Form 497 GOLDMAN SACHS TRUST
| AN INVESTMENT IN A FUND IS NOT A BANK DEPOSIT AND IS NOT INSURED BY THE FEDERAL DEPOSIT INSURANCE CORPORATION OR ANY OTHER GOVERNMENT AGENCY. AN INVESTMENT IN A FUND INVOLVES INVESTMENT RISKS, AND YOU MAY LOSE MONEY IN A FUND. |
1 | |
6 | |
11 | |
16 | |
21 | |
27 | |
34 | |
40 | |
44 | |
45 | |
45 | |
54 | |
61 | |
63 | |
77 | |
109 |

| Investment Objective |
| Fees and Expenses of the Fund |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Service |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of offering price) |
5.50% | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of the lower of original purchase price or sale proceeds) 1 |
None | 1.00% | None | None | None | None | None |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Service |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Management Fees | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% |
| Distribution and/or Service (12b-1) Fees | 0.25% | 0.75% | 0.00% | 0.25% | 0.00% | 0.50% | 0.00% |
| Other Expenses | 0.24% | 0.49% | 0.12% | 0.37% | 0.24% | 0.24% | 0.11% |
| Service Fees | 0.00% | 0.25% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Shareholder Administration Fees | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.25% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| All Other Expenses | 0.24% | 0.24% | 0.12% | 0.12% | 0.24% | 0.24% | 0.11% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
1.20% | 1.95% | 0.83% | 1.33% | 0.95% | 1.45% | 0.82% |
| Expense Limitation 2 |
(0.08)% | (0.08)% | (0.08)% | (0.08)% | (0.08)% | (0.08)% | (0.08)% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Limitation |
1.12% | 1.87% | 0.75% | 1.25% | 0.87% | 1.37% | 0.74% |
1 |
A contingent deferred sales charge (“CDSC”) of 1% is imposed on Class C Shares redeemed within 12 months of purchase. |
2 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, service fees, shareholder administration fees, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.004% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. This arrangement will remain in effect through at least December 29, 2021, and prior to such date the Investment Adviser may not terminate the arrangement without the approval of the Board of Trustees. |
| Expense Example |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class A Shares | $658 | $903 | $1,166 | $1,918 |
| Class C Shares | ||||
| – Assuming complete redemption at end of period | $290 | $604 | $1,045 | $2,268 |
| – Assuming no redemption | $190 | $604 | $1,045 | $2,268 |
| Institutional Shares | $77 | $257 | $453 | $1,018 |
| Service Shares | $127 | $414 | $721 | $1,594 |
| Investor Shares | $89 | $295 | $518 | $1,159 |
| Class R Shares | $139 | $451 | $785 | $1,728 |
| Class R6 Shares | $76 | $254 | $447 | $1,006 |
| Portfolio Turnover |
| Principal Strategy |
| Principal Risks of the Fund |
| Performance |
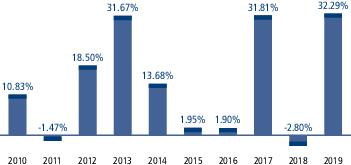
During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| Best Quarter Return | 16.94% | March 31, 2012 |
| Worst Quarter Return | -14.76% | September 30, 2011 |
| AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURN |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years |
Class A Shares (Inception 4/20/1990) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 24.99% | 10.72% | 12.41% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | 23.81% | 7.85% | 9.98% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 15.60% | 7.98% | 9.70% |
| Russell 1000 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.43% | 11.48% | 13.53% |
Class C Shares (Inception 8/15/1997) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 30.22% | 11.15% | 12.22% |
| Russell 1000 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.43% | 11.48% | 13.53% |
Institutional Shares (Inception 8/15/1997) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 32.75% | 12.41% | 13.49% |
| Russell 1000 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.43% | 11.48% | 13.53% |
Service Shares (Inception 8/15/1997) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 32.13% | 11.85% | 12.93% |
| Russell 1000 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.43% | 11.48% | 13.53% |
Investor Shares (Inception 11/30/2007) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 32.60% | 12.25% | 13.33% |
| Russell 1000 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.43% | 11.48% | 13.53% |
Class R Shares (Inception 11/30/2007) |
|||
| Returns | 31.94% | 11.69% | 12.77% |
| Russell 1000 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.43% | 11.48% | 13.53% |
Class R6 Shares (Inception 7/31/2015)* |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 32.75% | 12.42% | 13.50% |
| Russell 1000 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.43% | 11.48% | 13.53% |
* |
Class R6 Shares commenced operations on July 31, 2015. Prior to that date, the performance of Class R6 Shares shown in the table above is that of Institutional Shares. Performance has not been adjusted to reflect the lower expenses of Class R6 Shares. Class R6 Shares would have had higher returns because: (i) Institutional Shares and Class R6 Shares represent interests in the same portfolio of securities; and (ii) Class R6 Shares have lower expenses. |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |

| Investment Objective |
| Fees and Expenses of the Fund |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of offering price) | 5.50% | None | None | None | None | None |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of the lower of original purchase price or sale proceeds) 1 |
None | 1.00% | None | None | None | None |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Management Fees | 0.76% | 0.76% | 0.76% | 0.76% | 0.76% | 0.76% |
| Distribution and/or Service (12b-1) Fees | 0.25% | 0.75% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.50% | 0.00% |
| Other Expenses | 0.36% | 0.61% | 0.24% | 0.36% | 0.36% | 0.23% |
| Service Fees | 0.00% | 0.25% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| All Other Expenses | 0.36% | 0.36% | 0.24% | 0.36% | 0.36% | 0.23% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
1.37% | 2.12% | 1.00% | 1.12% | 1.62% | 0.99% |
| Fee Waiver and Expense Limitation 2 |
(0.27)% | (0.27)% | (0.20)% | (0.27)% | (0.27)% | (0.20)% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waiver and Expense Limitation |
1.10% | 1.85% | 0.80% | 0.85% | 1.35% | 0.79% |
1 |
A contingent deferred sales charge (“CDSC”) of 1% is imposed on Class C Shares redeemed within 12 months of purchase. |
2 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, service fees, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.004% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. Additionally, Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC (“Goldman Sachs”), the Fund’s transfer agent, has agreed to waive a portion of its transfer agency fee (a component of “Other Expenses”) equal to 0.07% as an annual percentage rate of the average daily net assets attributable to Class A, Class C, Investor and Class R Shares of the Fund. These arrangements will remain in effect through at least December 29, 2021, and prior to such date, the Investment Adviser and Goldman Sachs may not terminate the arrangements without the approval of the Board of Trustees. |
| Expense Example |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class A Shares | $656 | $935 | $1,234 | $2,084 |
| Class C Shares | ||||
| – Assuming complete redemption at end of period | $288 | $638 | $1,114 | $2,430 |
| – Assuming no redemption | $188 | $638 | $1,114 | $2,430 |
| Institutional Shares | $82 | $298 | $533 | $1,206 |
| Investor Shares | $87 | $329 | $591 | $1,339 |
| Class R Shares | $137 | $485 | $856 | $1,899 |
| Class R6 Shares | $81 | $295 | $528 | $1,195 |
| Portfolio Turnover |
| Principal Strategy |
| Principal Risks of the Fund |
| Performance |
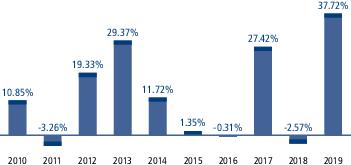
During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| Best Quarter Return | 17.33% | March 31, 2012 |
| Worst Quarter Return | -16.73% | December 31, 2018 |
| AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURN |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years |
Class A Shares (Inception 9/3/2002) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 30.18% | 10.30% | 11.68% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | 27.75% | 7.98% | 9.72% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 19.51% | 7.67% | 9.14% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Class C Shares (Inception 9/3/2002) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 35.51% | 10.70% | 11.47% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Institutional Shares (Inception 9/3/2002) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 38.13% | 11.96% | 12.75% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Investor Shares (Inception 11/30/2007) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 38.03% | 11.83% | 12.59% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Class R Shares (Inception 11/30/2007) |
|||
| Returns | 37.33% | 11.26% | 12.04% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Class R6 Shares (Inception 7/31/2015)* |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 38.18% | 11.97% | 12.76% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
* |
Class R6 Shares commenced operations on July 31, 2015. Prior to that date, the performance of Class R6 Shares shown in the table above is that of Institutional Shares. Performance has not been adjusted to reflect the lower expenses of Class R6 Shares. Class R6 Shares would have had higher returns because: (i) Institutional Shares and Class R6 Shares represent interests in the same portfolio of securities; and (ii) Class R6 Shares have lower expenses. |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |

| Investment Objective |
| Fees and Expenses of the Fund |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of offering price) | 5.50% | None | None | None | None | None |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of the lower of original purchase price or sale proceeds) 1 |
None | 1.00% | None | None | None | None |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Management Fees | 0.55% | 0.55% | 0.55% | 0.55% | 0.55% | 0.55% |
| Distribution and/or Service (12b-1) Fees | 0.25% | 0.75% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.50% | 0.00% |
| Other Expenses | 1.55% | 1.80% | 1.43% | 1.55% | 1.55% | 1.42% |
| Service Fees | 0.00% | 0.25% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| All Other Expenses | 1.55% | 1.55% | 1.43% | 1.55% | 1.55% | 1.42% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
2.35% | 3.10% | 1.98% | 2.10% | 2.60% | 1.97% |
| Expense Limitation 2 |
(1.39)% | (1.39)% | (1.39)% | (1.39)% | (1.39)% | (1.39)% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Limitation |
0.96% | 1.71% | 0.59% | 0.71% | 1.21% | 0.58% |
1 |
A contingent deferred sales charge (“CDSC”) of 1% is imposed on Class C Shares redeemed within 12 months of purchase. |
2 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, service fees, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.004% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. This arrangement will remain in effect through at least December 29, 2021, and prior to such date, the Investment Adviser may not terminate the arrangement without the approval of the Board of Trustees. |
| Expense Example |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class A Shares | $643 | $1,117 | $1,617 | $2,987 |
| Class C Shares | ||||
| – Assuming complete redemption at end of period | $274 | $826 | $1,504 | $3,314 |
| – Assuming no redemption | $174 | $826 | $1,504 | $3,314 |
| Institutional Shares | $60 | $486 | $939 | $2,194 |
| Investor Shares | $73 | $523 | $1,001 | $2,321 |
| Class R Shares | $123 | $676 | $1,256 | $2,831 |
| Class R6 Shares | $59 | $483 | $933 | $2,183 |
| Portfolio Turnover |
| Principal Strategy |
| Principal Risks of the Fund |
| Performance |
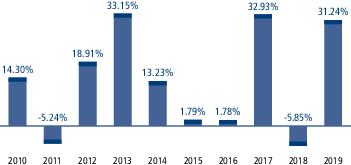
During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| Best Quarter Return | 17.17% | March 31, 2012 |
| Worst Quarter Return | -16.64% | September 30, 2011 |
| AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURN |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years |
Class A Shares (Inception 1/31/2008) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 24.01% | 9.96% | 12.06% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | 22.38% | 7.48% | 9.70% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 15.34% | 7.40% | 9.40% |
Class C Shares (Inception 1/31/2008) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 28.94% | 10.38% | 11.86% |
Institutional Shares (Inception 1/31/2008) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 31.69% | 11.61% | 13.14% |
Investor Shares (Inception 1/31/2008) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 31.48% | 11.47% | 12.98% |
Class R Shares (Inception 1/31/2008) |
|||
| Returns | 30.88% | 10.92% | 12.43% |
Class R6 Shares (Inception 7/31/2015)* |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 31.68% | 11.61% | 13.14% |
| S&P 500 ® Index (Total Return, Unhedged, USD) (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.49% | 11.69% | 13.55% |
* |
Class R6 Shares commenced operations on July 31, 2015. Prior to that date, the performance of Class R6 Shares shown in the table above is that of Institutional Shares. Performance has not been adjusted to reflect the lower expenses of Class R6 Shares. Class R6 Shares would have had higher returns because: (i) Institutional Shares and Class R6 Shares represent interests in the same portfolio of securities; and (ii) Class R6 Shares have lower expenses. |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |

| Investment Objective |
| Fees and Expenses of the Fund |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Service |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of offering price) |
5.50% | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of the lower of original purchase price or sale proceeds) 1 |
None | 1.00% | None | None | None | None | None |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Service |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Management Fees | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% | 0.71% |
| Distribution and/or Service (12b-1) Fees | 0.25% | 0.75% | 0.00% | 0.25% | 0.00% | 0.50% | 0.00% |
| Other Expenses | 0.39% | 0.64% | 0.27% | 0.52% | 0.39% | 0.39% | 0.26% |
| Service Fees | 0.00% | 0.25% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Shareholder Administration Fees | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.25% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| All Other Expenses | 0.39% | 0.39% | 0.27% | 0.27% | 0.39% | 0.39% | 0.26% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
1.35% | 2.10% | 0.98% | 1.48% | 1.10% | 1.60% | 0.97% |
| Expense Limitation 2 |
(0.23)% | (0.23)% | (0.23)% | (0.23)% | (0.23)% | (0.23)% | (0.23)% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Limitation |
1.12% | 1.87% | 0.75% | 1.25% | 0.87% | 1.37% | 0.74% |
1 |
A contingent deferred sales charge (“CDSC”) of 1% is imposed on Class C Shares redeemed within 12 months of purchase. |
2 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, service fees, shareholder administration fees, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.004% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. This arrangement will remain in effect through at least December 29, 2021, and prior to such date the Investment Adviser may not terminate the arrangement without the approval of the Board of Trustees. |
| Expense Example |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class A Shares | $658 | $933 | $1,228 | $2,066 |
| Class C Shares | ||||
| – Assuming complete redemption at end of period | $290 | $636 | $1,108 | $2,413 |
| – Assuming no redemption | $190 | $636 | $1,108 | $2,413 |
| Institutional Shares | $77 | $289 | $519 | $1,180 |
| Service Shares | $127 | $445 | $786 | $1,749 |
| Investor Shares | $89 | $327 | $584 | $1,320 |
| Class R Shares | $139 | $482 | $849 | $1,881 |
| Class R6 Shares | $76 | $286 | $514 | $1,169 |
| Portfolio Turnover |
| Principal Strategy |
| Principal Risks of the Fund |
| Performance |
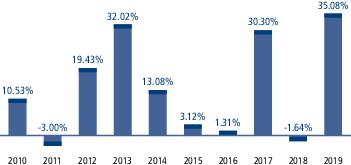
During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| Best Quarter Return | 16.80% | March 31, 2019 |
| Worst Quarter Return | -16.54% | December 31, 2018 |
| AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURN |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years |
Class A Shares (Inception 5/24/1999) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 27.65% | 11.32% | 12.56% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | 22.88% | 6.93% | 9.36% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 19.61% | 8.19% | 9.67% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Class C Shares (Inception 5/24/1999) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 32.68% | 11.73% | 12.37% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Institutional Shares (Inception 5/24/1999) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 35.57% | 13.01% | 13.66% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Service Shares (Inception 5/24/1999) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 34.90% | 12.48% | 13.12% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Investor Shares (Inception 1/6/2009) |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 35.43% | 12.86% | 13.49% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Class R Shares (Inception 1/6/2009) |
|||
| Returns | 34.70% | 12.31% | 12.97% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
Class R6 Shares (Inception 7/31/2015)* |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | 35.68% | 13.03% | 13.67% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 14.62% | 15.21% |
* |
Class R6 Shares commenced operations on July 31, 2015. Prior to that date, the performance of Class R6 Shares shown in the table above is that of Institutional Shares. Performance has not been adjusted to reflect the lower expenses of Class R6 Shares. Class R6 Shares would have had higher returns because: (i) Institutional Shares and Class R6 Shares represent interests in the same portfolio of securities; and (ii) Class R6 Shares have lower expenses. |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |

Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Purchases (as a percentage of offering price) | ||||||
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of the lower of original purchase price or sale proceeds) 1 |
Class A |
Class C |
Institutional |
Investor |
Class R |
Class R6 | |
| Management Fees | ||||||
| Distribution and/or Service (12b-1) Fees | ||||||
| Other Expenses 2 |
||||||
| Service Fees | ||||||
| All Other Expenses | ||||||
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
||||||
| Fee Waiver and Expense Limitation 3 |
( |
( |
( |
( |
( |
( |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Fee Waiver and Expense Limitation |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, service fees, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.084% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. Additionally, Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC (“Goldman Sachs”), the Fund’s transfer agent, has agreed to waive a portion of its transfer agency fee (a component of “Other Expenses”) equal to 0.02% as an annual percentage rate of the average daily net assets attributable to Class A, Class C, Investor, and Class R Shares of the Fund. These arrangements will remain in effect through at least |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class A Shares | $ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
| Class C Shares | ||||
| – |
$ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
| – |
$ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
| Institutional Shares | $ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
| Investor Shares | $ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
| Class R Shares | $ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
| Class R6 Shares | $ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
| ■ | gambling, |
| ■ | alcohol, |
| ■ | tobacco, |
| ■ | coal, and |
| ■ | weapons. |
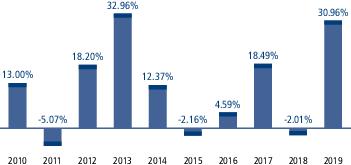
During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| - |
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
Class A Shares (Inception |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | |||
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | |||
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | |||
Class C Shares (Inception |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | |||
Institutional Shares (Inception |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | |||
Investor Shares (Inception |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | |||
Class R Shares (Inception |
|||
| Returns | |||
Class R6 Shares (Inception |
|||
| Returns Before Taxes | |||
| S&P 500 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
* |
Class R6 Shares commenced operations on July 31, 2015. Prior to that date, the performance of Class R6 Shares shown in the table above is that of Institutional Shares. Performance has not been adjusted to reflect the lower expenses of Class R6 Shares. Class R6 Shares would have had higher returns because: (i) Institutional Shares and Class R6 Shares represent interests in the same portfolio of securities; and (ii) Class R6 Shares have lower expenses. |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |
Additional Summary Information
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |
| INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE |
| PRINCIPAL INVESTMENT STRATEGIES |
| ■ | gambling, |
| ■ | alcohol, |
| ■ | tobacco, |
| ■ | coal, and |
| ■ | weapons. |
| ■ | quality of earnings; |
| ■ | concern for shareholder interests and minority shareholder rights; |
| ■ | unethical business conduct, for example unethical methods of obtaining contracts and/or close connections with authorities; |
| ■ | board structure; |
| ■ | board diversity; |
| ■ | executive management team, for example CEO/CFO effectiveness and acting in interest of shareholders; and |
| ■ | executive compensation. |
| ■ | environmental and social reporting, disclosure and transparency; |
| ■ | material environmental litigation and/or controversies; |
| ■ | material social litigation and/or controversies; |
| ■ | labor practices, for example track record in treatment of employees and supply chain management; |
| ■ | human rights considerations; and |
| ■ | climate change policies and environmental practices. |
| ■ | Has a class of securities whose principal securities market is in the United States; |
| ■ | Has its principal office in the United States; |
| ■ | Derives 50% or more of its total revenue or profit from goods produced, sales made or services provided in the United States; |
| ■ | Maintains 50% or more of its assets in the United States; or |
| ■ | Is otherwise determined to be economically tied to the United States by the Investment Adviser in its discretion. For example, the Investment Adviser may use the classifications assigned by third parties, including an issuer’s “country of risk” as determined by Bloomberg or the classifications assigned to an issuer by the Fund’s benchmark index provider. These classifications are generally based on a number of criteria, including an issuer’s country of domicile, the primary stock exchange on which an issuer’s securities trade, the location from which the majority of an issuer’s revenue is derived, and an issuer’s reporting currency. Although the Investment Adviser may rely on these classifications, it is not required to do so. |
| ■ | Market uncertainty exists. |
| ■ | Their economic value is not recognized by the market. |
| ■ | Sustainable operating or competitive advantage. |
| ■ | Excellent stewardship of capital. |
| ■ | Capability to earn above their cost of capital. |
| ■ | Strong or improving balance sheets and cash flow. |
| ■ | Understand the business, management, products and competition. |
| ■ | Perform intensive, hands-on fundamental research. |
| ■ | Seek businesses with strategic competitive advantages. |
| ■ | Over the long-term, expect each company’s stock price ultimately to track the growth in the value of the business. |
| ADDITIONAL FEES AND EXPENSES INFORMATION |
| ADDITIONAL PERFORMANCE INFORMATION |
| OTHER INVESTMENT PRACTICES AND SECURITIES |
10 Percent of total assets (including securities lending collateral) (italic type) 10 Percent of net assets (excluding borrowings for investment purposes) (roman type) • No specific percentage limitation on usage; limited only by the objectives and strategies of the Fund — Not permitted |
Capital Growth Fund |
Concentrated Growth Fund |
Flexible Cap Fund |
Strategic Growth Fund |
U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
|
Investment Practices |
||||||
| Borrowings | 33 1 ⁄3 |
33 1 ⁄3 |
33 1 ⁄3 |
33 1 ⁄3 |
33 1 ⁄3 |
|
| Credit, Currency, Index, Interest Rate, Total Return and Mortgage Swaps and Options on Swaps | — |
— |
• | — |
— |
|
| Cross Hedging of Currencies | • | • | • | — |
— |
|
| Custodial Receipts and Trust Certificates | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Equity Swaps | • | • | • | — |
— |
|
| Foreign Currency Transactions (including forward contracts)* | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Futures Contracts and Options and Swaps on Futures Contracts | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Illiquid Investments** | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| Investment Company Securities (including ETFs) 1 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
|
| Options on Foreign Currencies 2 |
• | • | • | • | — |
|
| Options 3 |
• | • | • | • | — |
|
| Preferred Stock, Warrants and Stock Purchase Rights | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Repurchase Agreements | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Securities Lending | 33 1 ⁄3 |
33 1 ⁄3 |
33 1 ⁄3 |
33 1 ⁄3 |
33 1 ⁄3 |
|
| Short Sales Against the Box | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | — |
|
| Unseasoned Companies | • | • | • | • | • | |
| When-Issued Securities and Forward Commitments | • | • | • | • | • |
* |
Limited by the amount the Fund invests in foreign securities. |
** |
Illiquid investments are any investments that a Fund reasonably expects cannot be sold or disposed of in current market conditions in seven calendar days or less without the sale or disposition significantly changing the market value of the investment. |
1 |
This percentage limitation does not apply to a Fund’s investments in investment companies (including ETFs) where a higher percentage limitation is permitted under the terms of an SEC exemptive order or SEC exemptive rule. |
2 |
The Funds (except for the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may purchase and sell call and put options on foreign currencies. |
3 |
The Funds (except for the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may sell call and put options and purchase call and put options on securities and other instruments in which the Funds may invest or any index consisting of securities or other instruments in which they may invest. |
10 Percent of total assets (italic type) 10 Percent of net assets (including borrowings for investment purposes) (roman type) • No specific percentage limitation on usage; limited only by the objectives and strategies of the Fund — Not permitted |
Capital Growth Fund |
Concentrated Growth Fund |
Flexible Cap Fund |
Strategic Growth Fund |
U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
|
Investment Securities |
||||||
| American, European and Global Depositary Receipts | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Asset-Backed and Mortgage-Backed Securities 4 |
• | • | • | • | — | |
| Bank Obligations 4 |
• | • | • | • | • | |
| Convertible Securities 5 |
• | • | • | • | • | |
| Corporate Debt Obligations 4 |
• | • | • | • | • | |
| Equity Investments | 90+ |
90+ |
80+ |
90+ |
80+ |
|
| Emerging Country Securities 6 |
10 |
10 |
25 |
10 |
— | |
| Fixed Income Securities 7 |
10 |
10 |
20 |
10 |
20 |
|
| Foreign Securities 6 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
20 |
|
| Initial Public Offerings (“IPOs”) | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Master Limited Partnerships | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Non-Investment Grade Fixed Income Securities 8 |
10 |
— |
10 |
10 |
— |
|
| Pre-IPO Investments (including late-stage private equity securities) | — |
— |
• | — |
— |
|
| Real Estate Investment Trusts (“REITs”) | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Structured Securities (which may include equity linked notes) 9 |
• | • | • | • | • | |
| Temporary Investments | • | • | • | • | • | |
| U.S. Government Securities 4 |
• | • | • | • | • |
4 |
Limited by the amount the Fund invests in fixed income securities. |
5 |
All Funds use the same rating criteria for convertible and non-convertible debt securities. |
6 |
The Capital Growth, Strategic Growth and Concentrated Growth Funds may each invest in the aggregate up to 25% of their total assets, and the Flexible Cap Fund may invest in the aggregate up to 25% of its net assets, in foreign securities, including emerging country securities. The U.S. Equity ESG Fund may invest in the aggregate up to 20% of its net assets in foreign securities and may not invest in emerging country securities. |
7 |
Except as noted under “Non-Investment Grade Fixed Income Securities,” fixed income securities must be investment grade (i.e., BBB– or higher by Standard & Poor’s, Baa3 or higher by Moody’s or have a comparable credit rating by another NRSRO or if unrated, determined by the Investment Adviser to be of comparable credit quality). |
8 |
May be BB+ or lower by Standard & Poor’s, Ba1 or lower by Moody’s or have a comparable credit rating by another NRSRO at the time of investment. |
9 |
Structured securities are not subject to the same minimum credit quality requirements as a Fund’s investments in fixed income securities. |
| ✓ Principal Risk • Additional Risk |
Capital Growth Fund |
Concentrated Growth Fund |
Flexible Cap Fund |
Strategic Growth Fund |
U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
|
| Credit/Default | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Derivatives | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Emerging Countries | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| ESG Standards | ✓ | |||||
| Foreign | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | • | |
| Geographic | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Initial Public Offering (“IPO”) | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Interest Rate | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Investment Style | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Issuer Concentration | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Large Shareholder Transactions | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Liquidity | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Management | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Market | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Master Limited Partnerships | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Mid-Cap and Small-Cap | • | ✓ | ✓ | • | • | |
| NAV | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Non-Investment Grade Fixed Income Securities | • | • | • | |||
| Portfolio Turnover Rate | ✓ | |||||
| Pre-IPO Investments | • | |||||
| Sector Risk | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Stock | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| U.S. Government Securities | • | • | • | • | • |
| ■ | Credit/Default Risk —An issuer or guarantor of fixed income securities or instruments held by the Fund (which may have low credit ratings), may default on its obligation to pay interest and repay principal or default on any other obligation. The credit quality of the Fund’s portfolio securities or instruments may meet the Fund’s credit quality requirements at the time of purchase but then deteriorate thereafter, and such a deterioration can occur rapidly. In certain instances, the downgrading or default of a single holding or guarantor of the Fund’s holdings may impair the Fund’s liquidity and have the potential to cause significant NAV deterioration. These risks are more pronounced in connection with a Fund’s investments in non-investment grade fixed income securities. |
| ■ | Derivatives Risk— The Fund’s use of options, futures, forwards, swaps, options on swaps, structured securities and other derivative instruments may result in losses. These instruments, which may pose risks in addition to and greater than those associated with investing directly in securities, currencies or other instruments, may be illiquid or less liquid, volatile, difficult to price and leveraged so that small changes in the value of the underlying instruments may produce disproportionate losses to the Fund. Certain derivatives are also subject to counter-party risk, which is the risk that the other party in the transaction will not fulfill its contractual obligations, liquidity risk and risks arising from margin requirements, which include the risk that the Fund will be required to pay additional margin or set aside additional collateral to maintain open derivative positions. Derivatives may be used for both hedging and non-hedging purposes. |
| The use of derivatives is a highly specialized activity that involves investment techniques and risks different from those associated with investments in more traditional securities and instruments, and there is no guarantee that the use of derivatives will achieve their intended result. If the Investment Adviser is incorrect in its expectation of the timing or level of fluctuation in securities prices, interest rates, currency prices or other variables, the use of derivatives could result in losses, which in some cases may be |
| significant. A lack of correlation between changes in the value of derivatives and the value of the portfolio assets (if any) being hedged could also result in losses. In addition, there is a risk that the performance of the derivatives or other instruments used by the Investment Adviser to replicate the performance of a particular asset class may not accurately track the performance of that asset class. | |
| As an investment company registered with the SEC, the Fund must identify on its books (often referred to as “asset segregation”) liquid assets, or engage in other SEC- or SEC staff-approved or other appropriate measures, to “cover” open positions with respect to certain kinds of derivative instruments. For more information about these practices, see Appendix A. As discussed in more detail in Appendix A and the SAI, the SEC adopted a final rule related to the use of derivatives, short sales, reverse repurchase agreements and certain other transactions by registered investment companies. In connection with the final rule, the SEC and its staff will rescind and withdraw applicable guidance and relief regarding asset segregation and coverage transactions reflected in the Fund’s asset segregation and cover practices discussed therein. | |
| ■ | Emerging Countries Risk— Investments in securities of issuers located in emerging countries are subject to the risks associated with investments in foreign securities. In addition, the securities markets of most emerging countries are less liquid, developed and efficient, are subject to greater price volatility, have smaller market capitalizations, have more or less government regulation and are not subject to as extensive and frequent accounting, auditing, financial and other reporting requirements as the securities markets of more developed countries. Further, investments in securities of issuers located in certain emerging countries involve the risk of loss resulting from problems in share registration, settlement or custody, substantial economic, political and social disruptions and the imposition of exchange controls (including repatriation restrictions). The legal remedies for investors in emerging markets may be more limited than the remedies available in the U.S., and the ability of U.S. authorities ( e.g. , SEC and the U.S. Department of Justice) to bring actions against bad actors may be limited. These risks are not normally associated with investments in more developed countries. For more information about these risks, see Appendix A. |
| ■ | ESG Standards Risk —The U.S. Equity ESG Fund’s adherence to its ESG criteria and the application of the Investment Adviser’s supplemental ESG analysis when selecting investments may affect the Fund’s exposure to certain companies, sectors, regions, and countries and may affect the Fund’s performance depending on whether such investments are in or out of favor. For example, the Fund generally will not seek to invest in companies that the Investment Adviser believes have adverse social or environmental impacts (i.e., gambling, alcohol, tobacco, coal or weapons companies), and the Fund generally will not seek to invest in companies that the Investment Adviser believes demonstrate weak corporate governance (e.g., certain state-owned enterprises). Adhering to the ESG criteria and applying the Investment Adviser’s supplemental ESG analysis may also affect the Fund’s performance relative to similar funds that do not adhere to such criteria or apply such analysis. Additionally, the Fund’s adherence to the ESG criteria and the application of the supplemental ESG analysis in connection with identifying and selecting equity investments in non-U.S. issuers often require subjective analysis and may be relatively more difficult than applying the ESG criteria or the supplemental ESG analysis to equity investments of all issuers because data availability may be more limited with respect to non- U.S. issuers. Certain investments may be dependent on U.S. and foreign government policies, including tax incentives and subsidies, which may change without notice. |
| The exclusionary criteria related to the Fund’s ESG criteria may result in the Fund forgoing opportunities to buy certain securities when it might otherwise be advantageous to do so, or selling securities for ESG reasons when it might be otherwise disadvantageous for it to do so. The Fund’s investments in certain companies may be susceptible to various factors that may impact their businesses or operations, including costs associated with government budgetary constraints that impact publicly funded projects and clean energy initiatives, the effects of general economic conditions throughout the world, increased competition from other providers of services, unfavorable tax laws or accounting policies and high leverage. The Fund may invest in companies that do not reflect the beliefs and values of any particular investor. When assessing whether an issuer meets the Fund’s ESG Criteria and conducting an ESG analysis of an issuer, the Investment Adviser may rely on third-party data that it believes to be reliable, but it does not guarantee the accuracy of such third-party data. The Fund’s ESG criteria and the application of the supplemental ESG analysis may be changed without shareholder approval. | |
| ■ | Foreign Risk —When the Fund invests in foreign securities, it may be subject to risk of loss not typically associated with U.S. issuers. Loss may result because of more or less foreign government regulation, less public information, less stringent investor protections and disclosure standards, less liquid, developed or efficient trading markets, greater volatility and less economic, political and social stability in the countries in which the Fund invests. Loss may also result from, among other things, deteriorating economic and business conditions in other countries, including the United States, regional and global conflicts, the imposition of exchange controls (including repatriation restrictions), sanctions, foreign taxes, confiscation of assets and property, trade restrictions (including tariffs), expropriations and other government restrictions by the United States and other governments, higher transaction costs, difficulty enforcing contractual obligations or from problems in share registration, settlement or custody. A Fund or the Investment Adviser may determine not to invest in, or may limit its overall investment in, a particular issuer, country or geographic region due to, among other things, heightened risks regarding repatriation restrictions, confiscation of assets and property, expropriation or nationalization. A Fund will also be subject to the risk of negative foreign currency rate fluctuations, |
| which may cause the value of securities denominated in such foreign currency (or other instruments through which the Fund has exposure to foreign currencies) to decline in value. Currency exchange rates may fluctuate significantly over short periods of time. Foreign risks will normally be greatest when a Fund invests in securities of issuers located in emerging countries. For more information about these risks, see Appendix A. | |
| The Fund's investments in foreign securities may also be subject to foreign currency risk, as described above, the risk of negative foreign currency rate fluctuations, which may cause the value of securities denominated in such foreign currency (or other instruments through which the Fund may have exposure to foreign currencies) to decline in value. Foreign risks will normally be greatest when the Fund invests in securities of issuers located in emerging countries. For more information about these risks, see Appendix A. | |
| ■ | Geographic Risk— If the Fund focuses its investments in securities of issuers located in a particular country or geographic region, the Fund may be subjected, to a greater extent than if its investments were less focused, to the risks of volatile economic cycles and/or conditions and developments that may be particular to that country or region, such as: adverse securities markets; adverse exchange rates; adverse social, political, regulatory, economic, business, environmental or other developments; or natural disasters. |
| ■ | IPO Risk— The market value of shares issued in an IPO may fluctuate considerably due to factors such as the absence of a prior public market, unseasoned trading, the small number of shares available for trading and limited information about a company’s business model, quality of management, earnings growth potential, and other criteria used to evaluate its investment prospects. The purchase of IPO shares may involve high transaction costs. Investments in IPO shares, which are subject to market risk and liquidity risk, involve greater risks than investments in shares of companies that have traded publicly on an exchange for extended periods of time. |
| ■ | Interest Rate Risk— When interest rates increase, fixed income securities or instruments held by the Fund (which may include inflation protected securities) will generally decline in value. Long-term fixed income securities or instruments will normally have more price volatility because of this risk than short-term fixed income securities or instruments. A wide variety of market factors can cause interest rates to rise, including central bank monetary policy, rising inflation and changes in general economic conditions. The risks associated with changing interest rates may have unpredictable effects on the markets and a Fund’s investments. Fluctuations in interest rates may also affect the liquidity of fixed income securities and instruments held by the Fund. |
| Interest rates in the United States are currently at historically low levels. Certain countries have experienced negative interest rates on certain fixed-income instruments. Very low or negative interest rates may magnify interest rate risk. Changing interest rates, including rates that fall below zero, may have unpredictable effects on markets, may result in heightened market volatility and may detract from Fund performance to the extent the Fund is exposed to such interest rates and/or volatility. | |
| ■ | Investment Style Risk —Different investment styles (e.g., “growth,” “value” or “quantitative”) tend to shift in and out of favor depending upon market and economic conditions and investor sentiment. The Fund may outperform or underperform other funds that invest in similar asset classes but employ different investment styles. Examples of different investment styles include growth and value investing. Growth stocks may be more volatile than other stocks because they are more sensitive to investor perceptions of the issuing company’s growth of earnings potential. Growth companies are often expected by investors to increase their earnings at a certain rate. When these expectations are not met, investors can punish the stocks inordinately even if earnings showed an absolute increase. Also, because growth companies usually invest a high portion of earnings in their business, growth stocks may lack the dividends of some value stocks that can cushion stock prices in a falling market. Growth oriented funds will typically underperform when value investing is in favor. Value stocks are those that are undervalued in comparison to their peers due to adverse business developments or other factors. |
| ■ | Issuer Concentration Risk —Under normal circumstances, the Concentrated Growth Fund and the U.S. Equity ESG Fund intend to invest in up to approximately 40 and 50 companies, respectively. As a result of the relatively small number of issuers in which a Fund generally invests, it may be subject to greater risks than a fund that invests in a greater number of issuers. A change in the value of any single investment held by a Fund may affect the overall value of the Fund more than it would affect a mutual fund that holds more investments. In particular, a Fund may be more susceptible to adverse developments affecting any single issuer in the Fund and may be susceptible to greater losses because of these developments. |
| ■ | Large Shareholder Transactions Risk —The Fund may experience adverse effects when certain large shareholders, such as other funds, institutional investors (including those trading by use of non-discretionary mathematical formulas), financial intermediaries (who may make investment decisions on behalf of underlying clients and/or include the Fund in their investment model), individuals, accounts and Goldman Sachs affiliates, purchase or redeem large amounts of shares of the Fund. Such large shareholder redemptions, which may occur rapidly or unexpectedly, may cause the Fund to sell portfolio securities at times when it would not otherwise do so, which may negatively impact the Fund’s NAV and liquidity. Similarly, large Fund share purchases may adversely affect the Fund’s performance to the extent that the Fund is delayed in investing new cash or otherwise maintains a larger |
| cash position than it ordinarily would. These transactions may also accelerate the realization of taxable income to shareholders if such sales of investments resulted in gains, and may also increase transaction costs. In addition, a large redemption could result in the Fund’s current expenses being allocated over a smaller asset base, leading to an increase in the Fund’s expense ratio. | |
| ■ | Liquidity Risk— The Fund may invest to a greater degree in securities or instruments that trade in lower volumes and may make investments that are less liquid than other investments. Also, the Fund may make investments that may become less liquid in response to market developments or adverse investor perceptions. Investments that are illiquid or that trade in lower volumes may be more difficult to value. When there is no willing buyer and investments cannot be readily sold at the desired time or price, the Fund may have to accept a lower price or may not be able to sell the security or instrument at all. An inability to sell one or more portfolio positions can adversely affect the Fund's value or prevent the Fund from being able to take advantage of other investment opportunities. |
| To the extent that the traditional dealer counterparties that engage in fixed income trading do not maintain inventories of bonds (which provide an important indication of their ability to “make markets”) that keep pace with the growth of the bond markets over time, relatively low levels of dealer inventories could lead to decreased liquidity and increased volatility in the fixed income markets. Additionally, market participants other than a Fund may attempt to sell fixed income holdings at the same time as the Fund, which could cause downward pricing pressure and contribute to decreased liquidity. | |
| Because the Fund may invest in non-investment grade fixed income securities, small- and mid-capitalization stocks, REITs and/or emerging country issuers, the Fund may be especially subject to the risk that during certain periods, the liquidity of particular issuers or industries, or all securities within a particular investment category, may shrink or disappear suddenly and without warning as a result of adverse economic, market or political events, or adverse investor perceptions, whether or not accurate. | |
| Liquidity risk may also refer to the risk that the Fund will not be able to pay redemption proceeds within the allowable time period stated in the Prospectus or without significant dilution to remaining investors’ interests because of unusual market conditions, an unusually high volume of redemption requests or other reasons. While the Fund reserves the right to meet redemption requests through in-kind distributions, the Fund may instead choose to raise cash to meet redemption requests through sales of portfolio securities or permissible borrowings. If the Fund is forced to sell securities at an unfavorable time and/or under unfavorable conditions, such sales may adversely affect the Fund's NAV and dilute remaining investors’ interests. | |
| Certain shareholders, including clients or affiliates of the Investment Adviser and/or other funds managed by the Investment Adviser, may from time to time own or control a significant percentage of the Fund's shares. Redemptions by these shareholders of their shares of the Fund may further increase the Fund's liquidity risk and may impact the Fund's NAV. These shareholders may include, for example, institutional investors, funds of funds, discretionary advisory clients, certain participating insurance companies, accounts or Goldman Sachs affiliates and other shareholders, whose buy-sell decisions are controlled by a single decision-maker. | |
| ■ | Management Risk —A strategy used by the Investment Adviser may fail to produce the intended results. |
| ■ | Market Risk— The value of the securities in which the Fund invests may go up or down in response to the prospects of individual companies, particular sectors or governments and/or general economic conditions throughout the world. Price changes may be temporary or last for extended periods. The Fund's investments may be overweighted from time to time in one or more sectors or countries, which will increase the Fund's exposure to risk of loss from adverse developments affecting those sectors or countries. |
| Global economies and financial markets are becoming increasingly interconnected, and conditions and events in one country, region or financial market may adversely impact issuers in a different country, region or financial market. Furthermore, local, regional and global events such as war, acts of terrorism, social unrest, natural disasters, the spread of infectious illness or other public health threats could also adversely impact issuers, markets and economies, including in ways that cannot necessarily be foreseen. The Fund could be negatively impacted if the value of a portfolio holding were harmed by such political or economic conditions or events. In addition, governmental and quasi-governmental organizations have taken a number of unprecedented actions designed to support the markets. Such conditions, events and actions may result in greater market risk. | |
| ■ | Master Limited Partnership Risk— The Fund’s investments in securities of a Master Limited Partnership (“MLP”) involve risks that differ from investments in common stock, including risks related to limited control and limited rights to vote on matters affecting the MLP, risks related to potential conflicts of interest between the MLP and the MLP’s general partner, cash flow risks, dilution risks and risks related to the general partner’s right to require unit-holders to sell their common units at an undesirable time or price, resulting from regulatory changes or other reasons. Certain MLP securities may trade in lower volumes due to their smaller capitalizations. Accordingly, those MLPs may be subject to more abrupt or erratic price movements and may lack sufficient market liquidity to enable the Fund to effect sales at an advantageous time or without a substantial drop in price. Investment in those MLPs may restrict the Fund’s ability to take advantage of other investment opportunities. MLPs are generally considered interest-rate sensitive investments. During periods of interest rate volatility, these investments may not provide attractive returns. |
| To the extent a distribution received by the Fund from an MLP is treated as a return of capital, the Fund’s adjusted tax basis in the interests of the MLP may be reduced, which will result in an increase in an amount of income or gain (or decrease in the amount of loss) that will be recognized by the Fund for tax purposes upon the sale of any such interests or upon subsequent distributions in respect of such interests. Furthermore, any return of capital distribution received from the MLP may require the Fund to restate the character of its distributions and amend any shareholder tax reporting previously issued. Moreover, a change in current tax law, or a change in the underlying business mix of a given MLP, could result in an MLP being treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, which could result in a reduction of the value of the Fund's investment in the MLP and lower income to the Fund. | |
| Under recent tax legislation, individuals and certain other noncorporate entities are generally eligible for a 20% deduction with respect to taxable income from MLPs. Currently, there is not a regulatory mechanism for regulated investment companies such as the Fund to pass through the 20% deduction to shareholders. As a result, in comparison, investors investing directly in MLPs would generally be eligible for the 20% deduction for such taxable income from these investments while investors investing in MLPs held indirectly if any through the Fund would not be eligible for the 20% deduction for their share of such taxable income. | |
| ■ | Mid-Cap and Small-Cap Risk— The securities of mid-capitalization and small-capitalization companies involve greater risks than those associated with larger, more established companies and may be subject to more abrupt or erratic price movements. Securities of such issuers may lack sufficient market liquidity to enable the Fund to effect sales at an advantageous time or without a substantial drop in price. Both mid-capitalization and small-capitalization companies often have narrower markets and more limited managerial and financial resources than larger, more established companies. As a result, their performance can be more volatile and they face greater risk of business failure, which could increase the volatility of the Fund's portfolio. Generally, the smaller the company size, the greater these risks become. |
| ■ | NAV Risk— The net asset value of the Fund and the value of your investment will fluctuate. |
| ■ | Non-Investment Grade Fixed Income Securities Risk— Non-investment grade fixed income securities and unrated securities of comparable credit quality (commonly known as “junk bonds”) are considered speculative and are subject to the increased risk of an issuer’s inability to meet principal and interest payment obligations. These securities may be subject to greater price volatility due to such factors as specific issuer developments, interest rate sensitivity, negative perceptions of the junk bond markets generally and less liquidity. |
| ■ | Portfolio Turnover Rate Risk —The Flexible Cap Fund may engage in active and frequent trading of portfolio securities to achieve its principal investment strategies. A high rate of portfolio turnover (100% or more) involves correspondingly greater expenses which must be borne by the Fund and its shareholders, and is also likely to result in short-term capital gains taxable to shareholders. |
| ■ | Pre-IPO Investments Risk— The Flexible Cap Fund may invest in privately held companies, including companies that may issue shares in IPOs. Investments in pre-IPO shares involve greater risks than investments in shares of companies that have traded publicly on an exchange for extended periods of time. Investments in these companies are less liquid and difficult to value, and there is significantly less information available about these companies’ business models, quality of management, earnings growth potential, and other criteria used to evaluate their investment prospects. Although there is a potential the pre-IPO shares that the Flexible Cap Fund buys may increase in value if the company does issue shares in an IPO, IPOs are risky and volatile and may cause the value of the Fund’s investments to decrease significantly. Moreover, because pre-IPO shares are generally not freely or publicly tradeable, the Flexible Cap Fund may not have access to purchase or the ability to sell these shares in the amounts or at the prices the Fund desires. The companies that the Flexible Cap Fund anticipates holding successful IPOs may not ever issue shares in an IPO and a liquid market for their shares may never develop, which may negatively affect the price at which the Fund can sell these shares and make it more difficult to sell these shares, which could also adversely affect the Fund’s liquidity. |
| ■ | Sector Risk —To the extent the Fund focuses its investments in securities of issuers in one or more sectors (such as the financial services or telecommunications sectors), the Fund will be subject to a greater extent than if its investments were diversified across different sectors, to the risks of volatile economic cycles and/or conditions and developments that may be particular to that sector, such as: adverse economic, business, political, environmental or other developments. |
| ■ | Stock Risk— Stock prices have historically risen and fallen in periodic cycles. U.S. and foreign stock markets have experienced periods of substantial price volatility in the past and may do so again in the future. Stock prices may fluctuate from time to time in response to the activities of individual companies and in response to general market and economic conditions. Individual companies may report poor results or be negatively affected by industry and/or economic trends and developments, and the stock prices of such companies may suffer a decline in response. |
| ■ | U.S. Government Securities Risk— The U.S. government may not provide financial support to U.S. government agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises if it is not obligated to do so by law. U.S. Government Securities issued by those agencies, instrumentalities and sponsored enterprises, including those issued by the Federal National Mortgage Association (“Fannie Mae”), Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“Freddie Mac”) and Federal Home Loan Banks, are neither issued nor |
| guaranteed by the U.S. Treasury and, therefore, are not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States. The maximum potential liability of the issuers of some U.S. Government Securities held by the Fund may greatly exceed their current resources, including any legal right to support from the U.S. Treasury. It is possible that issuers of U.S. Government Securities will not have the funds to meet their payment obligations in the future. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac have been operating under conservatorship, with the Federal Housing Finance Agency (“FHFA”) acting as their conservator, since September 2008. The entities are dependent upon the continued support of the U.S. Department of the Treasury and FHFA in order to continue their business operations. These factors, among others, could affect the future status and role of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac and the value of their securities and the securities which they guarantee. Additionally, the U.S. government and its agencies and instrumentalities do not guarantee the market values of their securities, which may fluctuate. |
| INVESTMENT ADVISER |
Investment Adviser |
Fund |
| Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P. (“GSAM”) 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 |
Capital Growth Concentrated Growth Flexible Cap Strategic Growth U.S. Equity ESG |
| ■ | Supervises all non-advisory operations of the Fund |
| ■ | Provides personnel to perform necessary executive, administrative and clerical services to the Fund |
| ■ | Arranges for the preparation of all required tax returns, reports to shareholders, prospectuses and statements of additional information and other reports filed with the SEC and other regulatory authorities |
| ■ | Maintains the records of the Fund |
| ■ | Provides office space and all necessary office equipment and services |
| MANAGEMENT FEES AND OTHER EXPENSES |
Fund |
Contractual Management Fee Annual Rate |
Average Daily Net Assets |
Actual Rate For the Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020* |
| Capital Growth | 0.71% | First $1 Billion | 0.71% |
| 0.64% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.61% | Over $2 Billion | ||
| Concentrated Growth | 0.76% | First $1 Billion | 0.76% |
| 0.68% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.65% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.64% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.62% | Over $8 Billion | ||
| Flexible Cap | 0.55% | First $1 Billion | 0.55% |
| 0.50% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.47% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.46% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.45% | Over $8 Billion | ||
| Strategic Growth | 0.71% | First $1 Billion | 0.71% |
| 0.64% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.61% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.59% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.58% | Over $8 Billion | ||
| U.S. Equity ESG | 0.55% | First $1 Billion | 0.55% |
| 0.50% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.47% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.46% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.45% | Over $8 Billion |
* |
The Actual Rate may not correlate to the Contractual Management Fee Annual Rate as a result of management fee waivers that may be in effect from time to time. |
| FUND MANAGERS |
Name and Title |
Fund Responsibility |
Years Primarily Responsible |
Five Year Employment History |
Steven M. Barry Managing Director Co-Chief Investment Officer, Fundamental Equity U.S. Equity |
Portfolio Manager— Capital Growth Concentrated Growth Flexible Cap Strategic Growth U.S. Equity ESG |
Since 2000 2002 2008 2000 2020 |
Mr. Barry joined the Investment Adviser as a portfolio manager in 1999. He is Managing Director and Co-Chief Investment Officer of Fundamental Equity U.S. Equity. |
Stephen E. Becker, CFA Managing Director Co-Chief Investment Officer, Fundamental Equity U.S. Equity |
Portfolio Manager— Capital Growth Concentrated Growth Strategic Growth U.S. Equity ESG |
Since 2013 2013 2013 2020 |
Mr. Becker joined the Investment Adviser in 1999. He is Managing Director and Co-Chief Investment Officer of Fundamental Equity U.S. Equity. |
Kevin Martens Vice PresidentPortfolio Manager |
Portfolio Manager— U.S. Equity ESG |
Since 2020 |
Mr. Martens joined the Investment Adviser in 2015. He is a portfolio manager on the GSAM US Equity ESG Strategy, as well as a portfolio manager on the US Equity Team where he has broad research responsibilities for the Industrials sector across the US Large- and Mid-Cap Equity strategies. |
| DISTRIBUTOR AND TRANSFER AGENT |
| ACTIVITIES OF GOLDMAN SACHS AND ITS AFFILIATES AND OTHER ACCOUNTS MANAGED BY GOLDMAN SACHS |
| ■ | Cash |
| ■ | Additional shares of the same class of the same Fund |
| ■ | Shares of the same or an equivalent class of another Goldman Sachs Fund. Special restrictions may apply. See the SAI. |
| How To Buy Shares |
| ■ | Investors who purchase Class R6 Shares through an Eligible Fee-Based Program; |
| ■ | Employee Benefit Plans; |
| ■ | Registered investment companies or bank collective trusts investing directly with the Transfer Agent; |
| ■ | Institutional investors, including companies, foundations, endowments, municipalities, trusts and other entities, investing at least $5,000,000 directly with the Transfer Agent; and |
| ■ | Other investors at the discretion of the Trust’s officers. |
Initial |
Additional* | |
| Regular Accounts | $1,000 | $50 |
| Employee Benefit Plans | No Minimum | No Minimum |
| Uniform Gift/Transfer to Minors Accounts (UGMA/UTMA) | $250 | $50 |
| Individual Retirement Accounts and Coverdell ESAs | $250 | $50 |
| Automatic Investment Plan Accounts | $250 | $50 |
* |
No minimum additional investment requirements are imposed with respect to investors trading through Intermediaries who aggregate shares in omnibus or similar accounts (e.g., employee benefit plan accounts, wrap program accounts or traditional brokerage house accounts). A maximum purchase limitation of $1,000,000 in the aggregate normally applies to purchases of Class C Shares across all Goldman Sachs Funds. |
| ■ | Personal and account maintenance services |
| ■ | Provide facilities to answer inquiries and respond to correspondence |
| ■ | Act as liaison between the Intermediary’s customers and the Trust |
| ■ | Assist customers in completing application forms, selecting dividend and other options, and similar services |
| ■ | Shareholder administration services |
| ■ | Act, directly or through an agent, as the sole shareholder of record |
| ■ | Maintain account records for customers |
| ■ | Process orders to purchase, redeem and exchange shares for customers |
| ■ | Process payments for customers |
| ■ | Refuse to open an account or require an Intermediary to refuse to open an account if you fail to (i) provide a taxpayer identification number, a Social Security Number or other government-issued identification (e.g., for an individual, a driver’s license or passport) or (ii) certify that such number or other information is correct (if required to do so under applicable law). |
| ■ | Reject or restrict any purchase or exchange order by a particular purchaser (or group of related purchasers) for any reason in its discretion. Without limiting the foregoing, the Trust may reject or restrict purchase and exchange orders by a particular purchaser (or group of related purchasers) when a pattern of frequent purchases, sales or exchanges of shares of the Fund is evident, or if purchases, sales or exchanges are, or a subsequent redemption might be, of a size that would disrupt the management of the Fund. |
| ■ | Close the Fund to new investors from time to time and reopen any such Fund whenever it is deemed appropriate by the Investment Adviser. |
| ■ | Provide for, modify or waive the minimum investment requirements. |
| ■ | Modify the manner in which shares are offered. |
| ■ | Modify the sales charge rate applicable to future purchases of shares. |
| NAV = | (Value of Assets of the Class) – (Liabilities of the Class) |
| Number of Outstanding Shares of the Class |
| ■ | NAV per share of each share class is generally calculated by the Fund’s fund accounting agent on each business day as of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange (normally 4:00 p.m. Eastern time) or such other times as the New York Stock Exchange or NASDAQ market may officially close. Fund shares will generally not be priced on any day the New York Stock Exchange is closed. |
| ■ | The Trust reserves the right to reprocess purchase (including dividend reinvestments), redemption and exchange transactions that were processed at a NAV that is subsequently adjusted, and to recover amounts from (or distribute amounts to) shareholders accordingly based on the official closing NAV, as adjusted. |
| ■ | The Trust reserves the right to advance the time by which purchase and redemption orders must be received for same business day credit as otherwise permitted by the SEC. |
| Common Questions Applicable to the Purchase of Class A Shares |
Amount of Purchase (including sales charge, if any) |
Sales Charge as Percentage of Offering Price |
Sales Charge as Percentage of Net Amount Invested |
Maximum Dealer Allowance as Percentage of Offering Price* |
| Less than $50,000 | 5.50% | 5.82% | 5.00% |
| $50,000 up to (but less than) $100,000 | 4.75 | 4.99 | 4.00 |
| $100,000 up to (but less than) $250,000 | 3.75 | 3.90 | 3.00 |
| $250,000 up to (but less than) $500,000 | 2.75 | 2.83 | 2.25 |
| $500,000 up to (but less than) $1 million | 2.00 | 2.04 | 1.75 |
| $1 million or more | 0.00** | 0.00** | *** |
* |
Dealer’s allowance may be changed periodically. During special promotions, the entire sales charge may be reallowed to Intermediaries. Intermediaries to whom substantially the entire sales charge is reallowed may be deemed to be “underwriters” under the Securities Act. |
** |
No sales charge is payable at the time of purchase of Class A Shares of $1 million or more, but a CDSC of 1.00% may be imposed in the event of certain redemptions within 18 months. For more information about Class A Shares’ CDSCs, please see “What Else Do I Need To Know About Class A Shares’ CDSC?” below. |
*** |
The Distributor may pay a one-time commission to Intermediaries who initiate or are responsible for purchases of $1 million or more of shares of the Fund equal to 1.00% of the amount under $3 million, 0.50% of the next $2 million, and 0.25% thereafter. In instances where this one-time commission is not paid to a particular Intermediary (including Goldman Sachs’ Private Wealth Management Unit), the CDSC on Class A Shares, generally, will be waived. The Distributor may also pay, with respect to all or a portion of the amount purchased, a commission in accordance with the foregoing schedule to Intermediaries who initiate or are responsible for purchases by Employee Benefit Plans investing in the Fund which satisfy the criteria set forth below in “When Are Class A Shares Not Subject To A Sales Load?” or $1 million or more by certain “wrap” accounts. Purchases by such plans will be made at NAV with no initial sales charge, but if shares are redeemed within 18 months, a CDSC of 1.00% may be imposed upon the plan, the plan sponsor or the third-party administrator. In addition, Intermediaries will remit to the Distributor such payments received in connection with “wrap” accounts in the event that shares are redeemed within 18 months. |
| (i) | Information or records regarding shares of the Fund or other Goldman Sachs Funds held in all accounts (e.g., retirement accounts) of the shareholder at all Intermediaries; or |
| (ii) | Information or records regarding shares of the Fund or other Goldman Sachs Funds held at any Intermediary by related parties of the shareholder, such as members of the same family or household. |
| ■ | Goldman Sachs, its affiliates or their respective officers, partners, directors or employees (including retired employees and former partners), any partnership of which Goldman Sachs is a general partner, any Trustee or officer of the Trust and designated family members of any of these individuals; |
| ■ | Qualified employee benefit plans of Goldman Sachs; |
| ■ | Trustees or directors of investment companies for which Goldman Sachs or an affiliate acts as sponsor; |
| ■ | Any employee or registered representative of any Intermediary (or such Intermediaries’ affiliates and subsidiaries) or their respective spouses or domestic partners, children and parents; |
| ■ | Banks, trust companies or other types of depository institutions; |
| ■ | Any state, county or city, or any instrumentality, department, authority or agency thereof, which is prohibited by applicable investment laws from paying a sales charge or commission in connection with the purchase of shares of the Fund; |
| ■ | Employee Benefit Plans, other than Employee Benefit Plans that purchase Class A Shares through brokerage relationships in which sales charges are customarily imposed. Under such circumstances, Plans will be assessed sales charges as described further in “Shareholder Guide—Common Questions Applicable To the Purchase of Class A Shares”; |
| ■ | Investors who purchase Class A Shares through an omnibus account sponsored by an Intermediary that has an agreement with the Distributor covering such investors to offer Class A Shares without charging an initial sales charge; |
| ■ | Insurance company separate accounts that make the Fund available as an underlying investment in certain group annuity contracts; |
| ■ | “Wrap” accounts for the benefit of clients of broker-dealers, financial institutions or financial planners, provided they have entered into an agreement with GSAM specifying aggregate minimums and certain operating policies and standards; |
| ■ | Investment advisers investing for accounts for which they receive asset-based fees; |
| ■ | Accounts over which GSAM or its advisory affiliates have investment discretion; |
| ■ | Shareholders who roll over distributions from any tax-qualified Employee Benefit Plan or tax-sheltered annuity to an IRA which invests in the Goldman Sachs Funds if the tax-qualified Employee Benefit Plan or tax-sheltered annuity receives administrative services provided by certain third party administrators that have entered into a special service arrangement with Goldman Sachs relating to such plan or annuity; |
| ■ | State sponsored 529 college savings plans; |
| ■ | Investors that purchase Class A Shares through the GS Retirement Plan Plus and Goldman Sachs 401(k) Programs; |
| ■ | Former shareholders of certain funds who (i) received shares of a Goldman Sachs Fund in connection with a reorganization of an acquired fund into a Goldman Sachs Fund, (ii) had previously qualified for purchases of Class A Shares of the acquired funds without the imposition of a sales load under the guidelines of the applicable acquired fund family, and (iii) as of August 24, 2012 held their Goldman Sachs Fund shares directly with the Goldman Sachs Funds’ Transfer Agent, as long as they continue to hold the shares directly at the Transfer Agent; or |
| ■ | Investors who purchase Class A Shares in accounts that are no longer associated with an Intermediary and held direct at the Transfer Agent, including retirement accounts. |
| ■ | Right of Accumulation: When buying Class A Shares in Goldman Sachs Funds, your current aggregate investment determines the initial sales load you pay. You may qualify for reduced sales charges when the current market value of holdings across Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares, plus new purchases, reaches $50,000 or more. Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares of any of the Goldman Sachs Funds may be combined under the Right of Accumulation. If the Fund’s Transfer Agent is properly notified, the “Amount of Purchase” in the chart in the section “What Is The Offering Price Of Class A Shares?” will be deemed to include all Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares of the Goldman Sachs Funds that were held at the time of purchase by any of the following persons: (i) you, your spouse or domestic partner, your parents and your children; and (ii) any trustee, guardian or other fiduciary of a single trust estate or a single fiduciary account. This includes, for example, any Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares held at an Intermediary other than the one handling your current purchase. For purposes of applying the Right of Accumulation, shares of the Fund and any other Goldman Sachs Funds purchased by an existing client of Goldman Sachs Private Wealth Management or GS Ayco Holding LLC will be combined with Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares and other assets held by all other Goldman Sachs Private Wealth Management accounts or accounts of GS Ayco Holding LLC, respectively. In addition, under some circumstances, Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares of the Fund and Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares of any other Goldman Sachs Fund purchased by partners, directors, officers or employees of certain organizations may be combined for the purpose of determining whether a purchase will qualify for the Right of Accumulation and, if qualifying, the applicable sales charge level. To qualify for a reduced sales load, you or your Intermediary must notify the Fund’s Transfer Agent at the time of investment that a quantity discount is applicable. If you do not notify your Intermediary at the time of your current purchase or a future purchase that you qualify for a quantity discount, you may not receive the benefit of a reduced sales charge that might otherwise apply. Use of this option is subject to a check of appropriate records. |
| In some circumstances, other Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares may be aggregated with your current purchase under the Right of Accumulation as described in the SAI. For purposes of determining the “Amount of Purchase,” all Class A Shares and/or Class C Shares currently held will be valued at their current market value. | |
| ■ | Statement of Intention: You may obtain a reduced sales charge by means of a written Statement of Intention which expresses your non-binding commitment to invest (not counting reinvestments of dividends and distributions) in the aggregate $50,000 or more within a period of 13 months in Class A Shares of one or more of the Goldman Sachs Funds. Any investments you make during the period will receive the discounted sales load based on the full amount of your investment commitment. Purchases made during the previous 90 days may be included; however, capital appreciation does not apply toward these combined purchases. If the investment commitment of the Statement of Intention is not met prior to the expiration of the 13-month period, the entire amount will be subject to the higher applicable sales charge unless the failure to meet the investment commitment is due to the death of the investor. By selecting the Statement of Intention, you authorize the Transfer Agent to escrow and redeem Class A Shares in your account to pay this additional charge if the Statement of Intention is not met. You must, however, inform the Transfer Agent (either directly or through your Intermediary) that the Statement of Intention is in effect each time shares are purchased. Each purchase will be made at the public offering price applicable to a single transaction of the dollar amount specified on the Statement of Intention. The SAI has more information about the Statement of Intention, which you should read carefully. |
| Common Questions Applicable to the Purchase Of Class C Shares |
| Common Questions Applicable to the Purchase Of Class A and C Shares |
| ■ | The CDSC is based on the lesser of the NAV of the shares at the time of redemption or the original offering price (which is the original NAV). |
| ■ | No CDSC is charged on shares acquired from reinvested dividends or capital gains distributions. |
| ■ | No CDSC is charged on the per share appreciation of your account over the initial purchase price. |
| ■ | When counting the number of months since a purchase of Class A or Class C Shares was made, all purchases made during a month will be combined and considered to have been made on the first day of that month. |
| ■ | To keep your CDSC as low as possible, each time you place a request to sell shares, the Fund will first sell any shares in your account that do not carry a CDSC and then the shares in your account that have been held the longest. |
| ■ | Mandatory retirement distributions or loans to participants or beneficiaries from Employee Benefit Plans; |
| ■ | Hardship withdrawals by a participant or beneficiary in an Employee Benefit Plan; |
| ■ | The separation from service by a participant or beneficiary in an Employee Benefit Plan; |
| ■ | Excess contributions distributed from an Employee Benefit Plan; |
| ■ | Distributions from a qualified Employee Benefit Plan invested in the Goldman Sachs Funds which are being rolled over to an IRA in the same share class of a Goldman Sachs Fund; |
| ■ | The death or disability (as defined in Section 72(m)(7) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”)) of a shareholder, participant or beneficiary in an Employee Benefit Plan; |
| ■ | Satisfying the minimum distribution requirements of the Code; |
| ■ | Establishing “substantially equal periodic payments” as described under Section 72(t)(2) of the Code; |
| ■ | Redemption proceeds which are to be reinvested in accounts or non-registered products over which GSAM or its advisory affiliates have investment discretion; |
| ■ | A systematic withdrawal plan. The Fund reserves the right to limit such redemptions, on an annual basis, to 12% of the value of your Class C Shares and 10% of the value of your Class A Shares; |
| ■ | Redemptions or exchanges of Fund shares held through an Employee Benefit Plan using the Fund as part of a qualified default investment alternative or “QDIA”; or |
| ■ | Other redemptions, at the discretion of the Trust’s officers, relating to shares purchased through Employee Benefit Plans. |
| How To Sell Shares |
| ■ | A request is made in writing to redeem Class A, Class C, Investor or Class R Shares in an amount over $50,000 via check; |
| ■ | You would like the redemption proceeds sent to an address that is not your address of record; or |
| ■ | You would like the redemption proceeds sent to a domestic bank account that is not designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent. |
| ■ | Telephone requests are recorded. |
| ■ | Proceeds of telephone redemption requests will be sent to your address of record or authorized account designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent (unless you provide written instructions and a Medallion signature guarantee indicating another address or account). |
| ■ | For the 30-day period following a change of address, telephone redemptions will only be filled by a wire transfer to the authorized account designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent (see immediately preceding bullet point). In order to receive the redemption by check during this time period, the redemption request must be in the form of a written, Medallion signature guaranteed letter. |
| ■ | The telephone redemption option does not apply to Shares held in an account maintained and serviced by your Intermediary. If your Shares are held in an account with an Intermediary, you should contact your registered representative of record, who may make telephone redemptions on your behalf. |
| ■ | The telephone redemption option may be modified or terminated at any time without prior notice. |
| ■ | The Fund may allow redemptions via check up to $50,000 in Class A, Class C, Investor and Class R Shares requested via telephone. |
| ■ | Redemption proceeds will normally be paid in federal funds, between one and two business days (or such other times in accordance with the requirements of your Intermediary) following receipt of a properly executed wire transfer redemption request. In certain circumstances, however (such as unusual market conditions or in cases of very large redemptions or excessive trading), it may take up to seven days to pay redemption proceeds. |
| ■ | Redemption requests may only be postponed or suspended for longer than seven days as permitted under Section 22(e) of the Investment Company Act of 1940 (the “Investment Company Act”) if (i) the New York Stock Exchange is closed for trading or trading is restricted; (ii) an emergency exists which makes the disposal of securities owned by the Fund or the fair determination of the value of the Fund’s net assets not reasonably practicable; or (iii) the SEC, by order or regulation, permits the suspension of the right of redemption. |
| ■ | If you are selling shares you recently paid for by check or purchased by Automated Clearing House (“ACH”), the Fund will pay you when your check or ACH has cleared, which may take up to 15 days. |
| ■ | If the Federal Reserve Bank is closed on the day that the redemption proceeds would ordinarily be wired, wiring the redemption proceeds may be delayed until the Federal Reserve Bank reopens. |
| ■ | To change the bank wiring instructions designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent, you must send written instructions signed by an authorized person designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent. A Medallion signature guarantee may be required if you are requesting a redemption in conjunction with the change. |
| ■ | None of the Trust, the Investment Adviser or Goldman Sachs assumes any responsibility for the performance of your bank or Intermediary in the transfer process. If a problem with such performance arises, you should deal directly with your bank or Intermediary. |
| ■ | Additional documentation may be required when deemed appropriate by the Transfer Agent. A redemption request will not be in proper form until such additional documentation has been received. |
| ■ | Intermediaries are responsible for the timely transmittal of redemption requests by their customers to the Transfer Agent. In order to facilitate the timely transmittal of redemption requests, Intermediaries may set times by which they must receive redemption requests. Intermediaries may also require additional documentation from you. |
| ■ | Redeem your shares in the event your Intermediary’s relationship with Goldman Sachs is terminated, and you do not transfer your account to another Intermediary or in the event that the Fund is no longer an option in your Employee Benefit Plan or no longer available through your Eligible Fee-Based Program. |
| ■ | Redeem your shares if your account balance is below the required Fund minimum. The Fund will not redeem your shares on this basis if the value of your account falls below the minimum account balance solely as a result of market conditions. The Fund will give you 60 days prior written notice to allow you to purchase sufficient additional shares of the Fund in order to avoid such redemption. Different rules may apply to investors who have established brokerage accounts with Goldman Sachs in accordance with the terms and conditions of their account agreements. |
| ■ | Redeem your shares in the case of actual or suspected threatening conduct or actual or suspected fraudulent, suspicious or illegal activity by you or any other individual associated with your account. |
| ■ | Subject to applicable law, redeem your shares in other circumstances determined by the Board of Trustees to be in the best interest of the Trust. |
| ■ | Pay redemptions by a distribution in-kind of securities (instead of cash). If you receive redemption proceeds in-kind, you should expect to incur transaction costs upon the disposition of those securities. In addition, if you receive redemption proceeds in-kind, you will be subject to market gains or losses upon the disposition of those securities. |
| ■ | Reinvest any amounts (e.g., dividends, distributions or redemption proceeds) which you have elected to receive by check should your check remain uncashed for more than 180 days. No interest will accrue on amounts represented by uncashed checks. Your check will be reinvested in your account at the NAV on the day of the reinvestment. When reinvested, those amounts are subject to the risk of loss like any Fund investment. If you elect to receive distributions in cash and a check remains uncashed for more than 180 days, your cash election may be changed automatically to reinvest and your future dividend and capital gains distributions will be reinvested in the Fund at the NAV as of the date of payment of the distribution. This provision may not apply to certain retirement or qualified accounts, accounts with a non-U.S. address or closed accounts. Your participation in a systematic withdrawal program may be terminated if a check remains uncashed. |
| ■ | Charge an additional fee in the event a redemption is made via wire transfer. |
| ■ | If you pay a CDSC upon redemption of Class A or Class C Shares and then reinvest in Class A or Class C Shares of another Goldman Sachs Fund as described above, your account will be credited with the amount of the CDSC you paid. The reinvested shares will, however, continue to be subject to a CDSC. The holding period of the shares acquired through reinvestment will include the holding period of the redeemed shares for purposes of computing the CDSC payable upon a subsequent redemption. |
| ■ | The reinvestment privilege may be exercised at any time in connection with transactions in which the proceeds are reinvested at NAV in a tax-sheltered Employee Benefit Plan. In other cases, the reinvestment privilege may be exercised once per year upon receipt of a written request. |
| ■ | You may be subject to tax as a result of a redemption. You should consult your tax adviser concerning the tax consequences of a redemption and reinvestment. |
| ■ | You should obtain and carefully read the prospectus of the Goldman Sachs Fund you are acquiring before making an exchange. You should be aware that not all Goldman Sachs Funds may offer all share classes. |
| ■ | Currently, the Fund does not impose any charge for exchanges although the Fund may impose a charge in the future. |
| ■ | The exchanged shares of the new Goldman Sachs Fund may later be exchanged for shares of the same class of the original Fund held at the next determined NAV without the imposition of an initial sales charge or CDSC. However, if additional shares of the new Goldman Sachs Fund were purchased after the initial exchange, and that Fund’s shares do not impose a sales charge or CDSC, then the applicable sales charge or CDSC of the original Fund’s shares will be imposed upon the exchange of those shares. |
| ■ | When you exchange shares subject to a CDSC, no CDSC will be charged at that time. However, for purposes of determining the amount of CDSC applicable to those shares acquired in the exchange, the length of time you have owned the shares will be measured from the date you acquired the original shares subject to a CDSC, and the amount and terms of the CDSC will be those applicable to the original shares acquired and will not be affected by a subsequent exchange. |
| ■ | Eligible investors may exchange certain classes of shares for another class of shares of the same Fund. For further information, contact your Intermediary. |
| ■ | All exchanges which represent an initial investment in a Goldman Sachs Fund must satisfy the minimum initial investment requirement of that Fund. This requirement may be waived at the discretion of the Trust. Exchanges into a Goldman Sachs Fund need not meet the traditional minimum investment requirement for that Fund if the entire balance of the original Fund account is exchanged. |
| ■ | Exchanges are available only in states where exchanges may be legally made. |
| ■ | It may be difficult to make telephone exchanges in times of unusual economic or market conditions. |
| ■ | Goldman Sachs and DST may use reasonable procedures described above in “How To Sell Shares—What Do I Need To Know About Telephone Redemption Requests?” in an effort to prevent unauthorized or fraudulent telephone exchange requests. |
| ■ | Normally, a telephone exchange will be made only to an identically registered account. |
| ■ | Exchanges into Goldman Sachs Funds or certain share classes of Goldman Sachs Funds that are closed to new investors may be restricted. |
| Shareholder Services |
| ■ | Shares will be purchased at NAV. |
| ■ | You may elect cross-reinvestment into an identically registered account or a similarly registered account provided that at least one name on the account is registered identically. |
| ■ | You cannot make cross-reinvestments into a Goldman Sachs Fund unless that Fund’s minimum initial investment requirement is met. |
| ■ | You should obtain and read the prospectus of the Goldman Sachs Fund into which distributions are invested. |
| ■ | Shares will be purchased at NAV if a sales charge had been imposed on the initial purchase. |
| ■ | You may elect to exchange into an identically registered account or a similarly registered account provided that at least one name on the account is registered identically. |
| ■ | Shares subject to a CDSC acquired under this program may be subject to a CDSC at the time of redemption from the Goldman Sachs Fund into which the exchange is made depending upon the date and value of your original purchase. |
| ■ | Automatic exchanges are made monthly on the 15th day of each month or the first business day thereafter. |
| ■ | Minimum dollar amount: $50 per month. |
| ■ | You cannot make automatic exchanges into a Goldman Sachs Fund unless that Fund’s minimum initial investment requirement is met. |
| ■ | You should obtain and read the prospectus of the Goldman Sachs Fund into which automatic exchanges are made. |
| ■ | An exchange is considered a redemption and a purchase and therefore may be a taxable transaction. |
| ■ | It is normally undesirable to maintain a systematic withdrawal plan at the same time that you are purchasing additional Class A or Class C Shares because of the sales charges that are imposed on certain purchases of Class A Shares and because of the CDSCs that are imposed on certain redemptions of Class A and Class C Shares. |
| ■ | Checks are normally mailed within two business days after your selected systematic withdrawal date of either the 15th or 25th of the month. ACH payments may take up to three business days to post to your account after your selected systematic withdrawal date between, and including, the 3rd and 26th of the month. |
| ■ | Each systematic withdrawal is a redemption and therefore may be a taxable transaction. |
| ■ | The CDSC applicable to Class A or Class C Shares redeemed under the systematic withdrawal plan may be waived. The Fund reserves the right to limit such redemptions, on an annual basis, to 12% each of the value of your Class C Shares and 10% of the value of your Class A Shares. |
| Distribution and Service Fees |
| ■ | Compensation paid to and expenses incurred by Intermediaries, Goldman Sachs and their respective officers, employees and sales representatives; |
| ■ | Commissions paid to Intermediaries; |
| ■ | Allocable overhead; |
| ■ | Telephone and travel expenses; |
| ■ | Interest and other costs associated with the financing of such compensation and expenses; |
| ■ | Printing of prospectuses for prospective shareholders; |
| ■ | Preparation and distribution of sales literature or advertising of any type; and |
| ■ | All other expenses incurred in connection with activities primarily intended to result in the sale of Class A, Class C and Class R Shares. |
| Class C Personal And Account Maintenance Services And Fees |
| Service Shares Service Plan And Shareholder Administration Plan |
| Restrictions on Excessive Trading Practices |
| DISTRIBUTIONS |
| SALES AND EXCHANGES |
| OTHER INFORMATION |
| A. General Portfolio Risks |
| B. Other Portfolio Risks |
| ■ | U.S. Government Securities |
| ■ | Commercial paper rated at least A-2 by Standard & Poor’s, P-2 by Moody’s or having a comparable rating by another NRSRO (or, if unrated, determined by the Investment Adviser to be of comparable credit quality) |
| ■ | Certificates of deposit |
| ■ | Bankers’ acceptances |
| ■ | Repurchase agreements |
| ■ | Non-convertible preferred stocks and non-convertible corporate bonds with a remaining maturity of less than one year |
| ■ | ETFs |
| ■ | Other investment companies |
| ■ | Cash items |
| C. Portfolio Securities and Techniques |
| ■ | While a Fund may benefit from the use of futures and options and swaps on futures, unanticipated changes in interest rates, securities prices or currency exchange rates may result in poorer overall performance than if the Fund had not entered into any futures contracts, options transactions or swaps. |
| ■ | Because perfect correlation between a futures position and a portfolio position that is intended to be protected is impossible to achieve, the desired protection may not be obtained and a Fund may be exposed to additional risk of loss. |
| ■ | The loss incurred by a Fund in entering into futures contracts and in writing call options and entering into swaps on futures is potentially unlimited and may exceed the amount of the premium received. |
| ■ | Futures markets are highly volatile and the use of futures may increase the volatility of a Fund’s NAV. |
| ■ | As a result of the low margin deposits normally required in futures trading, a relatively small price movement in a futures contract may result in substantial losses to a Fund. |
| ■ | Futures contracts and options and swaps on futures may be illiquid, and exchanges may limit fluctuations in futures contract prices during a single day. |
| ■ | Foreign exchanges may not provide the same protection as U.S. exchanges. |
Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund | |||||
Class A Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $13.59 | $14.00 | $14.84 | $13.08 | $13.92 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.09 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.09 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.56 | 0.64 | 2.15 | 1.76 | 0.50 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.65 | 0.76 | 2.26 | 1.83 | 0.59 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.15) | (0.08) | (0.09) | (0.07) | (0.07) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.46) | (1.09) | (3.01) | — (b) |
(1.36) |
| Total distributions | (0.61) | (1.17) | (3.10) | (0.07) | (1.43) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $15.63 | $13.59 | $14.00 | $14.84 | $13.08 |
Total Return (c) |
19.93% | 6.80% | 17.50% | 14.06% | 4.39% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $5,448 | $3,878 | $2,533 | $1,880 | $2,124 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.05% | 1.03% | 1.04% | 1.17% | 1.22% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 3.30% | 4.26% | 5.12% | 4.64% | 3.60% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.64% | 0.90% | 0.81% | 0.53% | 0.67% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
65% | 47% | 71% | 77% | 49% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund | |||||
Class C Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $12.91 | $13.40 | $14.36 | $12.69 | $13.56 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
(0.01) | 0.02 | 0.01 | (0.02) | (0.01) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.41 | 0.62 | 2.07 | 1.69 | 0.50 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.40 | 0.64 | 2.08 | 1.67 | 0.49 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.06) | (0.04) | (0.03) | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.46) | (1.09) | (3.01) | — (b) |
(1.36) |
| Total distributions | (0.52) | (1.13) | (3.04) | — (b) |
(1.36) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $14.79 | $12.91 | $13.40 | $14.36 | $12.69 |
Total Return (c) |
18.97% | 6.04% | 16.66% | 13.18% | 3.66% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $1,985 | $1,487 | $172 | $178 | $195 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.80% | 1.78% | 1.80% | 1.92% | 1.97% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 4.07% | 4.97% | 5.86% | 5.38% | 4.33% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets | (0.11)% | 0.18% | 0.05% | (0.18)% | (0.10)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
65% | 47% | 71% | 77% | 49% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund | |||||
Institutional Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $13.73 | $14.10 | $14.92 | $13.17 | $14.01 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.14 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.58 | 0.67 | 2.17 | 1.77 | 0.51 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.72 | 0.83 | 2.33 | 1.89 | 0.65 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.19) | (0.11) | (0.14) | (0.14) | (0.13) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.46) | (1.09) | (3.01) | — (b) |
(1.36) |
| Total distributions | (0.65) | (1.20) | (3.15) | (0.14) | (1.49) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $15.80 | $13.73 | $14.10 | $14.92 | $13.17 |
Total Return (c) |
20.29% | 7.27% | 17.92% | 14.43% | 4.84% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $1,009 | $791 | $4,969 | $3,499 | $4,754 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.70% | 0.67% | 0.68% | 0.79% | 0.82% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 2.99% | 3.97% | 4.65% | 4.28% | 3.16% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.99% | 1.22% | 1.20% | 0.88% | 1.10% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
65% | 47% | 71% | 77% | 49% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund | |||||
Investor Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $13.72 | $14.11 | $14.92 | $13.16 | $13.98 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.11 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.60 | 0.65 | 2.18 | 1.76 | 0.50 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.71 | 0.80 | 2.32 | 1.87 | 0.63 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.16) | (0.10) | (0.12) | (0.11) | (0.09) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.46) | (1.09) | (3.01) | — (b) |
(1.36) |
| Total distributions | (0.62) | (1.19) | (3.13) | (0.11) | (1.45) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $15.81 | $13.72 | $14.11 | $14.92 | $13.16 |
Total Return (c) |
20.23% | 7.05% | 17.86% | 14.27% | 4.67% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $344 | $1,064 | $235 | $188 | $156 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.85% | 0.78% | 0.79% | 0.92% | 0.97% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 3.75% | 4.06% | 4.87% | 4.47% | 3.54% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.76% | 1.16% | 1.06% | 0.78% | 0.97% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
65% | 47% | 71% | 77% | 49% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund | |||||
Class R Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $13.67 | $14.07 | $14.89 | $13.09 | $13.88 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.05 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.57 | 0.67 | 2.16 | 1.76 | 0.50 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.62 | 0.75 | 2.24 | 1.80 | 0.57 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.11) | (0.06) | (0.05) | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.46) | (1.09) | (3.01) | — (b) |
(1.36) |
| Total distributions | (0.57) | (1.15) | (3.06) | — (b) |
(1.36) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $15.72 | $13.67 | $14.07 | $14.89 | $13.09 |
Total Return (c) |
19.56% | 6.58% | 17.21% | 13.77% | 4.18% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $23 | $20 | $20 | $22 | $19 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.30% | 1.27% | 1.29% | 1.41% | 1.47% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 3.68% | 4.53% | 5.36% | 4.88% | 3.70% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.39% | 0.64% | 0.55% | 0.30% | 0.49% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
65% | 47% | 71% | 77% | 49% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund | |||||
Class R6 Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $13.73 | $14.11 | $14.93 | $13.17 | $14.01 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.13 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.14 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.60 | 0.65 | 2.17 | 1.77 | 0.51 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.73 | 0.82 | 2.33 | 1.90 | 0.65 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.19) | (0.11) | (0.14) | (0.14) | (0.13) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.46) | (1.09) | (3.01) | — (b) |
(1.36) |
| Total distributions | (0.65) | (1.20) | (3.15) | (0.14) | (1.49) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $15.81 | $13.73 | $14.11 | $14.93 | $13.17 |
Total Return (c) |
20.37% | 7.20% | 17.94% | 14.52% | 4.86% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $1,325 | $3,229 | $11 | $11 | $10 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.71% | 0.66% | 0.68% | 0.77% | 0.81% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 3.84% | 3.76% | 4.73% | 4.20% | 3.14% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.96% | 1.31% | 1.16% | 0.95% | 1.09% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
65% | 47% | 71% | 77% | 49% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund | ||||||
Class A Shares | ||||||
Year Ended August 31, | ||||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | ||
Per Share Data | ||||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $22.93 | $32.46 | $28.92 | $24.15 | $24.80 | |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.05 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 4.93 | (0.28) | 6.01 | 5.07 | 1.37 | |
| Total from investment operations | 4.98 | (0.20) | 6.03 | 5.11 | 1.40 | |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.08) | — (b) |
(0.02) | (0.01) | — | |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.89) | (9.33) | (2.47) | (0.33) | (2.05) | |
| Total distributions | (0.97) | (9.33) | (2.49) | (0.34) | (2.05) | |
| Net asset value, end of year | $26.94 | $22.93 | $32.46 | $28.92 | $24.15 | |
Total Return (c) |
22.26% | 3.72% | 22.01% | 21.47% | 5.79% | |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $776,919 | $708,827 | $745,362 | $671,371 | $630,091 | |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.14% | 1.14% | 1.14% | 1.15% | 1.15% | |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.22% | 1.22% | 1.31% | 1.51% | 1.51% | |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.23% | 0.36% | 0.06% | 0.14% | 0.11% | |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
47% | 55% | 93% | 48% | 45% | |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund | |||||
Class C Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $14.05 | $24.01 | $22.13 | $18.68 | $19.77 |
| Net investment loss (a) |
(0.06) | (0.07) | (0.16) | (0.12) | (0.12) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 2.95 | (0.56) | 4.51 | 3.90 | 1.08 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.89 | (0.63) | 4.35 | 3.78 | 0.96 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.89) | (9.33) | (2.47) | (0.33) | (2.05) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $16.05 | $14.05 | $24.01 | $22.13 | $18.68 |
Total Return (b) |
21.37% | 3.01% | 21.11% | 20.59% | 4.98% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $16,596 | $18,674 | $65,983 | $62,701 | $68,960 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.89% | 1.89% | 1.89% | 1.90% | 1.90% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.97% | 1.97% | 2.06% | 2.26% | 2.26% |
| Ratio of net investment (loss) to average net assets | (0.45)% | (0.41)% | (0.70)% | (0.61)% | (0.64)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
47% | 55% | 93% | 48% | 45% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund | |||||
Institutional Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $26.39 | $35.76 | $31.60 | $26.35 | $26.82 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.16 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.13 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 5.70 | (0.17) | 6.62 | 5.54 | 1.49 |
| Total from investment operations | 5.86 | 0.03 | 6.75 | 5.69 | 1.62 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.17) | (0.07) | (0.12) | (0.11) | (0.04) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.89) | (9.33) | (2.47) | (0.33) | (2.05) |
| Total distributions | (1.06) | (9.40) | (2.59) | (0.44) | (2.09) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $31.19 | $26.39 | $35.76 | $31.60 | $26.35 |
Total Return (b) |
22.71% | 4.14% | 22.50% | 21.96% | 6.19% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $64,708 | $60,169 | $77,293 | $165,948 | $141,442 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.76% | 0.75% | 0.75% | 0.75% | 0.75% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.84% | 0.83% | 0.93% | 1.11% | 1.11% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.58% | 0.74% | 0.40% | 0.54% | 0.50% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
47% | 55% | 93% | 48% | 45% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund | |||||
Service Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $21.73 | $31.33 | $28.00 | $23.40 | $24.12 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
0.03 | 0.06 | (0.01) | — | — (b) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 4.66 | (0.33) | 5.81 | 4.93 | 1.33 |
| Total from investment operations | 4.69 | (0.27) | 5.80 | 4.93 | 1.33 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.07) | — | — | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.89) | (9.33) | (2.47) | (0.33) | (2.05) |
| Total distributions | (0.96) | (9.33) | (2.47) | (0.33) | (2.05) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $25.46 | $21.73 | $31.33 | $28.00 | $23.40 |
Total Return (c) |
22.12% | 3.57% | 21.91% | 21.36% | 5.66% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $1,814 | $1,546 | $1,802 | $1,437 | $1,561 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.26% | 1.25% | 1.25% | 1.25% | 1.25% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.34% | 1.33% | 1.41% | 1.61% | 1.61% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets | 0.13% | 0.25% | (0.04)% | 0.02% | 0.01% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
47% | 55% | 93% | 48% | 45% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund | |||||
Investor Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $23.43 | $32.94 | $29.31 | $24.48 | $25.07 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.11 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 5.05 | (0.28) | 6.11 | 5.13 | 1.40 |
| Total from investment operations | 5.16 | (0.13) | 6.20 | 5.24 | 1.48 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.14) | (0.05) | (0.10) | (0.08) | (0.02) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.89) | (9.33) | (2.47) | (0.33) | (2.05) |
| Total distributions | (1.03) | (9.38) | (2.57) | (0.41) | (2.07) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $27.56 | $23.43 | $32.94 | $29.31 | $24.48 |
Total Return (b) |
22.56% | 3.96% | 22.35% | 21.77% | 6.05% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $8,703 | $6,649 | $9,259 | $8,496 | $4,297 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.89% | 0.89% | 0.89% | 0.90% | 0.90% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.96% | 0.97% | 1.06% | 1.26% | 1.26% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.46% | 0.60% | 0.31% | 0.43% | 0.35% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
47% | 55% | 93% | 48% | 45% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund | |||||
Class R6 Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $26.35 | $35.75 | $31.60 | $26.34 | $26.82 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.16 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.13 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 5.69 | (0.17) | 6.55 | 5.55 | 1.49 |
| Total from investment operations | 5.85 | 0.02 | 6.75 | 5.71 | 1.62 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.17) | (0.09) | (0.13) | (0.12) | (0.05) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.89) | (9.33) | (2.47) | (0.33) | (2.05) |
| Total distributions | (1.06) | (9.42) | (2.60) | (0.45) | (2.10) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $31.14 | $26.35 | $35.75 | $31.60 | $26.34 |
Total Return (b) |
22.71% | 4.12% | 22.53% | 21.99% | 6.19% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $2,454 | $2,313 | $60 | $16 | $10 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.75% | 0.74% | 0.74% | 0.75% | 0.74% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.83% | 0.83% | 0.90% | 1.10% | 1.09% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.59% | 0.75% | 0.60% | 0.56% | 0.52% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
47% | 55% | 93% | 48% | 45% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund | |||||
Class R Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $21.63 | $31.26 | $28.01 | $23.44 | $24.19 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
— (b) |
0.02 | (0.06) | (0.03) | (0.03) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 4.62 | (0.32) | 5.81 | 4.93 | 1.33 |
| Total from investment operations | 4.62 | (0.30) | 5.75 | 4.90 | 1.30 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.04) | — | (0.03) | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.89) | (9.33) | (2.47) | (0.33) | (2.05) |
| Total distributions | (0.93) | (9.33) | (2.50) | (0.33) | (2.05) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $25.32 | $21.63 | $31.26 | $28.01 | $23.44 |
Total Return (c) |
21.90% | 3.47% | 21.73% | 21.19% | 5.51% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $10,097 | $8,559 | $8,887 | $8,093 | $3,450 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.39% | 1.39% | 1.39% | 1.40% | 1.40% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.47% | 1.47% | 1.56% | 1.77% | 1.76% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets | 0.01% | 0.11% | (0.20)% | (0.10)% | (0.15)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
47% | 55% | 93% | 48% | 45% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund | |||||
Class A Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $17.55 | $19.33 | $17.62 | $15.06 | $16.06 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
(0.08) | (0.03) | (0.01) | 0.02 | — (b) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 6.92 | 0.35 | 3.82 | 2.64 | 0.81 |
| Total from investment operations | 6.84 | 0.32 | 3.81 | 2.66 | 0.81 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | — | — | — (c) |
(0.03) | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.48) | (2.10) | (2.10) | (0.07) | (1.81) |
| Total distributions | (1.48) | (2.10) | (2.10) | (0.10) | (1.81) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $22.91 | $17.55 | $19.33 | $17.62 | $15.06 |
Total Return (d) |
41.52% | 3.58% | 23.68% | 17.75% | 5.10% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $9,302 | $6,735 | $5,633 | $5,462 | $6,573 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.16% | 1.16% | 1.17% | 1.20% | 1.22% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.37% | 1.45% | 1.51% | 1.65% | 1.63% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss)to average net assets | (0.44)% | (0.18)% | (0.05)% | 0.11% | 0.03% (b) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (e) |
36% | 40% | 44% | 54% (f) |
55% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Reflects income recognized from a special dividend which amounted to $0.03 per share and 0.19% of average net assets. |
(c) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(d) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(e) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
(f) |
On July 28, 2017, Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund acquired all of the net assets of Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Reorganization. Portfolio turnover excludes purchases and sales of securities by Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund (acquired fund)prior to the merger date. |
Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund | |||||
Class C Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $13.87 | $15.88 | $14.93 | $12.84 | $14.05 |
| Net investment loss (a) |
(0.17) | (0.13) | (0.12) | (0.08) | (0.09) (b) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 5.34 | 0.22 | 3.17 | 2.24 | 0.69 |
| Total from investment operations | 5.17 | 0.09 | 3.05 | 2.16 | 0.60 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.48) | (2.10) | (2.10) | (0.07) | (1.81) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $17.56 | $13.87 | $15.88 | $14.93 | $12.84 |
Total Return (c) |
40.47% | 2.81% | 22.74% | 16.88% | 4.27% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $1,162 | $823 | $2,137 | $2,210 | $2,192 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.91% | 1.91% | 1.92% | 1.95% | 1.98% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 2.10% | 2.21% | 2.26% | 2.40% | 2.38% |
| Ratio of net investment loss to average net assets | (1.23)% | (0.98)% | (0.80)% | (0.61)% | (0.71)% (b) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
36% | 40% | 44% | 54% (e) |
55% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Reflects income recognized from a special dividend which amounted to $0.03 per share and 0.19% of average net assets. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
(e) |
On July 28, 2017, Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund acquired all of the net assets of Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Reorganization. Portfolio turnover excludes purchases and sales of securities by Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund (acquired fund)prior to the merger date. |
Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund | |||||
Institutional Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $18.93 | $20.61 | $18.65 | $15.94 | $16.88 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
(0.01) | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.07 (b) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 7.50 | 0.41 | 4.07 | 2.78 | 0.84 |
| Total from investment operations | 7.49 | 0.44 | 4.13 | 2.87 | 0.91 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.02) | (0.02) | (0.07) | (0.09) | (0.04) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.48) | (2.10) | (2.10) | (0.07) | (1.81) |
| Total distributions | (1.50) | (2.12) | (2.17) | (0.16) | (1.85) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $24.92 | $18.93 | $20.61 | $18.65 | $15.94 |
Total Return (c) |
41.98% | 3.98% | 24.13% | 18.22% | 5.47% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $13,744 | $12,497 | $15,286 | $142,623 | $134,818 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.81% | 0.80% | 0.81% | 0.82% | 0.82% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.01% | 1.07% | 1.20% | 1.26% | 1.23% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss)to average net assets | (0.07)% | 0.17% | 0.31% | 0.51% | 0.43% (b) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
36% | 40% | 44% | 54% (e) |
55% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Reflects income recognized from a special dividend which amounted to $0.03 per share and 0.19% of average net assets. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
(e) |
On July 28, 2017, Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund acquired all of the net assets of Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Reorganization. Portfolio turnover excludes purchases and sales of securities by Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund (acquired fund)prior to the merger date. |
Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund | |||||
Investor Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $17.90 | $19.66 | $17.88 | $15.28 | $16.26 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
(0.03) | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.04 (b) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 7.07 | 0.36 | 3.88 | 2.67 | 0.81 |
| Total from investment operations | 7.04 | 0.37 | 3.91 | 2.74 | 0.85 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | — (c) |
(0.03) | (0.03) | (0.07) | (0.02) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.48) | (2.10) | (2.10) | (0.07) | (1.81) |
| Total distributions | (1.48) | (2.13) | (2.13) | (0.14) | (1.83) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $23.46 | $17.90 | $19.66 | $17.88 | $15.28 |
Total Return (d) |
41.87% | 3.83% | 23.94% | 18.14% | 5.31% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $189 | $133 | $463 | $780 | $452 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.91% | 0.91% | 0.92% | 0.95% | 0.97% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.11% | 1.22% | 1.26% | 1.41% | 1.38% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss)to average net assets | (0.18)% | 0.03% | 0.17% | 0.45% | 0.27% (b) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (e) |
36% | 40% | 44% | 54% (f) |
55% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Reflects income recognized from a special dividend which amounted to $0.03 per share and 0.19% of average net assets. |
(c) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(d) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(e) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
(f) |
On July 28, 2017, Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund acquired all of the net assets of Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Reorganization. Portfolio turnover excludes purchases and sales of securities by Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund (acquired fund)prior to the merger date. |
Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund | |||||
Class R6 Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $18.88 | $20.60 | $18.65 | $15.95 | $16.88 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
(0.01) | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.07 (b) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 7.49 | 0.39 | 4.06 | 2.74 | 0.85 |
| Total from investment operations | 7.48 | 0.43 | 4.12 | 2.87 | 0.92 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.02) | (0.05) | (0.07) | (0.10) | (0.04) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.48) | (2.10) | (2.10) | (0.07) | (1.81) |
| Total distributions | (1.50) | (2.15) | (2.17) | (0.17) | (1.85) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $24.86 | $18.88 | $20.60 | $18.65 | $15.95 |
Total Return (c) |
42.05% | 4.00% | 24.09% | 18.17% | 5.56% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $806 | $538 | $99 | $68 | $10 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.80% | 0.79% | 0.80% | 0.82% | 0.81% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.98% | 1.04% | 1.09% | 1.32% | 1.21% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss)to average net assets | (0.07)% | 0.22% | 0.34% | 0.74% | 0.44% (b) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
36% | 40% | 44% | 54% (e) |
55% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Reflects income recognized from a special dividend which amounted to $0.03 per share and 0.19% of average net assets. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
(e) |
On July 28, 2017, Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund acquired all of the net assets of Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Reorganization. Portfolio turnover excludes purchases and sales of securities by Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund (acquired fund)prior to the merger date. |
Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund | |||||
Class R Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $16.84 | $18.68 | $17.13 | $14.65 | $15.71 |
| Net investment loss (a) |
(0.12) | (0.07) | (0.05) | (0.02) | (0.04) (b) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 6.60 | 0.33 | 3.70 | 2.57 | 0.79 |
| Total from investment operations | 6.48 | 0.26 | 3.65 | 2.55 | 0.75 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.48) | (2.10) | (2.10) | (0.07) | (1.81) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $21.84 | $16.84 | $18.68 | $17.13 | $14.65 |
Total Return (c) |
41.12% | 3.36% | 23.37% | 17.46% | 4.81% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $33 | $36 | $34 | $25 | $22 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.41% | 1.41% | 1.42% | 1.45% | 1.48% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.66% | 1.70% | 1.75% | 1.91% | 1.89% |
| Ratio of net investment loss to average net assets | (0.69)% | (0.43)% | (0.29)% | (0.14)% | (0.25)% (b) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
36% | 40% | 44% | 54% (e) |
55% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Reflects income recognized from a special dividend which amounted to $0.03 per share and 0.19% of average net assets. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
(e) |
On July 28, 2017, Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund acquired all of the net assets of Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Reorganization. Portfolio turnover excludes purchases and sales of securities by Goldman Sachs Focused Growth Fund (acquired fund)prior to the merger date. |
Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund | |||||
Class A Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $11.93 | $12.66 | $14.09 | $11.74 | $11.90 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
0.07 | 0.09 | 0.09 | — (b) |
(0.02) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.48 | 0.15 | 2.17 | 2.36 | 0.59 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.55 | 0.24 | 2.26 | 2.36 | 0.57 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.08) | (0.10) | (0.01) | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.62) | (0.87) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Total distributions | (0.70) | (0.97) | (3.69) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $13.78 | $11.93 | $12.66 | $14.09 | $11.74 |
Total Return (c) |
22.18% | 3.07% | 18.82% | 20.14% | 4.93% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $5,843 | $5,383 | $5,490 | $5,627 | $5,927 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.00% | 0.97% | 0.95% | 1.20% | 1.22% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 2.47% | 2.88% | 2.47% | 3.01% | 3.07% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss)to average net assets | 0.58% | 0.74% | 0.73% | (0.01)% | (0.21)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
69% | 50% | 157% | 47% | 46% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund | |||||
Class C Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $10.23 | $11.00 | $12.75 | $10.71 | $11.00 |
| Net investment loss (a) |
(0.02) | — (b) |
— (b) |
(0.09) | (0.10) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.10 | 0.13 | 1.93 | 2.14 | 0.54 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.08 | 0.13 | 1.93 | 2.05 | 0.44 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.02) | (0.03) | — | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.62) | (0.87) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Total distributions | (0.64) | (0.90) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $11.67 | $10.23 | $11.00 | $12.75 | $10.71 |
Total Return (c) |
21.16% | 2.30% | 18.00% | 19.18% | 4.12% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $1,516 | $1,288 | $1,304 | $1,512 | $1,474 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.75% | 1.72% | 1.70% | 1.95% | 1.97% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 3.19% | 3.63% | 3.20% | 3.76% | 3.82% |
| Ratio of net investment loss to average net assets | (0.16)% | —% (d) |
(0.02)% | (0.75)% | (0.96)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (e) |
69% | 50% | 157% | 47% | 46% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
Amount is less than 0.005% per share. |
(e) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund | |||||
Institutional Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $12.94 | $13.61 | $14.88 | $12.35 | $12.44 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.12 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.70 | 0.19 | 2.33 | 2.49 | 0.62 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.82 | 0.32 | 2.47 | 2.54 | 0.64 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.13) | (0.12) | (0.06) | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.62) | (0.87) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Total distributions | (0.75) | (0.99) | (3.74) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $15.01 | $12.94 | $13.61 | $14.88 | $12.35 |
Total Return (b) |
22.53% | 3.47% | 19.29% | 20.61% | 5.29% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $594 | $587 | $1,633 | $11,111 | $9,330 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.62% | 0.59% | 0.59% | 0.82% | 0.82% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 2.11% | 2.41% | 2.01% | 2.62% | 2.68% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.95% | 1.08% | 1.04% | 0.38% | 0.20% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
69% | 50% | 157% | 47% | 46% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund | |||||
Investor Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $12.65 | $13.35 | $14.63 | $12.16 | $12.27 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.10 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.05 | — (b) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.64 | 0.18 | 2.28 | 2.43 | 0.62 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.74 | 0.30 | 2.40 | 2.48 | 0.62 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.11) | (0.13) | — | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.62) | (0.87) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Total distributions | (0.73) | (1.00) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $14.66 | $12.65 | $13.35 | $14.63 | $12.16 |
Total Return (c) |
22.43% | 3.40% | 19.08% | 20.43% | 5.20% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $38 | $70 | $68 | $379 | $197 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.76% | 0.72% | 0.70% | 0.95% | 0.97% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 2.66% | 2.63% | 2.08% | 2.83% | 2.76% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.78% | 0.99% | 0.88% | 0.35% | 0.03% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (d) |
69% | 50% | 157% | 47% | 46% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Amount is less than $0.005 per share. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(d) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund | |||||
Class R6 Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $12.91 | $13.61 | $14.88 | $12.35 | $12.44 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.13 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.69 | 0.18 | 2.32 | 2.49 | 0.61 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.82 | 0.32 | 2.47 | 2.54 | 0.64 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.13) | (0.15) | (0.06) | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.62) | (0.87) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Total distributions | (0.75) | (1.02) | (3.74) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $14.98 | $12.91 | $13.61 | $14.88 | $12.35 |
Total Return (b) |
22.60% | 3.47% | 19.27% | 20.61% | 5.29% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $226 | $202 | $14 | $12 | $10 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.61% | 0.59% | 0.58% | 0.82% | 0.81% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 2.10% | 2.59% | 2.09% | 2.61% | 2.66% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.96% | 1.17% | 1.11% | 0.39% | 0.22% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
69% | 50% | 157% | 47% | 46% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund | |||||
Class R Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $11.40 | $12.14 | $13.67 | $11.42 | $11.63 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | (0.03) | (0.05) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.36 | 0.16 | 2.09 | 2.29 | 0.57 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.40 | 0.21 | 2.15 | 2.26 | 0.52 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.05) | (0.08) | — | — | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.62) | (0.87) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Total distributions | (0.67) | (0.95) | (3.68) | (0.01) | (0.73) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $13.13 | $11.40 | $12.14 | $13.67 | $11.42 |
Total Return (b) |
21.78% | 2.89% | 18.50% | 19.83% | 4.61% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $49 | $39 | $49 | $39 | $37 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.25% | 1.22% | 1.20% | 1.45% | 1.47% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 2.63% | 3.13% | 2.74% | 3.28% | 3.33% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss)to average net assets | 0.33% | 0.49% | 0.48% | (0.23)% | (0.45)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
69% | 50% | 157% | 47% | 46% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund | |||||
Class A Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $9.25 | $13.83 | $13.79 | $11.91 | $11.86 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
(0.03) | (0.01) | (0.02) | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 3.58 | (0.30) | 3.03 | 2.26 | 0.74 |
| Total from investment operations | 3.55 | (0.31) | 3.01 | 2.28 | 0.76 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | — | — | — | (0.04) | (0.02) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.97) | (0.36) | (0.69) |
| Total distributions | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.97) | (0.40) | (0.71) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $11.24 | $9.25 | $13.83 | $13.79 | $11.91 |
Total Return (b) |
43.98% | 2.86% | 25.59% | 19.79% | 6.48% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $36,688 | $28,311 | $30,174 | $46,114 | $46,093 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.14% | 1.14% | 1.14% | 1.15% | 1.15% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.35% | 1.40% | 1.39% | 1.55% | 1.54% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets | (0.35)% | (0.07)% | (0.15)% | 0.15% | 0.19% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
39% | 28% | 40% | 54% | 56% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund | |||||
Class C Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $6.09 | $10.81 | $11.46 | $10.00 | $10.12 |
| Net investment loss (a) |
(0.07) | (0.06) | (0.09) | (0.06) | (0.05) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 2.17 | (0.39) | 2.41 | 1.88 | 0.62 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.10 | (0.45) | 2.32 | 1.82 | 0.57 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.97) | (0.36) | (0.69) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $6.63 | $6.09 | $10.81 | $11.46 | $10.00 |
Total Return (b) |
42.88% | 2.07% | 24.61% | 18.89% | 5.70% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $4,522 | $4,142 | $9,081 | $9,326 | $11,103 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.89% | 1.89% | 1.89% | 1.90% | 1.90% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 2.11% | 2.14% | 2.13% | 2.30% | 2.29% |
| Ratio of net investment loss to average net assets | (1.25)% | (0.83)% | (0.85)% | (0.60)% | (0.56)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
39% | 28% | 40% | 54% | 56% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund | |||||
Institutional Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $10.39 | $14.92 | $14.67 | $12.64 | $12.53 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 4.07 | (0.26) | 3.25 | 2.40 | 0.78 |
| Total from investment operations | 4.08 | (0.23) | 3.29 | 2.47 | 0.85 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.03) | (0.03) | (0.07) | (0.08) | (0.05) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.97) | (0.36) | (0.69) |
| Total distributions | (1.59) | (4.30) | (3.04) | (0.44) | (0.74) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $12.88 | $10.39 | $14.92 | $14.67 | $12.64 |
Total Return (b) |
44.36% | 3.31% | 26.11% | 20.29% | 6.89% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $60,474 | $52,461 | $75,470 | $211,311 | $294,952 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.76% | 0.75% | 0.75% | 0.75% | 0.75% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.98% | 1.00% | 0.99% | 1.14% | 1.14% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.10% | 0.32% | 0.31% | 0.51% | 0.59% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
39% | 28% | 40% | 54% | 56% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund | |||||
Service Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $9.08 | $13.67 | $13.70 | $11.85 | $11.81 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
(0.04) | (0.01) | (0.03) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 3.49 | (0.31) | 3.00 | 2.24 | 0.73 |
| Total from investment operations | 3.45 | (0.32) | 2.97 | 2.25 | 0.74 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | — | — | (0.03) | (0.04) | (0.01) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.97) | (0.36) | (0.69) |
| Total distributions | (1.56) | (4.27) | (3.00) | (0.40) | (0.70) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $10.97 | $9.08 | $13.67 | $13.70 | $11.85 |
Total Return (b) |
43.67% | 2.79% | 25.48% | 19.66% | 6.40% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $505 | $622 | $597 | $478 | $272 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.26% | 1.25% | 1.25% | 1.25% | 1.25% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.53% | 1.53% | 1.48% | 1.65% | 1.64% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets | (0.47)% | (0.14)% | (0.21)% | 0.09% | 0.11% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
39% | 28% | 40% | 54% | 56% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund | |||||
Investor Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $10.34 | $14.89 | $14.66 | $12.63 | $12.53 |
| Net investment income (loss) (a) |
(0.01) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 4.07 | (0.27) | 3.24 | 2.40 | 0.78 |
| Total from investment operations | 4.06 | (0.25) | 3.26 | 2.46 | 0.83 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.01) | (0.03) | (0.06) | (0.07) | (0.04) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.97) | (0.36) | (0.69) |
| Total distributions | (1.57) | (4.30) | (3.03) | (0.43) | (0.73) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $12.83 | $10.34 | $14.89 | $14.66 | $12.63 |
Total Return (b) |
44.28% | 3.14% | 25.90% | 20.15% | 6.69% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $2,758 | $1,533 | $2,578 | $2,264 | $829 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.89% | 0.89% | 0.89% | 0.90% | 0.90% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.06% | 1.14% | 1.12% | 1.30% | 1.29% |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets | (0.09)% | 0.16% | 0.15% | 0.48% | 0.44% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
39% | 28% | 40% | 54% | 56% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund | |||||
Class R6 Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $10.37 | $14.91 | $14.66 | $12.63 | $12.53 |
| Net investment income (a) |
0.01 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.07 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 4.07 | (0.27) | 3.25 | 2.40 | 0.77 |
| Total from investment operations | 4.08 | (0.23) | 3.29 | 2.48 | 0.84 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.03) | (0.04) | (0.07) | (0.09) | (0.05) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.97) | (0.36) | (0.69) |
| Total distributions | (1.59) | (4.31) | (3.04) | (0.45) | (0.74) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $12.86 | $10.37 | $14.91 | $14.66 | $12.63 |
Total Return (b) |
44.49% | 3.33% | 26.15% | 20.33% | 6.83% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $509 | $477 | $15 | $12 | $10 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.75% | 0.74% | 0.74% | 0.75% | 0.76% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.99% | 1.03% | 0.97% | 1.14% | 1.15% |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.10% | 0.40% | 0.30% | 0.57% | 0.59% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
39% | 28% | 40% | 54% | 56% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund | |||||
Class R Shares | |||||
Year Ended August 31, | |||||
2020 |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 | |
Per Share Data | |||||
| Net asset value, beginning of year | $8.88 | $13.49 | $13.56 | $11.75 | $11.74 |
| Net investment loss (a) |
(0.06) | (0.03) | (0.04) | (0.01) | (0.01) |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 3.41 | (0.31) | 2.96 | 2.23 | 0.73 |
| Total from investment operations | 3.35 | (0.34) | 2.92 | 2.22 | 0.72 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | — | — | (0.02) | (0.05) | (0.02) |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.97) | (0.36) | (0.69) |
| Total distributions | (1.56) | (4.27) | (2.99) | (0.41) | (0.71) |
| Net asset value, end of year | $10.67 | $8.88 | $13.49 | $13.56 | $11.75 |
Total Return (b) |
43.52% | 2.67% | 25.29% | 19.56% | 6.18% |
| Net assets, end of year (in 000’s) | $66 | $292 | $255 | $169 | $81 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 1.40% | 1.39% | 1.39% | 1.40% | 1.40% |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.75% | 1.65% | 1.62% | 1.80% | 1.79% |
| Ratio of net investment loss to average net assets | (0.66)% | (0.31)% | (0.34)% | (0.07)% | (0.05)% |
| Portfolio turnover rate (c) |
39% | 28% | 40% | 54% | 56% |
(a) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(b) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the year, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. |
(c) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
| MERRILL LYNCH |
| ■ | Employer-sponsored retirement, deferred compensation and employee benefit plans (including health savings accounts) and trusts used to fund those plans, provided that the shares are not held in a commission-based brokerage account and shares are held for the benefit of the plan |
| ■ | Shares purchased by a 529 Plan (does not include 529 Plan units or 529-specific share classes or equivalents) |
| ■ | Shares purchased through a Merrill Lynch affiliated investment advisory program |
| ■ | Shares exchanged due to the holdings moving from a Merrill Lynch affiliated investment advisory program to a Merrill Lynch brokerage (non-advisory) account pursuant to Merrill Lynch’s policies relating to sales load discounts and waivers |
| ■ | Shares purchased by third party investment advisors on behalf of their advisory clients through Merrill Lynch’s platform |
| ■ | Shares of funds purchased through the Merrill Edge Self-Directed platform (if applicable) |
| ■ | Shares purchased through reinvestment of capital gains distributions and dividend reinvestment when purchasing shares of the same fund (but not any other fund within the fund family) |
| ■ | Shares exchanged from Class C (i.e., level-load) shares of the same fund pursuant to Merrill Lynch’s policies relating to sales load discounts and waivers |
| ■ | Employees and registered representatives of Merrill Lynch or its affiliates and their family members |
| ■ | Directors or Trustees of the Fund, and employees of the Fund’s investment adviser or any of its affiliates, as described in the prospectus |
| ■ | Eligible shares purchased from the proceeds of redemptions within the same fund family, provided (1) the repurchase occurs within 90 days following the redemption, (2) the redemption and purchase occur in the same account, and (3) redeemed shares were subject to a front-end or deferred sales load (known as Rights of Reinstatement). Automated transactions (i.e. systematic purchases and withdrawals) and purchases made after shares are automatically sold to pay Merrill Lynch’s account maintenance fees are not eligible for reinstatement |
| ■ | Death or disability of the shareholder |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a systematic withdrawal plan as described in the Funds’ prospectus |
| ■ | Return of excess contributions from an IRA Account |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a required minimum distribution for IRA and retirement accounts pursuant to the Internal Revenue Code |
| ■ | Shares sold to pay Merrill Lynch fees but only if the transaction is initiated by Merrill Lynch |
| ■ | Shares acquired through a right of reinstatement |
| ■ | Shares held in retirement brokerage accounts, that are exchanged for a lower cost share class due to transfer to certain fee based accounts or platforms (applicable to A and C shares only) |
| ■ | Shares received through an exchange due to the holdings moving from a Merrill Lynch affiliated investment advisory program to a Merrill Lynch brokerage (non-advisory) account pursuant to Merrill Lynch’s policies relating to sales load discounts and waivers |
| ■ | Breakpoints as described in this prospectus |
| ■ | Rights of Accumulation (ROA) which entitle shareholders to breakpoint discounts as described in the Funds’ prospectus will be automatically calculated based on the aggregated holding of fund family assets held by accounts (including 529 program holdings, where applicable) within the purchaser’s household at Merrill Lynch. Eligible fund family assets not held at Merrill Lynch may be included in the ROA calculation only if the shareholder notifies his or her financial advisor about such assets |
| ■ | Letters of Intent (LOI) which allow for breakpoint discounts based on anticipated purchases within a fund family, through Merrill Lynch, over a 13-month period of time (if applicable) |
| AMERIPRISE FINANCIAL |
| ■ | Employer-sponsored retirement plans (e.g., 401(k) plans, 457 plans, employer-sponsored 403(b) plans, profit sharing and money purchase pension plans and defined benefit plans). For purposes of this provision, employer-sponsored retirement plans do not include SEP IRAs, Simple IRAs or SAR-SEPs. |
| ■ | Shares purchased through reinvestment of capital gains distributions and dividend reinvestment when purchasing shares of the same Fund (but not any other fund within the same fund family). |
| ■ | Shares exchanged from Class C shares of the same fund in the month of or following the 7-year anniversary of the purchase date. To the extent that this prospectus elsewhere provides for a waiver with respect to exchanges of Class C shares or conversion of Class C shares following a shorter holding period, that waiver will apply. |
| ■ | Employees and registered representatives of Ameriprise Financial or its affiliates and their immediate family members. |
| ■ | Shares purchased by or through qualified accounts (including IRAs, Coverdell Education Savings Accounts, 401(k)s, 403(b) TSCAs subject to ERISA and defined benefit plans) that are held by a covered family member, defined as an Ameriprise financial advisor and/or the advisor’s spouse, advisor’s lineal ascendant (mother, father, grandmother, grandfather, great grandmother, great grandfather), advisor’s lineal descendant (son, step-son, daughter, step-daughter, grandson, granddaughter, great grandson, great granddaughter) or any spouse of a covered family member who is a lineal descendant. |
| ■ | Shares purchased from the proceeds of redemptions within the same fund family, provided (1) the repurchase occurs within 90 days following the redemption, (2) the redemption and purchase occur in the same account, and (3) redeemed shares were subject to a front-end or deferred sales load (i.e. Rights of Reinstatement). |
| MORGAN STANLEY WEALTH MANAGEMENT |
| ■ | Employer-sponsored retirement plans ( e.g |
| ■ | Morgan Stanley employee and employee-related accounts according to Morgan Stanley’s account linking rules |
| ■ | Shares purchased through reinvestment of dividends and capital gains distributions when purchasing shares of the same fund |
| ■ | Shares purchased through a Morgan Stanley self-directed brokerage account |
| ■ | Class C ( i.e |
| ■ | Shares purchased from the proceeds of redemptions within the same fund family, provided (i) the repurchase occurs within 90 days following the redemption, (ii) the redemption and purchase occur in the same account, and (iii) redeemed shares were subject to a front-end or deferred sales charge. |
| RAYMOND JAMES & ASSOCIATES, INC., RAYMOND JAMES FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND EACH ENTITY’S AFFILIATES (“RAYMOND JAMES”) |
| ■ | Shares purchased in an investment advisory program. |
| ■ | Shares purchased within the same fund family through a systematic reinvestment of capital gains and dividend distributions. |
| ■ | Employees and registered representatives of Raymond James or its affiliates and their family members as designated by Raymond James. |
| ■ | Shares purchased from the proceeds of redemptions within the same fund family, provided (1) the repurchase occurs within 90 days following the redemption, (2) the redemption and purchase occur in the same account, and (3) redeemed shares were subject to a front-end or deferred sales load (known as Rights of Reinstatement). |
| ■ | A Shareholder in the Fund’s Class C shares will have their shares converted at net asset value to Class A shares (or the appropriate share class) of the Fund if the shares are no longer subject to a CDSC and the conversion is in line with the policies and procedures of Raymond James. |
| ■ | Death or disability of the shareholder. |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a systematic withdrawal plan as described in the Fund’s Prospectus. |
| ■ | Return of excess contributions from an IRA Account. |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a required minimum distribution for IRA and retirement accounts due to the shareholder reaching the qualified age based on applicable IRS regulations as described in the Fund’s Prospectus. |
| ■ | Shares sold to pay Raymond James fees but only if the transaction is initiated by Raymond James. |
| ■ | Shares acquired through a Right of Reinstatement. |
| ■ | Breakpoints as described in this Prospectus. |
| ■ | Rights of accumulation which entitle shareholders to breakpoint discounts will be automatically calculated based on the aggregated holding of fund family assets held by accounts within the purchaser’s household at Raymond James. Eligible fund family assets not held at Raymond James may be included in the calculation of rights of accumulation only if the shareholder notifies his or her financial advisor about such assets. |
| ■ | Letters of intent which allow for breakpoint discounts based on anticipated purchases within a fund family, over a 13-month time period. Eligible fund family assets not held at Raymond James may be included in the calculation of letters of intent only if the shareholder notifies his or her financial advisor about such assets. |
| JANNEY MONTGOMERY SCOTT LLC |
| ■ | Shares purchased through reinvestment of capital gains distributions and dividend reinvestment when purchasing shares of the same fund (but not any other fund within the fund family). |
| ■ | Shares purchased by employees and registered representatives of Janney or its affiliates and their family members as designated by Janney. |
| ■ | Shares purchased from the proceeds of redemptions within the same fund family, provided (1) the repurchase occurs within ninety (90) days following the redemption, (2) the redemption and purchase occur in the same account, and (3) redeemed shares were subject to a front-end or deferred sales load (i.e., right of reinstatement). |
| ■ | Employer-sponsored retirement plans (e.g., 401(k) plans, 457 plans, employer-sponsored 403(b) plans, profit sharing and money purchase pension plans and defined benefit plans). For purposes of this provision, employer-sponsored retirement plans do not include SEP IRAs, Simple IRAs, SAR-SEPs or Keogh plans. |
| ■ | Shares acquired through a right of reinstatement. |
| ■ | Class C Shares that are no longer subject to a contingent deferred sales charge and are converted to Class A Shares of the same fund pursuant to Janney’s policies and procedures. |
| ■ | Shares sold upon the death or disability of the shareholder. |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a systematic withdrawal plan as described in the Funds’ Prospectus. |
| ■ | Shares purchased in connection with a return of excess contributions from an IRA account. |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a required minimum distribution for IRA and other retirement accounts due to the shareholder reaching age 70½ as described in the Funds’ Prospectus. |
| ■ | Shares sold to pay Janney fees but only if the transaction is initiated by Janney. |
| ■ | Shares acquired through a right of reinstatement. |
| ■ | Shares exchanged into the same share class of a different fund. |
| ■ | Breakpoints as described in the Funds’ Prospectus. |
| ■ | Rights of accumulation (“ROA”), which entitle shareholders to breakpoint discounts, will be automatically calculated based on the aggregated holding of fund family assets held by accounts within the purchaser’s household at Janney. Eligible fund family assets not held at Janney may be included in the ROA calculation only if the shareholder notifies his or her financial advisor about such assets. |
| ■ | Letters of intent which allow for breakpoint discounts based on anticipated purchases within a fund family, over a 13-month time period. Eligible fund family assets not held at Janney may be included in the calculation of letters of intent only if the shareholder notifies his or her financial advisor about such assets. |
* |
Also referred to as an “initial sales charge.” |
| EDWARD D. JONES & CO. |
| ■ | The applicable sales charge on a purchase of Class A Shares is determined by taking into account all share classes (except any money market funds and retirement plan share classes) of Goldman Sachs Funds held by the shareholder or in an account grouped by Edward Jones with other accounts for the purpose of providing certain pricing considerations (“pricing groups”). This includes all share classes held on the Edward Jones platform and/or held on another platform. The inclusion of eligible fund family assets in the rights of accumulation calculation is dependent on the shareholder notifying his or her financial advisor of such assets at the time of calculation. |
| ■ | ROA is determined by calculating the higher of cost or market value (current shares x NAV). |
| ■ | Through a LOI, shareholders can receive the sales charge and breakpoint discounts for purchases shareholders intend to make over a 13-month period from the date Edward Jones receives the LOI. The LOI is determined by calculating the higher of cost or market value of qualifying holdings at LOI initiation in combination with the value that the shareholder intends to buy over a 13-month period to calculate the front-end sales charge and any breakpoint discounts. Each purchase the shareholder makes during that 13-month period will receive the sales charge and breakpoint discount that applies to the total amount. The inclusion of eligible fund family assets in the LOI calculation is dependent on the shareholder notifying his or her financial advisor of such assets at the time of calculation. Purchases made before the LOI is received by Edward Jones are not covered under the LOI and will not reduce the sales charge previously paid. Sales charges will be adjusted if LOI is not met. |
| ■ | Associates of Edward Jones and its affiliates and their family members who are in the same pricing group (as determined by Edward Jones under its policies and procedures) as the associate. This waiver will continue for the remainder of the associate’s life if the associate retires from Edward Jones in good-standing. |
| ■ | Shares purchased in an Edward Jones fee-based program. |
| ■ | Shares purchased through reinvestment of capital gains distributions and dividend reinvestment. |
| ■ | Shares purchased from the proceeds of redeemed shares of the same fund family so long as the following conditions are met: 1) the proceeds are from the sale of shares within 60 days of the purchase, and 2) the sale and purchase are made in the same share class and the same account or the purchase is made in an individual retirement account with proceeds from liquidations in a non-retirement account. |
| ■ | Shares exchanged into Class A Shares from another share class so long as the exchange is into the same fund and was initiated at the discretion of Edward Jones. Edward Jones is responsible for any remaining CDSC due to the fund company, if applicable. Any future purchases are subject to the applicable sales charge as disclosed in the prospectus. |
| ■ | Exchanges from Class C Shares to Class A Shares of the same fund, generally, in the 84th month following the anniversary of the purchase date or earlier at the discretion of Edward Jones. |
| ■ | The death or disability of the shareholder |
| ■ | Systematic withdrawals with up to 10% per year of the account value |
| ■ | Return of excess contributions from an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a required minimum distribution for IRA and retirement accounts if the redemption is taken in or after the year the shareholder reaches qualified age based on applicable IRS regulations |
| ■ | Shares sold to pay Edward Jones fees or costs in such cases where the transaction is initiated by Edward Jones |
| ■ | Shares exchanged in an Edward Jones fee-based program |
| ■ | Shares acquired through NAV reinstatement Other Important Information related to Edward Jones |
| ■ | $250 initial purchase minimum |
| ■ | $50 subsequent purchase minimum |
| ■ | Edward Jones has the right to redeem at its discretion fund holdings with a balance of $250 or less. The following are examples of accounts that are not included in this policy: |
| ■ | A fee-based account held on an Edward Jones platform |
| ■ | A 529 account held on an Edward Jones platform |
| ■ | An account with an active systematic investment plan or letter of intent (LOI) |
| ■ | At any time it deems necessary, Edward Jones has the authority to change a share class to Class A shares of the same fund at NAV. |
| OPPENHEIMER & CO. INC. |
| ■ | Employer-sponsored retirement, deferred compensation and employee benefit plans (including health savings accounts) and trusts used to fund those plans, provided that the shares are not held in a commission-based brokerage account and shares are held for the benefit of the plan |
| ■ | Shares purchased by or through a 529 Plan |
| ■ | Shares purchased through a OPCO affiliated investment advisory program |
| ■ | Shares purchased through reinvestment of capital gains distributions and dividend reinvestment when purchasing shares of the same fund (but not any other fund within the fund family) |
| ■ | Shares purchased from the proceeds of redemptions within the same fund family, provided (1) the repurchase occurs within 90 days following the redemption, (2) the redemption and purchase occur in the same account, and (3) redeemed shares were subject to a front-end or deferred sales load (known as Rights of Restatement). |
| ■ | A shareholder in the Fund’s Class C shares will have their shares converted at net asset value to Class A shares (or the appropriate share class) of the Fund if the shares are no longer subject to a CDSC and the conversion is in line with the policies and procedures of OPCO |
| ■ | Employees and registered representatives of OPCO or its affiliates and their family members |
| ■ | Directors or Trustees of the Fund, and employees of the Fund’s investment adviser or any of its affiliates, as described in this prospectus |
| ■ | Death or disability of the shareholder |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a systematic withdrawal plan as described in the Fund’s prospectus |
| ■ | Return of excess contributions from an IRA Account |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a required minimum distribution for IRA and retirement accounts due to the shareholder reaching the qualified age based on applicable IRS regulations as described in the prospectus |
| ■ | Shares sold to pay OPCO fees but only if the transaction is initiated by OPCO |
| ■ | Shares acquired through a right of reinstatement |
| ■ | Breakpoints as described in this prospectus. |
| ■ | Rights of Accumulation (ROA) which entitle shareholders to breakpoint discounts will be automatically calculated based on the aggregated holding of fund family assets held by accounts within the purchaser’s household at OPCO. Eligible fund family assets not held at OPCO may be included in the ROA calculation only if the shareholder notifies his or her financial advisor about such assets. |
| ROBERT W. BAIRD & CO. (“BAIRD”) |
| ■ | Shares purchased through reinvestment of capital gains distributions and dividend reinvestment when purchasing share of the same fund |
| ■ | Share purchase by employees and registers representatives of Baird or its affiliate and their family members as designated by Baird |
| ■ | Shares purchase from the proceeds of redemptions within the same fund family, provided (1) the repurchase occurs within 90 days following the redemption, (2) the redemption and purchase occur in the same accounts, and (3) redeemed shares were subject to a front-end or deferred sales charge (known as rights of reinstatement) |
| ■ | A shareholder in the Funds Class C shares will have their shares converted at net asset value to Class A shares of the fund if the shares are no longer subject to CDSC and the conversion is in line with the policies and procedures of Baird |
| ■ | Employer-sponsored retirement plans or charitable accounts in a transactional brokerage account at Baird, including 401(k) plans, 457 plans, employer-sponsored 403(b) plans, profit sharing and money purchase pension plans and defined benefit plans. For purposes of this provision, employer-sponsored retirement plans do not include SEP IRAs, Simple IRAs or SAR-SEPs |
| ■ | Shares sold due to death or disability of the shareholder |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a systematic withdrawal plan as described in the Fund’s Prospectus |
| ■ | Shares bought due to returns of excess contributions from an IRA Account |
| ■ | Shares sold as part of a required minimum distribution for IRA and retirement accounts due to the shareholder reaching age 72 as described in the Fund’s prospectus |
| ■ | Shares sold to pay Baird fees but only if the transaction is initiated by Baird |
| ■ | Shares acquired through a right of reinstatement |
| ■ | Breakpoints as described in this prospectus |
| ■ | Rights of accumulations which entitles shareholders to breakpoint discounts will be automatically calculated based on the aggregated holding of fund family assets held by accounts within the purchaser’s household at Baird. Eligible fund family assets not held at Baird may be included in the rights of accumulations calculation only if the shareholder notifies his or her financial advisor about such assets |
| ■ | Letters of Intent (LOI) allow for breakpoint discounts based on anticipated purchases within a fund family through Baird, over a 13-month period of time |
| FOR MORE INFORMATION |
1-800-526-7384. You can also access and download the annual and semi-annual reports and the SAI at the Fund’s website:
| Institutional, Service & Class R6 | Class A, C, Investor & R | ||
| ■ By telephone: |
1-800-621-2550 | 1-800-526-7384 | |
| ■ By mail: |
Goldman Sachs Funds P.O. Box 06050 Chicago, IL 60606 |
Goldman Sachs Funds P.O. Box 219711 Kansas City, MO 64121 | |
| ■ On the Internet: |
SEC EDGAR database – http://www.sec.gov |
| AN INVESTMENT IN A FUND IS NOT A BANK DEPOSIT AND IS NOT INSURED BY THE FEDERAL DEPOSIT INSURANCE CORPORATION OR ANY OTHER GOVERNMENT AGENCY. AN INVESTMENT IN A FUND INVOLVES INVESTMENT RISKS, AND YOU MAY LOSE MONEY IN A FUND. |

| Investment Objective |
| Fees and Expenses of the Fund |
Class P | |
| Management Fees | 0.71% |
| Other Expenses | 0.11% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
0.82% |
| Expense Limitation 1 |
(0.08)% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Limitation |
0.74% |
1 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.004% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. This arrangement will remain in effect through at least December 29, 2021, and prior to such date the Investment Adviser may not terminate the arrangement without the approval of the Board of Trustees. |
| Expense Example |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class P Shares | $76 | $254 | $447 | $1,006 |
| Portfolio Turnover |
| Principal Strategy |
| Principal Risks of the Fund |
| Performance |

During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| Best Quarter Return | 14.88% | March 31, 2019 |
| Worst Quarter Return | -14.34% | December 31, 2018 |
| AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURN |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
Since Inception |
Class P Shares (Inception 4/17/2018) |
||
| Returns Before Taxes | 32.78% | 12.50% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | 31.58% | 7.22% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 20.22% | 8.80% |
| Russell 1000 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.43% | 12.84% |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |

| Investment Objective |
| Fees and Expenses of the Fund |
Class P | |
| Management Fees | 0.76% |
| Other Expenses 1 |
0.23% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
0.99% |
| Expense Limitation 2 |
(0.20)% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Limitation |
0.79% |
1 |
The “Other Expenses” for Class P Shares have been restated to reflect expenses expected to be incurred during the current fiscal year. |
2 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.004% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. This arrangement will remain in effect through at least December 29, 2021, and prior to such date, the Investment Adviser may not terminate the arrangement without the approval of the Board of Trustees. |
| Expense Example |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class P Shares | $81 | $295 | $528 | $1,195 |
| Portfolio Turnover |
| Principal Strategy |
| Principal Risks of the Fund |
| Performance |

During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| Best Quarter Return | 17.37% | March 31, 2019 |
| Worst Quarter Return | -16.59% | December 31, 2018 |
| AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURN |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
Since Inception |
Class P Shares (Inception 4/17/2018) |
||
| Returns Before Taxes | 38.11% | 15.80% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | 35.68% | 12.69% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 24.20% | 11.77% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 15.82% |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |

| Investment Objective |
| Fees and Expenses of the Fund |
Class P | |
| Management Fees | 0.55% |
| Other Expenses 1 |
1.42% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
1.97% |
| Expense Limitation 2 |
(1.39)% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Limitation |
0.58% |
1 |
The “Other Expenses” for Class P Shares have been restated to reflect expenses expected to be incurred during the current fiscal year. |
2 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.004% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. This arrangement will remain in effect through at least December 29, 2021, and prior to such date, the Investment Adviser may not terminate the arrangement without the approval of the Board of Trustees. |
| Expense Example |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class P Shares | $59 | $483 | $933 | $2,183 |
| Portfolio Turnover |
| Principal Strategy |
| Principal Risks of the Fund |
| Performance |

During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| Best Quarter Return | 14.23% | March 31, 2019 |
| Worst Quarter Return | -14.71% | December 31, 2018 |
| AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURN |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
Since Inception |
Class P Shares (Inception 4/17/2018) |
||
| Returns Before Taxes | 31.77% | 11.90% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | 30.07% | 9.55% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 19.98% | 8.71% |
| S&P 500 ® Index (Total Return, Unhedged, USD) (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
31.49% | 13.15% |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |

| Investment Objective |
| Fees and Expenses of the Fund |
Class P | |
| Management Fees | 0.71% |
| Other Expenses 1 |
0.26% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
0.97% |
| Expense Limitation 2 |
(0.23)% |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Limitation |
0.74% |
1 |
The “Other Expenses” for Class P Shares have been restated to reflect expenses expected to be incurred during the current fiscal year. |
2 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.004% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. This arrangement will remain in effect through at least December 29, 2021, and prior to such date the Investment Adviser may not terminate the arrangement without the approval of the Board of Trustees. |
| Expense Example |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class P Shares | $76 | $286 | $514 | $1,169 |
| Portfolio Turnover |
| Principal Strategy |
| Principal Risks of the Fund |
| Performance |

During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| Best Quarter Return | 16.82% | March 31, 2019 |
| Worst Quarter Return | -16.47% | December 31, 2018 |
| AVERAGE ANNUAL TOTAL RETURN |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
Since Inception |
Class P Shares (Inception 4/17/2018) |
||
| Returns Before Taxes | 35.57% | 14.33% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | 30.96% | 6.71% |
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | 24.20% | 9.96% |
| Russell 1000 ® Growth Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
36.39% | 15.82% |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |

Class P | |
| Management Fees | |
| Other Expenses | |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses |
|
| Expense Limitation 1 |
( |
Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses After Expense Limitation |
1 |
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit “Other Expenses” (excluding acquired fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, taxes, interest, brokerage fees, expenses of shareholder meetings, litigation and indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to 0.084% of the Fund’s average daily net assets. This arrangement will remain in effect through at least |
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
| Class P Shares | $ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
■ |
gambling, |
■ |
alcohol, |
■ |
tobacco, |
■ |
coal, and |
■ |
weapons. |

During the periods shown in the chart above: |
Returns |
Quarter ended |
| - |
For the period ended December 31, 2019 |
1 Year |
Since Inception |
Class P Shares (Inception |
||
| Returns Before Taxes | ||
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions | ||
| Returns After Taxes on Distributions and Sale of Fund Shares | ||
| S&P 500 ® Index (reflects no deduction for fees or expenses) |
| Portfolio Management |
| Buying and Selling Fund Shares |
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |
Additional Summary Information
| Tax Information |
| Payments to Broker-Dealers and Other Financial Intermediaries |
| INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE |
| PRINCIPAL INVESTMENT STRATEGIES |
| ■ | gambling, |
| ■ | alcohol, |
| ■ | tobacco, |
| ■ | coal, and |
| ■ | weapons. |
| ■ | quality of earnings; |
| ■ | concern for shareholder interests and minority shareholder rights; |
| ■ | unethical business conduct, for example unethical methods of obtaining contracts and/or close connections with authorities; |
| ■ | board structure; |
| ■ | board diversity; |
| ■ | executive management team, for example CEO/CFO effectiveness and acting in interest of shareholders; and |
| ■ | executive compensation. |
| ■ | environmental and social reporting, disclosure and transparency; |
| ■ | material environmental litigation and/or controversies; |
| ■ | material social litigation and/or controversies; |
| ■ | labor practices, for example track record in treatment of employees and supply chain management; |
| ■ | human rights considerations; and |
| ■ | climate change policies and environmental practices. |
| ■ | Has a class of securities whose principal securities market is in the United States; |
| ■ | Has its principal office in the United States; |
| ■ | Derives 50% or more of its total revenue or profit from goods produced, sales made or services provided in the United States; |
| ■ | Maintains 50% or more of its assets in the United States; or |
| ■ | Is otherwise determined to be economically tied to the United States by the Investment Adviser in its discretion. For example, the Investment Adviser may use the classifications assigned by third parties, including an issuer’s “country of risk” as determined by Bloomberg or the classifications assigned to an issuer by the Fund’s benchmark index provider. These classifications are generally based on a number of criteria, including an issuer’s country of domicile, the primary stock exchange on which an issuer’s securities trade, the location from which the majority of an issuer’s revenue is derived, and an issuer’s reporting currency. Although the Investment Adviser may rely on these classifications, it is not required to do so. |
| ■ | Market uncertainty exists. |
| ■ | Their economic value is not recognized by the market. |
| ■ | Sustainable operating or competitive advantage. |
| ■ | Excellent stewardship of capital. |
| ■ | Capability to earn above their cost of capital. |
| ■ | Strong or improving balance sheets and cash flow. |
| ■ | Understand the business, management, products and competition. |
| ■ | Perform intensive, hands-on fundamental research. |
| ■ | Seek businesses with strategic competitive advantages. |
| ■ | Over the long-term, expect each company’s stock price ultimately to track the growth in the value of the business. |
| ADDITIONAL PERFORMANCE INFORMATION |
| OTHER INVESTMENT PRACTICES AND SECURITIES |
10 Percent of total assets (including securities lending collateral) (italic type) 10 Percent of net assets (excluding borrowings for investment purposes) (roman type) • No specific percentage limitation on usage; limited only by the objectives and strategies of the Fund — Not permitted |
Capital Growth Fund |
Concentrated Growth Fund |
Flexible Cap Fund |
Strategic Growth Fund |
U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
|
Investment Practices |
||||||
| Borrowings | 33 1 3 |
33 1 3 |
33 1 3 |
33 1 3 |
33 1 3 |
|
| Credit, Currency, Index, Interest Rate, Total Return and Mortgage Swaps and Options on Swaps | — | — | • | — | — | |
| Cross Hedging of Currencies | • | • | • | — | — | |
| Custodial Receipts and Trust Certificates | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Equity Swaps | • | • | • | — | — | |
| Foreign Currency Transactions (including forward contracts)* | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Futures Contracts and Options and Swaps on Futures Contracts | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Illiquid Investments** | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| Investment Company Securities (including ETFs) 1 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
|
| Options on Foreign Currencies 2 |
• | • | • | • | — | |
| Options 3 |
• | • | • | • | — | |
| Preferred Stock, Warrants and Stock Purchase Rights | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Repurchase Agreements | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Securities Lending | 33 1 3 |
33 1 3 |
33 1 3 |
33 1 3 |
33 1 3 |
|
| Short Sales Against the Box | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | — | |
| Unseasoned Companies | • | • | • | • | • | |
| When-Issued Securities and Forward Commitments | • | • | • | • | • |
* |
Limited by the amount the Fund invests in foreign securities. |
** |
Illiquid investments are any investments that a Fund reasonably expects cannot be sold or disposed of in current market conditions in seven calendar days or less without the sale or disposition significantly changing the market value of the investment. |
1 |
This percentage limitation does not apply to a Fund’s investments in investment companies (including ETFs) where a higher percentage limitation is permitted under the terms of an SEC exemptive order or SEC exemptive rule. |
2 |
The Funds (except for the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may purchase and sell call and put options on foreign currencies. |
3 |
The Funds (except for the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may sell call and put options and purchase call and put options on securities and other instruments in which the Funds may invest or any index consisting of securities or other instruments in which they may invest. |
10 Percent of total assets (italic type) 10 Percent of net assets (including borrowings for investment purposes) (roman type) • No specific percentage limitation on usage; limited only by the objectives and strategies of the Fund — Not permitted |
Capital Growth Fund |
Concentrated Growth Fund |
Flexible Cap Fund |
Strategic Growth Fund |
U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
|
Investment Securities |
||||||
| American, European and Global Depositary Receipts | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Asset-Backed and Mortgage-Backed Securities 4 |
• | • | • | • | — | |
| Bank Obligations 4 |
• | • | • | • | • | |
| Convertible Securities 5 |
• | • | • | • | • | |
| Corporate Debt Obligations 4 |
• | • | • | • | • | |
| Equity Investments | 90+ |
90+ |
80+ | 90+ |
80+ | |
| Emerging Country Securities 6 |
10 |
10 |
25 | 10 |
— | |
| Fixed Income Securities 7 |
10 |
10 |
20 | 10 |
20 | |
| Foreign Securities 6 |
25 |
25 |
25 | 25 |
20 | |
| Initial Public Offerings (“IPOs”) | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Master Limited Partnerships | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Non-Investment Grade Fixed Income Securities 8 |
10 |
— | 10 |
10 |
— | |
| Pre-IPO Investments (including late-stage private equity securities) | — | — | • | — | — | |
| Real Estate Investment Trusts (“REITs”) | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Structured Securities (which may include equity linked notes) 9 |
• | • | • | • | • | |
| Temporary Investments | • | • | • | • | • | |
| U.S. Government Securities 4 |
• | • | • | • | • |
4 |
Limited by the amount the Fund invests in fixed income securities. |
5 |
All Funds use the same rating criteria for convertible and non-convertible debt securities. |
6 |
The Capital Growth, Strategic Growth and Concentrated Growth Funds may each invest in the aggregate up to 25% of their total assets, and the Flexible Cap Fund may invest in the aggregate up to 25% of its net assets, in foreign securities, including emerging country securities. The U.S. Equity ESG Fund may invest in the aggregate up to 20% of its net assets in foreign securities and may not invest in emerging country securities. |
7 |
Except as noted under “Non-Investment Grade Fixed Income Securities,” fixed income securities must be investment grade (i.e., BBB– or higher by Standard & Poor’s, Baa3 or higher by Moody’s or have a comparable credit rating by another NRSRO or if unrated, determined by the Investment Adviser to be of comparable credit quality). |
8 |
May be BB+ or lower by Standard & Poor’s, Ba1 or lower by Moody’s or have a comparable credit rating by another NRSRO at the time of investment. |
9 |
Structured securities are not subject to the same minimum credit quality requirements as a Fund’s investments in fixed income securities. |
| ✓ Principal Risk • Additional Risk |
Capital Growth Fund |
Concentrated Growth Fund |
Flexible Cap Fund |
Strategic Growth Fund |
U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
|
| Credit/Default | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Derivatives | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Emerging Countries | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| ESG Standards | ✓ | |||||
| Foreign | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | • | |
| Geographic | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Initial Public Offering (“IPO”) | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Interest Rate | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Investment Style | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Issuer Concentration | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Large Shareholder Transactions | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Liquidity | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Management | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Market | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Master Limited Partnerships | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Mid-Cap and Small-Cap | • | ✓ | ✓ | • | • | |
| NAV | • | • | • | • | • | |
| Non-Investment Grade Fixed Income Securities | • | • | • | |||
| Portfolio Turnover Rate | ✓ | |||||
| Pre-IPO Investments | • | |||||
| Sector Risk | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Stock | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| U.S. Government Securities | • | • | • | • | • |
| ■ | Credit/Default Risk —An issuer or guarantor of fixed income securities or instruments held by the Fund (which may have low credit ratings), may default on its obligation to pay interest and repay principal or default on any other obligation. The credit quality of the Fund’s portfolio securities or instruments may meet the Fund’s credit quality requirements at the time of purchase but then deteriorate thereafter, and such a deterioration can occur rapidly. In certain instances, the downgrading or default of a single holding or guarantor of the Fund’s holdings may impair the Fund’s liquidity and have the potential to cause significant NAV deterioration. These risks are more pronounced in connection with a Fund’s investments in non-investment grade fixed income securities. |
| ■ | Derivatives Risk— The Fund’s use of options, futures, forwards, swaps, options on swaps, structured securities and other derivative instruments may result in losses. These instruments, which may pose risks in addition to and greater than those associated with investing directly in securities, currencies or other instruments, may be illiquid or less liquid, volatile, difficult to price and leveraged so that small changes in the value of the underlying instruments may produce disproportionate losses to the Fund. Certain derivatives are also subject to counter-party risk, which is the risk that the other party in the transaction will not fulfill its contractual obligations, liquidity risk and risks arising from margin requirements, which include the risk that the Fund will be required to pay additional margin or set aside additional collateral to maintain open derivative positions. Derivatives may be used for both hedging and non-hedging purposes. |
| The use of derivatives is a highly specialized activity that involves investment techniques and risks different from those associated with investments in more traditional securities and instruments, and there is no guarantee that the use of derivatives will achieve their intended result. If the Investment Adviser is incorrect in its expectation of the timing or level of fluctuation in securities prices, interest rates, currency prices or other variables, the use of derivatives could result in losses, which in some cases may be |
| significant. A lack of correlation between changes in the value of derivatives and the value of the portfolio assets (if any) being hedged could also result in losses. In addition, there is a risk that the performance of the derivatives or other instruments used by the Investment Adviser to replicate the performance of a particular asset class may not accurately track the performance of that asset class. | |
| As an investment company registered with the SEC, the Fund must identify on its books (often referred to as “asset segregation”) liquid assets, or engage in other SEC- or SEC staff-approved or other appropriate measures, to “cover” open positions with respect to certain kinds of derivative instruments. For more information about these practices, see Appendix A. As discussed in more detail in Appendix A and the SAI, the SEC adopted a final rule related to the use of derivatives, short sales, reverse repurchase agreements and certain other transactions by registered investment companies. In connection with the final rule, the SEC and its staff will rescind and withdraw applicable guidance and relief regarding asset segregation and coverage transactions reflected in the Fund’s asset segregation and cover practices discussed therein. | |
| ■ | Emerging Countries Risk— Investments in securities of issuers located in emerging countries are subject to the risks associated with investments in foreign securities. In addition, the securities markets of most emerging countries are less liquid, developed and efficient, are subject to greater price volatility, have smaller market capitalizations, have more or less government regulation and are not subject to as extensive and frequent accounting, auditing, financial and other reporting requirements as the securities markets of more developed countries. Further, investments in securities of issuers located in certain emerging countries involve the risk of loss resulting from problems in share registration, settlement or custody, substantial economic, political and social disruptions and the imposition of exchange controls (including repatriation restrictions). The legal remedies for investors in emerging markets may be more limited than the remedies available in the U.S., and the ability of U.S. authorities ( e.g. , SEC and the U.S. Department of Justice) to bring actions against bad actors may be limited. These risks are not normally associated with investments in more developed countries. For more information about these risks, see Appendix A. |
| ■ | ESG Standards Risk —The U.S. Equity ESG Fund’s adherence to its ESG criteria and the application of the Investment Adviser’s supplemental ESG analysis when selecting investments may affect the Fund’s exposure to certain companies, sectors, regions, and countries and may affect the Fund’s performance depending on whether such investments are in or out of favor. For example, the Fund generally will not seek to invest in companies that the Investment Adviser believes have adverse social or environmental impacts (i.e., gambling, alcohol, tobacco, coal or weapons companies), and the Fund generally will not seek to invest in companies that the Investment Adviser believes demonstrate weak corporate governance (e.g., certain state-owned enterprises). Adhering to the ESG criteria and applying the Investment Adviser’s supplemental ESG analysis may also affect the Fund’s performance relative to similar funds that do not adhere to such criteria or apply such analysis. Additionally, the Fund’s adherence to the ESG criteria and the application of the supplemental ESG analysis in connection with identifying and selecting equity investments in non-U.S. issuers often require subjective analysis and may be relatively more difficult than applying the ESG criteria or the supplemental ESG analysis to equity investments of all issuers because data availability may be more limited with respect to non- U.S. issuers. Certain investments may be dependent on U.S. and foreign government policies, including tax incentives and subsidies, which may change without notice. |
| The exclusionary criteria related to the Fund’s ESG criteria may result in the Fund forgoing opportunities to buy certain securities when it might otherwise be advantageous to do so, or selling securities for ESG reasons when it might be otherwise disadvantageous for it to do so. The Fund’s investments in certain companies may be susceptible to various factors that may impact their businesses or operations, including costs associated with government budgetary constraints that impact publicly funded projects and clean energy initiatives, the effects of general economic conditions throughout the world, increased competition from other providers of services, unfavorable tax laws or accounting policies and high leverage. The Fund may invest in companies that do not reflect the beliefs and values of any particular investor. When assessing whether an issuer meets the Fund’s ESG Criteria and conducting an ESG analysis of an issuer, the Investment Adviser may rely on third-party data that it believes to be reliable, but it does not guarantee the accuracy of such third-party data. The Fund’s ESG criteria and the application of the supplemental ESG analysis may be changed without shareholder approval. | |
| ■ | Foreign Risk —When the Fund invests in foreign securities, it may be subject to risk of loss not typically associated with U.S. issuers. Loss may result because of more or less foreign government regulation, less public information, less stringent investor protections and disclosure standards, less liquid, developed or efficient trading markets, greater volatility and less economic, political and social stability in the countries in which the Fund invests. Loss may also result from, among other things, deteriorating economic and business conditions in other countries, including the United States, regional and global conflicts, the imposition of exchange controls (including repatriation restrictions), sanctions, foreign taxes, confiscation of assets and property, trade restrictions (including tariffs), expropriations and other government restrictions by the United States and other governments, higher transaction costs, difficulty enforcing contractual obligations or from problems in share registration, settlement or custody. A Fund or the Investment Adviser may determine not to invest in, or may limit its overall investment in, a particular issuer, country or geographic region due to, among other things, heightened risks regarding repatriation restrictions, confiscation of assets and property, expropriation or nationalization. A Fund will also be subject to the risk of negative foreign currency rate fluctuations, |
| which may cause the value of securities denominated in such foreign currency (or other instruments through which the Fund has exposure to foreign currencies) to decline in value. Currency exchange rates may fluctuate significantly over short periods of time. Foreign risks will normally be greatest when a Fund invests in securities of issuers located in emerging countries. For more information about these risks, see Appendix A. | |
| The Fund's investments in foreign securities may also be subject to foreign currency risk, as described above, the risk of negative foreign currency rate fluctuations, which may cause the value of securities denominated in such foreign currency (or other instruments through which the Fund may have exposure to foreign currencies) to decline in value. Foreign risks will normally be greatest when the Fund invests in securities of issuers located in emerging countries. For more information about these risks, see Appendix A. | |
| ■ | Geographic Risk— If the Fund focuses its investments in securities of issuers located in a particular country or geographic region, the Fund may be subjected, to a greater extent than if its investments were less focused, to the risks of volatile economic cycles and/or conditions and developments that may be particular to that country or region, such as: adverse securities markets; adverse exchange rates; adverse social, political, regulatory, economic, business, environmental or other developments; or natural disasters. |
| ■ | IPO Risk— The market value of shares issued in an IPO may fluctuate considerably due to factors such as the absence of a prior public market, unseasoned trading, the small number of shares available for trading and limited information about a company’s business model, quality of management, earnings growth potential, and other criteria used to evaluate its investment prospects. The purchase of IPO shares may involve high transaction costs. Investments in IPO shares, which are subject to market risk and liquidity risk, involve greater risks than investments in shares of companies that have traded publicly on an exchange for extended periods of time. |
| ■ | Interest Rate Risk— When interest rates increase, fixed income securities or instruments held by the Fund (which may include inflation protected securities) will generally decline in value. Long-term fixed income securities or instruments will normally have more price volatility because of this risk than short-term fixed income securities or instruments. A wide variety of market factors can cause interest rates to rise, including central bank monetary policy, rising inflation and changes in general economic conditions. The risks associated with changing interest rates may have unpredictable effects on the markets and a Fund’s investments. Fluctuations in interest rates may also affect the liquidity of fixed income securities and instruments held by the Fund. |
| Interest rates in the United States are currently at historically low levels. Certain countries have experienced negative interest rates on certain fixed-income instruments. Very low or negative interest rates may magnify interest rate risk. Changing interest rates, including rates that fall below zero, may have unpredictable effects on markets, may result in heightened market volatility and may detract from Fund performance to the extent the Fund is exposed to such interest rates and/or volatility. | |
| ■ | Investment Style Risk —Different investment styles (e.g., “growth,” “value” or “quantitative”) tend to shift in and out of favor depending upon market and economic conditions and investor sentiment. The Fund may outperform or underperform other funds that invest in similar asset classes but employ different investment styles. Examples of different investment styles include growth and value investing. Growth stocks may be more volatile than other stocks because they are more sensitive to investor perceptions of the issuing company’s growth of earnings potential. Growth companies are often expected by investors to increase their earnings at a certain rate. When these expectations are not met, investors can punish the stocks inordinately even if earnings showed an absolute increase. Also, because growth companies usually invest a high portion of earnings in their business, growth stocks may lack the dividends of some value stocks that can cushion stock prices in a falling market. Growth oriented funds will typically underperform when value investing is in favor. Value stocks are those that are undervalued in comparison to their peers due to adverse business developments or other factors. |
| ■ | Issuer Concentration Risk —Under normal circumstances, the Concentrated Growth Fund and the U.S. Equity ESG Fund intend to invest in up to approximately 40 and 50 companies, respectively. As a result of the relatively small number of issuers in which a Fund generally invests, it may be subject to greater risks than a fund that invests in a greater number of issuers. A change in the value of any single investment held by a Fund may affect the overall value of the Fund more than it would affect a mutual fund that holds more investments. In particular, a Fund may be more susceptible to adverse developments affecting any single issuer in the Fund and may be susceptible to greater losses because of these developments. |
| ■ | Large Shareholder Transactions Risk —The Fund may experience adverse effects when certain large shareholders, such as other funds, institutional investors (including those trading by use of non-discretionary mathematical formulas), financial intermediaries (who may make investment decisions on behalf of underlying clients and/or include the Fund in their investment model), individuals, accounts and Goldman Sachs affiliates, purchase or redeem large amounts of shares of the Fund. Such large shareholder redemptions, which may occur rapidly or unexpectedly, may cause the Fund to sell portfolio securities at times when it would not otherwise do so, which may negatively impact the Fund’s NAV and liquidity. Similarly, large Fund share purchases may adversely affect the Fund’s performance to the extent that the Fund is delayed in investing new cash or otherwise maintains a larger |
| cash position than it ordinarily would. These transactions may also accelerate the realization of taxable income to shareholders if such sales of investments resulted in gains, and may also increase transaction costs. In addition, a large redemption could result in the Fund’s current expenses being allocated over a smaller asset base, leading to an increase in the Fund’s expense ratio. | |
| ■ | Liquidity Risk— The Fund may invest to a greater degree in securities or instruments that trade in lower volumes and may make investments that are less liquid than other investments. Also, the Fund may make investments that may become less liquid in response to market developments or adverse investor perceptions. Investments that are illiquid or that trade in lower volumes may be more difficult to value. When there is no willing buyer and investments cannot be readily sold at the desired time or price, the Fund may have to accept a lower price or may not be able to sell the security or instrument at all. An inability to sell one or more portfolio positions can adversely affect the Fund's value or prevent the Fund from being able to take advantage of other investment opportunities. |
| To the extent that the traditional dealer counterparties that engage in fixed income trading do not maintain inventories of bonds (which provide an important indication of their ability to “make markets”) that keep pace with the growth of the bond markets over time, relatively low levels of dealer inventories could lead to decreased liquidity and increased volatility in the fixed income markets. Additionally, market participants other than a Fund may attempt to sell fixed income holdings at the same time as the Fund, which could cause downward pricing pressure and contribute to decreased liquidity. | |
| Because the Fund may invest in non-investment grade fixed income securities, small- and mid-capitalization stocks, REITs and/or emerging country issuers, the Fund may be especially subject to the risk that during certain periods, the liquidity of particular issuers or industries, or all securities within a particular investment category, may shrink or disappear suddenly and without warning as a result of adverse economic, market or political events, or adverse investor perceptions, whether or not accurate. | |
| Liquidity risk may also refer to the risk that the Fund will not be able to pay redemption proceeds within the allowable time period stated in the Prospectus or without significant dilution to remaining investors’ interests because of unusual market conditions, an unusually high volume of redemption requests or other reasons. While the Fund reserves the right to meet redemption requests through in-kind distributions, the Fund may instead choose to raise cash to meet redemption requests through sales of portfolio securities or permissible borrowings. If the Fund is forced to sell securities at an unfavorable time and/or under unfavorable conditions, such sales may adversely affect the Fund's NAV and dilute remaining investors’ interests. | |
| Certain shareholders, including clients or affiliates of the Investment Adviser and/or other funds managed by the Investment Adviser, may from time to time own or control a significant percentage of the Fund's shares. Redemptions by these shareholders of their shares of the Fund may further increase the Fund's liquidity risk and may impact the Fund's NAV. These shareholders may include, for example, institutional investors, funds of funds, discretionary advisory clients, certain participating insurance companies, accounts or Goldman Sachs affiliates and other shareholders, whose buy-sell decisions are controlled by a single decision-maker. | |
| ■ | Management Risk —A strategy used by the Investment Adviser may fail to produce the intended results. |
| ■ | Market Risk— The value of the securities in which the Fund invests may go up or down in response to the prospects of individual companies, particular sectors or governments and/or general economic conditions throughout the world. Price changes may be temporary or last for extended periods. The Fund's investments may be overweighted from time to time in one or more sectors or countries, which will increase the Fund's exposure to risk of loss from adverse developments affecting those sectors or countries. |
| Global economies and financial markets are becoming increasingly interconnected, and conditions and events in one country, region or financial market may adversely impact issuers in a different country, region or financial market. Furthermore, local, regional and global events such as war, acts of terrorism, social unrest, natural disasters, the spread of infectious illness or other public health threats could also adversely impact issuers, markets and economies, including in ways that cannot necessarily be foreseen. The Fund could be negatively impacted if the value of a portfolio holding were harmed by such political or economic conditions or events. In addition, governmental and quasi-governmental organizations have taken a number of unprecedented actions designed to support the markets. Such conditions, events and actions may result in greater market risk. | |
| ■ | Master Limited Partnership Risk— The Fund’s investments in securities of a Master Limited Partnership (“MLP”) involve risks that differ from investments in common stock, including risks related to limited control and limited rights to vote on matters affecting the MLP, risks related to potential conflicts of interest between the MLP and the MLP’s general partner, cash flow risks, dilution risks and risks related to the general partner’s right to require unit-holders to sell their common units at an undesirable time or price, resulting from regulatory changes or other reasons. Certain MLP securities may trade in lower volumes due to their smaller capitalizations. Accordingly, those MLPs may be subject to more abrupt or erratic price movements and may lack sufficient market liquidity to enable the Fund to effect sales at an advantageous time or without a substantial drop in price. Investment in those MLPs may restrict the Fund’s ability to take advantage of other investment opportunities. MLPs are generally considered interest-rate sensitive investments. During periods of interest rate volatility, these investments may not provide attractive returns. |
| To the extent a distribution received by the Fund from an MLP is treated as a return of capital, the Fund’s adjusted tax basis in the interests of the MLP may be reduced, which will result in an increase in an amount of income or gain (or decrease in the amount of loss) that will be recognized by the Fund for tax purposes upon the sale of any such interests or upon subsequent distributions in respect of such interests. Furthermore, any return of capital distribution received from the MLP may require the Fund to restate the character of its distributions and amend any shareholder tax reporting previously issued. Moreover, a change in current tax law, or a change in the underlying business mix of a given MLP, could result in an MLP being treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, which could result in a reduction of the value of the Fund's investment in the MLP and lower income to the Fund. | |
| Under recent tax legislation, individuals and certain other noncorporate entities are generally eligible for a 20% deduction with respect to taxable income from MLPs. Currently, there is not a regulatory mechanism for regulated investment companies such as the Fund to pass through the 20% deduction to shareholders. As a result, in comparison, investors investing directly in MLPs would generally be eligible for the 20% deduction for such taxable income from these investments while investors investing in MLPs held indirectly if any through the Fund would not be eligible for the 20% deduction for their share of such taxable income. | |
| ■ | Mid-Cap and Small-Cap Risk— The securities of mid-capitalization and small-capitalization companies involve greater risks than those associated with larger, more established companies and may be subject to more abrupt or erratic price movements. Securities of such issuers may lack sufficient market liquidity to enable the Fund to effect sales at an advantageous time or without a substantial drop in price. Both mid-capitalization and small-capitalization companies often have narrower markets and more limited managerial and financial resources than larger, more established companies. As a result, their performance can be more volatile and they face greater risk of business failure, which could increase the volatility of the Fund's portfolio. Generally, the smaller the company size, the greater these risks become. |
| ■ | NAV Risk— The net asset value of the Fund and the value of your investment will fluctuate. |
| ■ | Non-Investment Grade Fixed Income Securities Risk— Non-investment grade fixed income securities and unrated securities of comparable credit quality (commonly known as “junk bonds”) are considered speculative and are subject to the increased risk of an issuer’s inability to meet principal and interest payment obligations. These securities may be subject to greater price volatility due to such factors as specific issuer developments, interest rate sensitivity, negative perceptions of the junk bond markets generally and less liquidity. |
| ■ | Portfolio Turnover Rate Risk —The Flexible Cap Fund may engage in active and frequent trading of portfolio securities to achieve its principal investment strategies. A high rate of portfolio turnover (100% or more) involves correspondingly greater expenses which must be borne by the Fund and its shareholders, and is also likely to result in short-term capital gains taxable to shareholders. |
| ■ | Pre-IPO Investments Risk— The Flexible Cap Fund may invest in privately held companies, including companies that may issue shares in IPOs. Investments in pre-IPO shares involve greater risks than investments in shares of companies that have traded publicly on an exchange for extended periods of time. Investments in these companies are less liquid and difficult to value, and there is significantly less information available about these companies’ business models, quality of management, earnings growth potential, and other criteria used to evaluate their investment prospects. Although there is a potential the pre-IPO shares that the Flexible Cap Fund buys may increase in value if the company does issue shares in an IPO, IPOs are risky and volatile and may cause the value of the Fund’s investments to decrease significantly. Moreover, because pre-IPO shares are generally not freely or publicly tradeable, the Flexible Cap Fund may not have access to purchase or the ability to sell these shares in the amounts or at the prices the Fund desires. The companies that the Flexible Cap Fund anticipates holding successful IPOs may not ever issue shares in an IPO and a liquid market for their shares may never develop, which may negatively affect the price at which the Fund can sell these shares and make it more difficult to sell these shares, which could also adversely affect the Fund’s liquidity. |
| ■ | Sector Risk —To the extent the Fund focuses its investments in securities of issuers in one or more sectors (such as the financial services or telecommunications sectors), the Fund will be subject to a greater extent than if its investments were diversified across different sectors, to the risks of volatile economic cycles and/or conditions and developments that may be particular to that sector, such as: adverse economic, business, political, environmental or other developments. |
| ■ | Stock Risk— Stock prices have historically risen and fallen in periodic cycles. U.S. and foreign stock markets have experienced periods of substantial price volatility in the past and may do so again in the future. Stock prices may fluctuate from time to time in response to the activities of individual companies and in response to general market and economic conditions. Individual companies may report poor results or be negatively affected by industry and/or economic trends and developments, and the stock prices of such companies may suffer a decline in response. |
| ■ | U.S. Government Securities Risk— The U.S. government may not provide financial support to U.S. government agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises if it is not obligated to do so by law. U.S. Government Securities issued by those agencies, instrumentalities and sponsored enterprises, including those issued by the Federal National Mortgage Association (“Fannie Mae”), Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“Freddie Mac”) and Federal Home Loan Banks, are neither issued nor |
| guaranteed by the U.S. Treasury and, therefore, are not backed by the full faith and credit of the United States. The maximum potential liability of the issuers of some U.S. Government Securities held by the Fund may greatly exceed their current resources, including legal right to support from the U.S. Treasury. It is possible that issuers of U.S. Government Securities will not have the funds to meet their payment obligations in the future. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac have been operating under conservatorship, with the Federal Housing Finance Agency (“FHFA”) acting as their conservator, since September 2008. The entities are dependent upon the continued support of the U.S. Department of the Treasury and FHFA in order to continue their business operations. These factors, among others, could affect the future status and role of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac and the value of their securities and the securities which they guarantee. Additionally, the U.S. government and its agencies and instrumentalities do not guarantee the market values of their securities, which may fluctuate. |
| INVESTMENT ADVISER |
Investment Adviser |
Fund |
| Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P. (“GSAM”) 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 |
Capital Growth Concentrated Growth Flexible Cap Strategic Growth U.S. Equity ESG |
| ■ | Supervises all non-advisory operations of the Fund |
| ■ | Provides personnel to perform necessary executive, administrative and clerical services to the Fund |
| ■ | Arranges for the preparation of all required tax returns, reports to shareholders, prospectuses and statements of additional information and other reports filed with the SEC and other regulatory authorities |
| ■ | Maintains the records of the Fund |
| ■ | Provides office space and all necessary office equipment and services |
| MANAGEMENT FEES AND OTHER EXPENSES |
Fund |
Contractual Management Fee Annual Rate |
Average Daily Net Assets |
Actual Rate For the Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020* |
| Capital Growth | 0.71% | First $1 Billion | 0.71% |
| 0.64% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.61% | Over $2 Billion | ||
| Concentrated Growth | 0.76% | First $1 Billion | 0.76% |
| 0.68% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.65% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.64% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.62% | Over $8 Billion | ||
| Flexible Cap | 0.55% | First $1 Billion | 0.55% |
| 0.50% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.47% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.46% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.45% | Over $8 Billion | ||
| Strategic Growth | 0.71% | First $1 Billion | 0.71% |
| 0.64% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.61% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.59% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.58% | Over $8 Billion | ||
| U.S. Equity ESG | 0.55% | First $1 Billion | 0.55% |
| 0.50% | Next $1 Billion | ||
| 0.47% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.46% | Next $3 Billion | ||
| 0.45% | Over $8 Billion |
* |
The Actual Rate may not correlate to the Contractual Management Fee Annual Rate as a result of management fee waivers that may be in effect from time to time. |
| FUND MANAGERS |
Name and Title |
Fund Responsibility |
Years Primarily Responsible |
Five Year Employment History |
Steven M. Barry Managing Director Co-Chief Investment Officer, Fundamental Equity U.S. Equity |
Portfolio Manager— Capital Growth Concentrated Growth Flexible Cap Strategic Growth U.S. Equity ESG |
Since 2000 2002 2008 2000 2020 |
Mr. Barry joined the Investment Adviser as a portfolio manager in 1999. He is Managing Director and Co-Chief Investment Officer of Fundamental Equity U.S. Equity. |
Stephen E. Becker, CFA Managing Director Co-Chief Investment Officer, Fundamental Equity U.S. Equity |
Portfolio Manager— Capital Growth Concentrated Growth Strategic Growth U.S. Equity ESG |
Since 2013 2013 2013 2020 |
Mr. Becker joined the Investment Adviser in 1999. He is Managing Director and Co-Chief Investment Officer of Fundamental Equity U.S. Equity. |
Kevin Martens Vice PresidentPortfolio Manager |
Portfolio Manager— U.S. Equity ESG |
Since 2020 |
Mr. Martens joined the Investment Adviser in 2015. He is a portfolio manager on the GSAM US Equity ESG Strategy, as well as a portfolio manager on the US Equity Team where he has broad research responsibilities for the Industrials sector across the US Large- and Mid-Cap Equity strategies. |
| DISTRIBUTOR AND TRANSFER AGENT |
| ACTIVITIES OF GOLDMAN SACHS AND ITS AFFILIATES AND OTHER ACCOUNTS MANAGED BY GOLDMAN SACHS |
| ■ | Cash |
| ■ | Additional shares of the same class of the same Fund |
| ■ | Shares of the same or an equivalent class of another fund managed by the Investment Adviser and/or certain of its advisory affiliates (each, a “Goldman Sachs Fund”). Special restrictions may apply. See the SAI. |
Important Notice: |
| Class P Shares generally are available to the following investors: |
| ■ Clients of the Goldman Sachs Private Wealth Management business unit (“GS PWM”) that custody their positions at Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC (“Goldman Sachs”); |
| ■ Clients of The Goldman Sachs Trust Company, N.A. or The Goldman Sachs Trust Company of Delaware (collectively, the “Trust Companies”) that custody their positions at Goldman Sachs; |
| ■ Clients of The Ayco Company, L.P. (“Ayco”) that either custody their positions at Goldman Sachs or with certain intermediaries that are authorized to offer Class P Shares (“Authorized Institutions”) (such clients of GS PWM, the Trust Companies, and Ayco are collectively referred to herein as “GS Clients”); or |
| ■ Other investors at the discretion of Goldman Sachs Trust’s (the “Trust”) officers. |
| You may only purchase Class P Shares in accordance with the eligibility criteria described above. If you are a GS Client and propose to transfer your shares to another institution for any reason, or if you are no longer a GS Client, you may be required to redeem your shares of the Fund, or at the discretion of the Trust’s officers, you may be able hold Class P Shares through another institution, which must be an Authorized Institution and the basis on which you hold such Class P Shares may be limited to hold and redeem only. If available in such circumstances, in the alternative you may be able to choose to exchange your shares of the Fund for a different share class offered by the Fund or another Goldman Sachs Fund, which may be offered in another Prospectus. There is no guarantee that a different share class offered by the Fund will be available to clients of the institution to which you intend to transfer your shares or that an option to exchange will be made available. Moreover, the shares you receive in any exchange are subject to different (and possibly higher) fees and expenses (which affect performance). Information regarding these other share classes may be obtained from the institution to which you intend to transfer your shares or from the Transfer Agent by calling the number on the back cover of the Prospectus. |
| A redemption is a taxable transaction for federal income tax purposes, and may also be subject to state and local taxes. You should consult your tax adviser concerning the potential tax consequences of investing in Class P Shares. None of the Trust, the Investment Adviser, Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco or an Authorized Institution will be responsible for any loss in an investor’s account or tax liability resulting from a redemption or exchange of Class P Shares. For more information about exchanges, please see “How to Sell Shares—Can I Exchange My Investment From One Goldman Sachs Fund To Another Goldman Sachs Fund.” |
| How To Buy Shares |
| ■ | Require Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco, or an Authorized Institution to refuse to open an account if you fail to (i) provide a taxpayer identification number, a Social Security Number or other government-issued identification (e.g., for an individual, a driver’s license or passport) or (ii) certify that such number or other information is correct (if required to do so under applicable law). |
| ■ | Reject or restrict any purchase or exchange order by a particular purchaser (or group of related purchasers) for any reason in its discretion. Without limiting the foregoing, the Trust may reject or restrict purchase and exchange orders by a particular purchaser (or group of related purchasers) when a pattern of frequent purchases, sales or exchanges of shares of the Fund is evident, or if purchases, sales or exchanges are, or a subsequent redemption might be, of a size that would disrupt the management of the Fund. |
| ■ | Close the Fund to new investors from time to time and reopen any such Fund whenever it is deemed appropriate by the Investment Adviser. |
| ■ | Provide for, modify or waive the minimum investment requirements. |
| ■ | Modify the manner in which shares are offered. |
| ■ | Modify the sales charge rate applicable to future purchases of shares. |
| NAV = | (Value of Assets of the Class) – (Liabilities of the Class) |
| Number of Outstanding Shares of the Class |
| ■ | NAV per share of each share class is generally calculated by the Fund’s fund accounting agent on each business day as of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange (normally 4:00 p.m. Eastern time) or such other times as the New York Stock Exchange or NASDAQ market may officially close. Fund shares will generally not be priced on any day the New York Stock Exchange is closed. |
| ■ | The Trust reserves the right to reprocess purchase (including dividend reinvestments), redemption and exchange transactions that were processed at a NAV that is subsequently adjusted, and to recover amounts from (or distribute amounts to) shareholders accordingly based on the official closing NAV, as adjusted. |
| ■ | The Trust reserves the right to advance the time by which purchase and redemption orders must be received for same business day credit as otherwise permitted by the SEC. |
| How To Sell Shares |
| ■ | You would like the redemption proceeds sent to an address that is not your address of record; or |
| ■ | You would like the redemption proceeds sent to a domestic bank account that is not designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent. |
| ■ | Telephone requests are recorded. |
| ■ | Proceeds of telephone redemption requests will be sent to your address of record or authorized account designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent (unless you provide written instructions and a Medallion signature guarantee indicating another address or account). |
| ■ | For the 30-day period following a change of address, telephone redemptions will only be filled by a wire transfer to the authorized account designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent (see immediately preceding bullet point). In order to receive the redemption by check during this time period, the redemption request must be in the form of a written, Medallion signature guaranteed letter. |
| ■ | The telephone redemption option does not apply to shares held in an account maintained and serviced by your Authorized Institution. If your shares are held in an account with an Authorized Institution, you should contact your registered representative of record, who may make telephone redemptions on your behalf. |
| ■ | The telephone redemption option may be modified or terminated at any time without prior notice. |
| ■ | Redemption proceeds will normally be paid in federal funds, between one and two business days (or such other times in accordance with the requirements of Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco, or your Authorized Institution) following receipt of a properly executed wire transfer redemption request. In certain circumstances, however (such as unusual market conditions or in cases of very large redemptions or excessive trading), it may take up to seven days to pay redemption proceeds. |
| ■ | Redemption requests may only be postponed or suspended for longer than seven days as permitted under Section 22(e) of the Investment Company Act of 1940 (the “Investment Company Act”) if (i) the New York Stock Exchange is closed for trading or trading is restricted; (ii) an emergency exists which makes the disposal of securities owned by the Fund or the fair determination of the value of the Fund’s net assets not reasonably practicable; or (iii) the SEC, by order or regulation, permits the suspension of the right of redemption. |
| ■ | If you are selling shares you recently paid for by check, the Fund will pay you when your check has cleared, which may take up to 15 days. |
| ■ | If the Federal Reserve Bank is closed on the day that the redemption proceeds would ordinarily be wired, wiring the redemption proceeds may be delayed until the Federal Reserve Bank reopens. |
| ■ | To change the bank wiring instructions designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent, you must send written instructions signed by an authorized person designated in the current records of the Transfer Agent. A Medallion signature guarantee may be required if you are requesting a redemption in conjunction with the change. |
| ■ | None of the Trust, the Investment Adviser or the Transfer Agent assumes any responsibility for the performance of your bank, Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco, or Authorized Institution in the transfer process. If a problem with such performance arises, you should deal directly with your bank, Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco, or Authorized Institution. |
| ■ | Additional documentation may be required when deemed appropriate by the Transfer Agent. A redemption request will not be in proper form until such additional documentation has been received. |
| ■ | Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco and Authorized Institutions are responsible for the timely transmittal of redemption requests by GS Clients to the Transfer Agent. In order to facilitate the timely transmittal of redemption requests, Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco and Authorized Institutions may set times by which they must receive redemption requests. Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco or Authorized Institutions may also require additional documentation from you. |
| ■ | As disclosed above, if you are a GS Client and propose to transfer your shares to another institution for any reason, you may be required to either redeem your shares of the Fund or if available, you may be able to choose to exchange your shares of the Fund for a different share class offered by the Fund, which may be offered in another Prospectus. |
| ■ | Redeem your shares in the event any of Goldman Sachs, the Trust Companies, Ayco or your Authorized Institution is no longer authorized to offer Class P Shares. |
| ■ | Redeem your shares in the case of actual or suspected threatening conduct or actual or suspected fraudulent, suspicious or illegal activity by you or any other individual associated with your account. |
| ■ | Subject to applicable law, redeem your shares in other circumstances determined by the Board of Trustees to be in the best interest of the Trust. |
| ■ | Pay redemptions by a distribution in-kind of securities (instead of cash). If you receive redemption proceeds in-kind, you should expect to incur transaction costs upon the disposition of those securities. In addition, if you receive redemption proceeds in-kind, you will be subject to market gains or losses upon the disposition of those securities. |
| ■ | Reinvest any amounts (e.g., dividends, distributions or redemption proceeds) which you have elected to receive by check should your check remain uncashed for more than 180 days. No interest will accrue on amounts represented by uncashed checks. Your check will be reinvested in your account at the NAV on the day of the reinvestment. When reinvested, those amounts are subject to the risk of loss like any Fund investment. If you elect to receive distributions in cash and a check remains uncashed for more than 180 days, your cash election may be changed automatically to reinvest and your future dividend and capital gains distributions will be reinvested in the Fund at the NAV as of the date of payment of the distribution. This provision may not apply to certain retirement or qualified accounts, accounts with a non-U.S. address or closed accounts. Your participation in a systematic withdrawal program may be terminated if a check remains uncashed. |
| ■ | Charge an additional fee in the event a redemption is made via wire transfer. |
| ■ | Terminate your account if you are no longer a GS Client, or otherwise no longer eligible to invest in Class P Shares of the Fund. |
| ■ | You should obtain and carefully read the prospectus of the Goldman Sachs Fund you are acquiring before making an exchange. You should be aware that not all Goldman Sachs Funds may offer all share classes. |
| ■ | Currently, the Fund does not impose any charge for exchanges, although the Fund may impose a charge in the future. |
| ■ | All exchanges which represent an initial investment in a Goldman Sachs Fund must satisfy the minimum initial investment requirement of that Fund. This requirement may be waived at the discretion of the Trust. Exchanges into a Goldman Sachs Fund need not meet the traditional minimum investment requirement for that Fund if the entire balance of the original Fund account is exchanged. |
| ■ | Exchanges are available only in states where exchanges may be legally made. |
| ■ | It may be difficult to make telephone exchanges in times of unusual economic or market conditions. |
| ■ | Goldman Sachs and DST may use reasonable procedures described above in “How To Sell Shares—What Do I Need To Know About Telephone Redemption Requests?” in an effort to prevent unauthorized or fraudulent telephone exchange requests. |
| ■ | Normally, a telephone exchange will be made only to an identically registered account. |
| ■ | Exchanges into Goldman Sachs Funds or certain share classes of Goldman Sachs Funds that are closed to new investors may be restricted. |
| Shareholder Services |
| ■ | Shares will be purchased at NAV. |
| ■ | You may elect cross-reinvestment into an identically registered account or a similarly registered account provided that at least one name on the account is registered identically. |
| ■ | You cannot make cross-reinvestments into a Goldman Sachs Fund unless that Fund’s minimum initial investment requirement is met. |
| ■ | You should obtain and read the prospectus of the Goldman Sachs Fund into which distributions are invested. |
| Restrictions on Excessive Trading Practices |
| DISTRIBUTIONS |
| SALES AND EXCHANGES |
| OTHER INFORMATION |
| A. General Portfolio Risks |
| B. Other Portfolio Risks |
| ■ | U.S. Government Securities |
| ■ | Commercial paper rated at least A-2 by Standard & Poor’s, P-2 by Moody’s or having a comparable rating by another NRSRO (or, if unrated, determined by the Investment Adviser to be of comparable credit quality) |
| ■ | Certificates of deposit |
| ■ | Bankers’ acceptances |
| ■ | Repurchase agreements |
| ■ | Non-convertible preferred stocks and non-convertible corporate bonds with a remaining maturity of less than one year |
| ■ | ETFs |
| ■ | Other investment companies |
| ■ | Cash items |
| C. Portfolio Securities and Techniques |
| ■ | While a Fund may benefit from the use of futures and options and swaps on futures, unanticipated changes in interest rates, securities prices or currency exchange rates may result in poorer overall performance than if the Fund had not entered into any futures contracts, options transactions or swaps. |
| ■ | Because perfect correlation between a futures position and a portfolio position that is intended to be protected is impossible to achieve, the desired protection may not be obtained and a Fund may be exposed to additional risk of loss. |
| ■ | The loss incurred by a Fund in entering into futures contracts and in writing call options and entering into swaps on futures is potentially unlimited and may exceed the amount of the premium received. |
| ■ | Futures markets are highly volatile and the use of futures may increase the volatility of a Fund’s NAV. |
| ■ | As a result of the low margin deposits normally required in futures trading, a relatively small price movement in a futures contract may result in substantial losses to a Fund. |
| ■ | Futures contracts and options and swaps on futures may be illiquid, and exchanges may limit fluctuations in futures contract prices during a single day. |
| ■ | Foreign exchanges may not provide the same protection as U.S. exchanges. |
Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund | |||
Class P Shares | |||
Year Ended August 31, |
Period Ended August 31, 2018 (a) | ||
2020 |
2019 | ||
Per Share Data |
|||
| Net asset value, beginning of period | $13.73 | $14.11 | $13.06 |
| Net investment income (b) |
0.14 | 0.17 | 0.06 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.58 | 0.65 | 0.99 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.72 | 0.82 | 1.05 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.19) | (0.11) | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.46) | (1.09) | — |
| Total distributions | (0.65) | (1.20) | — |
| Net asset value, end of period | $15.80 | $13.73 | $14.11 |
Total Return (c) |
20.30% | 7.22% | 8.04% |
| Net assets, end of period (in 000’s) | $830 | $2,135 | $2,026 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.71% | 0.66% | 0.66% (d) |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 3.98% | 3.88% | 5.72% (d) |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.98% | 1.26% | 1.23% (d) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (e) |
65% | 47% | 71% |
(a) |
Commenced operations on April 17, 2018. |
(b) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the period, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the year and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. Total returns for periods less than one full year are not annualized. |
(d) |
Annualized. |
(e) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund | |||
Class P Shares | |||
Year Ended August 31, |
Period Ended August 31, 2018 (a) | ||
2020 |
2019 | ||
Per Share Data | |||
| Net asset value, beginning of period | $26.34 | $35.74 | $33.39 |
| Net investment income (b) |
0.16 | 0.20 | 0.09 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 5.69 | (0.18) | 2.26 |
| Total from investment operations | 5.85 | 0.02 | 2.35 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.17) | (0.09) | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.89) | (9.33) | — |
| Total distributions | (1.06) | (9.42) | — |
| Net asset value, end of period | $31.13 | $26.34 | $35.74 |
Total Return (c) |
22.73% | 4.13% | 7.04% |
| Net assets, end of period (in 000’s) | $95,182 | $85,422 | $104,131 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.75% | 0.74% | 0.74% (d) |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.83% | 0.82% | 0.85% (d) |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.59% | 0.75% | 0.72% (d) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (e) |
47% | 55% | 93% |
(a) |
Commenced operations on April 17, 2018. |
(b) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the period, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the period and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. Total returns for periods less than one full year are not annualized. |
(d) |
Annualized. |
(e) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund | |||
Class P Shares | |||
Year Ended August 31, |
Period Ended August 31, 2018 (a) | ||
2020 |
2019 | ||
Per Share Data | |||
| Net asset value, beginning of period | $18.88 | $20.60 | $18.54 |
| Net investment income (loss) (b) |
(0.01) | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 7.48 | 0.40 | 2.04 |
| Total from investment operations | 7.47 | 0.43 | 2.06 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.02) | (0.05) | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.48) | (2.10) | — |
| Total distributions | (1.50) | (2.15) | — |
| Net asset value, end of period | $24.85 | $18.88 | $20.60 |
Total Return (c) |
42.00% | 4.01% | 11.11% |
| Net assets, end of period (in 000’s) | $160,582 | $128,289 | $143,078 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.80% | 0.79% | 0.79% (d) |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.99% | 1.06% | 0.72% (d) |
| Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets | (0.06)% | 0.18% | 0.32% (d) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (e) |
36% | 40% | 44% |
(a) |
Commenced operations on April 17, 2018. |
(b) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the period, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the period and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. Total returns for periods less than one full year are not annualized. |
(d) |
Annualized. |
(e) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund | |||
Class P Shares | |||
Year Ended August 31, |
Period Ended August 31, 2018 (a) | ||
2020 |
2019 | ||
Per Share Data | |||
| Net asset value, beginning of period | $12.92 | $13.61 | $12.75 |
| Net investment income (b) |
0.13 | 0.14 | 0.09 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain | 2.69 | 0.19 | 0.77 |
| Total from investment operations | 2.82 | 0.33 | 0.86 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.13) | (0.15) | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (0.62) | (0.87) | — |
| Total distributions | (0.75) | (1.02) | — |
| Net asset value, end of period | $14.99 | $12.92 | $13.61 |
Total Return (c) |
22.58% | 3.56% | 6.75% |
| Net assets, end of period (in 000’s) | $15,263 | $11,110 | $12,616 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.61% | 0.58% | 0.58% (d) |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 1.94% | 2.47% | 3.14% (d) |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.96% | 1.13% | 1.79% (d) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (e) |
69% | 50% | 157% |
(a) |
Commenced operations on April 17, 2018. |
(b) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the period, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the period and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. Total returns for periods less than one full year are not annualized. |
(d) |
Annualized. |
(e) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund | |||
Class P Shares | |||
Year Ended August 31, |
Period Ended August 31, 2018 (a) | ||
2020 |
2019 |
||
Per Share Data | |||
| Net asset value, beginning of period | $10.35 | $14.90 | $13.53 |
| Net investment income (b) |
0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | 4.07 | (0.28) | 1.36 |
| Total from investment operations | 4.08 | (0.24) | 1.37 |
| Distributions to shareholders from net investment income | (0.03) | (0.04) | — |
| Distributions to shareholders from net realized gains | (1.56) | (4.27) | — |
| Total distributions | (1.59) | (4.31) | — |
| Net asset value, end of period | $12.84 | $10.35 | $14.90 |
| Total Return (c) |
44.56% | 3.26% | 10.13% |
| Net assets, end of period (in 000’s) | $78,539 | $73,132 | $104,590 |
| Ratio of net expenses to average net assets | 0.75% | 0.74% | 0.74% (d) |
| Ratio of total expenses to average net assets | 0.98% | 0.99% | 0.96% (d) |
| Ratio of net investment income to average net assets | 0.12% | 0.32% | 0.22% (d) |
| Portfolio turnover rate (e) |
39% | 28% | 40% |
(a) |
Commenced operations on April 17, 2018. |
(b) |
Calculated based on the average shares outstanding methodology. |
(c) |
Assumes investment at the NAV at the beginning of the period, reinvestment of all dividends and distributions, a complete redemption of the investment at the NAV at the end of the period and no sales or redemption charges (if any). Total returns would be reduced if a sales or redemption charge was taken into account. Returns do not reflect the impact of taxes to shareholders relating to Fund distributions or the redemption of Fund shares. Total returns for periods less than one full year are not annualized. |
(d) |
Annualized. |
(e) |
The Fund’s portfolio turnover rate is calculated in accordance with regulatory requirements, without regard to transactions involving short term investments. If such transactions were included, the Fund’s portfolio turnover rate may be higher. |
| FOR MORE INFORMATION |
1-800-526-7384. You can also access and download the annual and semi-annual reports and the SAI at the Fund’s website:
| ■ By telephone: |
1-800-621-2550 |
| ■ By mail: |
Goldman Sachs Funds P.O. Box 06050 Chicago, IL 60606 |
| ■ On the Internet: |
SEC EDGAR database – http://www.sec.gov |
PART B
STATEMENT OF ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
DATED DECEMBER 29, 2020
| FUND |
Class A Shares |
Class C Shares |
Class R Shares |
Investor Shares |
Class R6 Shares |
Service Shares |
Institutional Shares |
Class P Shares | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS U.S. EQUITY ESG FUND |
GAGVX | GCGVX | GRGVX | GIRGX | GDEUX | — | GINGX | GALPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS CAPITAL GROWTH FUND |
GSCGX | GSPCX | GSPRX | GSPTX | GSPUX | GSPSX | GSPIX | GGGPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS CONCENTRATED GROWTH FUND |
GCGAX | GCGCX | GGCRX | GGCTX | GCGUX | — | GCRIX | GACPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS FLEXIBLE CAP FUND |
GALLX | GCLLX | GRLLX | GSLLX | GFCUX | — | GILLX | GGZPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS GROWTH OPPORTUNITIES FUND |
GGOAX | GGOCX | GGORX | GGOTX | GGOUX | GGOSX | GGOIX | GGQPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS SMALL CAP GROWTH FUND |
GSBDX | GSBAX | GSANX | GSAHX | GSBEX | — | GSAJX | GSADX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS SMALL/MID CAP GROWTH FUND |
GSMAX | GSMGX | GTMRX | GTMTX | GTMUX | GSMQX | GSMYX | GSWPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS STRATEGIC GROWTH FUND |
GGRAX | GGRCX | GSTRX | GSTTX | GGRUX | GSTSX | GSTIX | GSPPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS TECHNOLOGY OPPORTUNITIES FUND |
GITAX | GITCX | — | GISTX | GTORX | GITSX | GITIX | GSJPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS EQUITY INCOME FUND |
GSGRX | GSGCX | GRGRX | GRGTX | GRGUX | GSGSX | GSIIX | GABPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS FOCUSED VALUE FUND |
GFVAX | GFVCX | GFVRX | GFVIX | GFVUX | — | GFVSX | GGYPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS LARGE CAP VALUE FUND |
GSLAX | GSVCX | GSVRX | GSVTX | GSVUX | GSVSX | GSLIX | GMYPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS MID CAP VALUE FUND |
GCMAX | GCMCX | GCMRX | GCMTX | GCMUX | GSMSX | GSMCX | GMPPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS SMALL CAP VALUE FUND |
GSSMX | GSSCX | GSQRX | GSQTX | GSSUX | GSSSX | GSSIX | GSYPX | ||||||||
| GOLDMAN SACHS SMALL/MID CAP VALUE FUND |
GMVAX | GMVCX | GMVRX | GMVIX | GMCUX | — | GSMVX | GSVPX | ||||||||
(Fundamental Equity Growth and Fundamental Equity Value Funds of Goldman Sachs Trust)
71 South Wacker Drive
Chicago, Illinois 60606
This Statement of Additional Information (the “SAI”) is not a prospectus. This SAI should be read in conjunction with the prospectuses for the Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund (formerly, Goldman Sachs Blue Chip Fund), Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund, Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund, Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund, Goldman Sachs Growth Opportunities Fund, Goldman Sachs Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund, Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund, Goldman Sachs Technology Opportunities Fund, Goldman Sachs Equity Income Fund, Goldman Sachs Focused Value Fund, Goldman Sachs Large Cap Value Fund, Goldman Sachs Mid Cap Value Fund, Goldman Sachs Small Cap Value Fund and Goldman Sachs Small/Mid Cap Value Fund (collectively, the “Funds” and each individually, a “Fund”), dated December 29, 2020, as they may be further amended and/or supplemented from time to time (the “Prospectuses”). The Prospectuses may be obtained without charge from Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC by calling the telephone numbers or writing to one of the addresses listed below or from institutions (“Intermediaries”) acting on behalf of their customers.
The audited financial statements and related report of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, for each Fund contained in the Funds’ 2020 Annual Reports are incorporated herein by reference in the section “FINANCIAL STATEMENTS.” No other portions of the Funds’ Annual Reports are incorporated by reference herein. A Fund’s Annual Report may be obtained upon request and without charge by calling Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC toll free at 1-800-526-7384 (for Class A, Class C, Investor and Class R Shareholders) or 1-800-621-2550 (for Institutional, Service, Class R6 and Class P Shareholders).
GSAM® is a registered service mark of Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| B-3 | ||||
| B-3 | ||||
| B-6 | ||||
| B-41 | ||||
| B-48 | ||||
| B-59 | ||||
| B-74 | ||||
| B-87 | ||||
| B-90 | ||||
| B-92 | ||||
| B-96 | ||||
| B-101 | ||||
| B-101 | ||||
| B-102 | ||||
| B-108 | ||||
| B-112 | ||||
| OTHER INFORMATION REGARDING MAXIMUM SALES CHARGE, PURCHASES, REDEMPTIONS, EXCHANGES AND DIVIDENDS |
B-117 | |||
| B-119 | ||||
| B-122 | ||||
| 1-A | ||||
| 1-B | ||||
| 1-C | ||||
B-1
GOLDMAN SACHS ASSET MANAGEMENT, L.P.
Investment Adviser
200 West Street
New York, New York 10282
GOLDMAN SACHS & CO. LLC
Distributor
200 West Street
New York, New York 10282
GOLDMAN SACHS & CO. LLC
Transfer Agent
71 South Wacker Drive
Chicago, Illinois 60606
Toll free (in U.S.) 800-621-2550 (for Class R6, Institutional, Service and Class P Shareholders) or 800-526-7384 (for Class A, Class C, Investor and Class R Shareholders).
B-2
INTRODUCTION
Goldman Sachs Trust (the “Trust”) is an open-end management investment company. The Trust is organized as a Delaware statutory trust and was established by a Declaration of Trust dated January 28, 1997. The Trust is a successor to a Massachusetts business trust that was combined with the Trust on April 30, 1997. The following series of the Trust are described in this SAI: Goldman Sachs U.S. Equity ESG Fund (prior to August 31, 2020, the Goldman Sachs Blue Chip Fund) (“U.S. Equity ESG Fund”), Goldman Sachs Capital Growth Fund (“Capital Growth Fund”), Goldman Sachs Concentrated Growth Fund (“Concentrated Growth Fund”), Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Fund (prior to August 31, 2017, the Goldman Sachs Flexible Cap Growth Fund) (“Flexible Cap Fund”), Goldman Sachs Growth Opportunities Fund (“Growth Opportunities Fund”), Goldman Sachs Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund (“Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund”), Goldman Sachs Strategic Growth Fund (“Strategic Growth Fund”), Goldman Sachs Technology Opportunities Fund (prior to July 31, 2015, the Goldman Sachs Technology Tollkeeper Fund) (“Technology Opportunities Fund”), Goldman Sachs Equity Income Fund (prior to June 20, 2017, the Goldman Sachs Growth and Income Fund) (“Equity Income Fund”), Goldman Sachs Focused Value Fund (“Focused Value Fund”), Goldman Sachs Large Cap Value Fund (“Large Cap Value Fund”), Goldman Sachs Mid Cap Value Fund (“Mid Cap Value Fund”), Goldman Sachs Small Cap Value Fund (“Small Cap Value Fund”) and Goldman Sachs Small/Mid Cap Value Fund (“Small/Mid Cap Value Fund”) (collectively referred to herein as the “Funds”).
The Capital Growth, Equity Income, Mid Cap Value and Small Cap Value Funds were initially organized as series of a corporation formed under the laws of the State of Maryland on September 27, 1989, and were reorganized as series of the Trust as of April 30, 1997. The Trustees of the Trust have authority under the Declaration of Trust to create and classify shares into separate series and to classify and reclassify any series or portfolio of shares into one or more classes without further action by shareholders. Pursuant thereto, the Trustees have created the Funds and other series. Additional series may be added in the future from time to time. Each Fund (other than the U.S. Equity ESG, Concentrated Growth, Flexible Cap, Technology Opportunities, Focused Value and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds) currently offers nine classes of shares: Class A, Class C, Institutional, Investor, Class R, Class R6, Service and Class P Shares. The Concentrated Growth, Flexible Cap, Focused Value and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds currently offer eight classes of shares: Class A, Class C, Institutional, Investor, Class R, Class R6 and Class P Shares. The Technology Opportunities Fund currently offers eight classes of shares: Class A, Class C, Institutional, Investor, Service, Class R6 and Class P Shares. The Small Cap Growth and U.S. Equity ESG Funds currently offers seven classes of shares: Class A, Class C, Institutional, Investor, Class R, Class R6 and Class P Shares. See “SHARES OF THE TRUST.”
Goldman Sachs Asset Management, L.P. (“GSAM” or the “Investment Adviser”), an affiliate of Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC (“Goldman Sachs”), serves as the investment adviser to each Fund. In addition, Goldman Sachs serves as each Fund’s distributor (the “Distributor”) and transfer agent (the “Transfer Agent”). Each Fund’s custodian is The Bank of New York Mellon (“BNYM”).
The following information relates to and supplements the description of each Fund’s investment policies contained in the Prospectuses. See the Prospectuses for a more complete description of the Funds’ investment objectives and policies. Investing in the Funds entails certain risks, and there is no assurance that a Fund will achieve its objective. Capitalized terms used but not defined herein have the same meaning as in the Prospectuses.
INVESTMENT OBJECTIVES AND POLICIES
Each Fund has a distinct investment objective and policies. There can be no assurance that a Fund’s objective will be achieved. Each Fund, except the Focused Value Fund, is a diversified open-end management company as defined in the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “Act”). The Focused Value Fund is a non-diversified, open-end management company (as defined in the Act). The investment objective and policies of each Fund, and the associated risks of each Fund, are discussed in the Funds’ Prospectuses, which should be read carefully before an investment is made. All investment objectives and investment policies not specifically designated as fundamental may be changed without shareholder approval. However, with respect to the U.S. Equity ESG, Flexible Cap, Small/Mid Cap Growth, Small Cap Growth, Equity Income, Focused Value, Large Cap Value, Mid Cap Value, Small Cap Value, and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds, shareholders will be provided with sixty (60) days’ notice in the manner prescribed by the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) before any change in a Fund’s policy to invest at least 80% of its net assets plus any borrowings for investment purposes (measured at the time of purchase (“Net Assets”)) in the particular type of investment suggested by its name. Additional information about the Funds, their policies, and the investment instruments they may hold, is provided below.
Each Fund’s share price will fluctuate with market, economic and, to the extent applicable, foreign exchange conditions, so that an investment in any of the Funds may be worth more or less when redeemed than when purchased. None of the Funds should be relied upon as a complete investment program.
The Trust, on behalf of the U.S. Equity ESG Fund, Small Cap Growth Fund, Flexible Cap Fund, Strategic Growth Fund and Technology Opportunities Fund, has filed a notice of eligibility claiming an exclusion from the definition of the term “commodity pool operator” (“CPO”) under the Commodity Exchange Act (“CEA”) and therefore is not subject to registration or regulation as a CPO under the CEA. The Investment Adviser has claimed temporary relief from registration as a CPO under the CEA for the Capital Growth Fund, Concentrated Growth Fund, Equity Income Fund, Focused Value Fund, Growth Opportunities Fund, Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund, Large Cap Value Fund, Mid Cap Value Fund, Small Cap Value Fund and Small/Mid Cap Value Fund and therefore is not subject to registration or regulation as a CPO under the CEA.
B-3
The following discussion supplements the information in the Funds’ Prospectuses.
General Information about the Value and Growth Style Funds
The Investment Adviser may purchase for the Funds common stocks, preferred stocks, interests in real estate investment trusts, convertible debt obligations, convertible preferred stocks, equity interests in trusts, partnerships, joint ventures, limited liability companies and similar enterprises, master limited partnerships (“MLPs”), shares of other investment companies (including exchange-traded funds (“ETFs”)), warrants, stock purchase rights and synthetic and derivative instruments (such as swaps and futures contracts) that have economic characteristics similar to equity securities (“equity investments”). The Investment Adviser utilizes first-hand fundamental research, including visiting company facilities to assess operations and to meet decision-makers, in choosing a Fund’s securities. The Investment Adviser may also use macro analysis of numerous economic and valuation variables to anticipate changes in company earnings and the overall investment climate. The Investment Adviser is able to draw on the research and market expertise of the Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research Department and other affiliates of the Investment Adviser, as well as information provided by other securities dealers. Equity investments in a Fund’s portfolio will generally be sold when the Investment Adviser believes that the market price fully reflects or exceeds the investments’ fundamental valuation or when other more attractive investments are identified.
Value Style Funds. The Equity Income, Focused Value, Large Cap Value, Mid Cap Value, Small Cap Value and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds are managed using a value oriented approach. The Investment Adviser evaluates securities using fundamental analysis and intends to purchase equity investments that are, in its view, underpriced relative to a combination of such companies’ long-term earnings prospects, growth rate, free cash flow and/or dividend-paying ability. Consideration will be given to the business quality of the issuer. Factors positively affecting the Investment Adviser’s view of that quality include the competitiveness and degree of regulation in the markets in which the company operates, the existence of a management team with a record of success, the position of the company in the markets in which it operates, the level of the company’s financial leverage and the sustainable return on capital invested in the business. The Investment Adviser may also consider environmental, social, and governance factors as part of the fundamental research and stock selection process. The Funds may also purchase securities of companies that have experienced difficulties and that, in the opinion of the Investment Adviser, are available at attractive prices. No one factor or consideration is determinative in the fundamental research and stock selection process.
The Equity Income Fund seeks to generate additional cash flow and may reduce volatility by the sale of call options. It is anticipated that the calls will typically be written against the S&P 500® Index (or against ETFs linked to the S&P 500® Index) or against other regional stock market indices. The goal of the Fund’s call writing is to generate an amount of premium that, when annualized and added to the Fund’s expected dividend yield, provides an attractive level of cash flow. The Investment Adviser anticipates generally writing call options with expirations of one month or less.
The Small Cap Value Fund is open for investment by new investors for such period as the Trust and Goldman Sachs deem appropriate based on various considerations, including the Fund’s capacity. Exchanges into the Fund from other Goldman Sachs Funds are also permitted. The Trust and Goldman Sachs reserve the right to close the Fund without prior notice. Please see the “Shareholder Guide – How to Buy Shares – What Else Should I Know About Share Purchases?” in the Fund’s Prospectus, as supplemented, for more information.
Growth Style Funds. The Concentrated Growth, Flexible Cap, Growth Opportunities, Small/Mid Cap Growth, Small Cap Growth, Strategic Growth and Technology Opportunities Funds are managed using a growth equity oriented approach. Equity investments for these Funds are selected based on their long-term prospects for above average growth. The Investment Adviser employs an investment strategy with three primary components. The first is to buy a business with the belief that wealth is created by the long-term ownership of a growing business. The second is to buy a high quality business that exhibits high-quality growth criteria including strong business franchise, favorable long-term trends and excellent management. The third component of the strategy is to buy the business at an attractive valuation. The Investment Adviser may also consider environmental, social, and governance factors as part of the fundamental research and stock selection process. The Investment Adviser maintains a long term outlook when implementing this disciplined investment process. No one factor or consideration is determinative in the fundamental research and stock selection process.
The U.S. Equity ESG and Capital Growth Funds may invest in securities of companies of any investment style and are managed using both the value and growth styles discussed above.
Additional Information about the Technology Opportunities Fund
The Technology Opportunities Fund intends to invest a substantial portion of its assets in technology companies. In general, the Investment Adviser defines a technology company as a high-quality technology, services, media or telecommunications company that adopts or uses technology to improve its cost structure, revenue opportunities or competitive advantage. The Investment Adviser seeks to identify technology companies that exhibit many of the following characteristics:
| • | Strong brand name |
B-4
| • | Dominant market share |
| • | Recurring revenue streams |
| • | Free cash flow generation |
| • | Long product life cycle |
| • | Enduring competitive advantage |
| • | Excellent management |
The Investment Adviser seeks to identify technology companies that are promising growth businesses. These companies may grow revenue by increasing sales volumes, prices, customers and market share. The Internet is an example of a technology that the Investment Adviser believes will drive growth for many technology businesses. The Internet has had, and is expected to continue to have, a significant impact on the global economy, as it changes the way many companies operate. Benefits of the Internet for businesses may include global scalability, acquisition of new clients, new revenue sources and increased efficiencies. Technology companies adopting innovative Internet technologies to improve their business models include providers of infrastructure, software, hardware and services.
Because of its focus on technology, telecommunications, Internet, services and media companies, the Fund’s investment performance will be closely tied to many factors which affect these companies. These factors include intense competition, consumer preferences, problems with product compatibility and government regulation. The Fund’s investments may experience significant price movements caused by disproportionate investor optimism or pessimism with little or no basis in fundamental economic conditions. The Fund may also invest in a relatively few number of issuers. As a result, the Fund’s net asset value (“NAV”) is more likely to have greater fluctuations than that of a fund which is more diversified or invests in other industries.
Risk Considerations Regarding the Internet Industry
The value of the Technology Opportunities Fund’s shares will fluctuate based upon risk factors affecting the Internet industry and related industries. Market or economic factors impacting companies in these industries could have a major effect on the value of the Technology Opportunities Fund’s investments. The value of stocks of these companies is particularly vulnerable to rapid changes in technological product cycles, frequent new service and product announcements, evolving industry standards, changes in government regulation and policies, loss or impairment of patents and other intellectual property, intense worldwide competition, restrictions on internet usage or access, damage to the internet infrastructure, obsolescence caused by scientific and technological advances, departure of key personnel and changing customer demand. The failure of an Internet company to adapt to such changes could have a material adverse effect on the company’s business, results of operations and financial condition. Technology stocks, especially those of smaller, less seasoned companies, tend to be more volatile than the overall market. Products developed by Internet and Internet-related companies may be commercially unsuccessful. Internet companies are heavily dependent on patents and other intellectual property, and there can be no assurance that the steps taken by internet companies to protect their proprietary rights will be adequate to prevent misappropriation of their technology, or that competitors will not independently develop technologies that are substantially equivalent or superior to such companies’ technology. In addition, the widespread adoption of new Internet, networking or telecommunications technologies or other technological changes could require substantial expenditures by an Internet company to modify or adapt its services or infrastructure, which could have a material adverse effect on an Internet company’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
Despite the implementation of security measures, an Internet company’s website and networks may be vulnerable to unauthorized access, viruses and other disruptive problems. Internet companies have in the past experienced, and may in the future experience, losses as a result of natural disasters, telecommunications failures, power failures, other system failures, maintenance, viruses, hacking or other events. Unauthorized access could also potentially jeopardize the security of information stored in the computer systems of a company and subject the companies to risk of loss, litigation and possible liability.
Internet companies are subject to general business regulations and laws, as well as regulations and laws specifically governing the Internet and e-commerce. Existing and future laws and regulations may impede the growth of the Internet or online services. There is, and will likely continue to be, an increasing number of laws and regulations pertaining to the internet, online commerce and cable, broadcast, broadband and telephone services covering taxation of Internet usage and transactions, defamation, libel, privacy, data protection, pricing, content, liability for information retrieved from or transmitted over the internet, copyrights, distribution, mobile communications, electronic contracts and other communications, consumer protection, the provision of online payment services, obscene or indecent communications, child protection, unencumbered Internet access, the design and operation of websites, and the
characteristics and quality of products and services. Unfavorable regulations and laws could diminish the demand for the products and services produced by internet companies, subject them to increased liability and increase costs, all of which could materially and adversely harm their business.
B-5
DESCRIPTION OF INVESTMENT SECURITIES AND PRACTICES
The investment securities and practices and related risks applicable to each Fund are presented below in alphabetical order, and not in the order of importance or potential exposure.
Asset Segregation
As investment companies registered with the SEC, the Funds must identify on their books (often referred to as “asset segregation”) liquid assets, or engage in other SEC- or SEC staff-approved or other appropriate measures, to “cover” open positions with respect to certain kinds of derivative instruments. In the case of swaps, futures contracts, options, forward contracts and other derivative instruments that do not cash settle, for example, a Fund must identify on its books liquid assets equal to the full notional amount of the instrument while the positions are open, to the extent there is not a permissible offsetting position or a contractual “netting” agreement with respect to swaps (other than credit default swaps where the Fund is the protection seller). However, with respect to certain swaps, futures contracts, options, forward contracts and other derivative instruments that are required to cash settle, a Fund may identify liquid assets in an amount equal to the Fund’s daily marked-to-market net obligations (i.e., the Fund’s daily net liability) under the instrument, if any, rather than their full notional amount. Forwards and futures contracts that do not cash settle may be treated as cash settled for asset segregation purposes when the Funds have entered into a contractual arrangement with a third party futures commission merchant (“FCM”) or other counterparty to off-set the Funds’ exposure under the contract and, failing that, to assign their delivery obligation under the contract to the counterparty. The Funds reserve the right to modify their asset segregation policies in the future in their discretion, consistent with the Act and SEC or SEC staff guidance. By identifying assets equal to only its net obligations under certain instruments, a Fund will have the ability to employ leverage to a greater extent than if the Fund were required to identify assets equal to the full notional amount of the instrument.
In October 2020, the SEC adopted a final rule related to the use of derivatives, short sales, reverse repurchase agreements and certain other transactions by registered investment companies. In connection with the final rule, the SEC and its staff will rescind and withdraw applicable guidance and relief regarding asset segregation and coverage transactions reflected in a Fund’s asset segregation and cover practices discussed herein. Subject to certain exceptions, the final rule requires a Fund to trade derivatives and other transactions that create future payment or delivery obligations subject to a value-at-risk (“VaR”) leverage limit and certain derivatives risk management program and reporting requirements. Generally, these requirements apply unless a Fund satisfies a “limited derivatives users” exception that is included in the final rule. Under the final rule, when a Fund trades reverse repurchase agreements or similar financing transactions, including certain tender option bonds, it needs to aggregate the amount of indebtedness associated with the reverse repurchase agreements or similar financing transactions with the aggregate amount of any other senior securities representing indebtedness (e.g., bank borrowings, if applicable) when calculating the Fund’s asset coverage ratio or treat all such transactions as derivatives transactions. Reverse repurchase agreements or similar financing transactions aggregated with other indebtedness do not need to be included in the calculation of whether a Fund satisfies the limited derivatives users exception, but for funds subject to the VaR testing requirement, reverse repurchase agreements and similar financing transactions must be included for purposes of such testing whether treated as derivatives transactions or not. The SEC also provided guidance in connection with the final rule regarding the use of securities lending collateral that may limit securities lending activities. Compliance with these new requirements will be required after an eighteen-month transition period. Following the compliance date, these requirements may limit the ability of a Fund to use derivatives, short sales, and reverse repurchase agreements and similar financing transactions as part of its investment strategies. These requirements may increase the cost of a Fund’s investments and cost of doing business, which could adversely affect investors. The Investment Adviser cannot predict the effects of these regulations on a Fund. The Investment Adviser intends to monitor developments and seek to manage each Fund in a manner consistent with achieving the Fund’s investment objective.
Asset-Backed Securities
Each Fund (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may invest in asset-backed securities. Asset-backed securities represent participations in, or are secured by and payable from, assets such as motor vehicle installment sales, installment loan contracts, leases of various types of real and personal property, receivables from revolving credit (credit card) agreements and other categories of receivables. Such assets are securitized through the use of trusts and special purpose corporations. Payments or distributions of principal and interest may be guaranteed up to certain amounts and for a certain time period by a letter of credit or a pool insurance policy issued by a financial institution unaffiliated with the trust or corporation, or other credit enhancements may be present.
Such securities are often subject to more rapid repayment than their stated maturity date would indicate as a result of the pass-through of prepayments of principal on the underlying loans. During periods of declining interest rates, prepayment of loans underlying asset-backed securities can be expected to accelerate. Accordingly, a Fund’s ability to maintain positions in such securities will be affected by reductions in the principal amount of such securities resulting from prepayments, and its ability to reinvest the returns of principal at comparable yields is subject to generally prevailing interest rates at that time. To the extent that a Fund invests in asset-backed securities, the values of the Fund’s portfolio securities will vary with changes in market interest rates generally and the differentials in yields among various kinds of asset-backed securities.
B-6
Asset-backed securities present certain additional risks because asset-backed securities generally do not have the benefit of a security interest in collateral that is comparable to mortgage assets. Credit card receivables are generally unsecured and the debtors on such receivables are entitled to the protection of a number of state and federal consumer credit laws, many of which give such debtors the right to set-off certain amounts owed on the credit cards, thereby reducing the balance due. Automobile receivables generally are secured, but by automobiles rather than residential real property. Most issuers of automobile receivables permit the loan servicers to retain possession of the underlying obligations. If the servicer were to sell these obligations to another party, there is a risk that the purchaser would acquire an interest superior to that of the holders of the asset-backed securities. In addition, because of the large number of vehicles involved in a typical issuance and technical requirements under state laws, the trustee for the holders of the automobile receivables may not have a proper security interest in the underlying automobiles. Therefore, if the issuer of an asset-backed security defaults on its payment obligations, there is the possibility that, in some cases, a Fund will be unable to possess and sell the underlying collateral and that the Fund’s recoveries on repossessed collateral may not be available to support payments on these securities.
Mortgage-related and other asset-backed securities are subject to certain additional risks. Generally, rising interest rates tend to extend the duration of fixed rate mortgage-backed securities, making them more sensitive to changes in interest rates. As a result, in a period of rising interest rates, if a Fund holds mortgage-backed securities, it may exhibit additional volatility. This is known as extension risk. In addition, adjustable and fixed rate mortgage-backed securities are subject to prepayment risk. When interest rates decline, borrowers may pay off their mortgages sooner than expected. This can reduce the returns of a Fund because the Fund may have to reinvest that money at the lower prevailing interest rates. A Fund’s investments in other asset-backed securities are subject to risks similar to those associated with mortgage-backed securities, as well as additional risks associated with the nature of the assets and the servicing of those assets. Certain Funds may invest in mortgage-backed securities issued by the U.S. Government (see “U.S. Government Securities Risk”). To the extent that an Fund invests in mortgage-backed securities offered by non-governmental issuers, such as commercial banks, savings and loan institutions, private mortgage insurance companies, mortgage bankers and other secondary market issuers, the Fund may be subject to additional risks. Timely payment of interest and principal of non-governmental issuers are supported by various forms of private insurance or guarantees, including individual loan, title, pool and hazard insurance purchased by the issuer. There can be no assurance that the private insurers can meet their obligations under the policies. An unexpectedly high rate of defaults on the mortgages held by a mortgage pool may adversely affect the value of a mortgage-backed security and could result in losses to a Fund. The risk of such defaults is generally higher in the case of mortgage pools that include subprime mortgages. Subprime mortgages refer to loans made to borrowers with weakened credit histories or with a lower capacity to make timely payments on their mortgages.
Bank Obligations
Each Fund may invest in obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. or foreign banks. Bank obligations, including without limitation, time deposits, bankers’ acceptances and certificates of deposit, may be general obligations of the parent bank or may be limited to the issuing branch by the terms of the specific obligations or by government regulation. Banks are subject to extensive but different governmental regulations which may limit both the amount and types of loans which may be made and interest rates which may be charged. In addition, the profitability of the banking industry is largely dependent upon the availability and cost of funds for the purpose of financing lending operations under prevailing money market conditions. General economic conditions as well as exposure to credit losses arising from possible financial difficulties of borrowers play an important part in the operation of this industry.
Certificates of deposit are certificates evidencing the obligation of a bank to repay funds deposited with it for a specified period of time at a specified rate. Certificates of deposit are negotiable instruments and are similar to saving deposits but have a definite maturity and are evidenced by a certificate instead of a passbook entry. Banks are required to keep reserves against all certificates of deposit. Fixed time deposits are bank obligations payable at a stated maturity date and bearing interest at a fixed rate. Fixed time deposits may be withdrawn on demand by the investor, but may be subject to early withdrawal penalties which vary depending upon market conditions and the remaining maturity of the obligation. The Funds may invest in deposits in U.S. and European banks satisfying the standards set forth above.
Commercial Paper and Other Short-Term Corporate Obligations
The Funds may invest in commercial paper and other short-term obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. corporations, non-U.S. corporations or other entities. Commercial paper represents short-term unsecured promissory notes issued in bearer form by banks or bank holding companies, corporations and finance companies.
Convertible Securities
Each Fund (other than the Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund) may invest in convertible securities. Convertible securities are bonds, debentures, notes, preferred stocks or other securities that may be converted into or exchanged for a specified amount of common stock (or other securities) of the same or different issuer within a particular period of time at a specified price or formula. A convertible security entitles the holder to receive interest that is generally paid or accrued on debt or a dividend that is paid or accrued on preferred stock until the convertible security matures or is redeemed, converted or exchanged. Convertible securities have unique investment characteristics, in that they generally (i) have higher yields than common stocks, but lower yields than comparable non-convertible securities, (ii) are less subject to fluctuation in value than the underlying common stock due to their fixed income characteristics and (iii) provide the potential for capital appreciation if the market price of the underlying common stock increases.
B-7
The value of a convertible security is a function of its “investment value” (determined by its yield in comparison with the yields of other securities of comparable maturity and quality that do not have a conversion privilege) and its “conversion value” (the security’s worth, at market value, if converted into the underlying common stock). The investment value of a convertible security is influenced by changes in interest rates, with investment value normally declining as interest rates increase and increasing as interest rates decline. The credit standing of the issuer and other factors may also have an effect on the convertible security’s investment value. The conversion value of a convertible security is determined by the market price of the underlying common stock. If the conversion value is low relative to the investment value, the price of the convertible security is governed principally by its investment value. To the extent the market price of the underlying common stock approaches or exceeds the conversion price, the price of the convertible security will be increasingly influenced by its conversion value. A convertible security generally will sell at a premium over its conversion value by the extent to which investors place value on the right to acquire the underlying common stock while holding a fixed income security.
A convertible security may be subject to redemption at the option of the issuer at a price established in the convertible security’s governing instrument. If a convertible security held by a Fund is called for redemption, the Fund will be required to convert the security into the underlying common stock, sell it to a third party, or permit the issuer to redeem the security. Any of these actions could have an adverse effect on a Fund’s ability to achieve its investment objective, which, in turn, could result in losses to the Fund. To the extent that a Fund holds a convertible security, or a security that is otherwise converted or exchanged for common stock (e.g., as a result of a restructuring), the Fund may, consistent with its investment objective, hold such common stock in its portfolio.
In evaluating a convertible security, the Investment Adviser will give primary emphasis to the attractiveness of the underlying common stock. Convertible debt securities are equity investments for purposes of each Fund’s investment policies.
Corporate Debt Obligations
Each Fund may, under normal market conditions, invest in corporate debt obligations, including obligations of industrial, utility and financial issuers. Corporate debt obligations include bonds, notes, debentures and other obligations of corporations to pay interest and repay principal. Corporate debt obligations are subject to the risk of an issuer’s inability to meet principal and interest payments on the obligations and may also be subject to price volatility due to such factors as market interest rates, market perception of the creditworthiness of the issuer and general market liquidity.
Another factor which causes fluctuations in the prices of fixed income securities is the supply and demand for similarly rated securities. In addition, the prices of fixed income securities fluctuate in response to the general level of interest rates. Fluctuations in the prices of portfolio securities subsequent to their acquisition will not affect cash income from such securities but will be reflected in a Fund’s NAV.
Corporate debt obligations rated BBB or Baa are considered medium grade obligations with speculative characteristics, and adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances may weaken their issuers’ capacity to pay interest and repay principal. Medium to lower rated and comparable non-rated securities tend to offer higher yields than higher rated securities with the same maturities because the historical financial condition of the issuers of such securities may not have been as strong as that of other issuers. The price of corporate debt obligations will generally fluctuate in response to fluctuations in supply and demand for similarly rated securities. In addition, the price of corporate debt obligations will generally fluctuate in response to interest rate levels. Fluctuations in the prices of portfolio securities subsequent to their acquisition will not affect cash income from such securities but will be reflected in each Fund’s NAV.
Because medium to lower rated securities generally involve greater risks of loss of income and principal than higher rated securities, investors should consider carefully the relative risks associated with investment in securities which carry medium to lower ratings and in comparable unrated securities. In addition to the risk of default, there are the related costs of recovery on defaulted issues. The Investment Adviser will attempt to reduce these risks through portfolio diversification and by analysis of each issuer and its ability to make timely payments of income and principal, as well as broad economic trends and corporate developments.
The Investment Adviser employs its own credit research and analysis, which includes a study of an issuer’s existing debt, capital structure, ability to service debt and pay dividends, sensitivity to economic conditions, operating history and current earnings trend. The Investment Adviser continually monitors the investments in a Fund’s portfolio and evaluates whether to dispose of or to retain corporate debt obligations whose credit ratings or credit quality may have changed. If after its purchase, a portfolio security is assigned a lower rating or ceases to be rated, a Fund may continue to hold the security if the Investment Adviser believes it is in the best interest of the Fund and its shareholders.
Custodial Receipts and Trust Certificates
Each Fund may invest in custodial receipts and trust certificates, which may be underwritten by securities dealers or banks, representing interests in securities held by a custodian or trustee. The securities so held may include obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises (“U.S. Government Securities”), municipal securities or other types of securities in which the Funds may invest. The custodial receipts or trust certificates are underwritten by securities dealers or banks and may evidence ownership of future interest payments, principal payments or both on the underlying securities, or, in some cases, the payment obligation of a third party that has entered into an interest rate swap or other arrangement with the custodian or
B-8
trustee. For purposes of certain securities laws, custodial receipts and trust certificates may not be considered obligations of the U.S. Government or other issuer of the securities held by the custodian or trustee. As a holder of custodial receipts and trust certificates, the Funds will bear their proportionate share of the fees and expenses charged to the custodial account or trust. The Funds may also invest in separately issued interests in custodial receipts and trust certificates.
Although under the terms of a custodial receipt or trust certificate the Funds would typically be authorized to assert their rights directly against the issuer of the underlying obligation, the Funds could be required to assert through the custodian bank or trustee those rights as may exist against the underlying issuers. Thus, in the event an underlying issuer fails to pay principal and/or interest when due, the Funds may be subject to delays, expenses and risks that are greater than those that would have been involved if the Funds had purchased a direct obligation of the issuer. In addition, in the event that the trust or custodial account in which the underlying securities have been deposited is determined to be an association taxable as a corporation, instead of a non-taxable entity, the yield on the underlying securities would be reduced in recognition of any taxes paid.
Certain custodial receipts and trust certificates may be synthetic or derivative instruments that have interest rates that reset inversely to changing short-term rates and/or have embedded interest rate floors and caps that require the issuer to pay an adjusted interest rate if market rates fall below or rise above a specified rate. Because some of these instruments represent relatively recent innovations, and the trading market for these instruments is less developed than the markets for traditional types of instruments, it is uncertain how these instruments will perform under different economic and interest-rate scenarios. Also, because these instruments may be leveraged, their market values may be more volatile than other types of fixed income instruments and may present greater potential for capital gain or loss. The possibility of default by an issuer or the issuer’s credit provider may be greater for these derivative instruments than for other types of instruments. In some cases, it may be difficult to determine the fair value of a derivative instrument because of a lack of reliable objective information and an established secondary market for some instruments may not exist. In many cases, the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) has not ruled on the tax treatment of the interest or payments received on the derivative instruments and, accordingly, purchases of such instruments are based on the opinion of counsel to the sponsors of the instruments.
Dividend-Paying Investments
A Fund’s investments in dividend-paying securities could cause the Fund to underperform other funds that invest in similar asset classes but employ a different investment style. Securities that pay dividends, as a group, can fall out of favor with the market, causing such securities to underperform securities that do not pay dividends. Depending upon market conditions and political and legislative responses to such conditions, dividend-paying securities that meet a Fund’s investment criteria may not be widely available and/or may be highly concentrated in only a few market sectors. For example, in response to the outbreak of a novel strain of coronavirus (known as COVID-19), the U.S. Government passed the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security Act in March 2020, which established loan programs for certain issuers impacted by COVID-19. Among other conditions, borrowers under these loan programs are generally restricted from paying dividends. The adoption of new legislation could further limit or restrict the ability of issuers to pay dividends. To the extent that dividend-paying securities are concentrated in only a few market sectors, a Fund may be subject to the risks of volatile economic cycles and/or conditions or developments that may be particular to a sector to a greater extent than if its investments were diversified across different sectors. In addition, issuers that have paid regular dividends or distributions to shareholders may not continue to do so at the same level or at all in the future. A sharp rise in interest rates or an economic downturn could cause an issuer to abruptly reduce or eliminate its dividend. This may limit the ability of the Fund to produce current income.
ESG Securities
The U.S. Equity ESG Fund will invest in securities of issuers that meet the Fund’s ESG criteria. The Fund’s adherence to its ESG criteria and the application of the Investment Adviser’s supplemental ESG analysis when selecting investments may affect the Fund’s exposure to certain companies, sectors, regions, and countries and may affect the Fund’s performance depending on whether such investments are in or out of favor. Adhering to the ESG criteria and applying the Investment Adviser’s supplemental ESG analysis may also affect the Fund’s performance relative to similar funds that do not adhere to such criteria or apply such analysis. Additionally, the Fund’s adherence to the ESG criteria and the application of the supplemental ESG analysis in connection with identifying and selecting equity investments in non-U.S. or emerging country issuers often require subjective analysis and may be relatively more difficult than applying the ESG criteria or the supplemental ESG analysis to equity investments of all issuers because data availability may be more limited with respect to non-U.S. or emerging country issuers. The exclusionary criteria related to the Fund’s ESG criteria may result in the Fund forgoing opportunities to buy certain securities when it might otherwise be advantageous to do so, or selling securities for ESG reasons when it might be otherwise disadvantageous for it to do so. When assessing whether an issuer meets the Fund’s ESG Criteria and conducting supplemental ESG analysis of an issuer, the Investment Adviser may rely on third-party data that it believes to be reliable, but it does not guarantee the accuracy of such third-party data. The Fund may invest in companies that do not reflect the beliefs and values of any particular investor. The Fund’s ESG criteria may be changed without shareholder approval.
Foreign Securities
Each Fund may invest in securities of foreign issuers, including securities quoted or denominated in a currency other than U.S. dollars. The Capital Growth, Concentrated Growth, Growth Opportunities, Strategic Growth, Technology Opportunities and Equity
B-9
Income Funds may each invest in the aggregate up to 25% of its total assets in foreign securities. The Flexible Cap, Small/Mid Cap Growth, Small Cap Growth, Mid Cap Value, Small Cap Value, and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds may each invest in the aggregate up to 25% of its net assets plus any borrowings in foreign securities. The U.S. Equity ESG and Large Cap Value Funds may invest up to 20% of its net assets plus any borrowings in foreign securities. The Focused Value Fund may invest up to 20% of its Net Assets in foreign securities.
Investments in foreign securities may offer potential benefits not available from investments solely in U.S. dollar-denominated or quoted securities of domestic issuers. Such benefits may include the opportunity to invest in foreign issuers that appear, in the opinion of the Investment Adviser, to offer the potential for better long term growth of capital and income than investments in U.S. securities, the opportunity to invest in foreign countries with economic policies or business cycles different from those of the United States and the opportunity to reduce fluctuations in portfolio value by taking advantage of foreign securities markets that do not necessarily move in a manner parallel to U.S. markets. Investing in the securities of foreign issuers also involves, however, certain special risks, including those discussed in the Funds’ Prospectuses and those set forth below, which are not typically associated with investing in U.S. dollar-denominated securities or quoted securities of U.S. issuers. Many of these risks are more pronounced for investments in emerging economies.
With respect to investments in certain foreign countries, there exist certain economic, political and social risks, including the risk of adverse political developments, nationalization, military unrest, social instability, war and terrorism, confiscation without fair compensation, expropriation or confiscatory taxation, limitations on the movement of funds and other assets between different countries, or diplomatic developments, any of which could adversely affect a Fund’s investments in those countries. Governments in certain foreign countries continue to participate to a significant degree, through ownership interest or regulation, in their respective economies. Action by these governments could have a significant effect on market prices of securities and dividend payments.
From time to time, certain of the companies in which a Fund may invest may operate in, or have dealings with, countries subject to sanctions or embargos imposed by the U.S. Government and the United Nations and/or countries identified by the U.S. Government as state sponsors of terrorism. For example, the United Nations Security Council has imposed certain sanctions relating to Iran and Sudan and both countries are embargoed countries by the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) of the U.S. Treasury.
In addition, from time to time, certain of the companies in which a Fund may invest may engage in, or have dealings with countries or companies that engage in, activities that may not be considered socially and/or environmentally responsible. Such activities may relate to human rights issues (such as patterns of human rights abuses or violations, persecution or discrimination), impacts to local communities in which companies operate and environmental sustainability. For a description of the Investment Adviser’s approach to responsible and sustainable investing, please see GSAM’s Statement on Responsible and Sustainable Investing at https://www.gsam.com/content/dam/gsam/pdfs/common/en/public/miscellaneous/GSAM_statement_on_respon_sustainable_investing.pdf.
As a result, a company may suffer damage to its reputation if it is identified as a company which engages in, or has dealings with countries or companies that engage in, the above referenced activities. As an investor in such companies, a Fund would be indirectly subject to those risks.
The Investment Adviser is committed to complying fully with sanctions in effect as of the date of this Statement of Additional Information and any other applicable sanctions that may be enacted in the future with respect to Sudan or any other country.
Many countries throughout the world are dependent on a healthy U.S. economy and are adversely affected when the U.S. economy weakens or its markets decline. Additionally, many foreign country economies are heavily dependent on international trade and are adversely affected by protective trade barriers and economic conditions of their trading partners. Protectionist trade legislation enacted by those trading partners could have a significant adverse effect on the securities markets of those countries. Individual foreign economies may differ favorably or unfavorably from the U.S. economy in such respects as growth of gross national product, rate of inflation, capital reinvestment, resource self-sufficiency and balance of payments position.
Investments in foreign securities often involve currencies of foreign countries. Accordingly, a Fund may be affected favorably or unfavorably by changes in currency rates and in exchange control regulations and may incur costs in connection with conversions between various currencies. The Funds may be subject to currency exposure independent of their securities positions. To the extent that a Fund is fully invested in foreign securities while also maintaining net currency positions, it may be exposed to greater combined risk.
Currency exchange rates may fluctuate significantly over short periods of time. They generally are determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange markets and the relative merits of investments in different countries, actual or anticipated changes in interest rates and other complex factors, as seen from an international perspective. Currency exchange rates also can be affected unpredictably by intervention (or the failure to intervene) by U.S. or foreign governments or central banks or by currency controls or political developments in the United States or abroad. To the extent that a portion of a Fund’s total assets, adjusted to reflect the Fund’s net position after giving effect to currency transactions, is denominated or quoted in the currencies of foreign countries, the Fund will be more susceptible to the risk of adverse economic and political developments within those countries. A Fund’s net currency positions may expose it to risks independent of its securities positions.
B-10
Because foreign issuers generally are not subject to uniform accounting, auditing and financial reporting standards, practices and requirements comparable to those applicable to U.S. companies, there may be less publicly available information about a foreign company than about a U.S. company. Volume and liquidity in most foreign securities markets are less than in the United States and securities of many foreign companies are less liquid and more volatile than securities of comparable U.S. companies. The securities of foreign issuers may be listed on foreign securities exchanges or traded in foreign over-the-counter markets. Fixed commissions on foreign securities exchanges are generally higher than negotiated commissions on U.S. exchanges, although each Fund endeavors to achieve the most favorable net results on its portfolio transactions. There is generally less government supervision and regulation of foreign securities exchanges, brokers, dealers and listed and unlisted companies than in the United States, and the legal remedies for investors may be more limited than the remedies available in the United States. For example, there may be no comparable provisions under certain foreign laws to insider trading and similar investor protections that apply with respect to securities transactions consummated in the United States. Mail service between the United States and foreign countries may be slower or less reliable than within the United States, thus increasing the risk of delayed settlement of portfolio transactions or loss of certificates for portfolio securities.
Foreign markets also have different clearance and settlement procedures, and in certain markets there have been times when settlements have been unable to keep pace with the volume of securities transactions, making it difficult to conduct such transactions. Such delays in settlement could result in temporary periods when a portion of a Fund’s assets are uninvested and no return is earned on such assets. The inability of a Fund to make intended security purchases due to settlement problems could cause the Fund to miss attractive investment opportunities. Inability to dispose of portfolio securities due to settlement problems could result either in losses to the Fund due to subsequent declines in value of the portfolio securities or, if the Fund has entered into a contract to sell the securities, in possible liability to the purchaser.
Each Fund may invest in foreign securities which take the form of sponsored and unsponsored American Depositary Receipts (“ADRs”), Global Depositary Receipts (“GDRs”), European Depositary Receipts (“EDRs”) or other similar instruments representing securities of foreign issuers (together, “Depositary Receipts”). ADRs represent the right to receive securities of foreign issuers deposited in a domestic bank or a correspondent bank. ADRs are traded on domestic exchanges or in the U.S. over-the-counter market and, generally, are in registered form. EDRs and GDRs are receipts evidencing an arrangement with a non-U.S. bank similar to that for ADRs and are designed for use in the non-U.S. securities markets. EDRs and GDRs are not necessarily quoted in the same currency as the underlying security. To the extent a Fund acquires Depositary Receipts through banks which do not have a contractual relationship with the foreign issuer of the security underlying the Depositary Receipts to issue and service such unsponsored Depositary Receipts, there is an increased possibility that the Fund will not become aware of and be able to respond to corporate actions such as stock splits or rights offerings involving the foreign issuer in a timely manner. In addition, the lack of information may result in inefficiencies in the valuation of such instruments. Investment in Depositary Receipts does not eliminate all the risks inherent in investing in securities of non-U.S. issuers. The market value of Depositary Receipts is dependent upon the market value of the underlying securities and fluctuations in the relative value of the currencies in which the Depositary Receipts and the underlying securities are quoted. However, by investing in Depositary Receipts, such as ADRs, which are quoted in U.S. dollars, a Fund may avoid currency risks during the settlement period for purchases and sales.
As described more fully below, each Fund may invest in countries with emerging economies or securities markets. Political and economic structures in many of such countries may be undergoing significant evolution and rapid development, and such countries may lack the social, political and economic stability characteristic of more developed countries. Certain of such countries have in the past failed to recognize private property rights and have at times nationalized or expropriated the assets of, or ignored internationally accepted standards of due process against, private companies. In addition, a country may take these and other retaliatory actions against a specific private company, including a Fund or the Investment Adviser. There may not be legal recourse against these actions, which could arise in connection with the commercial activities of Goldman Sachs or its affiliates or otherwise, and a Fund could be subject to substantial losses. In addition, a Fund or the Investment Adviser may determine not to invest in, or may limit its overall investment in, a particular issuer, country or geographic region due to, among other things, heightened risks regarding repatriation restrictions, confiscation of assets and property, expropriation or nationalization. See “Investing in Emerging Countries,” below.
These and other factors discussed in the section below, entitled “Illiquid Investments,” may impact the liquidity of investments in securities of foreign issuers.
Foreign Government Obligations. Foreign government obligations include securities, instruments and obligations issued or guaranteed by a foreign government, its agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises. Investment in foreign government obligations can involve a high degree of risk. The governmental entity that controls the repayment of foreign government obligations may not be able or willing to repay the principal and/or interest when due in accordance with the terms of such debt. A governmental entity’s willingness or ability to repay principal and interest due in a timely manner may be affected by, among other factors, its cash flow situation, the extent of its foreign reserves, the availability of sufficient foreign exchange on the date a payment is due, the relative size of the debt service burden to the economy as a whole, the governmental entity’s policy towards the International Monetary Fund and the political constraints to which a governmental entity may be subject. Governmental entities may also be dependent on expected disbursements from foreign governments, multilateral agencies and others abroad to reduce principal and interest on their debt. The commitment on the part of these governments, agencies and others to make such disbursements may be conditioned on a governmental
B-11
entity’s implementation of economic reforms and/or economic performance and the timely service of such debtor’s obligations. Failure to implement such reforms, achieve such levels of economic performance or repay principal or interest when due may result in the cancellation of such third parties’ commitments to lend funds to the governmental entity, which may further impair such debtor’s ability or willingness to service its debts in a timely manner. Consequently, governmental entities may default on their debt. Holders of foreign government obligations (including the Funds) may be requested to participate in the rescheduling of such debt and to extend further loans to governmental agencies.
Investing in Europe. The Funds may operate in euros and/ or may hold euros and/or euro-denominated bonds and other obligations. The euro requires participation of multiple sovereign states forming the Euro zone and is therefore sensitive to the credit, general economic and political position of each such state, including each state’s actual and intended ongoing engagement with and/or support for the other sovereign states then forming the EU, in particular those within the Euro zone. Changes in these factors might materially adversely impact the value of securities that a Fund has invested in.
European countries can be significantly affected by the tight fiscal and monetary controls that the European Economic and Monetary Union (“EMU”) imposes for membership. Europe’s economies are diverse, its governments are decentralized, and its cultures vary widely. Several EU countries, including Greece, Ireland, Italy, Spain and Portugal have faced budget issues, some of which may have negative long-term effects for the economies of those countries and other EU countries. There is continued concern about national-level support for the euro and the accompanying coordination of fiscal and wage policy among EMU member countries. Member countries are required to maintain tight control over inflation, public debt, and budget deficit to qualify for membership in the EMU. These requirements can severely limit the ability of EMU member countries to implement monetary policy to address regional economic conditions.
In a June 2016 referendum, citizens of the United Kingdom voted to leave the EU. In March 2017, the United Kingdom formally notified the European Council of its intention to withdraw from the EU (commonly known as “Brexit”) by invoking Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union, which triggered a two-year period of negotiations on the terms of Brexit. Brexit has resulted in volatility in European and global markets and may also lead to weakening in political, regulatory, consumer, corporate and financial confidence in the markets of the United Kingdom and throughout Europe. The longer term economic, legal, political, regulatory and social framework to be put in place between the United Kingdom and the EU remains unclear and may lead to ongoing political, regulatory and economic uncertainty and periods of exacerbated volatility in both the United Kingdom and in wider European markets for some time. Additionally, the decision made in the British referendum may lead to a call for similar referenda in other European jurisdictions, which may cause increased economic volatility in European and global markets. The mid-to long-term uncertainty may have an adverse effect on the economy generally and on the value of a Fund’s investments. This may be due to, among other things: fluctuations in asset values and exchange rates; increased illiquidity of investments located, traded or listed within the United Kingdom, the EU or elsewhere; changes in the willingness or ability of counterparties to enter into transactions at the price and terms on which a Fund is prepared to transact; and/or changes in legal and regulatory regimes to which certain of a Fund’s assets are or become subject. Fluctuations in the value of the British Pound and/or the Euro, along with the potential downgrading of the United Kingdom’s sovereign credit rating, may also have an impact on the performance of a Fund’s assets or investments economically tied to the United Kingdom or Europe.
The effects of Brexit will depend, in part, on whether the United Kingdom is able to negotiate agreements to retain access to EU markets including, but not limited to, trade and finance agreements. Brexit could lead to legal and tax uncertainty and potentially divergent national laws and regulations as the United Kingdom determines which EU laws to replace or replicate. The extent of the impact of the withdrawal in the United Kingdom and in global markets as well as any associated adverse consequences remain unclear, and the uncertainty may have a significant negative effect on the value of a Fund’s investments. While certain measures are being proposed and/or will be introduced, at the EU level or at the member state level, which are designed to minimize disruption in the financial markets, it is not currently possible to determine whether such measures would achieve their intended effects.
On January 31, 2020, the United Kingdom withdrew from the EU subject to a withdrawal agreement that permits the United Kingdom to effectively remain in the EU from an economic perspective during a transition phase that expires at the end of 2020. During this transition phase, the United Kingdom and the EU will seek to negotiate and finalize a new, more permanent trade deal. Negotiators representing the United Kingdom and EU came to a preliminary trade agreement on December 24, 2020. The trade agreement must be ratified by the UK Parliament and the European Parliament. If approved, the agreement would take effect on January 1, 2021, and many aspects of the United Kingdom-EU trade relationship would remain subject to further negotiation. Due to political uncertainty, it is not possible to anticipate whether the United Kingdom and the EU will be able to agree on and implement a new trade agreement or what the nature of such trade arrangement will be. In the event that no agreement is reached, the relationship between the United Kingdom and the EU would be based on the World Trade Organization rules.
Other economic challenges facing the region include high levels of public debt, significant rates of unemployment, aging populations, and heavy regulation in certain economic sectors. European policy makers have taken unprecedented steps to respond to the economic crisis and to boost growth in the region, which has increased the risk that regulatory uncertainty could negatively affect the value of the Fund’s investments.
Certain countries have applied to become new member countries of the EU, and these candidate countries’ accessions may become more controversial to the existing EU members. Some member states may repudiate certain candidate countries joining the EU upon concerns about the possible economic, immigration and cultural implications. Also, Russia may be opposed to the expansion of the EU to members of the former Soviet bloc and may, at times, take actions that could negatively impact EU economic activity.
B-12
Investing in Russia. In addition to the risks listed above under “Foreign Securities” and “Investing in Emerging Countries,” investing in Russia presents additional risks. Investing in Russian securities is highly speculative and involves significant risks and special considerations not typically associated with investing in the securities markets of the U.S. and most other developed countries. Over the past century, Russia has experienced political, social and economic turbulence and has endured decades of communist rule under which tens of millions of its citizens were collectivized into state agricultural and industrial enterprises. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia’s government has been faced with the daunting task of stabilizing its domestic economy, while transforming it into a modern and efficient structure able to compete in international markets and respond to the needs of its citizens. However, to date, many of the country’s economic reform initiatives have floundered as the proceeds of International Monetary Fund and other economic assistance have been squandered or stolen. In this environment, there is always the risk that the nation’s government will abandon the current program of economic reform and replace it with radically different political and economic policies that would be detrimental to the interests of foreign investors. This could entail a return to a centrally planned economy and nationalization of private enterprises similar to what existed under the old Soviet Union.
Poor accounting standards, inept management, pervasive corruption, insider trading and crime, and inadequate regulatory protection for the rights of investors all pose a significant risk, particularly to foreign investors. In addition, there is the risk that the Russian tax system will not be reformed to prevent inconsistent, retroactive, and/or exorbitant taxation, or, in the alternative, the risk that a reformed tax system may result in the inconsistent and unpredictable enforcement of the new tax laws.
Compared to most national stock markets, the Russian securities market suffers from a variety of problems not encountered in more developed markets. There is little long-term historical data on the Russian securities market because it is relatively new and a substantial proportion of securities transactions in Russia are privately negotiated outside of stock exchanges. The inexperience of the Russian securities market and the limited volume of trading in securities in the market may make obtaining accurate prices on portfolio securities from independent sources more difficult than in more developed markets. Additionally, because of less stringent auditing and financial reporting standards that apply to U.S. companies, there is little solid corporate information available to investors. As a result, it may be difficult to assess the value or prospects of an investment in Russian companies. Stocks of Russian companies also may experience greater price volatility than stocks of U.S. companies.
Because of the relatively recent formation of the Russian securities market as well as the underdeveloped state of the banking and telecommunications systems, settlement, clearing and registration of securities transactions are subject to significant risks. Prior to 2013, there was no central registration system for share registration in Russia and registration was carried out by the companies themselves or by registrars located throughout Russia. These registrars were not necessarily subject to effective state supervision nor were they licensed with any governmental entity. In 2013, Russia implemented the National Settlement Depository (NSD) as a recognized central securities depository (CSD). Title to Russian equities is now based on the records of the NSD rather than the registrars. The implementation of the NSD is expected to enhance the efficiency and transparency of the Russian securities market and decrease risk of loss in connection with recording and transferring title to securities. The Funds also may experience difficulty in obtaining and/or enforcing judgments in Russia.
The Russian economy is heavily dependent upon the export of a range of commodities including most industrial metals, forestry products, oil, and gas. Accordingly, it is strongly affected by international commodity prices and is particularly vulnerable to any weakening in global demand for these products.
Foreign investors also face a high degree of currency risk when investing in Russian securities and a lack of available currency hedging instruments. In a surprise move in August 1998, Russia devalued the ruble, defaulted on short-term domestic bonds, and imposed a moratorium on the repayment of its international debt and the restructuring of the repayment terms. These actions negatively affected Russian borrowers’ ability to access international capital markets and had a damaging impact on the Russian economy. In addition, there is the risk that the government may impose capital controls on foreign portfolio investments in the event of extreme financial or political crisis. Such capital controls would prevent the sale of a portfolio of foreign assets and the repatriation of investment income and capital.
Russia’s government has begun to take bolder steps, including use of the military, to re-assert its regional geo-political influence. These steps may increase tensions between its neighbors and Western countries, which may adversely affect its economic growth. These developments may continue for some time and create uncertainty in the region. Russia’s actions have induced the United States and other countries to impose economic sanctions and may result in additional sanctions in the future. Such sanctions, which impact many sectors of the Russian economy, may cause a decline in the value and liquidity of Russian securities and adversely affect the performance of the Fund or make it difficult for the Fund to achieve its investment objectives. In certain instances, sanctions could prohibit the Fund from buying or selling Russian securities, rendering any such securities held by the Fund unmarketable for an indefinite period of time. In addition, such sanctions, and the Russian government’s response, could result in a downgrade in Russia’s credit rating, devaluation of its currency and/or increased volatility with respect to Russian securities.
Investing in Emerging Countries. The securities markets of emerging countries are less liquid and subject to greater price volatility, and have a smaller market capitalization, than the U.S. securities markets. In certain countries, there may be fewer publicly traded securities and the market may be dominated by a few issuers or sectors. Issuers and securities markets in such countries are not
B-13
subject to as extensive and frequent accounting, financial and other reporting requirements or as comprehensive government regulations as are issuers and securities markets in the U.S. In particular, the assets and profits appearing on the financial statements of emerging country issuers may not reflect their financial position or results of operations in the same manner as financial statements for U.S. issuers. Substantially less information may be publicly available about emerging country issuers than is available about issuers in the United States.
Emerging country securities markets are typically marked by a high concentration of market capitalization and trading volume in a small number of issuers representing a limited number of industries, as well as a high concentration of ownership of such securities by a limited number of investors. The markets for securities in certain emerging countries are in the earliest stages of their development. Even the markets for relatively widely traded securities in emerging countries may not be able to absorb, without price disruptions, a significant increase in trading volume or trades of a size customarily undertaken by institutional investors in the securities markets of developed countries. The limited size of many of these securities markets can cause prices to be erratic for reasons apart from factors that affect the soundness and competitiveness of the securities issuers. For example, prices may be unduly influenced by traders who control large positions in these markets. Additionally, market making and arbitrage activities are generally less extensive in such markets, which may contribute to increased volatility and reduced liquidity of such markets. The limited liquidity of emerging country securities may also affect a Fund’s ability to accurately value its portfolio securities or to acquire or dispose of securities at the price and time it wishes to do so or in order to meet redemption requests.
With respect to investments in certain emerging market countries, antiquated legal systems may have an adverse impact on the Funds. For example, while the potential liability of a shareholder in a U.S. corporation with respect to acts of the corporation is generally limited to the amount of the shareholder’s investment, the notion of limited liability is less clear in certain emerging market countries. Similarly, the rights of investors in emerging market companies may be more limited than those of shareholders of U.S. corporations, and it may be more difficult for shareholders to bring derivative litigation. Moreover, the legal remedies for investors in emerging markets may be more limited than the remedies available in the United States, and the ability of U.S. authorities (e.g., SEC and the U.S. Department of Justice) to bring actions against bad actors may be limited. In addition, emerging countries may have less established accounting and financial reporting systems than those in more developed markets.
Transaction costs, including brokerage commissions or dealer mark-ups, in emerging countries may be higher than in the United States and other developed securities markets. In addition, existing laws and regulations are often inconsistently applied. As legal systems in emerging countries develop, foreign investors may be adversely affected by new or amended laws and regulations. In circumstances where adequate laws exist, it may not be possible to obtain swift and equitable enforcement of the law.
Custodial and/or settlement systems in emerging markets countries may not be fully developed. To the extent a Fund invests in emerging markets, Fund assets that are traded in such markets and which have been entrusted to such sub-custodians in those markets may be exposed to risks for which the sub-custodian will have no liability.
Foreign investment in the securities markets of certain emerging countries is restricted or controlled to varying degrees. These restrictions may limit a Fund’s investment in certain emerging countries and may increase the expenses of the Fund. Certain emerging countries require governmental approval prior to investments by foreign persons or limit investment by foreign persons to only a specified percentage of an issuer’s outstanding securities or a specific class of securities which may have less advantageous terms (including price) than securities of the company available for purchase by nationals.
The repatriation of investment income, capital or the proceeds of securities sales from emerging countries may be subject to restrictions which require governmental consents or prohibit repatriation entirely for a period of time, which may make it difficult for a Fund to invest in such emerging countries. A Fund could be adversely affected by delays in, or a refusal to grant, any required governmental approval for such repatriation. Even where there is no outright restriction on repatriation of capital, the mechanics of repatriation may affect certain aspects of the operation of a Fund. A Fund may be required to establish special custodial or other arrangements before investing in certain emerging countries.
Emerging countries may be subject to a substantially greater degree of economic, political and social instability and disruption than is the case in the United States, Japan and most Western European countries. This instability may result from, among other things, the following: (i) authoritarian governments or military involvement in political and economic decision making, including changes or attempted changes in governments through extra-constitutional means; (ii) popular unrest associated with demands for improved political, economic or social conditions; (iii) internal insurgencies; (iv) hostile relations with neighboring countries; (v) ethnic, religious and racial disaffection or conflict; and (vi) the absence of developed legal structures governing foreign private investments and private property. Such economic, political and social instability could disrupt the principal financial markets in which the Funds may invest and adversely affect the value of the Funds’ assets. A Fund’s investments can also be adversely affected by any increase in taxes or by political, economic or diplomatic developments.
Certain Funds may seek investment opportunities within former “Eastern bloc” countries. Most of these countries had a centrally planned, socialist economy for a substantial period of time. The governments of many of these countries have more recently been implementing reforms directed at political and economic liberalization, including efforts to decentralize the economic decision-making process and move towards a market economy. However, business entities in Eastern European countries do not have an extended history
B-14
of operating in a market-oriented economy, and the ultimate impact of these countries’ attempts to move toward more market-oriented economies is currently unclear. Any change in the leadership or policies of these countries may halt the expansion of or reverse the liberalization of foreign investment policies now occurring and adversely affect existing investment opportunities. In addition, Eastern European markets are particularly sensitive to social, economic and currency events in Western Europe and Russia. Russia may attempt to assert its influence in the region through military measures.
The economies of emerging countries may differ unfavorably from the U.S. economy in such respects as growth of gross domestic product, rate of inflation, capital reinvestment, resources, self-sufficiency and balance of payments. Many emerging countries have experienced in the past, and continue to experience, high rates of inflation. In certain countries inflation has at times accelerated rapidly to hyperinflationary levels, creating a negative interest rate environment and sharply eroding the value of outstanding financial assets in those countries. Other emerging countries, on the other hand, have recently experienced deflationary pressures and are in economic recessions. The economies of many emerging countries are heavily dependent upon international trade and are accordingly affected by protective trade barriers and the economic conditions of their trading partners. In addition, the economies of some emerging countries are vulnerable to weakness in world prices for their commodity exports.
A Fund’s income and, in some cases, capital gains from foreign stocks and securities will be subject to applicable taxation in certain of the countries in which it invests, and treaties between the U.S. and such countries may not be available in some cases to reduce the otherwise applicable tax rates. See “TAXATION.”
Foreign markets also have different clearance and settlement procedures, and in certain markets there have been times when settlements have been unable to keep pace with the volume of securities transactions, making it difficult to conduct such transactions. Such delays in settlement could result in temporary periods when a portion of the assets of a Fund remain uninvested and no return is earned on such assets. The inability of a Fund to make intended security purchases or sales due to settlement problems could result either in losses to the Fund due to subsequent declines in value of the portfolio securities or, if the Fund has entered into a contract to sell the securities, could result in possible liability to the purchaser.
These and other factors discussed in the section below, entitled “Illiquid Investments,” may impact the liquidity of investments in issuers of emerging country securities.
Forward Foreign Currency Exchange Contracts.
The Funds may, to the extent consistent with their investment policies, enter into forward foreign currency exchange contracts for hedging purposes and to seek to protect against anticipated changes in future foreign currency exchange rates. The Funds may also enter into forward foreign currency exchange contracts to seek to increase total return. A forward foreign currency exchange contract involves an obligation to purchase or sell a specific currency at a future date, which may be any fixed number of days from the date of the contract agreed upon by the parties, at a price set at the time of the contract. These contracts are traded in the interbank market between currency traders (usually large commercial banks) and their customers. A forward contract generally has no deposit requirement, and no commissions are generally charged at any stage for trades.
At the maturity of a forward contract a Fund may either accept or make delivery of the currency specified in the contract or, at or prior to maturity, enter into a closing purchase transaction involving the purchase or sale of an offsetting contract. Closing purchase transactions with respect to forward contracts are usually effected with the currency trader who is a party to the original forward contract.
The Fund may, from time to time, engage in non-deliverable forward transactions to manage currency risk or to gain exposure to a currency without purchasing securities denominated in that currency. A non-deliverable forward is a transaction that represents an agreement between the Fund and a counterparty (usually a commercial bank) to pay the other party the amount that it would have cost based on current market rates as of the termination date to buy or sell a specified (notional) amount of a particular currency at an agreed upon foreign exchange rate on an agreed upon future date. If the counterparty defaults, the Fund will have contractual remedies pursuant to the agreement related to the transaction, but the Fund may be delayed or prevented from obtaining payments owed to it pursuant to non-deliverable forward transactions. Such non-deliverable forward transactions will be settled in cash.
A Fund may enter into forward foreign currency exchange contracts for hedging purposes in several circumstances. First, when a Fund enters into a contract for the purchase or sale of a security denominated or quoted in a foreign currency, or when a Fund anticipates the receipt in a foreign currency of a dividend or interest payment on such a security which it holds, the Fund may desire to “lock in” the U.S. dollar price of the security or the U.S. dollar equivalent of such dividend or interest payment, as the case may be. By entering into a forward contract for the purchase or sale, for a fixed amount of U.S. dollars, of the amount of foreign currency involved in the underlying transactions, the Fund may attempt to protect itself against an adverse change in the relationship between the U.S. dollar and the subject foreign currency during the period between the date on which the security is purchased or sold, or on which the dividend or interest payment is declared, and the date on which such payments are made or received.
Additionally, when the Investment Adviser believes that the currency of a particular foreign country may suffer a substantial decline against the U.S. dollar, it may enter into a forward contract to sell, for a fixed amount of U.S. dollars, the amount of foreign currency approximating the value of some or all of a Fund’s portfolio securities quoted or denominated in such foreign currency. The
B-15
precise matching of the forward contract amounts and the value of the securities involved will not generally be possible because the future value of such securities in foreign currencies will change as a consequence of market movements in the value of those securities between the date on which the contract is entered into and the date it matures. Using forward contracts to protect the value of a Fund’s portfolio securities against a decline in the value of a currency does not eliminate fluctuations in the underlying prices of the securities. It simply establishes a rate of exchange, which a Fund can achieve at some future point in time. The precise projection of short-term currency market movements is not possible, and short-term hedging provides a means of fixing the U.S. dollar value of only a portion of a Fund’s foreign assets.
The Funds may engage in cross-hedging by using forward contracts in one currency to hedge against fluctuations in the value of securities denominated or quoted in a different currency if the Investment Adviser determines that there is a pattern or correlation between the two currencies. In addition, certain Funds may enter into foreign currency transactions to seek a closer correlation between a Fund’s overall currency exposure and the currency exposure of the Fund’s performance benchmark. The Flexible Cap, Small/Mid Cap Growth, Small Cap Growth and Focused Value Funds may also enter into forward contracts to seek to increase total return.
Unless otherwise covered in accordance with applicable regulations, a Fund will identify on its books cash or liquid assets in an amount equal to the value of the Fund’s total assets committed to the consummation of forward foreign currency exchange contracts requiring the Fund to purchase foreign currencies and forward contracts entered into to seek to increase total return. The segregated assets will be marked-to-market. If the value of the identified assets declines, additional cash or liquid assets will be identified so that the value of the assets will equal the amount of a Fund’s commitments with respect to such contracts. For more information about these practices, see “Description of Investment Securities and Practices – Asset Segregation.”
While a Fund may enter into forward contracts to seek to reduce currency exchange rate risks, transactions in such contracts involve certain other risks. Thus, while a Fund may benefit from such transactions, unanticipated changes in currency prices may result in a poorer overall performance for the Fund than if it had not engaged in any such transactions. Moreover, there may be imperfect correlation between a Fund’s portfolio holdings of securities quoted or denominated in a particular currency and forward contracts entered into by such Fund. Such imperfect correlation may cause a Fund to sustain losses which will prevent the Fund from achieving a complete hedge or expose the Fund to risk of foreign exchange loss.
Certain forward foreign currency exchange contracts and other currency transactions are not exchange traded or cleared. Markets for trading such forward foreign currency contracts offer less protection against defaults than is available when trading in currency instruments on an exchange. Such forward contracts are subject to the risk that the counterparty to the contract will default on its obligations. Because these contracts are not guaranteed by an exchange or clearinghouse, a default on a contract would deprive a Fund of unrealized profits, transaction costs or the benefits of a currency hedge or force the Fund to cover its purchase or sale commitments, if any, at the current market price. In addition, the institutions that deal in forward currency contracts are not required to continue to make markets in the currencies they trade and these markets can experience periods of illiquidity.
Forward contracts are subject to the risk that the counterparty to such contract will default on its obligations. Because a forward foreign currency exchange contract is not guaranteed by an exchange or clearinghouse, a default on the contract would deprive a Fund of unrealized profits, transaction costs or the benefits of a currency hedge or force the Fund to cover its purchase or sale commitments, if any, at the current market price. Certain Funds may not enter into such transactions unless the Fund considers the credit quality of the unsecured senior debt or the claims-paying ability of the counterparty to be investment grade. To the extent that a substantial portion of a Fund’s total assets, adjusted to reflect the Fund’s net position after giving effect to currency transactions, is denominated or quoted in the currencies of foreign countries, the Fund will be more susceptible to the risk of adverse economic and political developments within those countries.
Futures Contracts and Options on Futures Contracts
Each Fund may purchase and sell futures contracts and may also purchase and write call and put options on futures contracts. The futures contracts may be based on various securities, securities indices, foreign currencies and other financial instruments and indices. Each Fund may engage in futures and related options transactions in order to seek to increase total return or to hedge against changes in interest rates, securities prices or currency exchange rates, or to otherwise manage its term structure, sector selection and duration in accordance with its investment objective and policies. Each Fund may also enter into closing purchase and sale transactions with respect to such contracts and options.
Futures contracts entered into by mutual funds have historically been traded on U.S. exchanges or boards of trade that are licensed and regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”) or, with respect to certain funds, on foreign exchanges. More recently, certain futures may also be traded either over-the-counter or on trading facilities such as derivatives transaction execution facilities, exempt boards of trade or electronic trading facilities that are licensed and/or regulated to varying degrees by the CFTC. Also, certain single stock futures and narrow based security index futures may be traded either over-the-counter or on trading facilities such as contract markets, derivatives transaction execution facilities and electronic trading facilities that are licensed and/or regulated to varying degrees by both the CFTC and the SEC, or on foreign exchanges.
B-16
Neither the CFTC, National Futures Association (“NFA”), SEC nor any domestic exchange regulates activities of any foreign exchange or boards of trade, including the execution, delivery and clearing of transactions, or has the power to compel enforcement of the rules of a foreign exchange or board of trade or any applicable foreign law. This is true even if the exchange is formally linked to a domestic market so that a position taken on the market may be liquidated by a transaction on another market. Moreover, such laws or regulations will vary depending on the foreign country in which the foreign futures or foreign options transaction occurs. For these reasons, a Fund’s investments in foreign futures or foreign options transactions may not be provided the same protections in respect of transactions on United States exchanges. In particular, persons who trade foreign futures or foreign options contracts may not be afforded certain of the protective measures provided by the CEA, the CFTC’s regulations and the rules of the NFA and any domestic exchange, including the right to use reparations proceedings before the CFTC and arbitration proceedings provided by the NFA or any domestic futures exchange. Similarly, those persons may not have the protection of the U.S. securities laws.
Futures Contracts. A futures contract may generally be described as an agreement between two parties to buy and sell particular financial instruments for an agreed price during a designated month (or to deliver the final cash settlement price, in the case of a contract relating to an index or otherwise not calling for physical delivery at the end of trading in the contract).
When interest rates are rising or securities prices are falling, a Fund can seek through the sale of futures contracts to offset a decline in the value of its current portfolio securities. When interest rates are falling or securities prices are rising, a Fund, through the purchase of futures contracts, can attempt to secure better rates or prices than might later be available in the market when it effects anticipated purchases. Similarly, each Fund can purchase and sell futures contracts on a specified currency in order to seek to increase total return or to protect against changes in currency exchange rates. For example, each Fund can purchase futures contracts on foreign currency to establish the price in U.S. dollars of a security quoted or denominated in such currency that the Fund has acquired or expects to acquire. In addition, certain Funds may enter into futures transactions to seek a closer correlation between a Fund’s overall currency exposures and the currency exposures of a Fund’s performance benchmark.
Positions taken in the futures market are not normally held to maturity, but are instead liquidated through offsetting transactions which may result in a profit or a loss. While a Fund will usually liquidate futures contracts on securities or currency in this manner, the Fund may instead make or take delivery of the underlying securities or currency whenever it appears economically advantageous for the Fund to do so. A clearing corporation associated with the exchange on which futures are traded guarantees that, if still open, the sale or purchase will be performed on the settlement date.
Hedging Strategies Using Futures Contracts. When a Fund uses futures for hedging purposes, the Fund often seeks to establish with more certainty than would otherwise be possible the effective price or rate of return on portfolio securities (or securities that the Fund proposes to acquire) or the exchange rate of currencies in which portfolio securities are quoted or denominated. A Fund may, for example, take a “short” position in the futures market by selling futures contracts to seek to hedge against an anticipated rise in interest rates or a decline in market prices or foreign currency rates that would adversely affect the dollar value of such Fund’s portfolio securities. Such futures contracts may include contracts for the future delivery of securities held by a Fund or securities with characteristics similar to those of a Fund’s portfolio securities. Similarly, each Fund may sell futures contracts on a currency in which its portfolio securities are quoted or denominated, or sell futures contracts on one currency to seek to hedge against fluctuations in the value of securities quoted or denominated in a different currency if there is an established historical pattern of correlation between the two currencies. If, in the opinion of the Investment Adviser, there is a sufficient degree of correlation between price trends for a Fund’s portfolio securities and futures contracts based on other financial instruments, securities indices or other indices, the Fund may also enter into such futures contracts as part of a hedging strategy. Although under some circumstances prices of securities in a Fund’s portfolio may be more or less volatile than prices of such futures contracts, the Investment Adviser will attempt to estimate the extent of this volatility difference based on historical patterns and compensate for any such differential by having the Fund enter into a greater or lesser number of futures contracts or by attempting to achieve only a partial hedge against price changes affecting a Fund’s portfolio securities. When hedging of this character is successful, any depreciation in the value of portfolio securities will be substantially offset by appreciation in the value of the futures position. On the other hand, any unanticipated appreciation in the value of a Fund’s portfolio securities would be substantially offset by a decline in the value of the futures position.
On other occasions, a Fund may take a “long” position by purchasing such futures contracts. This may be done, for example, when a Fund anticipates the subsequent purchase of particular securities when it has the necessary cash, but expects the prices or currency exchange rates then available in the applicable market to be less favorable than prices or rates that are currently available.
Options on Futures Contracts. The acquisition of put and call options on futures contracts will give a Fund the right (but not the obligation), for a specified price, to sell or to purchase, respectively, the underlying futures contract at any time during the option period. As the purchaser of an option on a futures contract, a Fund obtains the benefit of the futures position if prices move in a favorable direction but limits its risk of loss in the event of an unfavorable price movement to the loss of the premium and transaction costs.
The writing of a call option on a futures contract generates a premium which may partially offset a decline in the value of a Fund’s assets. By writing a call option, a Fund becomes obligated, in exchange for the premium, to sell a futures contract if the option is exercised, which may have a value higher than the exercise price. The writing of a put option on a futures contract generates a premium, which may partially offset an increase in the price of securities that a Fund intends to purchase. However, a Fund becomes obligated (upon the exercise of the option) to purchase a futures contract if the option is exercised, which may have a value lower than the exercise price. Thus, the loss incurred by a Fund in writing options on futures is potentially unlimited and may exceed the amount of the premium received. A Fund will incur transaction costs in connection with the writing of options on futures.
B-17
The holder or writer of an option on a futures contract may terminate its position by selling or purchasing an offsetting option on the same financial instrument. There is no guarantee that such closing transactions can be effected. A Fund’s ability to establish and close out positions on such options will be subject to the development and maintenance of a liquid market.
Other Considerations. A Fund will engage in transactions in futures contracts and related options transactions only to the extent such transactions are consistent with the requirements of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”) for maintaining its qualification as a regulated investment company for federal income tax purposes. Transactions in futures contracts and options on futures involve brokerage costs, require margin deposits and, in certain cases, require the Fund to identify on its books cash or liquid assets in an amount equal to the underlying value of such contracts and options. A Fund may cover its transactions in futures contracts and related options by identifying on its books cash or liquid assets or by other means, in any manner permitted by applicable law. For more information about these practices, see “Description of Investment Securities and Practices – Asset Segregation.”
While transactions in futures contracts and options on futures may reduce certain risks, such transactions themselves entail certain other risks. Thus, unanticipated changes in interest rates, securities prices or currency exchange rates may result in a poorer overall performance for a Fund than if it had not entered into any futures contracts or options transactions. When futures contracts and options are used for hedging purposes, perfect correlation between a Fund’s futures positions and portfolio positions may be impossible to achieve, particularly where futures contracts based on individual equity or corporate fixed income securities are currently not available. In the event of an imperfect correlation between a futures position and a portfolio position which is intended to be protected, the desired protection may not be obtained and a Fund may be exposed to risk of loss.
In addition, it is not possible for a Fund to hedge fully or perfectly against currency fluctuations affecting the value of securities quoted or denominated in foreign currencies because the value of such securities is likely to fluctuate as a result of independent factors unrelated to currency fluctuations. The profitability of a Fund’s trading in futures depends upon the ability of the Investment Adviser to analyze correctly the futures markets.
High Yield Securities
The Funds, with the exception of the U.S. Equity ESG and Concentrated Growth Funds, may invest in bonds rated BB+ or below by Standard & Poor’s Ratings Group (“Standard & Poor’s”) or Ba1 or below by Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. (“Moody’s”) (B or higher by Standard & Poor’s or Moody’s for Mid Cap Value Fund) or comparable rated and unrated securities. These bonds are commonly referred to as “junk bonds,” are non-investment grade, and are considered speculative. The Capital Growth, Growth Opportunities, Strategic Growth, Equity Income and Mid Cap Value Funds may each invest up to 10% of their total assets, and the Flexible Cap, Small/Mid Cap Growth, Technology Opportunities, Focused Value, Large Cap Value, Small Cap Value, Small Cap Growth and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds may invest up to 10%, 20%, 20%, 20%, 10%, 10%, 20%, 20% and 20% of their net assets, respectively, in non-investment grade securities. The ability of issuers of high yield securities to make principal and interest payments may be questionable because such issuers are often less creditworthy or are highly leveraged and are generally less able than more established or less leveraged entities to make scheduled payments of principal and interest. High yield securities are also issued by governmental issuers that may have difficulty in making all scheduled interest and principal payments. In some cases, high yield securities may be highly speculative, have poor prospects for reaching investment grade standing and be in default. As a result, investment in such bonds will entail greater risks than those associated with investments in investment grade bonds (i.e., bonds rated AAA, AA, A or BBB by Standard & Poor’s or Aaa, Aa, A or Baa by Moody’s). Analysis of the creditworthiness of issuers of high yield securities may be more complex than for issuers of higher quality debt securities, and the ability of a Fund to achieve its investment objective may, to the extent of its investments in high yield securities, be more dependent upon such creditworthiness analysis than would be the case if the Fund were investing in higher quality securities. See Appendix A for a description of the corporate bond and preferred stock ratings by Standard & Poor’s, Moody’s, Fitch, Inc. and Dominion Bond Rating Service Limited.
The market values of high yield securities tend to reflect individual corporate or municipal developments to a greater extent than do those of higher rated securities, which react primarily to fluctuations in the general level of interest rates. Issuers of high yield securities that are highly leveraged may not be able to make use of more traditional methods of financing. Their ability to service debt obligations may be more adversely affected by economic downturns or their inability to meet specific projected business forecasts than would be the case for issuers of higher-rated securities. Negative publicity about the junk bond market and investor perceptions regarding lower-rated securities, whether or not based on fundamental analysis, may depress the prices for such high yield securities. In the lower quality segments of the fixed income securities market, changes in perceptions of issuers’ creditworthiness tend to occur more frequently and in a more pronounced manner than do changes in higher quality segments of the fixed income securities market, resulting in greater yield and price volatility. Another factor which causes fluctuations in the prices of high yield securities is the supply and demand for similarly rated securities. In addition, the prices of investments fluctuate in response to the general level of interest rates. Fluctuations in the prices of portfolio securities subsequent to their acquisition will not affect cash income from such securities but will be reflected in the Funds’ NAVs.
B-18
The risk of loss from default for the holders of high yield securities is significantly greater than is the case for holders of other debt securities because such high yield securities are generally unsecured and are often subordinated to the rights of other creditors of the issuers of such securities. Investment by a Fund in already defaulted securities poses an additional risk of loss should nonpayment of principal and interest continue in respect of such securities. Even if such securities are held to maturity, recovery by a Fund of its initial investment and any anticipated income or appreciation is uncertain. In addition, a Fund may incur additional expenses to the extent that it is required to seek recovery relating to the default in the payment of principal or interest on such securities or otherwise protect its interests. A Fund may be required to liquidate other portfolio securities to satisfy annual distribution obligations of the Fund in respect of accrued interest income on securities which are subsequently written off, even though the Fund has not received any cash payments of such interest.
The secondary market for high yield securities is concentrated in relatively few markets and is dominated by institutional investors, including mutual funds, insurance companies and other financial institutions. Accordingly, the secondary market for such securities may not be as liquid as and may be more volatile than the secondary market for higher-rated securities. In addition, the trading volume for high yield securities is generally lower than that of higher rated securities. The secondary market for high yield securities could contract under adverse market or economic conditions independent of any specific adverse changes in the condition of a particular issuer. These factors may have an adverse effect on the ability of the Funds to dispose of particular portfolio investments when needed to meet their redemption requests or other liquidity needs. The Investment Adviser could find it difficult to sell these investments or may be able to sell the investments only at prices lower than if such investments were widely traded. Prices realized upon the sale of such lower rated or unrated securities, under these circumstances, may be less than the prices used in calculating the NAVs of the Funds. A less liquid secondary market also may make it more difficult for the Funds to obtain precise valuations of the high yield securities in their portfolios.
The adoption of new legislation could adversely affect the secondary market for high yield securities and the financial condition of issuers of these securities. The form of any future legislation, and the probability of such legislation being enacted, is uncertain.
Non-investment grade or high yield securities also present risks based on payment expectations. High yield securities frequently contain “call” or buy-back features which permit the issuer to call or repurchase the security from its holder. If an issuer exercises such a “call option” and redeems the security, a Fund may have to replace such security with a lower-yielding security, resulting in a decreased return for investors. In addition, if a Fund experiences net redemptions of its shares, it may be forced to sell its higher-rated securities, resulting in a decline in the overall credit quality of its portfolio and increasing its exposure to the risks of high yield securities.
Credit ratings issued by credit rating agencies are designed to evaluate the safety of principal and interest payments of rated securities. They do not, however, evaluate the market value risk of high yield securities and, therefore, may not fully reflect the true risks of an investment. In addition, credit rating agencies may or may not make timely changes in a rating to reflect changes in the economy or in the conditions of the issuer that affect the market value of the security. Consequently, credit ratings are used only as a preliminary indicator of investment quality. Investments in non-investment grade and comparable unrated obligations will be more dependent on the Investment Adviser’s credit analysis than would be the case with investments in investment-grade debt obligations. The Investment Adviser employs its own credit research and analysis, which includes a study of an issuer’s existing debt, capital structure, ability to service debt and to pay dividends, sensitivity to economic conditions, operating history and current earnings trends. The Investment Adviser continually monitors the investments in the Funds’ portfolios and evaluates whether to dispose of or to retain non-investment grade and comparable unrated securities whose credit ratings or credit quality may have changed. If after its purchase, a portfolio security is assigned a lower rating or ceases to be rated, a Fund may continue to hold the security if the Investment Adviser believes it is in the best interest of the Fund and its shareholders.
An economic downturn could severely affect the ability of highly leveraged issuers of junk bond investments to service their debt obligations or to repay their obligations upon maturity. Factors having an adverse impact on the market value of junk bonds will have an adverse effect on a Fund’s NAV to the extent it invests in such investments. In addition, a Fund may incur additional expenses to the extent it is required to seek recovery upon a default in payment of principal or interest on its portfolio holdings.
These and other factors discussed in the section below, entitled “Illiquid Investments,” may impact the liquidity of investments in high yield securities.
Illiquid Investments
Pursuant to Rule 22e-4 under the 1940 Act, a Fund may not acquire any “illiquid investment” if, immediately after the acquisition, the Fund would have invested more than 15% of its net assets in illiquid investments that are assets. An “illiquid investment” is any investment that a Fund reasonably expects cannot be sold or disposed of in current market conditions in seven calendar days or less without the sale or disposition significantly changing the market value of the investment. The Trust has implemented a liquidity risk management program and related procedures to categorize each Fund’s portfolio investments and identify illiquid investments pursuant to Rule 22e-4, and the Trustees have approved the designation of the Investment Adviser to administer the Trust’s liquidity risk management program and related procedures. In determining whether an investment is an illiquid investment, the Investment Adviser will take into account actual or estimated daily transaction volume of an investment, group of related investments or asset class and other relevant market, trading, and investment-specific considerations. In addition, in determining the liquidity of an investment, the
B-19
Investment Adviser must determine whether trading varying portions of a position in a particular portfolio investment or asset class, in sizes that a Fund would reasonably anticipate trading, is reasonably expected to significantly affect its liquidity, and if so, the Fund must take this determination into account when classifying the liquidity of that investment or asset class.
In addition to actual or estimated daily transaction volume of an investment, group of related investments or asset class and other relevant market, trading, and investment-specific considerations, the following factors, among others, will generally impact the classification of an investment as an “illiquid investment”: (i) any investment that is placed on the Investment Adviser’s restricted trading list; and (ii) any investment that is delisted or for which there is a trading halt at the close of the trading day on the primary listing exchange at the time of classification (and in respect of which no active secondary market exists). Investments purchased by a Fund that are liquid at the time of purchase may subsequently become illiquid due to these and other events and circumstances. If one or more investments in a Fund’s portfolio become illiquid, the Fund may exceed the 15% limitation in illiquid investments. In the event that changes in the portfolio or other external events cause a Fund to exceed this limit, the Fund must take steps to bring its illiquid investments that are assets to or below 15% of its net assets within a reasonable period of time. This requirement would not force a Fund to liquidate any portfolio instrument where the Fund would suffer a loss on the sale of that instrument.
Index Swaps, Interest Rate Swaps, Mortgage Swaps, Credit Swaps, Currency Swaps, Total Return Swaps, Equity Swaps, and Options on Swaps
The Flexible Cap and Focused Value Funds may enter into index, interest rate, mortgage, credit, currency and total return swaps for both hedging purposes and to seek to increase total return. The Flexible Cap and Focused Value Funds may also purchase and write (sell) options contracts on swaps, commonly referred to as swaptions.
In a standard “swap” transaction, two parties agree to exchange the returns, differentials in rates of return or some other amount earned or realized on particular predetermined investments or instruments, which may be adjusted for an interest factor. The gross returns to be exchanged or “swapped” between the parties are generally calculated with respect to a “notional amount,” i.e., the return on or increase in value of a particular dollar amount invested at a particular interest rate, in a particular foreign currency or security, or in a “basket” of securities representing a particular index. Bilateral swap agreements are two party contracts entered into primarily by institutional investors. Cleared swaps are transacted through FCMs that are members of central clearinghouses with the clearinghouse serving as a central counterparty similar to transactions in futures contracts. Funds post initial and variation margin by making payments to their clearing member FCMs.
Interest rate swaps involve the exchange by a Fund with another party of commitments to pay or receive payments for floating rate payments based on interest rates at specified intervals in the future. Two types of interest rate swaps include “fixed-for-floating rate swaps” and “basis swaps.” Fixed-for-floating rate swaps involve the exchange of payments based on a fixed interest rate for payments based on a floating interest rate index. By contrast, basis swaps involve the exchange of payments based on two different floating interest rate indices.
Mortgage swaps are similar to interest rate swaps in that they represent commitments to pay and receive interest. The notional principal amount, however, is tied to a reference pool or pools of mortgages.
Index swaps involve the exchange by a Fund with another party of payments based on a notional principal amount of a specified index or indices.
Currency swaps involve the exchange by a Fund with another party of their respective rights to make or receive payments in specified currencies. Credit swaps (also referred to as credit default swaps) involve the exchange of a floating or fixed rate payment in return for assuming potential credit losses of an underlying security or pool of securities. Total return swaps are contracts that obligate a party to pay or receive interest in exchange for the payment by the other party of the total return generated by a security, a basket of securities, an index or an index component.
Equity swap contracts may be structured in different ways. For example, as a total return swap where a counterparty may agree to pay the Fund the amount, if any, by which the notional amount of the equity swap contract would have increased in value had it been invested in the particular stocks (or a group of stocks), plus the dividends that would have been received on those stocks. In other cases, the counterparty and the Fund may each agree to pay the difference between the relative investment performances that would have been achieved if the notional amount of the equity swap contract had been invested in different stocks (or a group of stocks).
A swaption is an option to enter into a swap agreement. Like other types of options, the buyer of a swaption pays a non-refundable premium for the option and obtains the right, but not the obligation, to enter into or modify an underlying swap or to modify the terms of an existing swap on agreed-upon terms. The seller of a swaption, in exchange for the premium, becomes obligated (if the option is exercised) to enter into or modify an underlying swap on agreed-upon terms, which generally entails a greater risk of loss than incurred in buying a swaption.
A great deal of flexibility may be possible in the way swap transactions are structured. However, generally a Fund will enter into interest rate, total return, credit, mortgage, equity and index swaps on a net basis, which means that the two payment streams are netted
B-20
out, with a Fund receiving or paying, as the case may be, only the net amount of the two payments. Interest rate, total return, credit, index, mortgage and equity swaps do not normally involve the delivery of securities, other underlying assets or principal. Accordingly, the risk of loss with respect to interest rate, total return, credit, index, mortgage and equity swaps is normally limited to the net amount of interest payments that a Fund is contractually obligated to make. If the other party to an interest rate, total return, credit, index, mortgage or equity swap defaults, a Fund’s risk of loss consists of the net amount of interest payments that the Fund is contractually entitled to receive, if any. In contrast, currency swaps usually involve the delivery of a gross payment stream in one designated currency in exchange for a gross payment stream in another designated currency. Therefore, the entire payment stream under a currency swap is subject to the risk that the other party to the swap will default on its contractual delivery obligations.
To the extent that a Fund’s exposure in a transaction involving a swap or a swaption is covered by identifying cash or liquid assets on the Fund’s books or is covered by other means in accordance with SEC- or SEC staff-approved guidance or other appropriate measures, the Fund and the Investment Adviser believe that swaps do not constitute senior securities under the Act and, accordingly, will not treat them as being subject to the Fund’s borrowing restrictions. For more information about these practices, see “Description of Investment Securities and Practices – Asset Segregation.”
As a result of recent regulatory developments, certain standardized swaps are currently subject to mandatory central clearing and some of these cleared swaps must be traded on an exchange or swap execution facility (“SEF”). A SEF is a trading platform in which multiple market participants can execute swap transactions by accepting bids and offers made by multiple other participants on the platform. Transactions executed on a SEF may increase market transparency and liquidity but may cause a Fund to incur increased expenses to execute swaps. Central clearing should decrease counterparty risk and increase liquidity compared to bilateral swaps because central clearing interposes the central clearinghouse as the counterparty to each participant’s swap. However, central clearing does not eliminate counterparty risk or liquidity risk entirely. In addition, depending on the size of a Fund and other factors, the margin required under the rules of a clearinghouse and by a clearing member may be in excess of the collateral required to be posted by a Fund to support its obligations under a similar bilateral swap. However, the CFTC and other applicable regulators have adopted rules imposing certain margin requirements, including minimums, on uncleared swaps which may result in the Fund and its counterparties posting higher margin amounts for uncleared swaps. Requiring margin on uncleared swaps may reduce, but not eliminate, counterparty credit risk.
The use of swaps and swaptions is a highly specialized activity which involves investment techniques and risks different from those associated with ordinary portfolio securities transactions. The use of a swap requires an understanding not only of the referenced asset, reference rate, or index but also of the swap itself, without the benefit of observing the performance of the swap under all possible market conditions. If the Investment Adviser is incorrect in its forecasts of market values, credit quality, interest rates and currency exchange rates, the investment performance of the Flexible Cap and Focused Value Fund would be less favorable than it would have been if this investment technique were not used.
In addition, these transactions can involve greater risks than if a Fund had invested in the reference obligation directly because, in addition to general market risks, swaps are subject to liquidity risk, counterparty risk, credit risk and pricing risk. Regulators also may impose limits on an entity’s or group of entities’ positions in certain swaps. However, certain risks are reduced (but not eliminated) if a Fund invests in cleared swaps. Bilateral swap agreements are two party contracts that may have terms of greater than seven days. Moreover, a Fund bears the risk of loss of the amount expected to be received under a swap agreement in the event of the default or bankruptcy of a swap counterparty. Many swaps are complex and often valued subjectively. Swaps and other derivatives may also be subject to pricing or “basis” risk, which exists when the price of a particular derivative diverges from the price of corresponding cash market instruments. Under certain market conditions it may not be economically feasible to imitate a transaction or liquidate a position in time to avoid a loss or take advantage of an opportunity. If a swap transaction is particularly large or if the relevant market is illiquid, it may not be possible to initiate a transaction or liquidate a position at an advantageous time or price, which may result in significant losses.
Regulators are in the process of developing rules that would require trading and execution of most liquid swaps on trading facilities. Moving trading to an exchange-type system may increase market transparency and liquidity but may require a Fund to incur increased expenses to access the same types of swaps.
Certain rules also require centralized reporting of detailed information about many types of cleared and uncleared swaps. This information is available to regulators and, to a more limited extent and on an anonymous basis, to the public. Reporting of swap data may result in greater market transparency, which may be beneficial to funds that use swaps to implement trading strategies. However, these rules place potential additional administrative obligations on these funds, and the safeguards established to protect anonymity may not function as expected.
The swap market has grown substantially in recent years with a large number of banks and investment banking firms acting both as principals and as agents utilizing standardized swap documentation. As a result, the swap market has become relatively liquid in comparison with the markets for other similar instruments which are traded in the interbank market. These and other factors discussed in the section above, entitled “Illiquid investments,” may impact the liquidity of investments in swaps.
B-21
Investments in Unseasoned Companies
Each Fund may invest in companies (including predecessors) which have operated less than three years. The securities of such companies may have limited liquidity, which can result in their being priced higher or lower than might otherwise be the case. In addition, investments in unseasoned companies are more speculative and entail greater risk than do investments in companies with an established operating record.
Lending of Portfolio Securities
Each Fund may lend its portfolio securities to brokers, dealers and other institutions, including Goldman Sachs. By lending its securities, a Fund attempts to increase its net investment income.
Securities loans are required to be secured continuously by collateral in cash, cash equivalents, letters of credit or U.S. Government Securities equal to at least 100% of the value of the loaned securities. This collateral must be valued, or “marked to market,” daily. Borrowers are required to furnish additional collateral to the Fund as necessary to fully cover their obligations.
With respect to loans that are collateralized by cash, the Fund may reinvest that cash in short-term investments and pay the borrower a pre-negotiated fee or “rebate” from any return earned on the investment. Investing the collateral subjects it to market depreciation or appreciation, and a Fund is responsible for any loss that may result from its investment of the borrowed collateral. Cash collateral may be invested in, among other things, other registered or unregistered funds, including private investing funds or money market funds that are managed by the Investment Adviser or its affiliates, and which pay the Investment Adviser or its affiliates for their services. If a Fund would receive non-cash collateral, the Fund receives a fee from the borrower equal to a negotiated percentage of the market value of the loaned securities.
For the duration of any securities loan, a Fund will continue to receive the equivalent of the interest, dividends or other distributions paid by the issuer on the loaned securities. A Fund will not have the right to vote its loaned securities during the period of the loan, but the Fund may attempt to recall a loaned security in anticipation of a material vote if it desires to do so. A Fund will have the right to terminate a loan at any time and recall the loaned securities within the normal and customary settlement time for securities transactions.
Securities lending involves certain risks. A Fund may lose money on its investment of cash collateral, resulting in a loss of principal, or may fail to earn sufficient income on its investment to cover the fee or rebate it has agreed to pay the borrower. A Fund may incur losses in connection with its securities lending activities that exceed the value of the interest income and fees received in connection with such transactions. Securities lending subjects a Fund to the risk of loss resulting from problems in the settlement and accounting process, and to additional credit, counterparty and market risk. These risks could be greater with respect to non-U.S. securities. Engaging in securities lending could have a leveraging effect, which may intensify the other risks associated with investments in a Fund. In addition, a Fund bears the risk that the price of the securities on loan will increase while they are on loan, or that the price of the collateral will decline in value during the period of the loan, and that the counterparty will not provide, or will delay in providing, additional collateral. A Fund also bears the risk that a borrower may fail to return securities in a timely manner or at all, either because the borrower fails financially or for other reasons. If a borrower of securities fails financially, a Fund may also lose its rights in the collateral. A Fund could experience delays and costs in recovering loaned securities or in gaining access to and liquidating the collateral, which could result in actual financial loss and which could interfere with portfolio management decisions or the exercise of ownership rights in the loaned securities. If a Fund is not able to recover the securities lent, the Fund may sell the collateral and purchase replacement securities in the market. However, a Fund will incur transaction costs on the purchase of replacement securities. These events could trigger adverse tax consequences for the Fund. In determining whether to lend securities to a particular borrower, and throughout the period of the loan, the creditworthiness of the borrower will be considered and monitored. Loans will only be made to firms deemed to be of good standing, and where the consideration that can be earned currently from securities loans of this type is deemed to justify the attendant risk. It is intended that the value of securities loaned by a Fund will not exceed one-third of the value of the Fund’s total assets (including the loan collateral).
The Fund will consider the loaned securities as assets of the Fund, but will not consider any collateral as a Fund asset except when determining total assets for the purpose of the above one-third limitation. Loan collateral (including any investment of the collateral) is not subject to the percentage limitations stated elsewhere in this SAI or in the Prospectuses regarding investing in fixed income securities and cash equivalents.
The Board of Trustees has approved each Fund’s participation in a securities lending program and has adopted policies and procedures relating thereto.
For its services, the securities lending agent may receive a fee from a Fund, including a fee based on the returns earned on the Fund’s investment of cash received as collateral for the loaned securities. In addition, a Fund may make brokerage and other payments to Goldman Sachs and its affiliates in connection with the Fund’s portfolio investment transactions. A Fund’s Board of Trustees periodically reviews reports on securities loan transactions for which a Goldman Sachs affiliate has acted as lending agent for compliance with the Fund’s securities lending procedures. Goldman Sachs may also be approved as a borrower under a Fund’s securities lending program, subject to certain conditions.
B-22
Mortgage Dollar Rolls
A Fund may enter into mortgage dollar rolls, in which a Fund sells securities for delivery in the current month and simultaneously contracts with the same counterparty to repurchase similar, but not identical securities on a specified future date. During the roll period, a Fund loses the right to receive principal and interest paid on the securities sold. However, a Fund would benefit to the extent of any difference between the price received for the securities sold and the lower forward price for the future purchase or fee income plus the interest earned on the cash proceeds of the securities sold until the settlement date of the forward purchase. All cash proceeds will be invested in instruments that are permissible investments for the applicable Fund. Each Fund will, until the settlement date, identify on its books cash or liquid assets, as permitted by applicable law, in an amount equal to its forward purchase price. For more information about these practices, see “Description of Investment Securities and Practices – Asset Segregation.”
For financial reporting and tax purposes, the Funds treat mortgage dollar rolls as two separate transactions; one involving the purchase of a security and a separate transaction involving a sale. The Funds do not currently intend to enter into mortgage dollar rolls for financing and do not treat them as borrowings.
Mortgage dollar rolls involve certain risks including the following: if the broker-dealer to whom a Fund sells the security becomes insolvent, a Fund’s right to purchase or repurchase the mortgage-related securities subject to the mortgage dollar roll may be restricted. Also, the instrument which a Fund is required to repurchase may be worth less than an instrument which a Fund originally held. Successful use of mortgage dollar rolls will depend upon the Investment Adviser’s ability to manage a Fund’s interest rate and mortgage prepayments exposure. For these reasons, there is no assurance that mortgage dollar rolls can be successfully employed. The use of this technique may diminish the investment performance of a Fund compared with what such performance would have been without the use of mortgage dollar rolls.
Mortgage Loans and Mortgage-Backed Securities
The Funds (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may each invest in mortgage loans, mortgage pass-through securities and other securities representing an interest in or collateralized by adjustable and fixed rate mortgage loans, including collateralized mortgage obligations, real estate mortgage investment conduits (“REMICs”) and stripped mortgage backed securities, as described below (“Mortgage-Backed Securities”).
Mortgage-Backed Securities are subject to both call risk and extension risk. Because of these risks, these securities can have significantly greater price and yield volatility than traditional fixed income securities.
General Characteristics of Mortgage Backed Securities.
In general, each mortgage pool underlying Mortgage-Backed Securities consists of mortgage loans evidenced by promissory notes secured by first mortgages or first deeds of trust or other similar security instruments creating a first lien on owner occupied and non-owner occupied one-unit to four-unit residential properties, multi-family (i.e., five-units or more) properties, agricultural properties, commercial properties and mixed use properties (the “Mortgaged Properties”). The Mortgaged Properties may consist of detached individual dwelling units, multi-family dwelling units, individual condominiums, townhouses, duplexes, triplexes, fourplexes, row houses, individual units in planned unit developments, other attached dwelling units (“Residential Mortgaged Properties”) or commercial properties, such as office properties, retail properties, hospitality properties, industrial properties, healthcare related properties or other types of income producing real property (“Commercial Mortgaged Properties”). Residential Mortgaged Properties may also include residential investment properties and second homes. In addition, the Mortgage-Backed Securities which are residential mortgage-backed securities may also consist of mortgage loans evidenced by promissory notes secured entirely or in part by second priority mortgage liens on Residential Mortgaged Properties.
The investment characteristics of adjustable and fixed rate Mortgage-Backed Securities differ from those of traditional fixed income securities. The major differences include the payment of interest and principal on Mortgage-Backed Securities on a more frequent (usually monthly) schedule, and the possibility that principal may be prepaid at any time due to prepayments on the underlying mortgage loans or other assets. These differences can result in significantly greater price and yield volatility than is the case with traditional fixed income securities. As a result, if a Fund purchases Mortgage-Backed Securities at a premium, a faster than expected prepayment rate will reduce both the market value and the yield to maturity from their anticipated levels. A prepayment rate that is slower than expected will have the opposite effect, increasing yield to maturity and market value. Conversely, if a Fund purchases Mortgage-Backed Securities at a discount, faster than expected prepayments will increase, while slower than expected prepayments will reduce yield to maturity and market value. To the extent that a Fund invests in Mortgage-Backed Securities, the Investment Adviser may seek to manage these potential risks by investing in a variety of Mortgage-Backed Securities and by using certain hedging techniques.
Prepayments on a pool of mortgage loans are influenced by changes in current interest rates and a variety of economic, geographic, social and other factors (such as changes in mortgagor housing needs, job transfers, unemployment, mortgagor equity in the mortgage properties and servicing decisions). The timing and level of prepayments cannot be predicted. A predominant factor affecting the prepayment rate on a pool of mortgage loans is the difference between the interest rates on outstanding mortgage loans and prevailing mortgage loan interest rates (giving consideration to the cost of any refinancing). Generally, prepayments on mortgage loans will increase during a period of falling mortgage interest rates and decrease during a period of rising mortgage interest rates. Accordingly,
B-23
the amounts of prepayments available for reinvestment by a Fund are likely to be greater during a period of declining mortgage interest rates. If general interest rates decline, such prepayments are likely to be reinvested at lower interest rates than a Fund was earning on the Mortgage-Backed Securities that were prepaid. Due to these factors, Mortgage-Backed Securities may be less effective than U.S. Treasury and other types of debt securities of similar maturity at maintaining yields during periods of declining interest rates. Because a Fund’s investments in Mortgage-Backed Securities are interest-rate sensitive, a Fund’s performance will depend in part upon the ability of the Fund to anticipate and respond to fluctuations in market interest rates and to utilize appropriate strategies to maximize returns to the Fund, while attempting to minimize the associated risks to its investment capital. Prepayments may have a disproportionate effect on certain Mortgage-Backed Securities and other multiple class pass-through securities, which are discussed below.
The rate of interest paid on Mortgage-Backed Securities is normally lower than the rate of interest paid on the mortgages included in the underlying pool due to (among other things) the fees paid to any servicer, special servicer and trustee for the trust fund which holds the mortgage pool, other costs and expenses of such trust fund, fees paid to any guarantor, such as Ginnie Mae (as defined below) or to any credit enhancers, mortgage pool insurers, bond insurers and/or hedge providers, and due to any yield retained by the issuer. Actual yield to the holder may vary from the coupon rate, even if adjustable, if the Mortgage-Backed Securities are purchased or traded in the secondary market at a premium or discount. In addition, there is normally some delay between the time the issuer receives mortgage payments from the servicer and the time the issuer (or the trustee of the trust fund which holds the mortgage pool) makes the payments on the Mortgage-Backed Securities, and this delay reduces the effective yield to the holder of such securities.
The issuers of certain mortgage-backed obligations may elect to have the pool of mortgage loans (or indirect interests in mortgage loans) underlying the securities treated as a REMIC, which is subject to special federal income tax rules. A description of the types of mortgage loans and Mortgage-Backed Securities in which certain of the Funds may invest is provided below. The descriptions are general and summary in nature, and do not detail every possible variation of the types of securities that are permissible investments for a Fund.
Delinquencies, defaults and losses on residential mortgage loans may increase substantially over certain periods, which may affect the performance of the Mortgage-Backed Securities in which certain Funds may invest. Mortgage loans backing non-agency Mortgage-Backed Securities are more sensitive to economic factors that could affect the ability of borrowers to pay their obligations under the mortgage loans backing these securities. In addition, housing prices and appraisal values in many states and localities over certain periods have declined or stopped appreciating. A sustained decline or an extended flattening of those values may result in additional increases in delinquencies and losses on Mortgage-Backed Securities generally (including the Mortgaged-Backed Securities that the Funds may invest in as described above).
Adverse changes in market conditions and regulatory climate may reduce the cash flow which a Fund, to the extent it invests in Mortgage-Backed Securities or other asset-backed securities, receives from such securities and increase the incidence and severity of credit events and losses in respect of such securities. In the event that interest rate spreads for Mortgage-Backed Securities and other asset-backed securities widen following the purchase of such assets by a Fund, the market value of such securities is likely to decline and, in the case of a substantial spread widening, could decline by a substantial amount. Furthermore, adverse changes in market conditions may result in reduced liquidity in the market for Mortgage-Backed Securities and other asset-backed securities (including the Mortgage-Backed Securities and other asset-backed securities in which certain Funds may invest) and an unwillingness by banks, financial institutions and investors to extend credit to servicers, originators and other participants in the market for Mortgage-Backed and other asset-backed securities. As a result, the liquidity and/or the market value of any Mortgage-Backed or asset-backed securities that are owned by a Fund may experience declines after they are purchased by a Fund.
General Regulatory Considerations of Mortgage-Backed Securities
The unprecedented disruption in the mortgage- and asset-backed securities markets in 2008-2009 resulted in significant downward price pressures as well as foreclosures and defaults in residential and commercial real estate. As a result of these events, the liquidity of the mortgage- and asset-backed securities markets was negatively impacted during that time. Following the market dislocation, the U.S. Congress passed the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”), which imposed a new regulatory framework over the U.S. financial services industry and the consumer credit markets in general. Among its other provisions, the Dodd-Frank Act creates a liquidation framework under which the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”), may be appointed as receiver following a “systemic risk determination” by the Secretary of Treasury (in consultation with the President) for the resolution of certain nonbank financial companies and other entities, defined as “covered financial companies”, and commonly referred to as “systemically important entities”, in the event such a company is in default or in danger of default and the resolution of such a company under other applicable law would have serious adverse effects on financial stability in the United States, and also for the resolution of certain of their subsidiaries. No assurances can be given that this new liquidation framework would not apply to the originators of asset-backed securities, including Mortgage-Backed Securities, or their respective subsidiaries, including the issuers and depositors of such securities, although the expectation embedded in the Dodd-Frank Act is that the framework will be invoked only very rarely. Guidance from the FDIC indicates that such new framework will largely be exercised in a manner consistent with the existing bankruptcy laws, which is the insolvency regime that would otherwise apply to the sponsors, depositors and issuing entities with respect to asset-backed securities, including Mortgage-Backed Securities. The application of such liquidation framework to such entities could result in decreases or delays in amounts paid on, and hence the market value of, the Mortgage-Backed or asset-backed securities that may be owned by a Fund.
B-24
Certain General Characteristics of Mortgage Loans
Adjustable Rate Mortgage Loans (“ARMs”). The Funds (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may invest in ARMs. ARMs generally provide for a fixed initial mortgage interest rate for a specified period of time. Thereafter, the interest rates (the “Mortgage Interest Rates”) may be subject to periodic adjustment based on changes in the applicable index rate (the “Index Rate”). The adjusted rate would be equal to the Index Rate plus a fixed percentage spread over the Index Rate established for each ARM at the time of its origination. ARMs allow a Fund to participate in increases in interest rates through periodic increases in the securities coupon rates. During periods of declining interest rates, coupon rates may readjust downward resulting in lower yields to a Fund.
Adjustable interest rates can cause payment increases that some mortgagors may find difficult to make. However, certain ARMs may provide that the Mortgage Interest Rate may not be adjusted to a rate above an applicable lifetime maximum rate or below an applicable lifetime minimum rate for such ARM. Certain ARMs may also be subject to limitations on the maximum amount by which the Mortgage Interest Rate may adjust for any single adjustment period (the “Maximum Adjustment”). Other ARMs (“Negatively Amortizing ARMs”) may provide instead or as well for limitations on changes in the monthly payment on such ARMs. Limitations on monthly payments can result in monthly payments which are greater or less than the amount necessary to amortize a Negatively Amortizing ARM by its maturity at the Mortgage Interest Rate in effect in any particular month. In the event that a monthly payment is not sufficient to pay the interest accruing on a Negatively Amortizing ARM, any such excess interest is added to the principal balance of the loan, causing negative amortization, and will be repaid through future monthly payments. It may take borrowers under Negatively Amortizing ARMs longer periods of time to build up equity and may increase the likelihood of default by such borrowers. In the event that a monthly payment exceeds the sum of the interest accrued at the applicable Mortgage Interest Rate and the principal payment which would have been necessary to amortize the outstanding principal balance over the remaining term of the loan, the excess (or “accelerated amortization”) further reduces the principal balance of the ARM. Negatively Amortizing ARMs do not provide for the extension of their original maturity to accommodate changes in their Mortgage Interest Rate. As a result, unless there is a periodic recalculation of the payment amount (which there generally is), the final payment may be substantially larger than the other payments. After the expiration of the initial fixed rate period and upon the periodic recalculation of the payment to cause timely amortization of the related mortgage loan, the monthly payment on such mortgage loan may increase substantially which may, in turn, increase the risk of the borrower defaulting in respect of such mortgage loan. These limitations on periodic increases in interest rates and on changes in monthly payments protect borrowers from unlimited interest rate and payment increases, but may result in increased credit exposure and prepayment risks for lenders. When interest due on a mortgage loan is added to the principal balance of such mortgage loan, the related mortgaged property provides proportionately less security for the repayment of such mortgage loan. Therefore, if the related borrower defaults on such mortgage loan, there is a greater likelihood that a loss will be incurred upon any liquidation of the mortgaged property which secures such mortgage loan.
ARMs also have the risk of prepayment. The rate of principal prepayments with respect to ARMs has fluctuated in recent years. The value of Mortgage-Backed Securities collateralized by ARMs is less likely to rise during periods of declining interest rates than the value of fixed-rate securities during such periods. Accordingly, ARMs may be subject to a greater rate of principal repayments in a declining interest rate environment resulting in lower yields to a Fund. For example, if prevailing interest rates fall significantly, ARMs could be subject to higher prepayment rates (than if prevailing interest rates remain constant or increase) because the availability of low fixed-rate mortgages may encourage mortgagors to refinance their ARMs to “lock-in” a fixed-rate mortgage. On the other hand, during periods of rising interest rates, the value of ARMs will lag behind changes in the market rate. ARMs are also typically subject to maximum increases and decreases in the interest rate adjustment which can be made on any one adjustment date, in any one year, or during the life of the security. In the event of dramatic increases or decreases in prevailing market interest rates, the value of a Fund’s investment in ARMs may fluctuate more substantially because these limits may prevent the security from fully adjusting its interest rate to the prevailing market rates. As with fixed-rate mortgages, ARM prepayment rates vary in both stable and changing interest rate environments.
There are two main categories of indices which provide the basis for rate adjustments on ARMs: those based on U.S. Treasury securities and those derived from a calculated measure, such as a cost of funds index or a moving average of mortgage rates. Indices commonly used for this purpose include the one-year, three-year and five-year constant maturity Treasury rates, the three-month Treasury bill rate, the 180-day Treasury bill rate, rates on longer-term Treasury securities, the 11th District Federal Home Loan Bank Cost of Funds, the National Median Cost of Funds, the one-month, three-month, six-month or one-year London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”), the prime rate of a specific bank, or commercial paper rates. Some indices, such as the one-year constant maturity Treasury rate, closely mirror changes in market interest rate levels. Others, such as the 11th District Federal Home Loan Bank Cost of Funds index, tend to lag behind changes in market rate levels and tend to be somewhat less volatile. The degree of volatility in the market value of ARMs in a Fund’s portfolio and, therefore, in the NAV of the Fund’s shares, will be a function of the length of the interest rate reset periods and the degree of volatility in the applicable indices.
Fixed-Rate Mortgage Loans. Generally, fixed-rate mortgage loans included in mortgage pools (the “Fixed-Rate Mortgage Loans”) will bear simple interest at fixed annual rates and have original terms to maturity ranging from 5 to 40 years. Fixed-Rate Mortgage
B-25
Loans generally provide for monthly payments of principal and interest in substantially equal installments for the term of the mortgage note in sufficient amounts to fully amortize principal by maturity, although certain Fixed-Rate Mortgage Loans provide for a large final “balloon” payment upon maturity.
Certain Legal Considerations of Mortgage Loans. The following is a discussion of certain legal and regulatory aspects of the mortgage loans in which the Funds may invest. This discussion is not exhaustive, and does not address all of the legal or regulatory aspects affecting mortgage loans. These regulations may impair the ability of a mortgage lender to enforce its rights under the mortgage documents. These regulations may also adversely affect a Fund’s investments in Mortgage-Backed Securities (including those issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities) by delaying the Fund’s receipt of payments derived from principal or interest on mortgage loans affected by such regulations.
| 1. | Foreclosure. A foreclosure of a defaulted mortgage loan may be delayed due to compliance with statutory notice or service of process provisions, difficulties in locating necessary parties or legal challenges to the mortgagee’s right to foreclose. Depending upon market conditions, the ultimate proceeds of the sale of foreclosed property may not equal the amounts owed on the Mortgage-Backed Securities. Furthermore, courts in some cases have imposed general equitable principles upon foreclosure generally designed to relieve the borrower from the legal effect of default and have required lenders to undertake affirmative and expensive actions to determine the causes for the default and the likelihood of loan reinstatement. |
| 2. | Rights of Redemption. In some states, after foreclosure of a mortgage loan, the borrower and foreclosed junior lienors are given a statutory period in which to redeem the property, which right may diminish the mortgagee’s ability to sell the property. |
| 3. | Legislative Limitations. In addition to anti-deficiency and related legislation, numerous other federal and state statutory provisions, including the federal bankruptcy laws and state laws affording relief to debtors, may interfere with or affect the ability of a secured mortgage lender to enforce its security interest. For example, a bankruptcy court may grant the debtor a reasonable time to cure a default on a mortgage loan, including a payment default. The court in certain instances may also reduce the monthly payments due under such mortgage loan, change the rate of interest, reduce the principal balance of the loan to the then-current appraised value of the related mortgaged property, alter the mortgage loan repayment schedule and grant priority of certain liens over the lien of the mortgage loan. If a court relieves a borrower’s obligation to repay amounts otherwise due on a mortgage loan, the mortgage loan servicer will not be required to advance such amounts, and any loss may be borne by the holders of securities backed by such loans. In addition, numerous federal and state consumer protection laws impose penalties for failure to comply with specific requirements in connection with origination and servicing of mortgage loans. |
| 4. | “Due-on-Sale” Provisions. Fixed-rate mortgage loans may contain a so-called “due-on-sale” clause permitting acceleration of the maturity of the mortgage loan if the borrower transfers the property. The Garn-St. Germain Depository Institutions Act of 1982 sets forth nine specific instances in which no mortgage lender covered by that Act may exercise a “due-on-sale” clause upon a transfer of property. The inability to enforce a “due-on-sale” clause or the lack of such a clause in mortgage loan documents may result in a mortgage loan being assumed by a purchaser of the property that bears an interest rate below the current market rate. |
| 5. | Usury Laws. Some states prohibit charging interest on mortgage loans in excess of statutory limits. If such limits are exceeded, substantial penalties may be incurred and, in some cases, enforceability of the obligation to pay principal and interest may be affected. |
| 6. | Governmental Action, Legislation and Regulation. Legislative, regulatory and enforcement actions seeking to prevent or restrict foreclosures or providing forbearance relief to borrowers of residential mortgage loans may adversely affect the value of Mortgage-Backed Securities (e.g., the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act). Legislative or regulatory initiatives by federal, state or local legislative bodies or administrative agencies, if enacted or adopted, could delay foreclosure or the exercise of other remedies, provide new defenses to foreclosure, or otherwise impair the ability of the loan servicer to foreclose or realize on a defaulted residential mortgage loan included in a pool of residential mortgage loans backing such residential Mortgage-Backed Securities. While the nature or extent of limitations on foreclosure or exercise of other remedies that may be enacted cannot be predicted, any such governmental actions that interfere with the foreclosure process or are designed to protect customers could increase the costs of such foreclosures or exercise of other remedies in respect of residential mortgage loans which collateralize Mortgage-Backed Securities held by a Fund, delay the timing or reduce the amount of recoveries on defaulted residential mortgage loans which collateralize Mortgage-Backed Securities held by a Fund, and consequently, could adversely impact the yields and distributions a Fund may receive in respect of its ownership of Mortgage-Backed Securities collateralized by residential mortgage loans. |
Government Guaranteed Mortgage-Backed Securities. There are several types of government guaranteed Mortgage-Backed Securities currently available, including guaranteed mortgage pass-through certificates and multiple class securities, which include guaranteed Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduit Certificates (“REMIC Certificates”), other collateralized mortgage obligations and stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities. Each of the Funds (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) is permitted to invest in other types of Mortgage-Backed Securities that may be available in the future, to the extent consistent with its investment policies and objective.
B-26
A Fund’s investments in Mortgage-Backed Securities may include securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or one of its agencies, authorities, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises, such as the Government National Mortgage Association (“Ginnie Mae”), Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Ginnie Mae securities are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government, which means that the U.S. Government guarantees that the interest and principal will be paid when due. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac securities are not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac have the ability to borrow from the U.S. Treasury, and as a result, they have historically been viewed by the market as high quality securities with low credit risks. From time to time, proposals have been introduced before Congress for the purpose of restricting or eliminating federal sponsorship of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. The Trust cannot predict what legislation, if any, may be proposed in the future in Congress as regards such sponsorship or which proposals, if any, might be enacted. Such proposals, if enacted, might materially and adversely affect the availability of government guaranteed Mortgage-Backed Securities and the liquidity and value of a Fund’s portfolio.
There is risk that the U.S. Government will not provide financial support to its agencies, authorities, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises. A Fund may purchase U.S. Government Securities that are not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government, such as those issued by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. The maximum potential liability of the issuers of some U.S. Government Securities held by a Fund may greatly exceed such issuers’ current resources, including such issuers’ legal right to support from the U.S. Treasury. It is possible that these issuers will not have the funds to meet their payment obligations in the future.
Below is a general discussion of certain types of guaranteed Mortgage-Backed Securities in which the Fund may invest.
• Ginnie Mae Certificates. Ginnie Mae is a wholly-owned corporate instrumentality of the United States. Ginnie Mae is authorized to guarantee the timely payment of the principal of and interest on certificates that are based on and backed by a pool of mortgage loans insured by the Federal Housing Administration (“FHA”), or guaranteed by the Veterans Administration (“VA”), or by pools of other eligible mortgage loans. In order to meet its obligations under any guaranty, Ginnie Mae is authorized to borrow from the U.S. Treasury in an unlimited amount. The National Housing Act provides that the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government is pledged to the timely payment of principal and interest by Ginnie Mae of amounts due on Ginnie Mae certificates.
• Fannie Mae Certificates. Fannie Mae is a stockholder-owned corporation chartered under an act of the United States Congress. Generally, Fannie Mae Certificates are issued and guaranteed by Fannie Mae and represent an undivided interest in a pool of mortgage loans (a “Pool”) formed by Fannie Mae. A Pool consists of residential mortgage loans either previously owned by Fannie Mae or purchased by it in connection with the formation of the Pool. The mortgage loans may be either conventional mortgage loans (i.e., not insured or guaranteed by any U.S. Government agency) or mortgage loans that are either insured by the FHA or guaranteed by the VA. However, the mortgage loans in Fannie Mae Pools are primarily conventional mortgage loans. The lenders originating and servicing the mortgage loans are subject to certain eligibility requirements established by Fannie Mae. Fannie Mae has certain contractual responsibilities. With respect to each Pool, Fannie Mae is obligated to distribute scheduled installments of principal and interest after Fannie Mae’s servicing and guaranty fee, whether or not received, to Certificate holders. Fannie Mae also is obligated to distribute to holders of Certificates an amount equal to the full principal balance of any foreclosed mortgage loan, whether or not such principal balance is actually recovered. The obligations of Fannie Mae under its guaranty of the Fannie Mae Certificates are obligations solely of Fannie Mae. See “Certain Additional Information with Respect to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae” below.
• Freddie Mac Certificates. Freddie Mac is a publicly held U.S. Government sponsored enterprise. A principal activity of Freddie Mac currently is the purchase of first lien, conventional, residential and multifamily mortgage loans and participation interests in such mortgage loans and their resale in the form of mortgage securities, primarily Freddie Mac Certificates. A Freddie Mac Certificate represents a pro rata interest in a group of mortgage loans or participations in mortgage loans (a “Freddie Mac Certificate group”) purchased by Freddie Mac. Freddie Mac guarantees to each registered holder of a Freddie Mac Certificate the timely payment of interest at the rate provided for by such Freddie Mac Certificate (whether or not received on the underlying loans). Freddie Mac also guarantees to each registered Certificate holder ultimate collection of all principal of the related mortgage loans, without any offset or deduction, but does not, generally, guarantee the timely payment of scheduled principal. The obligations of Freddie Mac under its guaranty of Freddie Mac Certificates are obligations solely of Freddie Mac. See “Certain Additional Information with Respect to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae” below.
The mortgage loans underlying the Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae Certificates consist of adjustable rate or fixed-rate mortgage loans with original terms to maturity of up to forty years. These mortgage loans are usually secured by first liens on one-to-four-family residential properties or multi-family projects. Each mortgage loan must meet the applicable standards set forth in the law creating Freddie Mac or Fannie Mae. A Freddie Mac Certificate group may include whole loans, participation interests in whole loans, undivided interests in whole loans and participations comprising another Freddie Mac Certificate group.
Under the direction of FHFA (as defined below), Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac have entered into a joint initiative to develop a common securitization platform (“CSP”) for the issuance of a uniform Mortgage-Backed Security (“UMBS”) (the “Single Security Initiative”), which would generally align the characteristics of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac Certificates. The Single Security Initiative is intended to maximize liquidity for both Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac Mortgage-Backed Securities in the “to-be-announced” market.
B-27
The CSP began issuing UMBS in June 2019. While the initial effects of the issuance of UMBS on the market for mortgage-related securities have been relatively minimal, the long-term effects are still uncertain.
Conventional Mortgage Loans. The conventional mortgage loans underlying the Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae Certificates consist of adjustable rate or fixed-rate mortgage loans normally with original terms to maturity of between five and thirty years. Substantially all of these mortgage loans are secured by first liens on one- to four-family residential properties or multi-family projects. Each mortgage loan must meet the applicable standards set forth in the law creating Freddie Mac or Fannie Mae. A Freddie Mac Certificate group may include whole loans, participation interests in whole loans, undivided interests in whole loans and participations comprising another Freddie Mac Certificate group.
Certain Additional Information with Respect to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae. The volatility and disruption that impacted the capital and credit markets during late 2008 and into 2009 have led to increased market concerns about Freddie Mac’s and Fannie Mae’s ability to withstand future credit losses associated with securities held in their investment portfolios, and on which they provide guarantees, without the direct support of the federal government. On September 6, 2008, both Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae were placed under the conservatorship of the Federal Housing Finance Agency (“FHFA”). Under the plan of conservatorship, the FHFA has assumed control of, and generally has the power to direct, the operations of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae, and is empowered to exercise all powers collectively held by their respective shareholders, directors and officers, including the power to (1) take over the assets of and operate Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae with all the powers of the shareholders, the directors, and the officers of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae and conduct all business of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae; (2) collect all obligations and money due to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae; (3) perform all functions of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae which are consistent with the conservator’s appointment; (4) preserve and conserve the assets and property of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae; and (5) contract for assistance in fulfilling any function, activity, action or duty of the conservator. In addition, in connection with the actions taken by the FHFA, the U.S. Treasury entered into certain preferred stock purchase agreements with each of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae which established the U.S. Treasury as the holder of a new class of senior preferred stock in each of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae, which stock was issued in connection with financial contributions from the U.S. Treasury to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae. The conditions attached to the financial contribution made by the U.S. Treasury to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae and the issuance of this senior preferred stock placed significant restrictions on the activities of Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae. Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae must obtain the consent of the U.S. Treasury to, among other things, (i) make any payment to purchase or redeem its capital stock or pay any dividend other than in respect of the senior preferred stock issued to the U.S. Treasury, (ii) issue capital stock of any kind, (iii) terminate the conservatorship of the FHFA except in connection with a receivership, or (iv) increase its debt beyond certain specified levels. In addition, significant restrictions were placed on the maximum size of each of Freddie Mac’s and Fannie Mae’s respective portfolios of mortgages and Mortgage-Backed Securities, and the purchase agreements entered into by Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae provide that the maximum size of their portfolios of these assets must decrease by a specified percentage each year. On June 16, 2010, FHFA ordered Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac’s stock de-listed from the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) after the price of common stock in Fannie Mae fell below the NYSE minimum average closing price of $1 for more than 30 days.
The FHFA and the White House have made public statements regarding plans to consider ending the conservatorships of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. In the event that Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are taken out of conservatorship, it is unclear how the capital structure of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac would be constructed and what effects, if any, there may be on Fannie Mae’s and Freddie Mac’s creditworthiness and guarantees of certain Mortgage-Backed Securities. It is also unclear whether the Treasury would continue to enforce its rights or perform its obligations under the senior preferred stock programs. Should Fannie Mae’s and Freddie Mac’s conservatorship end, there could be an adverse impact on the value of their securities, which could cause losses to a Fund.
Privately Issued Mortgage-Backed Securities. The Funds (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may invest in privately issued Mortgage-Backed Securities. Privately issued Mortgage-Backed Securities are generally backed by pools of conventional (i.e., non-government guaranteed or insured) mortgage loans. The seller or servicer of the underlying mortgage obligations will generally make representations and warranties to certificate-holders as to certain characteristics of the mortgage loans and as to the accuracy of certain information furnished to the trustee in respect of each such mortgage loan. Upon a breach of any representation or warranty that materially and adversely affects the interests of the related certificate-holders in a mortgage loan, the seller or servicer generally will be obligated either to cure the breach in all material respects, to repurchase the mortgage loan or, if the related agreement so provides, to substitute in its place a mortgage loan pursuant to the conditions set forth therein. Such a repurchase or substitution obligation may constitute the sole remedy available to the related certificate-holders or the trustee for the material breach of any such representation or warranty by the seller or servicer.
Mortgage Pass-Through Securities
To the extent consistent with their investment policies, the Funds (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may invest in both government guaranteed and privately issued mortgage pass-through securities (“Mortgage Pass-Throughs”) that are fixed or adjustable rate Mortgage-Backed Securities which provide for monthly payments that are a “pass-through” of the monthly interest and principal payments (including any prepayments) made by the individual borrowers on the pooled mortgage loans, net of any fees or other amounts paid to any guarantor, administrator and/or servicer of the underlying mortgage loans. The seller or servicer of the underlying mortgage obligations will generally make representations and warranties to certificate-holders as to certain characteristics of the mortgage loans
B-28
and as to the accuracy of certain information furnished to the trustee in respect of each such mortgage loan. Upon a breach of any representation or warranty that materially and adversely affects the interests of the related certificate-holders in a mortgage loan, the seller or servicer generally may be obligated either to cure the breach in all material respects, to repurchase the mortgage loan or, if the related agreement so provides, to substitute in its place a mortgage loan pursuant to the conditions set forth therein. Such a repurchase or substitution obligation may constitute the sole remedy available to the related certificate-holders or the trustee for the material breach of any such representation or warranty by the seller or servicer.
The following discussion describes certain aspects of only a few of the wide variety of structures of Mortgage Pass-Throughs that are available or may be issued.
General Description of Certificates. Mortgage Pass-Throughs may be issued in one or more classes of senior certificates and one or more classes of subordinate certificates. Each such class may bear a different pass-through rate. Generally, each certificate will evidence the specified interest of the holder thereof in the payments of principal or interest or both in respect of the mortgage pool comprising part of the trust fund for such certificates.
Any class of certificates may also be divided into subclasses entitled to varying amounts of principal and interest. If a REMIC election has been made, certificates of such subclasses may be entitled to payments on the basis of a stated principal balance and stated interest rate, and payments among different subclasses may be made on a sequential, concurrent, pro rata or disproportionate basis, or any combination thereof. The stated interest rate on any such subclass of certificates may be a fixed rate or one which varies in direct or inverse relationship to an objective interest index.
Generally, each registered holder of a certificate will be entitled to receive its pro rata share of monthly distributions of all or a portion of principal of the underlying mortgage loans or of interest on the principal balances thereof, which accrues at the applicable mortgage pass-through rate, or both. The difference between the mortgage interest rate and the related mortgage pass-through rate (less the amount, if any, of retained yield) with respect to each mortgage loan will generally be paid to the servicer as a servicing fee. Because certain adjustable rate mortgage loans included in a mortgage pool may provide for deferred interest (i.e., negative amortization), the amount of interest actually paid by a mortgagor in any month may be less than the amount of interest accrued on the outstanding principal balance of the related mortgage loan during the relevant period at the applicable mortgage interest rate. In such event, the amount of interest that is treated as deferred interest will generally be added to the principal balance of the related mortgage loan and will be distributed pro rata to certificate-holders as principal of such mortgage loan when paid by the mortgagor in subsequent monthly payments or at maturity.
Ratings. The ratings assigned by a rating organization to Mortgage Pass-Throughs generally address the likelihood of the receipt of distributions on the underlying mortgage loans by the related certificate-holders under the agreements pursuant to which such certificates are issued. A rating organization’s ratings normally take into consideration the credit quality of the related mortgage pool, including any credit support providers, structural and legal aspects associated with such certificates, and the extent to which the payment stream on such mortgage pool is adequate to make payments required by such certificates. A rating organization’s ratings on such certificates do not, however, constitute a statement regarding frequency of prepayments on the related mortgage loans. In addition, the rating assigned by a rating organization to a certificate may not address the possibility that, in the event of the insolvency of the issuer of certificates where a subordinated interest was retained, the issuance and sale of the senior certificates may be recharacterized as a financing and, as a result of such recharacterization, payments on such certificates may be affected. A rating organization may downgrade or withdraw a rating assigned by it to any Mortgage Pass-Through at any time, and no assurance can be made that any ratings on any Mortgage Pass-Throughs included in a Fund will be maintained, or that if such ratings are assigned, they will not be downgraded or withdrawn by the assigning rating organization.
In the past, rating agencies have placed on credit watch or downgraded the ratings previously assigned to a large number of mortgage-backed securities (which may include certain of the Mortgage-Backed Securities in which certain of the Funds may have invested or may in the future be invested), and may continue to do so in the future. In the event that any Mortgage-Backed Security held by a Fund is placed on credit watch or downgraded, the value of such Mortgage-Backed Security may decline and the Fund may consequently experience losses in respect of such Mortgage-Backed Security.
Credit Enhancement. Mortgage pools created by non-governmental issuers generally offer a higher yield than government and government-related pools because of the absence of direct or indirect government or agency payment guarantees. To lessen the effect of failures by obligors on underlying assets to make payments, Mortgage Pass-Throughs may contain elements of credit support. Credit support falls generally into two categories: (i) liquidity protection and (ii) protection against losses resulting from default by an obligor on the underlying assets. Liquidity protection refers to the provision of advances, generally by the entity administering the pools of mortgages, the provision of a reserve fund, or a combination thereof, to ensure, subject to certain limitations, that scheduled payments on the underlying pool are made in a timely fashion. Protection against losses resulting from default ensures ultimate payment of the obligations on at least a portion of the assets in the pool. Such credit support can be provided by, among other things, payment guarantees, letters of credit, pool insurance, subordination, or any combination thereof.
Subordination; Shifting of Interest; Reserve Fund. In order to achieve ratings on one or more classes of Mortgage Pass-Throughs, one or more classes of certificates may be subordinate certificates which provide that the rights of the subordinate certificate-holders to
B-29
receive any or a specified portion of distributions with respect to the underlying mortgage loans may be subordinated to the rights of the senior certificate holders. If so structured, the subordination feature may be enhanced by distributing to the senior certificate-holders on certain distribution dates, as payment of principal, a specified percentage (which generally declines over time) of all principal payments received during the preceding prepayment period (“shifting interest credit enhancement”). This will have the effect of accelerating the amortization of the senior certificates while increasing the interest in the trust fund evidenced by the subordinate certificates. Increasing the interest of the subordinate certificates relative to that of the senior certificates is intended to preserve the availability of the subordination provided by the subordinate certificates. In addition, because the senior certificate-holders in a shifting interest credit enhancement structure are entitled to receive a percentage of principal prepayments which is greater than their proportionate interest in the trust fund, the rate of principal prepayments on the mortgage loans may have an even greater effect on the rate of principal payments and the amount of interest payments on, and the yield to maturity of, the senior certificates.
In addition to providing for a preferential right of the senior certificate-holders to receive current distributions from the mortgage pool, a reserve fund may be established relating to such certificates (the “Reserve Fund”). The Reserve Fund may be created with an initial cash deposit by the originator or servicer and augmented by the retention of distributions otherwise available to the subordinate certificate-holders or by excess servicing fees until the Reserve Fund reaches a specified amount.
The subordination feature, and any Reserve Fund, are intended to enhance the likelihood of timely receipt by senior certificate-holders of the full amount of scheduled monthly payments of principal and interest due to them and will protect the senior certificate-holders against certain losses; however, in certain circumstances the Reserve Fund could be depleted and temporary shortfalls could result. In the event that the Reserve Fund is depleted before the subordinated amount is reduced to zero, senior certificate-holders will nevertheless have a preferential right to receive current distributions from the mortgage pool to the extent of the then outstanding subordinated amount. Unless otherwise specified, until the subordinated amount is reduced to zero, on any distribution date any amount otherwise distributable to the subordinate certificates or, to the extent specified, in the Reserve Fund will generally be used to offset the amount of any losses realized with respect to the mortgage loans (“Realized Losses”). Realized Losses remaining after application of such amounts will generally be applied to reduce the ownership interest of the subordinate certificates in the mortgage pool. If the subordinated amount has been reduced to zero, Realized Losses generally will be allocated pro rata among all certificate-holders in proportion to their respective outstanding interests in the mortgage pool.
Alternative Credit Enhancement. As an alternative, or in addition to the credit enhancement afforded by subordination, credit enhancement for Mortgage Pass-Throughs may be provided through bond insurers, or at the mortgage loan-level through mortgage insurance, hazard insurance, or through the deposit of cash, certificates of deposit, letters of credit, a limited guaranty or by such other methods as are acceptable to a rating agency. In certain circumstances, such as where credit enhancement is provided by bond insurers, guarantees or letters of credit, the security is subject to credit risk because of its exposure to the credit risk of an external credit enhancement provider.
Voluntary Advances. Generally, in the event of delinquencies in payments on the mortgage loans underlying the Mortgage Pass-Throughs, the servicer may agree to make advances of cash for the benefit of certificate-holders, but generally will do so only to the extent that it determines such voluntary advances will be recoverable from future payments and collections on the mortgage loans or otherwise.
Optional Termination. Generally, the servicer may, at its option with respect to any certificates, repurchase all of the underlying mortgage loans remaining outstanding at such time if the aggregate outstanding principal balance of such mortgage loans is less than a specified percentage (generally 5-10%) of the aggregate outstanding principal balance of the mortgage loans as of the cut-off date specified with respect to such series.
Multiple Class Mortgage-Backed Securities and Collateralized Mortgage Obligations. Each Fund (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may invest in multiple class securities including collateralized mortgage obligations (“CMOs”) and REMIC Certificates. These securities may be issued by U.S. Government agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises such as Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac or by trusts formed by private originators of, or investors in, mortgage loans, including savings and loan associations, mortgage bankers, commercial banks, insurance companies, investment banks and special purpose subsidiaries of the foregoing. In general, CMOs are debt obligations of a legal entity that are collateralized by, and multiple class Mortgage-Backed Securities represent direct ownership interests in, a pool of mortgage loans or Mortgage-Backed Securities the payments on which are used to make payments on the CMOs or multiple class Mortgage-Backed Securities.
Fannie Mae REMIC Certificates are issued and guaranteed as to timely distribution of principal and interest by Fannie Mae. In addition, Fannie Mae will be obligated to distribute the principal balance of each class of REMIC Certificates in full, whether or not sufficient funds are otherwise available.
Freddie Mac guarantees the timely payment of interest on Freddie Mac REMIC Certificates and also guarantees the payment of principal as payments are required to be made on the underlying mortgage participation certificates (“PCs”). PCs represent undivided interests in specified level payment, residential mortgages or participations therein purchased by Freddie Mac and placed in a PC pool. With respect to principal payments on PCs, Freddie Mac generally guarantees ultimate collection of all principal of the related mortgage loans without offset or deduction but the receipt of the required payments may be delayed. Freddie Mac also guarantees timely payment of principal of certain PCs.
B-30
CMOs and guaranteed REMIC Certificates issued by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are types of multiple class Mortgage-Backed Securities. The REMIC Certificates represent beneficial ownership interests in a REMIC trust, generally consisting of mortgage loans or Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac or Ginnie Mae guaranteed Mortgage-Backed Securities (the “Mortgage Assets”). The obligations of Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac under their respective guaranty of the REMIC Certificates are obligations solely of Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, respectively. See “Certain Additional Information with Respect to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae.”
CMOs and REMIC Certificates are issued in multiple classes. Each class of CMOs or REMIC Certificates, often referred to as a “tranche,” is issued at a specific adjustable or fixed interest rate and must be fully retired no later than its final distribution date. Principal prepayments on the mortgage loans or the Mortgage Assets underlying the CMOs or REMIC Certificates may cause some or all of the classes of CMOs or REMIC Certificates to be retired substantially earlier than their final distribution dates. Generally, interest is paid or accrues on all classes of CMOs or REMIC Certificates on a monthly basis.
The principal of and interest on the Mortgage Assets may be allocated among the several classes of CMOs or REMIC Certificates in various ways. In certain structures (known as “sequential pay” CMOs or REMIC Certificates), payments of principal, including any principal prepayments, on the Mortgage Assets generally are applied to the classes of CMOs or REMIC Certificates in the order of their respective final distribution dates. Thus, no payment of principal will be made on any class of sequential pay CMOs or REMIC Certificates until all other classes having an earlier final distribution date have been paid in full.
Additional structures of CMOs and REMIC Certificates include, among others, “parallel pay” CMOs and REMIC Certificates. Parallel pay CMOs or REMIC Certificates are those which are structured to apply principal payments and prepayments of the Mortgage Assets to two or more classes concurrently on a proportionate or disproportionate basis. These simultaneous payments are taken into account in calculating the final distribution date of each class.
A wide variety of REMIC Certificates may be issued in parallel pay or sequential pay structures. These securities include accrual certificates (also known as “Z-Bonds”), which only accrue interest at a specified rate until all other certificates having an earlier final distribution date have been retired and are converted thereafter to an interest-paying security, and planned amortization class (“PAC”) certificates, which are parallel pay REMIC Certificates that generally require that specified amounts of principal be applied on each payment date to one or more classes or REMIC Certificates (the “PAC Certificates”), even though all other principal payments and prepayments of the Mortgage Assets are then required to be applied to one or more other classes of the PAC Certificates. The scheduled principal payments for the PAC Certificates generally have the highest priority on each payment date after interest due has been paid to all classes entitled to receive interest currently. Shortfalls, if any, are added to the amount payable on the next payment date. The PAC Certificate payment schedule is taken into account in calculating the final distribution date of each class of PAC. In order to create PAC tranches, one or more tranches generally must be created that absorb most of the volatility in the underlying mortgage assets. These tranches tend to have market prices and yields that are much more volatile than other PAC classes.
Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities. Commercial mortgage-backed securities (“CMBS”) are a type of Mortgage Pass-Through that are primarily backed by a pool of commercial mortgage loans. The commercial mortgage loans are, in turn, generally secured by commercial mortgaged properties (such as office properties, retail properties, hospitality properties, industrial properties, healthcare related properties or other types of income producing real property). CMBS generally entitle the holders thereof to receive payments that depend primarily on the cash flow from a specified pool of commercial or multifamily mortgage loans. CMBS will be affected by payments, defaults, delinquencies and losses on the underlying mortgage loans. The underlying mortgage loans generally are secured by income producing properties such as office properties, retail properties, multifamily properties, manufactured housing, hospitality properties, industrial properties and self-storage properties. Because issuers of CMBS have no significant assets other than the underlying commercial real estate loans and because of the significant credit risks inherent in the underlying collateral, credit risk is a correspondingly important consideration with respect to the related CMBS. Certain of the mortgage loans underlying CMBS constituting part of the collateral interests may be delinquent, in default or in foreclosure.
Commercial real estate lending may expose a lender (and the related Mortgage-Backed Security) to a greater risk of loss than certain other forms of lending because it typically involves making larger loans to single borrowers or groups of related borrowers. In addition, in the case of certain commercial mortgage loans, repayment of loans secured by commercial and multifamily properties depends upon the ability of the related real estate project to generate income sufficient to pay debt service, operating expenses and leasing commissions and to make necessary repairs, tenant improvements and capital improvements, and in the case of loans that do not fully amortize over their terms, to retain sufficient value to permit the borrower to pay off the loan at maturity through a sale or refinancing of the mortgaged property. The net operating income from and value of any commercial property is subject to various risks, including changes in general or local economic conditions and/or specific industry segments; declines in real estate values; declines in rental or occupancy rates; increases in interest rates, real estate tax rates and other operating expenses; changes in governmental rules, regulations and fiscal policies; acts of God; terrorist threats and attacks and social unrest and civil disturbances. In addition, certain of the mortgaged properties securing the pools of commercial mortgage loans underlying CMBS may have a higher degree of geographic concentration in a few states or regions. Any deterioration in the real estate market or economy or adverse events in such states or regions, may increase the rate of delinquency and default experience (and as a consequence, losses) with respect to mortgage loans
B-31
related to properties in such state or region. Pools of mortgaged properties securing the commercial mortgage loans underlying CMBS may also have a higher degree of concentration in certain types of commercial properties. Accordingly, such pools of mortgage loans represent higher exposure to risks particular to those types of commercial properties. Certain pools of commercial mortgage loans underlying CMBS consist of a fewer number of mortgage loans with outstanding balances that are larger than average. If a mortgage pool includes mortgage loans with larger than average balances, any realized losses on such mortgage loans could be more severe, relative to the size of the pool, than would be the case if the aggregate balance of the pool were distributed among a larger number of mortgage loans. Certain borrowers or affiliates thereof relating to certain of the commercial mortgage loans underlying CMBS may have had a history of bankruptcy. Certain mortgaged properties securing the commercial mortgage loans underlying CMBS may have been exposed to environmental conditions or circumstances. The ratings in respect of certain of the CMBS comprising the Mortgage-Backed Securities may have been withdrawn, reduced or placed on credit watch since issuance. In addition, losses and/or appraisal reductions may be allocated to certain of such CMBS and certain of the collateral or the assets underlying such collateral may be delinquent and/or may default from time to time.
CMBS held by a Fund may be subordinated to one or more other classes of securities of the same series for purposes of, among other things, establishing payment priorities and offsetting losses and other shortfalls with respect to the related underlying mortgage loans. Realized losses in respect of the mortgage loans included in the CMBS pool and trust expenses generally will be allocated to the most subordinated class of securities of the related series. Accordingly, to the extent any CMBS is or becomes the most subordinated class of securities of the related series, any delinquency or default on any underlying mortgage loan may result in shortfalls, realized loss allocations or extensions of its weighted average life and will have a more immediate and disproportionate effect on the related CMBS than on a related more senior class of CMBS of the same series. Further, even if a class is not the most subordinate class of securities, there can be no assurance that the subordination offered to such class will be sufficient on any date to offset all losses or expenses incurred by the underlying trust. CMBS are typically not guaranteed or insured, and distributions on such CMBS generally will depend solely upon the amount and timing of payments and other collections on the related underlying commercial mortgage loans.
Stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities. The Funds (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may invest in stripped mortgage-backed securities (“SMBS”), which are derivative multiclass mortgage securities, issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities or non-governmental originators. SMBS are usually structured with two different classes: one that receives substantially all of the interest payments (the interest-only, or “IO” and/or the high coupon rate with relatively low principal amount, or “IOette”), and the other that receives substantially all of the principal payments (the principal-only, or “PO”), from a pool of mortgage loans.
Certain SMBS may not be readily marketable. The market value of POs generally is unusually volatile in response to changes in interest rates. The yields on IOs and IOettes are generally higher than prevailing market yields on other Mortgage-Backed Securities because their cash flow patterns are more volatile and there is a greater risk that the initial investment will not be fully recouped. A Fund’s investments in SMBS may require the Fund to sell certain of its portfolio securities to generate sufficient cash to satisfy certain income distribution requirements. These and other factors discussed in the section above, entitled “Illiquid Investments,” may impact the liquidity of investments in SMBS.
Non-Diversified Status
Because the Focused Value Fund is “non-diversified” under the Act, the Fund is subject only to certain federal tax diversification requirements. Pursuant to such requirements, the Fund must diversify its holdings so that, in general, at the close of each quarter of its taxable year, (a) at least 50% of the fair market value of the Fund’s total (gross) assets is comprised of cash, cash items, U.S. Government Securities and, securities of other regulated investment companies. and other securities limited in respect of any one issuer to an amount not greater in value than 5% of the value of the Fund’s total assets and to not more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer, and (b) not more than 25% of the value of its total (gross) assets is invested in the securities of any one issuer (other than U.S. Government Securities and securities of other regulated investment companies), two or more issuers controlled by the Fund and engaged in the same, similar or related trades or businesses, or certain publicly traded partnerships.
Options on Securities and Securities Indices and Foreign Currencies
Special Risks Associated with Options on Currency. An exchange-traded options position may be closed out only on an options exchange that provides a secondary market for an option of the same series. Although a Fund will generally purchase or write only those options for which there appears to be an active secondary market, there is no assurance that a liquid secondary market on an exchange will exist for any particular option, or at any particular time. For some options no secondary market on an exchange may exist. In such event, it might not be possible to effect closing transactions in particular options, with the result that a Fund would have to exercise its options in order to realize any profit and would incur transaction costs pursuant to the exercise of put options. If a Fund as an option writer is unable to effect a closing purchase transaction in a secondary market, it will not be able to sell the underlying currency (or security quoted or denominated in that currency), or dispose of the identified assets, until the option expires or it delivers the underlying currency upon exercise.
B-32
There is no assurance that higher than anticipated trading activity or other unforeseen events might not, at times, render certain of the facilities of the relevant clearinghouse inadequate, and thereby result in the institution by an exchange of special procedures which may interfere with the timely execution of customers’ orders.
A Fund may purchase and write over-the-counter options. Trading in over-the-counter options is subject to the risk that the other party will be unable or unwilling to close out options purchased or written by a Fund.
The amount of the premiums that a Fund may pay or receive may be adversely affected as new or existing institutions, including other investment companies, engage in or increase their option purchasing and writing activities.
Writing and Purchasing Call and Put Options on Securities and Securities Indices. Each Fund (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may write (sell) call and put options on any securities in which it may invest or any securities index consisting of securities in which it may invest. A Fund may write such options on securities that are listed on national domestic securities exchanges or foreign securities exchanges or traded in the over-the-counter market. A Fund may also, to the extent that it invests in foreign securities, write (sell) put and call options on foreign currencies. A call option written by a Fund obligates that Fund to sell specified securities to the holder of the option at a specified price if the option is exercised on or before the expiration date. Depending upon the type of call option, the purchaser of a call option either (i) has the right to any appreciation in the value of the security over a fixed price (the “exercise price”) on a certain date in the future (the “expiration date”) or (ii) has the right to any appreciation in the value of the security over the exercise price at any time prior to the expiration of the option. If the purchaser exercises the option, a Fund pays the purchaser the difference between the price of the security and the exercise price of the option. The premium, the exercise price and the market value of the security determine the gain or loss realized by a Fund as the seller of the call option. A Fund can also repurchase the call option prior to the expiration date, ending its obligation. In this case, the cost of entering into closing purchase transactions will determine the gain or loss realized by the Fund. All call options written by a Fund are covered, which means that such Fund will own the securities subject to the option as long as the option is outstanding or such Fund will use the other methods described below. A Fund’s purpose in writing call options is to realize greater income than would be realized on portfolio securities transactions alone. However, a Fund may forego the opportunity to profit from an increase in the market price of the underlying security.
A put option written by a Fund would obligate the Fund to purchase specified securities from the option holder at a specified price if, depending upon the type of put option, either (i) the option is exercised at any time on or before the expiration date or (ii) the option is exercised on the expiration date. All put options written by a Fund would be covered, which means that such Fund will identify on its books cash or liquid assets with a value at least equal to the exercise price of the put option (less any margin on deposit) or will use the other methods described below. For more information about these practices, see “Description of Investment Securities and Practices – Asset Segregation.”
The purpose of writing such options is to generate additional income for the Fund. However, in return for the option premium, each Fund accepts the risk that it may be required to purchase the underlying securities at a price in excess of the securities’ market value at the time of purchase.
In the case of a call option, the option may be “covered” if a Fund owns the instrument underlying the call or has an absolute and immediate right to acquire that instrument without additional cash consideration (or, if additional cash consideration is required, liquid assets in such amount are identified on the Fund’s books) upon conversion or exchange of other instruments held by it. A call option may also be covered if a Fund holds a call on the same instrument as the option written where the exercise price of the option held is (i) equal to or less than the exercise price of the option written, or (ii) greater than the exercise price of the option written provided the Fund identifies liquid assets in the amount of the difference. A put option is also covered if a Fund holds a put on the same instrument as the option written where the exercise price of the option held is (i) equal to or higher than the exercise price of the option written, or (ii) less than the exercise price of the option written provided the Fund identifies on its books liquid assets in the amount of the difference. A Fund may also cover options on securities by identifying cash or liquid assets, as permitted by applicable law, with a value, when added to any margin on deposit that is equal to the market value of the securities in the case of a call option. Identified cash or liquid assets may be quoted or denominated in any currency.
Each Fund may also write (sell) call and put options on any securities index comprised of securities in which it may invest. Options on securities indices are similar to options on securities, except that the exercise of securities index options requires cash payments and does not involve the actual purchase or sale of securities. In addition, securities index options are designed to reflect price fluctuations in a group of securities or segment of the securities market rather than price fluctuations in a single security.
A Fund may cover call options on a securities index by owning securities whose price changes are expected to be similar to those of the underlying index, or by having an absolute and immediate right to acquire such securities without additional cash consideration (or for additional consideration which has been identified by the Fund on its books) upon conversion or exchange of other securities in its portfolio. A Fund may also cover call and put options on a securities index by identifying cash or liquid assets, as permitted by applicable law, with a value, when added to any margin on deposit, that is equal to the market value of the underlying securities in the case of a call option, or the exercise price in the case of a put option, or by owning offsetting options as described above.
B-33
A Fund may terminate its obligations under an exchange traded call or put option by purchasing an option identical to the one it has written. Obligations under over-the-counter options may be terminated only by entering into an offsetting transaction with the counterparty to such option. Such purchases are referred to as “closing purchase transactions.”
Each Fund (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may also purchase put and call options on any securities in which it may invest or any securities index comprised of securities in which it may invest. A Fund may also enter into closing sale transactions in order to realize gains or minimize losses on options it had purchased.
A Fund may purchase call options in anticipation of an increase, or put options in anticipation of a decrease (“protective puts”), in the market value of securities or other instruments of the type in which it may invest. The purchase of a call option would entitle a Fund, in return for the premium paid, to purchase specified securities or other instruments at a specified price during the option period. A Fund would ordinarily realize a gain on the purchase of a call option if, during the option period, the value of such securities or other instruments exceeded the sum of the exercise price, the premium paid and transaction costs; otherwise the Fund would realize either no gain or a loss on the purchase of the call option.
The purchase of a put option would entitle a Fund, in exchange for the premium paid, to sell specified securities or other instruments at a specified price during the option period. The purchase of protective puts is usually designed to offset or hedge against a decline in the market value of a Fund’s securities or other instruments. Put options may also be purchased by a Fund for the purpose of affirmatively benefiting from a decline in the price of securities or other instruments which it does not own. A Fund would ordinarily realize a gain if, during the option period, the value of the underlying securities or other instruments decreased below the exercise price sufficiently to more than cover the premium and transaction costs; otherwise the Fund would realize either no gain or a loss on the purchase of the put option. Gains and losses on the purchase of protective put options would tend to be offset by countervailing changes in the value of the underlying portfolio securities or other instruments.
A Fund would purchase put and call options on securities indices for the same purposes as it would purchase options on individual securities. For a description of options on securities indices, see “Writing and Purchasing Call and Put Options on Securities and Securities Indices” above.
Risks Associated with Options Transactions. There is no assurance that a liquid secondary market on an options exchange will exist for any particular exchange-traded option or at any particular time. If a Fund is unable to effect a closing purchase transaction with respect to options it has written, the Fund will not be able to sell the underlying securities or dispose of the assets identified on its books to cover the position until the options expire or are exercised. Similarly, if a Fund is unable to effect a closing sale transaction with respect to options it has purchased, it will have to exercise the options in order to realize any profit and will incur transaction costs upon the purchase or sale of underlying securities.
Reasons for the absence of a liquid secondary market on an exchange include the following: (i) there may be insufficient trading interest in certain options; (ii) restrictions may be imposed by an exchange on opening or closing transactions or both; (iii) trading halts, suspensions or other restrictions may be imposed with respect to particular classes or series of options; (iv) unusual or unforeseen circumstances may interrupt normal operations on an exchange; (v) the facilities of an exchange or the Options Clearing Corporation may not at all times be adequate to handle current trading volume; or (vi) one or more exchanges could, for economic or other reasons, decide or be compelled at some future date to discontinue the trading of options (or a particular class or series of options), in which event the secondary market on that exchange (or in that class or series of options) would cease to exist, although outstanding options on that exchange that had been issued by the Options Clearing Corporation as a result of trades on that exchange would continue to be exercisable in accordance with their terms.
There can be no assurance that higher trading activity, order flow or other unforeseen events will not, at times, render certain of the facilities of the Options Clearing Corporation or various exchanges inadequate. Such events have, in the past, resulted in the institution by an exchange of special procedures, such as trading rotations, restrictions on certain types of order or trading halts or suspensions with respect to one or more options. These special procedures may limit liquidity.
A Fund may purchase and sell both options that are traded on U.S. and foreign exchanges and options traded over-the-counter with broker-dealers who make markets in these options. The ability to terminate over-the-counter options is more limited than with exchange-traded options and may involve the risk that broker-dealers participating in such transactions will not fulfill their obligations.
Transactions by each Fund in options will be subject to limitations established by each of the exchanges, boards of trade or other trading facilities on which such options are traded governing the maximum number of options in each class which may be written or purchased by a single investor or group of investors acting in concert regardless of whether the options are written or purchased on the same or different exchanges, boards of trade or other trading facility or are held in one or more accounts or through one or more brokers. Thus, the number of options which a Fund may write or purchase may be affected by options written or purchased by other investment advisory clients of the Investment Adviser. An exchange, board of trade or other trading facility may order the liquidation of positions found to be in excess of these limits, and it may impose certain other sanctions.
B-34
The writing and purchase of options is a highly specialized activity which involves investment techniques and risks different from those associated with ordinary portfolio securities transactions. The use of options to seek to increase total return involves the risk of loss if the Investment Adviser is incorrect in its expectation of fluctuations in securities prices or interest rates. The successful use of options for hedging purposes also depends in part on the ability of the Investment Adviser to manage future price fluctuations and the degree of correlation between the options and securities (or currency) markets. If the Investment Adviser is incorrect in its expectation of changes in securities prices or determination of the correlation between the securities or securities indices on which options are written and purchased and the securities in a Fund’s investment portfolio, the Fund may incur losses that it would not otherwise incur. The writing of options could increase a Fund’s portfolio turnover rate and, therefore, associated brokerage commissions or spreads.
Writing and Purchasing Call and Put Options on Currency. A Fund (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may, to the extent that it invests in foreign securities, write and purchase put and call options on foreign currencies for the purpose of protecting against declines in the U.S. dollar value of foreign portfolio securities and against increases in the U.S. dollar cost of foreign securities to be acquired. As with other kinds of option transactions, however, the writing of an option on foreign currency will constitute only a partial hedge, up to the amount of the premium received. If an option that a Fund has written is exercised, the Fund could be required to purchase or sell foreign currencies at disadvantageous exchange rates, thereby incurring losses. The purchase of an option on foreign currency may constitute an effective hedge against exchange rate fluctuations; however, in the event of exchange rate movements adverse to a Fund’s position, the Fund may forfeit the entire amount of the premium plus related transaction costs. Options on foreign currencies may be traded on U.S. and foreign exchanges or over-the-counter.
Options on currency may also be used for cross-hedging purposes, which involves writing or purchasing options on one currency to seek to hedge against changes in exchange rates for a different currency with a pattern of correlation, or to seek to increase total return when the Investment Adviser anticipates that the currency will appreciate or depreciate in value, but the securities quoted or denominated in that currency do not present attractive investment opportunities and are not included in the Fund’s portfolio.
A currency call option written by a Fund obligates the Fund to sell a specified currency to the holder of the option at a specified price if the option is exercised before the expiration date. A currency put option written by a Fund obligates the Fund to purchase a specified currency from the option holder at a specified price if the option is exercised before the expiration date. The writing of currency options involves a risk that a Fund will, upon exercise of the option, be required to sell currency subject to a call at a price that is less than the currency’s market value or be required to purchase currency subject to a put at a price that exceeds the currency’s market value. Written put and call options on foreign currencies may be covered in a manner similar to written put and call options on securities and securities indices described under “Writing and Purchasing Call and Put Options on Securities and Securities Indices” above.
A Fund may terminate its obligations under a call or put option by purchasing an option identical to the one it has written. Such purchases are referred to as “closing purchase transactions.” A Fund may enter into closing sale transactions in order to realize gains or minimize losses on options purchased by the Fund.
A Fund may purchase call options on foreign currency in anticipation of an increase in the U.S. dollar value of currency in which securities to be acquired by a Fund are quoted or denominated. The purchase of a call option would entitle the Fund, in return for the premium paid, to purchase specified currency at a specified price during the option period. A Fund would ordinarily realize a gain if, during the option period, the value of such currency exceeded the sum of the exercise price, the premium paid and transaction costs; otherwise the Fund would realize either no gain or a loss on the purchase of the call option.
A Fund may purchase put options in anticipation of a decline in the U.S. dollar value of currency in which securities in its portfolio are quoted or denominated (“protective puts”). The purchase of a put option would entitle a Fund, in exchange for the premium paid, to sell specified currency at a specified price during the option period. The purchase of protective puts is usually designed to offset or hedge against a decline in the dollar value of a Fund’s portfolio securities due to currency exchange rate fluctuations. A Fund would ordinarily realize a gain if, during the option period, the value of the underlying currency decreased below the exercise price sufficiently to more than cover the premium and transaction costs; otherwise the Fund would realize either no gain or a loss on the purchase of the put option. Gains and losses on the purchase of protective put options would tend to be offset by countervailing changes in the value of the underlying currency.
In addition to using options for the hedging purposes described above, the Funds may use options on currency to seek to increase total return. The Funds may write (sell) put and call options on any currency in an attempt to realize greater income than would be realized on portfolio securities transactions alone. However, in writing call options for additional income, the Funds may forego the opportunity to profit from an increase in the market value of the underlying currency. Also, when writing put options, the Funds accept, in return for the option premium, the risk that they may be required to purchase the underlying currency at a price in excess of the currency’s market value at the time of purchase.
Pooled Investment Vehicles
Each Fund may invest in securities of pooled investment vehicles, including other investment companies and ETFs. A Fund will indirectly bear its proportionate share of any management fees and other expenses paid by pooled investment vehicles in which it invests, in addition to the management fees (and other expenses) of the Fund. A Fund’s investments in other investment companies are subject
B-35
to statutory limitations prescribed by the Act, including in certain circumstances a prohibition on the Fund acquiring more than 3% of the voting shares of any other investment company, and a prohibition on investing more than 5% of the Fund’s total assets in securities of any one investment company or more than 10% of its total assets in the securities of all investment companies.
Subject to applicable law and/or pursuant to an exemptive order obtained from the SEC or under an exemptive rule adopted by the SEC, the Fund may invest in other investment companies, including ETFs and money market funds, beyond the statutory limits described above or otherwise provided that certain conditions are met. Some of those other investment companies may be funds for which an Investment Adviser or any of its affiliates serves as investment adviser, administrator and/or distributor. Although each Fund does not expect to do so in the foreseeable future, each Fund is authorized to invest substantially all of its assets in a single open-end investment company or series thereof that has substantially the same investment policies and fundamental restrictions as the Fund. Additionally, if a Fund serves as an “underlying fund” to another Goldman Sachs Fund or unaffiliated investment company, the Fund’s ability to invest in other investment companies and private funds may be limited and, under these circumstances, the Fund’s investments in other investment companies and private funds will be consistent with applicable law and/or exemptive relief obtained from the SEC.
Each Fund may purchase shares of investment companies investing primarily in foreign securities, including “country funds.” Country funds have portfolios consisting primarily of securities of issuers located in specified foreign countries or regions.
ETFs are shares of pooled investment vehicles issuing shares which are traded like traditional equity securities on a stock exchange. An ETF generally represents a portfolio of securities or other assets, which is often designed to track a particular market segment or index. An investment in an ETF, like one in any pooled investment vehicle, carries risks of its underlying securities. An ETF may fail to accurately track the returns of the market segment or index that it is designed to track, and the price of an ETF’s shares may fluctuate or lose money. In addition, because they, unlike other pooled investment vehicles, are traded on an exchange, ETFs are subject to the following risks: (i) the market price of the ETF’s shares may trade at a premium or discount to the ETF’s NAV; (ii) an active trading market for an ETF may not develop or be maintained; and (iii) there is no assurance that the requirements of the exchange necessary to maintain the listing of the ETF will continue to be met or remain unchanged. In the event substantial market or other disruptions affecting ETFs should occur in the future, the liquidity and value of a Fund’s shares could also be substantially and adversely affected.
Portfolio Turnover
Each Fund may engage in active short-term trading to benefit from price disparities among different issues of securities or among the markets for equity securities, or for other reasons. As a result of active management, it is anticipated that the portfolio turnover rate may vary greatly from year to year as well as within a particular year, and may be affected by changes in the holdings of specific issuers, changes in country and currency weightings, cash requirements for redemption of shares and by requirements which enable the Funds to receive favorable tax treatment. The Funds are not restricted by policy with regard to portfolio turnover and will make changes in their investment portfolio from time to time as business and economic conditions as well as market prices may dictate.
Preferred Stock, Warrants and Stock Purchase Rights
Each Fund may invest in preferred stock, warrants and stock purchase rights (“rights”) (in addition to those acquired in units or attached to other securities). Preferred stocks are securities that represent an ownership interest providing the holder with claims on the issuer’s earnings and assets before common stock owners but after bond owners. Unlike debt securities, the obligations of an issuer of preferred stock, including dividend and other payment obligations, may not typically be accelerated by the holders of such preferred stock on the occurrence of an event of default (such as a covenant default or filing of a bankruptcy petition) or other non-compliance by the issuer with the terms of the preferred stock. Often, however, on the occurrence of any such event of default or non-compliance by the issuer, preferred stockholders will be entitled to gain representation on the issuer’s board of directors or increase their existing board representation. In addition, preferred stockholders may be granted voting rights with respect to certain issues on the occurrence of any event of default.
Warrants and other rights are options that entitle the holder to buy equity securities at a specific price for a specific period of time. A Fund will invest in warrants and rights only if such equity securities are deemed appropriate by the Investment Adviser for investment by the Fund. Warrants and rights have no voting rights, receive no dividends and have no rights with respect to the assets of the issuer.
Private Investments in Public Equity
The Focused Value, Small Cap Value and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds may purchase equity securities in a private placement that are issued by issuers who have outstanding, publicly-traded equity securities of the same class (“private investments in public equity” or “PIPES”). Shares in PIPES generally are not registered with the SEC until after a certain time period from the date the private sale is completed. This restricted period can last many months. Until the public registration process is completed, PIPES are restricted as to resale and the Funds cannot freely trade the securities. Generally such restrictions cause the PIPES to be illiquid during this time. PIPES may contain provisions that the issuer will pay specified financial penalties to the holder if the issuer does not publicly register the restricted equity securities within a specified period of time, but there is no assurance that the restricted equity securities will be publicly registered, or that the registration will remain in effect.
B-36
Real Estate Investment Trusts
Each Fund may invest in shares of real estate investment trusts (“REITs”). REITs are pooled investment vehicles which invest primarily in real estate or real estate related loans. REITs are generally classified as equity REITs, mortgage REITs or a combination of equity and mortgage REITs. Equity REITs invest the majority of their assets directly in real property and derive income primarily from the collection of rents. Equity REITs can also realize capital gains by selling properties that have appreciated in value. Mortgage REITs invest the majority of their assets in real estate mortgages and derive income from the collection of interest payments. Like regulated investment companies such as the Funds, REITs are not taxed on income distributed to shareholders provided they comply with certain requirements under the Code. A Fund will indirectly bear its proportionate share of any expenses paid by REITs in which it invests in addition to the expenses paid by a Fund.
Investing in REITs involves certain unique risks. Equity REITs may be affected by changes in the value of the underlying property owned by such REITs, while mortgage REITs may be affected by the quality of any credit extended. REITs are dependent upon management skills, are not diversified (except to the extent the Code requires), and are subject to the risks of financing projects. REITs are subject to heavy cash flow dependency, default by borrowers, self-liquidation, and the possibilities of failing to qualify for the exemption from tax for distributed income under the Code and failing to maintain their exemptions from the Act. REITs (especially mortgage REITs) are also subject to interest rate risks.
Repurchase Agreements
Each Fund may enter into repurchase agreements with counterparties approved by the Investment Adviser pursuant to procedures approved by the Board of Trustees that furnish collateral at least equal in value or market price to the amount of the repurchase obligation. The collateral may consist of security (government or corporate) of any or no credit rating. Each Fund may also enter into repurchase agreements involving obligations other than U.S. Government Securities (such as foreign government securities, commercial paper, corporate bonds, mortgage loans and equities), which may be subject to additional risks. A repurchase agreement is an arrangement under which a Fund purchases securities and the seller agrees to repurchase the securities within a particular time and at a specified price. Custody of the securities is maintained by a Fund’s custodian (or subcustodian). The repurchase price may be higher than the purchase price, the difference being income to a Fund, or the purchase and repurchase prices may be the same, with interest at a stated rate due to a Fund together with the repurchase price on repurchase. In either case, the income to a Fund is unrelated to the interest rate on the security subject to the repurchase agreement.
For purposes of the Act and generally for tax purposes, a repurchase agreement is deemed to be a loan from a Fund to the seller of the security. For other purposes, it is not always clear whether a court would consider the security purchased by a Fund subject to a repurchase agreement as being owned by a Fund or as being collateral for a loan by a Fund to the seller. In the event of commencement of bankruptcy or insolvency proceedings with respect to the seller of the security before repurchase of the security under a repurchase agreement, a Fund may encounter delay and incur costs before being able to sell the security. Such a delay may involve loss of interest or a decline in value of the security. If the court characterizes the transaction as a loan and a Fund has not perfected a security interest in the security, a Fund may be required to return the security to the seller’s estate and be treated as an unsecured creditor of the seller. As an unsecured creditor, a Fund would be at risk of losing some or all of the principal and interest involved in the transaction.
Apart from the risk of bankruptcy or insolvency proceedings, there is also the risk that the seller may fail to repurchase the security. However, if the market value of the security subject to the repurchase agreement becomes less than the repurchase price (including accrued interest), a Fund will direct the seller of the security to deliver additional securities so that the market value of all securities subject to the repurchase agreement equals or exceeds the repurchase price. Certain repurchase agreements which provide for settlement in more than seven days can be liquidated before the nominal fixed term on seven days or less notice.
The Funds, together with other registered investment companies having management agreements with the Investment Adviser or its affiliates, may transfer uninvested cash balances into a single joint account, the daily aggregate balance of which will be invested in one or more repurchase agreements.
Risks of Qualified Financial Contracts
Regulations adopted by federal banking regulators under Dodd-Frank, which took effect throughout 2019, require that certain qualified financial contracts (“QFCs”) with counterparties that are part of U.S. or foreign global systemically important banking organizations be amended to include contractual restrictions on close-out and cross-default rights. QFCs include, but are not limited to, securities contracts, commodities contracts, forward contracts, repurchase agreements, securities lending agreements and swaps agreements, as well as related master agreements, security agreements, credit enhancements, and reimbursement obligations. If a covered counterparty of a Fund or certain of the covered counterparty’s affiliates were to become subject to certain insolvency proceedings, the Fund may be temporarily unable to exercise certain default rights, and the QFC may be transferred to another entity. These requirements may impact a Fund’s credit and counterparty risks.
B-37
Short Sales Against the Box
The Funds (other than the U.S. Equity ESG Fund) may engage in short sales against the box. In a short sale, the seller sells a borrowed security and has a corresponding obligation to the lender to return the identical security. The seller does not immediately deliver the securities sold and is said to have a short position in those securities until delivery occurs. While a short sale is made by selling a security the seller does not own. A short sale is “against the box” to the extent that the seller contemporaneously owns or has the right to obtain, at no added cost, securities identical to those sold short. It may be entered into by a Fund, for example, to lock in a sales price for a security the Fund does not wish to sell immediately. If a Fund sells securities short against the box, it may protect itself from loss if the price of the securities declines in the future, but will lose the opportunity to profit on such securities if the price rises.
If a Fund effects a short sale of securities at a time when it has an unrealized gain on the securities, it may be required to recognize that gain as if it had actually sold the securities (as a “constructive sale”) on the date it effects the short sale. However, such constructive sale treatment may not apply if a Fund closes out the short sale with securities other than the appreciated securities held at the time of the short sale and if certain other conditions are satisfied. Uncertainty regarding the tax consequences of effecting short sales may limit the extent to which a Fund may effect short sales.
Temporary Investments
Each Fund may, for temporary defensive purposes, invest up to 100% of its total assets in: U.S. Government Securities; commercial paper rated at least A-2 by Standard & Poor’s, P-2 by Moody’s or having a comparable credit rating by another nationally recognized statistical rating organization (“NRSRO”) (or if unrated, determined by the Investment Adviser to be of comparable credit quality); certificates of deposit; bankers’ acceptances; repurchase agreements; non-convertible preferred stocks and non-convertible corporate bonds with a remaining maturity of less than one year; ETFs and other investment companies; and cash items. When a Fund’s assets are invested in such instruments, the Fund may not be achieving its investment objective.
U.S. Government Securities
Each Fund may invest in U.S. Government Securities. Some U.S. Government Securities (such as Treasury bills, notes and bonds, which differ only in their interest rates, maturities and times of issuance) are supported by the full faith and credit of the United States. Others, such as obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises, are supported either by (i) the right of the issuer to borrow from the U.S. Treasury, (ii) the discretionary authority of the U.S. Government to purchase certain obligations of the issuer or (iii) only the credit of the issuer. The U.S. Government is under no legal obligation, in general, to purchase the obligations of its agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises. No assurance can be given that the U.S. Government will provide financial support to U.S. Government agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises in the future, and the U.S. Government may be unable to pay debts when due.
U.S. Government Securities include (to the extent consistent with the Act) securities for which the payment of principal and interest is backed by an irrevocable letter of credit issued by the U.S. Government, or its agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises. U.S. Government Securities may also include (to the extent consistent with the Act) participations in loans made to foreign governments or their agencies that are guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. Government or its agencies, instrumentalities or sponsored enterprises. The secondary market for certain of these participations is extremely limited. These and other factors discussed in the section above, entitled “Illiquid Investments,” may impact the liquidity of investments in these participations.
Each Fund may also purchase U.S. Government Securities in private placements and may also invest in separately traded principal and interest components of securities guaranteed or issued by the U.S. Treasury that are traded independently under the separate trading of registered interest and principal of securities program (“STRIPS”). Each Fund may also invest in zero coupon U.S. Treasury securities and in zero coupon securities issued by financial institutions which represent a proportionate interest in underlying U.S. Treasury securities.
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities. The Focused Value Fund may invest in U.S. Government Securities called “Treasury inflation-protected securities” or “TIPS,” which are fixed income securities whose principal value is periodically adjusted according to the rate of inflation. The interest rate on TIPS is fixed at issuance, but over the life of the bond this interest may be paid on an increasing or decreasing principal value that has been adjusted for inflation. Although repayment of the greater of the adjusted or original bond principal upon maturity is guaranteed, the market value of TIPS is not guaranteed, and will fluctuate.
The values of TIPS generally fluctuate in response to changes in real interest rates, which are in turn tied to the relationship between nominal interest rates and the rate of inflation. If inflation were to rise at a faster rate than nominal interest rates, real interest rates will decline, leading to an increase in the value of TIPS. In contrast, if nominal interest rates were to increase at a faster rate than inflation, real interest rates will rise, leading to a decrease in the value of TIPS. If inflation is lower than expected during the period the Fund holds TIPS, the Fund may earn less on the TIPS than on a conventional bond. If interest rates rise due to reasons other than inflation
B-38
(for example, due to changes in the currency exchange rates), investors in TIPS may not be protected to the extent that the increase is not reflected in the bonds’ inflation measure. There can be no assurance that the inflation index for TIPS will accurately measure the real rate of inflation in the prices of goods and services.
Any increase in principal value of TIPS caused by an increase in the consumer price index is taxable in the year the increase occurs, even though the Fund holding TIPS will not receive cash representing the increase at that time. As a result, the Fund could be required at times to liquidate other investments, including when it is not advantageous to do so, in order to satisfy its distribution requirements as a regulated investment company.
If the Fund invests in TIPS, it will be required to treat as original issue discount any increase in the principal amount of the securities that occurs during the course of its taxable year. If the Fund purchases such inflation protected securities that are issued in stripped form, either as stripped bonds or coupons, it will be treated as if it had purchased a newly issued debt instrument having original issue discount.
Because the Fund is required to distribute substantially all of its net investment income (including accrued original issue discount), the Fund’s investment in either zero coupon bonds or TIPS may require it to distribute to shareholders an amount greater than the total cash income it actually receives. Accordingly, in order to make the required distributions, the Fund may be required to borrow or liquidate securities.
Variable and Floating Rate Securities
The interest rates payable on certain debt securities in which a Fund may invest are not fixed and may fluctuate based upon changes in market rates. Variable and floating rate obligations are debt instruments issued by companies or other entities with interest rates that reset periodically (typically, daily, monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually) in response to changes in the market rate of interest on which the interest rate is based. Moreover, such obligations may fluctuate in value in response to interest rate changes if there is a delay between changes in market interest rates and the interest reset date for the obligation, or for other reasons. The value of these obligations is generally more stable than that of a fixed rate obligation in response to changes in interest rate levels, but they may decline in value if their interest rates do not rise as much, or as quickly, as interest rates in general. Conversely, floating rate securities will not generally increase in value if interest rates decline.
When-Issued Securities and Forward Commitments
Each Fund may purchase securities on a when-issued basis or purchase or sell securities on a forward commitment basis beyond the customary settlement time. These transactions involve a commitment by a Fund to purchase or sell securities at a future date. The price of the underlying securities (usually expressed in terms of yield) and the date when the securities will be delivered and paid for (the settlement date) are fixed at the time the transaction is negotiated. In addition, recently finalized rules of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (“FINRA”) include mandatory margin requirements that require a Fund to post collateral in connection with its TBA transactions. There is no similar requirement applicable to a Fund’s TBA counterparties. The required collateralization of TBA trades could increase the cost of TBA transactions to a Fund and impose added operational complexity. When-issued purchases and forward commitment transactions are negotiated directly with the other party, and such commitments are not traded on exchanges. A Fund will generally purchase securities on a when-issued basis or purchase or sell securities on a forward commitment basis only with the intention of completing the transaction and actually purchasing or selling the securities. If deemed advisable as a matter of investment strategy, however, a Fund may dispose of or negotiate a commitment after entering into it. A Fund may also sell securities it has committed to purchase before those securities are delivered to the Fund on the settlement date. A Fund may realize capital gains or losses in connection with these transactions. For purposes of determining a Fund’s duration, the maturity of when-issued or forward commitment securities for fixed rate obligations will be calculated from the commitment date. A Fund is generally required to identify on its books cash and liquid assets in an amount sufficient to meet the purchase price unless the Fund’s obligations are otherwise covered. Alternatively, a Fund may enter into offsetting contracts for the forward sale of other securities that it owns. Securities purchased or sold on a when-issued or forward commitment basis involve a risk of loss if the value of the security to be purchased declines prior to the settlement date or if the value of the security to be sold increases prior to the settlement date.
Zero Coupon Bonds
Each Fund’s investments in fixed income securities may include zero coupon bonds. Zero coupon bonds are debt obligations issued or purchased at a discount from face value. The discount approximates the total amount of interest the bonds would have accrued and compounded over the period until maturity. A zero coupon bond pays no interest to its holder during its life and its value consists of the difference between its face value at maturity and its cost. Such investments benefit the issuer by mitigating its need for cash to meet debt service but also require a higher rate of return to attract investors who are willing to defer receipt of such cash. Such investments may experience greater volatility in market value than debt obligations which provide for regular payments of interest. Moreover, zero coupon bonds involve the additional risk that, unlike securities that periodically pay interest to maturity, the Fund will realize no cash until a specified future payment date unless a portion of such securities is sold and, if the issuer of such securities defaults, the Fund may obtain no return at all on its investment. The valuation of such investments requires judgment regarding the collection of
B-39
futures payments. The Fund will accrue income on such investments for each taxable year which (net of deductible expenses, if any) is distributable to shareholders and which, because no cash is generally received at the time of accrual, may require the liquidation of other portfolio securities to obtain sufficient cash to satisfy the Fund’s distribution obligations.
Special Note Regarding Regulatory Changes and Other Market Events
Federal, state, and foreign governments, regulatory agencies, and self-regulatory organizations may take actions that affect the regulation of the Funds or the instruments in which the Funds invest, or the issuers of such instruments, in ways that are unforeseeable. Future legislation or regulation or other governmental actions could limit or preclude the Funds’ ability to achieve its investment objective or otherwise adversely impact an investment in the Funds. Furthermore, worsened market conditions, including as a result of U.S. government shutdowns or the perceived creditworthiness of the United States, could have a negative impact on securities markets.
The Funds’ investments, payment obligations and financing terms may be based on floating rates, such as London Interbank Offer Rate (“LIBOR”), EURIBOR and other similar types of reference rates (each, a “Reference Rate”). On July 27, 2017, the Chief Executive of the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) which regulates LIBOR, announced that the FCA will no longer persuade nor compel banks to submit rates for the calculation of LIBOR and certain other Reference Rates after 2021. Such announcement indicates that the continuation of LIBOR and other Reference Rates on the current basis cannot and will not be guaranteed after 2021. This announcement and any additional regulatory or market changes may have an adverse impact on a Fund’s investments, performance or financial condition. Until then, the Funds may continue to invest in instruments that reference such rates or otherwise use such Reference Rates due to favorable liquidity or pricing.
In advance of 2021, regulators and market participants will seek to work together to identify or develop successor Reference Rates (e.g., the Secured Overnight Financing Rate, which is likely to replace U.S. dollar LIBOR and measures the cost of overnight borrowings through repurchase agreement transactions collateralized with U.S. Treasury securities) and how the calculation of associated spreads (if any) should be adjusted. Additionally, prior to 2021, it is expected that industry trade associations and participants will focus on the transition mechanisms by which the Reference Rates and spreads (if any) in existing contracts or instruments may be amended, whether through marketwide protocols, fallback contractual provisions, bespoke negotiations or amendments or otherwise. Nonetheless, the termination of certain Reference Rates presents risks to the Funds. At this time, it is not possible to exhaustively identify or predict the effect of any such changes, any establishment of alternative Reference Rates or any other reforms to Reference Rates that may be enacted in the United Kingdom or elsewhere. The elimination of a Reference Rate or any other changes or reforms to the determination or supervision of Reference Rates may affect the value, liquidity or return on certain Fund investments and may result in costs incurred in connection with closing out positions and entering into new trades, adversely impacting a Fund’s overall financial condition or results of operations. The impact of any successor or substitute Reference Rate, if any, will vary on an investment-by-investment basis, and any differences may be material and/or create material economic mismatches, especially if investments are used for hedging or similar purposes. In addition, although certain Fund investments may provide for a successor or substitute Reference Rate (or terms governing how to determine a successor or substitute Reference Rate) if the Reference Rate becomes unavailable, certain Fund investments may not provide such a successor or substitute Reference Rate (or terms governing how to determine a successor or substitute Reference Rate). Accordingly, there may be disputes as to: (i) any successor or substitute Reference Rate; or (ii) the enforceability of any Fund investment that does not provide such a successor or substitute Reference Rate (or terms governing how to determine a successor or substitute Reference Rate). The Investment Adviser, Goldman Sachs and/or their affiliates may have discretion to determine a successor or substitute Reference Rate, including any price or other adjustments to account for differences between the successor or substitute Reference Rate and the previous rate. The successor or substitute Reference Rate and any adjustments selected may negatively impact a Fund’s investments, performance or financial condition, including in ways unforeseen by the Investment Adviser, Goldman Sachs and/or their affiliates. In addition, any successor or substitute Reference Rate and any pricing adjustments imposed by a regulator or by counterparties or otherwise may adversely affect a Fund’s performance and/or NAV, and may expose a Fund to additional tax, accounting and regulatory risks.
In the aftermath of the 2007-2008 financial crisis, the financial sector experienced reduced liquidity in credit and other fixed income markets, and an unusually high degree of volatility, both domestically and internationally. While entire markets were impacted, issuers that had exposure to the real estate, mortgage and credit markets were particularly affected. The instability in the financial markets led the U.S. Government to take a number of unprecedented actions designed to support certain financial institutions and certain segments of the financial markets. For example, Dodd-Frank, which was enacted in 2010, provides for broad regulation of financial institutions, consumer financial products and services, broker-dealers, over-the-counter derivatives, investment advisers, credit rating agencies and mortgage lending.
Governments or their agencies may also acquire distressed assets from financial institutions and acquire ownership interests in those institutions. The implications of government ownership and disposition of these assets are unclear, and such ownership or disposition may have positive or negative effects on the liquidity, valuation and performance of the Funds’ portfolio holdings.
In addition, global economies and financial markets are becoming increasingly interconnected, and political, economic and other conditions and events (including, but not limited to, natural disasters, pandemics, epidemics, and social unrest) in one country, region, or financial market may adversely impact issuers in a different country, region or financial market. Furthermore, the occurrence of, among other events, natural or man-made disasters, severe weather or geological events, fires, floods, earthquakes, outbreaks of disease (such as COVID-19, avian influenza or H1N1/09), epidemics, pandemics, malicious acts, cyber-attacks, terrorist acts or the
B-40
occurrence of climate change, may also adversely impact the performance of a Fund. Such events may result in, among other things, closing borders, exchange closures, health screenings, healthcare service delays, quarantines, cancellations, supply chain disruptions, lower consumer demand, market volatility and general uncertainty. Such events could adversely impact issuers, markets and economies over the short- and long-term, including in ways that cannot necessarily be foreseen. A Fund could be negatively impacted if the value of a portfolio holding were harmed by such political or economic conditions or events. Moreover, such negative political and economic conditions and events could disrupt the processes necessary for a Fund’s operations. See “Special Note Regarding Operational, Cyber Security and Litigation Risks” for additional information on operational risks.
Moreover, in response to the outbreak of COVID-19, as with other serious economic disruptions, governmental authorities and regulators are enacting significant fiscal and monetary policy changes, including, among other things, lowering interest rates. Interest rates in the United States are currently at historically low levels. During periods when interest rates are low (or negative), a Fund’s yield (or total return) may also be low and fall below zero. Very low or negative interest rates may magnify interest rate risk. Changing interest rates, including rates that fall below zero, may have unpredictable effects on markets, may result in heightened market volatility and may detract from Fund performance to the extent a Fund is exposed to such interest rates and/or volatility. Certain European countries and Japan have pursued negative interest rate policies. A negative interest rate policy is an unconventional central bank monetary policy tool where nominal target interest rates are set with negative value intended to help create self-sustaining growth in the local economy. To the extent a Fund holds a debt instrument with a negative interest rate, the Fund would generate a negative return on that investment. If negative interest rates become more prevalent in the market, investors may seek to reallocate their investment to other income-producing assets, which could further reduce the value of instruments with a negative yield.
Special Note Regarding Operational, and Cyber Security and Litigation Risks
An investment in a Fund may be negatively impacted because of the operational risks arising from factors such as processing errors and human errors, inadequate or failed internal or external processes, failures in systems and technology, changes in personnel, and errors caused by third-party service providers or trading counterparties. The use of certain investment strategies that involve manual or additional processing, such as over-the-counter derivatives, increases these risks. Although a Fund attempts to minimize such failures through controls and oversight, it is not possible to identify all of the operational risks that may affect a Fund or to develop processes and controls that completely eliminate or mitigate the occurrence of such failures. A Fund and its shareholders could be negatively impacted as a result.
A Fund is also susceptible to operational and information security risks resulting from cyber-attacks. In general, cyber-attacks result from deliberate attacks, but other events may have effects similar to those caused by cyber-attacks. Cyber-attacks include, among others, stealing or corrupting confidential information and other data that is maintained online or digitally for financial gain, denial-of-service attacks on websites causing operational disruption, and the unauthorized release of confidential information and other data. Cyber-attacks affecting a Fund or its investment adviser, sub-adviser, custodian, transfer agent, intermediary or other third-party service provider may adversely impact a Fund and its shareholders. These cyber-attacks have the ability to cause significant disruptions and impact business operations; to result in financial losses; to prevent shareholders from transacting business; to interfere with a Fund’s calculation of NAV and to lead to violations of applicable privacy and other laws, regulatory fines, penalties, reputational damage, reimbursement or other compensation costs and/or additional compliance costs. Similar to operational risk in general, a Fund and its service providers, including GSAM, have instituted risk management systems designed to minimize the risks associated with cyber security. However, there is a risk that these systems will not succeed (or that any remediation efforts will not be successful), especially because a Fund does not directly control the risk management systems of the service providers to a Fund, its trading counterparties or the issuers in which a Fund may invest. Moreover, there is a risk that cyber-attacks will not be detected.
The Funds may be subject to third-party litigation, which could give rise to legal liability. These matters involving the Funds may arise from their activities and investments and could have a materially adverse effect on the Funds, including the expense of defending against claims and paying any amounts pursuant to settlements or judgments. There can be no guarantee that these matters will not arise in the normal course of business. If the Funds were to be found liable in any suit or proceeding, any associated damages and/or penalties could have a materially adverse effect on the Funds’ finances, in addition to being materially damaging to their reputation.
INVESTMENT RESTRICTIONS
The investment restrictions set forth below have been adopted by the Trust as fundamental policies that cannot be changed with respect to a Fund without the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the outstanding voting securities (as defined in the Act) of the affected Fund. The investment objective of each Fund and all other investment policies or practices of each Fund are considered by the Trust not to be fundamental and accordingly may be changed without shareholder approval. For the purposes of the Act, a “majority” of the outstanding voting securities means the lesser of (i) 67% or more of the shares of the Trust or a Fund present at a meeting, if the holders of more than 50% of the outstanding shares of the Trust or a Fund are present or represented by proxy, or (ii) more than 50% of the outstanding shares of the Trust or a Fund.
B-41
For purposes of the following limitations (except for the asset coverage requirement with respect to borrowings, which is subject to different requirements under the Act), any limitation which involves a maximum percentage shall not be considered violated unless an excess over the percentage occurs immediately after, and is caused by, an acquisition or encumbrance of securities or assets of, or borrowings by, a Fund. In applying fundamental investment restriction number (1) below to derivative transactions or instruments, including, but not limited to, futures, swaps, forwards, options and structured notes, the Funds will look to the industry of the reference asset(s) and not to the counterparty or issuer. With respect to the Funds’ fundamental investment restriction number (2) below, in the event that asset coverage (as defined in the Act) at any time falls below 300%, a Fund, within three days thereafter (not including Sundays and holidays) or such longer period as the SEC may prescribe by rules and regulations, will reduce the amount of its borrowings to the extent required so that the asset coverage of such borrowings will be at least 300%.
Fundamental Investment Restrictions
Each Fund may, notwithstanding any other fundamental investment restriction or policy, invest some or all of its assets in a single open-end investment company or series thereof with substantially the same fundamental investment restrictions and policies as the Fund.
Capital Growth Fund, Growth Opportunities Fund, Strategic Growth Fund, Equity Income Fund, Large Cap Value Fund, Mid Cap Value Fund, and Small Cap Value Fund
As a matter of fundamental policy, each Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest 25% or more of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (excluding the U.S. Government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities). |
| (2) | Borrow money, except (a) each Fund may borrow from banks (as defined in the Act) or through reverse repurchase agreements in amounts up to 33-1/3% of its total assets (including the amount borrowed), (b) each Fund may, to the extent permitted by applicable law, borrow up to an additional 5% of its total assets for temporary purposes, (c) each Fund may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, (d) each Fund may purchase securities on margin to the extent permitted by applicable law and (e) each Fund may engage in transactions in mortgage dollar rolls which are accounted for as financings. |
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances.
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies, (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions and (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law. |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting. |
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although the Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate acquired by the Fund as a result of the ownership of securities. |
| (6) | Invest in commodities or commodity contracts, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts that are commodities or commodity contracts. |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
| (8) | Make any investment inconsistent with the Fund’s classification as a diversified company under the Act. |
U.S. Equity ESG Fund
As a matter of fundamental policy, the Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest 25% or more of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (excluding the U.S. Government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities). |
B-42
| (2) | Borrow money, except (a) the Fund may borrow from banks (as defined in the Act) or through reverse repurchase agreements in amounts up to 33-1/3% of its total assets (including the amount borrowed), (b) the Fund may, to the extent permitted by applicable law, borrow up to an additional 5% of its total assets for temporary purposes, (c) the Fund may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, (d) the Fund may purchase securities on margin to the extent permitted by applicable law and (e) the Fund may engage in transactions in mortgage dollar rolls which are accounted for as financings. |
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances.
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies, (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions, (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law, and (d) loans to affiliates of the Fund to the extent permitted by law. |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting. |
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although the Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate acquired by the Fund as a result of the ownership of securities. |
| (6) | Invest in commodities or commodity contracts, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts that are commodities or commodity contracts. |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
| (8) | Make any investment inconsistent with the Fund’s classification as a diversified company under the Act. |
Concentrated Growth Fund
As a matter of fundamental policy, the Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest 25% or more of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (excluding the U.S. Government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities). |
| (2) | Borrow money, except (a) the Fund, to the extent permitted by applicable law, may borrow from banks (as defined in the Act), other affiliated investment companies and other persons or through reverse repurchase agreements in amounts up to 33 1/3% of its total assets (including the amount borrowed), (b) the Fund may, to the extent permitted by applicable law, borrow up to an additional 5% of its total assets for temporary purposes, (c) the Fund may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, (d) the Fund may purchase securities on margin to the extent permitted by applicable law and (e) the Fund may engage in transactions in mortgage dollar rolls which are accounted for as financings. |
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances.
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies, (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions, (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law, and (d) loans to affiliates of the Fund to the extent permitted by law. |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting. |
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although a Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate acquired by a Fund as a result of the ownership of securities. |
B-43
| (6) | Invest in commodities or commodity contracts, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts that are commodities or commodity contracts. |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
The Fund was previously registered as a non-diversified investment company. Pursuant to current positions of the SEC staff, the Fund’s classification has changed from non-diversified to diversified, and the Fund will not be able to become non-diversified unless it seeks and obtains the approval of shareholders. Accordingly, the Fund may not make any investment inconsistent with the Fund’s classification as a diversified company under the Act.
Flexible Cap Fund
As a matter of fundamental policy, the Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest 25% or more of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (excluding the U.S. Government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities). |
| (2) | Borrow money, except (a) the Fund, to the extent permitted by applicable law, may borrow from banks (as defined in the Act), other affiliated investment companies and other persons or through reverse repurchase agreements in amounts up to 33 1/3% of its total assets (including the amount borrowed), (b) the Fund may, to the extent permitted by applicable law, borrow up to an additional 5% of its total assets for temporary purposes, (c) the Fund may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities and (d) the Fund may purchase securities on margin to the extent permitted by applicable law. |
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances.
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies, (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions, (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law, and (d) loans to affiliates of the Fund to the extent permitted by law. |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting. |
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although a Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate acquired by a Fund as a result of the ownership of securities. |
| (6) | Invest in commodities or commodity contracts, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts that are commodities or commodity contracts. |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
| (8) | Make any investment inconsistent with the Fund’s classification as a diversified company under the Act. |
Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund
As a matter of fundamental policy, the Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest 25% or more of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (excluding the U.S. Government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities). |
| (2) | Borrow money, except (a) the Fund, to the extent permitted by applicable law, may borrow from banks (as defined in the Act), other affiliated investment companies and other persons or through reverse repurchase agreements in amounts up to 33 1/3% of its total assets (including the amount borrowed), (b) the Fund may, to the extent permitted by applicable law, borrow up to an additional 5% of its total assets for temporary purposes, (c) the Fund may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, (d) the Fund may purchase securities on margin to the extent permitted by applicable law and (e) the Fund may engage in transactions in mortgage dollar rolls which are accounted for as financings. |
B-44
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances.
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies, (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions, (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law, and (d) loans to affiliates of the Fund to the extent permitted by law. |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting. |
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although the Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate acquired by the Fund as a result of the ownership of securities. |
| (6) | Invest in commodities or commodity contracts, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts that are commodities or commodity contracts. |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
| (8) | Make any investment inconsistent with the Fund’s classification as a diversified company under the Act. |
Technology Opportunities Fund
As a matter of fundamental policy, the Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest 25% or more of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (excluding the U.S. Government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities); except that the Fund will invest at least 25% of its total assets in companies in one or more of the media, telecommunications, technology and/or internet industries. |
| (2) | Borrow money, except (a) the Fund may borrow from banks (as defined in the Act or through reverse repurchase agreements in amounts up to 33 1/3% of its total assets (including the amount borrowed), (b) the Fund may, to the extent permitted by applicable law, borrow up to an additional 5% of its total assets for temporary purposes, (c) the Fund may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, (d) the Fund may purchase securities on margin to the extent permitted by applicable law and (e) the Fund may engage in transactions in mortgage dollar rolls which are accounted for as financings. |
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances.
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies, (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions and (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law. |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting. |
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although the Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate acquired by the Fund as a result of the ownership of securities. |
| (6) | Invest in commodities or commodity contracts, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts that are commodities or commodity contracts. |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
| (8) | Make any investment inconsistent with the Fund’s classification as a diversified company under the Act. |
Small Cap Growth Fund
B-45
As a matter of fundamental policy, the Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest more than 25% of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (for the purposes of this restriction, the U.S. Government, state and municipal governments and their agencies, authorities and instrumentalities are not deemed to be industries); |
| (2) | Borrow money, except as permitted by the Act, or interpretations or modifications by the SEC, SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction. |
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances;
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations, loan interests and other interests or obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies; (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions; (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law or pursuant to an exemptive order granted under the Act; and (d) loans to affiliates of the Fund to the extent permitted by law; |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting; |
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although the Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein or that reflect the return of an index of real estate values, securities of issuers which invest or deal in real estate, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate it has acquired as a result of the ownership of securities; |
| (6) | Invest in physical commodities, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts in accordance with its investment objective and policies, including, without limitation, structured notes, futures contracts, swaps, options on commodities, currencies, swaps and futures, ETFs, investment pools and other instruments, regardless of whether such instrument is considered to be a commodity; and |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
Focused Value Fund
As a matter of fundamental policy, the Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest more than 25% of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (for the purposes of this restriction, the U.S. Government, state and municipal governments and their agencies, authorities and instrumentalities are not deemed to be industries); |
| (2) | Borrow money, except as permitted by the Act, or interpretations or modifications by the SEC, SEC staff or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction. |
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances;
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations, loan interests and other interests or obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies, (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions, (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law or pursuant to an exemptive order granted under the Act, and (d) loans to affiliates of the Fund to the extent permitted by law; |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting; |
B-46
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although the Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein, or that reflect the return of an index of real estate values, securities of issuers which invest or deal in real estate, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate it has acquired as a result of the ownership of securities; |
| (6) | Invest in physical commodities, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts in accordance with its investment objective and policies, including without limitation, structured notes, futures contracts, swaps, options on commodities, currencies, swaps and futures, ETFs, investment pools and other instruments, regardless of whether such instrument is considered to be a commodity; and |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
Small/Mid Cap Value Fund
As a matter of fundamental policy, the Fund may not:
| (1) | Invest 25% or more of its total assets in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry (excluding the U.S. Government or any of its agencies or instrumentalities). |
| (2) | Borrow money, except (a) the Fund, to the extent permitted by applicable law, may borrow from banks (as defined in the Act), other affiliated investment companies and other persons or through reverse repurchase agreements in amounts up to 33 1/3% of its total assets (including the amount borrowed), (b) the Fund may, to the extent permitted by applicable law, borrow up to an additional 5% of its total assets for temporary purposes, (c) the Fund may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, (d) the Fund may purchase securities on margin to the extent permitted by applicable law and (e) the Fund may engage in transactions in mortgage dollar rolls which are accounted for as financings. |
The following interpretation applies to, but is not part of, this fundamental policy: In determining whether a particular investment in portfolio instruments or participation in portfolio transactions is subject to this borrowing policy, the accounting treatment of such instrument or participation shall be considered, but shall not by itself be determinative. Whether a particular instrument or transaction constitutes a borrowing shall be determined by the Board, after consideration of all of the relevant circumstances.
| (3) | Make loans, except through (a) the purchase of debt obligations, loan interests and other interests or obligations in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective and policies, (b) repurchase agreements with banks, brokers, dealers and other financial institutions, or (c) loans of securities as permitted by applicable law or pursuant to an exemptive order granted under the Act. |
| (4) | Underwrite securities issued by others, except to the extent that the sale of portfolio securities by the Fund may be deemed to be an underwriting. |
| (5) | Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, although the Fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or interests therein, securities of real estate investment trusts and mortgage-related securities and may hold and sell real estate acquired by the Fund as a result of the ownership of securities. |
| (6) | Invest in physical commodities, except that the Fund may invest in currency and financial instruments and contracts in accordance with its investment objective and policies, including without limitation, structured notes, futures contracts, swaps, options on commodities, currencies, swaps and futures, ETFs, investment pools and other instruments, regardless of whether such instrument is considered to be a commodity. |
| (7) | Issue senior securities to the extent such issuance would violate applicable law. |
| (8) | Make any investment inconsistent with the Fund’s classification as a diversified company under the Act. |
For purposes of the Funds’ industry concentration policies, the Investment Adviser may analyze the characteristics of a particular issuer and instrument and may assign an industry classification consistent with those characteristics. The Investment Adviser may, but need not, consider industry classifications provided by third parties, and the classifications applied to Fund investments will be informed by applicable law.
B-47
TRUSTEES AND OFFICERS
The Trust’s Leadership Structure
The business and affairs of the Funds are managed under the direction of the Board of Trustees (the “Board”), subject to the laws of the State of Delaware and the Trust’s Declaration of Trust. The Trustees are responsible for deciding matters of overall policy and reviewing the actions of the Trust’s service providers. The officers of the Trust conduct and supervise each Fund’s daily business operations. Trustees who are not deemed to be “interested persons” of the Trust as defined in the Act are referred to as “Independent Trustees.” Trustees who are deemed to be “interested persons” of the Trust are referred to as “Interested Trustees.” The Board is currently composed of seven Independent Trustees and one Interested Trustee. The Board has selected an Independent Trustee to act as Chair, whose duties include presiding at meetings of the Board and acting as a focal point to address significant issues that may arise between regularly scheduled Board and Committee meetings. In the performance of the Chair’s duties, the Chair will consult with the other Independent Trustees and the Funds’ officers and legal counsel, as appropriate. The Chair may perform other functions as requested by the Board from time to time.
The Board meets as often as necessary to discharge its responsibilities. Currently, the Board conducts regular, in-person meetings at least six times a year, and holds special in-person or telephonic meetings as necessary to address specific issues that require attention prior to the next regularly scheduled meeting. In addition, the Independent Trustees meet at least annually to review, among other things, investment management agreements, distribution (Rule 12b-1) and/or service plans and related agreements, transfer agency agreements and certain other agreements providing for the compensation of Goldman Sachs and/or its affiliates by the Funds, and to consider such other matters as they deem appropriate.
The Board has established five standing committees — Audit, Governance and Nominating, Compliance, Valuation and Contract Review Committees. The Board may establish other committees, or nominate one or more Trustees to examine particular issues related to the Board’s oversight responsibilities, from time to time. Each Committee meets periodically to perform its delegated oversight functions and reports its findings and recommendations to the Board. For more information on the Committees, see the section “STANDING BOARD COMMITTEES,” below.
The Trustees have determined that the Trust’s leadership structure is appropriate because it allows the Trustees to effectively perform their oversight responsibilities.
Trustees of the Trust
Information pertaining to the Trustees of the Trust as of December 29, 2020 is set forth below.
Independent Trustees
| Name, Address and |
Position(s) |
Term of |
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years |
Number of |
Other | |||||
| Jessica Palmer Age: 71 |
Chair of the Board of Trustees | Since 2018 (Trustee since 2007) |
Ms. Palmer is retired. She was formerly Consultant, Citigroup Human Resources Department (2007–2008); Managing Director, Citigroup Corporate and Investment Banking (previously, Salomon Smith Barney/Salomon Brothers) (1984–2006). Ms. Palmer was a Member of the Board of Trustees of Indian Mountain School (private elementary and secondary school) (2004–2009).
Chair of the Board of Trustees—Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. |
105 | None |
B-48
| Name, Address and |
Position(s) |
Term of |
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years |
Number of |
Other | |||||
| Dwight L. Bush Age: 63 |
Trustee | Since 2020 | Ambassador Bush is President and CEO of D.L. Bush & Associates (a financial advisory and private investment firm) (2002–2014 and 2017–present); and was formerly U.S. Ambassador to the Kingdom of Morocco (2014–2017) and a Member of the Board of Directors of Santander Bank, N.A. (2018–2019). Previously, Ambassador Bush served as an Advisory Board Member of Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust (October 2019–January 2020).
Trustee—Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. |
105 | None | |||||
| Kathryn A. Cassidy Age: 66 |
Trustee | Since 2015 | Ms. Cassidy is retired. Formerly, she was Advisor to the Chairman (May 2014–December 2014); and Senior Vice President and Treasurer (2008–2014), General Electric Company & General Electric Capital Corporation (technology and financial services companies).
Trustee—Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. |
105 | None | |||||
| Diana M. Daniels Age: 71 |
Trustee | Since 2007 | Ms. Daniels is retired. Formerly, she was Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary, The Washington Post Company (1991–2006). Ms. Daniels is a Trustee Emeritus and serves as a Presidential Councillor of Cornell University (2013–Present); former Member of the Legal Advisory Board, New York Stock Exchange (2003–2006) and of the Corporate Advisory Board, Standish Mellon Management Advisors (2006–2007).
Trustee—Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. |
105 | None | |||||
| Joaquin Delgado Age: 60 |
Trustee | Since 2020 | Dr. Delgado is retired. He is Director, Hexion Inc. (a specialty chemical manufacturer) (2019–present); and Director, Stepan Company (a specialty chemical manufacturer) (2011–present); and was formerly Executive Vice President, Consumer Business Group of 3M Company (July 2016–July 2019); and Executive Vice President, Health Care Business Group of 3M Company (October 2012–July 2016). Previously, Dr. Delgado served as an Advisory Board Member of Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust (October 2019– January 2020).
Trustee—Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. |
105 | Stepan Company (a specialty chemical manufacturer) | |||||
B-49
| Name, Address and |
Position(s) |
Term of |
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years |
Number of |
Other | |||||
| Roy W. Templin Age: 60 |
Trustee | Since 2013 | Mr. Templin is retired. He is Director, Armstrong World Industries, Inc. (a designer and manufacturer of ceiling, wall and suspension system solutions) (2016–Present); and was formerly Chairman of the Board of Directors, Con-Way Incorporated (a transportation, logistics and supply chain management service company) (2014–2015); Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, Whirlpool Corporation (an appliance manufacturer and marketer) (2004–2012).
Trustee—Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. |
105 | Armstrong World Industries, Inc. (a ceiling, wall and suspension systems solutions manufacturer) | |||||
| Gregory G. Weaver Age: 69 |
Trustee | Since 2015 | Mr. Weaver is retired. He is Director, Verizon Communications Inc. (2015–Present); and was formerly Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Deloitte & Touche LLP (a professional services firm) (2001–2005 and 2012–2014); and Member of the Board of Directors, Deloitte & Touche LLP (2006–2012).
Trustee—Goldman Sachs Trust and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. |
105 | Verizon Communications Inc. | |||||
B-50
| Interested Trustee
| ||||||||||
| Name, Address and |
Position(s) |
Term of |
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years |
Number of |
Other | |||||
| James A. McNamara* Age: 58 |
President and Trustee | Since 2007 | Advisory Director, Goldman Sachs (January 2018–Present); Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (January 2000–December 2017); Director of Institutional Fund Sales, GSAM (April 1998–December 2000); and Senior Vice President and Manager, Dreyfus Institutional Service Corporation (January 1993–April 1998).
President and Trustee—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. |
158 | None | |||||
| * | Mr. McNamara is considered to be an “Interested Trustee” because he holds positions with Goldman Sachs and owns securities issued by The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. Mr. McNamara holds comparable positions with certain other companies of which Goldman Sachs, GSAM or an affiliate thereof is the investment adviser, administrator and/or distributor. |
| 1 | Each Trustee may be contacted by writing to the Trustee, c/o Goldman Sachs, 200 West Street, New York, New York, 10282, Attn: Caroline Kraus. |
| 2 | Subject to such policies as may be adopted by the Board from time-to-time, each Trustee holds office for an indefinite term, until the earliest of: (a) the election of his or her successor; (b) the date the Trustee resigns or is removed by the Board or shareholders, in accordance with the Trust’s Declaration of Trust; or (c) the termination of the Trust. The Board has adopted policies which provide that each Independent Trustee shall retire as of December 31st of the calendar year in which he or she reaches (a) his or her 75th birthday or (b) the 15th anniversary of the date he or she became a Trustee, whichever is earlier, unless a waiver of such requirements shall have been adopted by a majority of the other Trustees. These policies may be changed by the Trustees without shareholder vote. |
| 3 | The Goldman Sachs Fund Complex includes certain other companies listed above for each respective Trustee. As of December 29, 2020, Goldman Sachs Trust consisted of 92 portfolios (90 of which offered shares to the public); Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust consisted of 13 portfolios; Goldman Sachs Trust II consisted of 19 portfolios (17 of which offered shares to the public); Goldman Sachs ETF Trust consisted of 31 portfolios (20 of which offered shares to the public); and Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund, Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund each consisted of one portfolio. Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund did not offer shares to the public. |
| 4 | This column includes only directorships of companies required to report to the SEC under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (i.e., “public companies”) or other investment companies registered under the Act. |
The significance or relevance of a Trustee’s particular experience, qualifications, attributes and/or skills is considered by the Board on an individual basis. Experience, qualifications, attributes and/or skills common to all Trustees include the ability to critically review, evaluate and discuss information provided to them and to interact effectively with the other Trustees and with representatives of the Investment Adviser and its affiliates, other service providers, legal counsel and a Fund’s independent registered public accounting firm, the capacity to address financial and legal issues and exercise reasonable business judgment, and a commitment to the representation of the interests of a Fund and its shareholders. The Governance and Nominating Committee’s charter contains certain other factors that are considered by the Governance and Nominating Committee in identifying and evaluating potential nominees to serve as Independent Trustees. Based on each Trustee’s experience, qualifications, attributes and/or skills, considered individually and with respect to the experience, qualifications, attributes and/or skills of other Trustees, the Board has concluded that each Trustee should serve as a Trustee. Below is a brief discussion of the experience, qualifications, attributes and/or skills of each individual Trustee as of December 29, 2020 that led the Board to conclude that such individual should serve as a Trustee.
Jessica Palmer. Ms. Palmer has served as a Trustee since 2007 and Chair of the Board since 2018. Ms. Palmer worked at Citigroup Corporate and Investment Banking (previously, Salomon Smith Barney/Salomon Brothers) for over 20 years, where she was a Managing Director. While at Citigroup Corporate and Investment Banking, Ms. Palmer was Head of Global Risk Management, Chair of the Global Commitment Committee, Co-Chair of International Investment Banking (New York) and Head of Fixed Income Capital Markets. Ms. Palmer was also a member of the Management Committee and Risk Management Operating Committee of Citigroup, Inc. Ms. Palmer was also Assistant Vice President of the International Division at Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. Ms. Palmer was also a member of the Board of Trustees of a private elementary and secondary school. Based on the foregoing, Ms. Palmer is experienced with financial and investment matters.
B-51
Dwight L. Bush. Ambassador Bush has served as a Trustee since 2020. Ambassador Bush also serves as President and CEO of D.L. Bush & Associates, a financial advisory and private investment firm. From 2014 to 2017, he served as U.S. Ambassador to the Kingdom of Morocco. Prior to his service as U.S. Ambassador, he established and served as CEO of Urban Trust Bank and UTB Education Finance, LLC, an integrated provider of education credit services. Ambassador Bush was previously Vice President of Corporate Development for SLM Corporation (commonly known as Sallie Mae). Formerly, he served as a member of the Board of Directors of Santander Bank, N.A., JER Investors Trust, a specialty real estate finance company, and as Vice Chairman of the Board of Directors of CASI Pharmaceuticals (formerly Entremed, Inc.) where he was Chairman of the Audit Committee. He also serves as a member of the Board of Directors for several philanthropic organizations, including the Middle East Investment Initiative and the American Council of Young Political Leaders, and has served on the executive committee of Cornell University. Ambassador Bush previously served on the Trust’s Advisory Board. Based on the foregoing, Ambassador Bush is experienced with financial and investment matters.
Kathryn A. Cassidy. Ms. Cassidy has served as a Trustee since 2015. Previously, Ms. Cassidy held several senior management positions at General Electric Company (“GE”) and General Electric Capital Corporation (“GECapital”) and its subsidiaries, where she worked for 35 years, most recently as Advisor to the Chairman of GECapital and Senior Vice President and Treasurer of GE and GECapital. As Senior Vice President and Treasurer, Ms. Cassidy led capital markets and treasury matters of multiple initial public offerings. Ms. Cassidy was responsible for managing global treasury operations, including global funding, hedging, derivative accounting and execution, cash and liquidity management, cash operations and treasury services, and global regulatory compliance and reporting for liquidity, derivatives, market risk and counterparty credit risk. Ms. Cassidy also serves as a Director of buildOn, a not-for-profit organization, where she serves as Chair of the Finance Committee. Based on the foregoing, Ms. Cassidy is experienced with financial and investment matters.
Diana M. Daniels. Ms. Daniels has served as a Trustee since 2007. Ms. Daniels also serves as a Trustee Emeritus and Presidential Councillor of Cornell University. Ms. Daniels held several senior management positions at The Washington Post Company and its subsidiaries, where she worked for 29 years. While at The Washington Post Company, Ms. Daniels served as Vice President, General Counsel, Secretary to the Board of Directors and Secretary to the Audit Committee. Previously, Ms. Daniels served as Vice President and General Counsel of Newsweek, Inc. Ms. Daniels has also served as Vice Chair and Chairman of the Executive Committee of the Board of Trustees of Cornell University and as a member of the Corporate Advisory Board of Standish Mellon Management Advisors and of the Legal Advisory Board of New York Stock Exchange. Ms. Daniels is also a member of the American Law Institute and of the Advisory Council of the Inter-American Press Association. Based on the foregoing, Ms. Daniels is experienced with legal, financial and investment matters.
Joaquin Delgado. Dr. Delgado has served as a Trustee since 2020. Dr. Delgado is a member of the Board of Directors for Stepan Company, a publicly-traded specialty chemical manufacturer, and Hexion Inc., a privately held specialty chemical manufacturer. Previously, Dr. Delgado held several senior management positions at 3M Company, where he worked for over 30 years, most recently as Executive Vice President of 3M Company’s Consumer Business Group. As Executive Vice President, Vice President, and General Manager at 3M Company, Dr. Delgado directed mergers and acquisitions worldwide, and was responsible for managing global operations in specialized markets such as semiconductors, consumer electronics, communications, medical and office supplies and software. Dr. Delgado also serves as a Director of MacPhail Center for Music, a not-for-profit organization. Dr. Delgado previously served on the Trust’s Advisory Board. Based on the foregoing, Dr. Delgado is experienced with financial and investment matters.
Roy W. Templin. Mr. Templin has served as a Trustee since 2013. Mr. Templin is a member of the Board of Directors of Armstrong World Industries, Inc., a ceiling, wall and suspension system solutions manufacturer, where he serves as Chair of the Finance Committee and the Audit Committee, and as a member of the Nominating and Governance Committee. Previously, Mr. Templin served as Chairman of the Board of Directors of Con-Way Incorporated, a transportation, logistics and supply-chain management services company, prior to its sale to XPO Logistics, Inc. in 2015. Mr. Templin held a number of senior management positions at Whirlpool Corporation, an appliance manufacturer and marketer, including Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, Vice President and Corporate Controller there. At Whirlpool, Mr. Templin served on the Executive Committee and was responsible for all aspects of finance globally, including treasury, accounting, risk management, investor relations, internal auditing, tax and facilities. Prior to joining Whirlpool, Mr. Templin served in several roles at Kimball International, a furniture and electronic assemblies manufacturer, including Vice President of Finance and Chief Accounting Officer. Mr. Templin was also a Director of Corporate Finance for Cummins, Inc., a diesel engine manufacturer, a Director of Financial Development at NCR Corporation, a computer hardware and electronics company, and a member of the audit staff of Price Waterhouse (now PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP). Mr. Templin is a certified public accountant and a certified management accountant. Based on the foregoing, Mr. Templin is experienced with accounting, financial and investment matters.
Gregory G. Weaver. Mr. Weaver has served as a Trustee since 2015. Mr. Weaver has been designated as the Board’s “audit committee financial expert” given his extensive accounting and finance experience. Mr. Weaver also serves as a Director of Verizon Communications Inc., where he serves as Chair of the Audit Committee. Previously, Mr. Weaver was a partner with Deloitte & Touche LLP for 30 years. He was the firm’s first chairman and chief executive officer from 2001–2005, and was elected to serve a second term (2012–2014). While serving as chairman at Deloitte & Touche LLP, Mr. Weaver led the audit and enterprise risk services practice, overseeing all operations, strategic positioning, audit quality, and talent matters. Mr. Weaver also served as a member of the firm’s Board of Directors for six years where he served on the Governance Committee and Partner Earnings and Benefits Committee and was chairman of the Elected Leaders Committee and Strategic Investment Committee. Mr. Weaver is also a Board member and Audit
B-52
Committee chair of the YMCA of Westfield, New Jersey. Mr. Weaver has also served as President of the Council of Boy Scouts of America in Long Rivers, Connecticut, President of A Better Chance in Glastonbury, Connecticut, as a member of the Financial Accounting Standards Advisory Council and as a board member of the Stan Ross Department of Accountancy, Baruch College. Based on the foregoing, Mr. Weaver is experienced with accounting, financial and investment matters.
James A. McNamara. Mr. McNamara has served as a Trustee and President of the Trust since 2007 and has served as an officer of the Trust since 2001. Mr. McNamara is an Advisory Director to Goldman Sachs. Prior to retiring as Managing Director at Goldman Sachs in 2017, Mr. McNamara was head of Global Third Party Distribution at GSAM and was previously head of U.S. Third Party Distribution. Prior to that role, Mr. McNamara served as Director of Institutional Fund Sales. Prior to joining Goldman Sachs, Mr. McNamara was Vice President and Manager at Dreyfus Institutional Service Corporation. Based on the foregoing, Mr. McNamara is experienced with financial and investment matters.
B-53
Officers of the Trust
Information pertaining to the officers of the Trust as of December 29, 2020 is set forth below.
|
|
Position(s) Held |
Term of Office and |
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years | |||
| James A. McNamara 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 58 |
Trustee and President |
Since 2007 | Advisory Director, Goldman Sachs (January 2018 – Present); Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (January 2000 – December 2017); Director of Institutional Fund Sales, GSAM (April 1998 – December 2000); and Senior Vice President and Manager, Dreyfus Institutional Service Corporation (January 1993 – April 1998).
President and Trustee—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| Joseph F. DiMaria 30 Hudson Street Jersey City, NJ 07302 Age: 52 |
Treasurer, Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer | Since 2017 (Treasurer and Principal Financial Officer since 2019) | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (November 2015 – Present) and Vice President – Mutual Fund Administration, Columbia Management Investment Advisers, LLC (May 2010 – October 2015).
Treasurer, Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer—Goldman Sachs Trust (previously Assistant Treasurer (2016)); Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust (previously Assistant Treasurer (2016)); Goldman Sachs Trust II (previously Assistant Treasurer (2017)); Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund (previously Assistant Treasurer (2017)); Goldman Sachs ETF Trust (previously Assistant Treasurer (2017)); Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| Julien Yoo 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 49 |
Chief Compliance Officer | Since 2019 | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (January 2020–Present); Vice President, Goldman Sachs (December 2014–December 2019); and Vice President, Morgan Stanley Investment Management (2005–2010).
Chief Compliance Officer—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs BDC, Inc.; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit LLC; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit II LLC; Goldman Sachs Middle Market Lending Corp.; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| Peter W. Fortner 30 Hudson Street Jersey City, NJ 07302 Age: 62 |
Assistant Treasurer | Since 2000 | Vice President, Goldman Sachs (July 2000–Present); Principal Accounting Officer, Commerce Bank Mutual Fund Complex (2008–Present); and Treasurer of Goldman Sachs Philanthropy Fund (2019–Present).
Assistant Treasurer—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| Allison Fracchiolla 30 Hudson Street Jersey City, NJ 07302 Age: 37 |
Assistant Treasurer | Since 2014 | Vice President, Goldman Sachs (January 2013–Present).
Assistant Treasurer—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; and Goldman Sachs ETF Trust. | |||
B-54
|
|
Position(s) Held |
Term of Office and |
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years | |||
| Tyler Hanks 222 S. Main St Salt Lake City, UT 84101 Age: 38 |
Assistant Treasurer | Since 2019 | Vice President, Goldman Sachs (January 2016—Present); and Associate, Goldman Sachs (January 2014—January 2016).
Assistant Treasurer—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| Kirsten Frivold Imohiosen 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 50 |
Assistant Treasurer | Since 2019 | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (January 2018–Present); and Vice President, Goldman Sachs (May 1999–December 2017).
Assistant Treasurer—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs BDC, Inc.; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit LLC; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit II LLC; Goldman Sachs Middle Market Lending Corp.; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| Steven Z. Indich 30 Hudson Street Jersey City, NJ 07302 Age: 51 |
Assistant Treasurer | Since 2019 | Vice President, Goldman Sachs (February 2010 – Present).
Assistant Treasurer—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs BDC, Inc.; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit LLC; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit II LLC; Goldman Sachs Middle Market Lending Corp.; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| Carol Liu 30 Hudson Street Jersey City, NJ 07302 Age: 45 |
Assistant Treasurer | Since 2019 | Vice President, Goldman Sachs (October 2017 – Present); Tax Director, The Raine Group LLC (August 2015 – October 2017); and Tax Director, Icon Investments LLC (January 2012 – August 2015).
Assistant Treasurer—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs BDC, Inc.; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit LLC; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit II LLC; Goldman Sachs Middle Market Lending Corp.; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| Christopher Bradford 30 Hudson Street Jersey City, NJ 07302 Age: 39 |
Vice President | Since 2020 | Vice President, Goldman Sachs (January 2014–Present).
Vice President—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund. | |||
| Jesse Cole 71 South Wacker Drive Chicago, IL 60606 Age: 57 |
Vice President | Since 1998 | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (December 2006 – Present); Vice President, GSAM (June 1998 – Present); and Vice President, AIM Management Group, Inc. (investment adviser) (April 1996 – June 1998).
Vice President—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; and Goldman Sachs Trust II. | |||
B-55
|
|
Position(s) Held |
Term of Office and |
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years | |||
| Miriam L. Cytryn 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 62 |
Vice President | Since 2008 | Vice President, GSAM (2008 – Present); Vice President of Divisional Management, Investment Management Division (2007 – 2008); Vice President and Chief of Staff, GSAM US Distribution (2003 – 2007); and Vice President of Employee Relations, Goldman Sachs (1996 – 2003).
Vice President—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; and Goldman Sachs Trust II. | |||
| Kimberly MacKenzie 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 40 |
Vice President | Since 2020 | Vice President, GSAM (2010–Present); Associate, Goldman Sachs (2006–2010).
Vice President—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; and Goldman Sachs Trust II. | |||
| Frank Murphy 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 46 |
Vice President | Since 2019 | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (2015 – Present); Vice President, Goldman Sachs (2003 – 2014); Associate, Goldman Sachs (2001 – 2002); and Analyst, Goldman Sachs (1999 – 2001).
Vice President—Goldman Sachs Trust; and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. | |||
| Emily Stecher 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 33 |
Vice President | Since 2020 | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (January 2020–Present); Vice President, Goldman Sachs (January 2015–December 2019).
Vice President—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund. | |||
| Caroline L. Kraus 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 43 |
Secretary | Since 2012 | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (January 2016–Present); Vice President, Goldman Sachs (August 2006–December 2015); Senior Counsel, Goldman Sachs (January 2020–Present); Associate General Counsel, Goldman Sachs (2012–December 2019); Assistant General Counsel, Goldman Sachs (August 2006–December 2011); and Associate, Weil, Gotshal & Manges, LLP (2002–2006).
Secretary—Goldman Sachs Trust (previously Assistant Secretary (2012)); Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust (previously Assistant Secretary (2012)); Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs BDC, Inc.; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit LLC; Goldman Sachs Private Middle Market Credit II LLC; Goldman Sachs Middle Market Lending Corp.; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
| David A. Fishman 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 56 |
Assistant Secretary | Since 2001 | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (December 2001 – Present); and Vice President, Goldman Sachs (1997 – December 2001).
Assistant Secretary—Goldman Sachs Trust; and Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust. | |||
| Robert Griffith 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 46 |
Assistant Secretary | Since 2011 | Vice President, Goldman Sachs (August 2011 – Present); Associate General Counsel, Goldman Sachs (December 2014 – Present); Assistant General Counsel, Goldman Sachs (August 2011 – December 2014); Vice President and Counsel, Nomura Holding America, Inc. (2010 – 2011); and Associate, Simpson Thacher & Bartlett LLP (2005 – 2010).
Assistant Secretary—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; Goldman Sachs Trust II; Goldman Sachs MLP and Energy Renaissance Fund; Goldman Sachs ETF Trust; Goldman Sachs Credit Income Fund; and Goldman Sachs Real Estate Diversified Income Fund. | |||
B-56
|
|
Position(s) Held |
Term of Office and |
Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years | |||
| Shaun Cullinan 200 West Street New York, NY 10282 Age: 41 |
Assistant Secretary | Since 2018 | Managing Director, Goldman Sachs (2018 – Present); Vice President, Goldman Sachs (2009 – 2017); Associate, Goldman Sachs (2006 – 2008); Analyst, Goldman Sachs (2004 – 2005).
Assistant Secretary—Goldman Sachs Trust; Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust; and Goldman Sachs Trust II. |
| 1 | Officers hold office at the pleasure of the Board of Trustees or until their successors are duly elected and qualified. Each officer holds comparable positions with certain other companies of which Goldman Sachs, GSAM or an affiliate thereof is the investment adviser, administrator and/or distributor. |
Standing Board Committees
The Audit Committee oversees the audit process and provides assistance to the Board with respect to fund accounting, tax compliance and financial statement matters. In performing its responsibilities, the Audit Committee selects and recommends annually to the Board an independent registered public accounting firm to audit the books and records of the Trust for the ensuing year, and reviews with the firm the scope and results of each audit. All of the Independent Trustees serve on the Audit Committee and Mr. Weaver serves as Chair of the Audit Committee. The Audit Committee held six meetings during the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020.
The Governance and Nominating Committee has been established to: (i) assist the Board in matters involving mutual fund governance, which includes making recommendations to the Board with respect to the effectiveness of the Board in carrying out its responsibilities in governing the Funds and overseeing their management; (ii) select and nominate candidates for appointment or election to serve as Independent Trustees; and (iii) advise the Board on ways to improve its effectiveness. All of the Independent Trustees serve on the Governance and Nominating Committee. The Governance and Nominating Committee held three meetings during the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020. As stated above, each Trustee holds office for an indefinite term until the occurrence of certain events. In filling Board vacancies, the Governance and Nominating Committee will consider nominees recommended by shareholders. Nominee recommendations should be submitted to the Trust at its mailing address stated in the Funds’ Prospectuses and should be directed to the attention of the Goldman Sachs Trust Governance and Nominating Committee.
The Compliance Committee has been established for the purpose of overseeing the compliance processes: (i) of the Funds; and (ii) insofar as they relate to services provided to the Funds, of the Funds’ Investment Adviser, Distributor, administrator (if any), and Transfer Agent, except that compliance processes relating to the accounting and financial reporting processes, and certain related matters, are overseen by the Audit Committee. In addition, the Compliance Committee provides assistance to the full Board with respect to compliance matters. The Compliance Committee met six times during the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020. All of the Independent Trustees serve on the Compliance Committee.
The Valuation Committee is authorized to act for the Board in connection with the valuation of portfolio securities held by the Funds in accordance with the Trust’s Valuation Procedures. Messrs. McNamara and DiMaria serve on the Valuation Committee. The Valuation Committee met twelve times during the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020.
The Contract Review Committee has been established for the purpose of overseeing the processes of the Board for reviewing and monitoring performance under the Funds’ investment management, distribution, transfer agency and certain other agreements with the Funds’ Investment Adviser and its affiliates. The Contract Review Committee is also responsible for overseeing the Board’s processes for considering and reviewing performance under the operation of the Funds’ distribution, service, shareholder administration and other plans, and any agreements related to the plans, whether or not such plans and agreements are adopted pursuant to Rule 12b-1 under the Act. The Contract Review Committee also provides appropriate assistance to the Board in connection with the Board’s approval, oversight and review of the Funds’ other service providers including, without limitation, the Funds’ custodian/accounting agent, sub-transfer agents, professional (legal and accounting) firms and printing firms. The Contract Review Committee met two times during the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020. All of the Independent Trustees serve on the Contract Review Committee.
Risk Oversight
The Board is responsible for the oversight of the activities of the Funds, including oversight of risk management. Day-to-day risk management with respect to the Funds is the responsibility of GSAM or other service providers (depending on the nature of the risk), subject to supervision by GSAM. The risks of the Funds include, but are not limited to, liquidity risk, investment risk, compliance risk, operational risk, reputational risk, credit risk and counterparty risk. Each of GSAM and the other service providers have their own independent interest in risk management and their policies and methods of risk management may differ from the Funds and each other’s in the setting of priorities, the resources available or the effectiveness of relevant controls. As a result, the Board recognizes that it is not possible to identify all of the risks that may affect the Funds or to develop processes and controls to eliminate or mitigate their occurrence or effects, and that some risks are simply beyond the control of the Funds or GSAM, its affiliates or other service providers.
B-57
The Board effectuates its oversight role primarily through regular and special meetings of the Board and Board committees. In certain cases, risk management issues are specifically addressed in reports, presentations and discussions. For example, on an annual basis, GSAM will provide the Board with a written report that addresses the operation, adequacy and effectiveness of the Trust’s liquidity risk management program, which is designed to assess and manage the Fund’s liquidity risk. GSAM also has a risk management team that assists GSAM in managing investment risk. Representatives from the risk management team meet regularly with the Board to discuss their analysis and methodologies. In addition, investment risk is discussed in the context of regular presentations to the Board on Fund strategy and performance. Other types of risk are addressed as part of presentations on related topics (e.g. compliance policies) or in the context of presentations focused specifically on one or more risks. The Board also receives reports from GSAM management on operational risks, reputational risks and counterparty risks relating to the Funds.
Board oversight of risk management is also performed by various Board committees. For example, the Audit Committee meets with both the Funds’ independent registered public accounting firm and GSAM’s internal audit group to review risk controls in place that support the Funds as well as test results, and the Compliance Committee meets with the CCO and representatives of GSAM’s compliance group to review testing results of the Funds’ compliance policies and procedures and other compliance issues. Board oversight of risk is also performed as needed between meetings through communications between GSAM and the Board. The Board may, at any time and in its discretion, change the manner in which it conducts risk oversight. The Board’s oversight role does not make the Board a guarantor of the Fund’s investments or activities.
Trustee Ownership of Fund Shares
The following table shows the dollar range of shares beneficially owned by each Trustee (then serving) in the Funds and other portfolios of the Goldman Sachs Fund Complex as of December 31, 2019, unless otherwise noted.
| Name of Trustee |
Dollar Range of Equity Securities in the Funds(1) |
Aggregate Dollar Range of Equity Securities in All Portfolios in Fund Complex Overseen By Trustee | ||
| Jessica Palmer |
Growth Opportunities Fund: Over $100,000 | Over $100,000 | ||
| Mid Cap Value Fund: Over $100,000 | ||||
| Dwight L. Bush(2) |
None | None | ||
| Kathryn A. Cassidy |
Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund: $50,001—$100,000 | Over $100,000 | ||
| Mid Cap Value Fund: $50,001—$100,000 | ||||
| Small Cap Value Fund: $50,001—$100,000 | ||||
| Diana M. Daniels |
None | Over $100,000 | ||
| Joaquin Delgado(2) |
None | None | ||
| James A. McNamara |
None | Over $100,000 | ||
| Roy W. Templin |
Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund: Over $100,000 | Over $100,000 | ||
| Gregory G. Weaver |
None | Over $100,000 |
| 1 | Includes the value of shares beneficially owned by each Trustee in each Fund described in this SAI. |
| 2 | Ambassador Bush and Dr. Delgado began serving as Trustees effective January 23, 2020. |
As of December 1, 2020, the Trustees and Officers of the Trust as a group owned less than 1% of the outstanding shares of beneficial interest of each class of the Funds.
Board Compensation
Each Independent Trustee is compensated with a unitary annual fee for his or her services as a Trustee of the Trust and as a member of the Governance and Nominating Committee, Compliance Committee, Contract Review Committee, and Audit Committee. The Chair and “audit committee financial expert” receive additional compensation for their services. The Independent Trustees are also reimbursed for reasonable travel expenses incurred in connection with attending meetings. The Trust may also pay the reasonable incidental costs of a Trustee to attend training or other types of conferences relating to the investment company industry.
B-58
The following tables set forth certain information with respect to the compensation of each Trustee of the Trust (then serving) for the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020:
Trustee Compensation
| Name of Trustee |
U.S. Equity ESG |
Concentrated Growth |
Capital Growth |
Flexible Cap |
Growth Opportunities |
Small Cap Growth |
Small/Mid Cap Growth |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Jessica Palmer(1) |
$ | 3,749 | $ | 3,797 | $ | 4,046 | $ | 3,752 | $ | 4,139 | $ | 2,813 | $ | 4,391 | ||||||||||||||
| Dwight L. Bush(2) |
$ | 1,878 | $ | 1,901 | $ | 2,017 | $ | 1,879 | $ | 2,057 | $ | 1,877 | $ | 2,179 | ||||||||||||||
| Kathryn A. Cassidy |
$ | 2,501 | $ | 2,533 | $ | 2,699 | $ | 2,503 | $ | 2,761 | $ | 1,877 | $ | 2,930 | ||||||||||||||
| Diana M. Daniels |
$ | 2,501 | $ | 2,533 | $ | 2,699 | $ | 2,503 | $ | 2,761 | $ | 1,877 | $ | 2,930 | ||||||||||||||
| Joaquin Delgado(2) |
$ | 1,878 | $ | 1,901 | $ | 2,017 | $ | 1,879 | $ | 2,057 | $ | 1,877 | $ | 2,179 | ||||||||||||||
| James A. McNamara(3) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Roy W. Templin |
$ | 2,501 | $ | 2,533 | $ | 2,699 | $ | 2,503 | $ | 2,761 | $ | 1,877 | $ | 2,930 | ||||||||||||||
| Gregory G. Weaver(4) |
$ | 2,911 | $ | 2,948 | $ | 3,141 | $ | 2,913 | $ | 3,214 | $ | 2,185 | $ | 3,410 | ||||||||||||||
| Name of Trustee |
Strategic Growth |
Technology Opportunities |
Equity Income |
Focused Value |
Large Cap Value |
Mid Cap Value |
Small Cap Value |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Jessica Palmer(1) |
$ | 3,799 | $ | 3,921 | $ | 3,864 | $ | 3,748 | $ | 3,893 | $ | 4,113 | $ | 5,490 | ||||||||||||||
| Dwight L. Bush(2) |
$ | 1,901 | $ | 1,962 | $ | 1,931 | $ | 1,878 | $ | 1,943 | $ | 2,041 | $ | 2,659 | ||||||||||||||
| Kathryn A. Cassidy |
$ | 2,534 | $ | 2,616 | $ | 2,578 | $ | 2,501 | $ | 2,597 | $ | 2,744 | $ | 3,663 | ||||||||||||||
| Diana M. Daniels |
$ | 2,534 | $ | 2,616 | $ | 2,578 | $ | 2,501 | $ | 2,597 | $ | 2,744 | $ | 3,663 | ||||||||||||||
| Joaquin Delgado(2) |
$ | 1,901 | $ | 1,962 | $ | 1,931 | $ | 1,878 | $ | 1,943 | $ | 2,041 | $ | 2,659 | ||||||||||||||
| James A. McNamara(3) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Roy W. Templin |
$ | 2,534 | $ | 2,616 | $ | 2,578 | $ | 2,501 | $ | 2,597 | $ | 2,744 | $ | 3,663 | ||||||||||||||
| Gregory G. Weaver(4) |
$ | 2,949 | $ | 3,045 | $ | 3,000 | $ | 2,910 | $ | 3,023 | $ | 3,193 | $ | 4,263 | ||||||||||||||
| Name of Trustee |
Small/Mid Cap Value |
Pension or Retirement Benefits Accrued as Part of the Trust’s Expenses |
Total Compensation From Fund Complex (including the Funds)(5) |
|||||||||
| Jessica Palmer(1) |
$ | 3,784 | $ | 0 | $ | 504,500 | ||||||
| Dwight L. Bush(2) |
$ | 1,894 | $ | 0 | $ | 253,500 | ||||||
| Kathryn A. Cassidy |
$ | 2,524 | $ | 0 | $ | 336,500 | ||||||
| Diana M. Daniels |
$ | 2,524 | $ | 0 | $ | 336,500 | ||||||
| Joaquin Delgado(2) |
$ | 1,894 | $ | 0 | $ | 253,500 | ||||||
| James A. McNamara(3) |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Roy W. Templin |
$ | 2,524 | $ | 0 | $ | 336,500 | ||||||
| Gregory G. Weaver(4) |
$ | 2,938 | $ | 0 | $ | 391,500 | ||||||
| 1 | Includes compensation as Board Chair. |
| 2 | Includes compensation Ambassador Bush and Dr. Delgado received as Advisory Board Members during the fiscal year. Ambassador Bush and Dr. Delgado began serving as Advisory Board Members effective October 16, 2019 and as Trustees effective January 23, 2020. |
| 3 | Mr. McNamara is an Interested Trustee, and, as such, receives no compensation from the Funds or the Goldman Sachs Fund Complex. |
| 4 | Includes compensation as “audit committee financial expert,” as defined in Item 3 of Form N-CSR. |
| 5 | Represents fees paid to each Trustee during the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020 from the Goldman Sachs Fund Complex. |
The Trust, its Investment Adviser and principal underwriter have adopted codes of ethics under Rule 17j-1 of the Act that permit personnel subject to their particular codes of ethics to invest in securities, including securities that may be purchased or held by the Funds.
MANAGEMENT SERVICES
As stated in the Funds’ Prospectuses, GSAM, 200 West Street, New York, New York 10282, serves as Investment Adviser to the Funds. GSAM is an indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. and an affiliate of Goldman Sachs. Prior to the end of April 2003, Goldman Sachs Asset Management, a business unit of the Investment Management Division of Goldman Sachs, served as the investment adviser to the Concentrated Growth, Growth Opportunities, Strategic Growth, Equity Income, Large Cap Value, Mid Cap Value and Small Cap Value Funds. In April 2003, GSAM assumed investment advisory responsibilities for those Funds. See “Service Providers” in the Funds’ Prospectuses for a description of the Investment Adviser’s duties to the Funds.
Founded in 1869, The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. is a publicly-held financial holding company and a leading global investment banking, securities and investment management firm. Goldman Sachs is a leader in developing portfolio strategies and in many fields of investing and financing, participating in financial markets worldwide and serving individuals, institutions, corporations and governments. Goldman Sachs is also among the principal market sources for current and thorough information on companies, industrial sectors, markets, economies and currencies, and trades and makes markets in a wide range of equity and debt securities 24 hours a day. The firm is headquartered in New York with offices in countries throughout the world. It has trading professionals throughout the United States, as well as in London, Frankfurt, Tokyo, Seoul, Sao Paulo and other major financial centers around the world. The active participation of Goldman Sachs in the world’s financial markets enhances its ability to identify attractive investments. Goldman Sachs has agreed to permit the Funds to use the name “Goldman Sachs” or a derivative thereof as part of each Fund’s name for as long as each Fund’s Management Agreement (as described below) is in effect.
B-59
The Funds’ management agreement (the “Management Agreement”) provides that GSAM, in its capacity as Investment Adviser, may render similar services to others so long as the services under the Management Agreement are not impaired thereby. The Funds’ Management Agreement was most recently approved by the Trustees of the Trust, including a majority of the Trustees of the Trust who are not parties to such agreement or “interested persons” (as such term is defined in the Act) of any party thereto (the “non-interested Trustees”) on June 16-17, 2020 with respect to each of the Funds. A discussion regarding the Trustees’ basis for approving the Management Agreement is available in the Funds’ annual reports for the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020.
These management arrangements were last approved by the shareholders of the Funds then in existence on April 21, 1997. The management arrangements for those Funds that commenced investment operations after April 21, 1997 were last approved by the initial sole shareholder of each such Fund, prior to the Fund’s commencement of operations.
The Management Agreement will remain in effect until June 30, 2021, and will continue in effect with respect to each Fund from year to year thereafter provided such continuance is specifically approved at least annually as set forth in the Management Agreement.
The Management Agreement will terminate automatically if assigned (as defined in the Act). The Management Agreement is also terminable at any time without penalty by the Trustees of the Trust or by vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the applicable Fund on 60 days’ written notice to the Investment Adviser or by the Investment Adviser on 60 days’ written notice to the Trust.
Pursuant to the Management Agreement, the Investment Adviser is entitled to receive the fees set forth below, payable monthly based on each respective Fund’s average daily net assets. Also included below are the actual management fee rates paid by each Fund (after reflection of any management fee waivers) for the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020. The Actual Rate may not correlate to the Contractual Rate as a result of any management fee waivers that may be in effect from time to time. The Investment Adviser may waive a portion of its management fee payable by a Fund in an amount equal to any management fees it earns as an investment adviser to any of the affiliated funds in which the Fund invests.
| Fund |
Management Fee Annual Rate |
Actual Rate for the Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020 | ||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund | 0.55% on the first $1 billion 0.50% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.47% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.46% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.45% over $8 billion |
0.55% | ||
| Capital Growth Fund | 0.71% on the first $1 billion 0.64% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.61% over $2 billion |
0.71% | ||
| Concentrated Growth Fund | 0.76% on the first $1 billion 0.68% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.65% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.64% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.62% over $8 billion |
0.76% | ||
| Flexible Cap Fund | 0.55% on the first $1 billion 0.50% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.47% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.46% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.45% over $8 billion |
0.55% | ||
| Growth Opportunities Fund | 0.92% on the first $2 billion 0.83% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.79% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.77% over $8 billion |
0.86% | ||
| Small Cap Growth Fund | 0.85% on the first $2 billion 0.77% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.73% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.71% over $8 billion |
0.85% | ||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund | 0.85% on the first $2 billion 0.77% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.73% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.71% over $8 billion |
0.85% | ||
B-60
| Fund |
Management Fee Annual Rate |
Actual Rate for the Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020 | ||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
0.71% on the first $1 billion 0.64% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.61% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.59% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.58% over $8 billion |
0.71% | ||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
0.94% on the first $1 billion 0.85% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.80% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.79% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.77% over $8 billion |
0.94% | ||
| Equity Income Fund |
0.69% on the first $1 billion 0.62% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.59% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.58% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.57% over $8 billion |
0.69% | ||
| Focused Value Fund |
0.69% on the first $1 billion 0.62% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.59% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.58% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.57% over $8 billion |
0.69% | ||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
0.75% on the first $1 billion 0.68% over $1 billion up to $2 billion 0.65% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.64% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.63% over $8 billion |
0.71% | ||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
0.75% on the first $2 billion 0.68% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.65% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.64% over $8 billion |
0.75% | ||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
0.98% on the first $2 billion 0.88% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.84% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.82% over $8 billion |
0.92% | ||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
0.80% on the first $2 billion 0.72% over $2 billion up to $5 billion 0.68% over $5 billion up to $8 billion 0.67% over $8 billion |
0.80% | ||
For the fiscal years ended August 31, 2020, August 31, 2019 and August 31, 2018 the amounts of the fees incurred by each Fund then in existence under the Management Agreement were as follows (with and without the fee limitations that were then in effect):
| Fiscal year ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fund |
Without Fee Waivers |
With Fee Waivers |
Without Fee Waivers |
With Fee Waivers |
Without Fee Waivers |
With Fee Waivers |
||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 60,006 | $ | 59,754 | $ | 57,670 | $ | 57,263 | $ | 42,558 | $ | 42,241 | ||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
6,308,632 | 6,304,469 | 6,380,729 | 6,376,002 | 7,740,579 | 7,736,639 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
1,184,546 | 1,183,081 | 1,110,580 | 1,109,952 | 1,301,925 | 1,301,622 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
110,718 | 110,633 | 102,972 | 102,941 | 109,974 | 109,944 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
10,612,054 | 9,896,790 | 14,086,005 | 14,070,495 | 22,597,317 | 22,556,448 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund1 |
54,918 | 54,726 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
16,330,551 | 16,278,768 | 17,642,511 | 17,592,759 | 20,695,430 | 20,648,235 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
1,122,165 | 1,120,973 | 1,241,634 | 1,240,632 | 2,052,397 | 2,052,145 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
5,144,878 | 5,125,955 | 4,480,269 | 4,475,034 | 4,684,975 | 4,684,061 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
2,393,932 | 2,392,209 | 2,480,755 | 2,479,524 | 2,653,164 | 2,639,109 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
58,668 | 58,485 | 34,509 | 34,466 | 42,573 | 41,473 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
3,167,956 | 2,998,352 | 3,749,771 | 3,745,053 | 5,138,114 | 5,134,484 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
7,890,669 | 7,875,872 | 9,870,269 | 9,861,772 | 15,333,505 | 15,316,338 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
45,956,718 | 45,859,257 | 54,500,996 | 54,415,323 | 61,739,913 | 61,230,417 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
885,213 | 882,746 | 961,436 | 958,674 | 1,011,965 | 991,204 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
B-61
Unless required to be performed by others pursuant to agreements with the Funds, the Investment Adviser also performs certain administrative services for each Fund under the Management Agreement. Such administrative services include, subject to the general supervision of the Trustees of the Trust, (i) providing supervision of all aspects of the Fund’s non-investment operations; (ii) providing the Fund with personnel to perform such executive, administrative and clerical services as are reasonably necessary to provide effective administration of the Fund; (iii) arranging for, at the Fund’s expense, the preparation of all of the Fund’s required tax returns, the preparation and submission of reports to existing shareholders, the periodic updating of the Fund’s prospectus and statement of additional information, and the preparation of reports filed with the SEC and other regulatory authorities; (iv) maintaining all of the Fund’s records; and (v) providing the Fund with adequate office space and all necessary office equipment and services.
Legal Proceedings. On October 22, 2020, The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. announced a settlement of matters involving 1Malaysia Development Bhd. (1MDB), a Malaysian sovereign wealth fund, with the United States Department of Justice as well as criminal and civil authorities in the United Kingdom, Singapore and Hong Kong. Further information regarding the 1MDB settlement can be found at https://www.goldmansachs.com/media-relations/press-releases/current/goldman-sachs-2020-10-22.html. The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. previously entered into a settlement agreement with the Government of Malaysia and 1MDB to resolve all criminal and regulatory proceedings in Malaysia relating to 1MDB.
The Investment Adviser, Goldman Sachs and certain of their affiliates have received exemptive relief from the SEC to permit them to continue serving as investment adviser and principal underwriter for U.S.-registered investment companies.
Portfolio Managers—Other Accounts Managed by the Portfolio Managers
The following tables disclose other accounts within each type of category listed below for which the portfolio managers are jointly and primarily responsible for day to day portfolio management, as of August 31, 2020, unless otherwise noted.
For each portfolio manager listed below, the total number of accounts managed is a reflection of accounts within the strategy they oversee or manage, as well as accounts which participate in the sector in which they manage. There are multiple portfolio managers involved with each account.
B-62
| Number of Other Accounts Managed and Total Assets by Account Type | Number of Accounts and Total Assets for Which Advisory Fee is Performance Based |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered Investment Companies |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
Other Accounts |
Registered Investment Companies |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
Other Accounts |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name of Manager |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Barry |
16 | $ | 6,699 | 13 | $ | 10,355 | 41 | $ | 5,283 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stephen E. Becker |
7 | 1,983 | 6 | $ | 1,126 | 25 | $ | 4,932 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kevin Martens |
1 | $ | 5 | — | — | 2 | $ | 106 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Barry |
16 | $ | 6,699 | 13 | $ | 10,355 | 41 | $ | 5,283 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stephen E. Becker |
7 | 1,983 | 6 | $ | 1,126 | 25 | $ | 4,932 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Barry |
16 | $ | 6,699 | 13 | $ | 10,355 | 41 | $ | 5,283 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stephen E. Becker |
7 | 1,983 | 6 | $ | 1,126 | 25 | $ | 4,932 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Barry |
16 | $ | 6,699 | 13 | $ | 10,355 | 41 | $ | 5,283 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Barry |
16 | $ | 6,699 | 13 | $ | 10,355 | 41 | $ | 5,283 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jenny Chang |
3 | $ | 1,395 | — | — | 6 | $ | 254 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Barry |
16 | $ | 6,699 | 13 | $ | 10,355 | 41 | $ | 5,283 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gregory Tuorto |
4 | $ | 2,524 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jessica Katz |
4 | $ | 2,524 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Growth |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gregory Tuorto |
4 | $ | 2,524 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jessica Katz |
4 | $ | 2,524 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Barry |
16 | $ | 6,699 | 13 | $ | 10,355 | 41 | $ | 5,283 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stephen E. Becker |
7 | 1,983 | 6 | $ | 1,126 | 25 | $ | 4,932 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Barry |
16 | $ | 6,699 | 13 | $ | 10,355 | 41 | $ | 5,283 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sung Cho |
1 | $ | 771 | 7 | $ | 9,229 | 11 | $ | 123 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charles “Brook” Dane |
1 | $ | 771 | 7 | $ | 9,229 | 11 | $ | 123 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
B-63
| Number of Other Accounts Managed and Total Assets by Account Type | Number of Accounts and Total Assets for Which Advisory Fee is Performance Based |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered Investment Companies |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
Other Accounts |
Registered Investment Companies |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
Other Accounts |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name Manager |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
Number of Accounts |
Assets Managed |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charles “Brook” Dane |
5 | $ | 2,077 | — | — | 15 | $ | 2,009 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kevin Martens |
1 | $ | 5 | — | — | 2 | $ | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charles “Brook” Dane |
5 | $ | 2,077 | — | — | 15 | $ | 2,009 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kevin Martens |
4 | $ | 1,727 | — | — | 11 | $ | 448 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charles “Brook” Dane |
5 | $ | 2,077 | — | — | 15 | $ | 2,009 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kevin Martens |
4 | $ | 1,727 | — | — | 11 | $ | 448 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sung Cho |
3 | $ | 1,490 | — | — | 4 | $ | 161 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adam Agress |
3 | $ | 1,490 | — | — | 4 | $ | 161 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Robert Crystal |
8 | $ | 5,830 | — | — | 14 | $ | 2,098 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sally Pope Davis |
8 | $ | 5,830 | — | — | 14 | $ | 2,098 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sean A. Butkus |
8 | $ | 5,830 | — | — | 14 | $ | 2,098 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
— | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Robert Crystal |
8 | $ | 5,830 | — | — | 14 | $ | 2,098 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sally Pope Davis |
8 | $ | 5,830 | — | — | 14 | $ | 2,098 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sean A. Butkus |
8 | $ | 5,830 | — | — | 14 | $ | 2,098 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Assets are preliminary, in millions of USD.
B-64
Conflicts of Interest. The Investment Adviser’s portfolio managers are often responsible for managing one or more of the Funds as well as other accounts, including proprietary accounts, separate accounts and other pooled investment vehicles, such as unregistered hedge funds. A portfolio manager may manage a separate account or other pooled investment vehicle which may have materially higher fee arrangements than the Fund and may also have a performance-based fee. The side-by-side management of these funds may raise potential conflicts of interest relating to cross trading, the allocation of investment opportunities and the aggregation and allocation of trades.
The Investment Adviser has a fiduciary responsibility to manage all client accounts in a fair and equitable manner. It seeks to provide best execution of all securities transactions and aggregate and then allocate securities to client accounts in a fair and timely manner. To this end, the Investment Adviser has developed policies and procedures designed to mitigate and manage the potential conflicts of interest that may arise from side-by-side management. In addition, the Investment Adviser and the Funds have adopted policies limiting the circumstances under which cross-trades may be effected between a Fund and another client account. The Investment Adviser conducts periodic reviews of trades for consistency with these policies. For more information about conflicts of interests that may arise in connection with the portfolio manager’s management of the Funds’ investments and the investments of other accounts, see “POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST.”
Portfolio Managers — Compensation
Compensation for portfolio managers of the Investment Adviser is comprised of a base salary and year-end discretionary variable compensation. The base salary is fixed from year to year. Year-end discretionary variable compensation is primarily a function of each portfolio manager’s individual performance and his or her contribution to overall team performance; the performance of GSAM and Goldman Sachs; the team’s net revenues for the past year which in part is derived from advisory fees, and for certain accounts, performance-based fees; and anticipated compensation levels among competitor firms. Portfolio managers are rewarded, in part, for their delivery of investment performance, which is reasonably expected to meet or exceed the expectations of clients and fund shareholders in terms of: excess return over an applicable benchmark, peer group ranking, risk management and factors specific to certain funds such as yield or regional focus. Performance is judged over 1-, 3- and 5-year time horizons.
For compensation purposes, the benchmarks for these Funds are:
U.S. Equity ESG Fund: S&P 500® Index
Capital Growth Fund: Russell 1000® Index
Concentrated Growth Fund: Russell 1000® Growth Index
Flexible Cap Fund: S&P 500® Index
Growth Opportunities Fund: Russell Midcap® Growth Index
Small Cap Growth Fund: Russell 2000® Growth Index
Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund: Russell 2500® Growth Index
Strategic Growth Fund: Russell 1000® Growth Index
Technology Opportunities Fund: NASDAQ Composite Total Return Index
Equity Income Fund: Russell 1000® Value Index
Focused Value Fund: Russell 1000® Value Index
Large Cap Value Fund: Russell 1000® Value Index
Mid Cap Value Fund: Russell Midcap® Value Index
Small Cap Value Fund: Russell 2000® Value Index
Small/Mid Cap Value Fund: Russell 2500® Value Index
B-65
The discretionary variable compensation for portfolio managers is also significantly influenced by various factors, including: (1) effective participation in team research discussions and process; and (2) management of risk in alignment with the targeted risk parameters and investment objectives of a Fund. Other factors may also be considered including: (1) general client/shareholder orientation and (2) teamwork and leadership.
As part of their year-end discretionary variable compensation and subject to certain eligibility requirements, portfolio managers may receive deferred equity-based and similar awards, in the form of: (1) shares of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. (restricted stock units); and, (2) for certain portfolio managers, performance-tracking (or “phantom”) shares of a Fund or multiple funds. Performance-tracking shares are designed to provide a rate of return (net of fees) equal to that of the Fund(s) that a portfolio manager manages, or one or more other eligible funds, as determined by senior management, thereby aligning portfolio manager compensation with fund shareholder interests. The awards are subject to vesting requirements, deferred payment and clawback and forfeiture provisions. GSAM, Goldman Sachs or their affiliates expect, but are not required to, hedge the exposure of the performance-tracking shares of a Fund by, among other things, purchasing shares of the relevant Fund(s).
Other Compensation—In addition to base salary and year-end discretionary variable compensation, the Investment Adviser has a number of additional benefits in place including (1) a 401(k) program that enables employees to direct a percentage of their base salary and bonus income into a tax-qualified retirement plan; and (2) investment opportunity programs in which certain professionals may participate subject to certain eligibility requirements.
Portfolio Managers — Portfolio Managers’ Ownership of Securities in the Funds They Manage
The following table shows the portfolio managers’ ownership of securities, including those beneficially owned as well as those owned pursuant to the deferred compensation plan discussed above, in the Funds they manage as of August 31, 2020, unless otherwise noted:
| Name of Portfolio Manager |
Dollar Range of Equity Securities Beneficially Owned by Portfolio Manager | |
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
||
| Steven M. Barry |
$500,001—$1,000,000 | |
| Stephen E. Becker |
$50,001—$100,000 | |
| Kevin Martens |
None | |
| Capital Growth Fund |
||
| Steven M. Barry |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Stephen E. Becker |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
||
| Steven M. Barry |
Over $1,000,000 | |
| Stephen E. Becker |
$500,001—$1,000,000 | |
| Small Cap Growth Fund |
||
| Gregory Tuorto |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Jessica Katz |
$10,001—$50,000 | |
| Flexible Cap Fund |
||
| Steven M. Barry |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
||
| Steven M. Barry |
Over $1,000,000 | |
| Jenny Chang |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
||
| Steven M. Barry |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Gregory Tuorto |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Jessica Katz |
$10,001—$50,000 | |
| Strategic Growth Fund |
||
| Steven M. Barry |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Stephen E. Becker |
$500,001—$1,000,000 | |
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
||
| Steven M. Barry |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Sung Cho |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Charles “Brook” Dane |
$100,001—$500,000 |
B-66
| Equity Income Fund |
||
| Charles “Brook” Dane |
$10,001—$50,000 | |
| Focused Value Fund |
||
| Charles “Brook” Dane |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Kevin Martens |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Large Cap Value Fund |
||
| Charles “Brook” Dane |
$500,001—$1,000,000 | |
| Kevin Martens |
$10,001—$50,000 | |
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
||
| Sung Cho |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Adam Agress |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Small Cap Value Fund |
||
| Robert Crystal |
Over $1,000,000 | |
| Sally Pope Davis |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Sean A. Butkus |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
||
| Robert Crystal |
Over $1,000,000 | |
| Sally Pope Davis |
$100,001—$500,000 | |
| Sean A. Butkus |
$100,001—$500,000 |
Distributor and Transfer Agent
Distributor. Goldman Sachs, 200 West Street, New York, New York 10282, serves as the exclusive distributor of shares of the Funds pursuant to a “best efforts” arrangement as provided by a distribution agreement with the Trust on behalf of each Fund. Shares of the Funds are offered and sold on a continuous basis by Goldman Sachs, acting as agent. Pursuant to the distribution agreement, after the Prospectuses and periodic reports have been prepared, set in type and mailed to shareholders, Goldman Sachs will pay for the printing and distribution of copies thereof used in connection with the offering to prospective investors. Goldman Sachs will also pay for other supplementary sales literature and advertising costs. Goldman Sachs may enter into sales agreements with certain Intermediaries to solicit subscriptions for Class A, Class C, Investor, Class R, Class R6 and Class P Shares of the Funds. Goldman Sachs receives a portion of the sales charge imposed on the sale, in the case of Class A Shares, or redemption, in the case of Class C Shares (and in certain cases, Class A Shares), of such Fund shares. Goldman Sachs retained approximately the following combined commissions on sales of Class A and Class C Shares during the following periods:
| Fund |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2018 |
|||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 3,433 | $ | 2,824 | $ | 638 | ||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
17,899 | 23,279 | 23,032 | |||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
2,374 | 1,123 | 1,514 | |||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
1,309 | 1,593 | 927 | |||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
12,943 | 8,841 | 11,303 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund1 |
600 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
25,518 | 27,977 | 40,622 | |||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
3,645 | 1,993 | 1,486 | |||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
21,852 | 15,366 | 27,789 | |||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
12,029 | 15,963 | 11,827 | |||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
722 | — | 24 | |||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
6,744 | 3,350 | 3,057 | |||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
17,491 | 13,631 | 19,140 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
2,391 | 2,941 | 5,023 | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
1,452 | 1,044 | 1,917 | |||||||||
| 1 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
B-67
Dealer Reallowances. Class A Shares of the Funds are sold subject to a front-end sales charge, as described in the Prospectuses and in this SAI in the section “SHARES OF THE TRUST.” Goldman Sachs may pay commissions to Intermediaries that sell Class A Shares of the Funds in the form of a “reallowance” of all or a portion of the sales charge paid on the purchase of those shares. Goldman Sachs reallows the following amounts, expressed as a percentage of each Fund’s offering price with respect to purchases of Class A Shares under $50,000:
| Fund |
||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
4.69 | % | ||
| Capital Growth Fund |
4.62 | % | ||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
4.65 | % | ||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
4.72 | % | ||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
4.89 | % | ||
| Small Cap Growth Fund |
4.68 | % | ||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
4.82 | % | ||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
4.45 | % | ||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
4.75 | % | ||
| Equity Income Fund |
4.77 | % | ||
| Focused Value Fund |
4.38 | % | ||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
4.81 | % | ||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
4.77 | % | ||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
5.16 | % | ||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
4.73 | % | ||
Dealer allowances may be changed periodically. During special promotions, the entire sales charge may be reallowed to Intermediaries. Intermediaries to whom substantially the entire sales charge is reallowed may be deemed to be “underwriters” under the 1933 Act.
Transfer Agent. Goldman Sachs, 71 South Wacker Drive, Chicago, IL 60606 serves as the Trust’s transfer and dividend disbursing agent. Under its transfer agency agreement with the Trust, Goldman Sachs has undertaken with the Trust with respect to each Fund to: (i) record the issuance, transfer and redemption of shares, (ii) provide purchase and redemption confirmations and quarterly statements, as well as certain other statements, (iii) provide certain information to the Trust’s custodian and the relevant sub-custodian in connection with redemptions, (iv) provide dividend crediting and certain disbursing agent services, (v) maintain shareholder accounts, (vi) provide certain state Blue Sky and other information, (vii) provide shareholders and certain regulatory authorities with tax-related information, (viii) respond to shareholder inquiries, and (ix) render certain other miscellaneous services. For its transfer agency and dividend disbursing agent services, Goldman Sachs is entitled to receive a transfer agency fee equal, on an annualized basis, to 0.03% of average daily net assets with respect to each Fund’s Class R6 and Class P Shares (as applicable), 0.04% of average daily net assets with respect to each Fund’s Institutional and Service Shares (as applicable) and 0.16% of average daily net assets with respect to each Fund’s Class A, Class C, Investor and Class R Shares (as applicable). Goldman Sachs may pay to certain intermediaries who perform transfer agent services to shareholders a networking or sub-transfer agent fee. These payments will be made from the transfer agency fees noted above and in the Funds’ Prospectuses.
As compensation for services rendered to the Trust by Goldman Sachs as transfer and dividend disbursing agent and the assumption by Goldman Sachs of the expenses related thereto, Goldman Sachs received fees for the fiscal years ended August 31, 2020, August 31, 2019 and August 31, 2018 from each Fund then in existence as follows under the fee schedules then in effect:
| Class A and C Shares*,** | ||||||||||||
| Fund |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2018 |
|||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 10,185 | $ | 7,169 | $ | 4,231 | ||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
1,214,245 | 1,301,083 | 1,393,397 | |||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
13,955 | 12,760 | 13,463 | |||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
11,637 | 11,512 | 12,283 | |||||||||
B-68
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
579,894 | 717,560 | 957,239 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund(1) |
213 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
715,286 | 857,999 | 1,025,484 | |||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
55,787 | 58,880 | 73,598 | |||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
600,267 | 586,041 | 615,317 | |||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
510,352 | 570,717 | 614,922 | |||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
204 | 151 | 220 | |||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
165,820 | 203,610 | 266,799 | |||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
815,289 | 1,056,808 | 1,457,244 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
846,769 | 1,267,831 | 1,575,768 | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
3,600 | 4,474 | 5,175 |
| * | From July 28, 2017 through June 30, 2019, the fee for transfer agent and dividend disbursing agent services with respect to Class A and Class C Shares was 0.18%. |
| ** | From July 1, 2019 through June 30, 2020, the fee for transfer agent and dividend disbursing agent services with respect to Class A and Class C Shares was 0.17%. |
| 1 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
| Institutional Shares | Service Shares | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fund |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2018 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund(1) |
$ | 343 | $ | 900 | $ | 1,797 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
23,957 | 24,910 | 60,930 | $ | 656 | $ | 634 | $ | 649 | |||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund(1) |
4,946 | 5,124 | 48,280 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund(1) |
246 | 381 | 4,780 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
168,531 | 282,808 | 592,483 | 9,754 | 11,499 | 13,697 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund(2) |
2,182 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
319,969 | 351,369 | 467,896 | 7,154 | 6,927 | 7,250 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
20,455 | 23,284 | 75,616 | 201 | 332 | 206 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
38,762 | 30,096 | 38,989 | 12,559 | 12,167 | 10,159 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
8,031 | 8,329 | 13,649 | 64 | 47 | 35 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund(1) |
321 | 287 | 2,096 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
57,718 | 64,505 | 189,494 | 361 | 424 | 969 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
118,372 | 162,736 | 393,263 | 14,572 | 21,814 | 30,680 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
1,113,566 | 1,379,358 | 1,782,231 | 20,391 | 35,193 | 50,017 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund(1) |
2,644 | 2,389 | 16,395 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | The U.S. Equity ESG, Concentrated Growth, Flexible Cap, Focused Value and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds do not offer Service Shares. |
| 2 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. This Fund does not offer Service Shares. |
| Class R and Investor Shares*,** | Class R6 Shares** | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fund |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2018 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 724 | $ | 528 | $ | 413 | $ | 614 | $ | 573 | $ | 4 | ||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
27,207 | 28,780 | 31,427 | 665 | 741 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
294 | 498 | 916 | 177 | 107 | 24 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
154 | 205 | 311 | 61 | 39 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
196,437 | 219,491 | 312,748 | 54,684 | 59,656 | 56,642 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund(2) |
150 | N/A | N/A | 13 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
691,243 | 819,854 | 905,465 | 17,936 | 14,312 | 8,857 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
3,948 | 5,072 | 4,542 | 105 | 85 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund(1) |
44,532 | 33,996 | 39,933 | 132 | 12 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
B-69
| Equity Income Fund |
6,290 | 7,115 | 7,739 | 1,671 | 1,101 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
107 | 107 | 105 | 10 | 10 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
12,409 | 18,304 | 23,048 | 544 | 505 | 153 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
95,793 | 120,735 | 165,197 | 15,217 | 13,821 | 18,269 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
323,385 | 443,220 | 539,249 | 381,263 | 376,880 | 297,856 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
4,624 | 7,137 | 9,463 | 16,484 | 17,053 | 18,731 |
| * | From July 28, 2017 through June 30, 2019, the fee for transfer agent and dividend disbursing agent services with respect to Class R and Investor Shares was 0.18%. |
| ** | From July 1, 2019 through June 30, 2020, the fee for transfer agent and dividend disbursing agent services with respect to Class R and Investor Shares was 0.17%. |
| 1 | The Technology Opportunities Fund does not offer Class R Shares. Class R6 Shares of the Technology Opportunities Fund commenced operations on December 29, 2017. |
| 2 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
The Trust’s distribution and transfer agency agreements each provide that Goldman Sachs may render similar services to others so long as the services Goldman Sachs provides thereunder are not impaired thereby. Such agreements also provide that the Trust will indemnify Goldman Sachs against certain liabilities.
Expenses
The Trust, on behalf of each Fund, is responsible for the payment of each Fund’s respective expenses. The expenses include, without limitation, the fees payable to the Investment Adviser, service fees and shareholder administration fees paid to Intermediaries, the fees and expenses of the Trust’s custodian and subcustodians, transfer agent fees and expenses, pricing service fees and expenses, brokerage fees and commissions, filing fees for the registration or qualification of the Trust’s shares under federal or state securities laws, expenses of the organization of the Funds, fees and expenses incurred by the Trust in connection with membership in investment company organizations including, but not limited to, the Investment Company Institute, taxes, interest, costs of liability insurance, fidelity bonds or indemnification, any costs, expenses or losses arising out of any liability of, or claim for damages or other relief asserted against, the Trust for violation of any law, legal, tax and auditing fees and expenses (including the cost of legal and certain accounting services rendered by employees of Goldman Sachs or its affiliates with respect to the Trust), expenses of preparing and setting in type Prospectuses, SAIs, proxy material, reports and notices and the printing and distributing of the same to the Trust’s shareholders and regulatory authorities, shareholder expenses, any expenses assumed by a Fund pursuant to its distribution and service plans, compensation and expenses of its Independent Trustees, the fees and expenses of pricing services, dividend expenses on short sales and extraordinary expenses, if any, incurred by the Trust. Except for fees and expenses under any service plan, shareholder administration plan or distribution and service plans applicable to a particular class and transfer agency fees and expenses, all Fund expenses are borne on a non-class specific basis.
Fees and expenses borne by the Funds relating to legal counsel, registering shares of a Fund, holding meetings and communicating with shareholders may include an allocable portion of the cost of maintaining an internal legal and compliance department. Each Fund may also bear an allocable portion of the Investment Adviser’s costs of performing certain accounting services not being provided by a Fund’s custodian.
The imposition of the Investment Adviser’s fees, as well as other operating expenses, will have the effect of reducing the total return to investors. From time to time, the Investment Adviser may waive receipt of its fees and/or assume certain expenses of a Fund, which would have the effect of lowering that Fund’s overall expense ratio and increasing total return to investors at the time such amounts are waived or assumed, as the case may be.
The Investment Adviser has agreed to reduce or limit certain “Other Expenses” of the Funds (excluding acquired (underlying) fund fees and expenses, transfer agency fees and expenses, service fees and shareholder administration fees (as applicable), taxes, interest, brokerage fees, shareholder meeting, litigation, indemnification, and extraordinary expenses) to the following annual percentage rates of each Fund’s average daily net assets through at least December 29, 2021:
B-70
| Fund |
Other Expenses |
|||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
0.084 | % | ||
| Capital Growth Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Small Cap Growth Fund |
0.024 | % | ||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
0.044 | % | ||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Equity Income Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Focused Value Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Large Cap Value |
0.004 | % | ||
| Mid Cap Value |
0.104 | % | ||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
0.004 | % | ||
Such reductions or limits, if any, are calculated monthly on a cumulative basis during each Fund’s fiscal year. The Investment Adviser may not terminate the arrangements prior to December 29, 2021 without the approval of the Board of Trustees. The expense limitation may be modified or terminated by the Investment Adviser at its discretion and without shareholder approval after such date, although the Investment Adviser does not presently intend to do so. The Funds’ “Other Expenses” may be further reduced by any custody and transfer agency fee credits received by the Funds.
Reimbursement and Other Expense Reductions
For the fiscal years ended August 31, 2020, August 31, 2019 and August 31, 2018, the amounts of certain “Other Expenses” of each Fund then in existence were reduced or otherwise limited by the Investment Adviser as follows under the expense limitations with the Funds that were then in effect:
| Fund |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2018 |
|||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 279,792 | $ | 335,755 | $ | 302,192 | ||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
720,068 | 704,781 | 699,476 | |||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
297,968 | 385,277 | 362,360 | |||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
278,197 | 353,184 | 299,140 | |||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
657,423 | 578,094 | 522,558 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund1 |
463,305 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
349,237 | 438,426 | 333,932 | |||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
492,609 | 514,208 | 433,492 | |||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
430,113 | 446,204 | 549,542 | |||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
316,532 | 338,461 | 228,700 | |||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
424,953 | 495,579 | 393,544 | |||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
1,330,952 | 1,148,436 | 1,572,997 | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
295,298 | 392,532 | 279,027 | |||||||||
| 1 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
Custodian and Sub-Custodians
BNYM, 240 Greenwich Street, New York, New York 10286, is the custodian of each Fund’s portfolio securities and cash. BNYM also maintains the Fund’s accounting records. BNYM may appoint domestic and foreign sub-custodians and use depositories from time to time to hold securities and other instruments purchased by the Trust in foreign countries and to hold cash and currencies for the Trust.
B-71
Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, 101 Seaport Boulevard, Suite 500, Boston, MA 02210, is the Funds’ independent registered public accounting firm. In addition to audit services, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP provides assistance on certain non-audit matters.
Securities Lending
Pursuant to an agreement between the Funds and BNYM, the Funds may lend their securities through BNYM as securities lending agent to certain qualified borrowers, including Goldman Sachs and its affiliates (the “Securities Agency Lending Agreement”). As securities lending agent of the Funds, BNYM administers the Funds’ securities lending program. These services include arranging the securities loans with approved borrowers and collecting fees and rebates due to the Funds from each borrower. BNYM also collects and maintains collateral intended to secure the obligations of each borrower and marks to market daily the value of loaned securities. If a borrower defaults on a loan, BNYM is authorized to exercise contractual remedies as securities lending agent to the Fund and, pursuant to the terms of the Securities Lending Agency Agreement, has agreed to indemnify the Fund for losses due to a borrower’s failure to return a lent security, which exclude losses associated with collateral reinvestment. BNYM may also, in its capacity as securities lending agent, invest cash received as collateral in pre-approved investments in accordance with the Securities Lending Agency Agreement. BNYM maintains records of loans made and income derived therefrom and makes available such records that the Funds deem necessary to monitor the securities lending program.
For the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020, the Funds earned income and incurred the following costs and expenses as a result of their securities lending activities:
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
Capital Growth Fund |
Concentrated Growth Fund |
Flexible Cap Fund |
Growth Opportunities Fund |
Small Cap Growth Fund |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Income from Securities Lending Activities1 |
$ | 57 | $ | 48,955 | $ | 5,762 | $ | 501 | $ | 155,745 | $ | 0 | ||||||||||||
| Fees and/or Compensation for Securities Lending Activities and Related Services |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue Split2 |
0 | 2,886 | 443 | 0 | 6,237 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cash Collateral Management Fees3 |
54 | 4,004 | 1,329 | 500 | 29,775 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Administrative Fees |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Indemnification Fees |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Rebates to Borrowers |
1 | 16,088 | — | 1 | 63,588 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Fees |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregate Fees/Compensation for Securities Lending Activities |
55 | 22,978 | 1,773 | 501 | 99,601 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net Income from the Securities Lending Activities |
2 | 25,977 | 3,989 | 1 | 56,145 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||
B-72
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
Strategic Growth Fund |
Technology Opportunities Fund |
Equity Income Fund |
Focused Value Fund |
||||||||||||||||
| Gross Income from Securities Lending Activities1 |
$ | 1,507,230 | $ | 10,892 | $ | 24,282 | $ | 36,466 | $ | 555 | ||||||||||
| Fees and/or Compensation for Securities Lending Activities and Related Services |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue Split2 |
134,075 | 435 | 646 | 2,564 | 12 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash Collateral Management Fees3 |
38,512 | 3,112 | 4,288 | 5,745 | 196 | |||||||||||||||
| Administrative Fees |
— | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Indemnification Fees |
— | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Rebates to Borrowers |
127,927 | 3,422 | 13,530 | 5,071 | 236 | |||||||||||||||
| Other Fees |
— | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregate Fees/Compensation for Securities Lending Activities |
300,514 | 6,969 | 18,464 | 13,380 | 444 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Income from the Securities Lending Activities |
1,206,716 | 3,923 | 5,818 | 23,085 | 110 | |||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
Mid Cap Value Fund |
Small Cap Value Fund |
Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
|||||||||||||
| Gross Income from Securities Lending Activities1 |
$ | 14,436 | $ | 503,819 | $ | 439,972 | $ | 5,155 | ||||||||
| Fees and/or Compensation for Securities Lending Activities and Related Services |
||||||||||||||||
| Revenue Split2 |
655 | 46,366 | 27,592 | 250 | ||||||||||||
| Cash Collateral Management Fees3 |
7,886 | 22,875 | 92,963 | 933 | ||||||||||||
| Administrative Fees |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Indemnification Fees |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Rebates to Borrowers |
— | 17,269 | 71,053 | 1,720 | ||||||||||||
| Other Fees |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Aggregate Fees/Compensation for Securities Lending Activities |
8,541 | 86,511 | 191,608 | 2,902 | ||||||||||||
| Net Income from the Securities Lending Activities |
5,896 | 417,307 | 248,364 | 2,253 | ||||||||||||
Amounts shown above may differ from amounts disclosed in a Fund’s Annual Report as a result of timing differences, reconciliations, and certain other adjustments.
| 1 | Gross income includes income from the reinvestment of cash collateral, premium income (i.e., rebates paid by borrowers to the Fund), loan fees paid by borrowers when collateral is noncash, management fees from a pooled cash collateral reinvestment vehicle that are deducted from the vehicle’s assets before income is distributed, and any other income. |
| 2 | Revenue split represents the share of revenue generated by the securities lending program and paid to BNYM. |
| 3 | Cash collateral management fees include the contractual management fees deducted from a pooled cash collateral reinvestment vehicle that are not included in the revenue split. The contractual management fees are derived from the pooled cash collateral reinvestment vehicle’s most recently available prospectus or offering memorandum. Actual fees incurred from a pooled cash collateral reinvestment vehicle may differ due to other expenses, fee waivers and expense reimbursements. |
B-73
POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
General Categories of Conflicts Associated with the Funds
Goldman Sachs (which, for purposes of this “POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST” section, shall mean, collectively, The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc., the Investment Adviser and their affiliates, directors, partners, trustees, managers, members, officers and employees) is a worldwide, full-service investment banking, broker-dealer, asset management and financial services organization and a major participant in global financial markets. As such, it provides a wide range of financial services to a substantial and diversified client base that includes corporations, financial institutions, governments and individuals. Goldman Sachs acts as broker-dealer, investment adviser, investment banker, underwriter, research provider, administrator, financier, adviser, market maker, trader, prime broker, derivatives dealer, clearing agent, lender, counterparty, agent, principal, distributor, investor or in other commercial capacities for accounts or companies or affiliated or unaffiliated investment funds (including pooled investment vehicles and private funds). In those and other capacities, Goldman Sachs advises and deals with clients and third parties in all markets and transactions and purchases, sells, holds and recommends a broad array of investments, including securities, derivatives, loans, commodities, currencies, credit default swaps, indices, baskets and other financial instruments and products, for its own account and for the accounts of clients and of its personnel. In addition, Goldman Sachs has direct and indirect interests in the global fixed income, currency, commodity, equities, bank loan and other markets. In certain cases, the Investment Adviser causes the Funds to invest in products and strategies sponsored, managed or advised by Goldman Sachs or in which Goldman Sachs has an interest, either directly or indirectly, or otherwise restricts the Funds from making such investments, as further described herein. In this regard, Goldman Sachs’ activities and dealings with other clients and third parties may affect the Funds in ways that may disadvantage the Funds and/or benefit Goldman Sachs or other Accounts.
In addition, the Investment Adviser’s activities on behalf of certain other entities that are not investment advisory clients of the Investment Adviser create conflicts of interest between such entities, on the one hand, and Accounts (including the Funds), on the other hand, that are the same as or similar to the conflicts that arise between the Funds and other Accounts, as described herein. In managing conflicts of interest that arise as a result of the foregoing, the Investment Adviser generally will be subject to fiduciary requirements. For purposes of this “POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST” section, “Funds” shall mean, collectively, the Funds and any of the other Goldman Sachs Funds, and “Accounts” shall mean Goldman Sachs’ own accounts, accounts in which personnel of Goldman Sachs have an interest, accounts of Goldman Sachs’ clients, including separately managed accounts (or separate accounts), and investment vehicles that Goldman Sachs sponsors, manages or advises, including the Funds.
The conflicts herein do not purport to be a complete list or explanation of the conflicts associated with the financial or other interests the Investment Adviser or Goldman Sachs may have now or in the future. Additional information about potential conflicts of interest regarding the Investment Adviser and Goldman Sachs is set forth in the Investment Adviser’s Form ADV. A copy of Part 1 and Part 2A of the Investment Adviser’s Form ADV is available on the SEC’s website (www.adviserinfo.sec.gov).
The Sale of Fund Shares and the Allocation of Investment Opportunities
Sales Incentives and Related Conflicts Arising from Goldman Sachs’ Financial and Other Relationships with Intermediaries
Goldman Sachs and its personnel, including employees of the Investment Adviser, receive benefits and earn fees and compensation for services provided to Accounts (including the Funds) and in connection with the distribution of the Funds. Any such fees and compensation are generally paid directly or indirectly out of the fees payable to the Investment Adviser in connection with the management of such Accounts (including the Funds). Moreover, Goldman Sachs and its personnel, including employees of the Investment Adviser, have relationships (both involving and not involving the Funds, and including without limitation placement, brokerage, advisory and board relationships) with distributors, consultants and others who recommend, or engage in transactions with or for, the Funds. Such distributors, consultants and other parties may receive compensation from Goldman Sachs or the Funds in connection with such relationships. As a result of these relationships, distributors, consultants and other parties have conflicts that create incentives for them to promote the Funds.
To the extent permitted by applicable law, Goldman Sachs and the Funds have in the past made, and may in the future make, payments to authorized dealers and other financial intermediaries and to salespersons to promote the Funds. These payments may be made out of Goldman Sachs’ assets or amounts payable to Goldman Sachs. These payments create an incentive for such persons to highlight, feature or recommend the Funds.
B-74
Allocation of Investment Opportunities Among the Funds and Other Accounts
The Investment Adviser manages or advises multiple Accounts (including Accounts in which Goldman Sachs and its personnel have an interest) that have investment objectives that are the same or similar to the Funds and that seek to make or sell investments in the same securities or other instruments, sectors or strategies as the Funds. This creates potential conflicts, particularly in circumstances where the availability or liquidity of such investment opportunities is limited (e.g., in local and emerging markets, high yield securities, fixed income securities, regulated industries, small capitalization, direct or indirect investments in private investment funds, investments in master limited partnerships in the oil and gas industry and initial public offerings/new issues).
Accounts (including the Funds) may invest in other Accounts (including the Funds) at or near the establishment of such Accounts, which may facilitate the Accounts achieving a specified size or scale.
The Investment Adviser does not receive performance-based compensation in respect of its investment management activities on behalf of the Funds, but may simultaneously manage Accounts for which the Investment Adviser receives greater fees or other compensation (including performance-based fees or allocations) than it receives in respect of the Funds. The simultaneous management of Accounts that pay greater fees or other compensation and the Funds creates a conflict of interest as the Investment Adviser has an incentive to favor Accounts with the potential to receive greater fees when allocating resources, services, functions or investment opportunities among Accounts. For instance, the Investment Adviser will be faced with a conflict of interest when allocating scarce investment opportunities given the possibly greater fees from Accounts that pay performance-based fees. To address these types of conflicts, the Investment Adviser has adopted policies and procedures under which it will allocate investment opportunities in a manner that it believes is consistent with its obligations and fiduciary duties as an investment adviser. However, the availability, amount, timing, structuring or terms of an investment available to the Funds differ from, and performance may be lower than, the investments and performance of other Accounts in certain cases.
To address these potential conflicts, the Investment Adviser has developed allocation policies and procedures that provide that the Investment Adviser’s personnel making portfolio decisions for Accounts will make investment decisions for, and allocate investment opportunities among, such Accounts consistent with the Investment Adviser’s fiduciary obligations. These policies and procedures may result in the pro rata allocation (on a basis determined by the Investment Adviser) of limited opportunities across eligible Accounts managed by a particular portfolio management team, but in other cases such allocation may not be pro rata.
Allocation-related decisions for the Funds and other Accounts are made by reference to one or more factors. Factors may include: the Account’s portfolio and its investment horizons and objectives (including with respect to portfolio construction), guidelines and restrictions (including legal and regulatory restrictions affecting certain Accounts or affecting holdings across Accounts); client instructions; strategic fit and other portfolio management considerations, including different desired levels of exposure to certain strategies; the expected future capacity of the Funds and the applicable Accounts; limits on the Investment Adviser’s brokerage discretion; cash and liquidity needs and other considerations; the availability (or lack thereof) of other appropriate or substantially similar investment opportunities; and differences in benchmark factors and hedging strategies among Accounts. Suitability considerations, reputational matters and other considerations may also be considered.
In a case in which one or more Accounts are intended to be the Investment Adviser’s primary investment vehicles focused on, or to receive priority with respect to, a particular trading strategy, other Accounts (including the Funds) may not have access to such strategy or may have more limited access than would otherwise be the case. To the extent that such Accounts are managed by areas of Goldman Sachs other than the Investment Adviser, such Accounts will not be subject to the Investment Adviser’s allocation policies. Investments by such Accounts may reduce or eliminate the availability of investment opportunities to, or otherwise adversely affect, the Fund. Furthermore, in cases in which one or more Accounts are intended to be the Investment Adviser’s primary investment vehicles focused on, or receive priority with respect to, a particular trading strategy or type of investment, such Accounts have specific policies or guidelines with respect to Accounts or other persons receiving the opportunity to invest alongside such Accounts with respect to one or more investments (“Co-Investment Opportunities”). As a result, certain Accounts or other persons will receive allocations to, or rights to invest in, Co-Investment Opportunities that are not available generally to the Funds.
In addition, in some cases the Investment Adviser makes investment recommendations to Accounts that make investment decisions independently of the Investment Adviser. In circumstances in which there is limited availability of an investment opportunity, if such Accounts invest in the investment opportunity at the same time as, or prior to, a Fund, the availability of the investment opportunity for the Fund will be reduced irrespective of the Investment Adviser’s policies regarding allocations of investments.
The Investment Adviser, from time to time, develops and implements new trading strategies or seeks to participate in new trading strategies and investment opportunities. These strategies and opportunities are not employed in all Accounts or employed
B-75
pro rata among Accounts where they are used, even if the strategy or opportunity is consistent with the objectives of such Accounts. Further, a trading strategy employed for a Fund that is similar to, or the same as, that of another Account may be implemented differently, sometimes to a material extent. For example, a Fund may invest in different securities or other assets, or invest in the same securities and other assets but in different proportions, than another Account with the same or similar trading strategy. The implementation of the Fund’s trading strategy depends on a variety of factors, including the portfolio managers involved in managing the trading strategy for the Account, the time difference associated with the location of different portfolio management teams, and the factors described above and in Item 6 (“PERFORMANCE-BASED FEES AND SIDE-BY-SIDE MANAGEMENT—Side-by-Side Management of Advisory Accounts; Allocation of Opportunities”) of the Investment Adviser’s Form ADV.
During periods of unusual market conditions, the Investment Adviser may deviate from its normal trade allocation practices. For example, this may occur with respect to the management of unlevered and/or long-only Accounts that are typically managed on a side-by-side basis with levered and/or long-short Accounts.
The Investment Adviser and the Funds may receive notice of, or offers to participate in, investment opportunities from third parties for various reasons. The Investment Adviser in its sole discretion will determine whether a Fund will participate in any such investment opportunities and investors should not expect that the Fund will participate in any such investment opportunities unless the opportunities are received pursuant to contractual requirements, such as preemptive rights or rights offerings, under the terms of the Fund’s investments. Some or all Funds may, from time to time, be offered investment opportunities that are made available through Goldman Sachs businesses outside of the Investment Adviser, including, for example, interests in real estate and other private investments. In this regard, a conflict of interest exists to the extent that Goldman Sachs controls or otherwise influences the terms and pricing of such investments and/or retains other benefits in connection therewith. However, Goldman Sachs businesses outside of the Investment Adviser are under no obligation or other duty to provide investment opportunities to the Funds, and generally are not expected to do so. Further, opportunities sourced within particular portfolio management teams within the Investment Adviser may not be allocated to Accounts (including the Funds) managed by such teams or by other teams. Opportunities not allocated (or not fully allocated) to the Funds or other Accounts managed by the Investment Adviser may be undertaken by Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser), including for Goldman Sachs Accounts, or made available to other Accounts or third parties, and the Funds will not receive any compensation related to such opportunities. Additional information about the Investment Adviser’s allocation policies is set forth in Item 6 (“PERFORMANCE-BASED FEES AND SIDE-BY-SIDE MANAGEMENT—Side-by-Side Management of Advisory Accounts; Allocation of Opportunities”) of the Investment Adviser’s Form ADV.
As a result of the various considerations above, there will be cases in which certain Accounts (including Accounts in which Goldman Sachs and personnel of Goldman Sachs have an interest) receive an allocation of an investment opportunity at times that the Funds do not, or when the Funds receive an allocation of such opportunities but on different terms than other Accounts (which may be less favorable). The application of these considerations may cause differences in the performance of different Accounts that employ strategies the same or similar to those of the Funds.
Multiple Accounts (including the Funds) may participate in a particular investment or incur expenses applicable in connection with the operation or management of the Accounts, or otherwise may be subject to costs or expenses that are allocable to more than one Account (which may include, without limitation, research expenses, technology expenses, expenses relating to participation in bondholder groups, restructurings, class actions and other litigation, and insurance premiums). The Investment Adviser may allocate investment-related and other expenses on a pro rata or different basis. Certain Accounts are, by their terms or by determination of the Investment Adviser, on a case-by-case basis, not responsible for their share of such expenses, and, in addition, the Investment Adviser has agreed with certain Accounts to cap the amount of expenses (or the amount of certain types of expenses) borne by such Accounts, which results in such Accounts not bearing the full share of expenses they would otherwise have borne as described above. As a result, certain Accounts are responsible for bearing a different or greater amount of expenses, while other Accounts do not bear any, or do not bear their full share, of such expenses. The Investment Adviser may bear any such expenses on behalf of certain Accounts and not for others, as it determines in its sole discretion.
Accounts will generally incur expenses with respect to the consideration and pursuit of transactions that are not ultimately consummated (“broken-deal expenses”). Examples of broken-deal expenses include (i) research costs, (ii) fees and expenses of legal, financial, accounting, consulting or other advisers (including the Investment Adviser or its affiliates) in connection with conducting due diligence or otherwise pursuing a particular non-consummated transaction, (iii) fees and expenses in connection with arranging financing for a particular non-consummated transaction, (iv) travel, entertainment and overtime meal and transportation costs, (v) deposits or down payments that are forfeited in connection with, or amounts paid as a penalty for, a particular non-consummated transaction and (vi) other expenses incurred in connection with activities related to a particular non-consummated transaction.
B-76
The Investment Adviser has adopted a policy relating to the allocation of broken-deal expenses among Accounts (including the Funds) and other potential investors. Pursuant to the policy, broken-deal expenses generally will be allocated among Accounts in the manner that the Investment Adviser determines to be fair and equitable, which will be pro rata or on a different basis.
Goldman Sachs’ Financial and Other Interests May Incentivize Goldman Sachs to Promote the Sale of Fund Shares
Goldman Sachs and its personnel have interests in promoting sales of Fund shares, and the compensation from such sales may be greater than the compensation relating to sales of interests in other Accounts. Therefore, Goldman Sachs and its personnel may have a financial interest in promoting Fund shares over interests in other Accounts.
Management of the Funds by the Investment Adviser
Considerations Relating to Information Held by Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs has established certain information barriers and other policies to address the sharing of information between different businesses within Goldman Sachs. As a result of information barriers, the Investment Adviser generally will not have access, or will have limited access, to certain information and personnel in other areas of Goldman Sachs relating to business transactions for clients (including transactions in investing, banking, prime brokerage and certain other areas), and generally will not manage the Funds with the benefit of information held by such other areas. Goldman Sachs, due to its access to and knowledge of funds, markets and securities based on its prime brokerage and other businesses, may make decisions based on information or take (or refrain from taking) actions with respect to interests in investments of the kind held (directly or indirectly) by the Funds in a manner that may be adverse to the Funds, and will not have any obligation or other duty to share information with the Investment Adviser.
In limited circumstances, however, including for purposes of managing business and reputational risk, and subject to policies and procedures, personnel on one side of an information barrier may have access to information and personnel on the other side of the information barrier through “wall crossings.” The Investment Adviser faces conflicts of interest in determining whether to engage in such wall crossings. Information obtained in connection with such wall crossings may limit or restrict the ability of the Investment Adviser to engage in or otherwise effect transactions on behalf of the Funds (including purchasing or selling securities that the Investment Adviser may otherwise have purchased or sold for an Account in the absence of a wall crossing). In managing conflicts of interest that arise as a result of the foregoing, the Investment Adviser generally will be subject to fiduciary requirements. Information barriers also exist between certain businesses within the Investment Adviser, and the conflicts described herein with respect to information barriers and otherwise with respect to Goldman Sachs and the Investment Adviser will also apply to the businesses within the Investment Adviser. There may also be circumstances in which, as a result of information held by certain portfolio management teams in the Investment Adviser, the Investment Adviser limits an activity or transaction for a Fund, including if the Fund is managed by a portfolio management team other than the team holding such information.
In addition, regardless of the existence of information barriers, Goldman Sachs will not have any obligation or other duty to make available for the benefit of the Funds any information regarding Goldman Sachs’ trading activities, strategies or views, or the activities, strategies or views used for other Accounts. Furthermore, to the extent that the Investment Adviser has access to fundamental analysis and proprietary technical models or other information developed by Goldman Sachs and its personnel, or other parts of the Investment Adviser, the Investment Adviser will not be under any obligation or other duty to effect transactions on behalf of Accounts (including the Funds) in accordance with such analysis and models. In the event Goldman Sachs elects not to share certain information with the Investment Adviser or personnel involved in decision-making for Accounts (including the Funds), the Funds may make investment decisions that differ from those they would have made if Goldman Sachs had provided such information, which may be disadvantageous to the Funds.
Different areas of the Investment Adviser and Goldman Sachs take views, and make decisions or recommendations, that are different than other areas of the Investment Adviser and Goldman Sachs. Different portfolio management teams within the Investment Adviser make decisions based on information or take (or refrain from taking) actions with respect to Accounts they advise in a manner different than or adverse to the Funds. Such teams may not share information with the Funds’ portfolio management teams, including as a result of certain information barriers and other policies, and will not have any obligation or other duty to do so.
Goldman Sachs operates a business known as Goldman Sachs Securities Services (“GSS”), which provides prime brokerage, administrative and other services to clients which may involve investment funds (including pooled investment vehicles and private funds) in which one or more Accounts invest (“Underlying Funds”) or markets and securities in which Accounts invest. GSS and other
B-77
parts of Goldman Sachs have broad access to information regarding the current status of certain markets, investments and funds and detailed information about fund operators that is not available to the Investment Adviser. In addition, Goldman Sachs may act as a prime broker to one or more Underlying Funds, in which case Goldman Sachs will have information concerning the investments and transactions of such Underlying Funds that is not available to the Investment Adviser. As a result of these and other activities, parts of Goldman Sachs may be in possession of information in respect of markets, investments, investment advisers that are affiliated or unaffiliated with Goldman Sachs and Underlying Funds, which, if known to the Investment Adviser, might cause the Investment Adviser to seek to dispose of, retain or increase interests in investments held by Accounts or acquire certain positions on behalf of Accounts, or take other actions. Goldman Sachs will be under no obligation or other duty to make any such information available to the Investment Adviser or personnel involved in decision-making for Accounts (including the Funds).
Valuation of the Funds’ Investments
The Investment Adviser, while not the primary valuation agent of the Funds, performs certain valuation services related to securities and assets held in the Funds. The Investment Adviser performs such valuation services in accordance with its valuation policies. The Investment Adviser may value an identical asset differently than another division or unit within Goldman Sachs values the asset, including because such other division or unit has information or uses valuation techniques and models that it does not share with, or that are different than those of, the Investment Adviser. This is particularly the case in respect of difficult-to-value assets. The Investment Adviser may also value an identical asset differently in different Accounts, including because different Accounts are subject to different valuation guidelines pursuant to their respective governing agreements (e.g., in connection with certain regulatory restrictions applicable to different Accounts). Differences in valuation may also exist because different third-party vendors are hired to perform valuation functions for the Accounts, the Accounts are managed or advised by different portfolio management teams within the Investment Adviser that employ different valuation policies or procedures, or otherwise. The Investment Adviser will face a conflict with respect to valuations generally because of their effect on the Investment Adviser’s fees and other compensation. Furthermore, the application of particular valuation policies with respect to the Funds will, under certain circumstances, result in improved performance of the Funds.
Goldman Sachs’ and the Investment Adviser’s Activities on Behalf of Other Accounts
The Investment Adviser provides advisory services to the Funds. Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser), the clients it advises, and its personnel have interests in and advise Accounts that have investment objectives or portfolios similar to, related to or opposed to those of the Funds. Goldman Sachs may receive greater fees or other compensation (including performance-based fees) from such Accounts than it does from the Funds, in which case Goldman Sachs is incentivized to favor such Accounts. In addition, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser), the clients it advises, and its personnel may engage (or consider engaging) in commercial arrangements or transactions with Accounts, and/or may compete for commercial arrangements or transactions in the same types of companies, assets securities and other instruments, as the Funds. Such arrangements, transactions or investments may adversely affect such Funds by, for example, limiting their ability to engage in such activity or affecting the pricing or terms of such arrangements, transactions or investments. Moreover, a particular Fund on the one hand, and Goldman Sachs or other Accounts, on the other hand, may vote differently on or take or refrain from taking different actions with respect to the same security, which may be disadvantageous to the Fund. Additionally, as described below, the Investment Adviser faces conflicts of interest arising out of Goldman Sachs’ relationships and business dealings in connection with decisions to take or refrain from taking certain actions on behalf of Accounts when doing so would be adverse to Goldman Sachs’ relationships or other business dealings with such parties.
Transactions by, advice to and activities of Accounts (including with respect to investment decisions, voting and the enforcement of rights) may involve the same or related companies, securities or other assets or instruments as those in which the Funds invest, and such Accounts may engage in a strategy while a Fund is undertaking the same or a differing strategy, any of which could directly or indirectly disadvantage the Fund (including its ability to engage in a transaction or other activities).
For example, Goldman Sachs may be engaged to provide advice to an Account that is considering entering into a transaction with a Fund, and Goldman Sachs may advise the Account not to pursue the transaction with the Fund, or otherwise in connection with a potential transaction provide advice to the Account that would be adverse to the Fund. Additionally, a Fund may buy a security and an Account may establish a short position in that same security or in similar securities. This short position may result in the impairment of the price of the security that the Fund holds or may be designed to profit from a decline in the price of the security. A Fund could similarly be adversely impacted if it establishes a short position, following which an Account takes a long position in the same security or in similar securities. In addition, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) may make filings in connection with a shareholder class action lawsuit or similar matter involving a particular security on behalf of an Account (including a Fund), but not on behalf of a different Account (including a Fund) that holds or held the same security, or that is invested in or has extended credit to
B-78
different parts of the capital structure of the same issuer. Accounts may also have different rights in respect of an investment with the same issuer, or invest in different classes of the same issuer that have different rights, including, without limitation, with respect to liquidity. The determination to exercise such rights by the Investment Adviser on behalf of such other Accounts may have an adverse effect on the Funds.
The Funds are expected to transact with a variety of counterparties. Some of these counterparties will also engage in transactions with other Accounts managed by the Investment Adviser or another Goldman Sachs entity. For example, a Fund may directly or indirectly purchase assets from a counterparty at the same time the counterparty (or an affiliate thereof) is also negotiating to purchase different assets from another Account. This creates potential conflicts of interest, particularly with respect to the terms and purchase prices of the sales. For example, Goldman Sachs may receive fees or other compensation in connection with the sale of assets by an Account, which creates an incentive to negotiate a higher purchase price for those assets in a transaction where the Fund is a purchaser. To address these potential conflicts the Investment Adviser implements in such situations policies and procedures to ensure that any transaction is consistent with the Investment Adviser’s fiduciary obligations.
Shareholders may be offered access to advisory services through several different Goldman Sachs businesses (including through Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC and the Investment Adviser). Different advisory businesses within Goldman Sachs manage Accounts according to different strategies and may also apply different criteria to the same or similar strategies and may have differing investment views in respect of an issuer or a security or other investment. Similarly, within the Investment Adviser, certain investment teams or portfolio managers may have differing or opposite investment views in respect of an issuer or a security, and the positions a Fund’s investment team or portfolio managers take in respect of the Fund may be inconsistent with, or adversely affected by, the interests and activities of the Accounts advised by other investment teams or portfolio managers of the Investment Adviser. Research, analyses or viewpoints may be available to clients or potential clients at different times. Goldman Sachs will not have any obligation or other duty to make available to the Funds any research or analysis at any particular time or prior to its public dissemination. The Investment Adviser is responsible for making investment decisions on behalf of the Funds, and such investment decisions can differ from investment decisions or recommendations by Goldman Sachs on behalf of other Accounts. The timing of transactions entered into or recommended by Goldman Sachs, on behalf of itself or its clients, including the Funds, may negatively impact the Funds or benefit certain other Accounts. For example, if Goldman Sachs, on behalf of one or more Accounts, implements an investment decision or strategy ahead of, or contemporaneously with, or behind similar investment decisions or strategies made for the Funds (whether or not the investment decisions emanate from the same research analysis or other information), it could result, due to market impact or other factors, in liquidity constraints or in certain Funds receiving less favorable investment or trading results or incurring increased costs. Similarly, Goldman Sachs may implement an investment decision or strategy that results in a purchase (or sale) of a security for one Fund that may increase the value of such security already held by another Account (or decrease the value of such security that such other Account intends to purchase), thereby benefitting such other Account.
Subject to applicable law, the Investment Adviser may cause the Funds to invest in securities, bank loans or other obligations of companies affiliated with or advised by Goldman Sachs or in which Goldman Sachs or Accounts have an equity, debt or other interest, or to engage in investment transactions that may result in other Accounts being relieved of obligations or otherwise divested of investments, which may enhance the profitability of Goldman Sachs’ or other Accounts’ investment in and activities with respect to such companies. The Investment Adviser, in its discretion and in certain circumstances, recommends that certain Funds have ongoing business dealings, arrangements or agreements with persons who are (i) former employees of Goldman Sachs, (ii) affiliates or other portfolio companies of Goldman Sachs or other Accounts, (iii) Goldman Sachs’ employees’ family members and/or relatives and/or certain of their portfolio companies or (iv) persons otherwise associated with an investor in an Account or a portfolio company or service provider of Goldman Sachs or an Account. The Funds may bear, directly or indirectly, the costs of such dealings, arrangements or agreements. These recommendations, and recommendations relating to continuing any such dealings, arrangements or agreements, pose conflicts of interest and may be based on differing incentives due to Goldman Sachs’ relationships with such persons. In particular, when acting on behalf of, and making decisions for, Accounts, the Investment Adviser may take into account Goldman Sachs’ interests in maintaining its relationships and business dealings with such persons. As a result, the Investment Adviser faces conflicts of interest arising out of Goldman Sachs’ relationships and business dealings in connection with decisions to take or refrain from taking certain actions on behalf of Accounts when doing so would be adverse to Goldman Sachs’ relationships or other business dealings with such parties.
When the Investment Adviser wishes to place an order for different types of Accounts (including the Funds) for which aggregation is not practicable, the Investment Adviser may use a trade sequencing and rotation policy to determine which type of Account is to be traded first. Under this policy, each portfolio management team may determine the length of its trade rotation period and the sequencing schedule for different categories of clients within this period provided that the trading periods and these sequencing schedules are designed to be reasonable. Within a given trading period, the sequencing schedule establishes when and how frequently
B-79
a given client category will trade first in the order of rotation. The Investment Adviser may deviate from the predetermined sequencing schedule under certain circumstances, and the Investment Adviser’s trade sequencing and rotation policy may be amended, modified or supplemented at any time without prior notice to clients.
Potential Conflicts Relating to Follow-On Investments
From time to time, the Investment Adviser provides opportunities to Accounts (including potentially the Funds) to make investments in companies in which certain Accounts have already invested. Such follow-on investments can create conflicts of interest, such as the determination of the terms of the new investment and the allocation of such opportunities among Accounts (including the Funds). Follow-on investment opportunities may be available to the Funds notwithstanding that the Funds have no existing investment in the issuer, resulting in the assets of the Funds potentially providing value to, or otherwise supporting the investments of, other Accounts. Accounts (including the Funds) may also participate in releveraging, recapitalization, and similar transactions involving companies in which other Accounts have invested or will invest. Conflicts of interest in these and other transactions arise between Accounts (including the Funds) with existing investments in a company and Accounts making subsequent investments in the company, which may have opposing interests regarding pricing and other terms. The subsequent investments may dilute or otherwise adversely affect the interests of the previously-invested Accounts (including the Funds).
Diverse Interests of Shareholders
The various types of investors in and beneficiaries of the Funds, including to the extent applicable the Investment Adviser and its affiliates, may have conflicting investment, tax and other interests with respect to their interests in the Funds. When considering a potential investment for a Fund, the Investment Adviser will generally consider the investment objectives of the Fund, not the investment objectives of any particular investor or beneficiary. The Investment Adviser makes decisions, including with respect to tax matters, from time to time that may be more beneficial to one type of investor or beneficiary than another, or to the Investment Adviser and its affiliates than to investors or beneficiaries unaffiliated with the Investment Adviser. In addition, Goldman Sachs faces certain tax risks based on positions taken by the Funds, including as a withholding agent. Goldman Sachs reserves the right on behalf of itself and its affiliates to take actions adverse to the Funds or other Accounts in these circumstances, including withholding amounts to cover actual or potential tax liabilities.
Selection of Service Providers
The Funds expect to engage service providers (including attorneys and consultants) that in certain cases also provide services to Goldman Sachs and other Accounts. In addition, certain service providers to the Investment Adviser or Funds are also portfolio companies or other affiliates of the Investment Adviser or other Accounts (for example, a portfolio company of an Account may retain a portfolio company of another Account). To the extent it is involved in such selection, the Investment Adviser intends to select these service providers based on a number of factors, including expertise and experience, knowledge of related or similar products, quality of service, reputation in the marketplace, relationships with the Investment Adviser, Goldman Sachs or others, and price. These service providers may have business, financial, or other relationships with Goldman Sachs (including its personnel), which may influence the Investment Adviser’s selection of these service providers for the Funds. In such circumstances, there is a conflict of interest between Goldman Sachs (acting on behalf of the Funds) and the Funds or between Funds if the Funds determine not to engage or continue to engage these service providers.
The Investment Adviser may, in its sole discretion, determine to provide, or engage or recommend an affiliate of the Investment Adviser to provide, certain services to the Funds, instead of engaging or recommending one or more third parties to provide such services. Subject to the governance requirements of a particular Fund and applicable law, the Investment Adviser or its affiliates, as applicable, will receive compensation in connection with the provision of such services. As a result, the Investment Adviser faces a conflict of interest when selecting or recommending service providers for the Funds. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the selection or recommendation of service providers for the Funds will be conducted in accordance with the Investment Adviser’s fiduciary obligations to the Funds. The service providers selected or recommended by the Investment Adviser may charge different rates to different recipients based on the specific services provided, the personnel providing the services, the complexity of the services provided or other factors. As a result, the rates paid with respect to these service providers by a Fund, on the one hand, may be more or less favorable than the rates paid by Goldman Sachs, including the Investment Adviser, on the other hand. In addition, the rates paid by the Investment Adviser or the Funds, on the one hand, may be more or less favorable than the rates paid by other parts of Goldman Sachs or Accounts managed by other parts of Goldman Sachs, on the other hand. Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser), its personnel, and/or Accounts may hold investments in companies that provide services to entities in which the Funds invest generally, and, subject to applicable law, the Investment Adviser may refer or introduce such companies’ services to entities that have issued securities held by the Funds.
B-80
Investments in Goldman Sachs Funds
To the extent permitted by applicable law, the Funds will, from time to time invest in money market and/or other funds sponsored, managed or advised by Goldman Sachs. In connection with any such investments, a Fund, to the extent permitted by the Act, will pay all advisory, administrative or Rule 12b-1 fees applicable to the investment. To the extent consistent with applicable law, certain Funds that invest in other funds sponsored, managed or advised by Goldman Sachs pay advisory fees to the Investment Adviser that are not reduced by any fees payable by such other funds to Goldman Sachs as manager of such other funds (i.e., there will be “double fees” involved in making any such investment, which would not arise in connection with the direct allocation of assets by investors in the Funds to such other funds). In such circumstances, as well as in all other circumstances in which Goldman Sachs receives any fees or other compensation in any form relating to the provision of services, no accounting or repayment to the Funds will be required.
Goldman Sachs May In-Source or Outsource
Subject to applicable law, Goldman Sachs, including the Investment Adviser, may from time to time and without notice to investors in-source or outsource certain processes or functions in connection with a variety of services that it provides to the Funds in its administrative or other capacities. Such in-sourcing or outsourcing may give rise to additional conflicts of interest.
Distributions of Assets Other Than Cash
With respect to redemptions from the Funds, the Funds will, in certain circumstances, have discretion to decide whether to permit or limit redemptions and whether to make distributions in connection with redemptions in the form of securities or other assets, and in such case, the composition of such distributions. In making such decisions, the Investment Adviser will sometimes have a potentially conflicting division of loyalties and responsibilities to redeeming investors and remaining investors.
Goldman Sachs Will Act in a Capacity Other Than Investment Adviser to the Funds
Investments in and Advice Regarding Different Parts of an Issuer’s Capital Structure
In some cases, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) or Accounts, on the one hand, and the Funds, on the other hand, invest in or extend credit to different parts of the capital structure of a single issuer. As a result, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) or Accounts may take actions that adversely affect the Funds. In addition, in some cases, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) advises Accounts with respect to different parts of the capital structure of the same issuer, or classes of securities that are subordinate or senior to securities, in which the Funds invest. Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) may pursue rights, provide advice or engage in other activities, or refrain from pursuing rights, providing advice or engaging in other activities, on behalf of itself or other Accounts with respect to an issuer in which the Funds have invested, and such actions (or refraining from action) may have a material adverse effect on the Funds.
For example, in the event that Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) or an Account holds loans, securities or other positions in the capital structure of an issuer that ranks senior in preference to the holdings of a Fund in the same issuer, and the issuer experiences financial or operational challenges, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser), acting on behalf of itself or the Account, may seek a liquidation, reorganization or restructuring of the issuer, or terms in connection with the foregoing, that may have an adverse effect on or otherwise conflict with the interests of the Fund’s holdings in the issuer. In connection with any such liquidation, reorganization or restructuring, the Fund’s holdings in the issuer may be extinguished or substantially diluted, while Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) or another Account may receive a recovery of some or all of the amounts due to them. In addition, in connection with any lending arrangements involving the issuer in which Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) or an Account participates, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) or the Account may seek to exercise its rights under the applicable loan agreement or other document, which may be detrimental to the Fund. In situations in which Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) holds positions in multiple parts of the capital structure of an issuer across Accounts (including the Funds), the Investment Adviser may not pursue actions or remedies that may be available to the Fund, as a result of legal and regulatory requirements or otherwise.
B-81
These potential issues are examples of conflicts that Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) will face in situations in which the Funds, and Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) or other Accounts, invest in or extend credit to different parts of the capital structure of a single issuer. Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) addresses these issues based on the circumstances of particular situations. For example, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) may determine to rely on information barriers between different Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) business units or portfolio management teams. Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) may determine to rely on the actions of similarly situated holders of loans or securities rather than, or in connection with, taking such actions itself on behalf of the Funds.
As a result of the various conflicts and related issues described above and the fact that conflicts will not necessarily be resolved in favor of the interests of the Funds, the Funds could sustain losses during periods in which Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) and other Accounts (including Accounts sponsored, managed or advised by the Investment Adviser) achieve profits generally or with respect to particular holdings in the same issuer, or could achieve lower profits or higher losses than would have been the case had the conflicts described above not existed. The negative effects described above may be more pronounced in connection with transactions in, or the Funds’ use of, small capitalization, emerging market, distressed or less liquid strategies.
Principal and Cross Transactions
When permitted by applicable law and the Investment Adviser’s policies, the Investment Adviser, acting on behalf of certain Funds (for example, those employing taxable fixed income, municipal bond fixed income and structured investment strategies), may enter into transactions in securities and other instruments with or through Goldman Sachs or in Accounts managed by the Investment Adviser or its affiliates, and may (but is under no obligation or other duty to) cause the Funds to engage in transactions in which the Investment Adviser acts as principal on its own behalf (principal transactions), advises both sides of a transaction (cross transactions) and acts as broker for, and receives a commission from, the Funds on one side of a transaction and a brokerage account on the other side of the transaction (agency cross transactions). There are potential conflicts of interest, regulatory issues or restrictions contained in the Investment Adviser’s internal policies relating to these transactions which could limit the Investment Adviser’s determination to engage in these transactions for Accounts (including the Funds). In certain circumstances such as when Goldman Sachs is the only or one of a few participants in a particular market or is one of the largest such participants, such limitations may eliminate or reduce the availability of certain investment opportunities to Accounts (including the Funds) or impact the price or terms on which transactions relating to such investment opportunities may be effected.
Goldman Sachs will have a potentially conflicting division of loyalties and responsibilities to the parties in such transactions. The Investment Adviser has developed policies and procedures in relation to such transactions and conflicts. Cross transactions may disproportionately benefit some Accounts relative to other Accounts, including the Funds, due to the relative amount of market savings obtained by the Accounts, and cross transactions may be effected at different prices for different Accounts due to differing legal and/or regulatory requirements applicable to such Accounts. Principal, cross or agency cross transactions will be effected in accordance with fiduciary requirements and applicable law (which may include disclosure and consent).
Goldman Sachs Acting in Multiple Commercial Capacities
To the extent permitted by applicable law, an issuer in which a Fund has an interest may hire Goldman Sachs to provide underwriting, merger advisory, other financial advisory, placement agency, foreign currency hedging, research, asset management services, brokerage services or other services to the issuer. Furthermore, Goldman Sachs may sponsor, manage, advise or provide services to affiliated Underlying Funds (or their personnel) in which the Funds invest. Goldman Sachs may be entitled to compensation in connection with the provision of such services, and the Funds will not be entitled to any such compensation. Goldman Sachs will have an interest in obtaining fees and other compensation in connection with such services that are favorable to Goldman Sachs, and in connection with providing such services takes commercial steps in its own interest, or advises the parties to which it is providing services, or takes other actions. Such actions may benefit Goldman Sachs. For example, Goldman Sachs may require repayment of all or part of a loan from a company in which an Account (including a Fund) holds an interest, which could cause the company to default or be required to liquidate its assets more rapidly, which could adversely affect the value of the company and the value of the Funds invested therein. Goldman Sachs may also advise such a company to make changes to its capital structure the result of which would be a reduction in the value or priority of a security held (directly or indirectly) by one or more Funds. In addition, underwriters, placement agents or managers of initial public offerings, including Goldman Sachs, may require the Funds who hold privately placed securities of a company to execute a lock-up agreement prior to such company’s initial public offering restricting the resale of the securities for a period of time before and following the IPO. As a result, the Investment Adviser may be restricted from selling the securities in such Funds at a more favorable price. Actions taken or advised to be taken by Goldman Sachs in connection with other types of transactions may also result in adverse consequences for the Funds. Goldman Sachs faces conflicts of interest in providing and selecting services for the Funds because Goldman Sachs provides many services and has many commercial relationships with companies and affiliated and unaffiliated
B-82
Underlying Funds (or their applicable personnel). Providing services to the Funds and companies (or their personnel) in which the Funds invest enhances Goldman Sachs’ relationships with various parties, facilitates additional business development and enables Goldman Sachs to obtain additional business and/or generate additional revenue. The Funds will not be entitled to compensation related to any such benefit to businesses of Goldman Sachs. In addition, such relationships may adversely impact the Funds, including, for example, by restricting potential investment opportunities, as described below, incentivizing the Investment Adviser to take or refrain from taking certain actions on behalf of the Funds when doing so would be adverse to such business relationships, and/or influencing the Investment Adviser’s selection or recommendation of certain investment products and/or strategies over others.
Goldman Sachs’ activities on behalf of its clients may also restrict investment opportunities generally that may be available to the Funds. For example, Goldman Sachs is often engaged by companies as a financial advisor, or to provide financing or other services, in connection with commercial transactions that may be potential investment opportunities for the Funds. There may be circumstances in which the Funds are precluded from participating in such transactions as a result of Goldman Sachs’ engagement by such companies. Goldman Sachs reserves the right to act for these companies in such circumstances, notwithstanding the potential adverse effect on the Funds. Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) also represents creditor or debtor companies in proceedings under Chapter 11 of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code (and equivalent non-U.S. bankruptcy laws) or prior to these filings. From time to time, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) serves on creditor or equity committees. These actions, for which Goldman Sachs may be compensated, may limit or preclude the flexibility that the Funds may otherwise have to buy or sell securities issued by those companies, as well as certain other assets. Please also see “—Management of the Funds by the Investment Adviser—Considerations Relating to Information Held by Goldman Sachs” above and “—Potential Limitations and Restrictions on Investment Opportunities and Activities of Goldman Sachs and the Funds” below.
Subject to applicable law, the Investment Adviser may cause the Funds to invest in securities, bank loans or other obligations of companies affiliated with or advised by Goldman Sachs or in which Goldman Sachs or Accounts have an equity, debt or other interest, or to engage in investment transactions that may result in Goldman Sachs or other Accounts being relieved of obligations or otherwise divested of investments. For example, subject to applicable law a Fund may acquire securities or indebtedness of a company affiliated with Goldman Sachs directly or indirectly through syndicate or secondary market purchases, or may make a loan to, or purchase securities from, a company that uses the proceeds to repay loans made by Goldman Sachs. These activities by a Fund may enhance the profitability of Goldman Sachs or other Accounts with respect to their investment in and activities relating to such companies. The Fund will not be entitled to compensation as a result of this enhanced profitability.
To the extent permitted by applicable law, Goldman Sachs (including the Investment Adviser) creates, writes, sells, issues, invests in or acts as placement agent or distributor of derivative instruments related to the Funds, or with respect to underlying securities or assets of the Funds, or which may be otherwise based on or seek to replicate or hedge the performance of the Funds. Such derivative transactions, and any associated hedging activity, may differ from and be adverse to the interests of the Funds.
Goldman Sachs may make loans to, or enter into margin, asset-based or other credit facilities or similar transactions with, clients, companies or individuals that may (or may not) be secured by publicly or privately held securities or other assets, including a client’s Fund shares as described above. Some of these borrowers are public or private companies, or founders, officers or shareholders in companies in which the Funds (directly or indirectly) invest, and such loans may be secured by securities of such companies, which may be the same as, pari passu with, or more senior or junior to, interests held (directly or indirectly) by the Funds. In connection with its rights as lender, Goldman Sachs may act to protect its own commercial interest and may take actions that adversely affect the borrower, including by liquidating or causing the liquidation of securities on behalf of a borrower or foreclosing and liquidating such securities in Goldman Sachs’ own name. Such actions may adversely affect the Funds (e.g., if a large position in a security is liquidated, among the other potential adverse consequences, the value of such security may decline rapidly and the Funds may in turn decline in value or may be unable to liquidate their positions in such security at an advantageous price or at all). In addition, Goldman Sachs may make loans to shareholders or enter into similar transactions that are secured by a pledge of, or mortgage over, a shareholder’s Fund shares, which would provide Goldman Sachs with the right to redeem such Fund shares in the event that such shareholder defaults on its obligations. These transactions and related redemptions may be significant and may be made without notice to the shareholders.
Code of Ethics and Personal Trading
Each of the Funds and Goldman Sachs, as each Fund’s Investment Adviser and Distributor, has adopted a Code of Ethics (the “Code of Ethics”) in compliance with Section 17(j) of the Act designed to provide that personnel of the Investment Adviser, and certain additional Goldman Sachs personnel who support the Investment Adviser, comply with applicable federal securities laws and place the interests of clients first in conducting personal securities transactions. The Code of Ethics imposes certain restrictions on securities transactions in the personal accounts of covered persons to help avoid conflicts of interest. Subject to the limitations of the Code of
B-83
Ethics, covered persons may buy and sell securities or other investments for their personal accounts, including investments in the Funds, and may also take positions that are the same as, different from, or made at different times than, positions taken (directly or indirectly) by the Funds. The Codes of Ethics are available on the EDGAR Database on the SEC’s Internet site at http://www.sec.gov. Copies may also be obtained after paying a duplicating fee by electronic request to [email protected]. Additionally, all Goldman Sachs personnel, including personnel of the Investment Adviser, are subject to firm-wide policies and procedures regarding confidential and proprietary information, information barriers, private investments, outside business activities and personal trading.
Proxy Voting by the Investment Adviser
The Investment Adviser has implemented processes designed to prevent conflicts of interest from influencing proxy voting decisions that it makes on behalf of advisory clients, including the Funds, and to help ensure that such decisions are made in accordance with its fiduciary obligations to its clients. Notwithstanding such proxy voting processes, proxy voting decisions made by the Investment Adviser in respect of securities held by the Funds may benefit the interests of Goldman Sachs and/or Accounts other than the Funds. For a more detailed discussion of these policies and procedures, see the section of this SAI entitled “PROXY VOTING.”
Potential Limitations and Restrictions on Investment Opportunities and Activities of Goldman Sachs and the Funds
The Investment Adviser may restrict its investment decisions and activities on behalf of the Funds in various circumstances, including as a result of applicable regulatory requirements, information held by the Investment Adviser or Goldman Sachs, Goldman Sachs’ roles in connection with other clients and in the capital markets (including in connection with advice it may give to such clients or commercial arrangements or transactions that may be undertaken by such clients or by Goldman Sachs), Goldman Sachs’ internal policies and/or potential reputational risk in connection with Accounts (including the Funds). The Investment Adviser might not engage in transactions or other activities for, or enforce certain rights in favor of, one or more Funds due to Goldman Sachs’ activities outside the Funds (e.g., the Investment Adviser may refrain from making investments for the Funds that would cause Goldman Sachs to exceed position limits or cause Goldman Sachs to have additional disclosure obligations and may limit purchases or sales of securities in respect of which Goldman Sachs is engaged in an underwriting or other distribution) and regulatory requirements, policies and reputational risk assessments.
In addition, in certain circumstances, the Investment Adviser restricts, limits or reduces the amount of a Fund’s investment, or restricts the type of governance or voting rights it acquires or exercises, where the Fund (potentially together with Goldman Sachs and other Accounts) exceeds a certain ownership interest, or possesses certain degrees of voting or control or has other interests. For example, such limitations may exist if a position or transaction could require a filing or license or other regulatory or corporate consent, which could, among other things, result in additional costs and disclosure obligations for, or impose regulatory restrictions on, Goldman Sachs, including the Investment Adviser, or on other Accounts, or where exceeding a threshold is prohibited or may result in regulatory or other restrictions. In certain cases, restrictions and limitations will be applied to avoid approaching such threshold. Circumstances in which such restrictions or limitations may arise include, without limitation: (i) a prohibition against owning more than a certain percentage of an issuer’s securities; (ii) a “poison pill” that could have a dilutive impact on the holdings of the Fund should a threshold be exceeded; (iii) provisions that would cause Goldman Sachs to be considered an “interested stockholder” of an issuer; (iv) provisions that may cause Goldman Sachs to be considered an “affiliate” or “control person” of the issuer; and (v) the imposition by an issuer (through charter amendment, contract or otherwise) or governmental, regulatory or self-regulatory organization (through law, rule, regulation, interpretation or other guidance) of other restrictions or limitations. In addition, due to regulatory restrictions, certain Accounts are prohibited from, or are subject to certain restrictions when, trading with or through Goldman Sachs, engaging Goldman Sachs as a service provider or purchasing investments issued or managed by Goldman Sachs.
When faced with the foregoing limitations, Goldman Sachs will generally avoid exceeding the threshold because exceeding the threshold could have an adverse impact on the ability of the Investment Adviser or Goldman Sachs to conduct its business activities. The Investment Adviser may also reduce a Fund’s interest in, or restrict a Fund from participating in, an investment opportunity that has limited availability or where Goldman Sachs has determined to cap its aggregate investment in consideration of certain regulatory or other requirements so that other Accounts that pursue similar investment strategies may be able to acquire an interest in the investment opportunity. The Investment Adviser may determine not to engage in certain transactions or activities which may be beneficial to the Funds because engaging in such transactions or activities in compliance with applicable law would result in significant cost to, or administrative burden on, the Investment Adviser or create the potential risk of trade or other errors.
The Investment Adviser generally is not permitted to use material non-public information in effecting purchases and sales in transactions for the Funds that involve public securities. The Investment Adviser may limit an activity or transaction (such as a purchase or sale transaction) which might otherwise be engaged in by the Funds, including as a result of information held by Goldman Sachs
B-84
(including the Investment Adviser or its personnel). For example, directors, officers and employees of Goldman Sachs may take seats on the boards of directors of, or have board of directors observer rights with respect to, companies in which Goldman Sachs invests on behalf of the Funds. To the extent a director, officer or employee of Goldman Sachs were to take a seat on the board of directors of, or have board of directors observer rights with respect to, a public company, the Investment Adviser (or certain of its investment teams) may be limited and/or restricted in its or their ability to trade in the securities of the company. In addition, any such director, officer or employee of Goldman Sachs that is a member of the board of directors of a portfolio company may have duties in his or her capacity as a director that conflict with the Investment Adviser’s duties to Accounts, and may act in a manner that disadvantages or otherwise harms a Fund and/or Goldman Sachs. In the event the Investment Adviser declines access to, or otherwise does not receive, material non-public information regarding an issuer, the Investment Adviser may base investment decisions with respect to securities of such issuer solely on public information, thereby limiting the amount of information available to the Investment Adviser in connection with such investment decisions.
Different areas of Goldman Sachs may come into possession of material non-public information regarding an issuer of securities held by an Underlying Fund in which an Account invests. In the absence of information barriers between such different areas of Goldman Sachs or under certain other circumstances, the Account may be prohibited, including by internal policies, from trading such security or redeeming from such Underlying Fund during the period such material non-public information is held by such other part of Goldman Sachs, which period may be substantial. As a result, the Account may not be permitted to redeem from an Underlying Fund in whole or in part during periods when it otherwise would have been able to do so, which could adversely affect the Account. Other investors in the Underlying Fund that are not subject to such restrictions may be able to redeem from the Underlying Fund during such periods.
In addition, the Investment Adviser’s clients may partially or fully fund a new Account with in-kind securities in which the Investment Adviser may be restricted. In such circumstances, the Investment Adviser will sell any such securities at the next available trading window, subject to operational and technological limitations (unless such securities are subject to another express arrangement). As a result, such Accounts may be required to dispose of investments at an earlier or later date and/or at a less favorable price than would otherwise have been the case had the Investment Adviser not been so restricted. Accounts will be responsible for all tax liabilities that result from any such sale transactions.
The Investment Adviser operates a program reasonably designed to ensure compliance generally with economic and trade sanctions-related obligations applicable directly to its activities (although such obligations are not necessarily the same obligations that the Funds may be subject to). Such economic and trade sanctions may prohibit, among other things, transactions with and the provision of services to, directly or indirectly, certain countries, territories, entities and individuals. These economic and trade sanctions, and the application by the Investment Adviser of its compliance program in respect thereof, may restrict or limit the Funds’ investment activities.
The Investment Adviser may determine to limit or not engage at all in transactions and activities on behalf of the Funds for reputational or other reasons. Examples of when such determinations may be made include, but are not limited to, where Goldman Sachs is providing (or may provide) advice or services to an entity involved in such activity or transaction, where Goldman Sachs or an Account is or may be engaged in the same or a related activity or transaction to that being considered on behalf of the Funds, where Goldman Sachs or an Account has an interest in an entity involved in such activity or transaction, where there are political, public relations, or other reputational considerations relating to counterparties or other participants in such activity or transaction or where such activity or transaction on behalf of or in respect of the Funds could affect in tangible or intangible ways Goldman Sachs, the Investment Adviser, an Account or their activities.
In order to engage in certain transactions on behalf of a Fund, the Investment Adviser will also be subject to (or cause the Fund to become subject to) the rules, terms and/or conditions of any venues through which it trades securities, derivatives or other instruments. This includes, but is not limited to, where the Investment Adviser and/or the Fund are required to comply with the rules of certain exchanges, execution platforms, trading facilities, clearinghouses and other venues, or are required to consent to the jurisdiction of any such venues. The rules, terms and/or conditions of any such venue may result in the Investment Adviser and/or the Fund being subject to, among other things, margin requirements, additional fees and other charges, disciplinary procedures, reporting and recordkeeping, position limits and other restrictions on trading, settlement risks and other related conditions on trading set out by such venues.
From time to time, a Fund, the Investment Adviser or its affiliates and/or their service providers or agents are required, or may determine that it is advisable, to disclose certain information about the Fund, including, but not limited to, investments held by the Fund, and the names and percentage interest of beneficial owners thereof (and the underlying beneficial owners of such beneficial owners), to third parties, including local governmental authorities, regulatory organizations, taxing authorities, markets, exchanges, clearing facilities, custodians, brokers and trading counterparties of, or service providers to, the Investment Adviser or the Fund. The Investment
B-85
Adviser generally expects to comply with requests to disclose such information as it so determines including through electronic delivery platforms; however, the Investment Adviser may determine to cause the sale of certain assets for the Fund rather than make certain required disclosures, and such sale may be at a time that is inopportune from a pricing or other standpoint. In addition, the Investment Adviser may provide third parties with aggregated data regarding the activities of, or certain performance or other metrics associated with the Accounts, and the Investment Adviser may receive compensation from such third parties for providing them such information.
Goldman Sachs may become subject to additional restrictions on its business activities that could have an impact on the Funds’ activities. In addition, the Investment Adviser may restrict its investment decisions and activities on behalf of the Funds and not other Accounts, including Accounts sponsored, managed or advised by the Investment Adviser.
Brokerage Transactions
The Investment Adviser often selects U.S. and non-U.S. broker-dealers (including affiliates of the Investment Adviser) that furnish the Investment Adviser, the Funds, Investment Adviser affiliates and other Goldman Sachs personnel with proprietary or third-party brokerage and research services (collectively, “brokerage and research services”) that provide, in the Investment Adviser’s view, appropriate assistance to the Investment Adviser in the investment decision-making process. These brokerage and research services may be bundled with the trade execution, clearing or settlement services provided by a particular broker-dealer and, subject to applicable law, the Investment Adviser may pay for such brokerage and research services with client commissions (or “soft dollars”). There are instances or situations in which such practices are subject to restrictions under applicable law. For example, the EU’s Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (“MiFID II”) restricts EU domiciled investment advisers from receiving research and other materials that do not qualify as “acceptable minor non-monetary benefits” from broker-dealers unless the research or materials are paid for by the investment advisers from their own resources or from research payment accounts funded by and with the agreement of their clients.
Accounts differ with regard to whether and to what extent they pay for brokerage and research services through commissions and, subject to applicable law, brokerage and research services may be used to service the Funds and any or all other Accounts throughout the Investment Adviser, including Accounts that do not pay commissions to the broker-dealer relating to the brokerage and research service arrangements. As a result, brokerage and research services (including soft dollar benefits) may disproportionately benefit other Accounts relative to the Funds based on the relative amount of commissions paid by the Funds and in particular those Accounts that do not pay for brokerage and research services or do so to a lesser extent, including in connection with the establishment of maximum budgets for research costs (and switching to execution-only pricing when maximums are met). The Investment Adviser does not attempt to allocate soft dollar benefits proportionately among clients or to track the benefits of brokerage and research services to the commissions associated with a particular Account or group of Accounts.
Aggregation of Orders by the Investment Adviser
The Investment Adviser follows policies and procedures pursuant to which it may (but is not required to) combine or aggregate purchase or sale orders for the same security or other instrument for multiple Accounts (including Accounts in which Goldman Sachs or personnel of Goldman Sachs have an interest) (sometimes referred to as “bunching”), so that the orders can be executed at the same time and block trade treatment of any such orders can be elected when available. The Investment Adviser aggregates orders when the Investment Adviser considers doing so to be operationally feasible and appropriate and in the interests of its clients and may elect block trade treatment when available. In addition, under certain circumstances orders for the Funds may be aggregated with orders for Accounts that contain Goldman Sachs assets.
When a bunched order or block trade is completely filled, or if the order is only partially filled, at the end of the day, the Investment Adviser generally will allocate the securities or other instruments purchased or the proceeds of any sale pro rata among the participating Accounts, based on the Funds’ relative sizes. If an order is filled at several different prices, through multiple trades (whether at a particular broker-dealer or among multiple broker-dealers), generally all participating Accounts will receive the average price and pay the average commission, however, this may not always be the case (due to, e.g., odd lots, rounding, market practice or constraints applicable to particular Accounts).
Although it may do so in certain circumstances, the Investment Adviser does not always bunch or aggregate orders for different Funds, elect block trade treatment or net buy and sell orders for the same Fund, if portfolio management decisions relating to the orders are made by different portfolio management teams or if different portfolio management processes are used for different account types, if bunching, aggregating, electing block trade treatment or netting is not appropriate or practicable from the Investment Adviser’s operational or other perspective, or if doing so would not be appropriate in light of applicable regulatory considerations. For example, time zone differences, trading instructions, cash flows, separate trading desks or portfolio management processes may, among other
B-86
factors, result in separate, non-aggregated, non-netted executions, with orders in the same instrument being entered for different Accounts at different times or, in the case of netting, buy and sell trades for the same instrument being entered for the same Account. The Investment Adviser may be able to negotiate a better price and lower commission rate on aggregated orders than on orders for Funds that are not aggregated, and incur lower transaction costs on netted orders than orders that are not netted. The Investment Adviser is under no obligation or other duty to aggregate or net for particular orders. Where orders for a Fund are not aggregated with other orders, or not netted against orders for the Fund or other Accounts, the Fund will not benefit from a better price and lower commission rate or lower transaction cost that might have been available had the orders been aggregated or netted. Aggregation and netting of orders may disproportionately benefit some Accounts relative to other Accounts, including a Fund, due to the relative amount of market savings obtained by the Accounts. The Investment Adviser may aggregate orders of Accounts that are subject to MiFID II (“MiFID II Advisory Accounts”) with orders of Accounts not subject to MiFID II, including those that generate soft dollar commissions (including the Funds) and those that restrict the use of soft dollars. All Accounts included in an aggregated order with MiFID II Advisory Accounts pay (or receive) the same average price for the security and the same execution costs (measured by rate). However, MiFID II Advisory Accounts included in an aggregated order may pay commissions at “execution-only” rates below the total commission rates paid by Accounts included in the aggregated order that are not subject to MiFID II.
PORTFOLIO TRANSACTIONS AND BROKERAGE
The Investment Adviser is responsible for decisions to buy and sell securities for the Funds, the selection of brokers and dealers to effect the transactions and the negotiation of brokerage commissions, if any. Purchases and sales of securities may be executed internally by a broker-dealer, effected on an agency basis in a block transaction, or routed to competing market centers for execution. The compensation paid to the broker for providing execution services generally is negotiated and reflected in either a commission or a “net” price. Executions provided on a net price basis, with dealers acting as principal for their own accounts without a stated commission, usually include a profit to the dealer.
In underwritten offerings, securities are purchased at a fixed price which includes an amount of compensation to the underwriter, generally referred to as the underwriter’s concession or discount. On occasion, certain money market instruments may be purchased directly from an issuer, in which case no commissions or discounts are paid.
In placing orders for portfolio securities or other financial instruments of a Fund, the Investment Adviser is generally required to give primary consideration to obtaining the most favorable execution and net price available. This means that the Investment Adviser will seek to execute each transaction at a price and commission, if any, which provides the most favorable total cost or proceeds reasonably attainable in the circumstances. As permitted by Section 28(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (“Section 28(e)”), a Fund may pay a broker that provides brokerage and research services to the Fund an amount of disclosed commission in excess of the commission which another broker would have charged for effecting that transaction. Such practice is subject to a good faith determination that such commission is reasonable in light of the services provided and to such policies as the Trustees may adopt from time to time. While the Investment Adviser generally seeks reasonably competitive spreads or commissions, a Fund will not necessarily be paying the lowest spread or commission available. Within the framework of this policy, the Investment Adviser will consider research and investment services provided by brokers or dealers who effect or are parties to portfolio transactions of a Fund, the Investment Adviser and its affiliates, or their other clients. Such research and investment services are those which brokerage houses customarily provide to institutional investors and include research reports on particular industries and companies; economic surveys and analyses; recommendations as to specific securities; research products including quotation equipment and computer related programs; advice concerning the value of securities, the advisability of investing in, purchasing or selling securities and the availability of securities or the purchasers or sellers of securities; analyses and reports concerning issuers, industries, securities, economic factors and trends, portfolio strategy and performance of accounts; services relating to effecting securities transactions and functions incidental thereto (such as clearance and settlement); and other lawful and appropriate assistance to the Investment Adviser in the performance of their decision-making responsibilities.
Such services are used by the Investment Adviser in connection with all of its investment activities, and some of such services obtained in connection with the execution of transactions for a Fund may be used in managing other investment accounts. Conversely, brokers furnishing such services may be selected for the execution of transactions of such other accounts, whose aggregate assets may be larger than those of a Fund’s, and the services furnished by such brokers may be used by the Investment Adviser in providing management services for the Trust. The Investment Adviser may also participate in so-called “commission sharing arrangements” and “client commission arrangements” under which the Investment Adviser may execute transactions through a broker-dealer and request that the broker-dealer allocate a portion of the commissions or commission credits to another firm that provides research to the Investment Adviser. The Investment Adviser excludes from use under these arrangements those products and services that are not fully eligible under applicable law and regulatory interpretations—even as to the portion that would be eligible if accounted for separately.
B-87
The research services received as part of commission sharing and client commission arrangements will comply with Section 28(e) and may be subject to different legal requirements in the jurisdictions in which the Investment Adviser does business. Participating in commission sharing and client commission arrangements may enable the Investment Adviser to consolidate payments for research through one or more channels using accumulated client commissions or credits from transactions executed through a particular broker-dealer to obtain research provided by other firms. Such arrangements also help to ensure the continued receipt of research services while facilitating best execution in the trading process. The Investment Adviser believes such research services are useful in its investment decision-making process by, among other things, ensuring access to a variety of high quality research, access to individual analysts and availability of resources that the Investment Adviser might not be provided access to absent such arrangements.
On occasions when the Investment Adviser deems the purchase or sale of a security or other financial instruments to be in the best interest of a Fund as well as its other customers (including any other fund or other investment company or advisory account for which the Investment Adviser acts as investment adviser or sub-investment adviser), the Investment Adviser, to the extent permitted by applicable laws and regulations, may aggregate the securities to be sold or purchased for the Fund with those to be sold or purchased for such other customers in order to obtain the best net price and most favorable execution under the circumstances. In such event, allocation of the securities so purchased or sold, as well as the expenses incurred in the transaction, will be made by the Investment Adviser in the manner it considers to be equitable and consistent with its fiduciary obligations to such Fund and such other customers. In some instances, this procedure may adversely affect the price and size of the position obtainable for a Fund.
Certain Funds may participate in a commission recapture program. Under the program, participating broker-dealers rebate a percentage of commissions earned on Fund portfolio transactions to the particular Fund from which the commissions were generated. The rebated commissions are expected to be treated as realized capital gains of the Funds.
Subject to the above considerations, the Investment Adviser may use Goldman Sachs or an affiliate as a broker for a Fund. In order for Goldman Sachs or an affiliate acting as agent to effect any portfolio transactions for each Fund, the commissions, fees or other remuneration received by Goldman Sachs or an affiliate must be reasonable and fair compared to the commissions, fees or other remuneration received by other brokers in connection with comparable transactions involving similar securities or futures contracts. Furthermore, the Trustees, including a majority of the Independent Trustees, have adopted procedures which are reasonably designed to provide that any commissions, fees or other remuneration paid to Goldman Sachs are consistent with the foregoing standard. Brokerage transactions with Goldman Sachs are also subject to such fiduciary standards as may be imposed upon Goldman Sachs by applicable law.
Commission rates in the U.S. are established pursuant to negotiations with the broker based on the quality and quantity of execution services provided by the broker in the light of generally prevailing rates. The allocation of orders among brokers and the commission rates paid are reviewed periodically by the Trustees. The amount of brokerage commissions paid by a Fund may vary substantially from year to year because of differences in shareholder purchase and redemption activity, portfolio turnover rates and other factors.
For the fiscal years ended August 31, 2020, August 31, 2019 and August 31, 2018, each Fund in existence paid brokerage commissions as follows.
| Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2020 |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid to Goldman Sachs(1) |
Total Amount of Transactions on which Commissions Paid(2) |
Amount of Transactions Effected through Brokers Providing Proprietary Research(3) |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid for Proprietary Research(3) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 3,374 | $ | — | 0 | % | $ | 16,891,566 | 0 | % | $ | 16,879,597 | $ | 3,296 | ||||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
285,358 | 839 | 0 | % | 903,320,712 | 0 | % | 123,158,479 | 37,764 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
24,501 | — | 0 | % | 131,490,551 | 0 | % | 130,134,959 | 24,051 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
8,162 | — | 0 | % | 28,227,597 | 0 | % | 28,227,597 | 7,761 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
471,411 | 4,295 | 1 | % | 1,789,629,782 | 1 | % | 1,761,673,101 | 462,401 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund4 |
10,573 | 55 | 1 | % | 20,615,975 | 0 | % | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
1,106,375 | 24,653 | 2 | % | 3,063,066,620 | 5 | % | 2,946,734,830 | 1,060,561 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
34,805 | 1,636 | 5 | % | 156,811,982 | 2 | % | 156,879,892 | 33,916 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
123,272 | 4,904 | 4 | % | 468,007,705 | 3 | % | 449,244,589 | 121,229 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
141,032 | — | 0 | % | 304,492,627 | 0 | % | 300,687,400 | 137,220 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
5,592 | — | 0 | % | 20,253,234 | 0 | % | 20,147,773 | 5,339 | |||||||||||||||||||
B-88
| Large Cap Value Fund |
200,067 | — | 0 | % | 608,261,304 | 0 | % | 606,853,279 | 194,841 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
1,088,417 | 185 | 0 | % | 2,009,776,241 | 0 | % | 1,968,101,919 | 1,063,635 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
6,398,764 | — | 0 | % | 7,576,651,739 | 0 | % | 6,431,239,810 | 5,838,066 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
112,152 | 949 | 1 | % | 170,714,734 | 0 | % | 156,957,987 | 104,751 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2019 |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid to Goldman Sachs(1) |
Total Amount of Transactions on which Commissions Paid(2) |
Amount of Transactions Effected through Brokers Providing Proprietary Research(3) |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid for Proprietary Research(3) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 2,754 | $ | — | 0 | % | $ | 11,244,831 | 0 | % | $ | 10,232,743 | $ | 2,448 | ||||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
342,838 | 13,558 | 4 | % | 1,131,429,833 | 3 | % | 1,109,641,482 | 335,836 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
33,014 | — | 0 | % | 137,925,183 | 0 | % | 131,853,684 | 29,466 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
5,888 | 99 | 2 | % | 21,099,416 | 1 | % | 20,758,122 | 5,827 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
751,266 | 15,241 | 2 | % | 2,994,182,024 | 2 | % | 2,725,895,301 | 718,764 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
1,903,109 | 61,369 | 3 | % | 3,590,152,946 | 5 | % | 3,277,210,649 | 1,766,997 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
33,953 | 31 | 0 | % | 153,452,736 | 0 | % | 151,455,223 | 33,255 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
87,048 | 2,768 | 3 | % | 327,192,612 | 5 | % | 301,832,161 | 82,679 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
140,816 | — | 0 | % | 324,374,791 | 0 | % | 313,274,820 | 139,376 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
3,565 | 200 | 6 | % | 13,493,552 | 3 | % | 13,164,871 | 3,488 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
232,086 | 4,316 | 2 | % | 682,745,539 | 2 | % | 640,799,336 | 216,125 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
1,216,263 | 5,719 | 0 | % | 2,529,130,234 | 1 | % | 2,368,448,465 | 1,153,320 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
5,060,457 | 5,759 | 0 | % | 5,941,179,230 | 0 | % | 4,776,215,045 | 4,486,027 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
93,512 | 247 | 0 | % | 171,062,036 | 0 | % | 149,713,610 | 85,866 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal Year Ended August 31, 2018 |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid to Goldman Sachs(1) |
Total Amount of Transactions on which Commissions Paid(2) |
Amount of Transactions Effected through Brokers Providing Proprietary Research(3) |
Total Brokerage Commissions Paid for Proprietary Research(3) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 2,678 | $ | — | 0 | % | $ | 13,409,015 | 0 | % | $ | 77,718 | $ | 1,103 | ||||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
632,575 | — | 0 | % | 1,873,550,613 | 0 | % | 528,639 | 9,205 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
32,599 | — | 0 | % | 153,694,876 | 0 | % | 591,116 | 14,530 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
11,424 | — | 0 | % | 62,238,163 | 0 | % | 514,090 | 5,845 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
1,196,268 | — | 0 | % | 3,668,313,320 | 0 | % | 14,886,626 | 373,831 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
1,166,861 | — | 0 | % | 2,859,149,127 | 0 | % | 11,825,574 | 307,493 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
43,492 | — | 0 | % | 302,829,671 | 0 | % | 781,942 | 17,526 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
150,310 | — | 0 | % | 484,280,571 | 0 | % | 648,524 | 15,778 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
283,380 | 1,548 | 1 | % | 556,946,214 | 0 | % | 5,933,271 | 171,882 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
8,580 | — | 0 | % | 25,366,813 | 0 | % | 131,846 | 2,768 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
1,107,209 | 2,600 | 0 | % | 2,634,043,295 | 0 | % | 21,537,256 | 482,250 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
2,865,645 | 91,026 | 3 | % | 6,639,442,737 | 0 | % | 71,169,965 | 1,535,752 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
5,787,104 | 103,702 | 2 | % | 7,916,133,769 | 0 | % | 72,429,713 | 1,636,336 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
132,984 | — | 0 | % | 251,387,830 | 0 | % | 1,356,182 | 29,694 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Percentages refer to percentage of total commissions paid to Goldman Sachs. |
| 2 | Percentages refer to percentage of total amount of transactions involving the payment of commissions effected through Goldman Sachs. |
| 3 | The information above reflects the full commission amounts paid to brokers that provide research to the Investment Adviser. Only a portion of such commission pays for research and the remainder of such commission is to compensate the broker for execution services, commitment of capital and other services related to the execution of brokerage transactions. |
| 4 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
B-89
During the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020, the Trust’s regular “broker-dealers”, as defined in Rule 10b-1 under the Act, were: BofA Securities, Inc., BNY Mellon Capital Markets, LLC, Citigroup Global Markets Inc., Cowen and Company, LLC, International Strategy & Investment Group LLC, J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Jefferies LLC, Liquidnet, Inc., Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC, and National Financial Services LLC.
As of August 31, 2020, those Funds not listed below held no securities of their regular broker dealers. As of the same date, the following Funds held the following amounts of securities of their regular broker-dealers, as defined in Rule 10b-1 under the Act, or the parent entities of such broker-dealers ($ in thousands).
| Fund |
Broker/Dealer |
Amount | ||||
| U.S. Equity ESG |
J.P. Morgan Securities LLC | $ | 305 | |||
| Capital Growth |
BNY Mellon Capital Markets, LLC Citigroup Global Markets Inc. J.P. Morgan Securities LLC Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC |
|
848 1,213 6,784 3,913 |
| ||
| Equity Income |
Citigroup Global Markets Inc. J.P. Morgan Securities LLC Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC |
|
6,585 11,166 6,610 |
| ||
| Flexible Cap |
BofA Securities, Inc. Citigroup Global Markets Inc. J.P. Morgan Securities LLC |
|
48 182 342 |
| ||
| Focused Value |
Citigroup Global Markets Inc. J.P. Morgan Securities LLC |
|
187 305 |
| ||
| Large Cap Value |
Citigroup Global Markets Inc. J.P. Morgan Securities LLC Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC |
|
7,308 10,620 4,737 |
| ||
| Mid Cap Value |
BNY Mellon Capital Markets, LLC | 7,519 | ||||
NET ASSET VALUE
In accordance with procedures adopted by the Trustees, the NAV per share of each class of each Fund is calculated by determining the value of the net assets attributed to each class of that Fund and dividing by the number of outstanding shares of that class. All securities are generally valued on each Business Day as of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange (normally, but not always, 4:00 p.m. Eastern time) or such other time as the New York Stock Exchange or National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations System (“NASDAQ”) market may officially close. The term “Business Day” means any day the New York Stock Exchange is open for trading, which is Monday through Friday except for holidays. The New York Stock Exchange is closed on the following observed holidays: New Year’s Day, Martin Luther King, Jr. Day, Washington’s Birthday, Good Friday, Memorial Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving Day and Christmas.
The time at which transactions and shares are priced and the time by which orders must be received may be changed in case of an emergency or if regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange is stopped at a time other than its regularly scheduled closing time. The Trust reserves the right to reprocess purchase (including dividend reinvestments), redemption and exchange transactions that were processed at a NAV that is subsequently adjusted, and to recover amounts from (or distribute amounts to) shareholders accordingly based on the official closing NAV, as adjusted. The Trust reserves the right to advance the time by which purchase and redemption orders must be received for same business day credit as otherwise permitted by the SEC. In addition, each Fund may compute its NAV as of any time permitted pursuant to any exemption, order or statement of the SEC or its staff.
For the purpose of calculating the NAV per share of the Funds, investments are valued under valuation procedures established by the Trustees. Portfolio securities of a Fund for which accurate market quotations are readily available are generally valued as follows: (i) equity securities listed on any U.S. or foreign stock exchange or on the NASDAQ will be valued at the last sale price or the official closing price on the exchange or system in which they are principally traded on the valuation date. If there is no sale or official closing
B-90
price on the valuation date, equity securities may be valued at the closing bid price for long positions or the closing ask price for short positions at the time closest to, but no later than, the NAV calculation time. If the relevant exchange or system has not closed by the above-mentioned time for determining a Fund’s NAV, the securities will be valued at the last sale price or official closing price, or if not available at the bid price at the time the NAV is determined; (ii) over-the-counter equity securities not quoted on NASDAQ will be valued at the last sale price on the valuation day or, if no sale occurs, at the last bid price for long positions or the last ask price for short positions, at the time closest to, but no later than, the NAV calculation time; (iii) equity securities for which no prices are obtained under sections (i) or (ii) , including those for which a pricing service supplies no exchange quotation or a quotation that is believed by the Investment Adviser to not represent fair value, will be valued through the use of broker quotes, if possible; (iv) fixed income securities will be valued via electronic feeds from independent pricing services to the administrator using evaluated prices provided by a recognized pricing service and dealer-supplied quotations. Fixed income securities for which a pricing service either does not supply a quotation or supplies a quotation that is believed by the Investment Adviser to not represent fair value, will be valued through the use of broker quotes, if possible; (v) fixed income securities for which accurate market quotations are not readily available will be valued by the Investment Adviser based on Board-approved fair valuation policies that incorporate matrix pricing or valuation models, which utilize certain inputs and assumptions, including, but not limited to, yield or price with respect to comparable fixed income securities and various other factors; (vi) investments in open-end registered investment companies (excluding investments in ETFs) and investments in private funds are valued based on the NAV of those registered investment companies or private funds (which may use fair value pricing as discussed in their prospectus or offering memorandum); (vii) spot foreign exchange rates will be valued using a pricing service at the time closest to, but no later than, the NAV calculation time, and forward foreign currency contracts will be valued by adding forward points provided by an independent pricing service to the spot foreign exchange rates and interpolating based upon maturity dates of each contract or by using outright forward rates, where available (if quotations are unavailable from a pricing service or, if the quotations by the Investment Adviser are believed to be inaccurate, the contracts will be valued by calculating the mean between the last bid and ask quotations supplied by at least one dealer in such contracts); (viii) exchange-traded futures contracts will be valued at the last published settlement price on the exchange where they are principally traded (or, if a sale occurs after the last published settlement price but before the NAV calculation time, at the last sale price at the time closest to, but no later than, the NAV calculation time); (ix) exchange-traded options contracts with settlement prices will be valued at the last published settlement price on the exchange where they are principally traded (or, if a sale occurs after the last published settlement price but before the NAV calculation time, at the last sale price at the time closest to, but no later than, the NAV calculation time); (x) exchange-traded options contracts without settlement prices will be valued at the midpoint of the bid and ask prices on the exchange where they are principally traded (or, in the absence of two-way trading, at the last bid price for long positions and the last ask price for short positions at the time closest to, but no later than, the NAV calculation time); (xi) over-the-counter derivatives, including, but not limited to, interest rate swaps, credit default swaps, total return index swaps, put/call option combos, total return basket swaps, index volatility and FX variance swaps, will be valued at their fair market value as determined using counterparty supplied valuations, an independent pricing service or valuation models which use market data inputs supplied by an independent pricing service; and (xii) all other instruments, including those for which a pricing service supplies no exchange quotation/price or a quotation that is believed by the Investment Adviser to be inaccurate, will be valued in accordance with the valuation procedures approved by the Board of Trustees. Securities may also be valued at fair value in accordance with procedures approved by the Board of Trustees where the Funds’ fund accounting agent is unable for other reasons to facilitate pricing of individual securities or calculate the Funds’ NAV, or if the Investment Adviser believes that such quotations do not accurately reflect fair value. Fair values determined in accordance with the valuation procedures approved by the Board of Trustees may be based on subjective judgments and it is possible that the prices resulting from such valuation procedures may differ materially from the value realized on a sale.
The value of all assets and liabilities expressed in foreign currencies will be converted into U.S. dollar values at current exchange rates of such currencies against U.S. dollars as of the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange (normally, but not always, 4:00 p.m. Eastern time). If such quotations are not available, the rate of exchange will be determined in good faith under procedures established by the Board of Trustees.
Generally, trading in securities on European, Asian and Far Eastern securities exchanges and on over-the-counter markets in these regions is substantially completed at various times prior to the close of business on each Business Day in New York (i.e., a day on which the New York Stock Exchange is open for trading). In addition, European, Asian or Far Eastern securities trading generally or in a particular country or countries may not take place on all Business Days in New York. Furthermore, trading takes place in various foreign markets on days which are not Business Days in New York and days on which the Funds’ NAVs are not calculated. Such calculation does not take place contemporaneously with the determination of the prices of the majority of the portfolio securities used in such calculation. For investments in foreign equity securities, “fair value” prices will be provided by an independent third-party pricing (fair value) service (if available), in accordance with fair value procedures approved by the Trustees. Fair value prices are used because many foreign markets operate at times that do not coincide with those of the major U.S. markets. Events that could affect the values of foreign portfolio holdings may occur between the close of the foreign market and the time of determining the NAV, and would not otherwise
B-91
be reflected in the NAV. If the independent third-party pricing (fair value) service does not provide a fair value for a particular security or if the value does not meet the established criteria for the Funds, the most recent closing price for such a security on its principal exchange will generally be its fair value on such date.
The Investment Adviser, consistent with its procedures and applicable regulatory guidance, may (but need not) determine to make an adjustment to the previous closing prices of either domestic or foreign securities in light of significant events, to reflect what it believes to be the fair value of the securities at the time of determining a Fund’s NAV. Significant events that could affect a large number of securities in a particular market may include, but are not limited to: situations relating to one or more single issuers in a market sector; significant fluctuations in U.S. or foreign markets; market dislocations; market disruptions or unscheduled market closings; equipment failures; natural or man made disasters or acts of God; armed conflicts; governmental actions or other developments; as well as the same or similar events which may affect specific issuers or the securities markets even though not tied directly to the securities markets. Other significant events that could relate to a single issuer may include, but are not limited to: corporate actions such as reorganizations, mergers and buy-outs; corporate announcements, including those relating to earnings, products and regulatory news; significant litigation; ratings downgrades; bankruptcies; and trading limits or suspensions.
In general, fair value represents a good faith approximation of the current value of an asset and may be used when there is no public market or possibly no market at all for an asset. A security that is fair valued may be valued at a price higher or lower than actual market quotations or the value determined by other funds using their own fair valuation procedures or by other investors. The fair value of an asset may not be the price at which that asset is ultimately sold.
The proceeds received by each Fund and each other series of the Trust from the issue or sale of its shares, and all net investment income, realized and unrealized gain and proceeds thereof, subject only to the rights of creditors, will be specifically allocated to such Fund or particular series and constitute the underlying assets of that Fund or series. The underlying assets of each Fund will be segregated on the books of account, and will be charged with the liabilities in respect of such Fund and with a share of the general liabilities of the Trust. Expenses of the Trust with respect to the Funds and the other series of the Trust are generally allocated in proportion to the NAVs of the respective Funds or series except where allocations of expenses can otherwise be fairly made.
Each Fund relies on various sources to calculate its NAV. The ability of the Funds’ fund accounting agent to calculate the NAV per share of each share class of the Funds is subject to operational risks associated with processing or human errors, systems or technology failures, cyber attacks and errors caused by third party service providers, data sources, or trading counterparties. Such failures may result in delays in the calculation of a Fund’s NAV and/or the inability to calculate NAV over extended time periods. The Funds may be unable to recover any losses associated with such failures. In addition, if the third party service providers and/or data sources upon which a Fund directly or indirectly relies to calculate its NAV or price individual securities are unavailable or otherwise unable to calculate the NAV correctly, it may be necessary for alternative procedures to be utilized to price the securities at the time of determining the Fund’s NAV.
Errors and Corrective Actions
The Investment Adviser will report to the Board of Trustees any material breaches of investment objective, policies or restrictions and any material errors in the calculation of the NAV of a Fund or the processing of purchases and redemptions. Depending on the nature and size of an error, corrective action may or may not be required. Corrective action may involve a prospective correction of the NAV only, correction of any erroneous NAV and compensation to a Fund, or correction of any erroneous NAV, compensation to a Fund and reprocessing of individual shareholder transactions. The Trust’s policies on errors and corrective action limit or restrict when corrective action will be taken or when compensation to a Fund or its shareholders will be paid, and not all mistakes will result in compensable errors. As a result, neither a Fund nor its shareholders who purchase or redeem shares during periods in which errors accrue or occur may be compensated in connection with the resolution of an error. Shareholders will generally not be notified of the occurrence of a compensable error or the resolution thereof absent unusual circumstances.
As discussed in more detail under “NET ASSET VALUE,” a Fund’s portfolio securities may be priced based on quotations for those securities provided by pricing services. There can be no guarantee that a quotation provided by a pricing service will be accurate.
SHARES OF THE TRUST
Each Fund is a series of Goldman Sachs Trust, a Delaware statutory trust established by an Agreement and Declaration of Trust dated January 28, 1997. The Capital Growth, Equity Income, Mid Cap Value and Small Cap Value Funds were reorganized on April 30, 1997 from series of a Maryland corporation to series of Goldman Sachs Trust. The fiscal year end for each Fund is August 31.
B-92
The Trustees have authority under the Trust’s Declaration of Trust to create and classify shares of beneficial interest in separate series, without further action by shareholders. The Trustees also have authority to classify and reclassify any series of shares into one or more classes of shares. As of December 29, 2020, the Trustees have classified the shares of each of the Funds (other than the U.S. Equity ESG, Concentrated Growth, Flexible Cap, Technology Opportunities, Focused Value and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds) into eight classes: Class A, Class C, Institutional, Investor, Service, Class R, Class R6 and Class P Shares. The Trustees have classified shares of the U.S. Equity ESG Fund, Concentrated Growth Fund, Small Cap Growth, Flexible Cap, Focused Value and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds into seven classes of shares: Class A, Class C, Institutional, Investor, Class R, Class R6 and Class P Shares. The Trustees have classified the Technology Opportunities Fund into seven classes of shares: Class A, Class C, Institutional, Investor, Service, Class R6 and Class P Shares.
Each Class A Share, Class C Share, Institutional Share, Investor Share, Class R Share, Class R6 Share, and Service Share and Class P Share of a Fund represents a proportionate interest in the assets belonging to the applicable class of the Fund. All expenses of a Fund are borne at the same rate by each class of shares, except that fees under the Service Plan and Shareholder Administration Plan are borne exclusively by Service Shares, fees under Distribution and Service Plans (together with the Service Plan and Shareholder Administration Plan, the “Plans”) are borne exclusively by Class A, Class C or Class R Shares and transfer agency fees and expenses are borne at different rates by different share classes. The Trustees may determine in the future that it is appropriate to allocate other expenses differently among classes of shares and may do so to the extent consistent with the rules of the SEC and positions of the IRS. Each class of shares may have different minimum investment requirements and be entitled to different shareholder services. With limited exceptions, shares of a class may only be exchanged for shares of the same or an equivalent class of another fund. See “Shareholder Guide” in the applicable Prospectus and “OTHER INFORMATION REGARDING MAXIMUM SALES CHARGE, PURCHASES, REDEMPTIONS, EXCHANGES AND DIVIDENDS” below. In addition, the fees and expenses set forth below for each class may be subject to fee waivers or reimbursements, as discussed more fully in the Funds’ Prospectuses.
Institutional Shares may be purchased at NAV without a sales charge for accounts in the name of an investor or institution that is not compensated by a Fund under a Plan for services provided to the institution’s customers.
Service Shares may be purchased at NAV without a sales charge for accounts held in the name of an institution that, directly or indirectly, provides certain shareholder administration services and shareholder liaison services to its customers, including maintenance of account records and processing orders to purchase, redeem and exchange Service Shares. Service Shares bear the cost of service fees and shareholder administration fees at the annual rate of up to 0.25% and 0.25%, respectively, of the average daily net assets of the Fund attributable to Service Shares.
Investor and Class R Shares are sold at NAV without a sales charge. Investor and Class R Shares are not sold directly to the public. Instead, Investor and Class R Shares generally are available only to Section 401(k), 403(b), 457, profit sharing, money purchase pension, tax-sheltered annuity, defined benefit pension, non-qualified deferred compensation plans and non-qualified pension plans or other employee benefit plans (including health savings accounts) or SIMPLE plans that are sponsored by one or more employers (including governmental or church employers) or employee organizations (“Employee Benefit Plans”). Investor Shares may also be sold to accounts established under a fee-based program that is sponsored and maintained by an Intermediary that has entered into a contractual relationship with Goldman Sachs to offer such shares through such programs (“Eligible Fee-Based Program”). Investor and Class R Shares are not available to traditional and Roth Individual Retirement Accounts (“IRAs”), SEPs and SARSEPs; except that Investor Shares are available to such accounts or plans to the extent they are purchased through an Eligible Fee-Based Program. Employee Benefit Plans and Eligible Fee-Based Programs must purchase Investor or Class R Shares through an Intermediary using a plan level or omnibus account.
Class R6 Shares are sold at NAV without a sales charge. Class R6 Shares are generally available to the following investors who purchase shares of the Funds through certain Intermediaries that have a contractual relationship with Goldman Sachs, including banks, trust companies, brokers, registered investment advisers and other financial institutions, using a plan level or omnibus account, unless otherwise noted below.
| • | Investors who purchase Class R6 Shares through an Eligible Fee-Based Program; |
| • | Employee Benefit Plans; |
| • | Registered investment companies or bank collective trusts investing directly with the Transfer Agent; |
| • | Institutional investors, including companies, foundations, endowments, municipalities, trusts and other entities, investing at least $5,000,000 directly with the Transfer Agent; and |
B-93
| • | Other investors at the discretion of the Trust’s officers. |
Class R6 Shares may not be available through certain Intermediaries. For the purposes of Class R6 Shares eligibility, the term “Intermediary” does not include Goldman Sachs or its affiliates and Class R6 Shares will not be available to clients of Goldman Sachs Private Wealth Management, The Goldman Sachs Trust Company, N.A., The Goldman Sachs Trust Company of Delaware or The Ayco Company, L.P.
Class P Shares are sold at NAV without a sales charge. Class P Shares of the Funds are offered exclusively to clients of the Goldman Sachs Private Wealth Management business unit that custody their positions at Goldman Sachs; clients of The Goldman Sachs Trust Company, N.A. or The Goldman Sachs Trust Company of Delaware that custody their positions at Goldman Sachs; or clients of The Ayco Company, L.P. that either custody their positions at Goldman Sachs or with certain intermediaries that are authorized to offer Class P Shares; or other investors at the discretion of the Trust’s officers.
Participants in an Employee Benefit Plan should contact their Employee Benefit Plan service provider for information regarding purchases, sales and exchanges of Investor, Class R and Class R6 Shares. Class R Shares bear the cost of distribution (Rule 12b-1) fees at the aggregate rate of up to 0.50% of the average daily net assets attributable to Class R Shares. With respect to Class R Shares the Distributor at its discretion may use compensation for distribution services paid under the Distribution and Service Plan for personal and account maintenance services and expenses so long as such total compensation under the Plan does not exceed the maximum cap on “service fees” imposed by FINRA.
Class A Shares are sold with an initial sales charge of up to 5.50% through brokers and dealers who are members of FINRA and certain other financial service firms that have sales agreements with Goldman Sachs. Class A Shares bear the cost of distribution fees at the aggregate rate of up to 0.25% of the average daily net assets of such Class A Shares. With respect to Class A Shares, the Distributor at its discretion may use compensation for distribution services paid under the Distribution and Service Plan for personal and account maintenance services and expenses so long as such total compensation under the Plan does not exceed the maximum cap on “service fees” imposed by FINRA.
Class C Shares of the Funds are sold subject to a CDSC of up to 1.00% through brokers and dealers who are members of FINRA and certain other financial services firms that have sales arrangements with Goldman Sachs. Class C Shares bear the cost of distribution (Rule 12b-1) fees at the aggregate rate of up to 0.75% of the average daily net assets attributable to Class C Shares. Class C Shares also bear the cost of service fees at an annual rate of up to 0.25% of the average daily net assets attributable to Class C Shares.
It is possible that an institution or its affiliate may offer different classes of shares (i.e., Class A, Class C, Institutional, Investor, Class R, Class R6, Service or Class P Shares) to its customers and thus receive different compensation with respect to different classes of shares of each Fund. Dividends paid by each Fund, if any, with respect to each class of shares will be calculated in the same manner, at the same time on the same day and will be the same amount, except for differences caused by the fact that the respective transfer agency and Plan fees relating to a particular class will be borne exclusively by that class. Similarly, the NAV per share may differ depending upon the class of shares purchased.
Certain aspects of the shares may be altered after advance notice to shareholders if it is deemed necessary in order to satisfy certain tax regulatory requirements.
When issued for the consideration described in the Funds’ Prospectuses, shares are fully paid and non-assessable. The Trustees may, however, cause shareholders, or shareholders of a particular series or class, to pay certain custodian, transfer agency, servicing or similar agent charges by setting off the same against declared but unpaid dividends or by reducing share ownership (or by both means). In the event of liquidation, shareholders are entitled to share pro rata in the net assets of the applicable class of the relevant Fund available for distribution to such shareholders. All shares are freely transferable and have no preemptive, subscription or conversion rights. The Trustees may require shareholders to redeem Shares for any reason under terms set by the Trustees.
In the interest of economy and convenience, the Trust does not issue certificates representing the Funds’ shares. Instead, the Transfer Agent maintains a record of each shareholder’s ownership. Each shareholder receives confirmation of purchase and redemption orders from the Transfer Agent Fund shares and any distributions paid by the Funds are reflected in account statements from the Transfer Agent.
The Act requires that where more than one series of shares exists, each series must be preferred over all other series in respect of assets specifically allocated to such series. Rule 18f-2 under the Act provides that any matter required to be submitted by the provisions of the Act or applicable state law, or otherwise, to the holders of the outstanding voting securities of an investment company such as the
B-94
Trust shall not be deemed to have been effectively acted upon unless approved by the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of each series affected by such matter. Rule 18f-2 further provides that a series shall be deemed to be affected by a matter unless the interests of each series in the matter are substantially identical or the matter does not affect any interest of such series. However, Rule 18f-2 exempts the selection of independent public accountants, the approval of principal distribution contracts and the election of trustees from the separate voting requirements of Rule 18f-2.
The Trust is not required to hold annual meetings of shareholders and does not intend to hold such meetings. In the event that a meeting of shareholders is held, each share of the Trust will be entitled, as determined by the Trustees without the vote or consent of the shareholders, either to one vote for each share or to one vote for each dollar of NAV represented by such share on all matters presented to shareholders including the election of Trustees (this method of voting being referred to as “dollar based voting”). However, to the extent required by the Act or otherwise determined by the Trustees, series and classes of the Trust will vote separately from each other. Shareholders of the Trust do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of Trustees. Meetings of shareholders of the Trust, or any series or class thereof, may be called by the Trustees, certain officers or upon the written request of holders of 10% or more of the shares entitled to vote at such meetings. The Trustees will call a special meeting of shareholders for the purpose of electing Trustees, if, at any time, less than a majority of Trustees holding office at the time were elected by shareholders. The shareholders of the Trust will have voting rights only with respect to the limited number of matters specified in the Declaration of Trust and such other matters as the Trustees may determine or may be required by law.
The Declaration of Trust provides for indemnification of Trustees, officers, employees and agents of the Trust unless the recipient is adjudicated (i) to be liable by reason of willful misfeasance, bad faith, gross negligence or reckless disregard of the duties involved in the conduct of such person’s office or (ii) not to have acted in good faith in the reasonable belief that such person’s actions were in the best interest of the Trust. The Declaration of Trust provides that, if any shareholder or former shareholder of any series is held personally liable solely by reason of being or having been a shareholder and not because of the shareholder’s acts or omissions or for some other reason, the shareholder or former shareholder (or the shareholder’s heirs, executors, administrators, legal representatives or general successors) shall be held harmless from and indemnified against all loss and expense arising from such liability. The Trust, acting on behalf of any affected series, must, upon request by such shareholder, assume the defense of any claim made against such shareholder for any act or obligation of the series and satisfy any judgment thereon from the assets of the series.
The Declaration of Trust permits the termination of the Trust or of any series or class of the Trust (i) by a majority of the affected shareholders at a meeting of shareholders of the Trust, series or class; or (ii) by a majority of the Trustees without shareholder approval if the Trustees determine, in their sole discretion, that such action is in the best interest of the Trust, such series, such class or their shareholders. The Trustees may consider such factors as they, in their sole discretion, deem appropriate in making such determination, including (i) the inability of the Trust or any series or class to maintain its assets at an appropriate size; (ii) changes in laws or regulations governing the Trust, series, or class or affecting assets of the type in which it invests; or (iii) economic developments or trends having a significant adverse impact on the business or operations of the Trust or series.
The Declaration of Trust authorizes the Trustees, without shareholder approval, to cause the Trust, or any series thereof, to merge or consolidate with any corporation, association, trust or other organization or sell or exchange all or substantially all of the property belonging to the Trust or any series thereof. In addition, the Trustees, without shareholder approval, may adopt a master-feeder structure by investing all or a portion of the assets of a series of the Trust in the securities of another open-end investment company with substantially the same investment objective, restrictions and policies.
The Declaration of Trust permits the Trustees to amend the Declaration of Trust without a shareholder vote. However, shareholders of the Trust have the right to vote on any amendment (i) that would adversely affect the voting rights of shareholders; (ii) that is required by law to be approved by shareholders; (iii) that would amend the provisions of the Declaration of Trust regarding amendments and supplements thereto; or (iv) that the Trustees determine to submit to shareholders.
The Trustees may appoint separate Trustees with respect to one or more series or classes of the Trust’s shares (the “Series Trustees”). Series Trustees may, but are not required to, serve as Trustees of the Trust or any other series or class of the Trust. To the extent provided by the Trustees in the appointment of Series Trustees, the Series Trustees may have, to the exclusion of any other Trustees of the Trust, all the powers and authorities of Trustees under the Declaration of Trust with respect to such Series or Class, but may have no power or authority with respect to any other series or class.
Shareholder and Trustee Liability
Under Delaware law, the shareholders of the Funds are not generally subject to liability for the debts or obligations of the Trust. Similarly, Delaware law provides that a series of the Trust will not be liable for the debts or obligations of any other series of the Trust.
B-95
However, no similar statutory or other authority limiting statutory trust shareholder liability exists in other states. As a result, to the extent that a Delaware statutory trust or a shareholder is subject to the jurisdiction of courts of such other states, the courts may not apply Delaware law and may thereby subject the Delaware statutory trust shareholders to liability. To guard against this risk, the Declaration of Trust contains an express disclaimer of shareholder liability for acts or obligations of a series. Notice of such disclaimer will normally be given in each agreement, obligation or instrument entered into or executed by a series of the Trust. The Declaration of Trust provides for indemnification by the relevant series for all loss suffered by a shareholder as a result of an obligation of the series. The Declaration of Trust also provides that a series shall, upon request, assume the defense of any claim made against any shareholder for any act or obligation of the series and satisfy any judgment thereon. In view of the above, the risk of personal liability of shareholders of a Delaware statutory trust is remote.
In addition to the requirements under Delaware law, the Declaration of Trust provides that shareholders of a series may bring a derivative action on behalf of the series only if the following conditions are met: (a) shareholders eligible to bring such derivative action under Delaware law who hold at least 10% of the outstanding shares of the series, or 10% of the outstanding shares of the class to which such action relates, shall join in the request for the Trustees to commence such action; and (b) the Trustees must be afforded a reasonable amount of time to consider such shareholder request and to investigate the basis of such claim. The Trustees will be entitled to retain counsel or other advisers in considering the merits of the request and may require an undertaking by the shareholders making such request to reimburse the series for the expense of any such advisers in the event that the Trustees determine not to bring such action.
The Declaration of Trust further provides that the Trustees will not be liable for errors of judgment or mistakes of fact or law, but nothing in the Declaration of Trust protects a Trustee against liability to which he or she would otherwise be subject by reason of willful misfeasance, bad faith, gross negligence, or reckless disregard of the duties involved in the conduct of his or her office.
TAXATION
The following is a summary of the principal U.S. federal income tax considerations generally affecting the Funds and the purchase, ownership and disposition of shares of the Funds that are not described in the Prospectuses. The discussions below and in the Prospectuses are only summaries and are not intended as substitutes for careful tax planning. They do not address special tax rules applicable to certain classes of investors, such as tax-exempt entities, insurance companies and financial institutions. Each prospective shareholder is urged to consult his or her own tax adviser with respect to the specific federal, state, local and foreign tax consequences of investing in each Fund. The summary is based on the laws in effect on December 29, 2020, which are subject to change. Future changes in tax laws may adversely impact a fund and its shareholders.
Fund Taxation
Each Fund is a separate taxable entity. Each Fund has elected to be treated and intends to qualify for each taxable year as a regulated investment company under Subchapter M of Subtitle A, Chapter 1, of the Code. To qualify as such, a Fund must satisfy certain requirements relating to the sources of its income, diversification of its assets and distribution of its income to shareholders. As a regulated investment company, a Fund will not be subject to federal income or excise tax on any net investment income and net realized capital gains that are distributed to its shareholders in accordance with certain timing requirements of the Code.
There are certain tax requirements that each Fund must follow if it is to avoid federal taxation. In their efforts to adhere to these requirements, the Funds may have to limit their investment activities in some types of instruments. Qualification as a regulated investment company under the Code requires, among other things, that (1) the Fund derive at least 90% of its gross income for each taxable year from dividends, interest, gains from the sale or other disposition of stocks or securities or foreign currencies, net income from qualified publicly traded partnerships or other income (including but not limited to gains from options, futures, and forward contracts) derived with respect to the Fund’s business of investing in stocks, securities or currencies (the “90% gross income test”); and (2) the Fund diversify its holdings so that, in general, at the close of each quarter of its taxable year, (a) at least 50% of the fair market value of the Fund’s total (gross) assets is comprised of cash, cash items, U.S. Government Securities, securities of other regulated investment companies and other securities limited in respect of any one issuer to an amount not greater in value than 5% of the value of such Fund’s total assets and to not more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer, and (b) not more than 25% of the value of its total (gross) assets is invested in the securities of any one issuer (other than U.S. Government Securities and securities of other regulated investment companies), two or more issuers controlled by the Fund and engaged in the same, similar or related trades or businesses or certain publicly traded partnerships.
For purposes of the 90% gross income test, income that a Fund earns from equity interests in certain entities that are not treated as corporations or as qualified publicly traded partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes (e.g., partnerships or trusts) will
B-96
generally have the same character for the Fund as in the hands of such an entity; consequently, a Fund may be required to limit its equity investments in any such entities that earn fee income, rental income or other nonqualifying income. In addition, future Treasury regulations could provide that qualifying income under the 90% gross income test will not include gains from foreign currency transactions that are not directly related to a Fund’s principal business of investing in stock or securities or options and futures with respect to stock or securities. Using foreign currency positions or entering into foreign currency options, futures and forward or swap contracts for purposes other than hedging currency risk with respect to securities in a Fund’s portfolio or anticipated to be acquired may not qualify as “directly-related” under these tests.
If a Fund complies with the foregoing provisions, then in any taxable year in which the Fund distributes, in compliance with the Code’s timing and other requirements, an amount at least equal to the sum of 90% of its “investment company taxable income” (which includes dividends, taxable interest, taxable accrued original issue discount and market discount income, income from securities lending, any net short-term capital gain in excess of net long-term capital loss, certain net realized foreign exchange gains and any other taxable income other than “net capital gain,” as defined below, and is reduced by deductible expenses), plus 90% of the excess of its gross tax-exempt interest income (if any) over certain disallowed deductions, the Fund (but not its shareholders) will be relieved of federal income tax on any income of the Fund, including long-term capital gains, distributed to shareholders. If, instead, a Fund retains any investment company taxable income or “net capital gain” (the excess of net long-term capital gain over net short-term capital loss), it will be subject to a tax at regular corporate rates on the amount retained. Because there are some uncertainties regarding the computation of the amounts deemed distributed to Fund shareholders for these purposes—including, in particular, uncertainties regarding the portion, if any, of amounts paid in redemption of Fund shares that should be treated as such distributions—there can be no assurance that each Fund will avoid corporate-level tax in each year.
Each Fund generally intends to distribute for each taxable year to its shareholders all or substantially all of its investment company taxable income, net capital gain and any net tax-exempt interest. If for any taxable year a Fund does not qualify as a regulated investment company, it will be taxed on all of its taxable income and net capital gain at corporate rates, and its distributions to shareholders will generally be taxable as ordinary dividends to the extent of its current and accumulated earnings and profits.
If a Fund retains any net capital gain, the Fund may designate the retained amount as undistributed capital gains in a notice to its shareholders who (1) if subject to U.S. federal income tax on long-term capital gains, will be required to include in income for federal income tax purposes, as long-term capital gain, their shares of that undistributed amount, and (2) will be entitled to credit their proportionate shares of the tax paid by the Fund against their U.S. federal income tax liabilities, if any, and to claim refunds to the extent the credit exceeds those liabilities. For U.S. federal income tax purposes, the tax basis of shares owned by a shareholder of the Fund will be increased by the amount of any such undistributed net capital gain included in the shareholder’s gross income and decreased by the federal income tax paid by the Fund on that amount of net capital gain.
To avoid a 4% federal excise tax, each Fund must generally distribute (or be deemed to have distributed) by December 31 of each calendar year an amount at least equal to the sum of 98% of its taxable ordinary income (taking into account certain deferrals and elections) for the calendar year, 98.2% of the excess of its capital gains over its capital losses (generally computed on the basis of the one-year period ending on October 31 of such year), and all taxable ordinary income and the excess of capital gains over capital losses for all previous years that were not distributed for those years and on which the Fund paid no federal income tax. For federal income tax purposes, dividends declared by a Fund in October, November or December to shareholders of record on a specified date in such a month and paid during January of the following year are taxable to such shareholders, and deductible by the Fund, as if paid on December 31 of the year declared. Each Fund anticipates that it will generally make timely distributions of income and capital gains in compliance with these requirements so that it will generally not be required to pay the excise tax.
For federal income tax purposes, each Fund is generally permitted to carry forward a net capital loss in any taxable year to offset its own capital gains, if any, during the eight taxable years following the year of the loss. Capital loss carryforwards arising on taxable years of a Fund beginning after December 22, 2010 are generally able to be carried forward indefinitely. These amounts are available to be carried forward to offset future capital gains to the extent permitted by the Code and applicable tax regulations. As of August 31, 2020, the following Funds had capital loss carryforwards approximating the amounts indicated, expiring in the years indicated:
| Fund |
Amount ($) | Year of Expiration | ||||
| Equity Income |
$ | 2,090,486 | Perpetual Long-term | |||
| Small Cap Value |
46,420,689 | Perpetual Short-term | ||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value |
1,546,844 | Perpetual Short-term | ||||
Gains and losses on the sale, lapse, or other termination of options and futures contracts, options thereon and certain forward contracts (except certain foreign currency options, forward contracts and futures contracts) will generally be treated as capital gains and
B-97
losses. Certain of the futures contracts, forward contracts and options held by a Fund will be required to be “marked-to-market” for federal tax purposes — that is, treated as having been sold at their fair market value on the last day of the Fund’s taxable year (or, for excise tax purposes, on the last day of the relevant period). These provisions may require a Fund to recognize income or gains without a concurrent receipt of cash. Any gain or loss recognized on actual or deemed sales of these futures contracts, forward contracts, or options will (except for certain foreign currency options, forward contracts, and futures contracts) be treated as 60% long-term capital gain or loss and 40% short-term capital gain or loss. As a result of certain hedging transactions entered into by a Fund, it may be required to defer the recognition of losses on futures contracts, forward contracts, and options or underlying securities or foreign currencies to the extent of any unrecognized gains on related positions held by the Fund, and the characterization of gains or losses as long-term or short-term may be changed. The tax provisions described in this paragraph may affect the amount, timing and character of a Fund’s distributions to shareholders. The application of certain requirements for qualification as a regulated investment company and the application of certain other tax rules may be unclear in some respects in connection with certain investment practices such as dollar rolls, or investments in certain derivatives, including interest rate swaps, floors, caps and collars, currency swaps, total return swaps, mortgage swaps, index swaps, forward contracts and structured notes. As a result, a Fund may therefore be required to limit its investments in such transactions and it is also possible that the IRS may not agree with a Fund’s tax treatment of such transactions. In addition, the tax treatment of derivatives, and certain other investments, may be affected by future legislation, Treasury Regulations and guidance issued by the IRS that could affect the timing, character and amount of a Fund’s income and gains and distributions to shareholders. Certain tax elections may be available to a Fund to mitigate some of the unfavorable consequences described in this paragraph.
Section 988 of the Code contains special tax rules applicable to certain foreign currency transactions and instruments which may affect the amount, timing and character of income, gain or loss recognized by a Fund. Under these rules, foreign exchange gain or loss realized with respect to foreign currencies and certain futures and options thereon, foreign currency-denominated debt instruments, foreign currency forward contracts, and foreign currency-denominated payables and receivables will generally be treated as ordinary income or loss, although in some cases elections may be available that would alter this treatment. If a net foreign exchange loss treated as ordinary loss under Section 988 of the Code were to exceed a Fund’s investment company taxable income (computed without regard to that loss) for a taxable year, the resulting loss would not be deductible by the Fund or its shareholders in future years. Net loss, if any, from certain foreign currency transactions or instruments could exceed net investment income otherwise calculated for accounting purposes, with the result being either no dividends being paid or a portion of a Fund’s dividends being treated as a return of capital for tax purposes, nontaxable to the extent of a shareholder’s tax basis in his shares and, once such basis is exhausted, generally giving rise to capital gains.
A Fund’s investment, if any, in zero coupon securities, deferred interest securities, certain structured securities or other securities bearing original issue discount or, if a Fund elects to include market discount in income currently, market discount, as well as any “marked-to- market” gain from certain options, futures or forward contracts, as described above, will in many cases cause the Fund to realize income or gain before the receipt of cash payments with respect to these securities or contracts. For a Fund to obtain cash to enable the Fund to distribute any such income or gain, to maintain its qualification as a regulated investment company and to avoid federal income and excise taxes, the Fund may be required to liquidate portfolio investments sooner than it might otherwise have done.
Investments in lower-rated securities may present special tax issues for a Fund to the extent actual or anticipated defaults may be more likely with respect to those kinds of securities. Tax rules are not entirely clear about issues such as when an investor in such securities may cease to accrue interest, original issue discount, or market discount; when and to what extent deductions may be taken for bad debts or worthless securities; how payments received on obligations in default should be allocated between principal and income; and whether exchanges of debt obligations in a workout context are taxable. These and other issues will generally need to be addressed by a Fund, in the event it invests in such securities, so as to seek to eliminate or to minimize any adverse tax consequences.
Each Fund anticipates that it may be subject to foreign taxes on its income (possibly including, in some cases, capital gains) from foreign securities. Tax conventions between certain countries and the United States may reduce or eliminate such taxes in some cases. The Funds will not be eligible to elect to pass through foreign taxes to the shareholders but will be entitled to deduct such taxes in computing the amounts they are required to distribute.
If a Fund acquires stock (including, under proposed regulations, an option to acquire stock such as is inherent in a convertible bond) in certain foreign corporations that receive at least 75% of their annual gross income from passive sources (such as interest, dividends, rents, royalties or capital gain) or hold at least 50% of their assets in investments producing such passive income (“passive foreign investment companies”), the Fund could be subject to federal income tax and additional interest charges on “excess distributions” received from such companies or gain from the sale of stock in such companies, even if all income or gain actually received by the Fund is timely distributed to its shareholders. The Fund will not be able to pass through to its shareholders any credit or deduction for such a
B-98
tax. In some cases, elections may be available that will ameliorate these adverse tax consequences, but those elections will require the Fund to include each year certain amounts as income or gain (subject to the distribution requirements described above) without a concurrent receipt of cash. Each Fund may attempt to limit and/or to manage its holdings in passive foreign investment companies to minimize its tax liability or maximize its return from these investments.
If a Fund invests in certain REITs or in REMIC residual interests, a portion of the Fund’s income may be classified as “excess inclusion income.” A shareholder that is otherwise not subject to tax may be taxable on their share of any such excess inclusion income as “unrelated business taxable income.” In addition, tax may be imposed on a Fund on the portion of any excess inclusion income allocable to any shareholders that are classified as disqualified organizations.
Taxable U.S. Shareholders—Distributions
For U.S. federal income tax purposes, distributions by a Fund, whether reinvested in additional shares or paid in cash, generally will be taxable to shareholders who are subject to tax. Shareholders receiving a distribution in the form of newly issued shares will be treated for U.S. federal income tax purposes as receiving a distribution in an amount equal to the amount of cash they would have received had they elected to receive cash and will have a cost basis in each share received equal to such amount divided by the number of shares received.
In general, distributions from investment company taxable income for the year will be taxable as ordinary income. However, distributions to noncorporate shareholders attributable to dividends received by the Funds from U.S. and certain foreign corporations will generally be taxed at the long-term capital gain rate (described below), as long as certain other requirements are met. For these lower rates to apply, the noncorporate shareholders must have owned their Fund shares for at least 61 days during the 121-day period beginning 60 days before the Fund’s ex-dividend date and the Fund must also have owned the underlying stock for this same period beginning 60 days before the ex-dividend date for the stock. The amount of a Fund’s distributions that otherwise qualify for these lower rates may be reduced as a result of a Fund’s securities lending activities, hedging activities or a high portfolio turnover rate.
Distributions reported to shareholders as derived from a Fund’s dividend income, if any, that would be eligible for the dividends received deduction if such Fund were not a regulated investment company may be eligible for the dividends received deduction for corporate shareholders. The dividends received deduction, if available, is reduced to the extent the shares with respect to which the dividends are received are treated as debt-financed under federal income tax law and is eliminated if the shares are deemed to have been held for less than a minimum period, generally 46 days. The dividends received deduction also may be reduced as a result of a Fund’s securities lending activities, hedging activities or a high portfolio turnover rate. The dividend may, if it is treated as an “extraordinary dividend” under the Code, reduce a shareholder’s tax basis in its shares of a Fund. Capital gain dividends (i.e., dividends from net capital gain), if reported as such to shareholders, will be taxed to shareholders as long-term capital gain regardless of how long shares have been held by shareholders, but are not eligible for the dividends received deduction for corporations. The maximum individual rate applicable to long-term capital gains is generally either 15% or 20%, depending on whether the individual’s income exceeds certain threshold amounts. Distributions, if any, that are in excess of a Fund’s current and accumulated earnings and profits will first reduce a shareholder’s tax basis in his shares and, after such basis is reduced to zero, will generally constitute capital gains to a shareholder who holds his shares as capital assets.
Under recent tax legislation, individuals and certain other noncorporate entities are generally eligible for a 20% deduction with respect to ordinary dividends received from REITs (“qualified REIT dividends”) and certain taxable income from publicly traded partnerships. Applicable treasury regulations permit a RIC to pass through to its shareholders qualified REIT dividends eligible for the 20% deduction. However, the regulations do not provide a mechanism for a RIC to pass through to its shareholders income from publicly traded partnerships that would be eligible for such deduction.
Different tax treatment, including penalties on certain excess contributions and deferrals, certain pre-retirement and post-retirement distributions and certain prohibited transactions, is accorded to accounts maintained as qualified retirement plans. Shareholders should consult their tax advisers for more information.
Taxable U.S. Shareholders—Sale of Shares
When a shareholder’s shares are sold, redeemed or otherwise disposed of in a transaction that is treated as a sale for tax purposes, the shareholder will generally recognize gain or loss equal to the difference between the shareholder’s adjusted tax basis in the shares and the cash, or fair market value of any property, received. (To aid in computing that tax basis, a shareholder should generally retain its account statements for the period that it holds shares.) If the shareholder holds the shares as a capital asset at the time of sale, the
B-99
character of the gain or loss should be capital, and treated as long-term if the shareholder’s holding period is more than one year and short-term otherwise, subject to the rules below. Shareholders should consult their own tax advisers with reference to their particular circumstances to determine whether a redemption (including an exchange) or other disposition of Fund shares is properly treated as a sale for tax purposes, as is assumed in this discussion.
Certain special tax rules may apply to a shareholder’s capital gains or losses on Fund shares. If a shareholder receives a capital gain dividend with respect to shares and such shares have a tax holding period of six months or less at the time of a sale or redemption of such shares, then any loss the shareholder realizes on the sale or redemption will be treated as a long-term capital loss to the extent of such capital gain dividend. All or a portion of any sales load paid upon the purchase of shares of a Fund will generally not be taken into account in determining gain or loss on the redemption or exchange of such shares within 90 days after their purchase to the extent the redemption proceeds are reinvested, or the exchange is effected, on or before January 31 of the calendar year following the calendar year in which the original stock is disposed of without payment of an additional sales load pursuant to the reinvestment or exchange privilege. The load not taken into account will be added to the tax basis of the newly acquired shares. Additionally, any loss realized on a sale or redemption of shares of a Fund may be disallowed under “wash sale” rules to the extent the shares disposed of are replaced with other shares of the same Fund within a period of 61 days beginning 30 days before and ending 30 days after the shares are disposed of, such as pursuant to a dividend reinvestment in shares of such Fund. If disallowed, the loss will be reflected in an adjustment to the basis of the shares acquired.
Backup Withholding
Each Fund may be required to withhold, as “backup withholding,” federal income tax, currently at a 24% rate, from dividends (including capital gain dividends) and share redemption and exchange proceeds to individuals and other non exempt shareholders who fail to furnish the Fund with a correct taxpayer identification number (“TIN”) certified under penalties of perjury, or if the IRS or a broker notifies the Fund that the payee is subject to backup withholding as a result of failing properly to report interest or dividend income to the IRS or that the TIN furnished by the payee to the Portfolio is incorrect, or if (when required to do so) the payee fails to certify under penalties of perjury that it is not subject to backup withholding. A Portfolio may refuse to accept an application that does not contain any required TIN or certification that the TIN provided is correct. If the backup withholding provisions are applicable, any such dividends and proceeds, whether paid in cash or reinvested in additional shares, will be reduced by the amounts required to be withheld. Any amounts withheld may be credited against a shareholder’s U.S. federal income tax liability. If a shareholder does not have a TIN, it should apply for one immediately by contacting the local office of the Social Security Administration or the IRS. Backup withholding could apply to payments relating to a shareholder’s account while the shareholder is awaiting receipt of a TIN. Special rules apply for certain entities. For example, for an account established under a Uniform Gifts or Transfer to Minors Act, the TIN of the minor should be furnished.
Medicare Tax
An additional 3.8% Medicare tax is imposed on certain net investment income (including ordinary dividends and capital gain distributions received from a Fund and net gains from redemptions or other taxable dispositions of Fund shares) of U.S. individuals, estates and trusts to the extent that such person’s “modified adjusted gross income” (in the case of an individual) or “adjusted gross income” (in the case of an estate or trust) exceeds certain threshold amounts.
Non-U.S. Shareholders
The discussion above relates solely to U.S. federal income tax law as it applies to “U.S. persons” subject to tax under such law.
Except as discussed below, distributions to shareholders who, as to the United States, are not “U.S. persons,” (i.e., are nonresident aliens, foreign corporations, fiduciaries of foreign trusts or estates or other non-U.S. investors) generally will be subject to U.S. federal withholding tax at the rate of 30% on distributions treated as ordinary income unless the tax is reduced or eliminated pursuant to a tax treaty or the distributions are effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business of the shareholder; but distributions of net capital gain including amounts retained by a Fund which are designated as undistributed capital gains, to such a non-U.S. shareholder will not be subject to U.S. federal income or withholding tax unless the distributions are effectively connected with the shareholder’s trade or business in the United States or, in the case of a shareholder who is a nonresident alien individual, the shareholder is present in the United States for 183 days or more during the taxable year and certain other conditions are met.
Non-U.S. shareholders generally are not subject to U.S. federal income tax withholding on certain distributions of interest income and/or short-term capital gains that are designated by the Funds. It is expected that the Funds will generally make designations of short-
B-100
term gains, to the extent permitted, but the Funds do not intend to make designations of any distributions attributable to interest income. Therefore, all distributions of interest income will be subject to withholding when paid to non-U.S. investors.
Any capital gain realized by a non-U.S. shareholder upon a sale or redemption of shares of a Fund will not be subject to U.S. federal income or withholding tax unless the gain is effectively connected with the shareholder’s trade or business in the U.S., or in the case of a shareholder who is a nonresident alien individual, the shareholder is present in the U.S. for 183 days or more during the taxable year and certain other conditions are met.
Non-U.S. persons who fail to furnish a Fund with the proper IRS Form W-8 (i.e., W-8BEN, W-8BEN-E, W-8ECI, W-8IMY or W-8EXP), or an acceptable substitute, may be subject to backup withholding at a 24% rate on dividends (including capital gain dividends) and on the proceeds of redemptions and exchanges.
Also, non-U.S. shareholders of a Fund may be subject to U.S. estate tax with respect to their Fund shares.
The Funds are required to withhold U.S. tax (at a 30% rate) on payments of dividends made to certain non-U.S. entities that fail to comply (or be deemed compliant) with extensive new reporting and withholding requirements designed to inform the U.S. Department of the Treasury of U.S.-owned foreign investment accounts. Shareholders may be requested to provide additional information to the Funds to enable the Funds to determine whether withholding is required.
Each shareholder who is not a U.S. person should consult his or her tax adviser regarding the U.S. and non-U.S. tax consequences of ownership of shares of, and receipt of distributions from, the Funds.
State and Local Taxes
Each Fund may be subject to state or local taxes in jurisdictions in which the Fund is deemed to be doing business. In addition, in those states or localities that impose income taxes, the treatment of such a Fund and its shareholders under those jurisdictions’ tax laws may differ from the treatment under federal income tax laws, and investment in such a Fund may have tax consequences for shareholders that are different from those of a direct investment in the Fund’s portfolio securities. Shareholders should consult their own tax advisers concerning state and local tax matters.
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The audited financial statements and related reports of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, independent registered public accounting firm for the Funds, contained in the Funds’ 2020 Annual Reports are hereby incorporated by reference. The financial statements in each Fund’s Annual Report have been incorporated herein by reference in reliance upon such report given upon the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing. No other parts of any Annual Report are incorporated by reference herein. Copies of the 2020 Annual Reports may be obtained upon request and without charge by writing Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC, P.O. Box 06050, Chicago, Illinois 60606 or by calling Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC, at the telephone number on the back cover of each Fund’s Prospectus.
PROXY VOTING
The Trust, on behalf of the Funds, has delegated the voting of portfolio securities to the Investment Adviser. For client accounts for which the Investment Adviser has voting discretion, the Investment Adviser has adopted policies and procedures (the “Proxy Voting Policy”) for the voting of proxies. Under the Proxy Voting Policy, the Investment Adviser’s guiding principles in performing proxy voting are to make decisions that favor proposals that in the Investment Adviser’s view tend to maximize a company’s shareholder value and are not influenced by conflicts of interest. To implement these guiding principles for investments in publicly-traded equities, the Investment Adviser has developed customized proxy voting guidelines (the “Guidelines”) that it generally applies when voting on behalf of client accounts. Attached as Appendix B is a summary of the Guidelines. These Guidelines address a wide variety of individual topics, including, among other matters, shareholder voting rights, anti-takeover defenses, board structures, the election of directors, executive and director compensation, reorganizations, mergers, issues of corporate social responsibility and various shareholder proposals. The Guidelines embody the positions and factors the Investment Adviser generally considers important in casting proxy votes.
The Proxy Voting Policy, including the Guidelines, is reviewed periodically to ensure that it continues to be consistent with the Investment Adviser’s guiding principles.
B-101
The Investment Adviser has retained a third-party proxy voting service (“Proxy Service”), currently Institutional Shareholder Services, to assist in the implementation and administration of certain proxy voting-related functions including, without limitation, operational, recordkeeping and reporting services. The Proxy Service also prepares a written analysis and recommendation (a “Recommendation”) of each proxy vote that reflects the Proxy Service’s application of the Guidelines to particular proxy issues. While it is the Investment Adviser’s policy generally to follow the Guidelines and Recommendations from the Proxy Service, the Investment Adviser’s portfolio management teams (“Portfolio Management Teams”) may on certain proxy votes seek approval to diverge from the Guidelines or a Recommendation by following an “override” process. Such decisions are subject to a review and approval process, including a determination that the decision is not influenced by any conflict of interest. A Portfolio Management Team that receives approval through the override process to cast a proxy vote that diverges from the Guidelines and/or a Recommendation may vote differently than other Portfolio Management Teams that did not seek to override that vote. In forming their views on particular matters, the Portfolio Management Teams are also permitted to consider applicable regional rules and practices, including codes of conduct and other guides, regarding proxy voting, in addition to the Guidelines and Recommendations. The Investment Adviser may hire other service providers to replace or supplement the Proxy Service with respect to any of the services the Investment Adviser currently receives from the Proxy Service.
GSAM conducts periodic due diligence meetings with the Proxy Service which include, but are not limited to, a review of the Proxy Service’s general organizational structure, new developments with respect to research and technology, work flow improvements and internal due diligence with respect to conflicts of interest.
From time to time, the Investment Adviser may face regulatory, compliance, legal or logistical limits with respect to voting securities that it may purchase or hold for client accounts, which can affect the Investment Adviser’s ability to vote such proxies, as well as the desirability of voting such proxies. Among other limits, federal, state and foreign regulatory restrictions or company specific ownership limits, as well as legal matters related to consolidated groups, may restrict the total percentage of an issuer’s voting securities that the Investment Adviser can hold for clients and the nature of the Investment Adviser’s voting in such securities. The Investment Adviser’s ability to vote proxies may also be affected by, among other things: (i) late receipt of meeting notices; (ii) requirements to vote proxies in person: (iii) restrictions on a foreigner’s ability to exercise votes; (iv) potential difficulties in translating the proxy; (v) requirements to provide local agents with unrestricted powers of attorney to facilitate voting instructions; and (vi) requirements that investors who exercise their voting rights surrender the right to dispose of their holdings for some specified period in proximity to the shareholder meeting.
The Investment Adviser has adopted policies and procedures designed to prevent conflicts of interest from influencing its proxy voting decisions that the Investment Adviser makes on behalf of a client account. These policies and procedures include the Investment Adviser’s use of the Guidelines and Recommendations from the Proxy Service, the override approval process previously discussed, and the establishment of information barriers between the Investment Adviser and other businesses within The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. Notwithstanding such proxy voting policies and procedures, actual proxy voting decisions of the Investment Adviser may have the effect of benefitting the interests of other clients or businesses of other divisions or units of Goldman Sachs and/or its affiliates.
Voting decisions with respect to fixed income securities and the securities of privately held issuers generally will be made by a Fund’s managers based on their assessment of the particular transactions or other matters at issue.
Information regarding how the Funds voted proxies relating to portfolio securities during the most recent 12-month period ended June 30 is available on or through the Funds’ website at www.gsam.com/content/gsam/us/en/advisors/resources/client-service/proxy-voting.html without charge and on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
PAYMENTS TO OTHERS (INCLUDING INTERMEDIARIES)
The Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates may make payments to Intermediaries from time to time to promote the sale, distribution and/or servicing of shares of a Fund, except that the Investment Adviser, Distributor and its affiliates do not make such payments on behalf of Class R6 Shares. These payments (“Additional Payments”) are made out of the Investment Adviser’s, Distributor’s and/or their affiliates’ own assets (which may come directly or indirectly from fees paid by a Fund), are not an additional charge to a Fund or its shareholders, and do not change the price paid by investors for the purchase of a Fund’s shares or the amount a Fund receives as proceeds from such purchases. Although paid by the Investment Adviser, Distributor, and/or their affiliates, the Additional Payments are in addition to the distribution and service fees paid by a Fund to the Intermediaries as described in a Fund’s Prospectus and this SAI, and are also in addition to the sales commissions payable to Intermediaries as set forth in the Prospectus. For purposes of this “Payments to Others (Including Intermediaries)” section, “Funds” shall mean, collectively, a Fund and any of the other Goldman Sachs Funds.
B-102
The Additional Payments are intended to compensate Intermediaries for, among other things: marketing shares of a Fund, which may consist of payments relating to funds included on preferred or recommended fund lists or in certain sales programs from time to time sponsored by the Intermediaries; “due diligence” examination and/or review of the Funds from time to time; access to the Intermediaries’ registered representatives or salespersons, including at conferences and other meetings; assistance in training and education of personnel; “finders” or “referral fees” for directing investors to a Fund; marketing support fees for providing assistance in promoting the sale of Fund shares (which may include promotions in communications with the Intermediaries’ customers, registered representatives and salespersons); the support or purchase of technology platforms/software offered by the Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates or third parties (which may be used by Intermediaries to provide advisory and/or brokerage services to their customers); provision of analytical or other data to the Investment Adviser or its affiliates relating to sales of shares of the Funds; and/or other specified services intended to assist in the distribution and marketing of a Fund, including provision of consultative services to the Investment Adviser or its affiliates relating to marketing of the Funds and/or sale of shares of the Funds. In addition, the Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates may make Additional Payments (including through sub-transfer agency and networking agreements) for subaccounting, administrative and/or shareholder processing services that are in addition to the transfer agent, shareholder administration, servicing and processing fees paid by the Funds. These Additional Payments may exceed amounts earned on these assets by the Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates for the performance of these or similar services. The Additional Payments may be a fixed dollar amount; may be based on the number of customer accounts maintained by an Intermediary; may be based on a percentage of the value of shares sold to, or held by, customers of the Intermediary involved; or may be calculated on another basis. The Additional Payments are negotiated with each Intermediary based on a range of factors, including but not limited to the Intermediary’s ability to attract and retain assets (including particular classes of Fund shares), target markets, customer relationships, quality of service and industry reputation. Although the individual components may be higher or lower and the total amount of Additional Payments made to any Intermediary in any given year will vary, the amount of these Additional Payments (excluding payments made through sub-transfer agency and networking agreements), on average, is normally not expected to exceed 0.50% (annualized) of the amount sold or invested through an Intermediary.
These Additional Payments may be significant to certain Intermediaries, and may be an important factor in an Intermediary’s willingness to support the sale of the Funds through its distribution system.
The Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates may be motivated to make Additional Payments since they promote the sale of Fund shares to clients of Intermediaries and the retention of those investments by those clients. To the extent Intermediaries sell more shares of a Fund or retain shares of a Fund in their clients’ accounts, the Investment Adviser and Distributor benefit from the incremental management and other fees paid by a Fund with respect to those assets.
In addition, certain Intermediaries may have access to certain research and investment services from the Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates. Such research and investment services (“Additional Services”) may include research reports; economic analysis; portfolio analysis, portfolio construction and similar tools and software; business planning services; certain marketing and investor education materials; and strategic asset allocation modeling. The Intermediary may not pay for these products or services or may only pay for a portion of the total cost of these products or services. The cost of the Additional Services and the particular services provided may vary from Intermediary to Intermediary.
The Additional Payments made by the Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates or the Additional Services received by an Intermediary may vary with respect to the type of fund (e.g., equity, fund, fixed income fund, specialty fund, asset allocation portfolio or money market fund) sold by the Intermediary. In addition, the Additional Payment arrangements may include breakpoints in compensation which provide that the percentage rate of compensation varies as the dollar value of the amount sold or invested through an Intermediary increases.
The presence of these Additional Payments or Additional Services, the varying fee structure and the basis on which an Intermediary compensates its registered representatives or salespersons may create an incentive for a particular Intermediary, registered representative or salesperson to highlight, feature or recommend funds, including a Fund, or other investments based, at least in part, on the level of compensation paid. Additionally, if one mutual fund sponsor makes greater distribution payments than another, an Intermediary may have an incentive to recommend one fund complex over another. Similarly, if an Intermediary receives more distribution assistance for one share class versus another, that Intermediary may have an incentive to recommend that share class. Because Intermediaries may be paid varying amounts per class for sub-transfer agency and related recordkeeping services, the service requirements of which also may vary by class, this may create an additional incentive for financial firms and their financial advisors to favor one fund complex over another, or one fund class over another. You should consider whether such incentives exist when evaluating any recommendations from an Intermediary to purchase or sell Shares of a Fund and when considering which share class is most appropriate for you.
B-103
For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Investment Adviser, Distributor and their affiliates made Additional Payments out of their own assets to approximately 179 Intermediaries, totaling approximately $188.8 million (excluding payments made through sub-transfer agency and networking agreements and certain other types of payments described below), with respect to a Fund, Goldman Sachs Trust, all of the funds in an affiliated investment company, Goldman Sachs Variable Insurance Trust, and Goldman Sachs Trust II. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates had contractual arrangements to make Additional Payments to the Intermediaries listed below (or their affiliates or successors), among others. This list will change over time, and any additions, modifications or deletions thereto that have occurred since December 31, 2019 are not reflected. Additional Intermediaries may receive payments in 2020 and in future years. Certain arrangements are still being negotiated, and there is a possibility that payments will be made retroactively to Intermediaries not listed below.
| ADP Broker-Dealer, Inc. |
| ADP LLC |
| ADP, Inc. |
| Allstate Life Insurance Company |
| Allstate Life Insurance Company of New York |
| Amalgamated Bank of Chicago |
| American Enterprise Investment Services, Inc. (AEIS) |
| American General Life Insurance Company |
| American National Trust and Investment Management Company dba Old National Trust Company (Oltrust & Co.) |
| American United Life Insurance Company |
| Ascensus, LLC. |
| Associated Trust Company, N.A. |
| AXA Equitable Holdings LLC |
| Banc of America Securities LLC |
| BancorpSouth |
| Bank of New York |
| Bankers Trust Company |
| BB&T Capital Markets |
| BMO Harris Bank N.A. |
| BMO Nesbitt Burns |
| BNY Mellon National Association |
| BOSC, Inc. |
| Branch Banking and Trust Company |
| Brighthouse Life Insurance Company |
| Brown Brothers Harriman & Co. |
| C.M. Life Insurance Company |
| California Department of Human Resources |
| Cetera Financial Group |
| Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. |
| Chicago Mercantile Exchange, Inc. |
| Citi Custody |
| Citibank N.A. |
| Citigroup Global Markets, Inc. |
| CME Shareholder Servicing LLC |
B-104
| Comerica Bank |
| Comerica Securities, Inc. |
| Commerce Bank |
| Commerce Bank, N.A. |
| Commerce Trust Co. |
| Commonwealth Annuity and Life Insurance Company |
| Commonwealth Equity Services, Inc. dba Commonwealth Financial Network |
| Companion Life Insurance Company |
| Compass Bank |
| Computershare Trust Company, N.A. |
| Connecticut General Life Insurance Company |
| Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC |
| Dain Rauscher Inc. |
| Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas |
| Diversified Investment Advisors |
| Drexel Hamilton, LLC |
| Dubuque Bank & Trust |
| Edward D. Jones & Co., L.P. |
| Farmers New World Life Insurance Company |
| Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation |
| Fidelity Brokerage Services LLC |
| Fidelity Investments Institutional Operations Company, Inc. |
| Fifth Third Bank |
| Fifth Third Securities Inc. |
| First Hawaiian Bank |
| First National Bank of Omaha |
| FIS Business Systems LLC |
| Forethought Life Insurance Company |
| Fulton Bank, N.A. |
| Fulton Financial Advisors, National Association |
| Genworth Life and Annuity Insurance Company |
| Genworth Life Insurance Company |
| Genworth Life Insurance Company of New York |
| GreatBanc Trust Co. |
| Great-West Life & Annuity Insurance Company |
| GWFS Equities, Inc.; GWFS Equities, Incorporated; GW Capital Management, LLC; Great-West Financial Retirement Plan Services, LLC; Great-West Life & Annuity Insurance Company; SunTrust Bank; Fifth Third Bank |
| Hartford Life Insurance Company |
| Hazeltree Fund Services, Inc. |
| Hewitt Associates LLC; Alight Solutions LLC |
| Horace Mann Life Insurance Company |
| HSBC Bank U.S.A., N.A. |
| Hunt, Dupree & Rhine |
B-105
| Huntington Investment Company |
| ICMA RC-Services, LLC; ICMA Retirement Corporation; Matrix Financial Solutions; MSCS Financial Services Division of Broadridge Business Process Outsourcing, LLC; Matrix Trust Company; McCready and Keene, Inc; Wilmington Trust Retirement and Institutional Services Company; MSCS Financial Services, LLC |
| Institutional Cash Distributors (division of Merriman Curhan Ford & Co.) |
| Investmart, Inc. |
| Jefferies LLC |
| Jefferson National Life Insurance Company |
| Jefferson National Life Insurance Company of New York |
| Jefferson Pilot Financial Insurance Company |
| John Hancock Trust Company |
| JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. |
| JPMorgan Securities, Inc |
| Key Bank N.A. |
| LaSalle Bank, N.A. |
| Law Debenture Trust Company of New York |
| Lincoln Benefit Life Company |
| Lincoln Life & Annuity Company of New York |
| Lincoln Retirement Services Company, LLC |
| LPL Financial Corporation |
| LPL Financial LLC |
| M&I Brokerage Services, Inc. |
| M&I Data Services (division of The Marshall & Ilsley Corportation) |
| M&T Bank |
| M&T Securities, Inc. |
| Massachusetts Mutual Life Insurance Company; MassMutual Retirement Services, LLC; MML Distributors, LLC |
| Members Life Insurance Company |
| Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated |
| Midland National Life Insurance Company |
| Minnesota Life Insurance Company |
| Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC |
| Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC |
| MSCS Financial Services Division of Broadridge Business Process Outsourcing, LLC |
| National Financial Services LLC |
| National Financial Services LLC |
| National Security Life and Annuity Company |
| Nationwide Financial Services, Inc. |
| Newport Group, Inc. |
| Newport Retirement Services, Inc. |
| Ohio National Equities, Inc. |
| Oppenheimer & Co. Inc. |
| Pershing LLC |
| PNC Bank, N.A. |
B-106
| PNC Bank, National Organization |
| PNC Capital Markets LLC |
| PNC Investments LLC |
| Principal Life Insurance Company |
| Protective Life Insurance Company |
| PruCo Life Insurance Company |
| PruCo Life Insurance Company of New Jersey |
| Raymond James & Associates, Inc. |
| Raymond James Financial Services |
| RBC Capital Markets, LLC |
| Regions Bank |
| Reliance Trust Company |
| Reliance Trust Company; Daily Access Concepts |
| RiverSource Life Insurance Co. of New York |
| RiverSource Life Insurance Company |
| Robert W. Baird & Co. Incorporated |
| Scott & Stringfellow |
| Security Benefit Life Insurance Company |
| Security Distributors, Inc. |
| Signature Bank |
| State Street Bank and Trust Company |
| State Street Global Markets, LLC |
| Sun Life Assurance Company of Canada (U.S.) |
| Sun Life Insurance and Annuity Company of New York |
| Sungard Institutional Brokerage, Inc. |
| SunTrust Robinson Humphrey, Inc. |
| Synovus Securities |
| T. Rowe Price Retirement Plan Services, Inc. |
| TD Bank National Association |
| Teachers Insurance and Annuity Association of America |
| The Glenmede Trust Company N.A. |
| The Guardian Insurance & Annuity Company, Inc. |
| The Lincoln National Life Insurance Company |
| The Ohio National Life Insurance Company |
| The Prudential Insurance Company of America |
| The Prudential Insurance Company of America |
| The Travelers Insurance Company |
| The Travelers Life and Annuity Company |
| The United States Life Insurance Company in the City of New York |
| The Vanguard Group, Inc. |
| The Variable Annuity Life Insurance Company |
| Transamerica Financial Life Insurance Company |
| Transamerica Life Insurance Company |
B-107
| Treasury Curve, LLC |
| Trustmark National Bank |
| U.S. Bank, N.A. |
| UBS Financial Services Inc. |
| Union Bank, N.A. |
| United of Omaha Life Insurance Company |
| VALIC Retirement Services Company |
| Voya Financial Partners, LLC |
| Voya Institutional Plan Services, LLC |
| Voya Retirement Advisors, LLC |
| Voya Retirement Insurance and Annuity Company |
| Wachovia Capital Markets, LLC |
| Wells Fargo Bank |
| Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. |
| Wells Fargo Clearing Services, LLC. |
| Wells Fargo Corporate Trust Services |
| Zions Bank |
| Zurich American Life Insurance Company |
Your Authorized Dealer or other Intermediary may charge you additional fees or commissions other than those disclosed in the Prospectus. Shareholders should contact their Authorized Dealer or other Intermediary for more information about the Additional Payments or Additional Services they receive and any potential conflicts of interest, as well as for information regarding any fees and/or commissions it charges. For additional questions, please contact Goldman Sachs Funds at 1-800-621-2550.
Not included on the list above are other subsidiaries of Goldman Sachs who may receive revenue from the Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates through intra-company compensation arrangements and for financial, distribution, administrative and operational services.
Furthermore, the Investment Adviser, Distributor and/or their affiliates may, to the extent permitted by applicable regulations, sponsor various trainings and educational programs and reimburse investors for certain expenses incurred in connection with accessing the Funds through portal arrangements. The Investment Adviser, Distributor and their affiliates may also pay for the travel expenses, meals, lodging and entertainment of Intermediaries and their salespersons and guests in connection with educational, sales and promotional programs subject to applicable FINRA regulations. Other compensation may also be offered from time to time to the extent not prohibited by applicable federal or state laws or FINRA regulations. This compensation is not included in, and is made in addition to, the Additional Payments described above.
OTHER INFORMATION
Selective Disclosure of Portfolio Holdings Information and Portfolio Characteristics Information
The Board of Trustees of the Trust and the Investment Adviser have adopted a policy on the selective disclosure of portfolio holdings information and portfolio characteristics information. The policy seeks to (1) ensure that the disclosure of portfolio holdings information and portfolio characteristics information is in the best interest of Fund shareholders; and (2) address the conflicts of interest associated with the disclosure of portfolio holdings information and portfolio characteristics information. The policy provides that neither a Fund nor the Trust’s officers or Trustees, nor the Investment Adviser, Distributor or any agent, or any employee thereof (“Fund Representative”), will disclose a Fund’s portfolio holdings information or portfolio characteristics information to any person other than in accordance with the policy. For purposes of the policy, “portfolio holdings information” means a Fund’s actual portfolio holdings, as well as non-public information about its trading strategies or pending transactions. Portfolio holdings information does not include summary or statistical information which is derived from (but does not include) individual portfolio holdings (“portfolio characteristics information”).
B-108
Under the policy, neither a Fund nor any Fund Representative may solicit or accept any compensation or other consideration in connection with the disclosure of portfolio holdings information or portfolio characteristics information. A Fund Representative may generally provide portfolio holdings information and material portfolio characteristics information to third parties if such information has been included in a Fund’s public filings with the SEC or is disclosed on the Funds’ publicly accessible website or is otherwise publicly available.
Portfolio Holdings Information. Portfolio holdings information that is not filed with the SEC or disclosed on the Funds’ publicly available website may be provided to third parties (including, without limitation, individuals, institutional investors, intermediaries that sell shares of the Fund, consultants and third-party data providers) only for legitimate business purposes and only if the third-party recipients are required to keep all such portfolio holdings information confidential and are prohibited from trading on the information they receive in violation of the federal securities laws. Disclosure to such third parties must be approved in advance by the Investment Adviser’s legal or compliance department. Disclosure to providers of auditing, custody, proxy voting and other similar services; rating and ranking organizations; lenders and other third-party service providers that may obtain access to such information in the performance of their contractual duties to the Funds will generally be permitted. In general, each recipient of non-public portfolio holdings information must sign a confidentiality agreement and agree not to trade on the basis of such information in violation of the federal securities laws, although this requirement will not apply when the recipient is otherwise subject to a duty of confidentiality.
In accordance with the policy, the identity of those recipients who receive non-public portfolio holdings information on an ongoing basis is as follows: the Investment Adviser and its affiliates, the Funds’ independent registered public accounting firm, the Funds’ custodian, the Funds’ legal counsel—Dechert LLP, the Funds’ tax service provider—Deloitte & Touche LLP, the Funds’ financial printer—Donnelley Financial Solutions Inc., the Funds’ proxy voting service—ISS, and the Funds’ class action processing service provider—Financial Recovery Technologies, LLC. KPMG LLP, an investor in the Funds, also receives certain non-public portfolio holdings information on an ongoing basis in order to facilitate compliance with the auditor independence requirements to which it is subject. In addition, certain Goldman Sachs Fixed Income Funds provide non-public portfolio holdings information to Standard & Poor’s to allow such Funds to be rated by it, and certain Goldman Sachs Equity Funds provide non-public portfolio holdings information to FactSet, a provider of global financial and economic information. These entities are obligated to keep such information confidential. Third-party providers of custodial services to the Funds may release non-public portfolio holdings information of the Funds only with the permission of certain Fund Representatives. From time to time portfolio holdings information may be provided to broker-dealers, prime brokers, FCMs or derivatives clearing merchants in connection with a Fund’s portfolio trading activities. In providing this information, reasonable precautions, including, but not limited to, the execution of a non-disclosure agreement and limitations on the scope of the portfolio holdings information disclosed, are taken to avoid any potential misuse of the disclosed information. All marketing materials prepared by the Trust’s principal underwriter are reviewed by Goldman Sachs’ Compliance department for consistency with the policy.
The Funds described in this SAI currently intend to publish complete portfolio holdings on the Trust’s website (http://www.gsamfunds.com) as of the end of each calendar quarter, subject to a 15 calendar day lag between the date of the information and the date on which the information is disclosed. In addition, each Fund currently intends to post month-end top ten holdings on the Trust’s website subject to a 15 calendar day lag between the date of the information and the date on which the information is disclosed. A Fund may publish on the website complete portfolio holdings information more frequently if it has a legitimate business purpose for doing so. Operational disruptions and other systems disruptions may delay the posting of this information on the Trust’s website.
Each Fund files portfolio holdings information within 60 days after the end of each fiscal quarter on Form N-PORT. Portfolio holdings information for the third month of each fiscal quarter will be publicly available on the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov. Each Fund’s complete schedule of portfolio holdings for the second and fourth quarters of each fiscal year is included in the semi-annual and annual reports to shareholders, respectively, and is filed with the SEC on Form N-CSR. A semi-annual or annual report for each Fund will become available to investors within 60 days after the period to which it relates. Each Fund’s Forms N-PORT and Forms N-CSR are available on the SEC’s website listed above.
Portfolio Characteristics Information. Material portfolio characteristics information that is not publicly available (e.g., information that is not filed with the SEC or disclosed on the Funds’ publicly available website) or calculated from publicly available information may be provided to third parties only if the third-party recipients are required to keep all such portfolio characteristics information confidential and are prohibited from trading on the information they receive in violation of the federal securities laws. Disclosure to such third parties must be approved in advance by the Investment Adviser’s legal or compliance department, who must first determine that the Fund has a legitimate business purpose for doing so. In general, each recipient of material, non-public portfolio characteristics information must sign a confidentiality agreement and agree not to trade on the basis of such information in violation of the federal securities laws, although this requirement will not apply when the recipient is otherwise subject to a duty of confidentiality.
However, upon request, a Fund will provide certain non-public portfolio characteristics information to any (i) shareholder or (ii) non-shareholder (including, without limitation, individuals, institutional investors, intermediaries that sell shares of the Fund, consultants
B-109
and third-party data providers) whose request for such information satisfies and/or serves a legitimate business purpose for the Fund. Examples of portfolio characteristics information include, but are not limited to, statistical information about a Fund’s portfolio. Portfolio characteristics information that is made available upon request would normally include:
| • | Asset Allocation Information – The allocation of a Fund’s portfolio among asset classes, regions, countries, industries, sub-industries, sectors, sub-sectors, strategies or subadvisers; credit quality ratings; and weighted average market capitalization ranges. |
| • | Financial Characteristics Information – The financial characteristics of a Fund’s portfolio, such as alpha; beta; R-squared; Sharpe ratio; information ratio; standard deviation; tracking error; various earnings and price based ratios (e.g., price-to-earnings and price-to-book); value at risk (VaR); duration information; weighted-average maturity/life; portfolio turnover; attribution; and other aggregated risk statistics (e.g., aggregate liquidity classification information). |
In accordance with the policy, this type of portfolio characteristics information that is made available upon request will be disclosed in accordance with, and subject to the time lag indicated in, the schedule below. This portfolio characteristics information may be requested by calling Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC toll-free at 1-800-526-7384 (for Class A, Class C, Class R and Investor Shareholders) or 1-800-621-2550 (for Institutional, Service, Administration, Separate Account Institutional, Class R6 and Class P Shareholders). Portfolio characteristics information that is otherwise publicly available may be disclosed without these time lags.
The type and volume of portfolio characteristics information that is made available upon request will vary among the Goldman Sachs Funds (depending on the investment strategies and the portfolio management team of the applicable Fund). If portfolio characteristics information is disclosed to one recipient, it must also be disclosed to all other eligible recipients requesting the same information. However, under certain circumstances, the volume of portfolio characteristics information provided to one recipient may differ from the volume of portfolio characteristics information provided to other recipients.
| Type of Information |
When Available Upon Request | |
| Portfolio Characteristics Information (Except for Aggregate Liquidity Classification Information) |
Prior to 15 Business Days After Month-End: Cannot disclose without (i) a confidentiality agreement; (ii) an agreement not to trade on the basis of non-public information in violation of the federal securities laws; and (iii) legal or compliance approval.
15 Business Days After Month-End: May disclose to (i) shareholders and (ii) any non-shareholder whose request satisfies and/or serves a legitimate business purpose for the applicable Fund. | |
| Aggregate Liquidity Classification Information | Prior to 90 Calendar Days After Month-End: Cannot disclose without (i) a confidentiality agreement; (ii) an agreement not to trade on the basis of non-public information in violation of the federal securities laws; and (iii) legal or compliance approval.
90 Calendar Days After Month-End: May disclose to (i) shareholders and (ii) any non-shareholder whose request satisfies and/or serves a legitimate business purpose for the applicable Fund. | |
In addition, the Funds described in this SAI currently intend to publish certain portfolio characteristics information on the Trust’s website (http://www.gsamfunds.com) as of the end of each month or fiscal quarter, and such information will generally be subject to a 15 day lag. Operational disruptions and other systems disruptions may delay the posting of this information on the Trust’s website or the availability of this information by calling Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC at the toll-free numbers listed above.
Oversight of the Policy. Under the policy, Fund Representatives will periodically supply the Board of the Trustees with a list of third parties who receive non-public portfolio holdings information and material, non-public portfolio characteristics information pursuant to an ongoing arrangement subject to a confidentiality agreement and agreement not to trade on the basis of such information in violation of the federal securities laws. In addition, the Board receives information, on a quarterly basis, on such arrangements that were permitted during the preceding quarter. Under the policy, the Investment Adviser’s legal and compliance personnel authorize the disclosure of portfolio holdings information and portfolio characteristics information.
Disclosure of Current NAV Per Share
Each Fund’s current NAV per share is available through the Funds’ website at www.gsamfunds.com (except Class P Shares) or by contacting the Funds at 1-800-526-7384.
B-110
Miscellaneous
A Fund will redeem shares solely in cash up to the lesser of $250,000 or 1% of the NAV of the Fund during any 90-day period for any one shareholder. Each Fund, however, reserves the right, in its sole discretion, to pay redemptions by a distribution in-kind of securities (instead of cash) if (i) the redemption exceeds the lesser of $250,000 or 1% of the NAV of the Fund at the time of redemption; or (ii) with respect to lesser redemption amounts, the redeeming shareholder requests in writing a distribution in-kind of securities instead of cash. The securities distributed in-kind would be readily marketable and would be valued for this purpose using the same method employed in calculating each Fund’s NAV per share. See “NET ASSET VALUE.” If a shareholder receives redemption proceeds in-kind, the shareholder should expect to incur transaction costs upon the disposition of the securities received in the redemption. In addition, if you receive redemption proceeds in-kind, you will be subject to market gains or losses upon the disposition of those securities.
The right of a shareholder to redeem shares and the date of payment by each Fund may be suspended for more than seven days for any period during which the New York Stock Exchange is closed, other than the customary weekends or holidays, or when trading on such Exchange is restricted as determined by the SEC; or during any emergency, as determined by the SEC, as a result of which it is not reasonably practicable for such Fund to dispose of securities owned by it or fairly to determine the value of its net assets; or for such other period as the SEC may by order permit for the protection of shareholders of such Fund. (The Trust may also suspend or postpone the recordation of the transfer of shares upon the occurrence of any of the foregoing conditions.)
As stated in the Prospectuses, the Trust may authorize Intermediaries and other institutions that provide recordkeeping, reporting and processing services to their customers to accept on the Trust’s behalf purchase, redemption and exchange orders placed by or on behalf of their customers and, if approved by the Trust, to designate other intermediaries to accept such orders. These institutions may receive payments from the Trust or Goldman Sachs for their services. Certain Intermediaries or other institutions may enter into sub-transfer agency agreements with the Trust or Goldman Sachs with respect to their services.
In the interest of economy and convenience, the Trust does not issue certificates representing the Funds’ shares. Instead, the Transfer Agent maintains a record of each shareholder’s ownership. Each shareholder receives confirmation of purchase and redemption orders from the Transfer Agent. Fund shares and any dividends and distributions paid by the Funds are reflected in account statements from the Transfer Agent.
The Prospectuses and this SAI do not contain all the information included in the Registration Statement filed with the SEC under the 1933 Act with respect to the securities offered by the Prospectuses. Certain portions of the Registration Statement have been omitted from the Prospectuses and this SAI pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC. The Registration Statement including the exhibits filed therewith may be examined at the office of the SEC in Washington, D.C.
Statements contained in the Prospectuses or in this SAI as to the contents of any contract or other document referred to are not necessarily complete, and, in each instance, reference is made to the copy of such contract or other document filed as an exhibit to the Registration Statement of which the Prospectuses and this SAI form a part, each such statement being qualified in all respects by such reference.
Line of Credit
As of August 31, 2020, the Funds participated in a $700,000,000 committed, unsecured revolving line of credit facility together with other funds of the Trust and registered investment companies having management agreements with GSAM or its affiliates. This facility is to be used for temporary emergency purposes or to allow for an orderly liquidation of securities to meet redemption requests. The interest rate on borrowings is based on the federal funds rate. The facility also requires a fee to be paid by the Funds based on the amount of the commitment that has not been utilized. For the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020, the Funds did not have any borrowings under the facility.
Large Trade Notifications
The Transfer Agent may from time to time receive notice that an Intermediary has received a purchase, redemption or exchange order for a large trade in a Fund’s shares. The Funds may determine to enter into portfolio transactions in anticipation of that order, even though the order may not have been processed at the time the Fund entered into such portfolio transactions. This practice provides for a closer correlation between the time shareholders place large trade orders and the time a Fund enters into portfolio transactions based on those orders, and may permit the Fund to be more fully invested in investment securities, in the case of purchase orders, and to more orderly liquidate its investment positions, in the case of redemption orders. The Intermediary may not, however, ultimately process the order. In this case, (i) if the Fund enters into portfolio transactions in anticipation of an order for a large redemption of Fund shares; or
B-111
(ii) if the Fund enters into portfolio transactions in anticipation of an order for a large purchase of Fund shares and such portfolio transactions occur on the date on which the Intermediary indicated that such order would occur, the Fund will bear any borrowing, trading overdraft or other transaction costs or investment losses resulting from such portfolio transactions. Conversely, the Funds would benefit from any earnings and investment gains resulting from such portfolio transactions.
Corporate Actions
From time to time, the issuer of a security held in a Fund’s portfolio may initiate a corporate action relating to that security. Corporate actions relating to equity securities may include, among others, an offer to purchase new shares, or to tender existing shares, of that security at a certain price. Corporate actions relating to debt securities may include, among others, an offer for early redemption of the debt security, or an offer to convert the debt security into stock. Certain corporate actions are voluntary, meaning that a Fund may only participate in the corporate action if it elects to do so in a timely fashion. Participation in certain corporate actions may enhance the value of a Fund’s investment portfolio.
In cases where a Fund or its Investment Adviser receives sufficient advance notice of a voluntary corporate action, the Investment Adviser will exercise its discretion, in good faith, to determine whether the Fund will participate in that corporate action. If a Fund or its Investment Adviser does not receive sufficient advance notice of a voluntary corporate action, the Fund may not be able to timely elect to participate in that corporate action. Participation or lack of participation in a voluntary corporate action may result in a negative impact on the value of the Fund’s investment portfolio.
DISTRIBUTION AND SERVICE PLANS
(Class A Shares, Class C Shares and Class R Shares only)
Distribution and Service Plans. As described in the Prospectuses, the Trust has adopted, on behalf of Class A, Class C and Class R Shares of each Fund, distribution and service plans (collectively, the “Plans” and each individually, a “Plan”). See “Shareholder Guide — Distribution and Service Fees” in the Prospectuses. The distribution fees payable under the Plans are subject to Rule 12b-1 under the Act, and finance distribution and other services that are provided to investors in the Funds, and enable the Funds to offer investors the choice of investing in either Class A, Class C or Class R Shares when investing in the Funds. In addition, distribution fees payable under the Plans may be used to assist the Funds in reaching and maintaining asset levels that are efficient for the Funds’ operations and investments.
The Plans for Class A, Class C and Class R Shares of each applicable Fund were most recently approved by a majority vote of the Trustees of the Trust, including a majority of the non-interested Trustees of the Trust who have no direct or indirect financial interest in the Plans, cast at a meeting called for the purpose of approving the Plans on June 16-17, 2020.
The compensation for distribution services payable under a Plan to Goldman Sachs may not exceed 0.25%, 0.75% and 0.50% per annum of a Fund’s average daily net assets attributable to Class A, Class C and Class R Shares, respectively, of such Fund. Under the Plans for Class C Shares, Goldman Sachs is also entitled to receive a separate fee for personal and account maintenance services equal on an annual basis to 0.25% of each Fund’s average daily net assets attributable to Class C Shares. With respect to Class A and Class R Shares, the Distributor at its discretion may use compensation for distribution services paid under the Plan for personal and account maintenance services and expenses so long as such total compensation under the Plan does not exceed the maximum cap on “service fees” imposed by FINRA.
Each Plan is a compensation plan which provides for the payment of a specified fee without regard to the expenses actually incurred by Goldman Sachs. If such fee exceeds Goldman Sachs’ expenses, Goldman Sachs may realize a profit from these arrangements. The distribution fees received by Goldman Sachs under the Plans and CDSCs (as applicable) on Class A, Class C and Class R Shares may be sold by Goldman Sachs as Distributor to entities which provide financing for payments to Intermediaries in respect of sales of Class A, Class C and Class R Shares. To the extent such fees are not paid to such dealers, Goldman Sachs may retain such fees as compensation for its services and expenses of distributing the Funds’ Class A, Class C and Class R Shares.
Under each Plan, Goldman Sachs, as Distributor of each Fund’s Class A, Class C and Class R Shares, will provide to the Trustees of the Trust for their review, and the Trustees of the Trust will review at least quarterly, a written report of the services provided and amounts expended by Goldman Sachs under the Plans and the purposes for which such services were performed and expenditures were made.
B-112
The Plans will remain in effect until June 30, 2021 and from year to year thereafter, provided that such continuance is approved annually by a majority vote of the Trustees of the Trust, including a majority of the non-interested Trustees of the Trust who have no direct or indirect financial interest in the Plans. The Plans may not be amended to increase materially the amount of distribution compensation described therein without approval of a majority of the outstanding Class A, Class C or Class R Shares of the affected Fund and affected share class, but may be amended without shareholder approval to increase materially the amount of non-distribution compensation. All material amendments of a Plan must also be approved by the Trustees of the Trust in the manner described above. A Plan may be terminated at any time as to any Fund without payment of any penalty by a vote of a majority of the non-interested Trustees of the Trust or by vote of a majority of the Class A, Class C or Class R Shares, respectively, of the affected Fund and affected share class. If a Plan was terminated by the Trustees of the Trust and no successor plan was adopted, the Fund would cease to make payments to Goldman Sachs under the Plan and Goldman Sachs would be unable to recover the amount of any of its unreimbursed expenditures. So long as a Plan is in effect, the selection and nomination of non-interested Trustees of the Trust will be committed to the discretion of the non-interested Trustees of the Trust. The Trustees of the Trust have determined that in their judgment there is a reasonable likelihood that the Plans will benefit the Funds and their Class A, Class C and Class R shareholders.
The following chart shows the distribution and service fees paid to Goldman Sachs for the fiscal years ended August 31, 2020, August 31, 2019 and August 31, 2018 by each Fund then in existence pursuant to the Class A Plan:
| Fund |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2018 |
|||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 11,016 | $ | 7,524 | $ | 5,191 | ||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
1,761,709 | 1,769,857 | 1,772,107 | |||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
18,377 | 15,368 | 13,505 | |||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
13,868 | 13,126 | 13,577 | |||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
780,305 | 882,795 | 1,116,781 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund(1) |
183 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
684,418 | 745,509 | 863,573 | |||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
73,308 | 70,517 | 79,516 | |||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
830,497 | 750,270 | 720,639 | |||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
739,887 | 777,847 | 808,747 | |||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
229 | 140 | 222 | |||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
197,561 | 226,555 | 274,912 | |||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
1,154,975 | 1,388,258 | 1,794,784 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
1,240,768 | 1,740,798 | 2,091,531 | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
2,989 | 3,804 | 3,947 | |||||||||
| 1 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
The following chart shows the distribution and service fees paid to Goldman Sachs for the fiscal years ended August 31, 2020, August 31, 2019 and August 31, 2018 by each Fund then in existence pursuant to the Class C Plan:
| Fund |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2018 |
|||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 16,536 | $ | 10,221 | $ | 2,747 | ||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
170,201 | 218,377 | 652,666 | |||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
9,537 | 10,128 | 20,779 | |||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
13,685 | 12,084 | 13,930 | |||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
326,432 | 491,320 | 850,866 | |||||||||
B-113
| Small Cap Growth Fund(1) |
545 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
1,514,238 | 1,829,694 | 2,242,840 | |||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
38,633 | 48,110 | 90,811 | |||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
251,207 | 286,692 | 535,873 | |||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
71,285 | 89,818 | 181,250 | |||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
305 | 292 | 339 | |||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
194,151 | 235,373 | 382,570 | |||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
218,957 | 371,629 | 916,664 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
59,085 | 139,968 | 388,142 | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
9,413 | 9,871 | 12,960 |
| 1 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
The following chart shows the distribution and service fees paid to Goldman Sachs for the fiscal years ended August 31, 2020, August 31, 2019 and August 31, 2018 by each applicable Fund then in existence pursuant to the Class R Plan:
| Fund |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal year ended August 31, 2018 |
|||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 101 | $ | 95 | $ | 100 | ||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
43,202 | 41,972 | 42,847 | |||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
151 | 165 | 145 | |||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
208 | 242 | 222 | |||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
215,067 | 237,561 | 283,416 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund(1) |
222 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
66,738 | 91,304 | 122,495 | |||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
856 | 1,468 | 1,014 | |||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund(2) |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
6,882 | 7,338 | 7,448 | |||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
156 | 149 | 145 | |||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
17,803 | 24,725 | 28,475 | |||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
96,374 | 119,690 | 155,890 | |||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
347,960 | 494,899 | 630,017 | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
652 | 925 | 862 | |||||||||
| 1 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. |
| 2 | The Technology Opportunities Fund does not offer Class R Shares. |
B-114
During the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020, Goldman Sachs incurred the following expenses in connection with distribution under the Class A Plan of each Fund with Class A Shares:
| Fund |
Compensation to Dealers (1) |
Compensation and Expenses of the Distributor and Its Sales Personnel |
Allocable Overhead, Telephone and Travel Expenses |
Printing and Mailing of Prospectuses to Other Than Current Shareholders |
Preparation and Distribution of Sales Literature and Advertising |
Totals | ||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 11,426 | $ | 11,434 | $ | 1,624 | $ | 85 | $ | 155 | $ | 24,725 | ||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
1,545,936 | 938,351 | 315,234 | 16,543 | 30,066 | 2,846,131 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
18,739 | 13,175 | 4,269 | 224 | 407 | 36,814 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
14,187 | 7,471 | 1,317 | 69 | 126 | 23,169 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
777,214 | 382,517 | 135,290 | 7,100 | 12,903 | 1,315,024 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund |
70 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 73 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
706,962 | 494,315 | 171,796 | 9,016 | 16,385 | 1,398,474 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
74,956 | 48,318 | 15,978 | 839 | 1,524 | 141,615 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
815,583 | 551,317 | 182,853 | 9,596 | 17,440 | 1,576,788 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
743,737 | 290,446 | 101,642 | 5,334 | 9,694 | 1,150,854 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
156 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 189 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
205,871 | 56,326 | 19,257 | 1,011 | 1,837 | 284,302 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
1,182,816 | 453,882 | 162,294 | 8,517 | 15,479 | 1,822,988 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
1,227,979 | 394,064 | 146,056 | 7,665 | 13,930 | 1,789,694 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
3,095 | 73 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3,167 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Advance commissions paid to dealers of 1% on Class A Shares are considered deferred assets which are amortized over a period of 18 months; amounts presented above reflect amortization expense recorded during the period presented. |
During the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020, Goldman Sachs incurred the following expenses in connection with distribution under the Class C Plan of each Fund with Class C Shares:
| Fund |
Compensation to Dealers (1) |
Compensation and Expenses of the Distributor and Its Sales Personnel |
Allocable Overhead, Telephone and Travel Expenses |
Printing and Mailing of Prospectuses to Other Than Current Shareholders |
Preparation and Distribution of Sales Literature and Advertising |
Totals | ||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 15,581 | $ | 2,629 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | $ | 18,210 | ||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
137,282 | 19,604 | 6,364 | 334 | 607 | 164,191 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
7,211 | 1,470 | 469 | 25 | 45 | 9,220 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
11,822 | 397 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12,219 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
302,491 | 40,372 | 13,726 | 720 | 1,309 | 358,619 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund |
102 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 123 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
1,507,651 | 239,880 | 82,743 | 4,342 | 7,892 | 1,842,508 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
37,836 | 7,090 | 2,136 | 112 | 204 | 47,377 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
215,801 | 47,512 | 15,701 | 824 | 1,498 | 281,336 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
65,003 | 5,907 | 1,896 | 100 | 181 | 73,087 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
201,309 | 13,770 | 4,857 | 255 | 463 | 220,654 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
208,669 | 18,101 | 6,060 | 318 | 578 | 233,726 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
54,893 | 2,558 | 935 | 49 | 89 | 58,524 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
8,369 | 345 | 82 | 4 | 8 | 8,808 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Advance commissions paid to dealers of 1% on Class C Shares are considered deferred assets which are amortized over a period of 1 year; amounts presented above reflect amortization expense recorded during the period presented. |
B-115
During the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020, Goldman Sachs incurred the following expenses in connection with distribution under the Class R Plan of each Fund with Class R Shares:
| Fund(1) |
Compensation to Dealers |
Compensation and Expenses of the Distributor and Its Sales Personnel |
Allocable Overhead, Telephone and Travel Expenses |
Printing and Mailing of Prospectuses to Other Than Current Shareholders |
Preparation and Distribution of Sales Literature and Advertising |
Totals | ||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 0 | $ | 6 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | $ | 6 | ||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
42,716 | 8,716 | 3,261 | 171 | 311 | 55,174 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
54 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
211,347 | 43,399 | 15,985 | 839 | 1,525 | 273,094 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund |
0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
63,557 | 9,708 | 3,620 | 190 | 345 | 77,420 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
783 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 785 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
5,486 | 101 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 5,605 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
17,078 | 196 | 33 | 2 | 3 | 17,311 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
91,242 | 10,957 | 4,031 | 212 | 384 | 106,826 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
337,584 | 38,462 | 14,568 | 765 | 1,389 | 392,768 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
586 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 589 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | The Technology Opportunities Fund does not offer Class R Shares. |
B-116
OTHER INFORMATION REGARDING MAXIMUM SALES CHARGE, PURCHASES, REDEMPTIONS,
EXCHANGES AND DIVIDENDS
(Class A Shares and Class C Shares Only)
The following information supplements the information in the Prospectus under the captions “Shareholder Guide” and “Distributions.” Please see the Prospectuses for more complete information.
Maximum Sales Charges
Class A Shares of each Fund are sold with a maximum sales charge of 5.50%. Using the NAV per share and the maximum sales charge in effect as of August 31, 2020, the maximum offering price of each Fund’s Class A Shares would be as follows:
| Fund |
Net Asset Value |
Maximum Sales Charge |
Offering Price to Public |
|||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
$ | 15.63 | 5.50 | % | $ | 16.54 | ||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
26.94 | 5.50 | % | 28.51 | ||||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
22.91 | 5.50 | % | 24.24 | ||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund |
13.78 | 5.50 | % | 14.58 | ||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
17.14 | 5.50 | % | 18.14 | ||||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund |
12.81 | 5.50 | % | 13.56 | ||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
23.56 | 5.50 | % | 24.93 | ||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
11.24 | 5.50 | % | 11.89 | ||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
29.76 | 5.50 | % | 31.49 | ||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
37.94 | 5.50 | % | 40.15 | ||||||||
| Focused Value Fund |
11.25 | 5.50 | % | 11.90 | ||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
13.92 | 5.50 | % | 14.73 | ||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
31.22 | 5.50 | % | 33.04 | ||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
40.60 | 5.50 | % | 42.96 | ||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund |
11.50 | 5.50 | % | 12.17 | ||||||||
The actual sales charge that is paid by an investor on the purchase of Class A Shares may differ slightly from the sales charge listed above or in a Fund’s Prospectus due to rounding in the calculations. The actual sales charge that is paid by an investor will be rounded to two decimal places. As a result of such rounding in the calculations, the actual sales charge paid by an investor may be somewhat greater (e.g., 5.53% for Class A Shares) or somewhat lesser (e.g., 5.48% for Class A Shares) than that listed above or in the Prospectuses. Contact your financial advisor for further information.
Other Purchase Information/Sales Charge Waivers
The sales charge waivers on the Funds’ shares described in “Shareholder Guide-Common Questions Applicable to the Purchase of Class A Shares” in the Prospectuses are due to the nature of the investors involved and/or the reduced sales effort that is needed to obtain such investments.
If shares of a Fund are held in an account with an Intermediary, all recordkeeping, transaction processing and payments of distributions relating to the beneficial owner’s account will be performed by the Intermediary, and not by the Fund and its Transfer Agent. Since the Funds will have no record of the beneficial owner’s transactions, a beneficial owner should contact the Intermediary to purchase, redeem or exchange shares, to make changes in or give instructions concerning the account or to obtain information about the account. The transfer of shares in an account with one Intermediary to an account with another Intermediary or to an account directly with the Fund involves special procedures and will require the beneficial owner to obtain historical purchase information about the shares in the account from the Intermediary.
Right of Accumulation
A Class A shareholder qualifies for cumulative quantity discounts if the current purchase price of the new investment plus the shareholder’s current holdings of existing Class A and/or Class C Shares (acquired by purchase or exchange) of a Fund and Class A and/or Class C Shares of any other Goldman Sachs Fund total the requisite amount for receiving a discount. For example, for certain Funds, if a shareholder owns shares with a current market value of $65,000 and purchases additional Class A Shares of any Goldman Sachs Fund with a purchase price of $45,000, the sales charge for the $45,000 purchase would be 3.75% (the rate applicable to purchases of $100,000 but less than $250,000 for certain of the Funds). Class A and/or Class C Shares of the Funds and Class A and/or Class C Shares of any other Goldman Sachs Fund purchased (i) by an individual, his spouse, his parents and his children, and (ii) by a trustee, guardian or other fiduciary of a single trust estate or a single fiduciary account, will be combined for the purpose of determining whether a purchase will qualify for such right of accumulation and, if qualifying, the applicable sales charge level. For purposes of applying the right of accumulation, shares of the Funds and any other Goldman Sachs Fund purchased by an existing client of Goldman Sachs Private Wealth Management or GS Ayco Holding LLC will be combined with Class A and/or Class C Shares and other assets held by all other Goldman Sachs Private Wealth Management accounts or accounts of GS Ayco Holding LLC, respectively. In addition, Class A and/or Class C Shares of the Funds and Class A and/or Class C Shares of any other Goldman Sachs Fund purchased by partners, directors, officers or employees of the same business organization, or groups of individuals represented by and investing on the recommendation of the same accounting firm, certain affinity groups or other similar organizations (collectively, “eligible persons”) may be combined
B-117
for the purpose of determining whether a purchase will qualify for the right of accumulation and, if qualifying, the applicable sales charge level. This right of accumulation is subject to the following conditions: (i) the business organization’s or group’s or firm’s agreement to cooperate in the offering of the Funds’ shares to eligible persons; and (ii) notification to the relevant Fund at the time of purchase that the investor is eligible for this right of accumulation. In addition, in connection with SIMPLE IRA accounts, cumulative quantity discounts are available on a per plan basis if (i) your employee has been assigned a cumulative discount number by Goldman Sachs; and (ii) your account, alone or in combination with the accounts of other plan participants also invested in Class A and/or Class C Shares of Goldman Sachs Funds, totals the requisite aggregate amount as described in the Prospectus.
Statement of Intention (Class A)
If a shareholder anticipates purchasing at least $50,000, not counting reinvestments of distributions, of Class A Shares of a Fund alone or in combination with Class A Shares of any other Goldman Sachs Fund within a 13-month period, the shareholder may purchase shares of the Fund at a reduced sales charge by submitting a Statement of Intention (the “Statement”). Shares purchased pursuant to a Statement will be eligible for the same sales charge discount that would have been available if all of the purchases had been made at the same time. The shareholder or his Intermediary must inform Goldman Sachs that the Statement is in effect each time shares are purchased. There is no obligation to purchase the full amount of shares indicated in the Statement. A shareholder may include the value of all Class A Shares on which a sales charge has previously been paid as an “accumulation credit” toward the completion of the Statement, but a price readjustment will be made only on Class A Shares purchased within ninety (90) days before submitting the Statement. The Statement authorizes the Transfer Agent to hold in escrow a sufficient number of shares which can be redeemed to make up any difference in the sales charge on the amount actually invested. For purposes of satisfying the amount specified on the Statement, the gross amount of each investment, exclusive of any appreciation on shares previously purchased, will be taken into account.
The provisions applicable to the Statement, and the terms of the related escrow agreement, are set forth in Appendix C to this SAI.
Cross-Reinvestment of Distributions
Shareholders may receive distributions in additional shares of the same class of the Fund in which they have invested or they may elect to receive them in cash or shares of the same class of other Goldman Sachs Funds, or Service Shares of the Goldman Sachs Financial Square Prime Obligations Fund (“Prime Obligations Fund”), if they hold Class A Shares of a Fund.
A Fund shareholder should obtain and read the prospectus relating to the other Goldman Sachs Fund or Prime Obligations Fund and its shares and consider its investment objective, policies and applicable fees before electing cross-reinvestment into that Fund. The election to cross-reinvest distributions will not affect the tax treatment of such distributions, which will be treated as received by the shareholder and then used to purchase shares of the acquired fund. Such reinvestment of distributions in shares of other Goldman Sachs Funds or the Prime Obligations Fund is available only in states where such reinvestment may legally be made.
Automatic Exchange Program
A Fund shareholder may elect to exchange automatically a specified dollar amount of shares of a Fund for shares of the same class or an equivalent class of another Goldman Sachs Fund provided the minimum initial investment requirement has been satisfied. A Fund shareholder should obtain and read the prospectus relating to any other Goldman Sachs Fund and its shares and consider its investment objective, policies and applicable fees and expenses before electing an automatic exchange into that Goldman Sachs Fund.
Exchanges from Collective Investment Trusts to Goldman Sachs Funds
The Investment Adviser manages a number of collective investment trusts that hold assets of 401(k) plans and other retirement plans (each, a “Collective Investment Trust”). An investor in a Collective Investment Trust (or an Intermediary acting on behalf of the investor) may elect to exchange some or all of the interests it holds in a Collective Investment Trust for shares of one or more of the Goldman Sachs Funds. Generally speaking, Rule 22c-1 under the Act requires a purchase order for shares of a Goldman Sachs Fund to be priced based on the current NAV of the Goldman Sachs Fund that is next calculated after receipt of the purchase order. A Goldman Sachs Fund will treat a purchase order component of an exchange from an investor in a Collective Investment Trust as being received in good order at the time it is communicated to an Intermediary or the Transfer Agent, if the amount of shares to be purchased is expressed as a percentage of the value of the investor’s interest in a designated Collective Investment Trust that it is contemporaneously redeeming (e.g., if the investor communicates a desire to exchange 100% of its interest in a Collective Investment Trust for shares of a Goldman Sachs Fund). The investor’s purchase price and the number of Goldman Sachs Fund shares it will acquire will therefore be calculated as of the pricing of the Collective Investment Trust on the day of the purchase order. Such an order will be deemed to be irrevocable as of the time the Goldman Sachs Fund’s NAV is next calculated after receipt of the purchase order. An investor should
B-118
obtain and read the prospectus relating to any Goldman Sachs Fund and its shares and consider its investment objective, policies and applicable fees and expenses before electing an exchange into that Goldman Sachs Fund. For federal income tax purposes, an exchange of interests in a Collective Investment Trust for shares of a Goldman Sachs Fund may be subject to tax, and you should consult your tax adviser concerning the tax consequences of an exchange.
Systematic Withdrawal Plan
A systematic withdrawal plan (the “Systematic Withdrawal Plan”) is available to shareholders of a Fund whose shares are worth at least $5,000. The Systematic Withdrawal Plan provides for monthly payments to the participating shareholder of any amount not less than $50.
Distributions on shares held under the Systematic Withdrawal Plan are reinvested in additional full and fractional shares of the applicable Fund at NAV. The Transfer Agent acts as agent for the shareholder in redeeming sufficient full and fractional shares to provide the amount of the systematic withdrawal payment. The Systematic Withdrawal Plan may be terminated at any time. Goldman Sachs reserves the right to initiate a fee of up to $5 per withdrawal, upon 30 days’ written notice to the shareholder. Withdrawal payments should not be considered to be dividends, yield or income. If periodic withdrawals continuously exceed new purchases and reinvested distributions, the shareholder’s original investment will be correspondingly reduced and ultimately exhausted. The maintenance of a withdrawal plan concurrently with purchases of additional Class A or Class C Shares would be disadvantageous because of the sales charge imposed on purchases of Class A Shares or the imposition of a CDSC on redemptions of Class A or Class C Shares. The CDSC applicable to Class A or Class C Shares redeemed under a systematic withdrawal plan may be waived. See “Shareholder Guide” in the Prospectuses. In addition, each withdrawal constitutes a redemption of shares, and any gain or loss realized must be reported for federal and state income tax purposes. A shareholder should consult his or her own tax adviser with regard to the tax consequences of participating in the Systematic Withdrawal Plan. For further information or to request a Systematic Withdrawal Plan, please write or call the Transfer Agent.
SERVICE PLAN AND SHAREHOLDER ADMINISTRATION PLAN
(Service Shares Only)
The Trust, on behalf of all Funds offering Service Shares, has adopted a service plan (the “Service Plan”) and a separate shareholder administration plan (the “Shareholder Administration Plan”) with respect to the Service Shares (collectively, the “Service Shares Plans”), which authorize the Funds to compensate Intermediaries for providing certain personal and account maintenance services and shareholder administration services to their customers who are or may become beneficial owners of such Shares. Pursuant to the Service Shares Plans, each Fund enters into agreements with Intermediaries, which purchase Service Shares of the Fund on behalf of their customers (“Service Agreements”). Under such Service Agreements the Intermediaries may perform some or all of the following services:
(a) Personal and account maintenance services, including: (i) providing facilities to answer inquiries and respond to correspondence with customers and other investors about the status of their accounts or about other aspects of the Trust or the applicable Fund; (ii) acting as liaison between the Intermediary’s customers and the Trust, including obtaining information from the Trust and assisting the Trust in correcting errors and resolving problems; (iii) providing such statistical and other information as may be reasonably requested by the Trust or necessary for the Trust to comply with applicable federal or state law; (iv) responding to investor requests for prospectuses; (v) displaying and making prospectuses available on the Intermediary’s premises; and (vi) assisting customers in completing application forms, selecting dividend and other account options and opening custody accounts with the Intermediary.
(b) Shareholder administration services, including: (i) acting or arranging for another party to act, as recordholder and nominee of the Service Shares beneficially owned by the Intermediary’s customers; (ii) establishing and maintaining, or assisting in establishing and maintaining, individual accounts and records with respect to the Service Shares owned by each customer; (iii) processing, or assisting in processing, confirmations concerning customer orders to purchase, redeem and exchange Service Shares; (iv) receiving and transmitting, or assist in receiving and transmitting funds representing the purchase price or redemption proceeds of such Service Shares; (v) facilitating the inclusion of Service Shares in accounts, products or services offered to the Intermediary’s customers by or through the Intermediary; (vi) processing dividend payments on behalf of customers; and (vii) performing other related services which do not constitute “any activity which is primarily intended to result in the sale of shares” within the meaning of Rule 12b-1 under the Act or “personal and account maintenance services” within the meaning of FINRA’s Conduct Rules.
B-119
As compensation for such services, each Fund will pay each Intermediary a personal and account maintenance service fee and a shareholder administration service fee in an amount up to 0.25% and 0.25%, respectively, (on an annualized basis) of the average daily net assets of the Service Shares of such Fund attributable to or held in the name of such Intermediary.
The amount of the service and shareholder administration fees paid by each Fund then in existence to Intermediaries pursuant to the Service Shares Plans was as follows for the fiscal years ended August 31, 2020, August 31, 2019 and August 31, 2018.
| Fund |
Fiscal year Ended August 31, 2020 |
Fiscal year Ended August 31, 2019 |
Fiscal year Ended August 31, 2018 |
|||||||||
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund(1) |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
$ | 8,198 | $ | 7,932 | $ | 4,054 | ||||||
| Concentrated Growth Fund(1) |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Flexible Cap Fund(1) |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
$ | 121,928 | $ | 143,738 | 85,603 | |||||||
| Small Cap Growth Fund(2) |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
$ | 89,416 | $ | 86,584 | 45,310 | |||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
$ | 2,516 | $ | 4,148 | 1,286 | |||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
$ | 156,980 | $ | 152,094 | 63,492 | |||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
$ | 802 | $ | 586 | 428 | |||||||
| Focused Value Fund(1) |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
$ | 4,512 | $ | 5,298 | 12,116 | |||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
$ | 182,154 | $ | 272,678 | 383,502 | |||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
$ | 254,890 | $ | 439,908 | 625,216 | |||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund(1) |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| 1 | The U.S. Equity ESG, Concentrated Growth, Flexible Cap, Focused Value and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds do not offer Service Shares. |
| 1 | The Small Cap Growth Fund commenced operations on October 31, 2019. This Fund does not offer Service Shares. |
The Funds offering Service Shares have adopted the Service Plan, but not the Shareholder Administration Plan, pursuant to Rule 12b-1 under the Act in order to avoid any possibility that service fees paid to the Intermediaries pursuant to the Service Agreements might violate the Act. Rule 12b-1, which was adopted by the SEC under the Act, regulates the circumstances under which an investment company or series thereof may bear expenses associated with the distribution of its shares. In particular, such an investment company or series thereof cannot engage directly or indirectly in financing any activity which is primarily intended to result in the sale of shares issued by the company unless it has adopted a plan pursuant to, and complies with the other requirements of, such Rule. The Trust believes that fees paid for the services provided in the Service Plan and described above are not expenses incurred primarily for effecting the distribution of Service Shares. However, should such payments be deemed by a court or the SEC to be distribution expenses, such payments would be duly authorized by the Service Plan. The Shareholder Administration Plan has not been adopted pursuant to Rule 12b-1 under the Act.
Conflict of interest restrictions (including the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974) may apply to an Intermediary’s receipt of compensation paid by a Fund in connection with the investment of fiduciary assets in Service Shares of a Fund. Intermediaries, including banks regulated by the Comptroller of the Currency, the Federal Reserve Board or the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, and investment advisers and other money managers subject to the jurisdiction of the SEC, the Department of Labor or state securities commissions, are urged to consult their legal advisers before investing fiduciary assets in Service Shares of a Fund. In addition, under some state securities laws, banks and other financial institutions purchasing Service Shares on behalf of their customers may be required to register as dealers.
The Trustees, including a majority of the Trustees who are not interested persons of the Trust and who have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operation of the Service Shares Plans or the related Service Agreements, most recently voted to approve the Service Shares Plans and related Service Agreements at a meeting called for the purpose of voting on such Service Shares Plans and Service Agreements on June 16-17, 2020. The Service Shares Plans and related Service Agreements will remain in effect until June 30, 2021 and will continue in effect thereafter only if such continuance is specifically approved annually by a vote of the Trustees in the manner described above. The Service Plan may not be amended (but the Shareholder Administration Plan may be amended) to increase materially the amount to be spent for the services described therein without approval of the Shareholders of the affected Fund’s Service
B-120
Class and all material amendments of each Service Shares Plan must also be approved by the Trustees in the manner described above. The Service Shares Plans may be terminated at any time by a majority of the Trustees as described above or by a vote of a majority of the affected Fund’s outstanding Service Shares. The Service Agreements may be terminated at any time, without payment of any penalty, by vote of a majority of the Trustees as described above or by a vote of a majority of the outstanding Service Shares of the affected Fund on not more than sixty (60) days’ written notice to any other party to the Service Agreements. The Service Agreements will terminate automatically if assigned. So long as the Service Shares Plans are in effect, the selection and nomination of those Trustees who are not interested persons will be committed to the discretion of the Trust’s Governance and Nominating Committee, which consists of all of the non-interested members of the Board of Trustees. The Board of Trustees has determined that, in its judgment, there is a reasonable likelihood that the Service Shares Plans will benefit the Funds and the holders of Service Shares of the Funds.
During the fiscal year ended August 31, 2020, Goldman Sachs incurred the following expenses in connection with distribution under the Service Plan of each Fund with Service Shares:
| Fund(1) |
Compensation to Dealers |
Compensation and Expenses of the Distributor and Its Sales Personnel |
Allocable Overhead, Telephone and Travel Expenses |
Printing and Mailing of Prospectuses to Other Than Current Shareholders |
Preparation and Distribution of Sales Literature and Advertising |
Totals | ||||||||||||||||||
| Capital Growth Fund |
$ | 0 | $ | 465 | $ | 159 | $ | 8 | $ | 15 | $ | 647 | ||||||||||||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
0 | 36,629 | 10,505 | 551 | 1,002 | 48,687 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund |
0 | 45,429 | 17,751 | 932 | 1,693 | 65,804 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Strategic Growth Fund |
0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Technology Opportunities Fund |
0 | 26,207 | 9,492 | 498 | 905 | 37,102 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity Income Fund |
0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap Value Fund |
0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Cap Value Fund |
0 | 19,833 | 7,269 | 381 | 693 | 28,177 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Small Cap Value Fund |
0 | 24,103 | 9,304 | 488 | 887 | 34,783 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | The U.S. Equity ESG, Concentrated Growth, Flexible Cap, Focused Value, Small Cap Growth and Small/Mid Cap Value Funds do not offer Service Shares. |
B-121
CONTROL PERSONS AND PRINCIPAL HOLDERS OF SECURITIES
As of December 1, 2020, the following shareholders were shown in the Trust’s records as owning 5% or more of any class of a Fund’s shares. Except as listed below, the Trust does not know of any other person who owns of record or beneficially 5% or more of any class of a Fund’s shares:
| U.S. Equity ESG Fund |
||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 47.27 | % | |||
| Class A |
Raymond James & Associates, Omnibus Customer Account, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 17.36 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 5.82 | % | |||
| Class C |
Raymond James, Omnibus, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 58.05 | % | |||
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr. San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 28.56 | % | |||
| Institutional |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 52.71 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 24.79 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 22.50 | % | |||
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 29.55 | % | |||
| Investor |
Ascensus Trust Company FBO Customer, P.O. Box 10758, Fargo, ND 58106-0758 | 23.24 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 31.59 | % | |||
| Investor |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 6.95 | % | |||
| Class R |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 99.00 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 98.32 | % | |||
| Capital Growth Fund |
||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 12.74 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 6.40 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 7.96 | % | |||
| Class C |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 5.60 | % | |||
| Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 5.15 | % | |||
| Service |
DCGT as Trustee and/or Cust, FBO PLIC Various Retirement Plans, Omnibus, Attn: NPIO Trade Desk, 711 High St., Des Moines, IA 50392-0001 | 81.24 | % | |||
| Service |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 12.17 | % | |||
B-122
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 24.79 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 17.07 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, For the Sole Benefit of its Customers, Attn: Service Team, SEC #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds, 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 11.78 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 8.76 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 5.97 | % | |||
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 41.17 | % | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 21.10 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 9.22 | % | |||
| Investor |
State Street Bank and Trust, Trustee/Cust, FBO ADP Access Product, 1 Lincoln St., Boston, MA 02111-2900 | 8.15 | % | |||
| Investor |
Mid Atlantic Trust Company, FBO Customer, 1251 Waterfront Pl, Ste. 525, Pittsburgh, PA 15222-4228 | 7.81 | % | |||
| Class R |
State Street Bank and Trust, Trustee/Cust, FBO ADP Access Product, 1 Lincoln St., Boston, MA 02111-2901 | 88.47 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 89.35 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, For the Sole Benefit of its Customers, Attn: Service Team, SEC #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds, 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 8.29 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 98.98 | % | |||
| Concentrated Growth Fund |
||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 |
18.20 | % | |||
| Class A |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team SEQ #97PS0 Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 13.12 | % | |||
| Class A |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 12.78 | % | |||
| Class A |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 11.64 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 7.35 | % | |||
| Class A |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 5.89 | % | |||
| Class A |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 5.14 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 35.30 | % | |||
| Class C |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 14.83 | % | |||
| Class C |
Pershing LLC, 1 Pershing Plz., Jersey City, NJ 07399-0002 | 13.64 | % | |||
| Class C |
Stifel Nicolaus & Co. Exclusive Benefit of Customers, 501 N Broadway, St. Lous, MO 63102-2188 | 10.91 | % | |||
B-123
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 10.56 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 38.68 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Bank NA FBO RT Sherwin Williams Rabbi Trust, PO Box 1533, Minneapolis, MN 55480-1533 | 17.02 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 13.52 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Charles Schwab & Co., Inc., Special Custody Account FBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Department, 211 Main Street, San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 11.23 | % | |||
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 73.19 | % | |||
| Investor |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 17.42 | % | |||
| Investor |
TD Ameritrade Clearing Inc., TD Ameritrade Inc. FBO Clients, PO Box 2226, Omaha, NE 68103-2226 | 6.53 | % | |||
| Class R |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 70.96 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
MSCS Financial Services LLC, Pai Trust Company Inc., Smith Communication Partners, Inc., 1300 Enterprise Dr., De Pere, WI 54115-4934 | 26.32 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 97.48 | %* | |||
| Flexible Cap Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3729 | 31.26 | % | |||
| Class A |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 20.25 | % | |||
| Class A |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 10.36 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 7.77 | % | |||
| Class A |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 7.38 | % | |||
| Class A |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 5.59 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 38.18 | % | |||
| Class C |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 30.29 | % | |||
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 8.26 | % | |||
| Class C |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 5.66 | % | |||
| Class C |
Stifel Nicolaus & Co. Exclusive Benefit of Customers, 501 N Broadway, St. Lous, MO 63102-2188 | 5.00 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 38.93 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Charles Schwab & Co., Inc., Special Custody Account FBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Department, 211 Main Street, San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 32.96 | % | |||
| Institutional |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Crystal Downs Fl. 3, Embassy Golf Links Business Park, Bengaluru 560071 India | 14.93 | % | |||
B-124
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 11.48 | % | |||
| Investor |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | % | |||
| Class R |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 70.82 | % | |||
| Class R |
MSCS Financial Services LLC, MG Trust Company CUST FBO Ottawa Elementary Dist. #141403B, 717 17th St., Ste 1300, Denver CO 80202-3304 | 28.63 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 92.18 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 7.82 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 99.91 | %* | |||
| Growth Opportunities Fund |
| |||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 13.53 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 8.66 | % | |||
| Class A |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team SEC #97PR7 Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Drive East 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 7.66 | % | |||
| Class A |
State Street Bank and Trust, Trustee/Cust, FBO ADP Access Product, 1 Lincoln St., Boston, MA 02111-2901 | 6.91 | % | |||
| Class A |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 5.83 | % | |||
| Class A |
GWFS Equities, Inc., Wells Fargo Bank NA TTEE, C/O Fascore LLC, 8515 E Orchard Rd., 2T2 Greenwood Village, CO 80111-5002 | 5.45 | % | |||
| Class C |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 13.51 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 13.40 | % | |||
| Class C |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 9.90 | % | |||
| Class C |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 9.19 | % | |||
| Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 5.46 | % | |||
| Service |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 78.44 | % | |||
| Service |
GWFS Equities, Inc., Great-West Trust Company LLC FBO Various Fascore Recordkept Plans, CO Fasscore LLC, 8515 E Orchard RD 2T2, Greenwood Village, CO 80111-5002 | 6.67 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FEBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 27.54 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 16.16 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 10.08 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, For the Sole Benefit of its Customers, Attn: Service Team, SEC #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds, 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 6.07 | % | |||
| Investor |
Principal Securities, Inc., FBO PLIC Various Retirement Plans, Attn: NPIO Trade Desk, 711 High St., Des Moines, IA 50392-0001 | 41.30 | % | |||
B-125
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 13.83 | % | |||
| Investor |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 10.39 | % | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 8.53 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 7.00 | % | |||
| Class R |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account 401, 1 Griffin Rd., North Windsor, CT 06095-1512 | 42.41 | % | |||
| Class R |
State Street Bank and Trust, Trustee/Cust, FBO ADP Access Product, 1 Lincoln St., Boston, MA 02111-2901 | 26.25 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 26.87 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Associated Trust Company, PO Box 22037, Green Bay, WI 54305-2037 | 23.80 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Associated Trust Company, PO Box 22037, Green Bay, WI 54305-2037 | 5.94 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 99.98 | % | |||
| Small Cap Growth Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 43.52 | % | |||
| Class A |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 28.04 | %* | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 23.69 | %* | |||
| Class C |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 68.48 | % | |||
| Class C |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 29.67 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 49.07 | %* | |||
| Institutional |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 44.11 | %* | |||
| Investor |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | %* | |||
| Class R |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | %* | |||
| Class R6 |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | %* | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 97.73 | % | |||
| Small/Mid Cap Growth Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 14.47 | % | |||
| Class A |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Drive East 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 9.73 | % | |||
| Class A |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 9.48 | % | |||
| Class A |
Charles Schwab & Co Inc, Special Custody Acct. FBO Customers Attn: Mutual Funds 211 Main St., San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 8.79 | % | |||
| Class A |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 8.68 | % | |||
B-126
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 6.89 | % | |||
| Class A |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 6.87 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 28.49 | % | |||
| Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 19.58 | % | |||
| Class C |
UBS WM USA,, Omnibus Account M/F Special Custody A/C FEBO Customers UBSFSI 1000 Harbor Blvd., Weehawken, NJ 07086-6761 | 16.02 | % | |||
| Class C |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 9.06 | % | |||
| Class C |
Raymond James, Omnibus, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 5.72 | % | |||
| Service |
Great-West Trust Company LLC Trustee/C, FBO: Great West IRA Advantage, C/O Fascore LLC, 8515 E Orchard Rd., 2T2 Greenwood Village, CO 80111-5002 | 96.34 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 23.04 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Charles Schwab & Co Inc, Special Custody Account FBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds 211 Main St., San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 14.70 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 11.46 | % | |||
| Institutional |
UBS WM USA,, Omnibus Account M/F Special Custody A/C FEBO Customers UBSFSI 1000 Harbor Blvd., Weehawken, NJ 07086-6761 | 7.84 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, FEBO Cust, Attn: Service Team SEC #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 7.78 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 7.73 | % | |||
| Institutional |
TD Ameritrade Inc, FEBO Our Clients, PO Box 2226, Omaha, NE 68103-2226 | 5.76 | % | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 49.54 | % | |||
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 14.66 | % | |||
| Investor |
Charles Schwab & Co Inc, Special Custody Acct. FBO Customers Attn: Mutual Funds 211 Main St., San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 12.64 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 9.33 | % | |||
| Investor |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 7.82 | % | |||
| Class R |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account 401, 1 Griffin Rd., North Windsor, CT 06095-1512 | 26.63 | % | |||
| Class R |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, For the Sole Benefit of its Customers, Attn: Service Team, SEC #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds, 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 5.30 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Great West Trust Company LLC, Plans of Great West Financial, 8515 E Orchard Rd 2T2, Greenwood Village, CO 80111-5002 | 16.30 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
PIMS/Prudential Retirement, as Nominee for the Trustee/Cust PL 767, CGB Enterprises, Inc. 401(K) 1127 Highway 190 East Service Road Covington, LA 70433 | 15.53 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 16.43 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 10.66 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Hartford Life Insurance Company, The Hartford, 1 Hartford Plz., Hartford, CT 06155-0001 | 5.80 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
DCGT as Trustee and/or Cust, FBO PLIC Various Retirement Plans, Omnibus, Attn: NPIO Trade Desk, 711 High St., Des Moines, IA 50392-0001 | 5.65 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 99.32 | % |
B-127
| Strategic Growth Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 19.01 | % | |||
| Class A |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 13.22 | % | |||
| Class A |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 7.20 | % | |||
| Class A |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 7.03 | % | |||
| Class A |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team SEC #97PR7 Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Drive East 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 6.90 | % | |||
| Class A |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 6.04 | % | |||
| Class A |
FIIOC FBO Customer, 100 Magellan Way #KW1C Covington, KY 41015-1987 | 5.77 | % | |||
| Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 24.82 | % | |||
| Class C |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 14.17 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 12.46 | % | |||
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 7.30 | % | |||
| Class C |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 5.56 | % | |||
| Class C |
RBC Capital Markets LLC, Mutual Fund Omnibus Processing, Attn: Mutual Fund Ops., Manager 60 S 6th St., Ste. 700 # P08 Minneapolis, MN 55402-4413 | 5.20 | % | |||
| Service |
Lincoln Financial Group Trust CO, FBO Rollover IRA Plans, 1 Granite PL Concord, NH 03301-3271 | 32.54 | % | |||
| Service |
Lincoln Financial Group Trust CO, FBO Traditional IRA Plans, 1 Granite PL Concord, NH 03301-3271 | 32.48 | % | |||
| Service |
Lincoln Financial Group Trust CO, FBO Rollover SS IRA Plan, 1 Granite PL Concord, NH 03301-3271 | 10.03 | % | |||
| Service |
Lincoln Financial Group Trust CO, FBO Traditional SS IRA Plans-NY, 1 Granite PL Concord, NH 03301-3271 | 8.77 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 68.51 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 7.21 | % | |||
| Institutional |
UBS WM USA, Omnibus Account M/F Special Custody A/C FEBO Customers UBSFSI 1000 Harbor Blvd., Weehawken, NJ 07086-6761 | 5.75 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 5.64 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 5.07 | % | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 68.86 | % | |||
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 21.16 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 5.16 | % | |||
| Class R |
State Street Bank and Trust, Trustee/Cust, FBO ADP Access Product, 1 Lincoln St., Boston, MA 02111-2900 | 77.25 | % | |||
| Class R |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 22.46 | % | |||
B-128
| Strategic Growth Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 58.19 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team SEQ #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 30.47 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
JP Morgan Securities LLC, FEBO Customers, Mutual Fund Dept. 3 Chase Metrotech Center Floor 3 Brooklyn, NY 11245-0001 | 7.63 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 99.86 | %* | |||
| Technology Opportunities Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 15.83 | % | |||
| Class A |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 9.20 | % | |||
| Class A |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team SEC #9EH17 Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 6.87 | % | |||
| Class A |
TD Ameritrade Inc, FEBO Our Clients, PO Box 2226, Omaha, NE 68103-2226 | 9.55 | % | |||
| Class A |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 5.60 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 22.40 | % | |||
| Class C |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 11.27 | % | |||
| Class C |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 10.18 | % | |||
| Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 9.68 | % | |||
| Class C |
UBS WM USA,, Omnibus Account M/F Special Custody A/C FEBO Customers UBSFSI 1000 Harbor Blvd., Weehawken, NJ 07086-6761 | 6.76 | % | |||
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 6.65 | % | |||
| Service |
Great-West Trust Company LLC Trustee/C, FBO: Great West IRA Advantage, C/O Fascore LLC, 8515 E Orchard Rd., 2T2 Greenwood Village, CO 80111-5002 | 71.01 | % | |||
| Service |
WTRISC CO IRA Omnibus ACCT, C/O ICMA Retirement Corporation, 777 North Capitol Street, NE Washington DC 20002-4239 | 17.33 | % | |||
| Service |
American United Life Insurance Co., FBO Group Retirement Account, Attn: Separate Accounts PO Box 368, Indianapolis, IN 46206-0368 | 6.79 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 29.97 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Charles Schwab & Co Inc, Special Custody Account FBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds 211 Main St., San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 14.96 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 8.29 | % | |||
| Institutional |
American United Life Insurance Co., FBO Group Retirement Account, Attn: Separate Accounts PO Box 368, Indianapolis, IN 46206-0368 | 6.64 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 5.42 | % | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 64.28 | % | |||
B-129
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus for Mutual Funds, House Account Firm, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 15.41 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 12.97 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 70.38 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Great-West Trust Company LLC TTEE F, Employee Benefits Clients 401(k) – FG, 8515 E Orchard Rd. 2T2, Greenwood Village, CO 80111-5002 | 22.31 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Matrix Trust Custodian, FBO Customer, 717 17th Ste. 1300, Denver, CO 80202-3304 | 5.96 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 98.64 | % | |||
| Equity Income Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 53.78 | %* | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 17.70 | % | |||
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 10.08 | % | |||
| Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 7.88 | % | |||
| Class C |
Stifel Nicolaus & Co. Exclusive Benefit of Customers, 501 N Broadway, St. Lous, MO 63102-2188 | 5.73 | % | |||
| Class C |
Ascensus Trust Company FBO Customer, P.O. Box 10758, Fargo, ND 58106-0758 | 5.43 | % | |||
| Class C |
Mid Atlantic Trust Company, FBO Customer, 1251 Waterfront Pl, Ste. 525, Pittsburgh, PA 15222-4228 | 5.26 | % | |||
| Class C |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 5.15 | %* | |||
| Service |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 80.14 | % | |||
| Service |
Edward D. Jones & Co., Attn: Mutual Fund, Shareholder Accounting 201 Progress Pkwy., Maryland Heights, MO 63043-3042 | 7.79 | %* | |||
| Service |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team SEQ #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 6.62 | % | |||
| Institutional |
RBC Capital Markets LLC, Mutual Fund Omnibus Processing, Attn: Mutual Fund Ops., Manager 60 S 6th St., Ste. 700 # P08 Minneapolis, MN 55402-4413 | 21.42 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Matrix Trust CO Trustee FBO Customer, PO Box 52129 Phoenix, AZ 85072-2129 | 20.62 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 10.47 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 7.28 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Reliance Trust FBO Customer Omnibus PO Box 78846 Atlanta, GA 30357-2446 | 7.21 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Matrix Trust CO Trustee FBO Customer, PO Box 52129 Phoenix, AZ 85072-2129 | 7.05 | % | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 52.71 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 23.72 | % | |||
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 19.08 | % | |||
| Class R |
MSCS Financial Services LLC, Bridges Trust Co., Custodian, FBO Region V Services 457(B) Plan, PO Box 542021., Omaha, NE 68154-8021 | 51.88 | % | |||
B-130
| Class R |
Pam O’ FBO Customer, 327 Dahlonega St., Ste. 1005 Cumming, GA 30040-8210 | 26.94 | % | |||
| Class R |
Mid Atlantic Trust Company, William Grischo FBO Customer, 3213 Zuni St., Denver, CO 80211-3355 | 5.43 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 98.92 | %* | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 97.15 | %* | |||
| Focused Value Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 |
60.51 | % | |||
| Class A |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 22.43 | % | |||
| Class A |
Cadaret Grant & Co., Inc., FBO E.T.A.U. (NY), 9703 Versailles Rd., Angola NY 14006-9519 | 9.63 | % | |||
| Class C |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | % | |||
| Institutional |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 82.71 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 16.45 | % | |||
| Investor |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | % | |||
| Class R |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 59.36 | % | |||
| Class R |
Oppenheimer & Co. Inc.., FBO Customer, 116 Kingsbury Rd., Garden City, NY 11530-3110 | 40.64 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 100.00 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 99.88 | %* | |||
| Large Cap Value Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 31.94 | % | |||
| Class A |
UBS WM USA,, Omnibus Account M/F Special Custody A/C FEBO Customers UBSFSI 1000 Harbor Blvd., Weehawken, NJ 07086-6761 | 9.94 | % | |||
| Class A |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, For the Sole Benefit of its Customers, Attn: Service Team, SEC #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds, 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 6.69 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 6.45 | %* | |||
| Class A |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 5.25 | % | |||
| Class C |
UBS WM USA,, Omnibus Account M/F Special Custody A/C FEBO Customers UBSFSI 1000 Harbor Blvd., Weehawken, NJ 07086-6761 | 72.94 | % | |||
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 5.29 | % | |||
| Class C |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 5.18 | %* | |||
| Service |
TCA Trustcorp America, 5301 Wisconsin Ave. NW, Fourth Floor Washington, DC, 20015-2047 | 54.41 | % | |||
B-131
| Service |
Lincoln Financial Group Trust CO, FBO Rollover IRA Plans, 1 Granite PL Concord, NH 03301-3271 | 22.60 | % | |||
| Service |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account, 200 Hopmeadow St., Weatogue, CT 06089-9793 | 7.54 | % | |||
| Service |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Dr., E Fl. 3 Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 6.80 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 82.49 | %* | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 59.37 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 13.25 | % | |||
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 10.99 | % | |||
| Investor |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 5.98 | %* | |||
| Class R |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account 401, 1 Griffin Rd., North Windsor, CT 06095-1512 | 79.47 | % | |||
| Class R |
Principal Securities, Inc., DCGT as Trustee and/or Customer, FBO PLIC Various Retirement Plans, Omnibus, Attn: NPIO Trade Desk, 711 High St., Des Moines, IA 50392-0001 | 10.84 | % | |||
| Class R |
MML Distributors, LLC, Mass Mutual Life Insurance Co., MIP M200-INVST, 1295 State St., Springfield, MA 01111-0001 | 6.54 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 46.02 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
MML Distributors, LLC, Massachusetts Mutual Insurance Company, MIP M200-INVST, 1295 State Street, Springfield, MA 01111-0001 | 26.59 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Reliance Trust Company, FBO MassMutual Registered Product, PO Box 28004 Atlanta, GA 30358-0004 | 22.02 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 99.85 | %* | |||
| Mid Cap Value Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 30.77 | % | |||
| Class A |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account 401, 1 Griffin Rd., North Windsor, CT 06095-1512 | 6.39 | % | |||
| Class A |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, For the Sole Benefit of its Customers, Customers, Attn: Service Team Seq. #97RJ3, Goldman Sachs Funds, 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd floor, Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 6.01 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 5.17 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 22.15 | % | |||
| Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 10.88 | % | |||
| Class C |
Pershing LLC, PO Box 2052, Jersey City, NJ 07303-2052 | 9.44 | % | |||
| Class C |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FEBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 8.40 | % | |||
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 8.09 | % | |||
| Class C |
RBC Capital Markets LLC, Mutual Fund Omnibus Processing, Attn: Mutual Fund Ops., Manager 60 S 6th St., Ste. 700 # P08 Minneapolis, MN 55402-4413 | 6.42 | % | |||
B-132
| Mid Cap Value Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class C |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 5.67 | % | |||
| Service |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 57.12 | % | |||
| Service |
American United Life Insurance Co., FBO Group Retirement Account, Attn: Separate Accounts PO Box 368, Indianapolis, IN 46206-0368 | 10.62 | % | |||
| Service |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account, 200 Hopmeadow St., Weatogue, CT 06089-9793 | 6.37 | % | |||
| Service |
American United Life Insurance Co., FBO Unit Investment Trust, Attn: Separate Accounts PO Box 368, Indianapolis, IN 46206-0368 | 5.07 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 21.58 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, FBO its Customers, 1 New York Plz, Fl. 12, New York, NY 10004-1932 | 16.28 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, FEBO Cust, Attn: Service Team SEC 97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 9.73 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 8.99 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Charles Schwab & Co Inc, Special Custody Account FBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds 211 Main St., San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 5.39 | % | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 46.48 | % | |||
| Investor |
Raymond James, Omnibus, Attn: Courtney Waller, 880 Carillon Parkway, St. Petersburg, FL 33716-1102 | 22.97 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 11.10 | % | |||
| Investor |
Reliance Trust Company, FBO MassMutual Registered Product, PO Box 28004 Atlanta, GA 30358-0004 | 5.43 | % | |||
| Class R |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account 401, 1 Griffin Rd., North Windsor, CT 06095-1512 | 29.11 | % | |||
| Class R |
State Street Bank and Trust, Trustee/Cust, FBO ADP Access Product, 1 Lincoln St., Boston, MA 02111-2901 | 23.42 | % | |||
| Class R |
Mass Mutual Life Insurance Co., 1295 State St., MIP M200-INVST, Springfield, MA 01111-0001 | 9.13 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 57.11 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, For the Sole Benefit of its Customers, Attn: Service Team, SEC #97PR8 Goldman Sachs Funds, 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 10.65 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Great West Trust Company LLC Plans of Great West Financial 8515 E Orchard Rd 2T2, Greenwood Village, CO 80111-5002 | 6.23 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
American United Life Insurance Co., FBO Group Retirement Account, Attn: Separate Accounts PO Box 368, Indianapolis, IN 46206-0368 | 5.88 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 99.48 | % | |||
B-133
| Small Cap Value Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 14.96 | % | |||
| Class A |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account 401, 1 Griffin Rd., North Windsor, CT 06095-1512 | 11.26 | % | |||
| Class A |
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith, for the Sole Benefit of its Cust, Attn: Service Team SEC #97PY5 Goldman Sachs Fund 4800 Deer Lake Dr. East, 3rd Fl. Jacksonville, FL 32246-6484 | 11.21 | % | |||
| Class A |
State Street Bank and Trust, Trustee/Cust, FBO ADP Access Product, 1 Lincoln St., Boston, MA 02111-2901 | 9.24 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 6.28 | % | |||
| Class C |
UBS WM USA,, Omnibus Account M/F Special Custody A/C FEBO Customers UBSFSI 1000 Harbor Blvd., Weehawken, NJ 07086-6761 | 40.87 | % | |||
| Class C |
Wells Fargo Clearing Services LLC, Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customer 2801 Market St., Saint Louis, MO 63103-2523 | 12.20 | % | |||
| Service |
American United Life Insurance Co., FBO Group Retirement Account, Attn: Separate Accounts PO Box 368, Indianapolis, IN 46206-0368 | 40.42 | % | |||
| Service |
American United Life Insurance Co., FBO Unit Investment Trust, Attn: Separate Accounts PO Box 368, Indianapolis, IN 46206-0368 | 10.82 | % | |||
| Service |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 7.00 | % | |||
| Service |
Great-West Trust Company LLC, Plans of Great-West Financial, 8515 E Orchard Rd., 2T2 Greenwood Village, CO 80111-5002 | 5.31 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 29.00 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Bank FBO Various Retirement Plans, NC 1151 1525 West Wt Harris Blvd., Charlotte, NC 28262-8522 | 8.49 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Charles Schwab & Co Inc, Special Custody Account FBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds 211 Main St., San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 12.64 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Prudential Bank and Trust, FBO Customer, 280 Trumbull Street, Hartford, CT 06103-3509 | 6.64 | % | |||
| Investor |
Charles Schwab & Co Inc, Special Custody Acct. FBO Customers Attn: Mutual Funds 211 Main St., San Francisco, CA 94105-1905 | 20.50 | % | |||
| Investor |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 19.39 | % | |||
| Investor |
John Hancock Trust Company LLC, 690 Canton St., Ste. 100, Westwood, MA 02090-2324 | 9.03 | % | |||
| Class R |
Hartford Life Insurance Co., Separate Account 401, 1 Griffin Rd., North Windsor, CT 06095-1512 | 38.85 | % | |||
| Class R |
State Street Bank and Trust, Trustee/Cust, FBO ADP Access Product, 1 Lincoln St., Boston, MA 02111-2901 | 19.03 | % | |||
| Class R |
Mass Mutual Life Insurance Co., 1295 State St., MIP M200-INVST, Springfield, MA 01111-0001 | 16.59 | % | |||
| Class R |
DCGT as Trustee and/or Cust, FBO PLIC Various Retirement Plans, Omnibus, Attn: NPIO Trade Desk, 711 High St., Des Moines, IA 50392-0001 | 5.46 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Mutual Fund Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 30.65 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Edward D. Jones & Co., FBO Customers, 12555 Manchester Rd., Saint Louis, MO 63131-3710 | 7.97 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
JP Morgan Securities LLC, FEBO Customers, Mutual Fund Dept. 3 Chase Metrotech Center Floor 3 Brooklyn, NY 11245-0001 | 5.50 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
TIAA, Trustee FBO Retirement Plans for Which TIAA Acts as Recordkeeper, Attn: Trust Operations, 211 North Broadway Ste. 1000, Saint Louis, MO 63102-2748 | 5.50 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
PIMS/Prudential Retirement, as Nominee for the Trustee/Cust PL 767, Ferguson Enterprises, LLC, 12500 Jefferson Ave., Newport News, VA 23602-4314 | 5.39 | % | |||
B-134
| Small Cap Value Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 99.01 | % | |||
| Small/Mid Cap Value Fund | ||||||
| Class | Name/Address |
Percentage of Class |
||||
| Class A |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 26.42 | % | |||
| Class A |
Stifel Nicolaus & Co. Exclusive Benefit of Customers, 501 N Broadway, St. Lous, MO 63102-2188 | 14.35 | % | |||
| Class A |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 11.80 | % | |||
| Class A |
LPL Financial Corporation, U/A DTD 7-01-94, 7710 Welton Dr., Madison, WI 53719-3026 | 5.95 | % | |||
| Class A |
AXA Advisors, LLC, G.C.G. and L.J.G., 1269 Edenville Road, Chambersburg, PA 17202-8029 | 6.58 | % | |||
| Class A |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 5.10 | % | |||
| Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 51.65 | % | |||
| Class C |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 19.09 | % | |||
| Class C |
Stifel Nicolaus & Co. Exclusive Benefit of Customers, 501 N Broadway, St. Lous, MO 63102-2188 | 14.20 | % | |||
| Institutional |
National Financial Services LLC, FEBO Customers, Attn: Mutual Funds Dept. 4th Flr., 499 Washington Blvd., Jersey City, NJ 07310-1995 | 66.22 | % | |||
| Institutional |
Wells Fargo Bank NA, FBO MasterCard International Deferral Plan 10071000, PO Box 1533 Minneapolis, MN 55480-1533 | 21.10 | % | |||
| Institutional |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Crystal Downs Fl. 3, Embassy Golf Links Business Park, Bengaluru 560071 India | 6.42 | % | |||
| Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Svc, FBOC, 707 2nd Ave. S Minneapolis, MN 55402-2405 | 90.28 | % | |||
| Investor |
LPL Financial, Omnibus Customer Account, Attn: Mutual Fund Trading, 4707 Executive Dr., San Diego, CA 92121-3091 | 6.62 | % | |||
| Class R |
Pai Trust Company Inc, River Falls Eye Surgery & Laser Center, 1300 Enterprise Dr., De Pere, WI 54115-4934 | 74.79 | % | |||
| Class R |
Matrix Trust Custodian, FBO Hope Community Church (MI), 717 17th Ste. 1300, Denver, CO 80202-3304 | 5.70 | % | |||
| Class R |
GSAM Holdings LLC Seed Account, Attn: IMD-India-SAOS, Helios Business Park, 150 Outer Ring Road, Kadubeesanahalli, Bengaluru, 560103 India | 14.59 | % | |||
| Class R6 |
Voya Institutional Plan Services LLC, ING National Trust, As Trustee or Custodian for Core Market Retirement Plans, 1 Heritage Dr., North Quincy, MA 02171-2105 | 90.89 | %* | |||
| Class R6 |
Vanguard Fiduciary Trust Company, Attn: Outside Funds K22, P.O. Box 2600, Valley Forge, PA 19482-2600 | 9.08 | % | |||
| Class P |
Goldman Sachs & Co., FBO Omnibus 6600, C/O Mutual Fund Ops., 222 S Main St., Salt Lake City, UT, 84101-2199 | 98.99 | %* | |||
| * | Entity owned more than 25% of the outstanding shares of the Fund. A shareholder owning of record or beneficially more than 25% of a Fund’s outstanding shares may be considered a control person and could have a more significant effect on matters presented at a shareholders’ meeting than votes of other shareholders. |
B-135
APPENDIX A
DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES RATINGS
Short-Term Credit Ratings
An S&P Global Ratings short-term issue credit rating is a forward-looking opinion about the creditworthiness of an obligor with respect to a specific financial obligation having an original maturity of no more than 365 days. The following summarizes the rating categories used by S&P Global Ratings for short-term issues:
“A-1” – A short-term obligation rated “A-1” is rated in the highest category by S&P Global Ratings. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is strong. Within this category, certain obligations are designated with a plus sign (+). This indicates that the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on these obligations is extremely strong.
“A-2” – A short-term obligation rated “A-2” is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligations in higher rating categories. However, the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is satisfactory.
“A-3” – A short-term obligation rated “A-3” exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to weaken an obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation.
“B” – A short-term obligation rated “B” is regarded as vulnerable and has significant speculative characteristics. The obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitments; however, it faces major ongoing uncertainties that could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitments.
“C” – A short-term obligation rated “C” is currently vulnerable to nonpayment and is dependent upon favorable business, financial, and economic conditions for the obligor to meet its financial commitments on the obligation.
“D” – A short-term obligation rated “D” is in default or in breach of an imputed promise. For non-hybrid capital instruments, the “D” rating category is used when payments on an obligation are not made on the date due, unless S&P Global Ratings believes that such payments will be made within any stated grace period. However, any stated grace period longer than five business days will be treated as five business days. The “D” rating also will be used upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of a similar action and where default on an obligation is a virtual certainty, for example due to automatic stay provisions. An obligation’s rating is lowered to “D” if it is subject to a distressed exchange offer.
Local Currency and Foreign Currency Ratings – S&P Global Ratings’ issuer credit ratings make a distinction between foreign currency ratings and local currency ratings. An issuer’s foreign currency rating will differ from its local currency rating when the obligor has a different capacity to meet its obligations denominated in its local currency, vs. obligations denominated in a foreign currency.
Moody’s Investors Service (“Moody’s”) short-term ratings are forward-looking opinions of the relative credit risks of financial obligations with an original maturity of thirteen months or less and reflect both on the likelihood of a default on contractually promised payments and the expected financial loss suffered in the event of default.
Moody’s employs the following designations to indicate the relative repayment ability of rated issuers:
“P-1” – Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-1 have a superior ability to repay short-term debt obligations.
“P-2” – Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-2 have a strong ability to repay short-term debt obligations.
“P-3” – Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-3 have an acceptable ability to repay short-term obligations.
“NP” – Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Not Prime do not fall within any of the Prime rating categories.
Fitch, Inc. / Fitch Ratings Ltd. (“Fitch”) short-term issuer or obligation ratings are based in all cases on the short-term vulnerability to default of the rated entity and relates to the capacity to meet financial obligations in accordance with the documentation governing the relevant obligation. Short-term deposit ratings may be adjusted for loss severity. Short-Term Ratings are assigned to obligations whose initial maturity is viewed as “short term” based on market convention. Typically, this means up to 13 months for corporate, sovereign, and structured obligations and up to 36 months for obligations in U.S. public finance markets.
The following summarizes the rating categories used by Fitch for short-term obligations:
“F1” – Securities possess the highest short-term credit quality. This designation indicates the strongest intrinsic capacity for timely payment of financial commitments; may have an added “+” to denote any exceptionally strong credit feature.
1-A
“F2” – Securities possess good short-term credit quality. This designation indicates good intrinsic capacity for timely payment of financial commitments.
“F3” – Securities possess fair short-term credit quality. This designation indicates that the intrinsic capacity for timely payment of financial commitments is adequate.
“B” – Securities possess speculative short-term credit quality. This designation indicates minimal capacity for timely payment of financial commitments, plus heightened vulnerability to near term adverse changes in financial and economic conditions.
“C” – Securities possess high short-term default risk. Default is a real possibility.
“RD” – Restricted Default. Indicates an entity that has defaulted on one or more of its financial commitments, although it continues to meet other financial obligations. Typically applicable to entity ratings only.
“D” – Default. Indicates a broad-based default event for an entity, or the default of a short-term obligation.
“NR” – This designation indicates that Fitch does not publicly rate the associated issuer or issue.
“WD” – This designation indicates that the rating has been withdrawn and is no longer maintained by Fitch.
DBRS® Ratings Limited (“DBRS”) short-term debt rating scale provides an opinion on the risk that an issuer will not meet its short-term financial obligations in a timely manner. Ratings are based on quantitative and qualitative considerations relevant to the issuer and the relative ranking of claims. The “R-1” and “R-2” rating categories are further denoted by the sub-categories “(high)”, “(middle)”, and “(low)”.
The following summarizes the ratings used by DBRS for commercial paper and short-term debt:
“R-1 (high)” – Short-term debt rated “R-1 (high)” is of the highest credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is exceptionally high. Unlikely to be adversely affected by future events.
“R-1 (middle)” – Short-term debt rated “R-1 (middle)” is of superior credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is very high. Differs from “R-1 (high)” by a relatively modest degree. Unlikely to be significantly vulnerable to future events.
“R-1 (low)” – Short-term debt rated “R-1 (low)” is of good credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is substantial. Overall strength is not as favorable as higher rating categories. May be vulnerable to future events, but qualifying negative factors are considered manageable.
“R-2 (high)” – Short-term debt rated “R-2 (high)” is considered to be at the upper end of adequate credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is acceptable. May be vulnerable to future events.
“R-2 (middle)” – Short-term debt rated “R-2 (middle)” is considered to be of adequate credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is acceptable. May be vulnerable to future events or may be exposed to other factors that could reduce credit quality.
“R-2 (low)” – Short-term debt rated “R-2 (low)” is considered to be at the lower end of adequate credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is acceptable. May be vulnerable to future events. A number of challenges are present that could affect the issuer’s ability to meet such obligations.
“R-3” – Short-term debt rated “R-3” is considered to be at the lowest end of adequate credit quality. There is a capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due. May be vulnerable to future events and the certainty of meeting such obligations could be impacted by a variety of developments.
“R-4” – Short-term debt rated “R-4” is considered to be of speculative credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is uncertain.
“R-5” – Short-term debt rated “R-5” is considered to be of highly speculative credit quality. There is a high level of uncertainty as to the capacity to meet short-term financial obligations as they fall due.
“D” – Short-term debt rated “D” is assigned when the issuer has filed under any applicable bankruptcy, insolvency or winding up statute or there is a failure to satisfy an obligation after the exhaustion of grace periods, a downgrade to “D” may occur. DBRS may also use “SD” (Selective Default) in cases where only some securities are impacted, such as the case of a “distressed exchange”.
2-A
Long-Term Credit Ratings
The following summarizes the ratings used by S&P Global Ratings for long-term issues:
“AAA” – An obligation rated “AAA” has the highest rating assigned by S&P Global Ratings. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is extremely strong.
“AA” – An obligation rated “AA” differs from the highest-rated obligations only to a small degree. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is very strong.
“A” – An obligation rated “A” is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligations in higher-rated categories. However, the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is still strong.
“BBB” – An obligation rated “BBB” exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to weaken the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation.
Obligations rated “BB,” “B,” “CCC,” “CC” and “C” are regarded as having significant speculative characteristics. “BB” indicates the least degree of speculation and “C” the highest. While such obligations will likely have some quality and protective characteristics, these may be outweighed by large uncertainties or major exposures to adverse conditions.
“BB” – An obligation rated “BB” is less vulnerable to nonpayment than other speculative issues. However, it faces major ongoing uncertainties or exposure to adverse business, financial, or economic conditions that could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation.
“B” – An obligation rated “B” is more vulnerable to nonpayment than obligations rated “BB”, but the obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. Adverse business, financial, or economic conditions will likely impair the obligor’s capacity or willingness to meet its financial commitments on the obligation.
“CCC” – An obligation rated “CCC” is currently vulnerable to nonpayment and is dependent upon favorable business, financial, and economic conditions for the obligor to meet its financial commitments on the obligation. In the event of adverse business, financial, or economic conditions, the obligor is not likely to have the capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation.
“CC” – An obligation rated “CC” is currently highly vulnerable to nonpayment. The “CC” rating is used when a default has not yet occurred but S&P Global Ratings expects default to be a virtual certainty, regardless of the anticipated time to default.
“C” – An obligation rated “C” is currently highly vulnerable to nonpayment, and the obligation is expected to have lower relative seniority or lower ultimate recovery compared with obligations that are rated higher.
“D” – An obligation rated “D” is in default or in breach of an imputed promise. For non-hybrid capital instruments, the “D” rating category is used when payments on an obligation are not made on the date due, unless S&P Global Ratings believes that such payments will be made within five business days in the absence of a stated grace period or within the earlier of the stated grace period or 30 calendar days. The “D” rating also will be used upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of similar action and where default on an obligation is a virtual certainty, for example due to automatic stay provisions. An obligation’s rating is lowered to “D” if it is subject to a distressed exchange offer.
“NR” – This indicates that no rating has been requested, or that there is insufficient information on which to base a rating, or that S&P Global Ratings does not rate a particular obligation as a matter of policy.
Plus (+) or minus (-) – The ratings from “AA” to “CCC” may be modified by the addition of a plus (+) or minus (-) sign to show relative standing within the major rating categories.
Local Currency and Foreign Currency Ratings – S&P Global Ratings’ issuer credit ratings make a distinction between foreign currency ratings and local currency ratings. An issuer’s foreign currency rating will differ from its local currency rating when the obligor has a different capacity to meet its obligations denominated in its local currency, vs. obligations denominated in a foreign currency.
Moody’s long-term ratings are forward-looking opinions of the relative credit risks of financial obligations with an original maturity of one year or more and reflect both on the likelihood of a default on contractually promised payments and the expected financial loss suffered in the event of default. The following summarizes the ratings used by Moody’s for long-term debt:
“Aaa” – Obligations rated “Aaa” are judged to be of the highest quality, subject to the lowest level of credit risk.
“Aa” – Obligations rated “Aa” are judged to be of high quality and are subject to very low credit risk.
“A” – Obligations rated “A” are judged to be upper-medium grade and are subject to low credit risk.
“Baa” – Obligations rated “Baa” are judged to be medium-grade and subject to moderate credit risk and as such may possess certain speculative characteristics.
3-A
“Ba” – Obligations rated “Ba” are judged to be speculative and are subject to substantial credit risk.
“B” – Obligations rated “B” are considered speculative and are subject to high credit risk.
“Caa” – Obligations rated “Caa” are judged to be speculative of poor standing and are subject to very high credit risk.
“Ca” – Obligations rated “Ca” are highly speculative and are likely in, or very near, default, with some prospect of recovery of principal and interest.
“C” – Obligations rated “C” are the lowest rated and are typically in default, with little prospect for recovery of principal or interest.
Note: Moody’s appends numerical modifiers 1, 2, and 3 to each generic rating classification from “Aa” through “Caa.” The modifier 1 indicates that the obligation ranks in the higher end of its generic rating category; the modifier 2 indicates a mid-range ranking; and the modifier 3 indicates a ranking in the lower end of that generic rating category.
The following summarizes long-term ratings used by Fitch:
“AAA” – Securities considered to be of the highest credit quality. “AAA” ratings denote the lowest expectation of credit risk. They are assigned only in cases of exceptionally strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is highly unlikely to be adversely affected by foreseeable events.
“AA” – Securities considered to be of very high credit quality. “AA” ratings denote expectations of very low credit risk. They indicate very strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is not significantly vulnerable to foreseeable events.
“A” – Securities considered to be of high credit quality. “A” ratings denote expectations of low credit risk. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered strong. This capacity may, nevertheless, be more vulnerable to adverse business or economic conditions than is the case for higher ratings.
“BBB” – Securities considered to be of good credit quality. “BBB” ratings indicate that expectations of credit risk are currently low. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.
“BB” – Securities considered to be speculative. “BB” ratings indicate an elevated vulnerability to credit risk, particularly in the event of adverse changes in business or economic conditions over time; however, business or financial alternatives may be available to allow financial commitments to be met.
“B” – Securities considered to be highly speculative. “B” ratings indicate that material credit risk is present.
“CCC” – A “CCC” rating indicates that substantial credit risk is present.
“CC” – A “CC” rating indicates very high levels of credit risk.
“C” – A “C” rating indicates exceptionally high levels of credit risk.
Defaulted obligations typically are not assigned “RD” or “D” ratings but are instead rated in the “B” to “C” rating categories, depending on their recovery prospects and other relevant characteristics. Fitch believes that this approach better aligns obligations that have comparable overall expected loss but varying vulnerability to default and loss..
Plus (+) or minus (-) may be appended to a rating to denote relative status within major rating categories. Such suffixes are not added to the “AAA” category or to categories below “CCC”.
“NR” – Denotes that Fitch does not publicly rate the associated issue or issuer.
“WD” – Indicates that the rating has been withdrawn and is no longer maintained by Fitch.
The DBRS long-term rating scale provides an opinion on the risk of default. That is, the risk that an issuer will fail to satisfy its financial obligations in accordance with the terms under which an obligation has been issued. Ratings are based on quantitative and qualitative considerations relevant to the issuer, and the relative ranking of the claims. All rating categories other than “AAA” and “D” also contain subcategories “(high)” and “(low)”. The absence of either a “(high)” or “(low)” designation indicates the rating is in the middle of the category. The following summarizes the ratings used by DBRS for long-term debt:
“AAA” – Long-term debt rated “AAA” is of the highest credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is exceptionally high and unlikely to be adversely affected by future events.
“AA” – Long-term debt rated “AA” is of superior credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is considered high. Credit quality differs from “AAA” only to a small degree. Unlikely to be significantly vulnerable to future events.
4-A
“A” – Long-term debt rated “A” is of good credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is substantial, but of lesser credit quality than “AA.” May be vulnerable to future events, but qualifying negative factors are considered manageable.
“BBB” – Long-term debt rated “BBB” is of adequate credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is considered acceptable. May be vulnerable to future events.
“BB” – Long-term debt rated “BB” is of speculative , non-investment grade credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is uncertain. Vulnerable to future events.
“B” – Long-term debt rated “B” is of highly speculative credit quality. There is a high level of uncertainty as to the capacity to meet financial obligations.
“CCC”, “CC” and “C” – Long-term debt rated in any of these categories is of very highly speculative credit quality. In danger of defaulting on financial obligations. There is little difference between these three categories, although “CC” and “C” ratings are normally applied to obligations that are seen as highly likely to default, or subordinated to obligations rated in the “CCC” to “B” range. Obligations in respect of which default has not technically taken place but is considered inevitable may be rated in the “C” category.
“D” – A security rated “D” is assigned when the issuer has filed under any applicable bankruptcy, insolvency or winding up statute or there is a failure to satisfy an obligation after the exhaustion of grace periods, a downgrade to “D” may occur. DBRS may also use “SD” (Selective Default) in cases where only some securities are impacted, such as the case of a “distressed exchange”.
Municipal Note Ratings
An S&P Global Ratings U.S. municipal note rating reflects S&P Global Ratings’ opinion about the liquidity factors and market access risks unique to the notes. Notes due in three years or less will likely receive a note rating. Notes with an original maturity of more than three years will most likely receive a long-term debt rating. In determining which type of rating, if any, to assign, S&P Global Ratings’ analysis will review the following considerations:
Amortization schedule-the larger the final maturity relative to other maturities, the more likely it will be treated as a note; and
Source of payment-the more dependent the issue is on the market for its refinancing, the more likely it will be treated as a note.
Note rating symbols are as follows:
“SP-1” – A municipal note rated “SP-1” exhibits a strong capacity to pay principal and interest. An issue determined to possess a very strong capacity to pay debt service is given a plus (+) designation.
“SP-2” – A municipal note rated “SP-2” exhibits a satisfactory capacity to pay principal and interest, with some vulnerability to adverse financial and economic changes over the term of the notes.
“SP-3” – A municipal note rated “SP-3” exhibits a speculative capacity to pay principal and interest.
Moody’s uses the Municipal Investment Grade (“MIG”) scale to rate U.S. municipal bond anticipation notes of up to three years maturity. Municipal notes rated on the MIG scale may be secured by either pledged revenues or proceeds of a take-out financing received prior to note maturity. MIG ratings expire at the maturity of the obligation, and the issuer’s long-term rating is only one consideration in assigning the MIG rating. MIG ratings are divided into three levels – “MIG-1” through “MIG-3”—while speculative grade short-term obligations are designated “SG.” The following summarizes the ratings used by Moody’s for these short-term obligations:
“MIG-1” – This designation denotes superior credit quality. Excellent protection is afforded by established cash flows, highly reliable liquidity support, or demonstrated broad-based access to the market for refinancing.
“MIG-2” – This designation denotes strong credit quality. Margins of protection are ample, although not as large as in the preceding group.
“MIG-3” – This designation denotes acceptable credit quality. Liquidity and cash-flow protection may be narrow, and market access for refinancing is likely to be less well-established.
“SG” – This designation denotes speculative-grade credit quality. Debt instruments in this category may lack sufficient margins of protection.
In the case of variable rate demand obligations (“VRDOs”), a two-component rating is assigned; a long- or short-term debt rating and a demand obligation rating. The first element represents Moody’s evaluation of risk associated with scheduled principal and interest payments. The second element represents Moody’s evaluation of risk associated with the ability to receive purchase price upon demand (“demand feature”). The second element uses a rating from a variation of the MIG scale called the Variable Municipal Investment Grade (“VMIG”) scale. The rating transitions on the VMIG scale differ from those on the Prime scale to reflect the risk that external liquidity support generally will terminate if the issuer’s long-term rating drops below investment grade.
5-A
“VMIG-1” – This designation denotes superior credit quality. Excellent protection is afforded by the superior short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand.
“VMIG-2” – This designation denotes strong credit quality. Good protection is afforded by the strong short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand.
“VMIG-3” – This designation denotes acceptable credit quality. Adequate protection is afforded by the satisfactory short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand.
“SG” – This designation denotes speculative-grade credit quality. Demand features rated in this category may be supported by a liquidity provider that does not have an investment grade short-term rating or may lack the structural and/or legal protections necessary to ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand.
“NR” – Is assigned to an unrated obligation.
Fitch uses the same ratings for municipal securities as described above for other short-term credit ratings.
About Credit Ratings
An S&P Global Ratings issue credit rating is a forward-looking opinion about the creditworthiness of an obligor with respect to a specific financial obligation, a specific class of financial obligations, or a specific financial program (including ratings on medium-term note programs and commercial paper programs). It takes into consideration the creditworthiness of guarantors, insurers, or other forms of credit enhancement on the obligation and takes into account the currency in which the obligation is denominated. The opinion reflects S&P Global Ratings’ view of the obligor’s capacity and willingness to meet its financial commitments as they come due, and this opinion may assess terms, such as collateral security and subordination, which could affect ultimate payment in the event of default.
Moody’s credit ratings must be construed solely as statements of opinion and not statements of fact or recommendations to purchase, sell or hold any securities.
Fitch’s credit ratings relating to issuers are an opinion on the relative ability of an entity to meet financial commitments, such as interest, preferred dividends, repayment of principal, insurance claims or counterparty obligations. Fitch credit ratings are used by investors as indications of the likelihood of receiving the money owed to them in accordance with the terms on which they invested. Fitch’s credit ratings cover the global spectrum of corporate, sovereign financial, bank, insurance and public finance entities (including supranational and sub-national entities) and the securities or other obligations they issue, as well as structured finance securities backed by receivables or other financial assets.
Credit ratings provided by DBRS are forward-looking opinions about credit risk which reflect the creditworthiness of an issuer, rated entity, and/or security. Credit ratings are not statements of fact. While historical statistics and performance can be important considerations, credit ratings are not based solely on such; they include subjective considerations and involve expectations for future performance that cannot be guaranteed. To the extent that future events and economic conditions do not match expectations, credit ratings assigned to issuers and/or securities can change. Credit ratings are also based on approved and applicable methodologies, models and criteria (“Methodologies”), which are periodically updated and when material changes are deemed necessary, this may also lead to rating changes.
Credit ratings typically provide an opinion on the risk that investors may not be repaid in accordance with the terms under which the obligation was issued. In some cases, credit ratings may also include consideration for the relative ranking of claims and recovery, should default occur. Credit ratings are meant to provide opinions on relative measures of risk and are not based on expectations of any specific default probability, nor are they meant to predict such.
The data and information on which DBRS bases its opinions is not audited or verified by DBRS, although DBRS conducts a reasonableness review of information received and relied upon in accordance with its Methodologies and policies.
DBRS uses rating symbols as a concise method of expressing its opinion to the market but there are a limited number of rating categories for the possible slight risk differentials that exist across the rating spectrum and DBRS does not assert that credit ratings in the same category are of “exactly” the same quality.
6-A
| APPENDIX B | Effective March 2020 |
GSAM PROXY VOTING GUIDELINES SUMMARY
The following is a summary of the material GSAM Proxy Voting Guidelines (the “Guidelines”), which form the substantive basis of GSAM’s Policy and Procedures on Proxy Voting for Investment Advisory Clients (the “Policy”). As described in the main body of the Policy, one or more GSAM Portfolio Management Teams may diverge from the Guidelines and a related Recommendation on any particular proxy vote or in connection with any individual investment decision in accordance with the Policy. US proxy items:
| A. |
U.S. Proxy Items | 7 | ||||
| 1. |
Operational Items | 7 | ||||
| 2. |
Board of Directors | 7 | ||||
| 3. |
Executive Compensation | 10 | ||||
| 4. |
Director Nominees and Proxy Access | 13 | ||||
| 5. |
Shareholders Rights and Defenses | 13 | ||||
| 6. |
Mergers and Corporate Restructurings | 14 | ||||
| 7. |
State of Incorporation | 15 | ||||
| 8. |
Capital Structure | 15 | ||||
| 9. |
Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Issues | 15 | ||||
| B. |
Non-U.S. Proxy Items | 20 | ||||
| 1. |
Operational Items | 20 | ||||
| 2. |
Board of Directors | 21 | ||||
| 3. |
Compensation | 24 | ||||
| 4. |
Board Structure | 24 | ||||
| 5. |
Capital Structure | 24 | ||||
| 6. |
Mergers and Corporate Restructurings and Other | 26 | ||||
| 7. |
Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Issues | 27 | ||||
| C. |
Japan Proxy Items | 27 | ||||
| 1. |
Operational Items | 27 | ||||
| 2. |
Board of Directors | 28 | ||||
| 3. |
Compensation | 31 | ||||
| 4. |
Board Structure | 32 | ||||
| 5. |
Capital Structure | 32 | ||||
| 6. |
Mergers and Corporate Restructurings and Other | 34 | ||||
| 7. |
Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Issues | 35 | ||||
1-B
A. U.S. Proxy Items
The following section is a summary of the Guidelines, which form the substantive basis of the Policy with respect to U.S. public equity investments.
| 1. | Operational Items |
Auditor Ratification
Vote FOR proposals to ratify auditors, unless any of the following apply within the last year:
| • | An auditor has a financial interest in or association with the company, and is therefore not independent; |
| • | There is reason to believe that the independent auditor has rendered an opinion that is neither accurate nor indicative of the company’s financial position; |
| • | Poor accounting practices are identified that rise to a serious level of concern, such as: fraud; misapplication of GAAP; or material weaknesses identified in Section 404 disclosures; or |
| • | Fees for non-audit services are excessive (generally over 50% or more of the audit fees). |
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on shareholder proposals asking companies to prohibit or limit their auditors from engaging in non-audit services or asking for audit firm rotation.
| 2. | Board of Directors |
The board of directors should promote the interests of shareholders by acting in an oversight and/or advisory role; the board should consist of a majority of independent directors and should be held accountable for actions and results related to their responsibilities.
When evaluating board composition, GSAM believes a diversity of ethnicity, gender and experience is an important consideration.
Classification of Directors
Where applicable, the New York Stock Exchange or NASDAQ Listing Standards definition is to be used to classify directors as inside directors, affiliated outside directors, or independent outside directors.
Additionally, GSAM will consider compensation committee interlocking directors to be affiliated (defined as CEOs who sit on each other’s compensation committees).
Voting on Director Nominees in Uncontested Elections
Vote on director nominees should be determined on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from individual directors who:
| • | Attend less than 75% of the board and committee meetings without a disclosed valid excuse; |
| • | Sit on more than five public operating and/or holding company boards; |
| • | Are CEOs of public companies who sit on the boards of more than two public companies besides their own--withhold only at their outside boards. |
Other items considered for an AGAINST vote include specific concerns about the individual or the company, such as criminal wrongdoing or breach of fiduciary responsibilities, sanctions from government or authority, violations of laws and regulations, the presence of inappropriate related party transactions, or other issues related to improper business practices.
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from the Nominating Committee if:
| • | The board does not have at least one woman director |
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from inside directors and affiliated outside directors (per the Classification of Directors above) in the case of operating and/or holding companies when:
| • | The inside director or affiliated outside director serves on the Audit, Compensation or Nominating Committees; and |
2-B
| • | The company lacks an Audit, Compensation or Nominating Committee so that the full board functions as such committees and inside directors or affiliated outside directors are participating in voting on matters that independent committees should be voting on. |
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from members of the appropriate committee (or only the independent chairman or lead director as may be appropriate in situations such as where there is a classified board and members of the appropriate committee are not up for re-election or the appropriate committee is comprised of the entire board ) for the below reasons. Extreme cases may warrant a vote against the entire board.
| • | Material failures of governance, stewardship, or fiduciary responsibilities at the company; |
| • | Egregious actions related to the director(s)’ service on other boards that raise substantial doubt about his or her ability to effectively oversee management and serve the best interests of shareholders at any company; |
| • | At the previous board election, any director received more than 50% withhold/against votes of the shares cast and the company has failed to address the underlying issue(s) that caused the high withhold/against vote (members of the Nominating or Governance Committees); |
| • | The board failed to act on a shareholder proposal that received approval of the majority of shares cast for the previous two consecutive years (a management proposal with other than a FOR recommendation by management will not be considered as sufficient action taken); an adopted proposal that is substantially similar to the original shareholder proposal will be deemed sufficient; (vote against members of the committee of the board that is responsible for the issue under consideration). If GSAM did not support the shareholder proposal in both years, GSAM will still vote against the committee member(s). |
| • | The average board tenure exceeds 15 years, and there has not been a new nominee in the past 5 years. |
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from the members of the Audit Committee if:
| • | The non-audit fees paid to the auditor are excessive (generally over 50% or more of the audit fees); |
| • | The company receives an adverse opinion on the company’s financial statements from its auditor and there is not clear evidence that the situation has been remedied; |
| • | There is persuasive evidence that the Audit Committee entered into an inappropriate indemnification agreement with its auditor that limits the ability of the company, or its shareholders, to pursue legitimate legal recourse against the audit firm; or |
| • | No members of the Audit Committee hold sufficient financial expertise. |
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on members of the Audit Committee and/or the full board if poor accounting practices, which rise to a level of serious concern are identified, such as fraud, misapplication of GAAP and material weaknesses identified in Section 404 disclosures.
Examine the severity, breadth, chronological sequence and duration, as well as the company’s efforts at remediation or corrective actions, in determining whether negative vote recommendations are warranted against the members of the Audit Committee who are responsible for the poor accounting practices, or the entire board.
See section 3 on executive and director compensation for reasons to withhold from members of the Compensation Committee.
In limited circumstances, GSAM may vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from all nominees of the board of directors (except from new nominees who should be considered on a CASE-BY-CASE basis and except as discussed below) if:
| • | The company’s poison pill has a dead-hand or modified dead-hand feature for two or more years. Vote against/withhold every year until this feature is removed; however, vote against the poison pill if there is one on the ballot with this feature rather than the director; |
| • | The board adopts or renews a poison pill without shareholder approval, does not commit to putting it to shareholder vote within 12 months of adoption (or in the case of an newly public company, does not commit to put the pill to a shareholder vote within 12 months following the IPO), or reneges on a commitment to put the pill to a vote, and has not yet received a withhold/against recommendation for this issue; |
| • | The board failed to act on takeover offers where the majority of the shareholders tendered their shares; |
| • | If in an extreme situation the board lacks accountability and oversight, coupled with sustained poor performance relative to peers. |
Shareholder proposal regarding Independent Chair (Separate Chair/CEO)
Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
3-B
GSAM will generally recommend a vote AGAINST shareholder proposals requiring that the chairman’s position be filled by an independent director, if the company satisfies 3 of the 4 following criteria:
| • | Designated lead director, elected by and from the independent board members with clearly delineated and comprehensive duties; |
| • | Two-thirds independent board; |
| • | All independent “key” committees (audit, compensation and nominating committees); or |
| • | Established, disclosed governance guidelines. |
Shareholder proposal regarding board declassification
GSAM will generally vote FOR proposals requesting that the board adopt a declassified structure in the case of operating and holding companies.
Majority Vote Shareholder Proposals
GSAM will vote FOR proposals requesting that the board adopt majority voting in the election of directors provided it does not conflict with the state law where the company is incorporated. GSAM also looks for companies to adopt a post-election policy outlining how the company will address the situation of a holdover director.
Cumulative Vote Shareholder Proposals
GSAM will generally support shareholder proposals to restore or provide cumulative voting in the case of operating and holding companies unless:
| • | The company has adopted (i) majority vote standard with a carve-out for plurality voting in situations where there are more nominees than seats and (ii) a director resignation policy to address failed elections. |
| 3. | Executive Compensation |
Pay Practices
Good pay practices should align management’s interests with long-term shareholder value creation. Detailed disclosure of compensation criteria is preferred; proof that companies follow the criteria should be evident and retroactive performance target changes without proper disclosure is not viewed favorably. Compensation practices should allow a company to attract and retain proven talent. Some examples of poor pay practices include: abnormally large bonus payouts without justifiable performance linkage or proper disclosure, egregious employment contracts, excessive severance and/or change in control provisions, repricing or replacing of underwater stock options/stock appreciation rights without prior shareholder approval, and excessive perquisites. A company should also have an appropriate balance of short-term vs. long-term metrics and the metrics should be aligned with business goals and objectives.
If the company maintains problematic or poor pay practices, generally vote:
| • | AGAINST Management Say on Pay (MSOP) Proposals; or |
| • | AGAINST an equity-based incentive plan proposal if excessive non-performance-based equity awards are the major contributor to a pay-for-performance misalignment. |
| • | If no MSOP or equity-based incentive plan proposal item is on the ballot, vote AGAINST/WITHHOLD from compensation committee members. |
Equity Compensation Plans
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on equity-based compensation plans. Evaluation takes into account potential plan cost, plan features and grant practices. While a negative combination of these factors could cause a vote AGAINST, other reasons to vote AGAINST the equity plan could include the following factors:
| • | The plan permits the repricing of stock options/stock appreciation rights (SARs) without prior shareholder approval; or |
| • | There is more than one problematic material feature of the plan, which could include one of the following: unfavorable change-in-control features, presence of gross ups and options reload. |
Advisory Vote on Executive Compensation (Say-on-Pay, MSOP) Management Proposals
Vote FOR annual frequency and AGAINST all proposals asking for any frequency less than annual.
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on management proposals for an advisory vote on executive compensation. For U.S. companies, consider the following factors in the context of each company’s specific circumstances and the board’s disclosed rationale for its practices.
4-B
Factors Considered Include:
| • | Pay for Performance Disconnect; |
| • | GSAM will consider there to be a disconnect based on a quantitative assessment of the following: CEO pay vs. TSR (“Total Shareholder Return”) and peers, CEO pay as a percentage of the median peer group or CEO pay vs. shareholder return over time. |
| • | Long-term equity-based compensation is 100% time-based; |
| • | Board’s responsiveness if company received 70% or less shareholder support in the previous year’s MSOP vote; |
| • | Abnormally large bonus payouts without justifiable performance linkage or proper disclosure; |
| • | Egregious employment contracts; |
| • | Excessive perquisites or excessive severance and/or change in control provisions; |
| • | Repricing or replacing of underwater stock options without prior shareholder approval; |
| • | Excessive pledging or hedging of stock by executives; |
| • | Egregious pension/SERP (supplemental executive retirement plan) payouts; |
| • | Extraordinary relocation benefits; |
| • | Internal pay disparity; and |
| • | Lack of transparent disclosure of compensation philosophy and goals and targets, including details on short-term and long-term performance incentives. |
Other Compensation Proposals and Policies
Employee Stock Purchase Plans — Non-Qualified Plans
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on nonqualified employee stock purchase plans taking into account the following factors:
| • | Broad-based participation; |
| • | Limits on employee contributions; |
| • | Company matching contributions; and |
| • | Presence of a discount on the stock price on the date of purchase. |
Option Exchange Programs/Repricing Options
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on management proposals seeking approval to exchange/reprice options, taking into consideration:
| • | Historic trading patterns--the stock price should not be so volatile that the options are likely to be back “in-the-money” over the near term; |
Rationale for the re-pricing;
| • | If it is a value-for-value exchange; |
| • | If surrendered stock options are added back to the plan reserve; |
| • | Option vesting; |
| • | Term of the option--the term should remain the same as that of the replaced option; |
| • | Exercise price—should be set at fair market or a premium to market; |
| • | Participants—executive officers and directors should be excluded. |
Vote FOR shareholder proposals to put option repricings to a shareholder vote.
Other Shareholder Proposals on Compensation
Advisory Vote on Executive Compensation (Frequency on Pay)
Vote FOR annual frequency.
Stock retention holding period
Vote FOR shareholder proposals asking for a policy requiring that senior executives retain a significant percentage of shares acquired through equity compensation programs if the policy requests retention for two years or less following the termination of their employment (through retirement or otherwise) and a holding threshold percentage of 50% or less.
Also consider:
| • | Whether the company has any holding period, retention ratio, or officer ownership requirements in place and the terms/provisions of awards already granted. |
5-B
Elimination of accelerated vesting in the event of a change in control
Vote AGAINST shareholder proposals seeking a policy eliminating the accelerated vesting of time-based equity awards in the event of a change-in-control.
Performance-based equity awards and pay-for-superior-performance proposals
Generally support unless there is sufficient evidence that the current compensation structure is already substantially performance-based. GSAM considers performance-based awards to include awards that are tied to shareholder return or other metrics that are relevant to the business.
Say on Supplemental Executive Retirement Plans (SERP)
Generally vote AGAINST proposals asking for shareholder votes on SERP.
4. Director Nominees and Proxy Access
Voting for Director Nominees (Management or Shareholder)
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on the election of directors of operating and holding companies in contested elections, considering the following factors:
| • | Long-term financial performance of the target company relative to its industry; |
| • | Management’s track record; |
| • | Background of the nomination, in cases where there is a shareholder nomination; |
| • | Qualifications of director nominee(s); |
| • | Strategic plan related to the nomination and quality of critique against management; |
| • | Number of boards on which the director nominee already serves; and |
| • | Likelihood that the board will be productive as a result. |
Proxy Access
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on shareholder or management proposals asking for proxy access.
GSAM may support proxy access as an important right for shareholders of operating and holding companies and as an alternative to costly proxy contests and as a method for GSAM to vote for directors on an individual basis, as appropriate, rather than voting on one slate or the other. While this could be an important shareholder right, the following factors will be taken into account when evaluating the shareholder proposals:
| • | The ownership thresholds, percentage and duration proposed (GSAM generally will not support if the ownership threshold is less than 3%); |
| • | The maximum proportion of directors that shareholders may nominate each year (GSAM generally will not support if the proportion of directors is greater than 25%); and |
| • | Other restricting factors that when taken in combination could serve to materially limit the proxy access provision. |
GSAM will take the above factors into account when evaluating proposals proactively adopted by the company or in response to a shareholder proposal to adopt or amend the right. A vote against governance committee members could result if provisions exist that materially limit the right to proxy access.
Reimbursing Proxy Solicitation Expenses
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on proposals to reimburse proxy solicitation expenses. When voting in conjunction with support of a dissident slate, vote FOR the reimbursement of all appropriate proxy solicitation expenses associated with the election.
| 5. | Shareholders Rights and Defenses |
Shareholder Ability to Act by Written Consent
In the case of operating and holding companies, generally vote FOR shareholder proposals that provide shareholders with the ability to act by written consent, unless:
| • | The company already gives shareholders the right to call special meetings at a threshold of 25% or lower; and |
| • | The company has a history of strong governance practices. |
6-B
Shareholder Ability to Call Special Meetings
In the case of operating and holding companies, generally vote FOR management proposals that provide shareholders with the ability to call special meetings.
In the case of operating and holding companies, generally vote FOR shareholder proposals that provide shareholders with the ability to call special meetings at a threshold of 25% or lower if the company currently does not give shareholders the right to call special meetings. However, if a company already gives shareholders the right to call special meetings at a threshold of at least 25%, vote AGAINST shareholder proposals to further reduce the threshold.
Advance Notice Requirements for Shareholder Proposals/Nominations
In the case of operating and holding companies, vote CASE-BY-CASE on advance notice proposals, giving support to proposals that allow shareholders to submit proposals/nominations reasonably close to the meeting date and within the broadest window possible, recognizing the need to allow sufficient notice for company, regulatory and shareholder review.
Shareholder Voting Requirements
In the case of operating and holding companies, vote AGAINST proposals to require a supermajority shareholder vote. Generally vote FOR management and shareholder proposals to reduce supermajority vote requirements.
Poison Pills
Vote FOR shareholder proposals requesting that the company submit its poison pill to a shareholder vote or redeem it, unless the company has:
| • | a shareholder-approved poison pill in place; or |
| • | adopted a policy concerning the adoption of a pill in the future specifying certain shareholder friendly provisions. |
Vote FOR shareholder proposals calling for poison pills to be put to a vote within a time period of less than one year after adoption.
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on management proposals on poison pill ratification, focusing on the features of the shareholder rights plan.
In addition, the rationale for adopting the pill should be thoroughly explained by the company. In examining the request for the pill, take into consideration the company’s existing governance structure, including: board independence, existing takeover defenses, and any problematic governance concerns.
| 6. | Mergers and Corporate Restructurings |
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on mergers and acquisitions taking into account the following based on publicly available information:
| • | Valuation; |
| • | Market reaction; |
| • | Strategic rationale; |
| • | Management’s track record of successful integration of historical acquisitions; |
| • | Presence of conflicts of interest; and |
| • | Governance profile of the combined company. |
| 7. | State of Incorporation |
Reincorporation Proposals
GSAM may support management proposals to reincorporate as long as the reincorporation would not substantially diminish shareholder rights. GSAM may not support shareholder proposals for reincorporation unless the current state of incorporation is substantially less shareholder friendly than the proposed reincorporation, there is a strong economic case to reincorporate or the company has a history of making decisions that are not shareholder friendly.
Exclusive venue for shareholder lawsuits
Generally vote FOR on exclusive venue proposals, taking into account:
| • | Whether the company has been materially harmed by shareholder litigation outside its jurisdiction of incorporation, based on disclosure in the company’s proxy statement; |
| • | Whether the company has the following good governance features: |
| • | Majority independent board; |
7-B
| • | Independent key committees; |
| • | An annually elected board; |
| • | A majority vote standard in uncontested director elections; |
| • | The absence of a poison pill, unless the pill was approved by shareholders; and/or |
| • | Separate Chairman CEO role or, if combined, an independent chairman with clearly delineated duties. |
| 8. | Capital Structure |
Common and Preferred Stock Authorization
Generally vote FOR proposals to increase the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance.
Generally vote FOR proposals to increase the number of shares of preferred stock, as long as there is a commitment to not use the shares for anti-takeover purposes.
| 9. | Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Issues |
Overall Approach
GSAM recognizes that Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) factors can affect investment performance, expose potential investment risks and provide an indication of management excellence and leadership. When evaluating ESG proxy issues, GSAM balances the purpose of a proposal with the overall benefit to shareholders.
Shareholder proposals considered under this category could include, among others, reports on:
| 1) | employee labor and safety policies; |
| 2) | impact on the environment of the company’s production or manufacturing operations; |
| 3) | societal impact of products manufactured; |
| 4) | risks throughout the supply chain or operations including labor practices, animal treatment practices within food production and conflict minerals; and |
| 5) | overall board structure, including diversity. |
When evaluating environmental and social shareholder proposals, the following factors are generally considered:
| • | The company’s current level of publicly available disclosure, including if the company already discloses similar information through existing reports or policies; |
| • | If the company has implemented or formally committed to the implementation of a reporting program based on the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board’s (SASB) materiality standards or a similar standard; |
| • | Whether adoption of the proposal is likely to enhance or protect shareholder value; |
| • | Whether the information requested concerns business issues that relate to a meaningful percentage of the company’s business; |
| • | The degree to which the company’s stated position on the issues raised in the proposal could affect |
| • | its reputation or sales, or leave it vulnerable to a boycott or selective purchasing; |
| • | Whether the company has already responded in some appropriate manner to the request embodied in the proposal; |
| • | What other companies in the relevant industry have done in response to the issue addressed in the proposal; |
| • | Whether the proposal itself is well framed and the cost of preparing the report is reasonable; Whether the subject of the proposal is best left to the discretion of the board; |
| • | Whether the company has material fines or violations in the area and if so, if appropriate actions have already been taken to remedy going forward; |
| • | Whether providing this information would reveal proprietary or confidential information that would place the company at a competitive disadvantage. |
Environmental Sustainability, climate change reporting
Generally vote FOR proposals requesting the company to report on its policies, initiatives and oversight mechanisms related to environmental sustainability, or how the company may be impacted by climate change. The following factors will be considered:
| • | The company’s current level of publicly available disclosure including if the company already discloses similar information through existing reports or policies; |
8-B
| • | If the company has formally committed to the implementation of a reporting program based on the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board’s (SASB) materiality standards or a similar standard within a specified time frame; |
| • | If the company’s current level of disclosure is comparable to that of its industry peers; and |
| • | If there are significant controversies, fines, penalties, or litigation associated with the company’s environmental performance. |
Establishing goals or targets for emissions reduction
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on the following shareholder proposals if relevant to the company:
| • | Seeking information on the fmancial, physical, or regulatory risks a company faces related to climate change on its operations and investment, or on how the company identifies, measures and manages such risks; |
| • | Calling for the reduction of Greenhouse Gas (“GHG”) emissions; |
| • | Seeking reports on responses to regulatory and public pressures surrounding climate change, and for disclosure of research that aided in setting company policies around climate change; |
| • | Requesting a report/disclosure of goals on GHG emissions from company operations and/or products; |
| • | Requesting a company report on its energy efficiency policies; and |
| • | Requesting reports on the feasibility of developing renewable energy resources. |
Political Contributions and Trade Association Spending/Lobbying Expenditures and Initiatives
GSAM generally believes that it is the role of boards and management to determine the appropriate level of disclosure of all types of corporate political activity. When evaluating these proposals, GSAM considers the prescriptive nature of the proposal and the overall benefit to shareholders along with a company’s current disclosure of policies, practices and oversight.
Generally vote AGAINST proposals asking the company to affirm political nonpartisanship in the workplace so long as:
| • | There are no recent, significant controversies, fines or litigation regarding the company’s political contributions or trade association spending; and |
| • | The company has procedures in place to ensure that employee contributions to company-sponsored political action committees (PACs) are strictly voluntary and prohibits coercion. |
Vote AGAINST proposals requesting increased disclosure of a company’s policies with respect to political contributions, lobbying and trade association spending as long as:
| • | There is no significant potential threat or actual harm to shareholders’ interests; |
| • | There are no recent significant controversies or litigation related to the company’s political contributions or governmental affairs; and |
| • | There is publicly available information to assess the company’s oversight related to such expenditures of corporate assets. |
GSAM generally will vote AGAINST proposals asking for detailed disclosure of political contributions or trade association or lobbying expenditures.
Vote AGAINST proposals barring the company from making political contributions. Businesses are affected by legislation at the federal, state, and local level and barring political contributions can put the company at a competitive disadvantage.
Gender Identity and Sexual Orientation
A company should have a clear, public Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) statement and/or diversity policy. Generally vote FOR proposals seeking to amend a company’s EEO statement or diversity policies to additionally prohibit discrimination based on sexual orientation and/or gender identity.
Generally vote FOR proposals requesting reports on a company’s efforts to diversify the board, unless:
| • | The gender and racial minority representation of the company’s board is reasonably inclusive in relation to companies of similar size and business; and |
| • | The board already reports on its nominating procedures and gender and racial minority initiatives on the board. |
Gender Pay Gap
Generally vote CASE-BY-CASE on proposals requesting reports on a company’s pay data by gender, or a report on a company’s policies and goals to reduce any gender pay gap, taking into account:
9-B
| • | The company’s current policies and disclosure related to both its diversity and inclusion policies and practices and its compensation philosophy and fair and equitable compensation practices; |
| • | Whether the company has been the subject of recent controversy, litigation or regulatory actions related to gender pay gap issues; and |
| • | Whether the company’s reporting regarding gender pay gap policies or initiatives is lagging its peers. |
Labor and Human Rights Standards
Generally vote FOR proposals requesting a report on company or company supplier labor and/or human rights standards and policies, or on the impact of its operations on society, unless such information is already publicly disclosed considering:
| • | The degree to which existing relevant policies and practices are disclosed; |
| • | Whether or not existing relevant policies are consistent with internationally recognized standards; |
| • | Whether company facilities and those of its suppliers are monitored and how; |
| • | Company participation in fair labor organizations or other internationally recognized human rights initiatives; |
| • | Scope and nature of business conducted in markets known to have higher risk of workplace labor/human rights abuse; |
| • | Recent, significant company controversies, fines, or litigation regarding human rights at the company or its suppliers; |
| • | The scope of the request; and |
| • | Deviation from industry sector peer company standards and practices. |
10-B
B. Non-U.S. Proxy Items4
The following section is a broad summary of the Guidelines, which form the basis of the Policy with respect to non-U.S. and Japan public equity investments. Applying these guidelines is subject to certain regional and country-specific exceptions and modifications and is not inclusive of all considerations in each market.
| 1. | Operational Items |
Financial Results/Director and Auditor Reports
Vote FOR approval of financial statements and director and auditor reports, unless:
| • | There are concerns about the accounts presented or audit procedures used; or |
| • | The company is not responsive to shareholder questions about specific items that should be publicly disclosed. |
Appointment of Auditors and Auditor Fees
Vote FOR the re-election of auditors and proposals authorizing the board to fix auditor fees, unless:
| • | There are serious concerns about the accounts presented, audit procedures used or audit opinion rendered; |
| • | There is reason to believe that the auditor has rendered an opinion that is neither accurate nor indicative of the company’s financial position; |
| • | Name of the proposed auditor has not been published; |
| • | The auditors are being changed without explanation; |
| • | Non-audit-related fees are substantial or are in excess of standard annual audit-related fees; or |
| • | The appointment of external auditors if they have previously served the company in an executive capacity or can otherwise be considered affiliated with the company. |
Appointment of Statutory Auditors
Vote FOR the appointment or re-election of statutory auditors, unless:
| • | There are serious concerns about the statutory reports presented or the audit procedures used; |
| • | Questions exist concerning any of the statutory auditors being appointed; or |
| • | The auditors have previously served the company in an executive capacity or can otherwise be considered affiliated with the company. |
Allocation of Income
Vote FOR approval of the allocation of income, unless:
| • | The dividend payout ratio has been consistently low without adequate explanation; or |
| • | The payout is excessive given the company’s financial position. |
Stock (Scrip) Dividend Alternative
Vote FOR most stock (scrip) dividend proposals.
Vote AGAINST proposals that do not allow for a cash option unless management demonstrates that the cash option is harmful to shareholder value.
Amendments to Articles of Association
Vote amendments to the articles of association on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Change in Company Fiscal Term
Vote FOR resolutions to change a company’s fiscal term unless a company’s motivation for the change is to postpone its annual general meeting.
| 4 | Excludes Japan public equity investments, please see Section C. |
11-B
Lower Disclosure Threshold for Stock Ownership
Vote AGAINST resolutions to lower the stock ownership disclosure threshold below 5% unless specific reasons exist to implement a lower threshold.
Amend Quorum Requirements
Vote proposals to amend quorum requirements for shareholder meetings on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Transact Other Business
Vote AGAINST other business when it appears as a voting item.
| 2. | Board of Directors |
Director Elections
Vote FOR management nominees taking into consideration the following:
| • | Adequate disclosure has not been provided in a timely manner; or |
| • | There are clear concerns over questionable finances or restatements; or |
| • | There have been questionable transactions or conflicts of interest; or |
| • | There are any records of abuses against minority shareholder interests; or |
| • | The board fails to meet minimum corporate governance standards; or |
| • | There are reservations about: |
| • | Director terms |
| • | Bundling of proposals to elect directors |
| • | Board independence |
| • | Disclosure of named nominees |
| • | Combined Chairman/CEO |
| • | Election of former CEO as Chairman of the board |
| • | Overboarded directors |
| • | Composition of committees |
| • | Director independence |
| • | Number of directors on the board |
| • | Lack of gender diversity on the board |
| • | Specific concerns about the individual or company, such as criminal wrongdoing or breach of fiduciary responsibilities; or |
| • | Repeated absences at board meetings have not been explained (in countries where this information is disclosed); or |
Unless there are other considerations which may include sanctions from government or authority, violations of laws and regulations, or other issues related to improper business practice, failure to replace management, or egregious actions related to service on other boards. Vote AGAINST the Nominating Committee if the board does not have at least one woman director.
Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE basis in contested elections of directors, e.g., the election of shareholder nominees or the dismissal of incumbent directors, determining which directors are best suited to add value for shareholders.
The analysis will generally be based on, but not limited to, the following major decision factors:
| • | Company performance relative to its peers; |
| • | Strategy of the incumbents versus the dissidents; |
| • | Independence of board candidates; |
| • | Experience and skills of board candidates; |
| • | Governance profile of the company; |
| • | Evidence of management entrenchment; |
| • | Responsiveness to shareholders; |
| • | Whether a takeover offer has been rebuffed; |
| • | Whether minority or majority representation is being sought. |
12-B
Vote FOR employee and/or labor representatives if they sit on either the audit or compensation committee and are required by law to be on those committees.
Vote AGAINST employee and/or labor representatives if they sit on either the audit or compensation committee, if they are not required to be on those committees.
Classification of directors
Executive Director
| • | Employee or executive of the company; |
| • | Any director who is classified as a non-executive, but receives salary, fees, bonus, and/or other benefits that are in line with the highest-paid executives of the company. |
Non-Independent Non-Executive Director (NED)
| • | Any director who is attested by the board to be a non-independent NED; |
| • | Any director specifically designated as a representative of a significant shareholder of the company; |
| • | Any director who is also an employee or executive of a significant shareholder of the company; Beneficial owner (direct or indirect) of at least 10% of the company’s stock, either in economic terms or in voting rights (this may be aggregated if voting power is distributed among more than one member of a defined group, e.g., family members who beneficially own less than 10% individually, but collectively own more than 10%), unless market best practice dictates a lower ownership and/or disclosure threshold (and in other special market-specific circumstances); Government representative; |
| • | Currently provides (or a relative provides) professional services to the company, to an affiliate of the company, or to an individual officer of the company or of one of its affiliates in excess of $10,000 per year; |
| • | Represents customer, supplier, creditor, banker, or other entity with which company maintains transactional/commercial relationship (unless company discloses information to apply a materiality test); |
| • | Any director who has conflicting or cross-directorships with executive directors or the chairman of the company; |
| • | Relative of a current employee of the company or its affiliates; |
| • | Relative of a former executive of the company or its affiliates; |
| • | A new appointee elected other than by a formal process through the General Meeting (such as a contractual appointment by a substantial shareholder); |
| • | Founder/co-founder/member of founding family but not currently an employee; |
| • | Former executive (5 year cooling off period); |
| • | Years of service is generally not a determining factor unless it is recommended best practice in a market and/or in extreme circumstances, in which case it may be considered; and |
| • | Any additional relationship or principle considered to compromise independence under local corporate governance best practice guidance. |
Independent NED
| • | No material connection, either directly or indirectly, to the company other than a board seat. |
Employee Representative
| • | Represents employees or employee shareholders of the company (classified as “employee representative” but considered a non-independent NED). |
Discharge of Directors
Generally vote FOR the discharge of directors, including members of the management board and/or supervisory board, unless there is reliable information about significant and compelling controversies that the board is not fulfilling its fiduciary duties warranted by:
| • | A lack of oversight or actions by board members which invoke shareholder distrust related to malfeasance or poor supervision, such as operating in private or company interest rather than in shareholder interest; or |
| • | Any legal issues (e.g., civil/criminal) aiming to hold the board responsible for breach of trust in the past or related to currently alleged actions yet to be confirmed (and not only the fiscal year in question), such as price fixing, insider trading, bribery, fraud, and other illegal actions; or |
13-B
| • | Other egregious governance issues where shareholders may bring legal action against the company or its directors; or |
| • | Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE basis where a vote against other agenda items are deemed inappropriate. |
| 3. | Compensation |
Director Compensation
Vote FOR proposals to award cash fees to non-executive directors unless the amounts are excessive relative to other companies in the country or industry.
Vote non-executive director compensation proposals that include both cash and share-based components on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote proposals that bundle compensation for both non-executive and executive directors into a single resolution on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote AGAINST proposals to introduce retirement benefits for non-executive directors.
Compensation Plans
Vote compensation plans on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Director, Officer, and Auditor Indemnification and Liability Provisions
Vote proposals seeking indemnification and liability protection for directors and officers on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote AGAINST proposals to indemnify auditors.
| 4. | Board Structure |
Vote AGAINST the introduction of classified boards and mandatory retirement ages for directors.
Vote AGAINST proposals to alter board structure or size in the context of a fight for control of the company or the board.
Chairman CEO combined role (for applicable markets)
GSAM will generally recommend a vote AGAINST shareholder proposals requiring that the chairman’s position be filled by an independent director, if the company satisfies 3 of the 4 following criteria:
| • | Two-thirds independent board, or majority in countries where employee representation is common practice; |
| • | A designated, or a rotating, lead director, elected by and from the independent board members with clearly delineated and comprehensive duties; |
| • | Fully independent key committees; and/or |
| • | Established, publicly disclosed, governance guidelines and director biographies/profiles. |
| 5. | Capital Structure |
Share Issuance Requests
General Issuances:
Vote FOR issuance requests with preemptive rights to a maximum of 100% over currently issued capital.
Vote FOR issuance requests without preemptive rights to a maximum of 20% of currently issued capital.
Specific Issuances:
Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE basis on all requests, with or without preemptive rights.
Increases in Authorized Capital
Vote FOR non-specific proposals to increase authorized capital up to 100% over the current authorization unless the increase would leave the company with less than 30% of its new authorization outstanding.
Vote FOR specific proposals to increase authorized capital to any amount, unless:
14-B
| • | The specific purpose of the increase (such as a share-based acquisition or merger) does not meet guidelines for the purpose being proposed; or |
| • | The increase would leave the company with less than 30% of its new authorization outstanding after adjusting for all proposed issuances. |
Vote AGAINST proposals to adopt unlimited capital authorizations.
Reduction of Capital
Vote FOR proposals to reduce capital for routine accounting purposes unless the terms are unfavorable to shareholders.
Vote proposals to reduce capital in connection with corporate restructuring on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Capital Structures
Vote FOR resolutions that seek to maintain or convert to a one-share, one-vote capital structure.
Vote AGAINST requests for the creation or continuation of dual-class capital structures or the creation of new or additional super voting shares.
Preferred Stock
Vote FOR the creation of a new class of preferred stock or for issuances of preferred stock up to 50% of issued capital unless the terms of the preferred stock would adversely affect the rights of existing shareholders.
Vote FOR the creation/issuance of convertible preferred stock as long as the maximum number of common shares that could be issued upon conversion meets guidelines on equity issuance requests.
Vote AGAINST the creation of a new class of preference shares that would carry superior voting rights to the common shares.
Vote AGAINST the creation of blank check preferred stock unless the board clearly states that the authorization will not be used to thwart a takeover bid.
Vote proposals to increase blank check preferred authorizations on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Debt Issuance Requests
Vote non-convertible debt issuance requests on a CASE-BY-CASE basis, with or without preemptive rights.
Vote FOR the creation/issuance of convertible debt instruments as long as the maximum number of common shares that could be issued upon conversion meets guidelines on equity issuance requests.
Vote FOR proposals to restructure existing debt arrangements unless the terms of the restructuring would adversely affect the rights of shareholders.
Increase in Borrowing Powers
Vote proposals to approve increases in a company’s borrowing powers on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Share Repurchase Plans
GSAM will generally recommend FOR share repurchase programs taking into account whether:
| • | The share repurchase program can be used as a takeover defense; |
| • | There is clear evidence of historical abuse; |
| • | There is no safeguard in the share repurchase program against selective buybacks; |
| • | Pricing provisions and safeguards in the share repurchase program are deemed to be unreasonable in light of market practice. |
Reissuance of Repurchased Shares
Vote FOR requests to reissue any repurchased shares unless there is clear evidence of abuse of this authority in the past.
Capitalization of Reserves for Bonus Issues/Increase in Par Value
Vote FOR requests to capitalize reserves for bonus issues of shares or to increase par value.
15-B
| 6. | Mergers and Corporate Restructurings and Other |
Reorganizations/Restructurings
Vote reorganizations and restructurings on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on mergers and acquisitions taking into account the following based on publicly available information:
| • | Valuation; |
| • | Market reaction; |
| • | Strategic rationale; |
| • | Management’s track record of successful integration of historical acquisitions; |
| • | Presence of conflicts of interest; and |
| • | Governance profile of the combined company. |
Antitakeover Mechanisms
Generally vote AGAINST all antitakeover proposals, unless they are structured in such a way that they give shareholders the ultimate decision on any proposal or offer.
Reincorporation Proposals
Vote reincorporation proposals on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Related-Party Transactions
Vote related-party transactions on a CASE-BY-CASE basis, considering factors including, but not limited to, the following:
| • | The parties on either side of the transaction; |
| • | The nature of the asset to be transferred/service to be provided; |
| • | The pricing of the transaction (and any associated professional valuation); |
| • | The views of independent directors (where provided); |
| • | The views of an independent financial adviser (where appointed); |
| • | Whether any entities party to the transaction (including advisers) is conflicted; and |
| • | The stated rationale for the transaction, including discussions of timing. |
Shareholder Proposals
Vote all shareholder proposals on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote FOR proposals that would improve the company’s corporate governance or business profile at a reasonable cost.
Vote AGAINST proposals that limit the company’s business activities or capabilities or result in significant costs being incurred with little or no benefit.
7. Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Issues
Please refer to page 12 for our current approach to these important topics.
C. Japan Proxy Items
The following section is a broad summary of the Guidelines, which form the basis of the Policy with respect to Japanese public equity investments. Applying these guidelines is not inclusive of all considerations in the Japanese market.
| 1. | Operational Items |
Financial Results/Director and Auditor Reports
Vote FOR approval of financial statements and director and auditor reports, unless:
| • | There are concerns about the accounts presented or audit procedures used; or |
| • | The company is not responsive to shareholder questions about specific items that should be publicly disclosed. |
Appointment of Auditors and Auditor Fees
Vote FOR the re-election of auditors and proposals authorizing the board to fix auditor fees, unless:
| • | There are serious concerns about the accounts presented, audit procedures used or audit opinion rendered; |
16-B
| • | There is reason to believe that the auditor has rendered an opinion that is neither accurate nor indicative of the company’s financial position; |
| • | Name of the proposed auditor has not been published; |
| • | The auditors are being changed without explanation; |
| • | Non-audit-related fees are substantial or are in excess of standard annual audit-related fees; or |
| • | The appointment of external auditors if they have previously served the company in an executive capacity or can otherwise be considered affiliated with the company. |
Allocation of Income
Vote FOR approval of the allocation of income, unless:
| • | The dividend payout ratio is less than 20%; or |
| • | The company proposes the payments even though the company posted a net loss for the year under review; |
| • | The dividend payout ratio has been consistently low without adequate explanation; or |
| • | The payout is excessive given the company’s financial position. |
Stock (Scrip) Dividend Alternative
Vote FOR most stock (scrip) dividend proposals.
Vote AGAINST proposals that do not allow for a cash option unless management demonstrates that the cash option is harmful to shareholder value.
Amendments to Articles of Association
Vote amendments to the articles of association on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Change in Company Fiscal Term
Vote FOR resolutions to change a company’s fiscal term unless a company’s motivation for the change is to postpone its annual general meeting.
Lower Disclosure Threshold for Stock Ownership
Vote AGAINST resolutions to lower the stock ownership disclosure threshold below 5% unless specific reasons exist to implement a lower threshold.
Amend Quorum Requirements
Vote proposals to amend quorum requirements for shareholder meetings on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Transact Other Business
Vote AGAINST other business when it appears as a voting item.
2. Board of Directors
Director and Statutory Auditor Elections
Vote FOR management nominees taking into consideration the following:
| • | The company’s committee structure: statutory auditor board structure, U.S.-type three committee structure, or audit committee structure; or |
| • | Adequate disclosure has not been provided in a timely manner; or |
| • | There are clear concerns over questionable finances or restatements; or |
| • | There have been questionable transactions or conflicts of interest; or |
| • | There are any records of abuses against minority shareholder interests; or |
| • | The board fails to meet minimum corporate governance standards; or |
| • | There are reservations about: |
| • | Director terms |
| • | Bundling of proposals to elect directors |
| • | Board independence |
| • | Disclosure of named nominees |
| • | Combined Chairman/CEO |
17-B
| • | Election of former CEO as Chairman of the board |
| • | Overboarded directors who sit on more than four public operating and/or holding company boards or are CEOs of public companies who sit on the boards of more than one public companies besides their own |
| • | Composition of committees |
| • | Director independence |
| • | Number of directors on the board |
| • | Lack of gender diversity on the board |
| • | Specific concerns about the individual or company, such as criminal wrongdoing or breach of fiduciary responsibilities; or |
| • | Attendance at less than 75% of the board and committee meetings without a disclosed valid excuse; or |
| • | Unless there are other considerations which may include sanctions from government or authority, violations of laws and regulations, or other issues related to improper business practice, failure to replace management, or egregious actions related to service on other boards. |
Vote AGAINST the Nominating Committee if the board does not have at least one woman director.
Vote AGAINST top executives when the board consists of more than 15 directors and less than 15% of outside directors.
Vote AGAINST top executives when the company has posted average return on equity (ROE) of less than five percent over the last five fiscal years.
Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE basis in contested elections of directors, e.g., the election of shareholder nominees or the dismissal of incumbent directors, determining which directors are best suited to add value for shareholders.
The analysis will generally be based on, but not limited to, the following major decision factors:
| • | Company performance relative to its peers; |
| • | Strategy of the incumbents versus the dissidents; |
| • | Independence of board candidates; |
| • | Experience and skills of board candidates; |
| • | Governance profile of the company; |
| • | Evidence of management entrenchment; |
| • | Responsiveness to shareholders; |
| • | Whether a takeover offer has been rebuffed; |
| • | Whether minority or majority representation is being sought. |
Vote FOR employee and/or labor representatives if they sit on either the audit or compensation committee and are required by law to be on those committees.
Vote AGAINST employee and/or labor representatives if they sit on either the audit or compensation committee, if they are not required to be on those committees.
Classification of directors
Internal Director
| • | Employee or executive of the company; |
| • | Any director who is classified as a non-executive, but receives salary, fees, bonus, and/or other benefits that are in line with the highest-paid executives of the company. |
Internal Non-Executive Director (NED)
| • | Any director who is attested by the board to be a non-independent NED; |
| • | Any director specifically designated as a representative of a significant shareholder of the company; |
| • | Any director who is also an employee or executive of a significant shareholder of the company; |
| • | Beneficial owner (direct or indirect) of at least 10% of the company’s stock, either in economic terms or in voting rights (this may be aggregated if voting power is distributed among more than one member of a defined group, e.g., family members who beneficially own less than 10% individually, but collectively own more than 10%), unless market best practice dictates a lower ownership and/or disclosure threshold (and in other special market-specific circumstances); |
18-B
| • | Government representative; |
| • | Currently provides (or a relative provides) professional services to the company, to an affiliate of the company, or to an individual officer of the company or of one of its affiliates in excess of $10,000 per year; |
| • | Represents customer, supplier, creditor, banker, or other entity with which company maintains transactional/commercial relationship (unless company discloses information to apply a materiality test); |
| • | Any director who has conflicting or cross-directorships with executive directors or the chairman of the company; |
| • | Relative of a current employee of the company or its affiliates; |
| • | Relative of a former executive of the company or its affiliates; |
| • | Any director who works or worked at companies whose shares are held by the company in question as cross-shareholdings; |
| • | A new appointee elected other than by a formal process through the General Meeting (such as a contractual appointment by a substantial shareholder); |
| • | Founder/co-founder/member of founding family but not currently an employee; |
| • | Former executive (5 year cooling off period); |
| • | Years of service is generally not a determining factor unless it is recommended best practice in a market and/or in extreme circumstances, in which case it may be considered; and |
| • | Any additional relationship or principle considered to compromise independence under local corporate governance best practice guidance. |
External NED
| • | No material connection, either directly or indirectly, to the company other than a board seat. |
Employee Representative
| • | Represents employees or employee shareholders of the company (classified as “employee representative” but considered a non-independent NED). |
Discharge of Directors
Generally vote FOR the discharge of directors, including members of the management board and/or supervisory board, unless there is reliable information about significant and compelling controversies that the board is not fulfilling its fiduciary duties warranted by:
| • | A lack of oversight or actions by board members which invoke shareholder distrust related to malfeasance or poor supervision, such as operating in private or company interest rather than in shareholder interest; or |
| • | Any legal issues (e.g., civil/criminal) aiming to hold the board responsible for breach of trust in the past or related to currently alleged actions yet to be confirmed (and not only the fiscal year in question), such as price fixing, insider trading, bribery, fraud, and other illegal actions; or |
| • | Other egregious governance issues where shareholders may bring legal action against the company or its directors; or |
| • | Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE basis where a vote against other agenda items are deemed inappropriate. |
| 3. | Compensation |
Director Compensation
Vote FOR proposals to award cash fees to non-executive directors unless the amounts are excessive relative to other companies in the country or industry.
Vote non-executive director compensation proposals that include both cash and share-based components on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote proposals that bundle compensation for both non-executive and executive directors into a single resolution on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote AGAINST proposals to introduce retirement benefits for non-executive directors.
19-B
Compensation Plans
Vote compensation plans on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Director, Officer, and Auditor Indemnification and Liability Provisions
Vote proposals seeking indemnification and liability protection for directors and officers on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote AGAINST proposals to indemnify auditors.
| 4. | Board Structure |
Vote AGAINST the introduction of classified boards and mandatory retirement ages for directors.
Vote AGAINST proposals to alter board structure or size in the context of a fight for control of the company or the board.
Chairman CEO combined role
GSAM will generally recommend a vote AGAINST shareholder proposals requiring that the chairman’s position be filled by an independent director, if the company satisfies 3 of the 4 following criteria:
| • | Two-thirds independent board, or majority in countries where employee representation is common practice; |
| • | A designated, or a rotating, lead director, elected by and from the independent board members with clearly delineated and comprehensive duties; |
| • | Fully independent key committees; and/or |
| • | Established, publicly disclosed, governance guidelines and director biographies/profiles. |
5. Capital Structure
Share Issuance Requests
General Issuances:
Vote FOR issuance requests with preemptive rights to a maximum of 100% over currently issued capital.
Vote FOR issuance requests without preemptive rights to a maximum of 20% of currently issued capital.
Specific Issuances:
Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE basis on all requests, with or without preemptive rights.
Increases in Authorized Capital
Vote FOR non-specific proposals to increase authorized capital up to 100% over the current authorization unless the increase would leave the company with less than 30% of its new authorization outstanding.
Vote FOR specific proposals to increase authorized capital to any amount, unless:
| • | The specific purpose of the increase (such as a share-based acquisition or merger) does not meet guidelines for the purpose being proposed; or |
| • | The increase would leave the company with less than 30% of its new authorization outstanding after adjusting for all proposed issuances. |
Vote AGAINST proposals to adopt unlimited capital authorizations.
Reduction of Capital
Vote FOR proposals to reduce capital for routine accounting purposes unless the terms are unfavorable to shareholders.
Vote proposals to reduce capital in connection with corporate restructuring on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Capital Structures
Vote FOR resolutions that seek to maintain or convert to a one-share, one-vote capital structure.
Vote AGAINST requests for the creation or continuation of dual-class capital structures or the creation of new or additional super voting shares.
20-B
Preferred Stock
Vote FOR the creation of a new class of preferred stock or for issuances of preferred stock up to 50% of issued capital unless the terms of the preferred stock would adversely affect the rights of existing shareholders.
Vote FOR the creation/issuance of convertible preferred stock as long as the maximum number of common shares that could be issued upon conversion meets guidelines on equity issuance requests.
Vote AGAINST the creation of a new class of preference shares that would carry superior voting rights to the common shares.
Vote AGAINST the creation of blank check preferred stock unless the board clearly states that the authorization will not be used to thwart a takeover bid.
Vote proposals to increase blank check preferred authorizations on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Debt Issuance Requests
Vote non-convertible debt issuance requests on a CASE-BY-CASE basis, with or without preemptive rights.
Vote FOR the creation/issuance of convertible debt instruments as long as the maximum number of common shares that could be issued upon conversion meets guidelines on equity issuance requests.
Vote FOR proposals to restructure existing debt arrangements unless the terms of the restructuring would adversely affect the rights of shareholders.
Increase in Borrowing Powers
Vote proposals to approve increases in a company’s borrowing powers on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Share Repurchase Plans
GSAM will generally recommend FOR share repurchase programs taking into account whether:
| • | The share repurchase program can be used as a takeover defense; |
| • | There is clear evidence of historical abuse; |
| • | There is no safeguard in the share repurchase program against selective buybacks; |
| • | Pricing provisions and safeguards in the share repurchase program are deemed to be unreasonable in light of market practice. |
Reissuance of Repurchased Shares
Vote FOR requests to reissue any repurchased shares unless there is clear evidence of abuse of this authority in the past.
Capitalization of Reserves for Bonus Issues/Increase in Par Value
Vote FOR requests to capitalize reserves for bonus issues of shares or to increase par value.
6. Mergers and Corporate Restructurings and Other
Reorganizations/Restructurings
Vote reorganizations and restructurings on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on mergers and acquisitions taking into account the following based on publicly available information:
| • | Valuation; |
| • | Market reaction; |
| • | Strategic rationale; |
| • | Management’s track record of successful integration of historical acquisitions; |
| • | Presence of conflicts of interest; and |
| • | Governance profile of the combined company. |
Antitakeover Mechanisms
Generally vote AGAINST all antitakeover proposals, unless they are structured in such a way that they give shareholders the ultimate decision on any proposal or offer.
21-B
Reincorporation Proposals
Vote reincorporation proposals on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Related-Party Transactions
Vote related-party transactions on a CASE-BY-CASE basis, considering factors including, but not limited to, the following:
| • | The parties on either side of the transaction; |
| • | The nature of the asset to be transferred/service to be provided; |
| • | The pricing of the transaction (and any associated professional valuation); |
| • | The views of independent directors (where provided); |
| • | The views of an independent financial adviser (where appointed); |
| • | Whether any entities party to the transaction (including advisers) is conflicted; and |
| • | The stated rationale for the transaction, including discussions of timing. |
Shareholder Proposals
Vote all shareholder proposals on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
Vote FOR proposals that would improve the company’s corporate governance or business profile at a reasonable cost.
Vote AGAINST proposals that limit the company’s business activities or capabilities or result in significant costs being incurred with little or no benefit.
| 7. | Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Issues |
Please refer to page 12 for our current approach to these important topics.
22-B
APPENDIX C
STATEMENT OF INTENTION
(applicable only to Class A Shares)
If a shareholder anticipates purchasing within a 13-month period Class A Shares of the Fund alone or in combination with Class A Shares of another Goldman Sachs Fund in the amount of $50,000 or more, the shareholder may obtain shares of the Fund at the same reduced sales charge as though the total quantity were invested in one lump sum by checking and filing the Statement of Intention in the Account Application. Distributions taken in additional shares, as well as any appreciation on shares previously purchased, will not apply toward the completion of the Statement of Intention.
To ensure that the reduced price will be received on future purchases, the investor must inform Goldman Sachs that the Statement of Intention is in effect each time shares are purchased. Subject to the conditions mentioned below, each purchase will be made at the public offering price applicable to a single transaction of the dollar amount specified on the Account Application. The investor makes no commitment to purchase additional shares, but if the investor’s purchases within 13 months plus the value of shares credited toward completion do not total the sum specified, the investor will pay the increased amount of the sales charge prescribed in the Escrow Agreement.
Escrow Agreement
Out of the initial purchase (or subsequent purchases if necessary), 5% of the dollar amount specified on the Account Application will be held in escrow by the Transfer Agent in the form of shares registered in the investor’s name. All distributions on escrowed shares will be paid to the investor or to his or her order. When the minimum investment so specified is completed (either prior to or by the end of the 13th month), the investor will be notified and the escrowed shares will be released.
If the intended investment is not completed, the investor will be asked to remit to Goldman Sachs any difference between the sales charge on the amount specified and on the amount actually attained. If the investor does not within 20 days after written request by Goldman Sachs pay such difference in the sales charge, the Transfer Agent will redeem, pursuant to the authority given by the investor in the Account Application, an appropriate number of the escrowed shares in order to realize such difference. Shares remaining after any such redemption will be released by the Transfer Agent.
1-C
Serious News for Serious Traders! Try StreetInsider.com Premium Free!
You May Also Be Interested In
- T-Mobile (TMUS) and EQT Announce JV to Acquire Lumos
- What's next for natural gas prices? Goldman Sachs weighs in
- GXO Logistics, Inc. (GXO) Prices $1.1B Notes Offering
Create E-mail Alert Related Categories
SEC FilingsRelated Entities
Goldman SachsSign up for StreetInsider Free!
Receive full access to all new and archived articles, unlimited portfolio tracking, e-mail alerts, custom newswires and RSS feeds - and more!



 Tweet
Tweet Share
Share