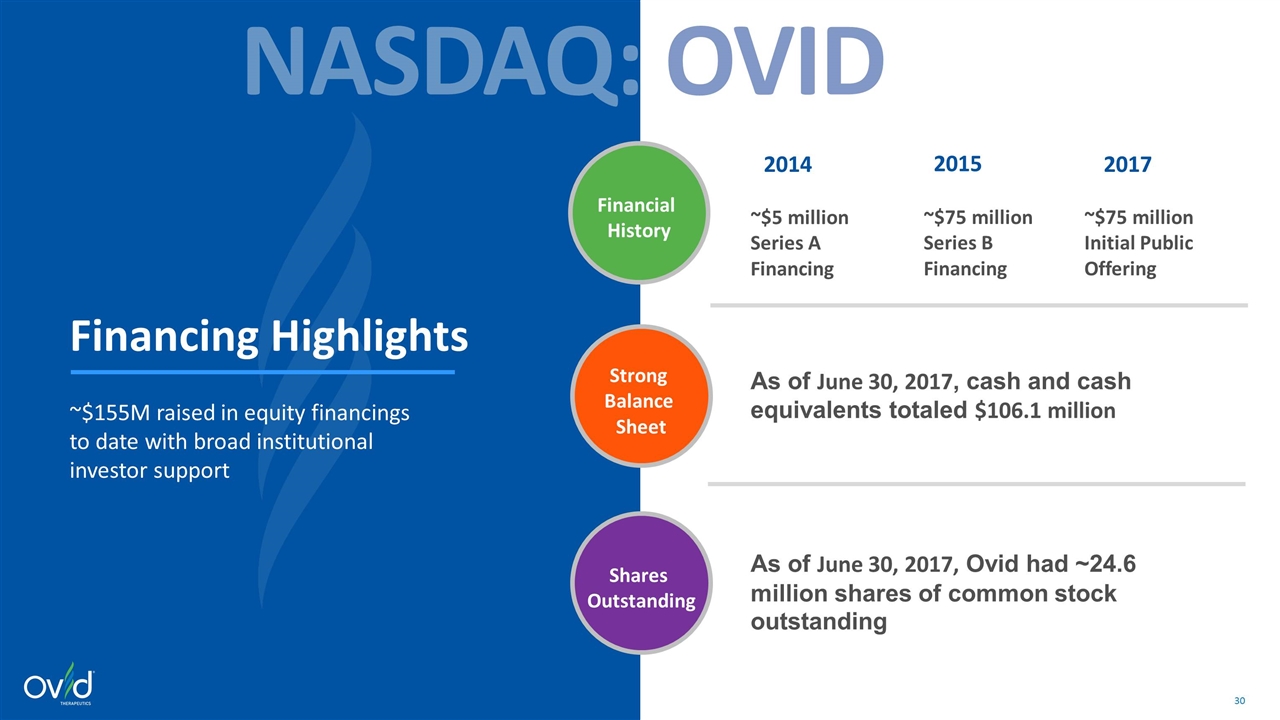
Financing Highlights ~$155M raised in equity financings to date with broad institutional investor support NASDAQ: OVID Financial History Strong Balance Sheet Shares Outstanding 2014 2015 2017 ~$75 million Series B Financing ~$5 million Series A Financing ~$75 million Initial Public Offering As of June 30, 2017, cash and cash equivalents totaled $106.1 million As of June 30, 2017, Ovid had ~24.6 million shares of common stock outstanding

OURPARTNER OV101 Agreement with Lundbeck Financial Terms with Lundbeck March 2015 exclusive license secured by Ovid Global rights Extensive patents Substantial active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) amounts Attractive financial terms to Ovid ~$4M of upfront equity to Lundbeck Up to $181M due to Lundbeck upon achievement of development, regulatory and sales milestones (first payment is $10M due upon successful completion of a Phase 3 trial) Low-to-mid double-digit royalties

COLLABORATION A Novel OneTeam Collaboration with Takeda Global OneTeam Global, equal development and commercialization collaboration for OV935 in Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathies (dEE) Joint collaboration and governance driven by OneTeam approach for development and commercialization Ovid leads clinical development and commercial role in US, Europe, Canada and Israel Ovid to assume regulatory lead following first approval in US, EU and Israel Takeda received ~$26M in upfront equity First patient enrolled in first Phase 3 in certain dEE triggers milestone to Takeda equal to the lesser of (i) 8% outstanding capital stock or (ii) $50M equity Takeda eligible for future regulatory and commercial milestones ~$35M Phase 1b/2a trial in dEE ongoing

INVESTMENTHIGHLIGHTS VALUE TEAM VALIDATED EXECUTION OPPORTUNITY Potential to create significant value for patients & stockholders Building leading company in rare neurological disorders ~$155M in equity financing Highly experienced management team Deep expertise in translational science, drug evaluation and orphan clinical drug development Track record of success in drug development and strategic transactions Two first-in-class assets in a growing pipeline OV101: Phase 2 trial in adults with AS and Phase 1 trial in adolescents with AS/FXS ongoing OV935: Phase 1b/2a ongoing in dEE Attractive markets with the opportunity for significant global sales Targeting novel MOAs that may offer differentiated profiles Scalable model allows expansion into additional patient populations Validated expertise with collaborations Takeda & Lundbeck transactions validate approach and expertise

Serious News for Serious Traders! Try StreetInsider.com Premium Free!
You May Also Be Interested In
- Flash News: OKX Lists Solana-Based Memecoins WIF and MEW on its Perpetual Futures Market
- IRLAB to Present at Redeye Investor Forum
- CubicFarm Systems Corp. Announces Successor Auditor and Anticipated Delay in the Filing of Annual Financial Statements and Related Documents
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share